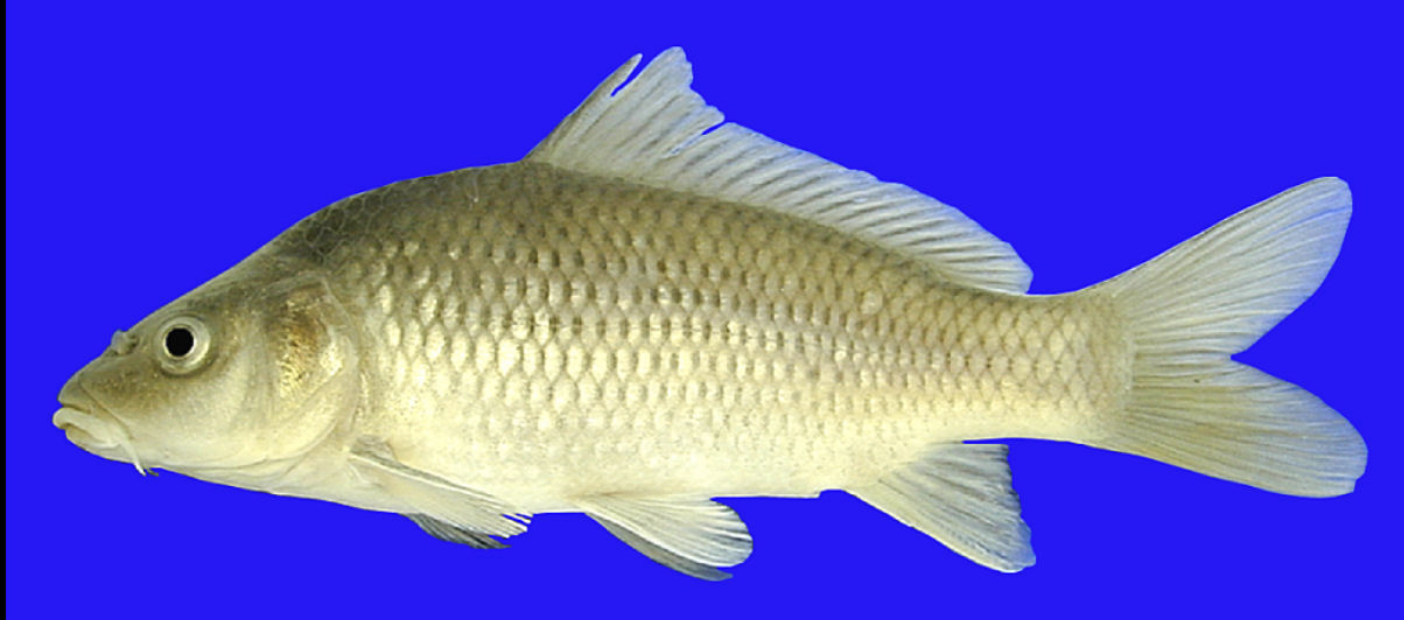
Freshwater Macroorganisms
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
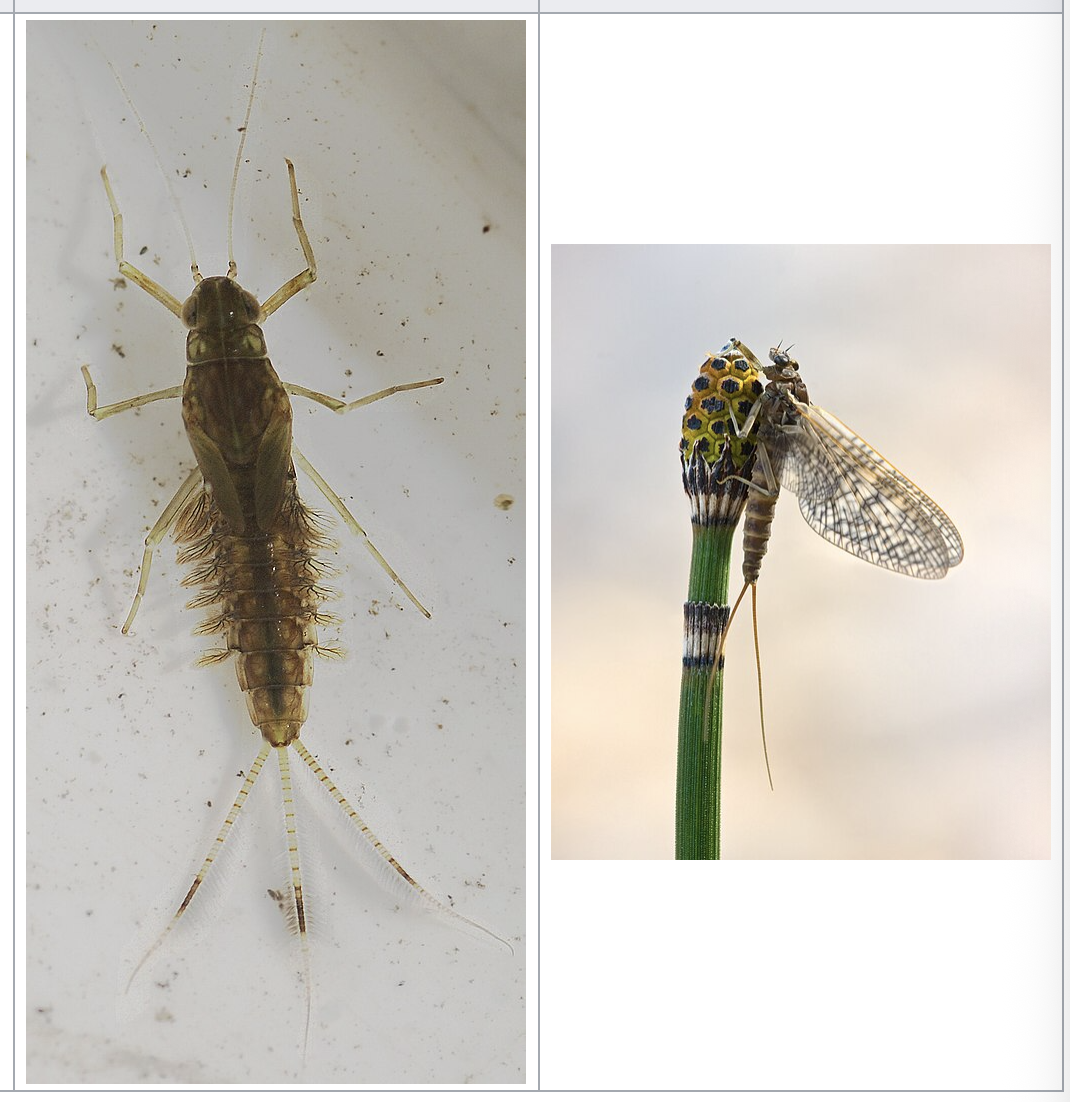
mayfly
importance: C1, clean water
ecology: eaten by fish
life: IM, egg → nymph → adult
feeding: omnivore, organic matter

