Speciation & Macroevolution
Species

multiple species concepts defined based on specific criteria; morphological similarity, reproductive compatibility, mate recognition, biological species
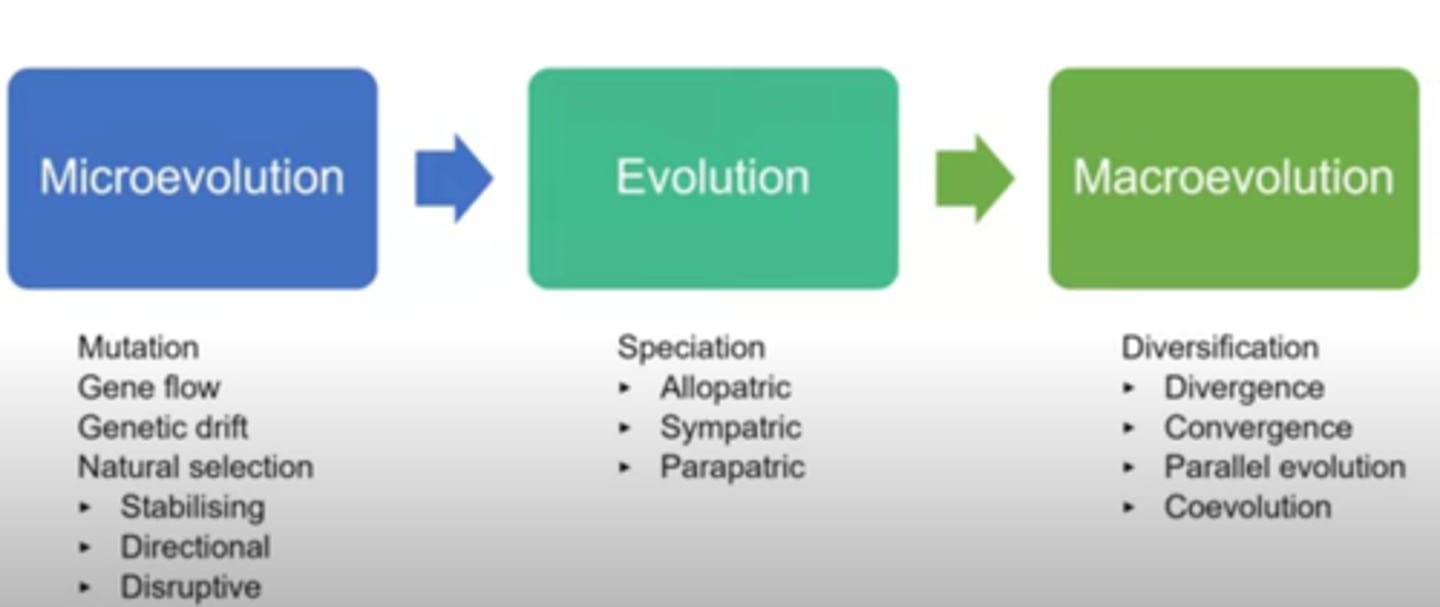
Microevolution
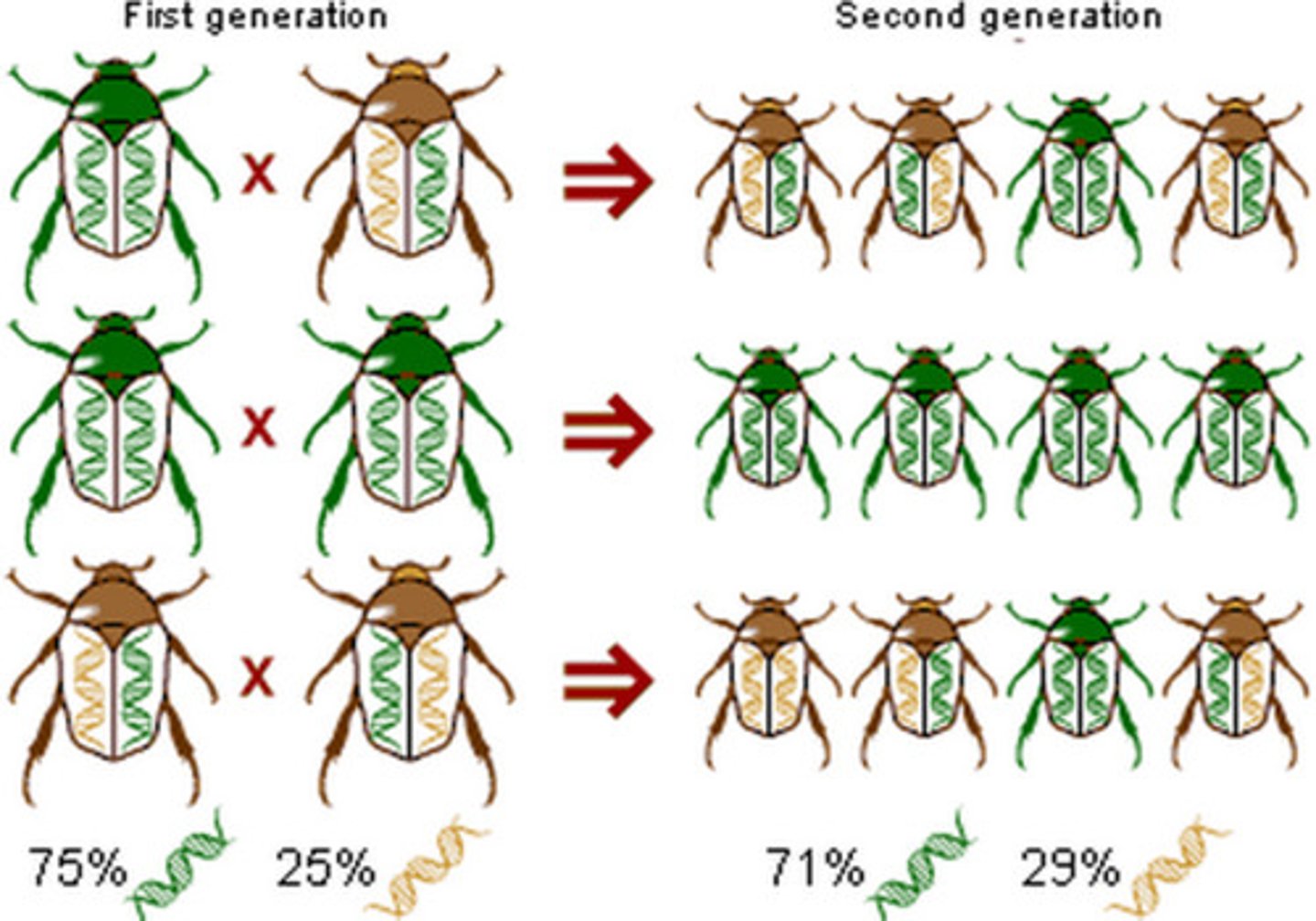
changes within populations
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Species
