Cell Transport
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.

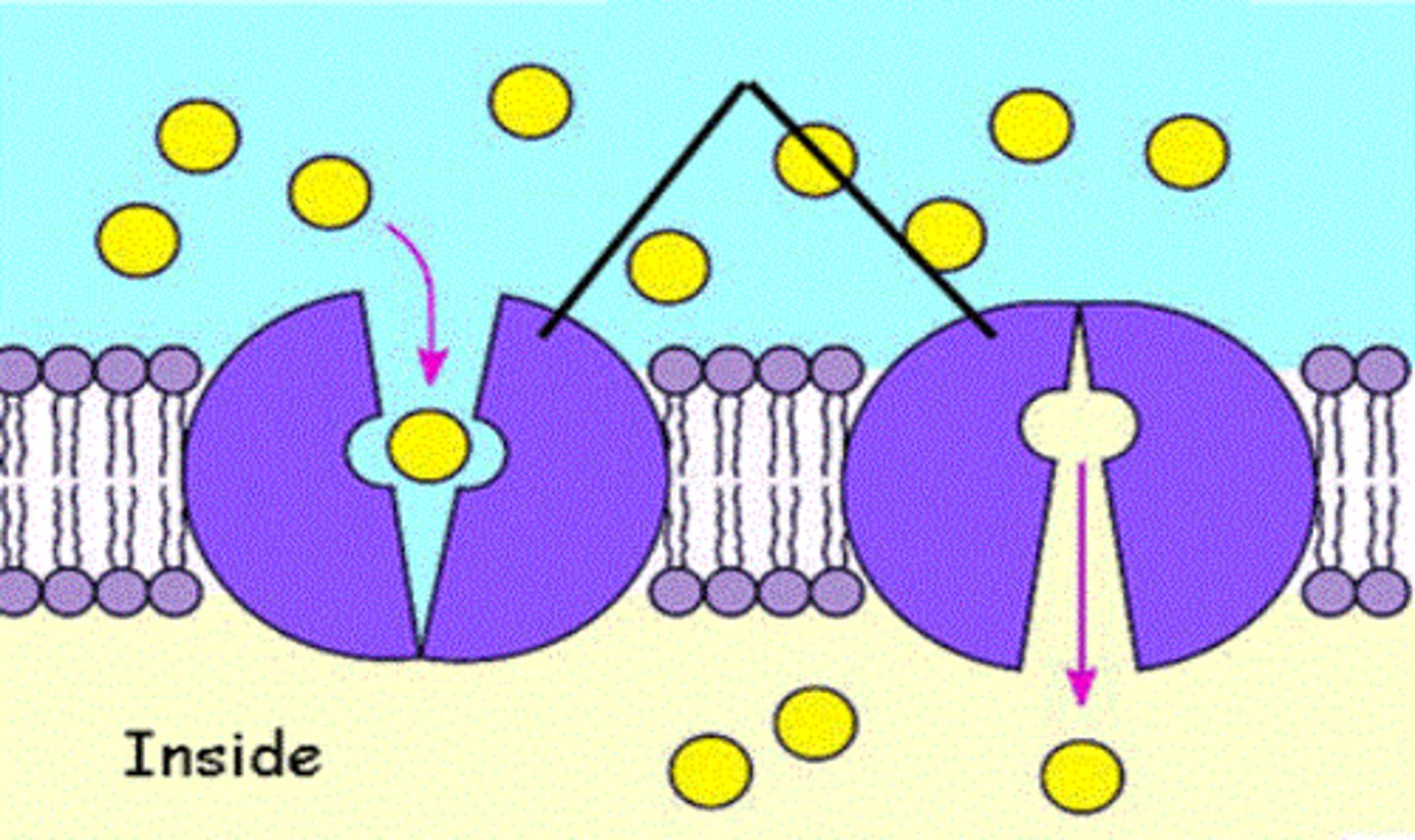
carrier protein
a protein that transports substances across a cell membrane
isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
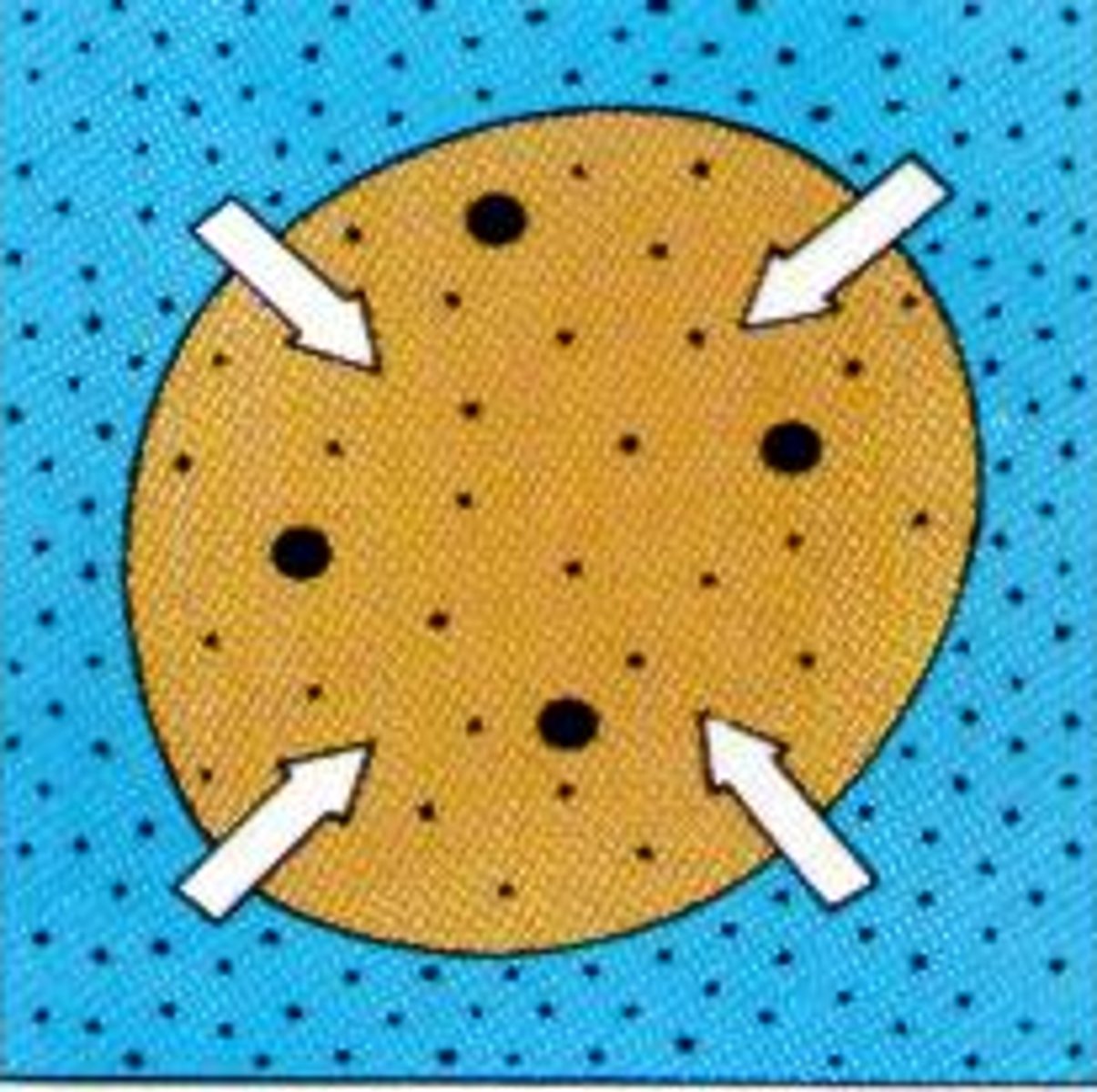
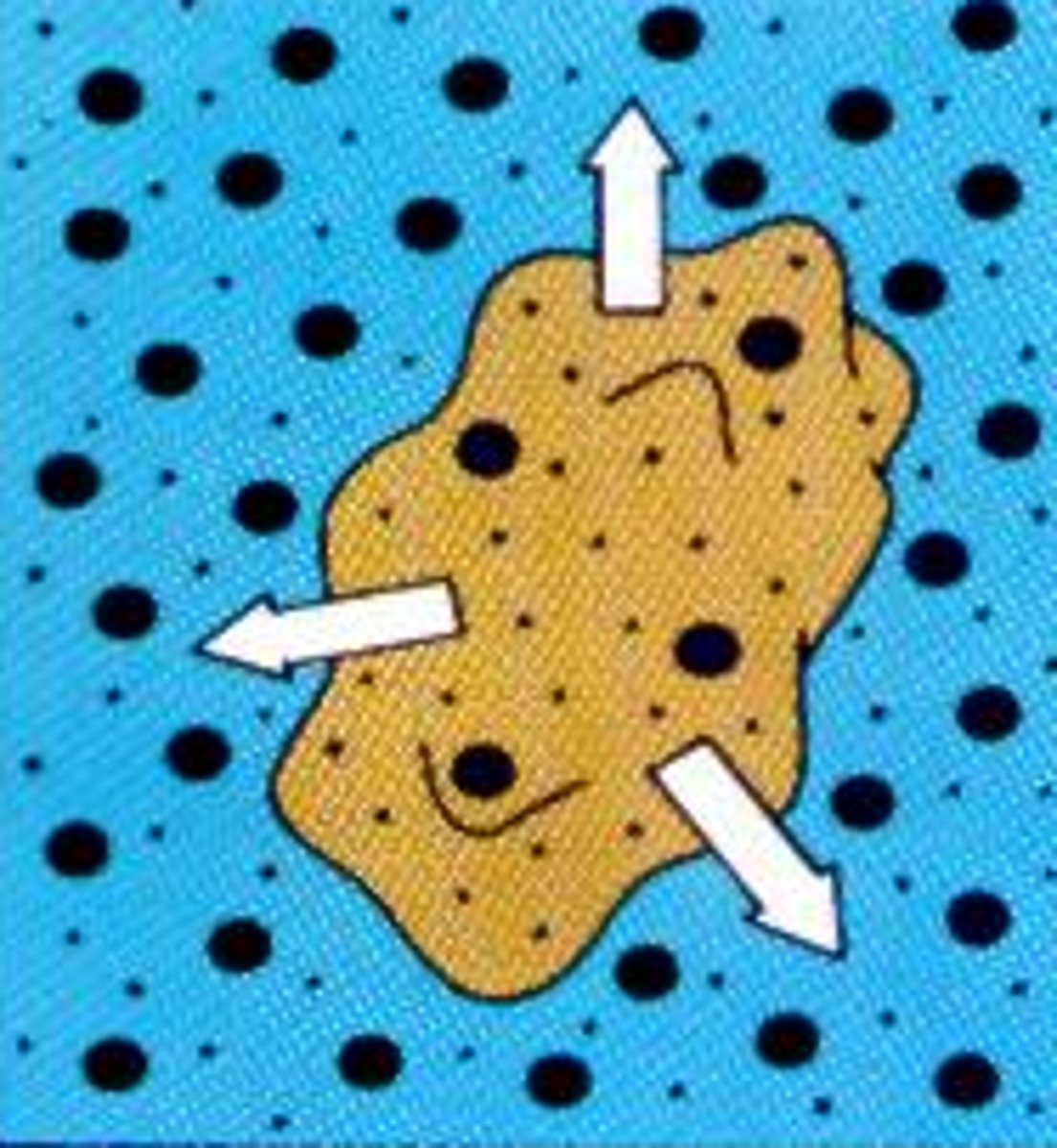
hypotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is less than that of the cell that resides in the solution
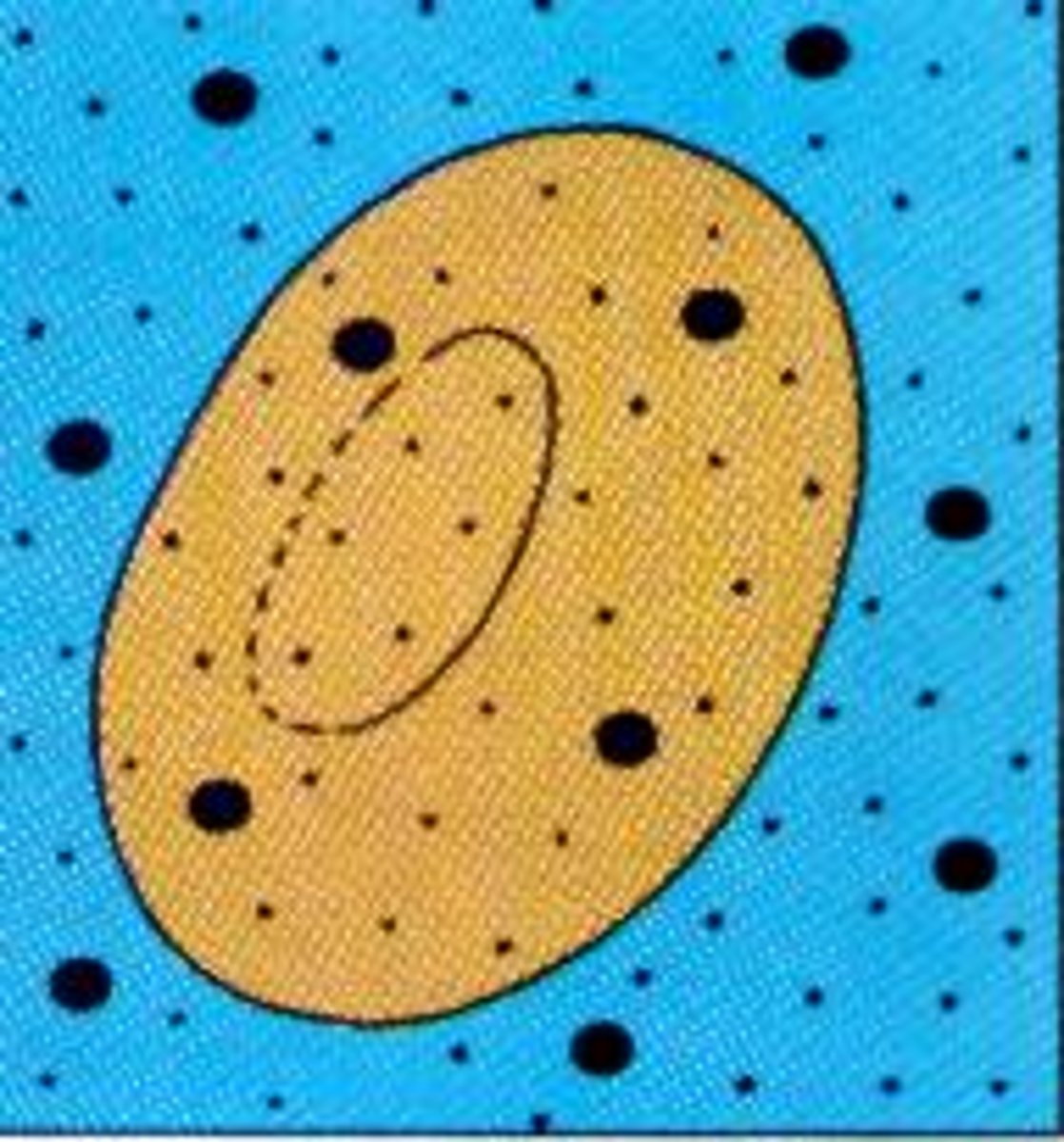
hypertonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is greater than that of the cell that resides in the solution

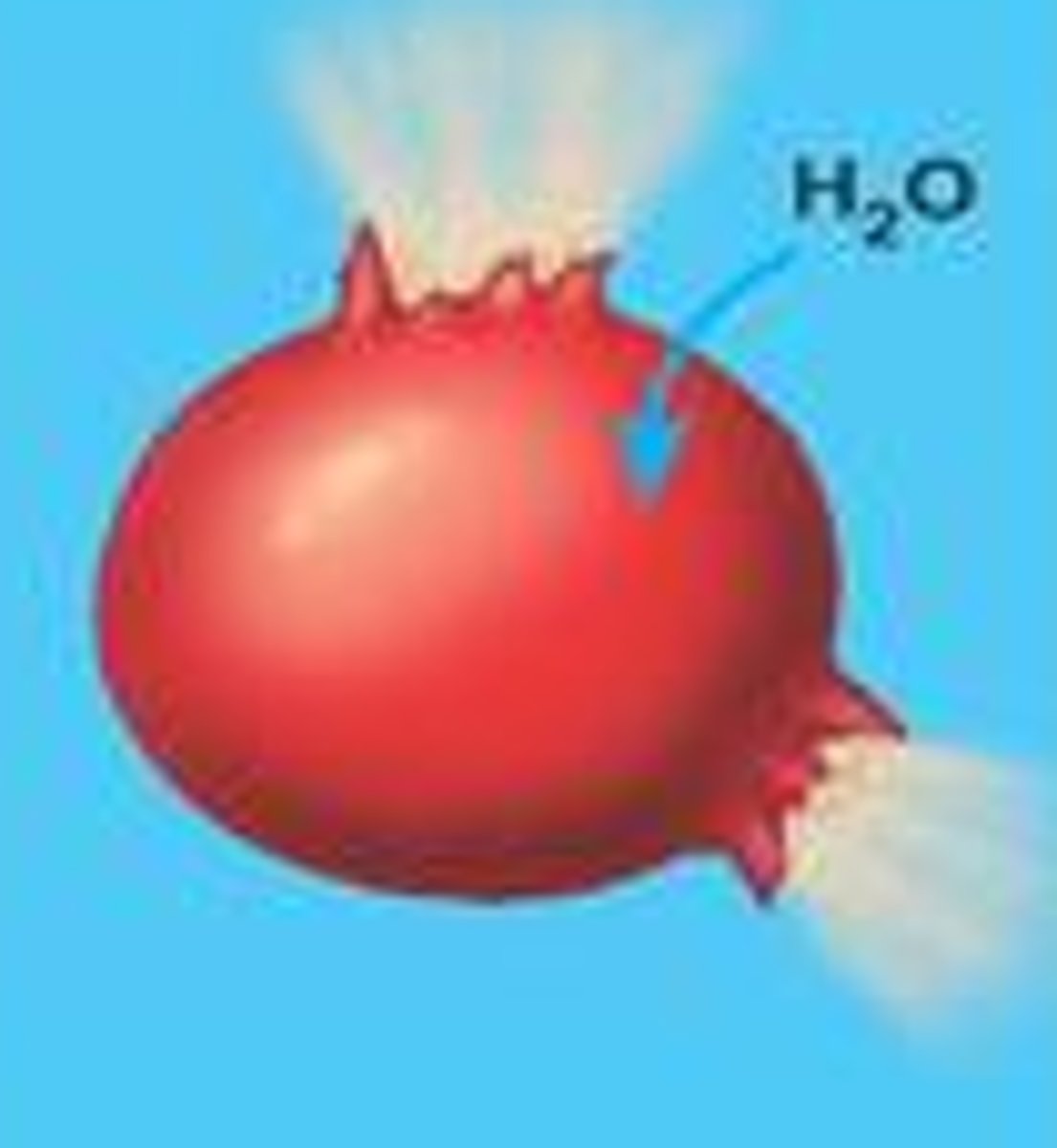
Plasmolysis
Collapse of a walled cell's cytoplasm due to a lack of water