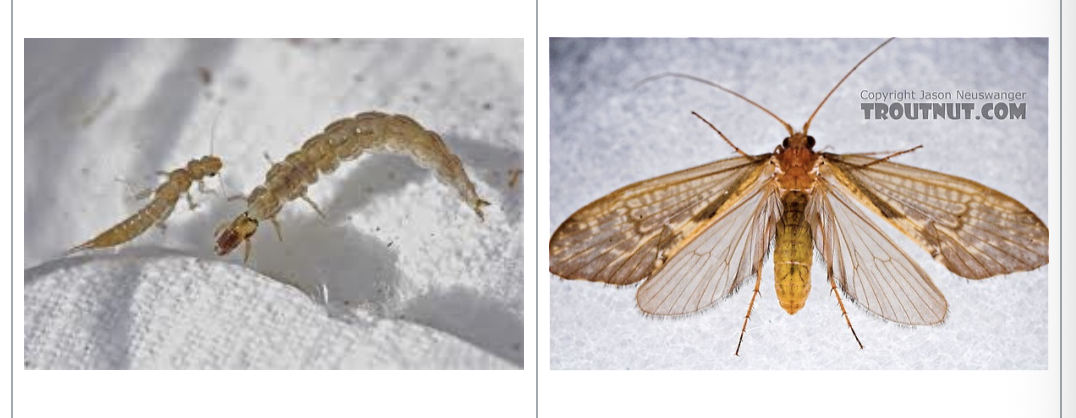
caddisfly
importance: C1, clean water
ecology: eaten by fish
life: CM, egg → larvae → pupae → adults
feeding: omnivore

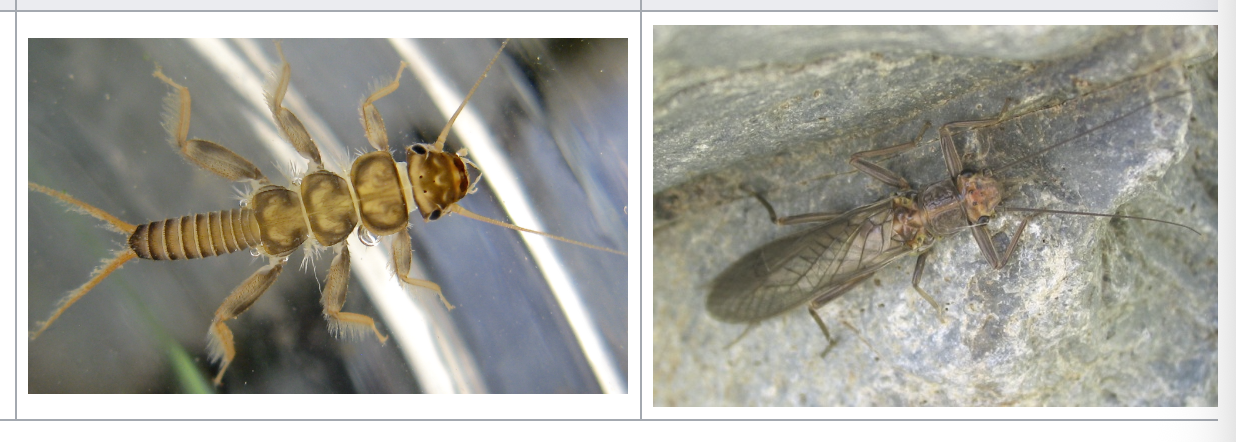
stonefly
importance: C1, clean water, high O2
ecology: eaten by fis
life: IM, egg → nymph → adult
feeding: carnivorous