multiple species concepts defined based on specific criteria; morphological similarity, reproductive compatibility, mate recognition, biological species

Microevolution
changes within populations

Macroevolution
formation of new species
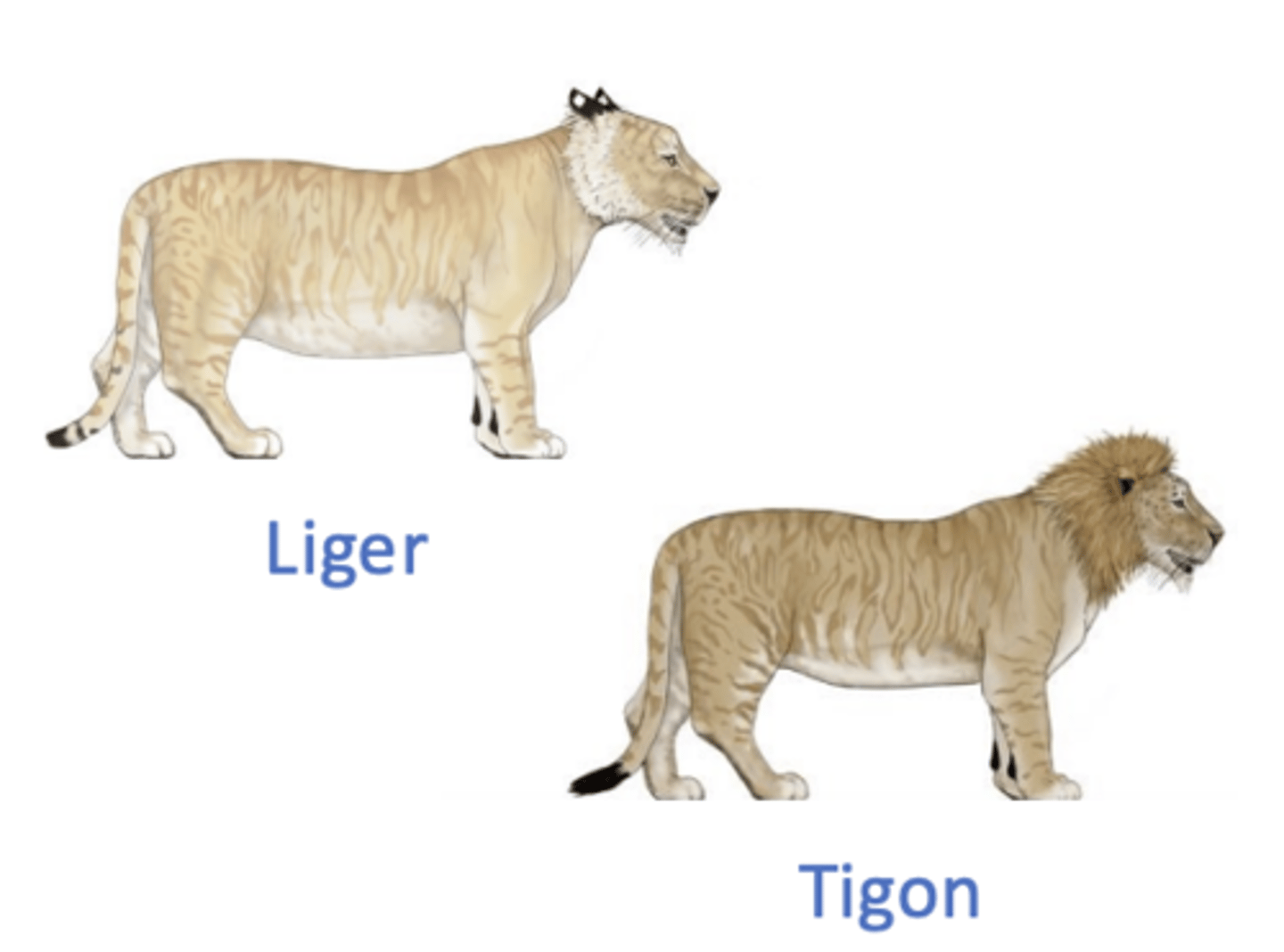
Liger/Tigon
tigon: female lion bred with male tiger, bigger than parents. liger: female tiger bred with male lion.
