Exam 1- Analytical Forensic Toxicology 470 WVU
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Define toxicology (brief)
The study of the adverse effects of chemical agents on a biological system
Define xenobiotic
a molecule or substance that is not normally found in that specific organism
Define forensic toxicology
The science of detecting and identifying the presence of drugs or poisons in body fluids, tissues, and organs
Who was Hippocrates?
The father of Greek medicine
Who was Dioscorides?
Wrote "The Preparation, Properties, and Testing of Drugs"
Who was Maimonides?
Wrote "Poisons and their Antidotes"
Who was Paracelsus?
Considered to be the Father of modern toxicology, and initiated the idea of dose-response
What was Paracelsus' full name?
Phillippus Aureolus Theophratus Bombastus von Hohenheim
What are the components of the Marsh Test? (general use)
sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and Zinc (Zn) to test for the presence of arsenic trioxide (As2O3)
If the Marsh Test was positive for Arsenic?
Arsine Gas (AsH3) would result from protonating the acid. When ignited, it would produce a black film
What are the components of the Marsh Test? (Forensic use)
Take a specimen and heating it with a reducing agent (zinc) in an acid medium will produce bubbles (arsenic trihydride). Black mirror deposit will confirm As
What happened during the Styrian defense?
Peasants consumed As2O3 (300 or 400 mg) every other day
What is a Fowler Solution
it is a potassium arsenite solution that contains 1% potassium arsenite and is dissolved in water
Who was Jean Servais Stas?
developed the first effective method for extracting alkaloids (marijuana) from biological specimens
Who modified the Stas method?
Friedrich Julius Otto worked to isolate higher-purity alkaloids
Who is considered the first forensic toxicologist?
Dr. Alexander Gettler
Who was Dr. Charles Norris, and what was he known for?
NYC Chief ME in 1918, who replaced the Coroner System with the ME system, quoted "justice is done based on Science."
Who was Alice Hamilton?
She was the first woman appointed as a professor at Harvard and a leading expert in the field of occupational health, and a pioneer in the industrial toxicology field
What is a toxicant?
A type of poison made by humans or introduced into the human environment by human activity
What is the basic definition of a drug?
a substance that is used to produce a physiological response in the body
What is the definition of a drug of abuse?
drugs that are used with no medical purpose
Define psychoactive drugs
any substance that alters the normal functioning of the CNS
What is an analgesic?
a drug or substance that lessens or eliminates pain
What is a narcotic?
An analgesic or pain-killer substance that depresses vital body functions such as blood pressure, pulse rate, etc
What is a hallucinogen?
a substance that induces changes in mood, attitude, thought, or perception
What is a depressant?
a substance used to depress the functions of the CNS
What is a stimulant?
a substance taken to increase alertness or activity
What is an anabolic steroid?
A drug taken to promote muscle growth
Examples of biological fluids for toxicology testing:
- urine
- saliva
- blood
- serum
- humus viterous
- billis
- gastric contents
Examples of organs for toxicology testing:
- kidney
- brain
- liver
What is the purpose of the chain of custody?
to guarantee the integrity, preservation, and conservation of the materials submitted as evidence, to know the status of the process where testing material was handled
What are the basic elements of the chain of custody
- sample collection
- reception at the main lab
- opening of the evidence
- report
What is involved in a toxicological analysis?
general drug screening (Immunoassay) and an extraction system for specific matrices (LLE, SPE, QuEChERS)
What is a qualitative analysis?
preliminary identification to assess the presence of the questioned materials in the biological matrix
What is a quantitative analysis?
identification and quantification of the material as present in the biological matrix
What type of testing is done in Human Performance Tox?
- DUI
- Clinical Emergencies
- SA
What does WADA stand for?
World Anti-Doping Agency
What type of testing is done in Post Mortem FS Tox
- accidental poisoning
- drug overdose
- suicidal poisoning
- homicidal poisoning
Why is post-mortem toxicology important?
It helps to determine the cause and manner of death
What is the general approach to drug analysis?