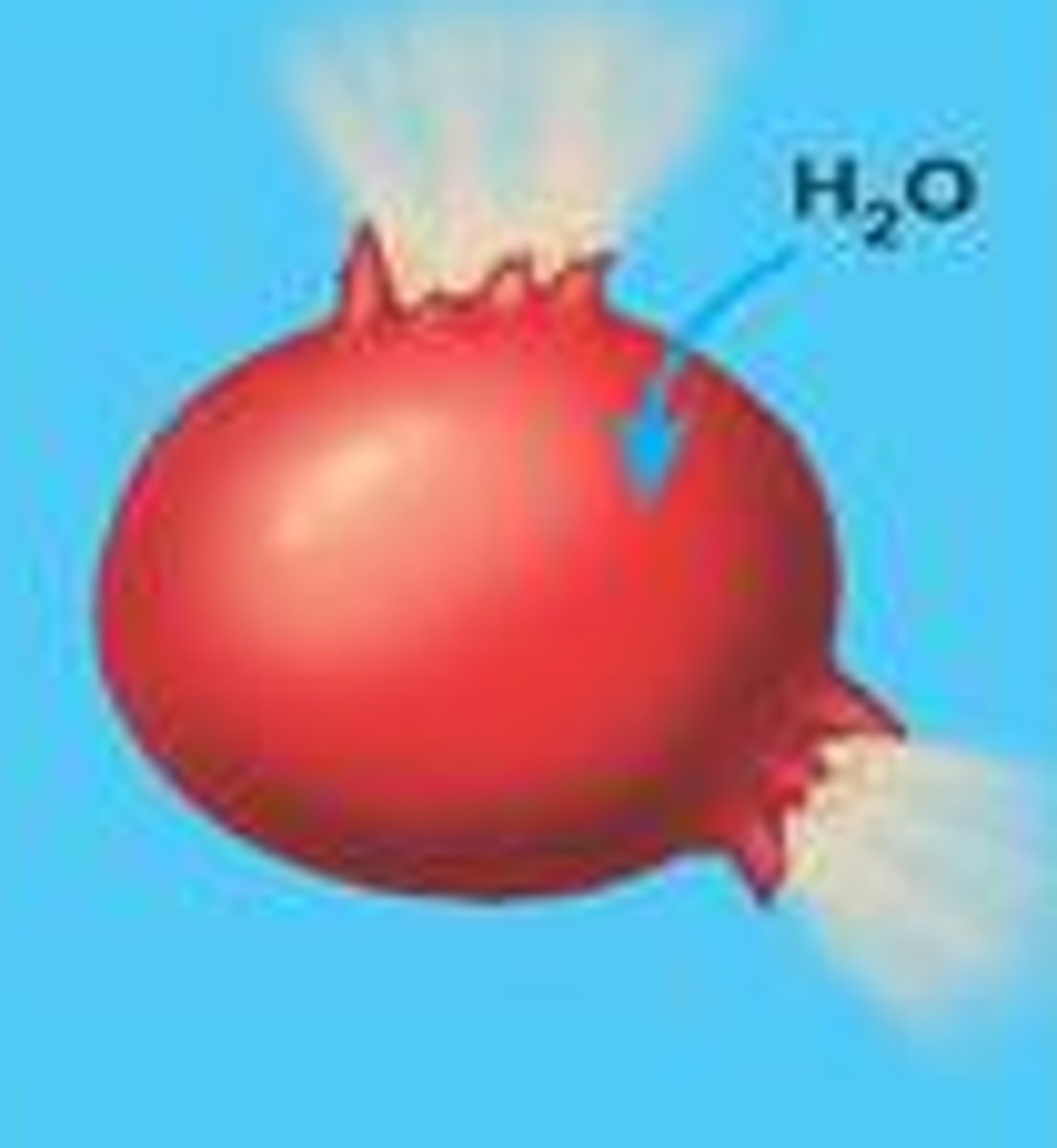
Cytolysis
When animal cells such as red blood cells swell and burst

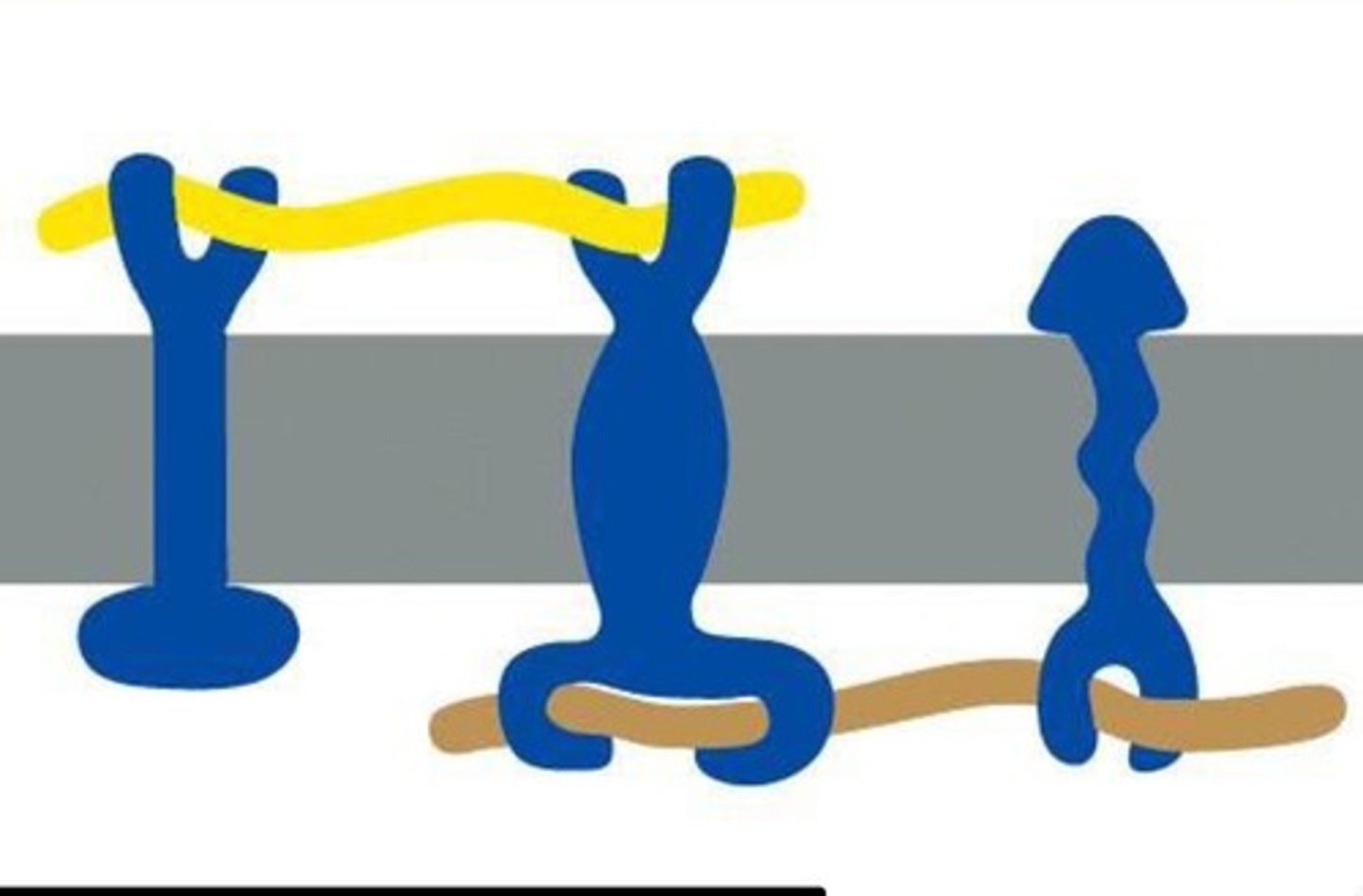
anchor proteins
attach to other proteins to help maintain cell structure and shape
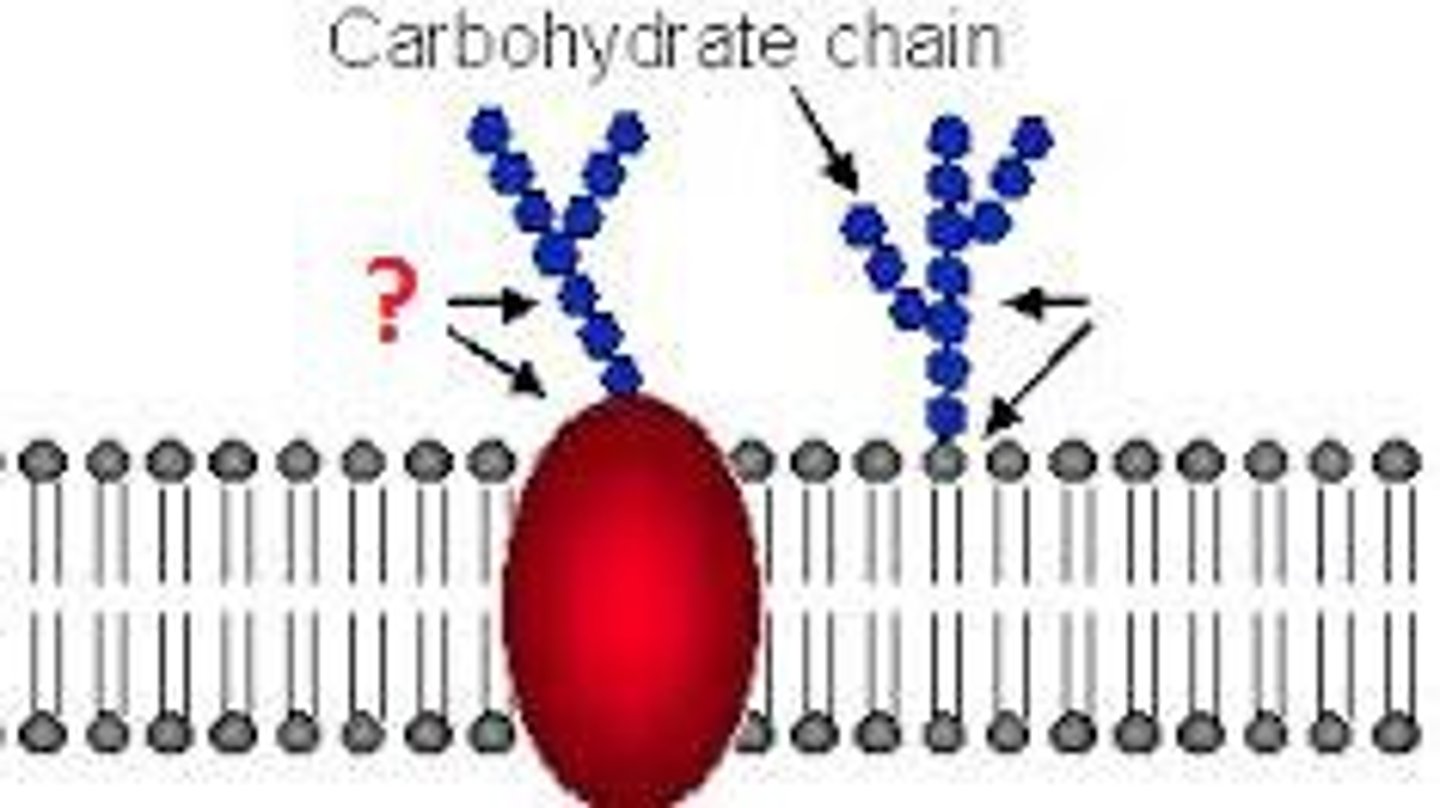
glycoproteins and glycolipids
involved in cell to cell recognition