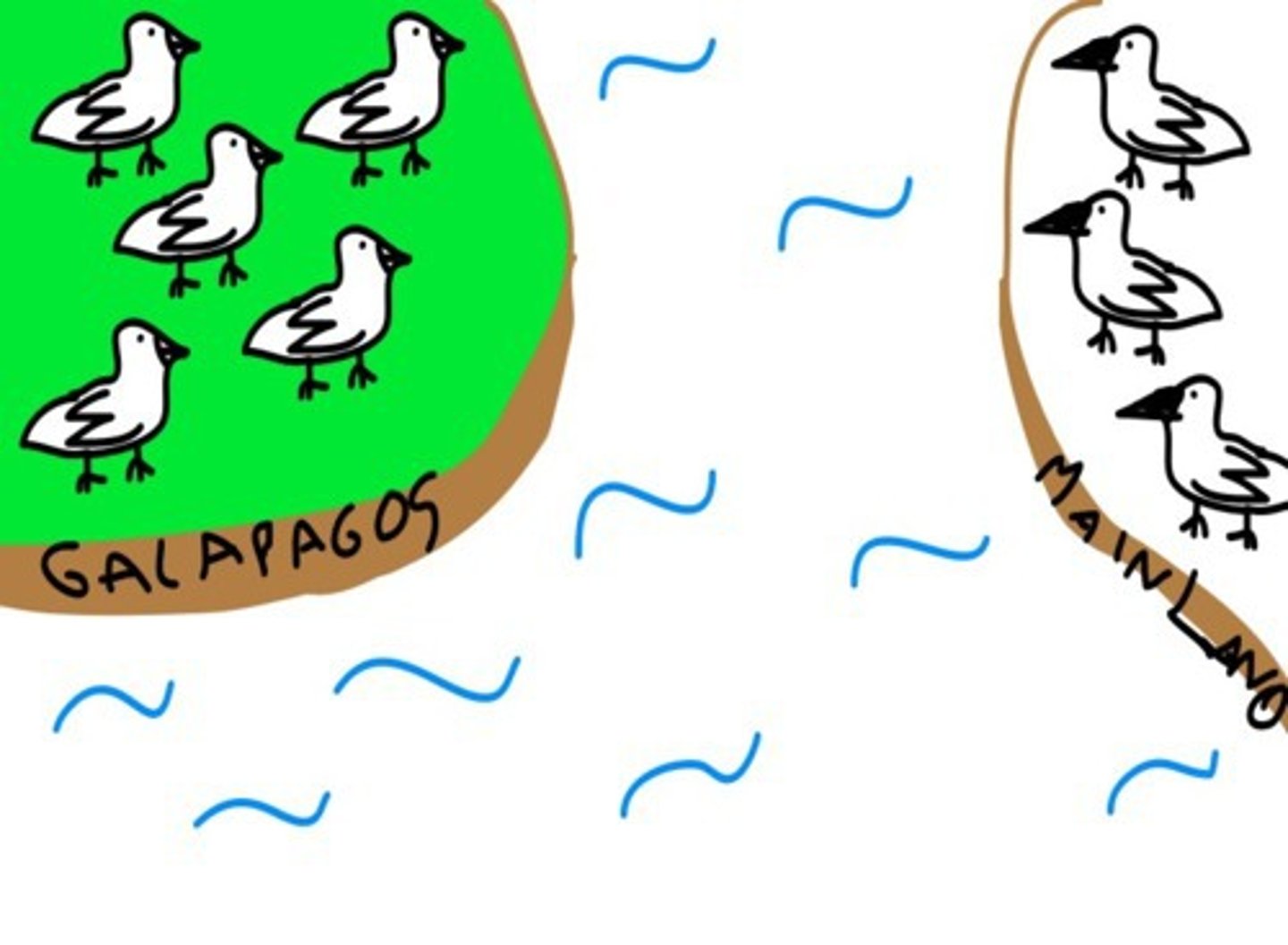
Reproductive Isolation
prevents breeding with closely related populations to form new species
Reinforcement
maintaining separate newly formed species; post-zygotic and pre-zygotic

Post-zygotic Isolation