- screening/presumptive
- separation/ purification
- confirmatory testing
- quant if appropriate
- other tests (if needed)
What is the cut-off for amphetamine for GC/MS confirmation? (in ppb)
500 ppb
What is the cut-off for methamphetamine for GC/MS confirmation? (in ppb)
500 ppb
What is the cut-off for cannabinoids for GC/MS confirmation? (in ppb)
15 ppb
What is the cut-off for cocaine metabolites for GC/MS confirmation? (in ppb)
150 ppb
What is the cut-off for opiates for GC/MS confirmation? (in ppb)
2000 ppb
What is the cut-off for codeine for GC/MS confirmation? (in ppb)
2000 ppb
What is the cut-off for 6-acetylmorphine for GC/MS confirmation? (in ppb)
2000 ppb
What is the cut-off for Phenecyclidine (PCP) for GC/MS confirmation? (in ppb)
25 ppb
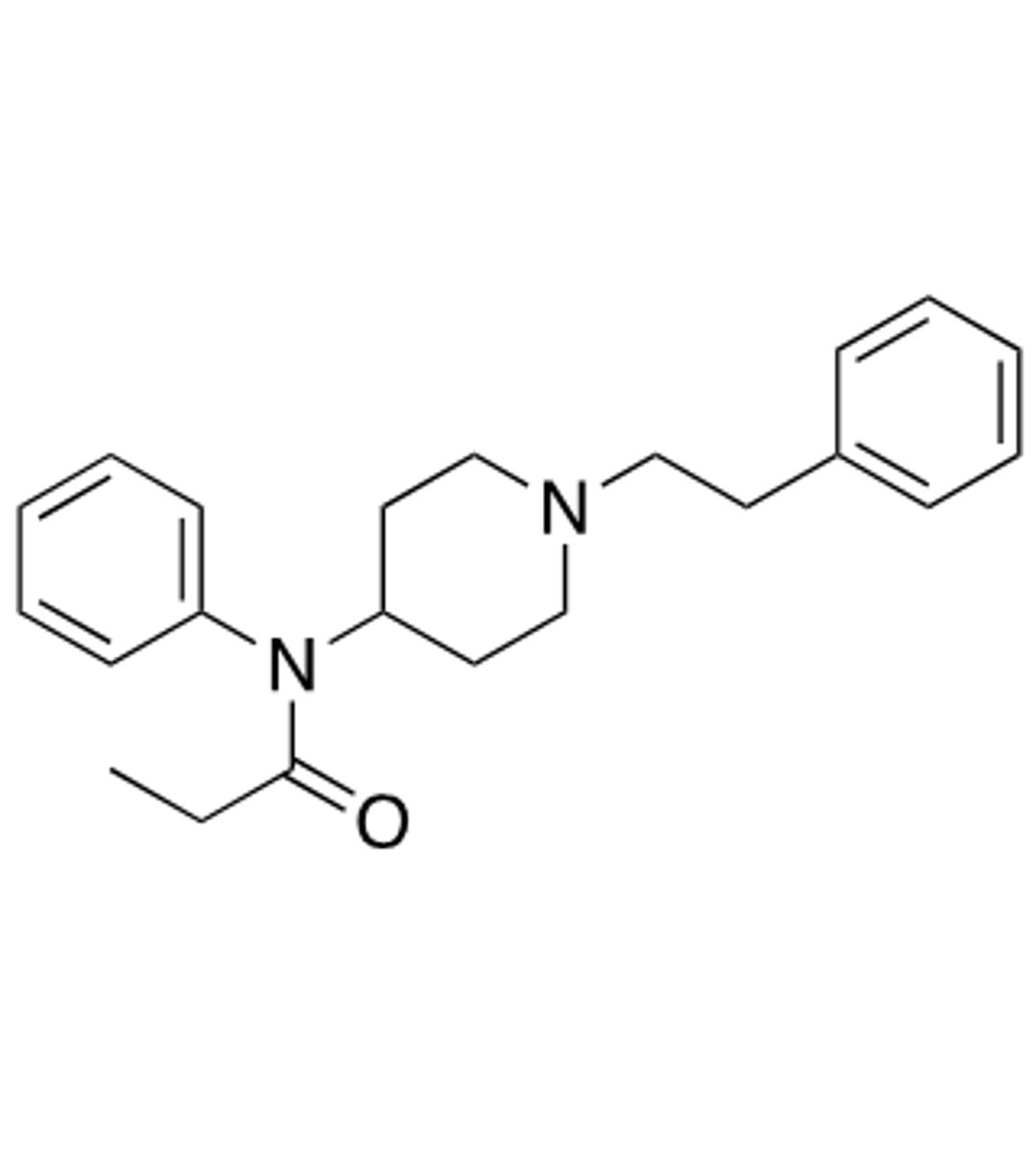
What is the structure of fentanyl
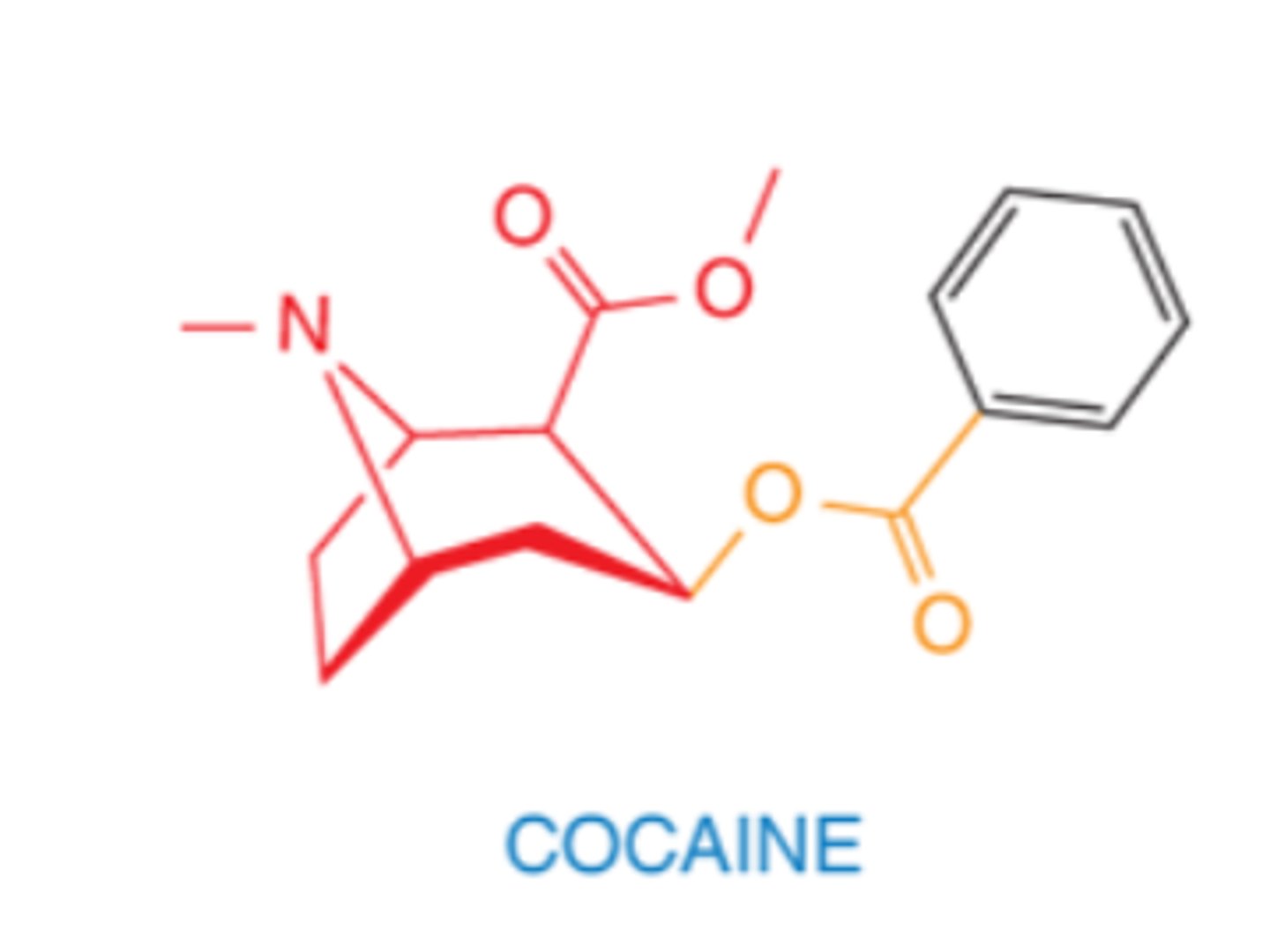
What is the structure of cocaine
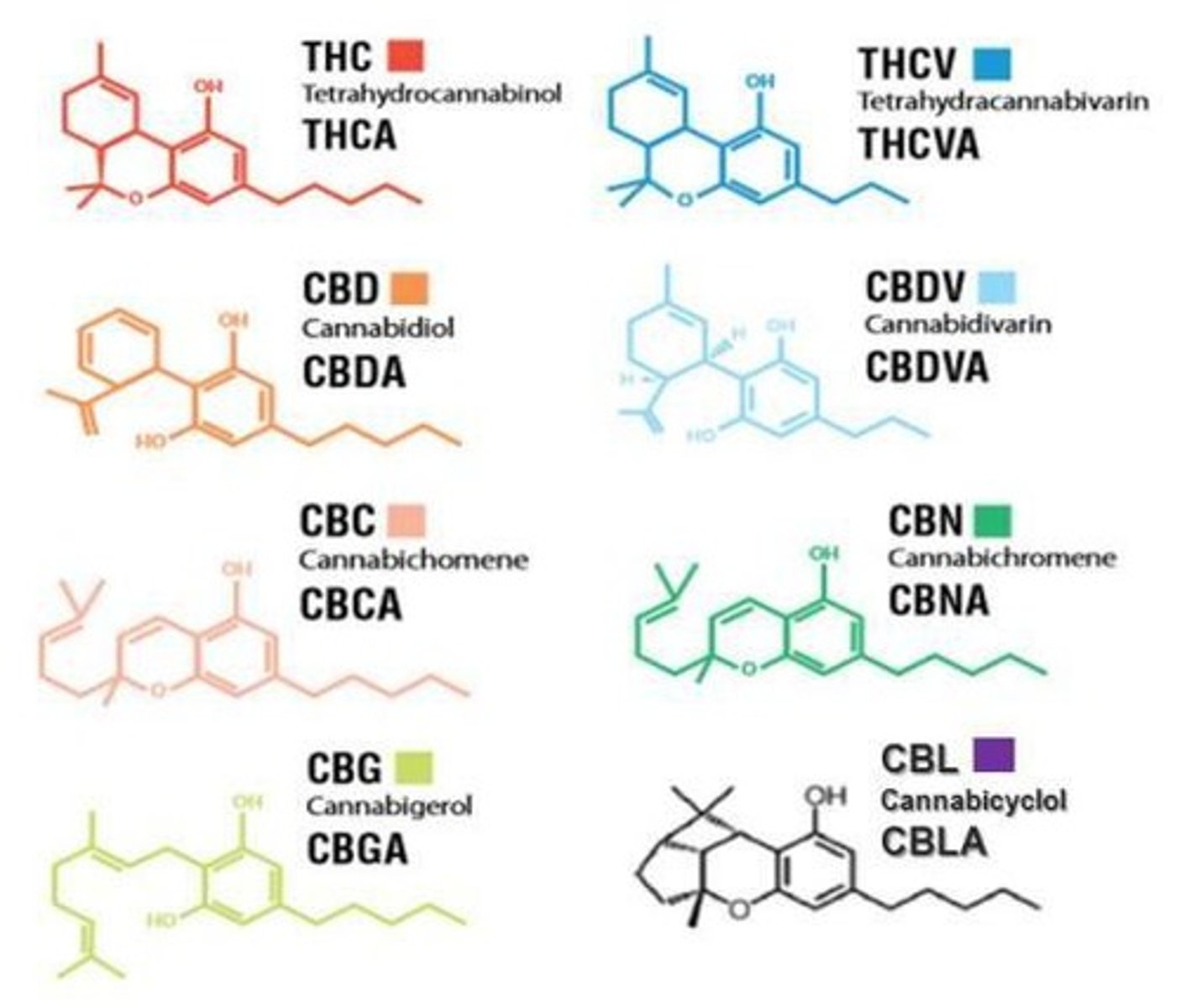
What is the structure of cannabinoids
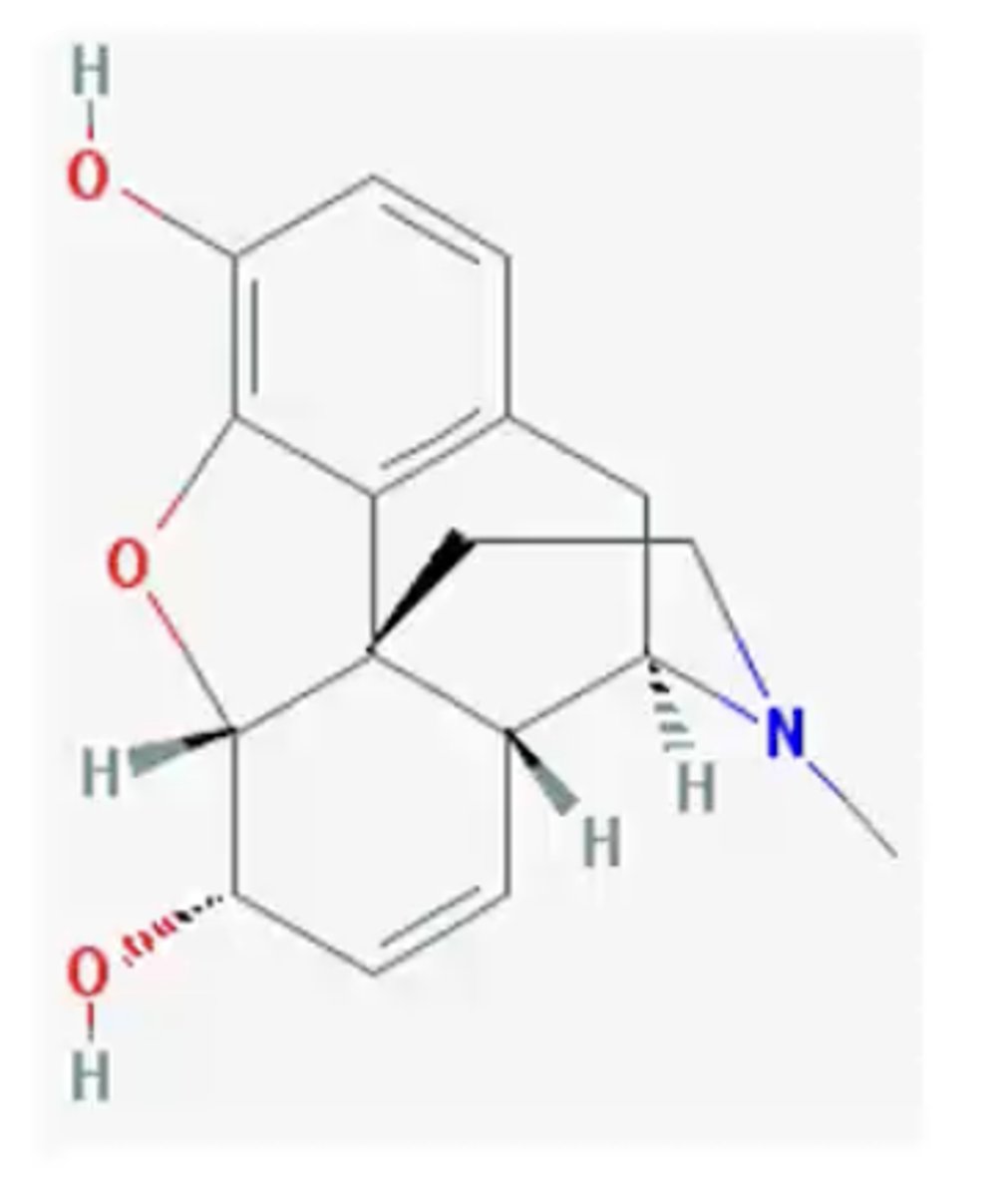
What is the structure of morphine
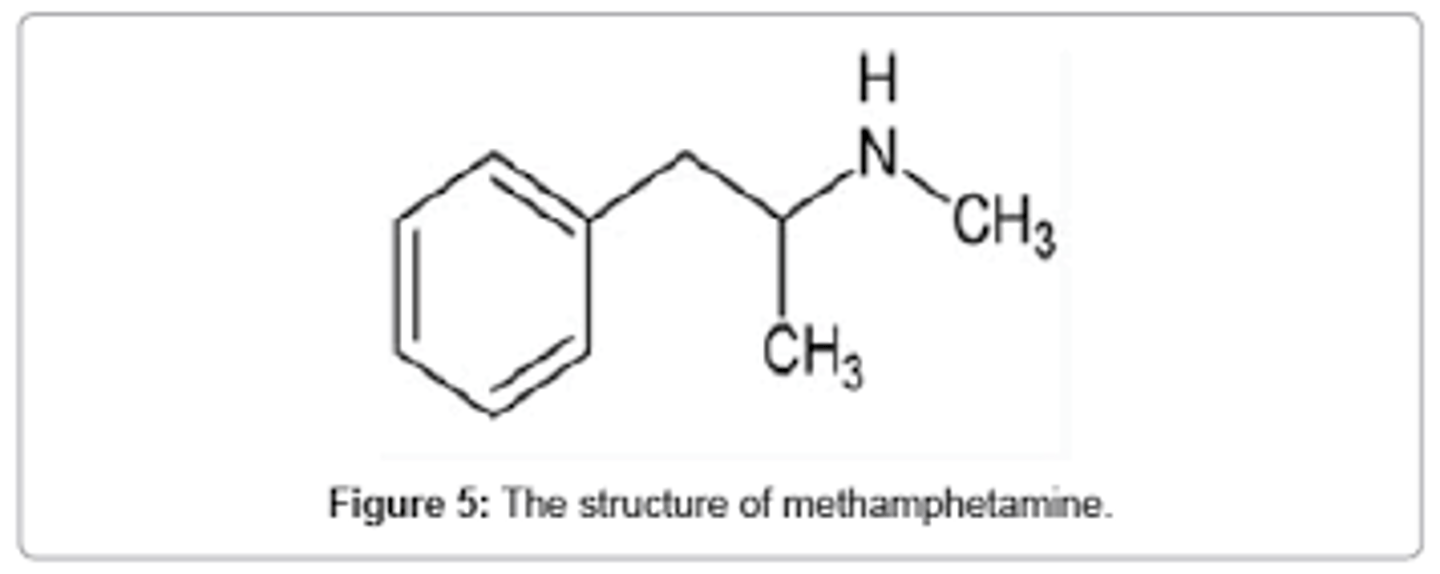
What is the structure of methamphetamine
What are the advantages of using blood in toxicology testing?
- widely used
- screening potential unlimited
- detection window is minutes to days
- original sample can be retested
What are the disadvantages of using blood in toxicology testing?
- invasive
- must be stored in the fridge