incomplete vs complete metamorphosis
incomplete: egg → nymph → adult
young are mini-adults
grow distinct body parts (e.g. wings) with successive molts
complete: egg → larvae → pupae → adult
young and adult look nothing alike
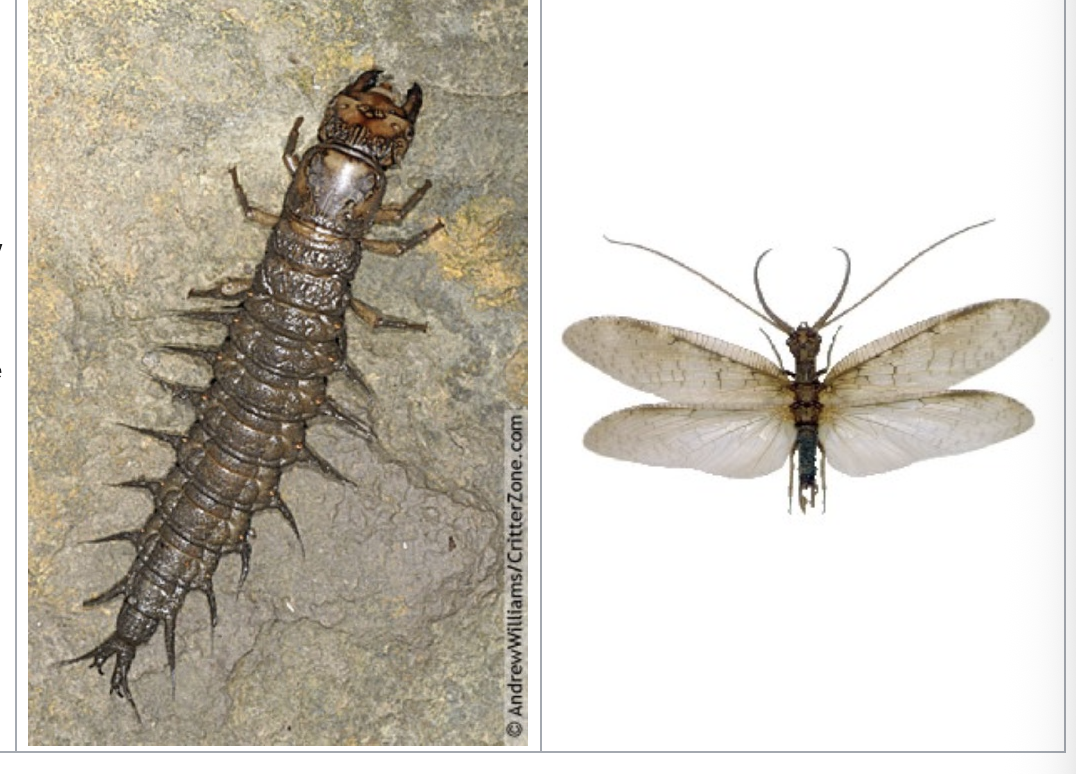
dobsonfly
importance: C1, very clean waters
ecology: eaten by fish
life: CM
feeding: carnivorous larvae (adults do not eat)

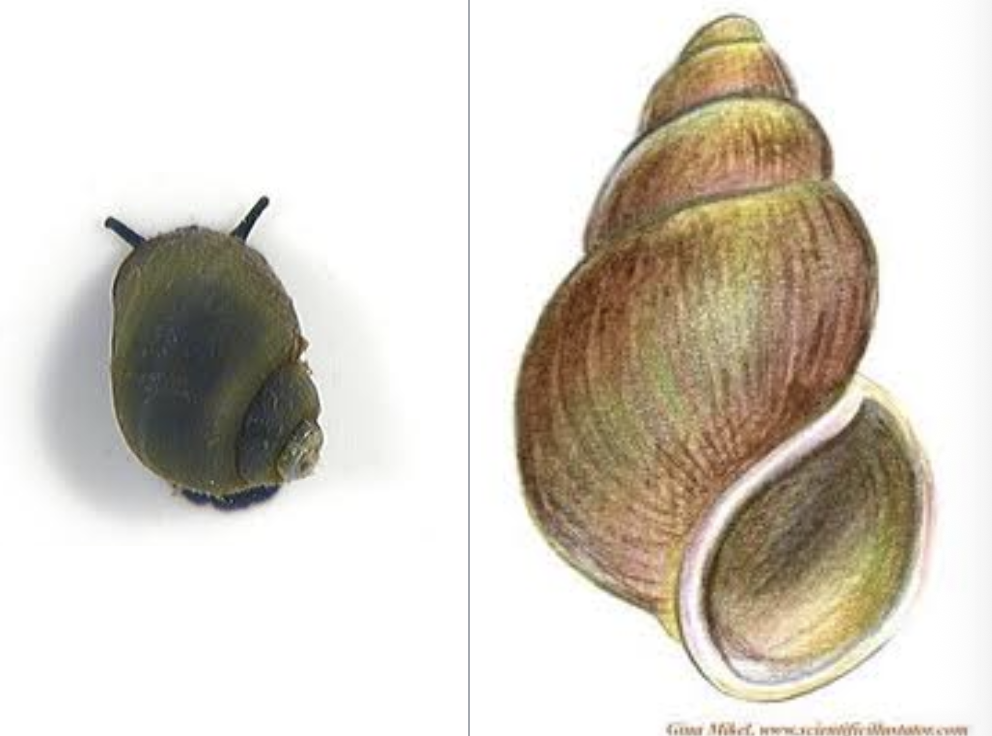
gilled snails
importance: C1, clean, O2 rich waters
ecology: eaten by fish and leeches
life: develop from eggs, no CM
feeding: algae

water penny
importance: C1, fast-moving, O2 rich waters
ecology: eaten by fish and insects
life: CM, larvae look like rocks, live on land as adults
feeding: herbivorous

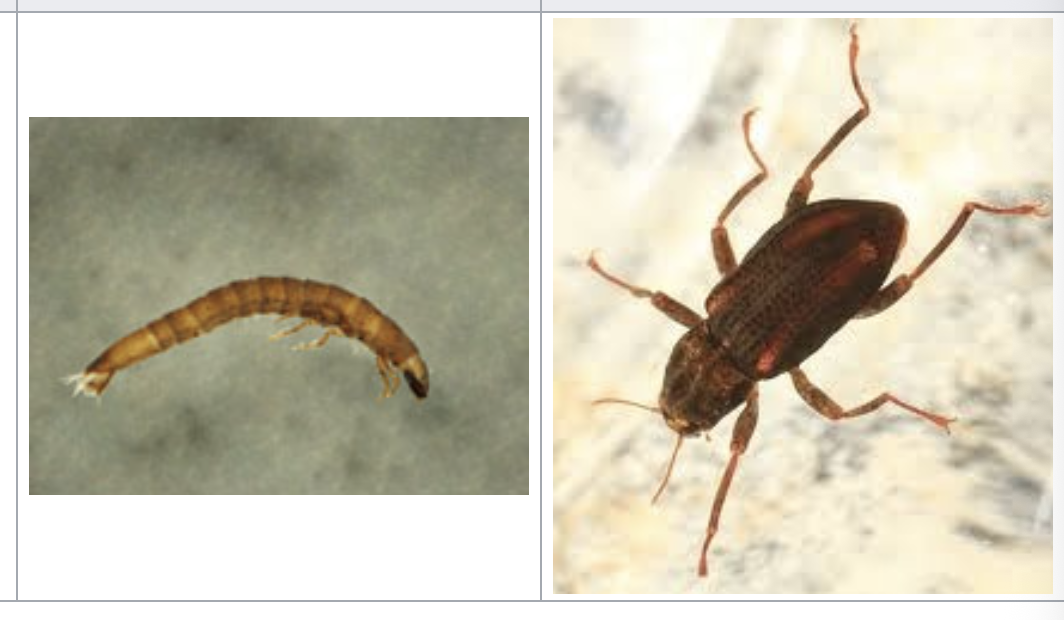
riffle beetle
importance: C1, clean, O2 rich, fast moving waters
ecology: eaten by fish
life: CM, adults are aquatic
feeding: herbivorous