after zygote forms, can result in non-viable zygote, un-viable adult (lower hybrid fitness), infertile adult

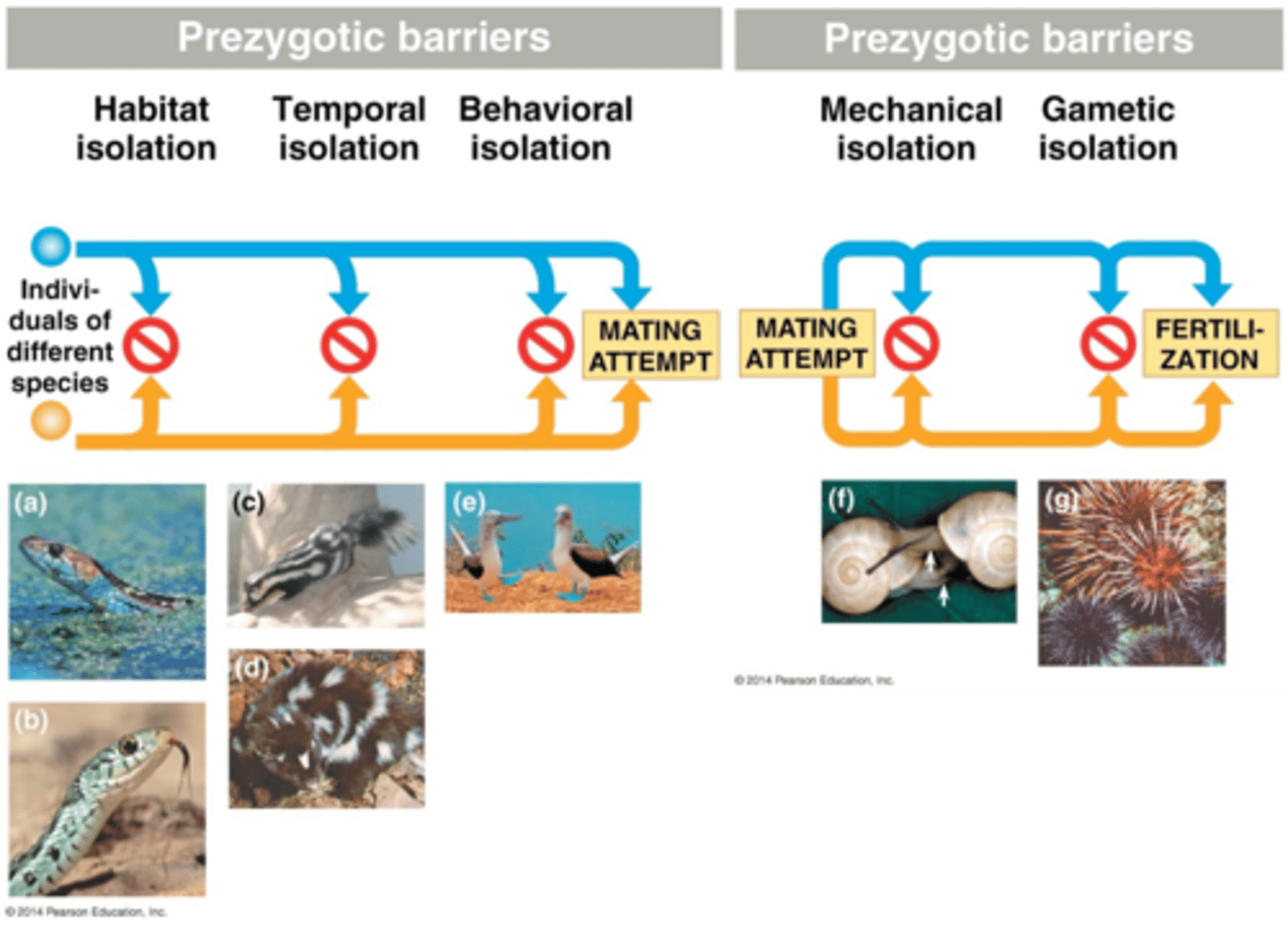
Pre-zygotic Isolation
prevents fertilized egg occurrence; due to geographic, temporal, mechanical, behavioral, and gametic isolation
