Electronic Components
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
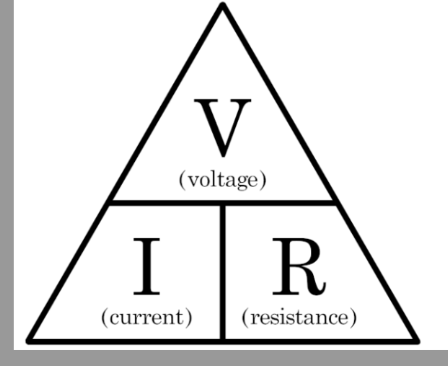
Draw the triangle for Ohm's law
...
Electric Current (definition)
The rate of flow of charge.
Electric Circuit (definition)
A complete loop around which electricity can flow.
Draw a battery in the sketchbook app
...
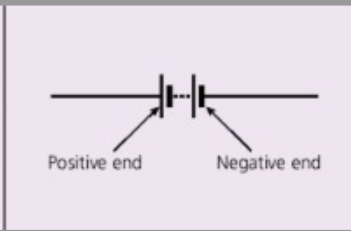
Voltage/Potential Difference (definition)
The energy available to push electrons around a circuit.
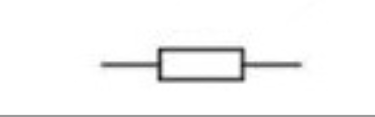
Resistor (features + function)
Passive component. Creates resistance. Controls current flow.
Draw a resistor
...
Passive Component
A component that doesn't do anything but sit there
What is the unit of Resistance?
Ohm
What is the unit of Voltage?
Volts
What is the unit of Current?
Amps (A)
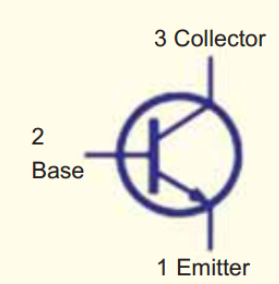
Transistors (features)
Semi-conductor. Small electronic switch. Amplifier
Draw a transistor
...
Capacitor (function)
Store potential energy
Draw a capacitor
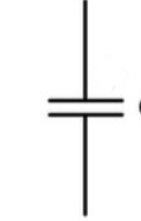
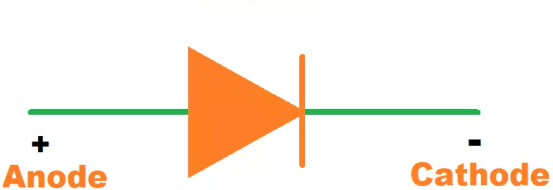
Diode (function)
Allows the flow of electrons/electricity in one direction only
Draw a diode
...
Transistor (definition)
A tiny electronic switch that can amplify and control the flow of electricity.
Integrated Circuit (IC)
A tiny chip that contains a complete electronic circuit on a semiconductor base, including transistors, resistors, and capacitors.
Name the two types of RAM
Dynamic RAM (Main Memory). Static RAM (Cache Memory)
Dynamic RAM
1 transistor + 1 capacitor for each bit. Hold a small charge for a few milliseconds. Slower because it needs to be refreshed. Power is always needed.
Bit
A one or a zero
Static RAM
4-5 transistors wired together for each bit of data, but it does not lose its charge. No need to refresh. Much faster as they don't need refreshing. Still needs constant electricity supply. Faster but more expensive.