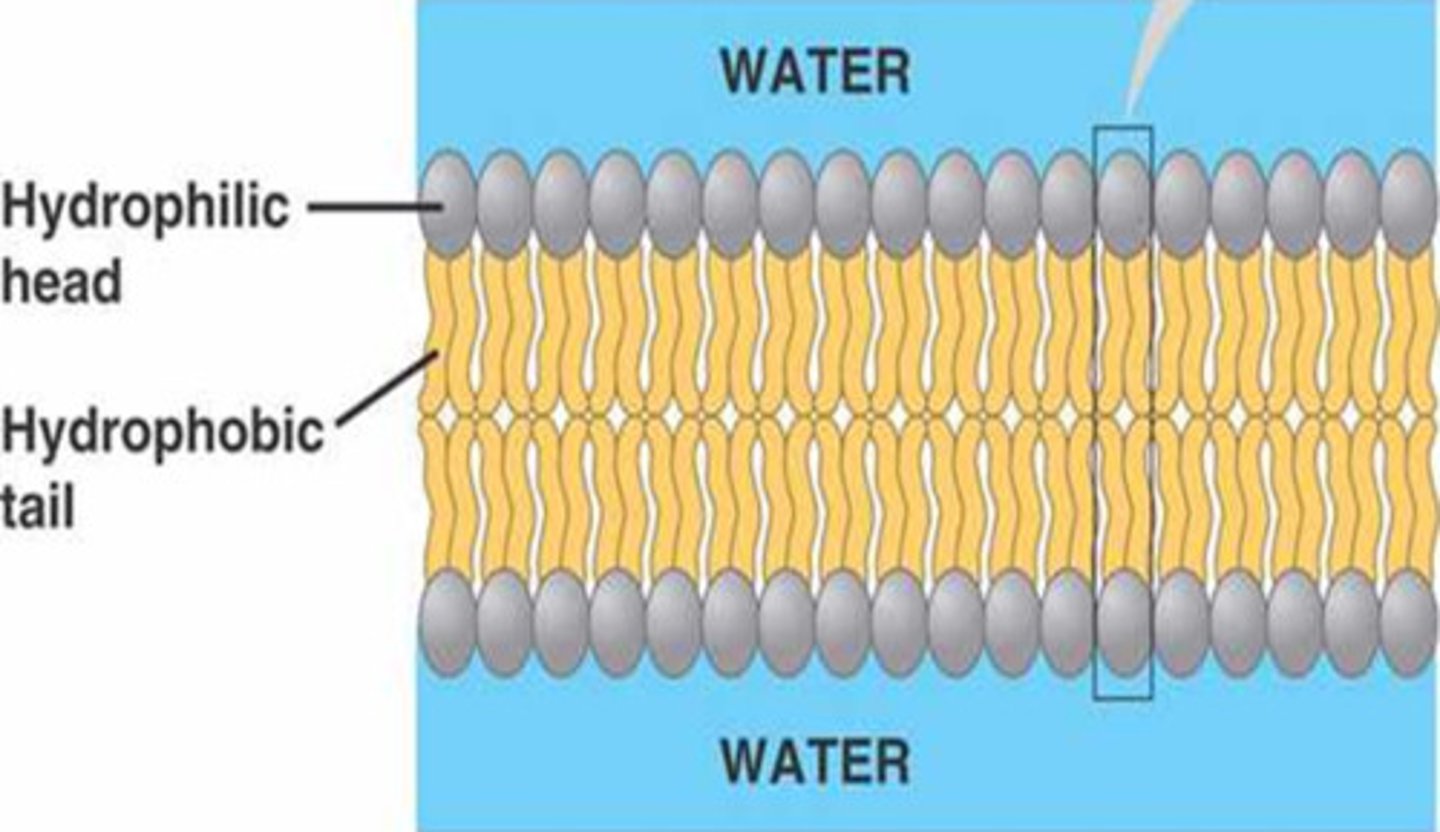
phopholipid bilayer
Main part of the membrane; common to all cells; seperates internal cell from external cell; made up of hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails
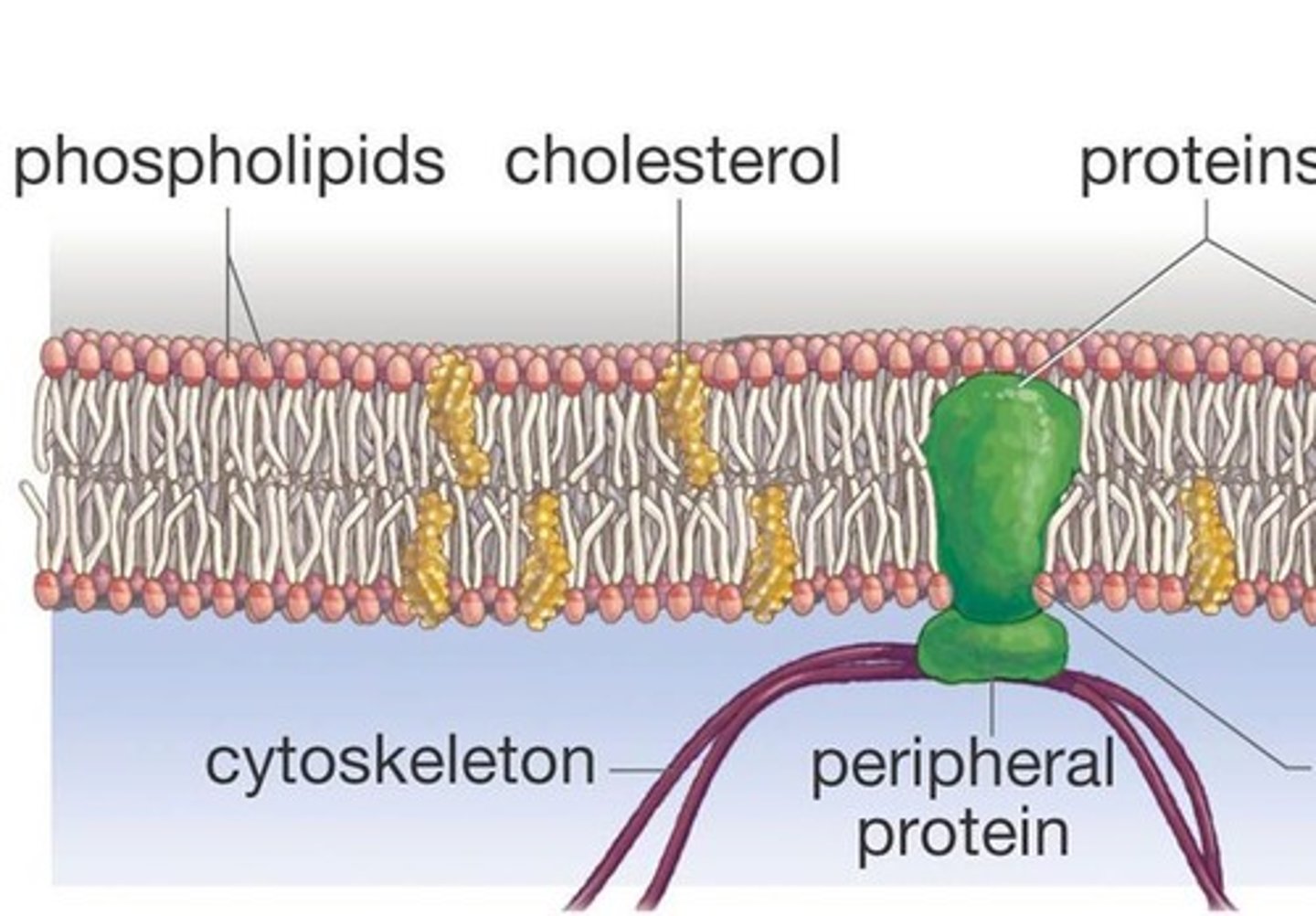
cholesterol in membranes