- Extraction and analysis are more complex due to matrix interference
What are the advantages of using urine in toxicology testing?
- most frequently used
- on-site testing
- Many drugs can be identified
- original sample can be retested
What are the disadvantages of using urine in toxicology testing?
- cheating
- sample handling and storage difficulties
- Interferences are common
What are the advantages of using sweat in toxicology testing?
- tests prospectively
- tamper-proof
- easier to detect the presence of parent drug in heroin, THC, and cocaine cases
What are the disadvantages of using sweat in toxicology testing?
- uses an electrical current to generate sweat
- limited experience
- limited range
- can become environmentally contaminated
What are the advantages of using hair in toxicology testing?
- not possible to cheat
- up to 90 days detection window
- can discriminate between light, moderate, and heavy users
- fewer interference
What are the disadvantages of using hair in toxicology testing?
- limited number of drugs
- fewer providers
- not useful for certain drugs (THC)
- Environmental contamination
What are the advantages of using oral fluid in toxicology testing?
- easy to collect
- cheating difficult
- cost-effective
What are the disadvantages of using oral fluid in toxicology testing?
- fewer databases
- short detection window
- sample handling issues
- individual saliva production
- not sensitive on-site for marijuana
Define toxicity
any adverse effect of a xenobiotic on a biological system; that can express damage to a living system elicited by a chemical of either endogenous or exogenous origin
Define toxin
a xenobiotic of biological origin
Define toxicant
a xenobiotic of manmade origin
Define hazard
The likelihood that a xenobiotic will cause toxicity at a specific dose or exposure level (probability)
Define risk
a quantitative description of hazard
Define safety
The reciprocal of hazard, the likelihood that toxicity will not occur
Define toxic
term used to describe a detrimental or negative impact or effect on subjects
What are local effects in toxicology?
