Workshop W2: Interest Rates (FINM1001)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What are the 3 types of Interest Rates?
Annual effective interest rate (re).
Annual nominal interest rate (rn).
Periodic interest rate (rp).
Annual effective interest rate (re)
Where the frequency of charging/payment matches the period specified by the interest rate (i.e., the rate is quoted annually and is applied annually).
E.g., 12% p.a. compounded annually.
Annual nominal interest rate (rn)
Where interest is charged more frequently than the time period specified in the interest rate.
E.g., 12% p.a. compounded monthly.
Periodic interest rate (rp)
The rate of interest applied per compound period in the case of a nominal interest rate.
E.g., if the nominal interest rate is 12% compounded semi-annually:
The periodic interest rate is 12%/2 = 6% per six-months.
When do you use an Annual Effective Rate?
To calculate future or present value when:
You have an annuity / perpetuity with annual cash flows. Here, you must also have n expressed in terms of number of years; or,
You have multiple uneven cash flows / a single cash flow and you want to express n in terms of the number of years.
When do you use a Periodic Interest Rate?
When:
You have an annuity / perpetuity with cash flows paid less than annually. Here, the periodic rate must be expressed as frequently as the cash flows.
You have multiple uneven cash flows / a single cash flow and you want to use a value of n calculated based on the same period as the period rate.
When do you use an Annual Nominal Rate?
Never.
What interest rate do you use if you have a single cash flow / multiple uneven cash flows?
You can choose whether to use an annual effective or a periodic rate, and you must use a value of n calculated based on the same period as the interest rate.
E.g., if you have a single cash flow in 5 years time:
If you use a monthly interest rate: n = 5×12 = 60.
If you use an annual effective interest rate: n = 5.
What interest rate do you use if you have a an annuity / perpetuity?
You must use an interest rate of the same frequency of the cash flows, and you must use a value of n calculated based on the same period (in the case of annuities).
Examples:
If you have monthly cash flows for 5 years, you must use a monthly interest rate and n = 5×12 = 60.
If you have yearly cash flows for 5 years, you must use an annual effective interest rate and n = 5.
If you have quarterly cash flows forever, you must use a quarterly interest rate.
The Interest Rate Wheel
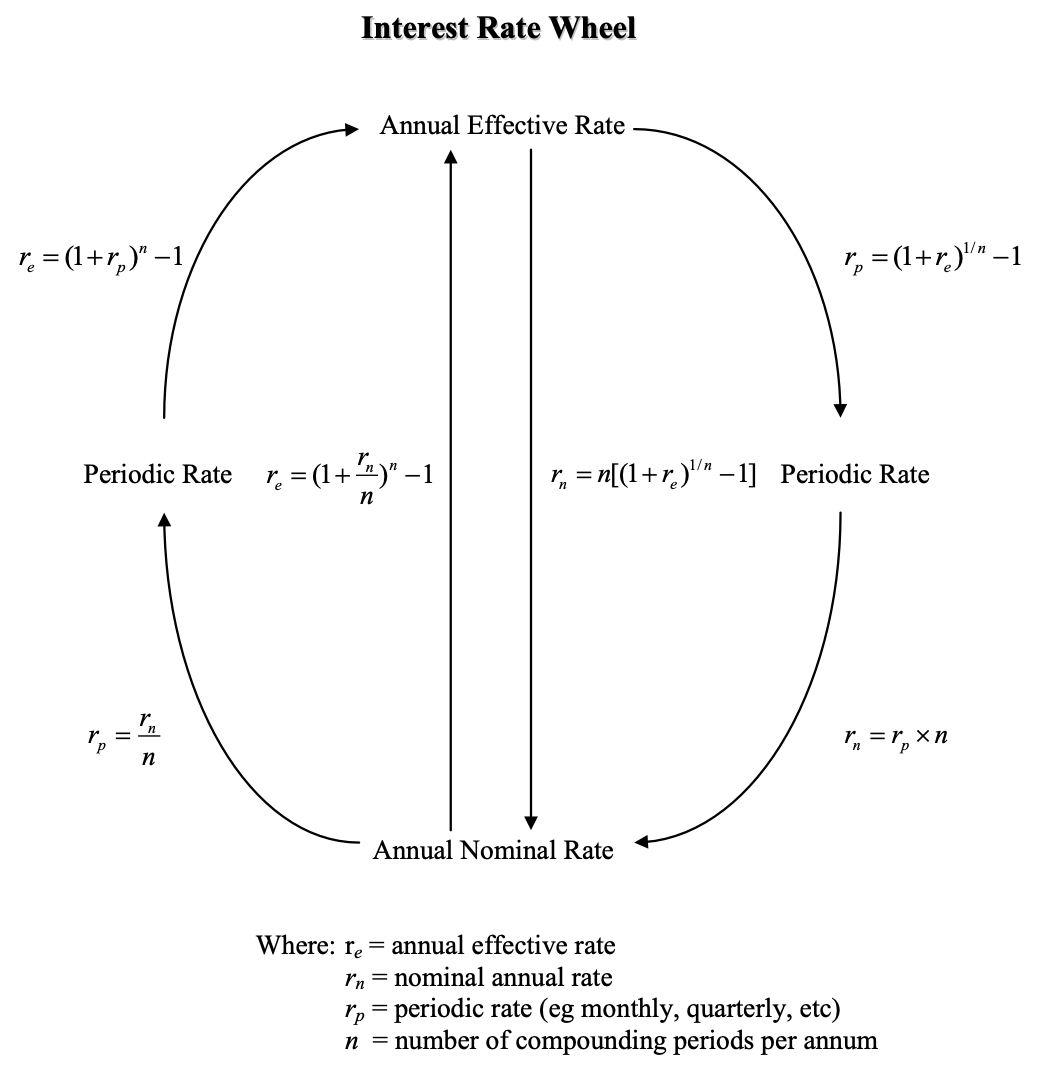
Interest Rate Quick Check: rn to rp
How frequently do cash flows occur?
How frequently is the annual nominal rate compounded?
If answers 1 and 2 match: rn → rp.
If answers 1 and 2 do not match:
a) Convert rn → re.
b) Convert re → rp.