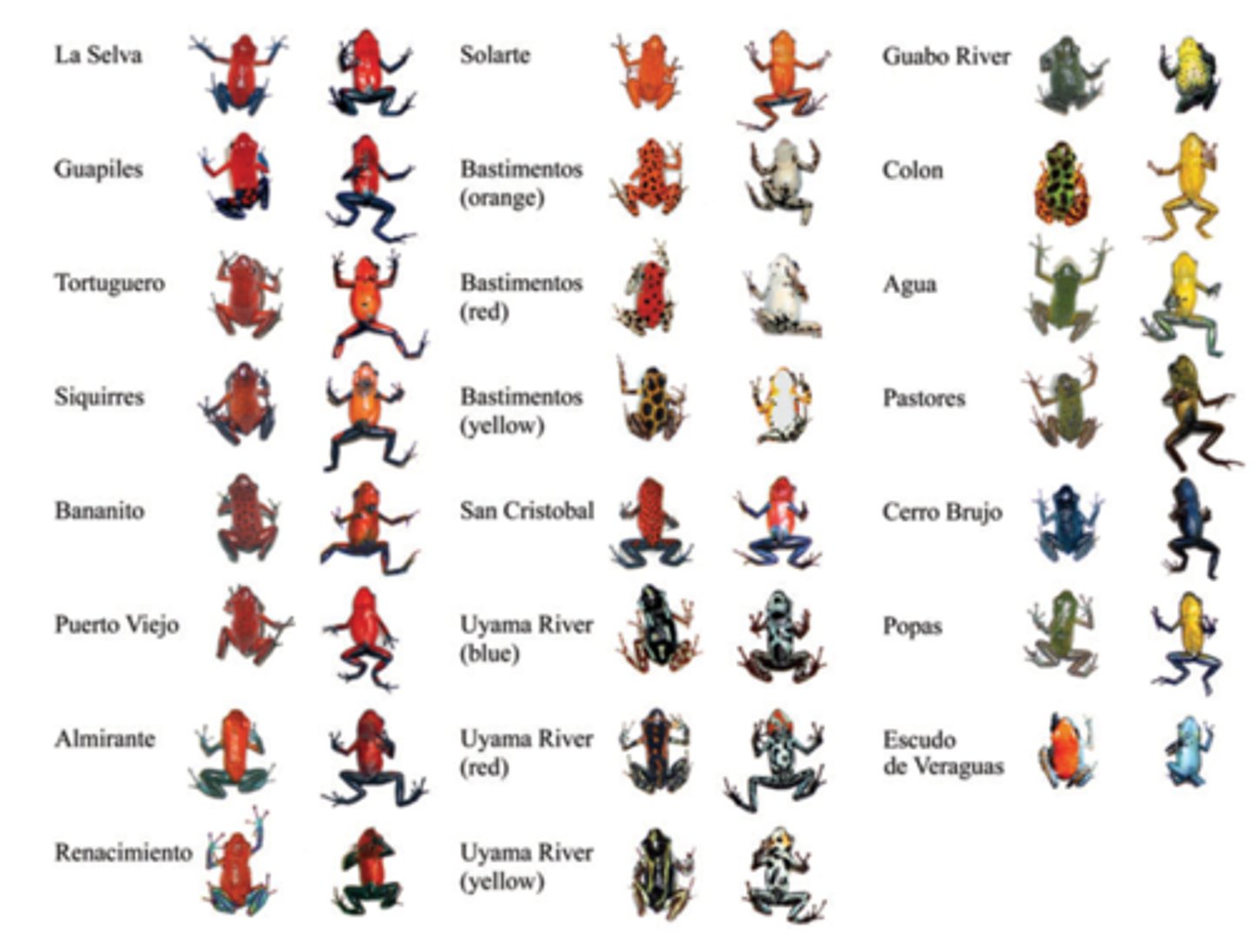
Polymorphic Species
individuals look different but aren't different species (e.g., O. pumilio strawberry poison dart frog)

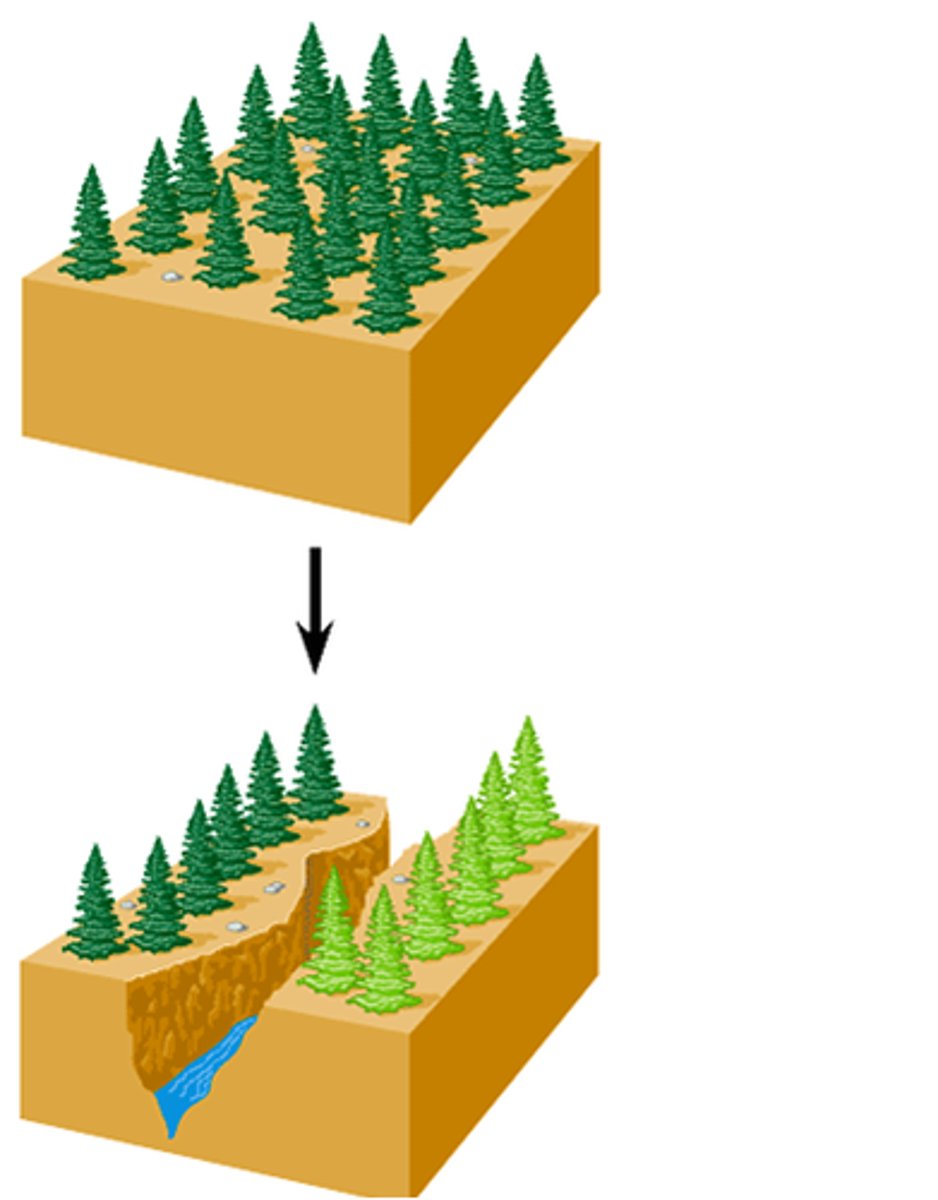
Allopatric Speciation