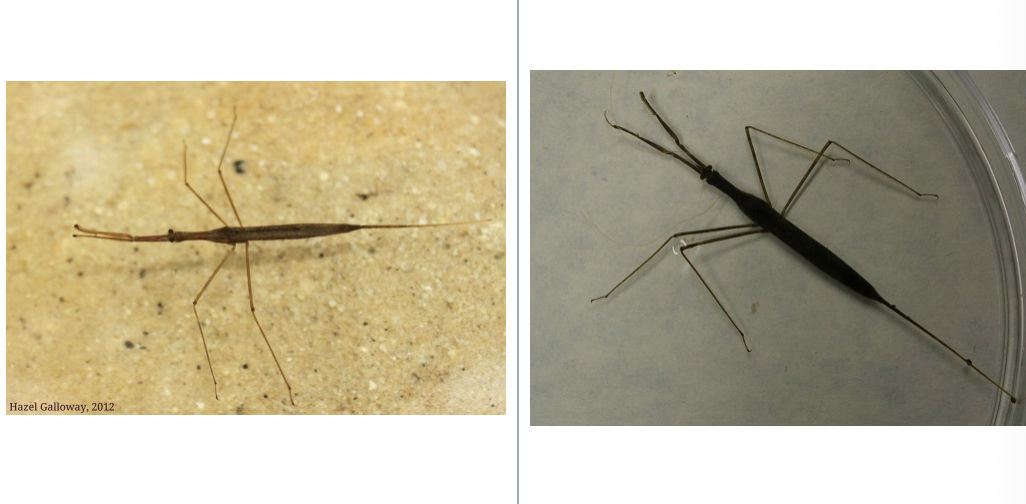
water scorpion
importance: C1, slow moving water bodies
ecology: eaten by fish and birds
life: IM, eggs laid in mud
feeding: carnivorous

aquatic sowbug
importance: C2, streams recovering from sewage pollution
ecology: eaten by vertebrates/invertebrates
life: IM
feeding: omnivorous, dead matter
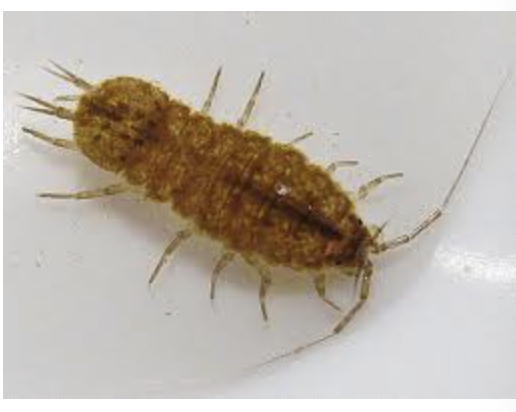

damselfly
importance: C2, slow-moving waters
ecology: eaten by fish, birds, insects
life: IM
feeding: carnivorous, adults eat mosquitos
*wings are parallel at rest, smaller than dragonflies

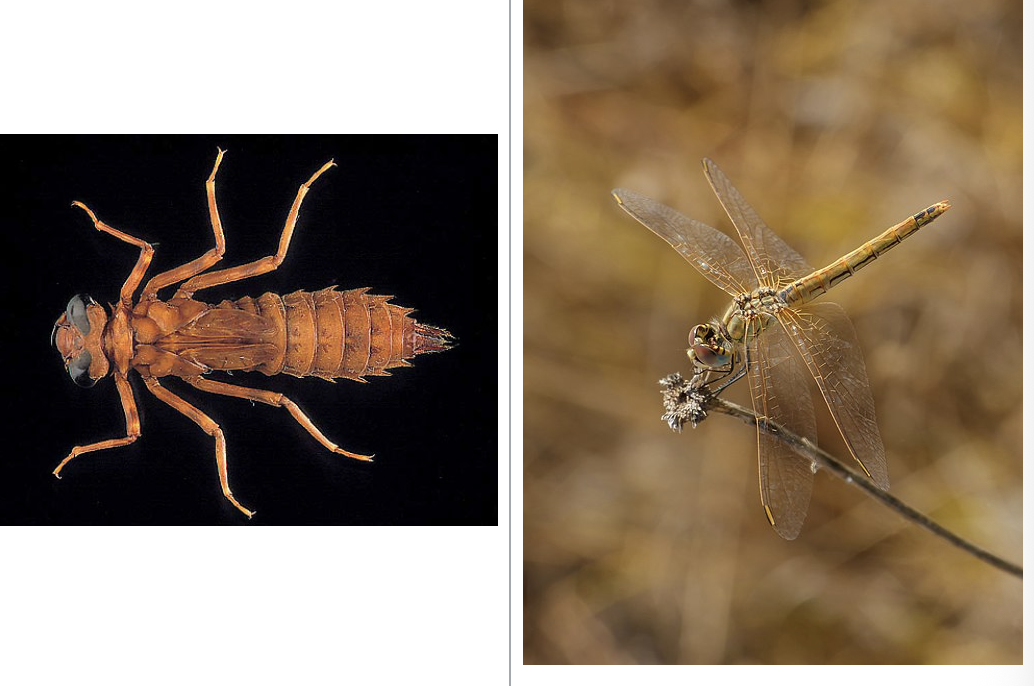
dragonfly
importance: C2, slow-moving waters
ecology: eaten by birds, insects, fish
life: IM
feeding: carnivorous, adults eat mosquitos
*wings perpendicular to bodies at rest

