exam 1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
darkroom safelight must be
red
x-rays are invisible and can cause biological damage to living tissue
which is a true statement
radiation protection to the individual is important
during all phases of life of males and females
kilovoltage (contrast)…
is the penetrating power of the x-ray photons
milliamperage ()…
controls primarily the density of the film
scattered radiation is
increased by an increase in kilovoltage
contrast on a radiograph image is mostly dependent on
the differences in x-ray penetration due to tissue density
kV affects the image primarily in the range of
contrast
the effect on the image as kV is increased beyond ideal will be
decreased contrast
stochastic effect
are usually random in nature
ALARA concept is primarily used to protect
the general public
ALARA
AS LOW AS RESONABLY ACHIEVABLE
which of the following is most effective in protecting a patient
high kVp, low mA, 40” distance
in the x-ray room, radiation is produced
within an x-ray tube that has an anode and cathode
three methods of protection for the x-ray personnel are time, distance, and shielding. which of the following is true regarding protection?
time measures the amount of exposure during the examination
the care of leaded aprons should include
handing them by the shoulders, with no folds or creases
accurate measurement of a patients body is essential
to accurately set the correct exposure factors
radiation workers should be equipped with a person dosimeter
that should be stored in a location where it will not be exposed to radiation
milliamperage - seconds contributes mainly to
density
an advantage of computerized radiography over film imaging is
easier access to the images by the veterinarian
25 milliseconds is equivalent to
0.025 seconds
the purpose of the rotating anode is to dissipate the large amount of heat generated by x-ray production
true
the thicker part of the patient should be placed on the x-ray table toward the (-) sign on the x-ray tube
true
anode heel effect
thicker part of patient should be placed towards the cathode side of x-ray tube
anode is
(+) charged
cathode is
(-) charged
kV
kilavoltage
mA