speciation by geographical separation; due to dispersal or vicariance, resulting from genetic drift, founder effect, and selection
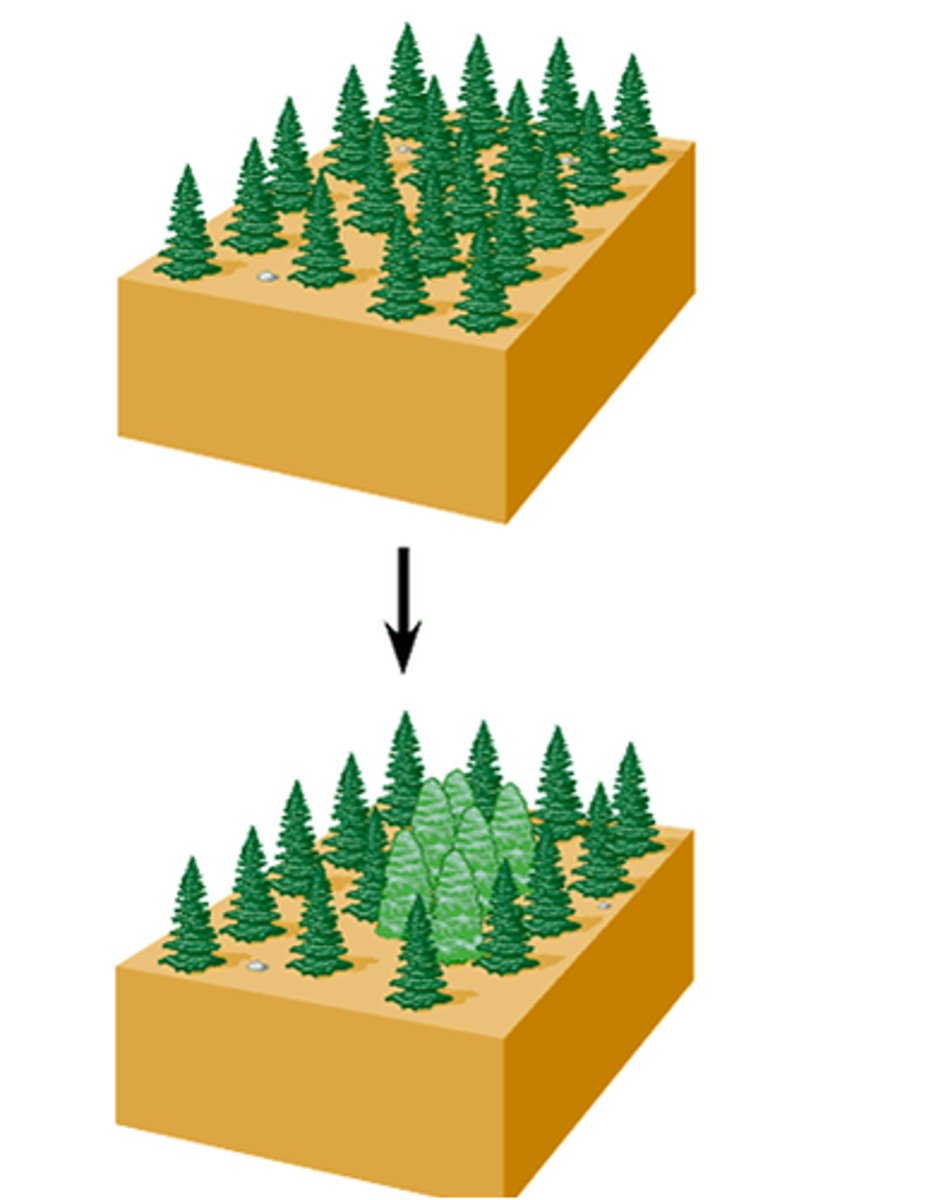
Sympatric Speciation
speciation by behavioral separation; disruptive selection or genetic changes leading to a new species