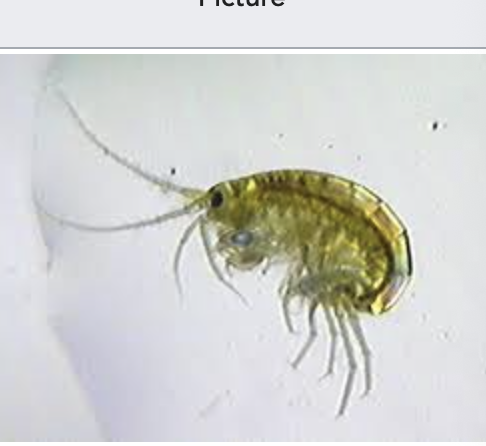
scuds
importance: C2, calcium rich waters, low pollution
ecology: eaten by fish
life: IM
feeding: omnivorous

crane fly
importance: C2, very clean water
ecology: helps clean lakes and ponds, eaten by birds, insects, fish
life: CM, resemble large mosquitos
feeding: omnivorous, some adults do not eat
*aka mosquito hawks, but only larvae eat mosquitos

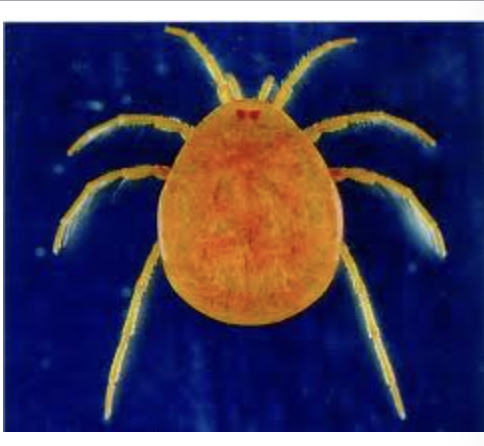
water mite
importance: C3, open, clean water
ecology: usually avoided by fish due to chemicals on their skin
life: CM
feeding: carnivorous, bloodsucking

midge
importance: C3, poor water quality
ecology: eaten by fish, spiders, birds
life: CM, adults resemble mosquitos
feeding: omnivorous
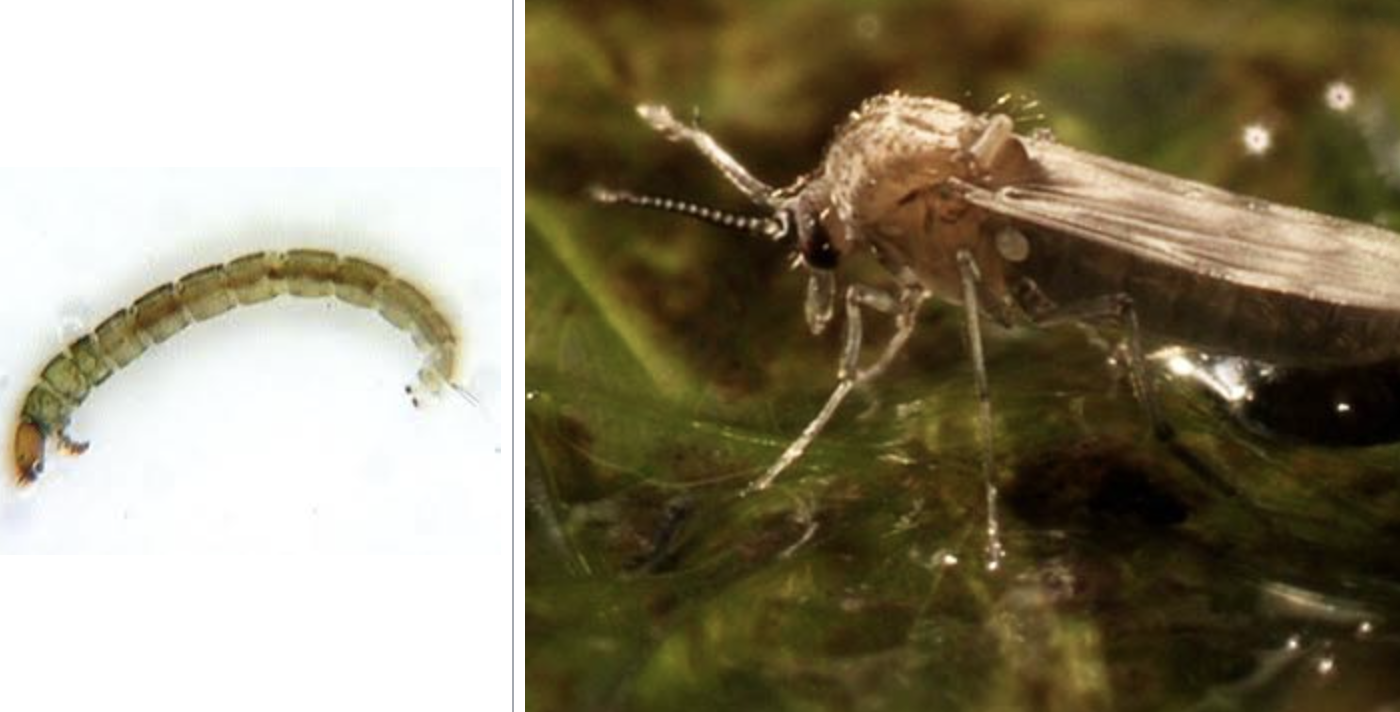