Contact is first made by the toxicant and the biological system by ingestion or inhalation, or irritant material
What are systemic effects in toxicology?
requires the absorption and distribution of a toxicant from its entry point to a distant site where the deleterious effects are produced
What is the difference between a drug and a toxin?
A drug is a beneficial pharmaceutical compound, whereas a toxin is capable of causing an injury
How much nicotine is in one cigarette?
10-12 milligrams (mg)
What is the graph for the dose-response relationship?
concentration (x-axis) v. intensity of response (y-axis)
How do we assess toxicity?
- animal toxicology studies
- controlled clinical studies
- epidemiological studies
What does ADME stand for?
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Elimination/Excretion
Define absorption
The processes by which the drug of poisons are brought into the blood and cells of the body
Define distribution
The process by which drugs and poisons are moved around the body and taken up into the organs and tissues
Define metabolism
The process by which the drugs and poisons are biochemically altered/ broken down
Define elimination
The process by which drugs and poisons are removed from the body
What are the components of a GC/MS system?
Carrier gas - an inert gas (usually helium) that moves the sample through the system.
Injector - where the liquid or gas sample is introduced and vaporized.
Column (inside oven) - separates the compounds based on their chemical properties.
Transfer line - heated pathway that carries compounds from the GC to the MS.
Ion source - turns compounds into charged particles (ions).
Mass analyzer - separates the ions by their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z).
Detector - records the ions and creates a signal.
Computer/data system - processes the signal into a chromatogram and mass spectra for identification.
What are the components of an LC/MS system?
Pump - pushes liquid solvent (mobile phase) through the system.
Injector/Autosampler - introduces the liquid sample.
LC Column - separates compounds based on their chemistry.
Ion Source (ESI) - turns liquid-phase molecules into gas-phase ions.
Mass Analyzer - separates ions by their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z).
Detector - records the ions.
Computer/Data System - processes the signals into chromatograms and spectra.
What is LD 50?
lethal dose for 50% of the test population.
What is ED 50?
effective dose for 50% of the population.
How to find the pH of an acid from a concentration example: 0.2M
- log (0.2M)= pH
How to find [H+] concentration from Ka and concentration example: 0.2M
sqrt(Ka)(0.2M)= [H+]
How to find pH from pOH
pH + pOH= 14
How to approx. for a weak acid HA⇌H++A−
[H+]≈sqrt(Ka)(concentration)
In water (assuming density ≈ 1.00 g/mL at room temp), ppb relationship
1 ppb = 1 µg/L
10 ppb = 10 µg/L
100 ppb = 0.1 mg/L
A forensic toxicology lab detects 0.050 mg/L of arsenic in a water sample. What is this in ppb?
0.050 mg/L (1000ppb/mL/L)= 50 ppb
Florence Maybrick
Poisoned her husband using arsenic. Used soaked flypapers and arsenic powder mixed with soot, Fowler's solution: K arsenic
Lafarge Murder
Used a cake containing arsenic, Matthieu Orfila best-known forensic toxicologist of the time
Forensic files video
The husband poisoned wife with insect traps and arsenic but small doses actually helped her build tolerance. Found in her hair dating back to certain months
Affected Organs
Hepatoxic = Liver
Nephrotoxic = Kidney
Hematoxic = Blood
Central Nervous System
Schedule 1 drug
High potential for abuse
No currently accepted medical use
lack of accepted safety for use
LSD, Heroin, Marijuana, Methaqualone
Schedule 2 drug
High potential for abuse
Currently accepted medical use with severe restrictions
abuse may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence
Morphine, PCP, Cocaine, Methadone, Methamphetamine
Schedule 3 drug
drugs potential for abuse is less than those in 1 and 2
there is currently accepted medical use in U.S, but abuse may lead to moderate or low physical dependence or high psychological dependence.
anabolic steroids, codeine, hydrocodone, some barbiturates
Schedule 4 drug
low potential for abuse relative to 3
currently accepted medical use
may lead to limited physical dependence or psychological dependence
Xanax, Valium, Darvon
Specimen collection (easy to difficult)
Hair
Nails
Saliva
Urine
Exhale Breath
Breast Milk
Blood
Cord Blood
Tissues