in cell membrane, helps regulate fluidity or stiffness of membrane but also generate all steroid hormones
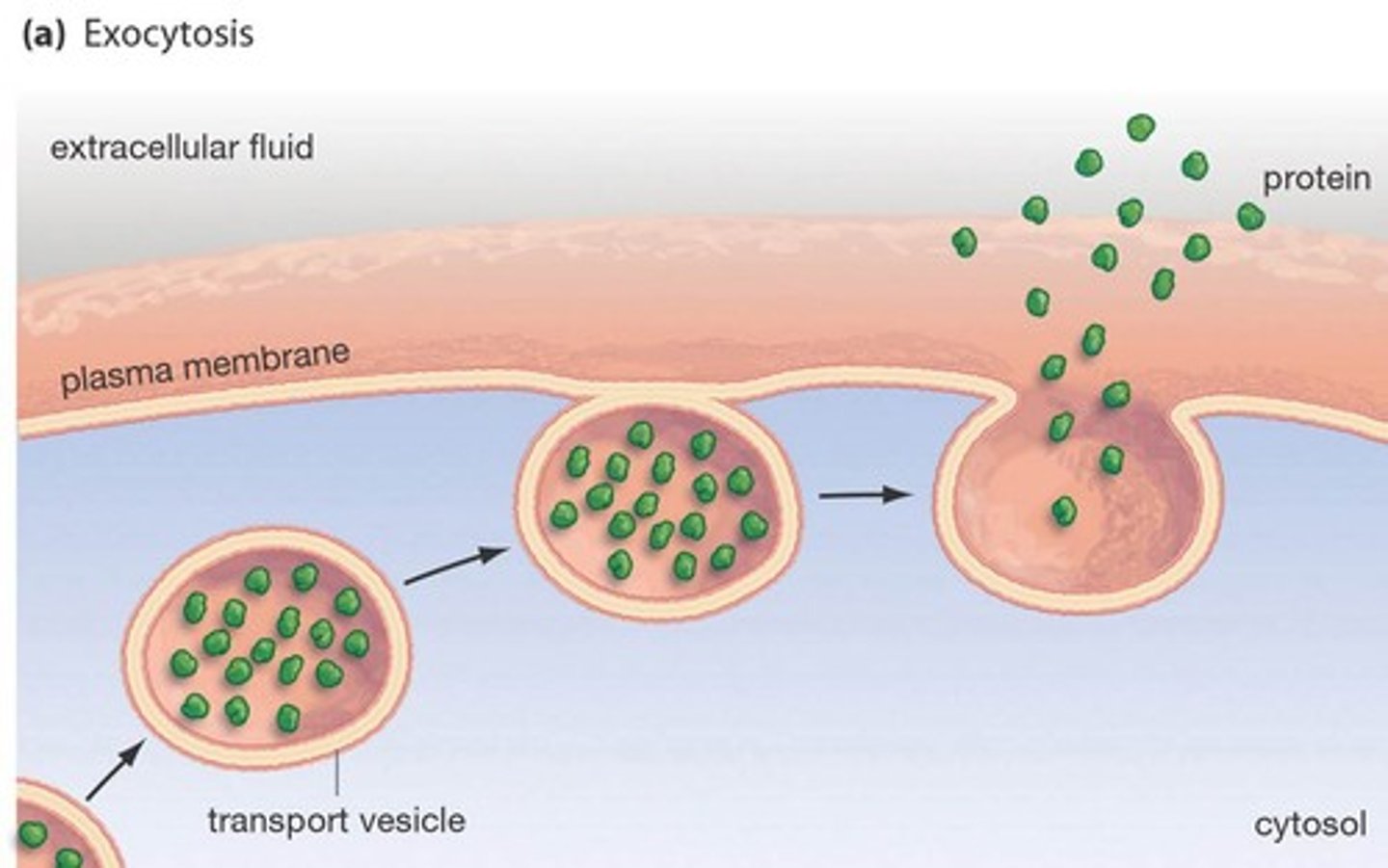
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking

Phagocytosis
Cell eating
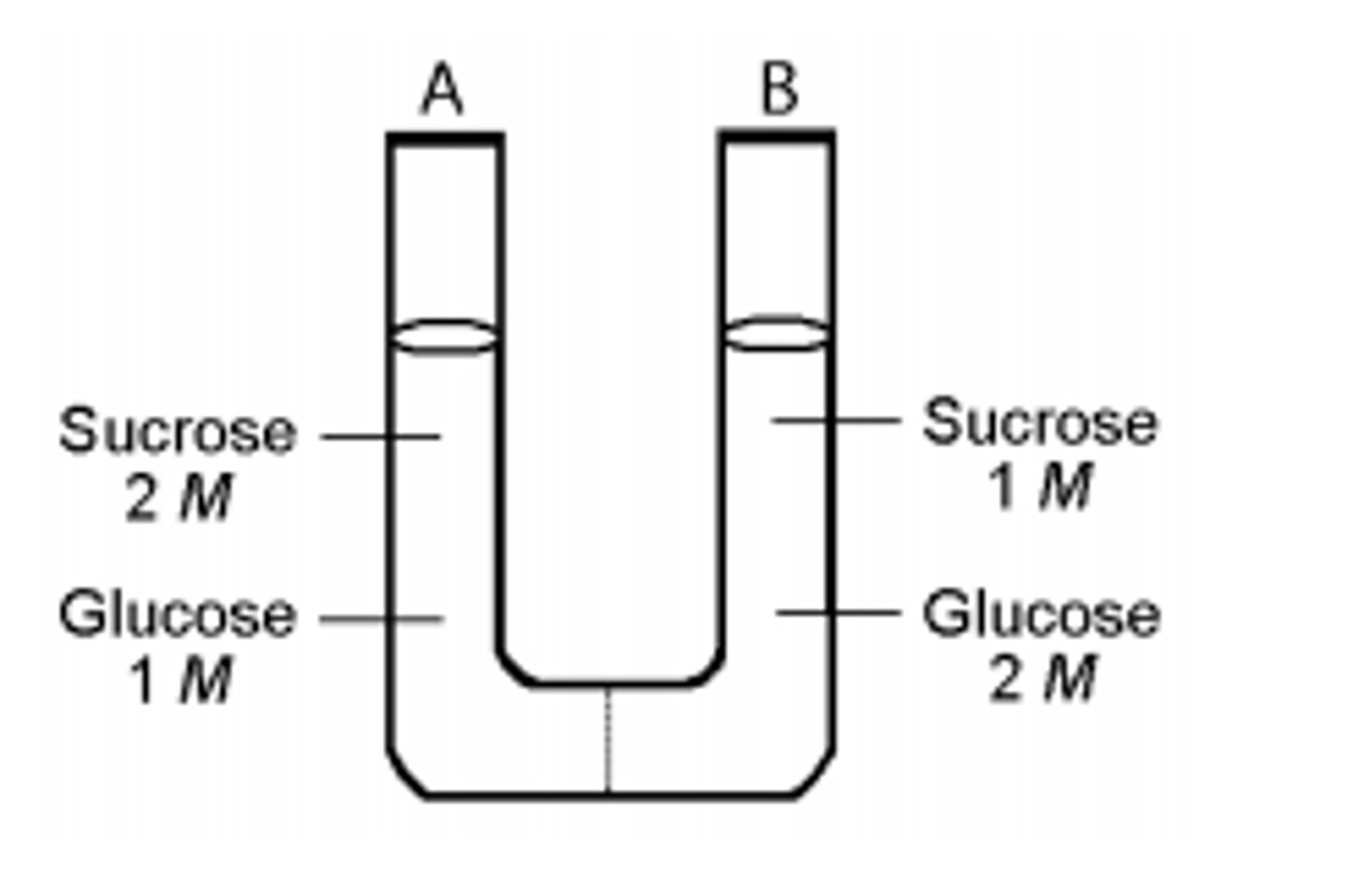
Tonicity of a solution
relates to how the solution influences the shape of body cells
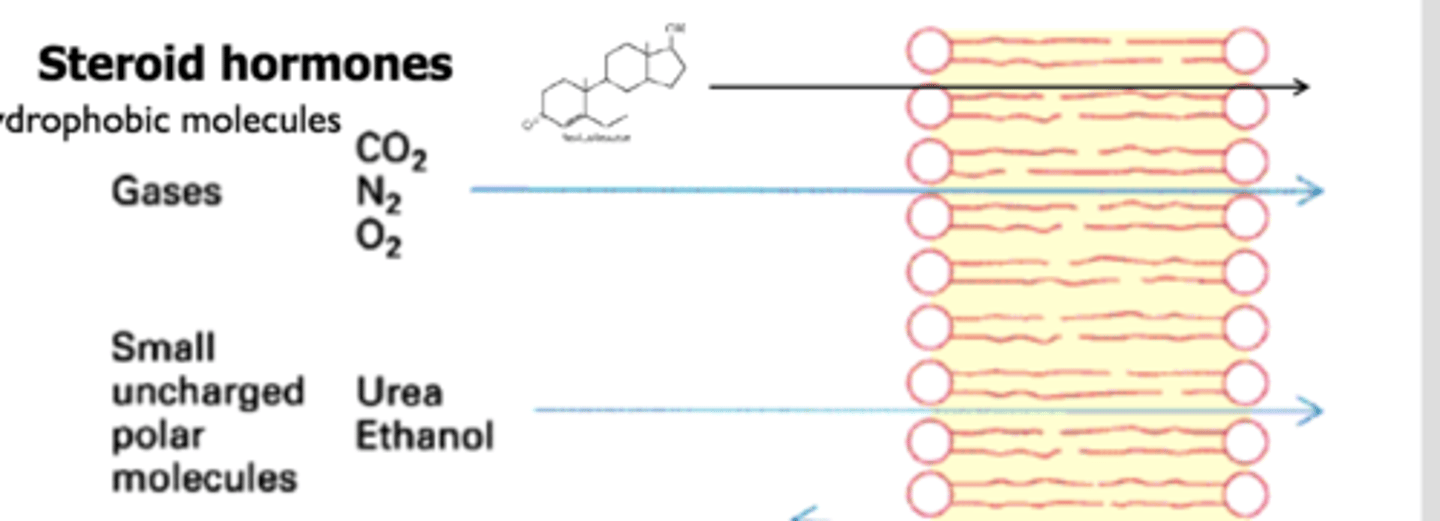
Lipids, small molecules , uncharged molecules
permeable to cell membrane
large molecules, charged ions like sodium
impermeable to cell membrane
proton pump
An active transport protein in a cell membrane that uses ATP to transport hydrogen ions out of a cell against their concentration gradient, generating a membrane potential in the process.