blackfly
importance: C3, fast-moving water, lots of nutrients
ecology: eaten by insects, fish, birds, vector of river blindness
life: CM
feeding: omnivorous
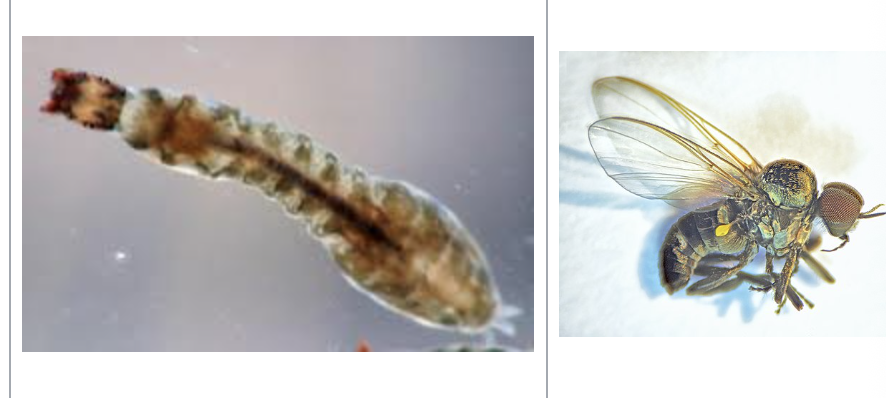
flatworm
importance: C3, poor water quality
ecology: eaten by fish
life: hermaphrodite - have both female and male sex organs
feeding: carnivorous
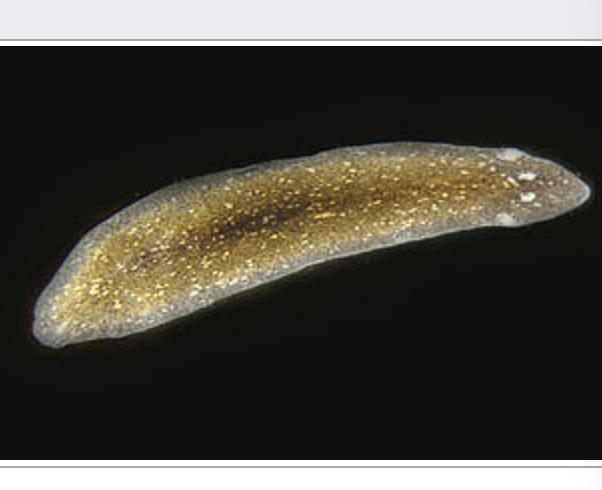
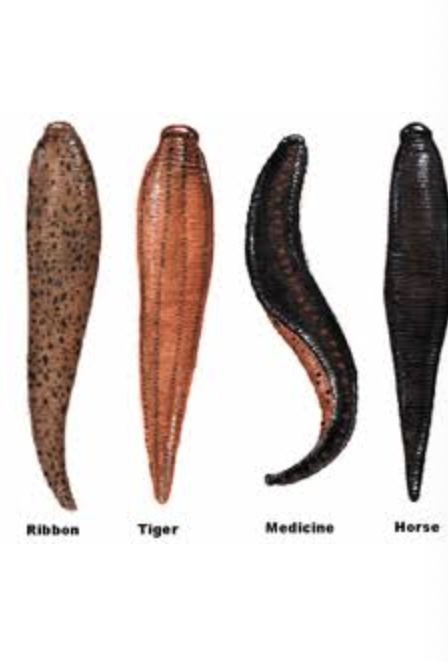
leeches
importance: C3, very poor water quality
ecology: eaten by fish, birds, insects, snails, lack gills
life: hermaphrodite, worm-like appearance, yellow/black
feeding: omnivorous, feed on blood and organic matter

air-breathing snail
importance: C4, too many nutrients, poor WQ
ecology: eaten by fish, birds, turtles
life: brown, gray/blue, no CM
feeding: omnivorous

deer/horse flies
importance: C4, slow-moving water, tolerant to pollution
ecology: eaten by wasps, hornets, dragonflies, pests to warm-blooded animals
life: CM, adults found near water
feeding: carnivorous, females feed on blood
*deerflies are smaller and skinnier, wasp-like
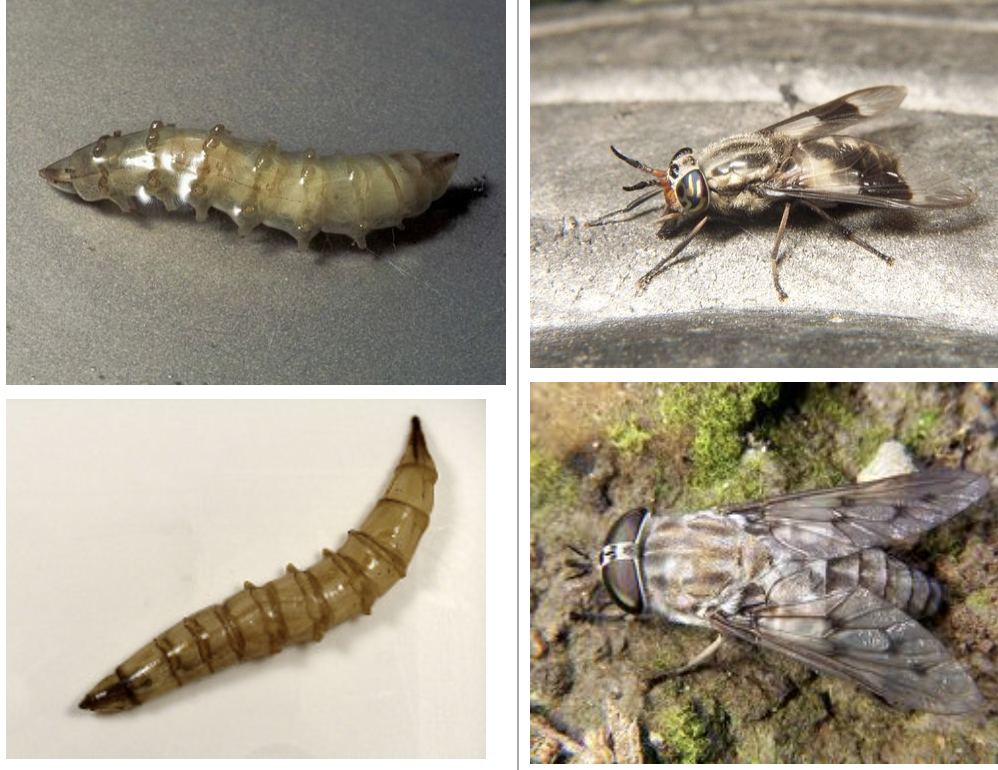