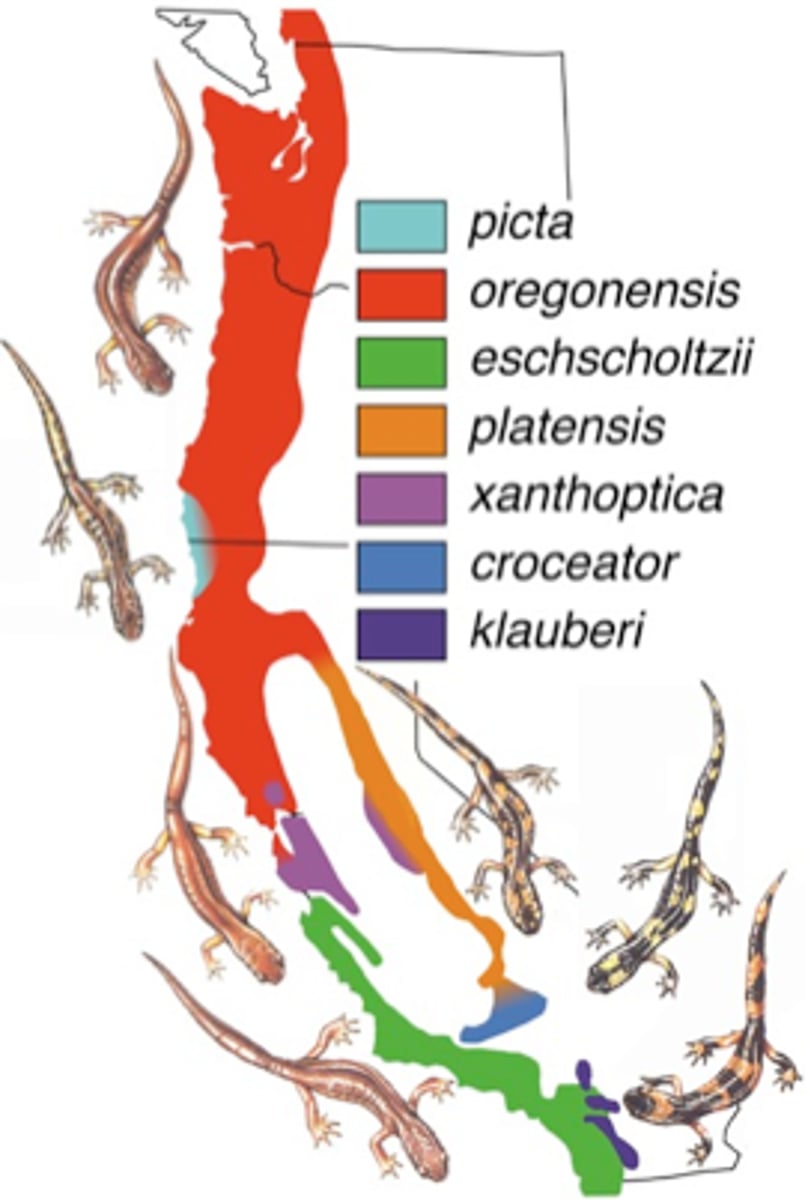
Ring Species Complex
type of allopatric speciation; original species splits due to geographic barrier and cannot interbreed when they meet again
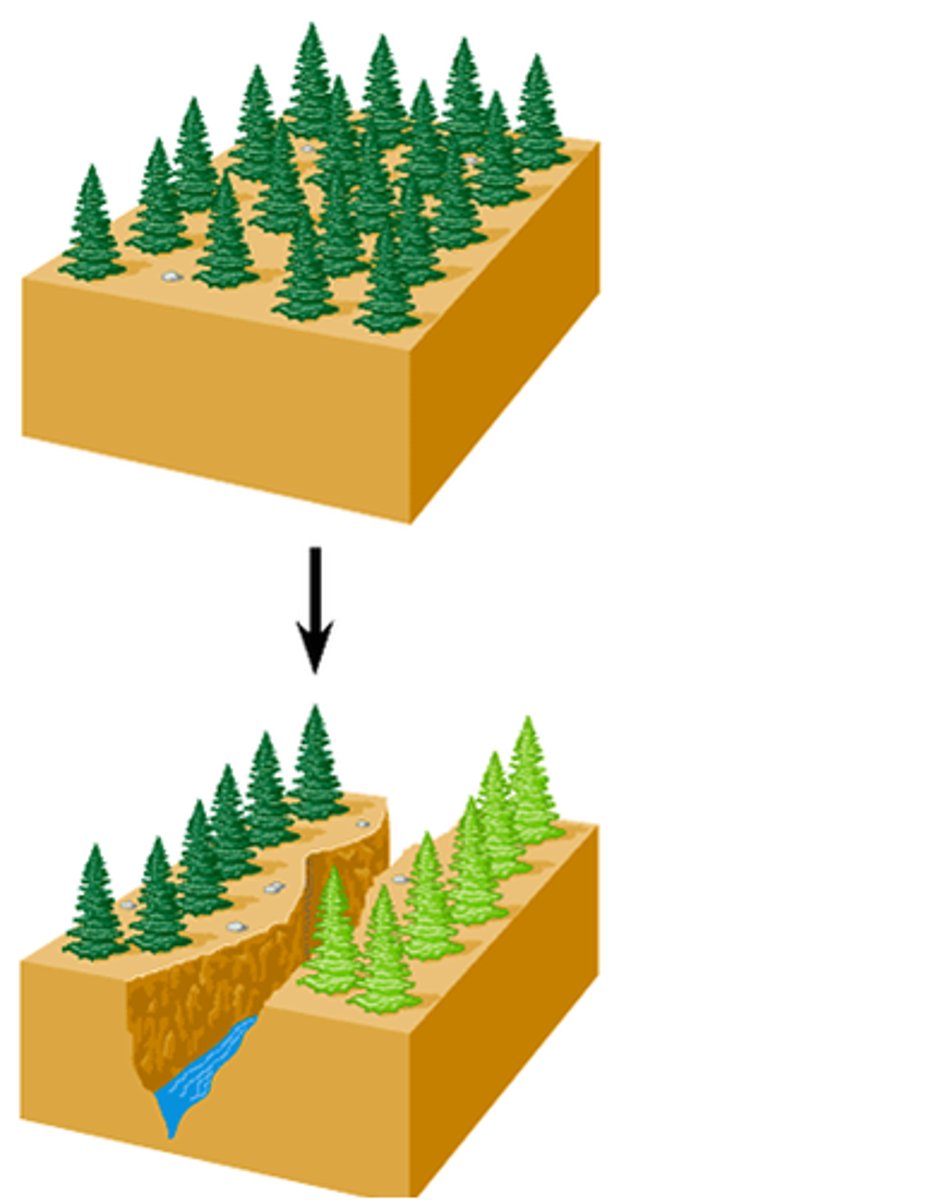
Vicariance