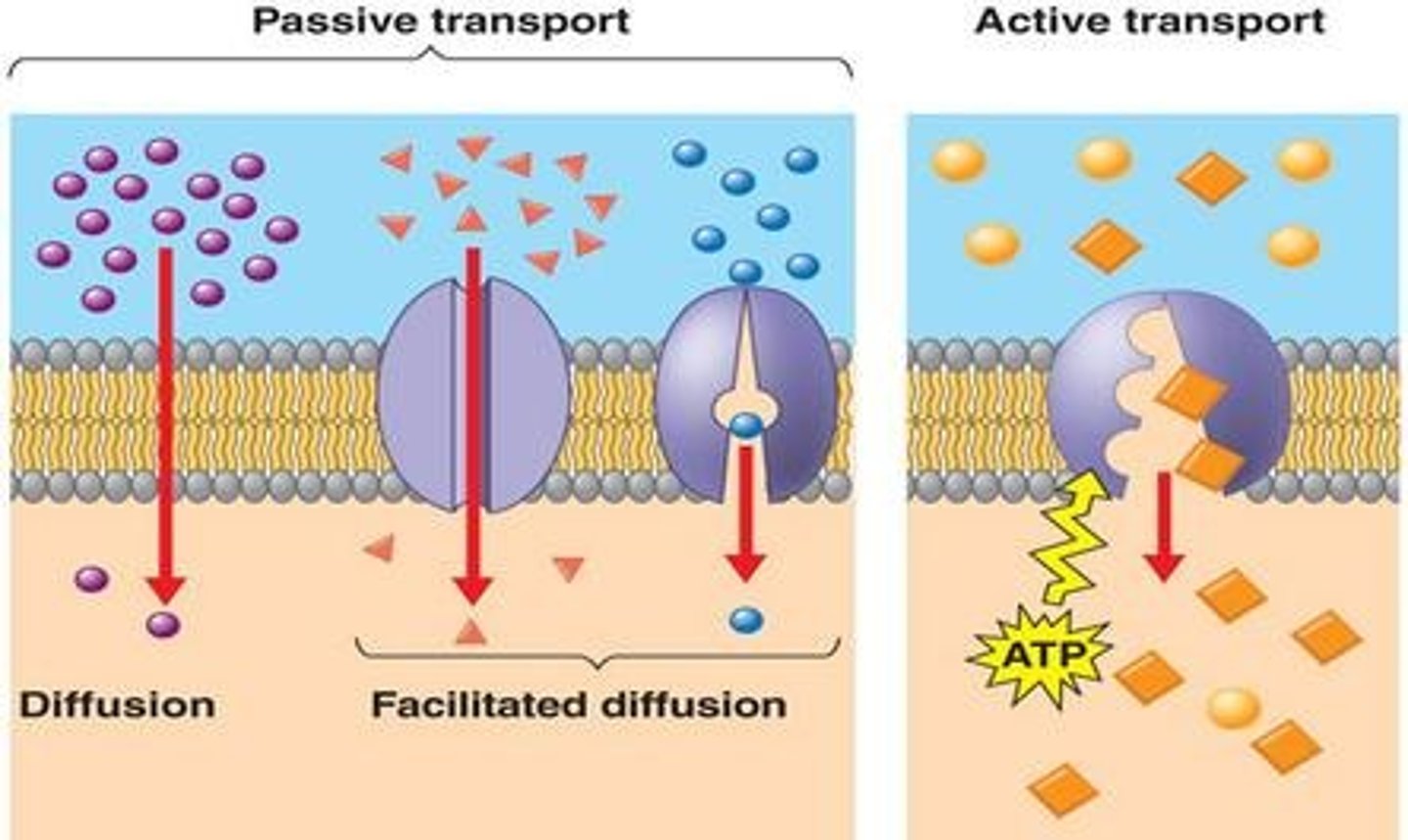
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
passive transport
Requires NO energy, Movement of molecules from high to low concentration, Moves with the concentration gradient
Plasmolysis
This happens when a cell shrinks inside its cell wall while the cell wall remains intact.
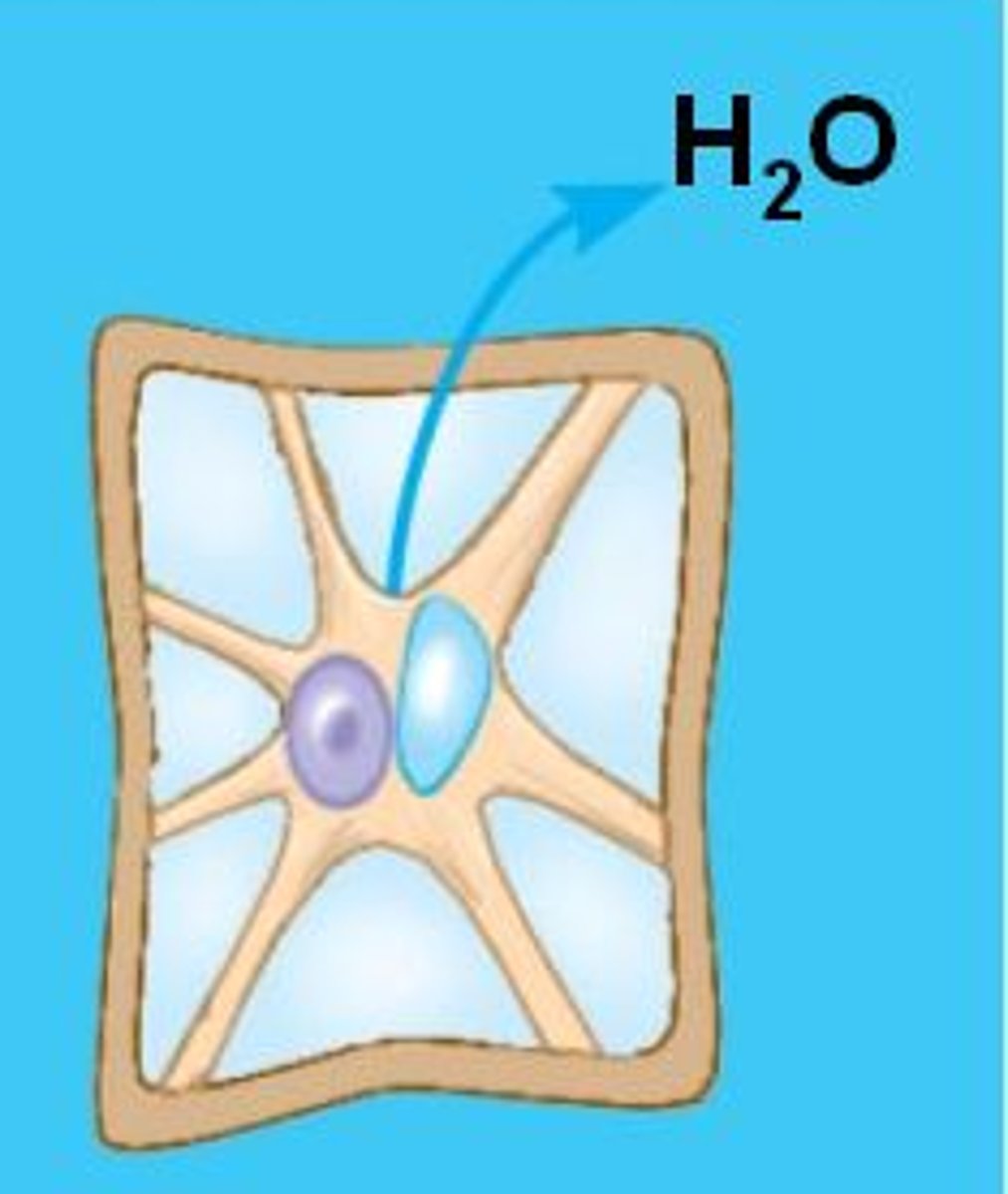
Cytolysis
The rupturing of a cell due to excess internal pressure.