tubifex
importance: C4, stagnant water, low O2, very poor WQ
ecology: live on bottoms of ponds/streams, eaten by fish/insects
life: hermaphrodites, produce cocoons
feeding: detritivores, eat decaying matter and mud

blood midge
importance: C4, low O2, nutrient-rich water, poor WQ
ecology: eaten by bats, birds, insects, few predators
life: CM
feeding: algae, detritus, adults do not feed

whirligig beetle
importance: C5, moderate WQ
ecology: eaten by fish
life: CM, adult spends life in water
feeding: aquatic insects
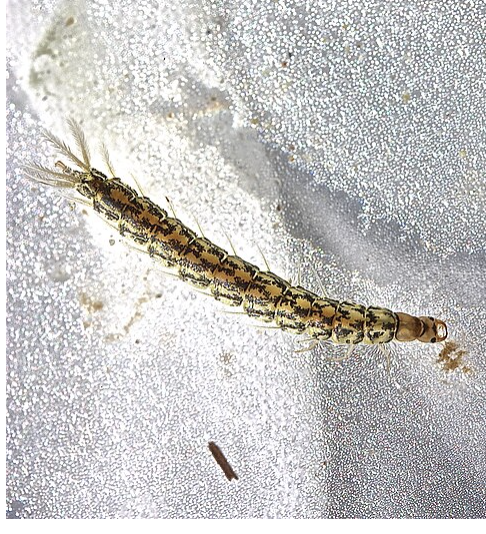

water strider
importance: C5, moderate WQ
ecology: eaten by birds, fish
life: IM
feeding: insects, spiders
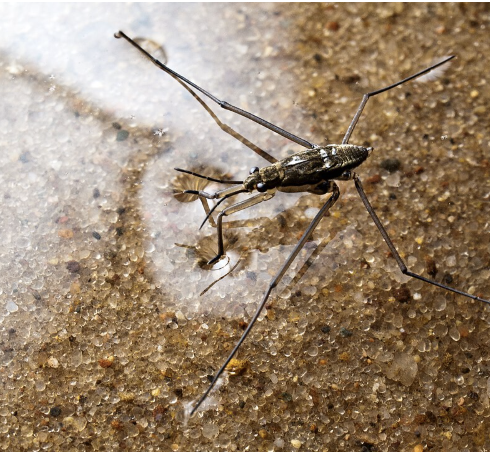

mosquito
importance: very-poor/acidic, stagnant water
ecology: eaten by fish, dragonflies
life: CM, females suck blood/are vectors
feeding: algae, bacteria, fungi, males eat nectar, females eat blood
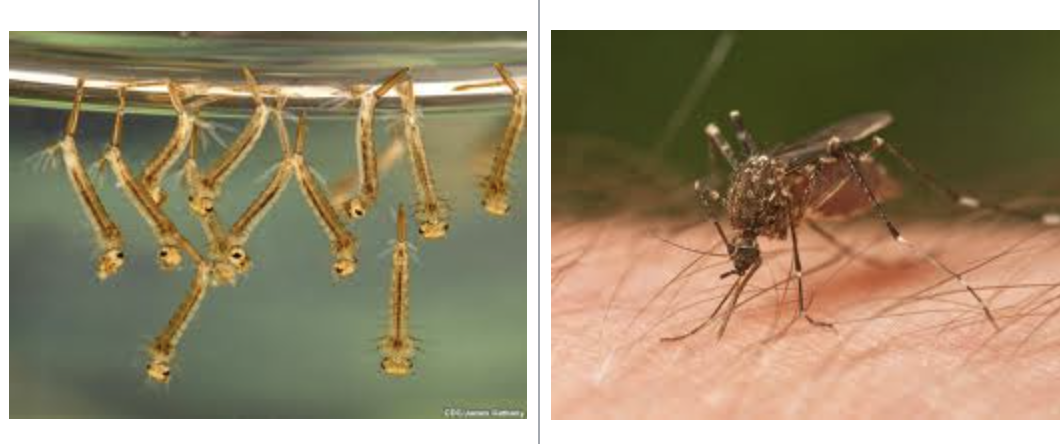

giant water bug
importance: C5, clear, slow-moving water
ecology: top of the food chain
life: IM
feeding: aquatic invertebrates, insects, salamanders, tadpoles, fish

backswimmer
importance: C5, polluted water
ecology: eaten by fish, amphibians
life: IM
feeding: insects, snails, fish, tadpoles
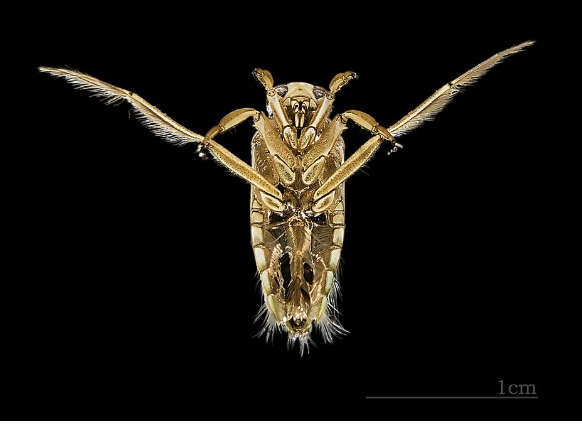

water boatman
importance: C5, pollutant tolerant
ecology: eaten by fish, insects, primary consumers
life: IM
feeding: herbivorous, plants, algae, detritus
*darker than backswimmers, swim right-side up

predacious diving beetle
importance: C5, larvae need oxygen
ecology: eaten by birds, mammals, fish
life: CM
feeding: fish, tadpoles, worms

purple loosestrife
origin: Eurasia
effect: dense growth crowds out other plants
introduction: use for medicine and decoration
distribution: almost all of continental U.S.
importance: indicate low water levels
ecology: eaten by insects/beetles
reproduction: seeds