miliamperage
kVp
kilovoltage peak
mAs
milliampere-seconds
ALARA
AS LOW AS RESONABILIY ACHIEVABLE
WHEN x-raying deep chest dog which side of the table should the head face
cathode side
how do you know what area to measure on an animal when taking an x-ray
thickest part with caliper
what are blockers used for?
pieces of leaded material that serve a specific purpose related to radiation safety and image quaility
what part of the machine sizes the x-ray beam for the image?
collimator
define contrast
gray
kVp
difference in brightness between structures or tissues on image
what is an illuminator
refers to the light box, used to uniformly illuminate radiographic films for viewing and interpretation
what 4 settings affect radiographic quality
kVp
mAs
Distance
time
motion on x-ray
this artifact are things such as: tail wagging, patient moving
blurred, smeared, fuzzy
how does foreshortening occur on x-ray
images that appear on the image to be shorter than the true object
misalignment, not perpendicular
how does blur occur on x-ray
patient moves, heartbeat, breathing
how does magnification occur on x-ray
collimated and cassette are closer to patient, “wrong distance”, cassette on table, collimated very close to patient
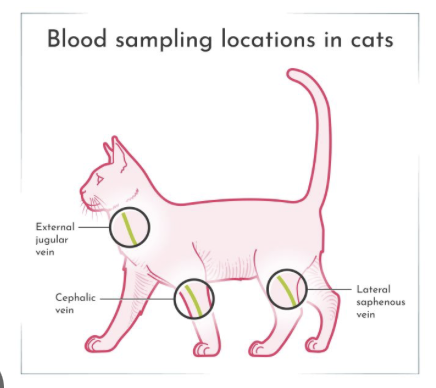
venous blood draws on cat
medial saphenous vein
jugular vein
cephalic vein
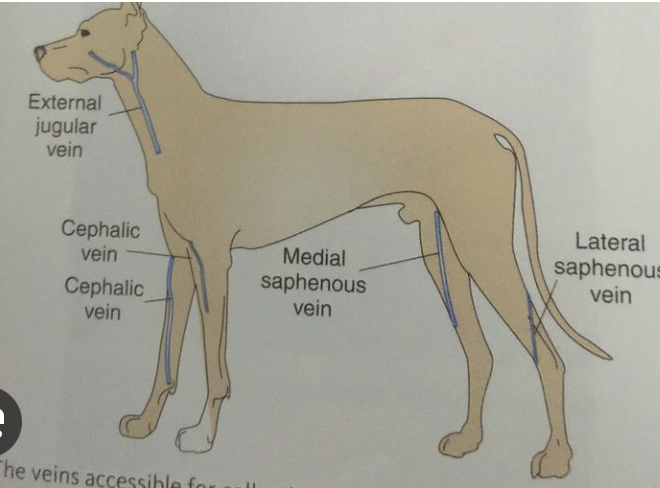
venous blood draw on dog
jugular vein
cephalic vein
lateral saphenous vein
IM injection on cat
epaxial
semi membranous and semitendonous
quadricep
IM injection dog
epaxial
quad
semimembranous and semitendonous
parts of rib cage
manubrium
xiphoid process
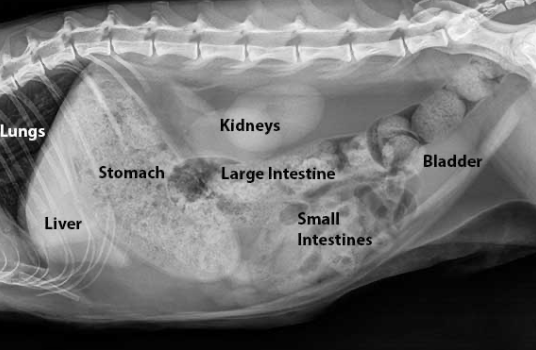
organs in the intestines of an x-ray
esophagus, trachea, heart,
lungs, liver, diaphragm, kidneys, large intestines, small intestines, bladder
vertebrae
cervical - 7
thoracic - 13
lumbar - 7
sacral - 3
coccygeal (caudal) - 5
coxofemoral
hip joint
lateral extended
extended
flexed x-ray
flexed
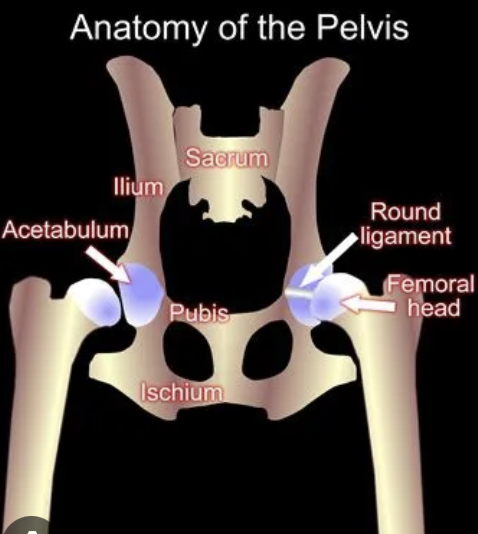
acetabulum
part of the pelvis where the head of the femur sits
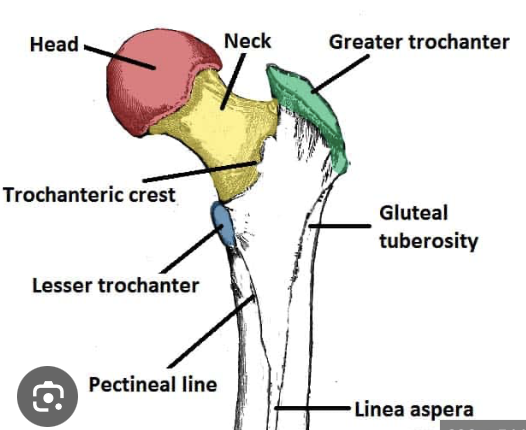
greater trochanter of femur
strong hip abductors
tarsus
joint
tarsals
bones