CF- Austin
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Define each of the following:
autosomal
exocrinopathy/exocrine glands
CFTR
mucolytic
corrector
potentiator
amplifier
CF is an…
a. autosomal dominant exocrinopathy
b. autosomal recessive exocrinopathy
c. sex-linked exocrinopathy
b. (exocrinopathy means effecting the exocrine glands, which are glands that secrete)
What gene is responsible for CF?
cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)
What is CFTR responsible for?
anion channel that transports chloride and bicarb
regulates amount and composition of exocrine gland secretions
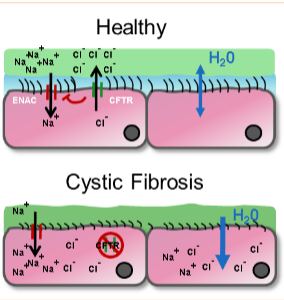
Describe the pathophysiology of CF:
what happens to the airways?
what happens to the pancreas?
what are some other exocrine tissues effected?
airways—> secretions obstruct small/medium airways
result: breeding ground for bacteria
profound damage to the pancreas—> obstructed ducts, impaired flow/production of digestive enzymes
result: chronic malabsorption, poor growth, fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies
other tissues affected:
liver (bile ducts)
intestines
reproductive organs
musculoskeletal
CNS
CF airway is characterized by aggressive ___________-induced inflammation driven by chronic respiratory infection.
neutrophil
What is the tx class for mucus in CF patients?
mucolytics, secretolytics, and mucoregulators
Answer the following about Dornase alfa:
is it a mucolytic, secretolytic, or mucoregulator?
what type of enzyme?
MOA
ADRs
mucolytic
recombinant human deoxyribonuclease I (rhDNase)
MOA: enzyme that selectively cleaves DNA, reduces sputum viscosity by hydrolyzing DNA to promote clearance of secretions
ADRs:
voice alteration
pharyn/laryngitis
rhinitis
What route of admin is 1st line for antibacterials in CF?
inhaled formulations (duh)
What oral and IV agents are also used for antibacterial tx in CF?
fluoroquinolones
aminoglycosides
vancomycin
What is the MOA and 2 key effects of aminoglycosides (-mycin/micin)?
MOA—> binds 16S rDNA of 30S subunit
effects:
misreading of mRNA= premature termination and incorporation of incorrect amino acids
inhibition of initiation= stuck at the start codon
What is the spectrum of activity of aminoglycosides (-mycin/micin)?
active against:
G- aerobes
INCLUDING PSEUDOMONAS
inactive against:
G+
anaerobes
facultative anaerobes
mycobacterium
What are the 3 significant toxicities associated with aminoglycosides?
What is the BBW?
nephrotoxicity—> may be reversible
ototoxicity—> irreversible
neuromuscular blockage (serious side effect where muscle contraction is inhibited, potentially leading to respiratory paralysis)
BBW: nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, pregnancy
What is the spectrum of activity of Aztreonam?
active against:
G- bacteria
INCLUDING PSEUDOMONAS
not active against:
G+ bacteria
anaerobes
Aztreonam is safe to use in what allergy?
penicillin/cephalosporin allergy
Answer the following about Polymyxins (Colistin):
what are polymyxins?
MOA
Main toxicities?
polymyxins—> cationic peptide detergents produced by Bacillus
polymyxins B and E are used clinically
polymyxin E is colistin
MOA: surface-active amphipathic agents
BACTERICIDAL against G-
interacts with and disrupts membrane phospholipids
toxicities:
nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity
Pancreatic insufficiency in CF is supplemented with enzymes from animals (pigs).
What are the contents of pancreas enzymes supplemented?
lipase: fats
protease: proteins
amylase: carbs
How are pancreatic enzymes dosed?
know this
based on LIPASE/grams of fat ingested
ADRs of pancreatic enzymes:
GI (pain, n/v/d/c)
HA
MOA of a CFTR CORRECTOR.
drug examples?
SAR considerations
ADRs
KNOW THIS. (maybe except for SAR considerations)
increase # of functional CFTR at cell surface—> act as chaperones during protein folding to increase trafficking to cell surface
drugs: lumacaftor, tezacaftor, elexacaftor
SAR considerations: R stereochemistry, para acidic group on distal ring, difluoromethoxy group
ADRs:
chest discomfort
GI (n/d/pain)
HA
respiratory (cough, congestion)
increased transaminases
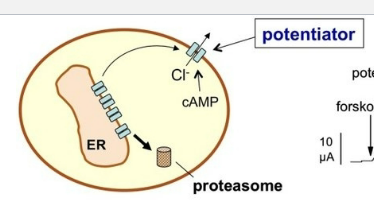
MOA of a CFTR POTENTIATOR.
drug examples?
ADRs
KNOW THIS.
keep channel open to increase chloride transport
drugs: ivacaftor
ADRs:
GI (n/d/pain)
HA
URI
nasal congestion/ nasopharyngitis
MOA of a CFTR AMPLIFIER.
drug examples?
KNOW THIS.
increase production of CFTR
drugs: nesolicaftor (in development still)
Which of the following correctly describes tobramycin (in monotherapy)?
A. May be effective against MRSA; potential ADR tendon rupture
B. May be effective against MRSA; potential ADR neuromuscular blockade
C. May be effective against Pseudomonas; potential ADR tendon rupture
D. May be effective against Pseudomonas; potential ADR neuromuscular blockade
D.
Which of the following drugs prevents CFTR misfolding?
A. Ivacaftor
B. Lumacaftor
C. Nesolicaftor
D. None of the above
B.