Eurasian water milfoil
origin: Eurasia
effect: crowds out native species
introduction: unclean trailers
distribution: most of continental U.S.
importance: low O2
ecology: eaten by fish, beetles
reproduction: fragmentation

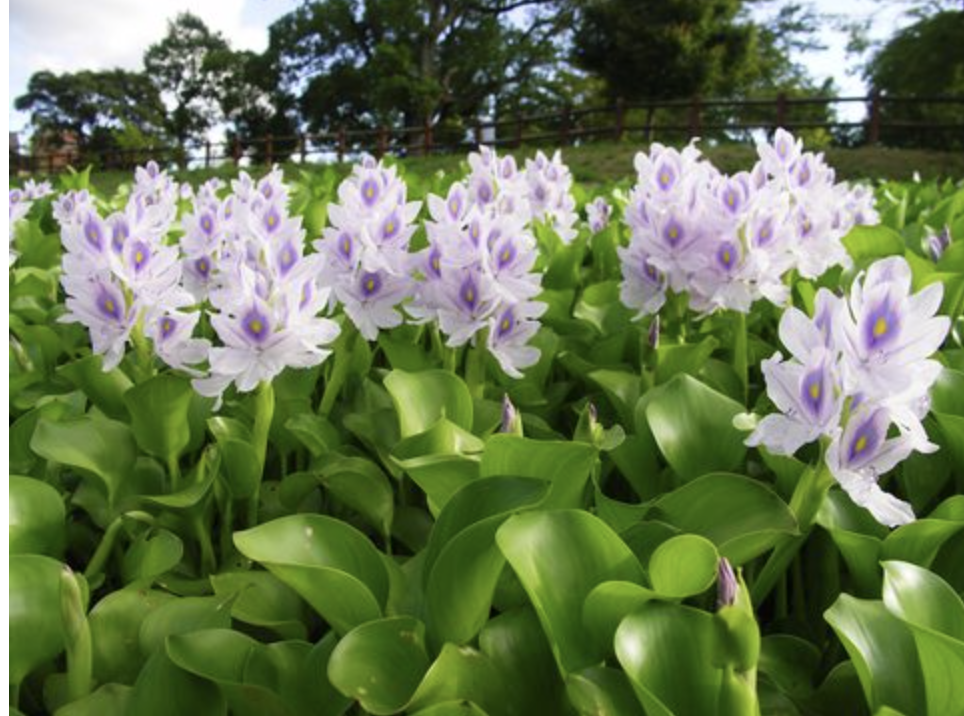
water hyacinth
origin: South America
effect: blocks sunlight, crowds out
introduction: cotton exposition
distribution: Atlantic & Pacific coast
importance: high pollution
ecology: grows very fast, eaten by mammals & fish
reproduction: stolons (a stem)

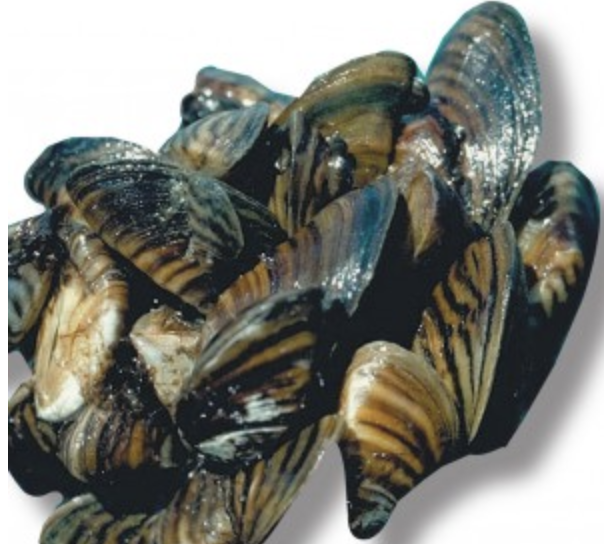
zebra mussel
origin: Eurasia
effect: clogged pipes
introduction: attached to ship hulls
distribution: Great Lakes
importance: low O2
ecology: eaten by fish and birds
life: 5 years max
feeding: filter-feeders

spiny water flea
origin: Europe
effect: depletes zooplankton population, lacks predator
introduction: ship hulls
distribution: Great Lakes
importance: cold, low-nutrients
ecology: carnivorous
life: parthenogenetic (embryo from unfertilized egg)
feeding: zooplankton
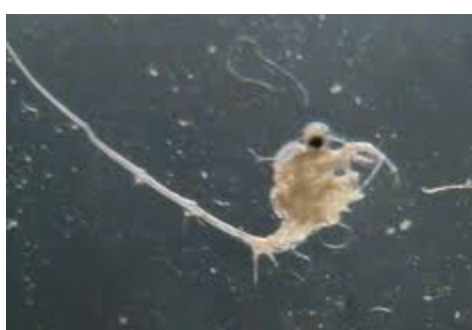
Asian tiger mosquito
origin: Asia
effect: vector of viruses (yellow fever, dengue fever)
introduction: importing Japanese tires
distribution: Southwest, Northeast of U.S.
importance: stagnant water
ecology: eaten by fish, dragonflies
life: CM
feeding: males eat nectar, females eat blood

Asian carp
origin: Asia
effect: increase turbidity
introduction: aquaculture farms
distribution: Great Lakes, Mississippi River
importance: lots of nutrients
ecology: few natural predators, fast reproduction
life: 16+ years
feeding: plankton