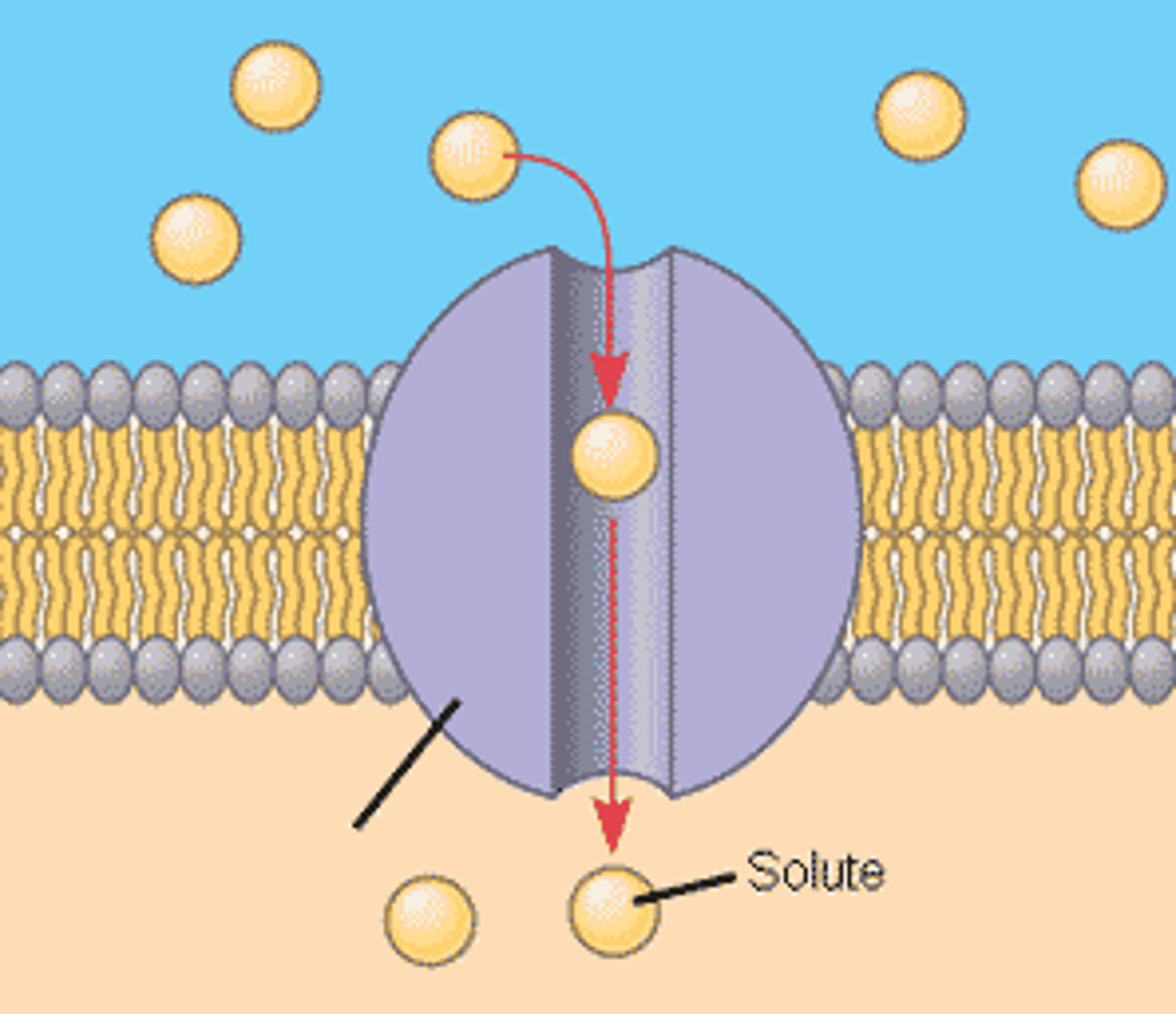
channel proteins
proteins that provide passageways through the membrane for certain hydrophilic (water-soluble) substances such as polar and charged molecules
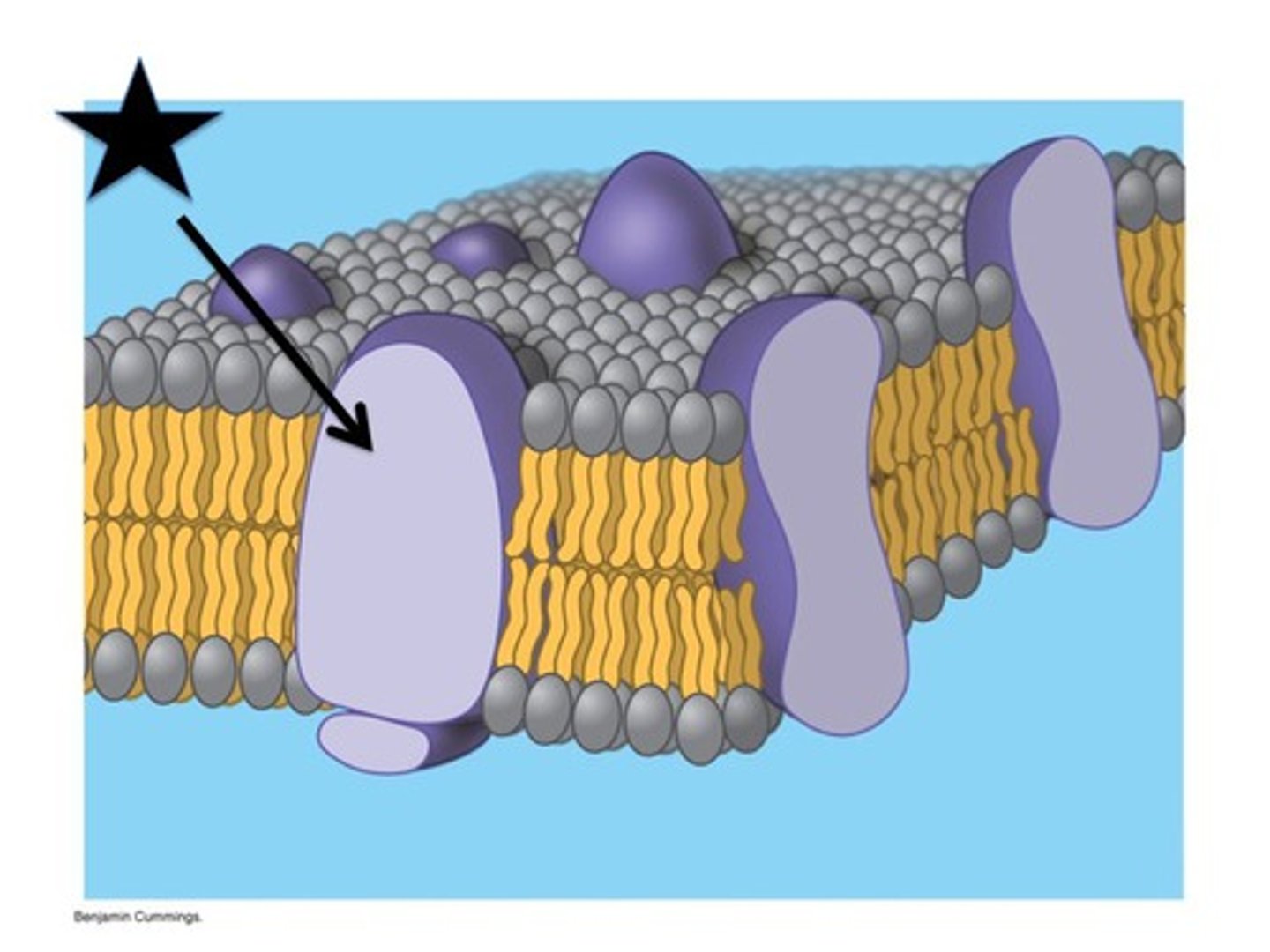
integral proteins
penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
peripheral proteins
bound to the surface of the membrane