geographic event splitting two populations (e.g., mountain range or river)
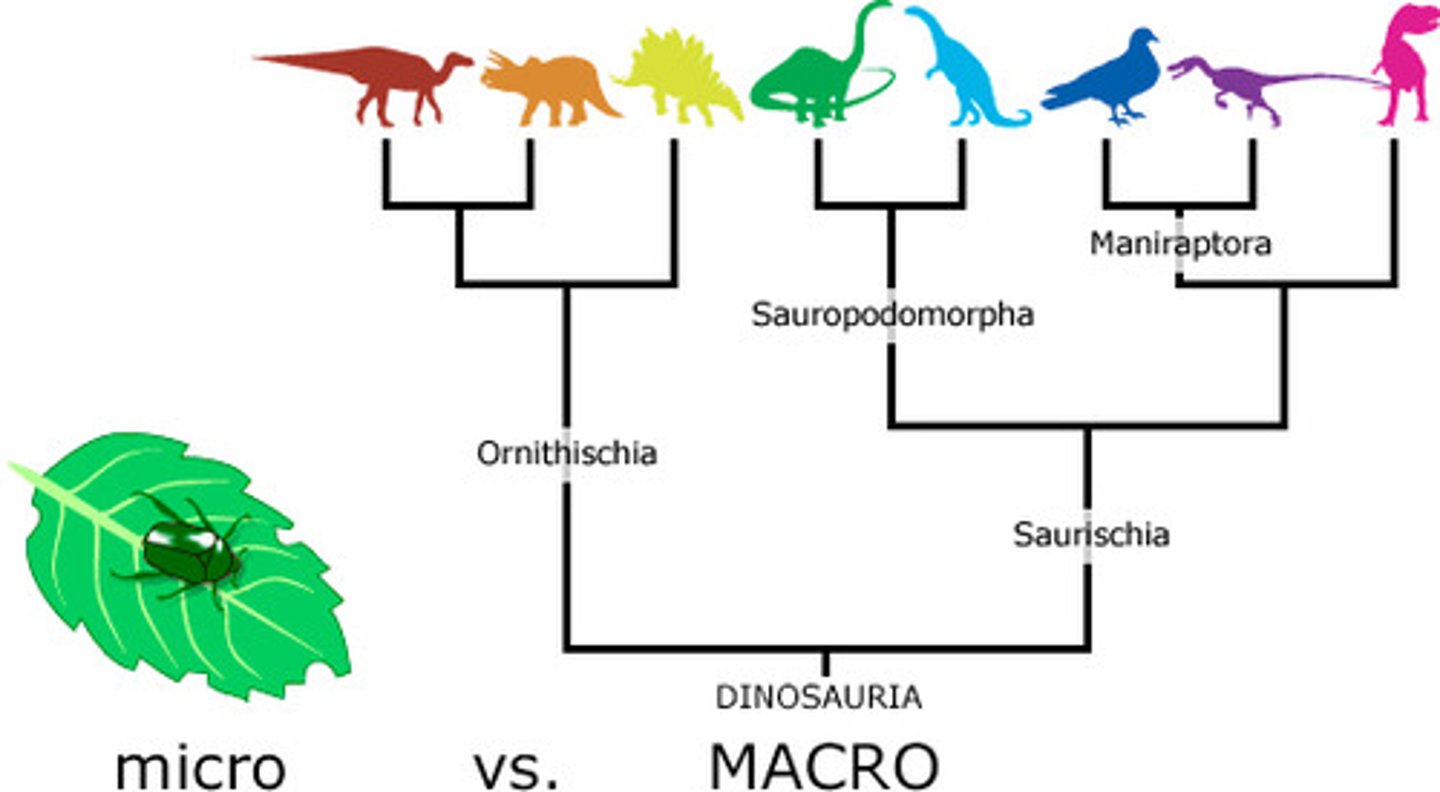
Extrapolation
deriving macroevolution based on microevolution
Stasis
equilibrium in stable environments; no morphological changes but changes in non-coding regions in genome

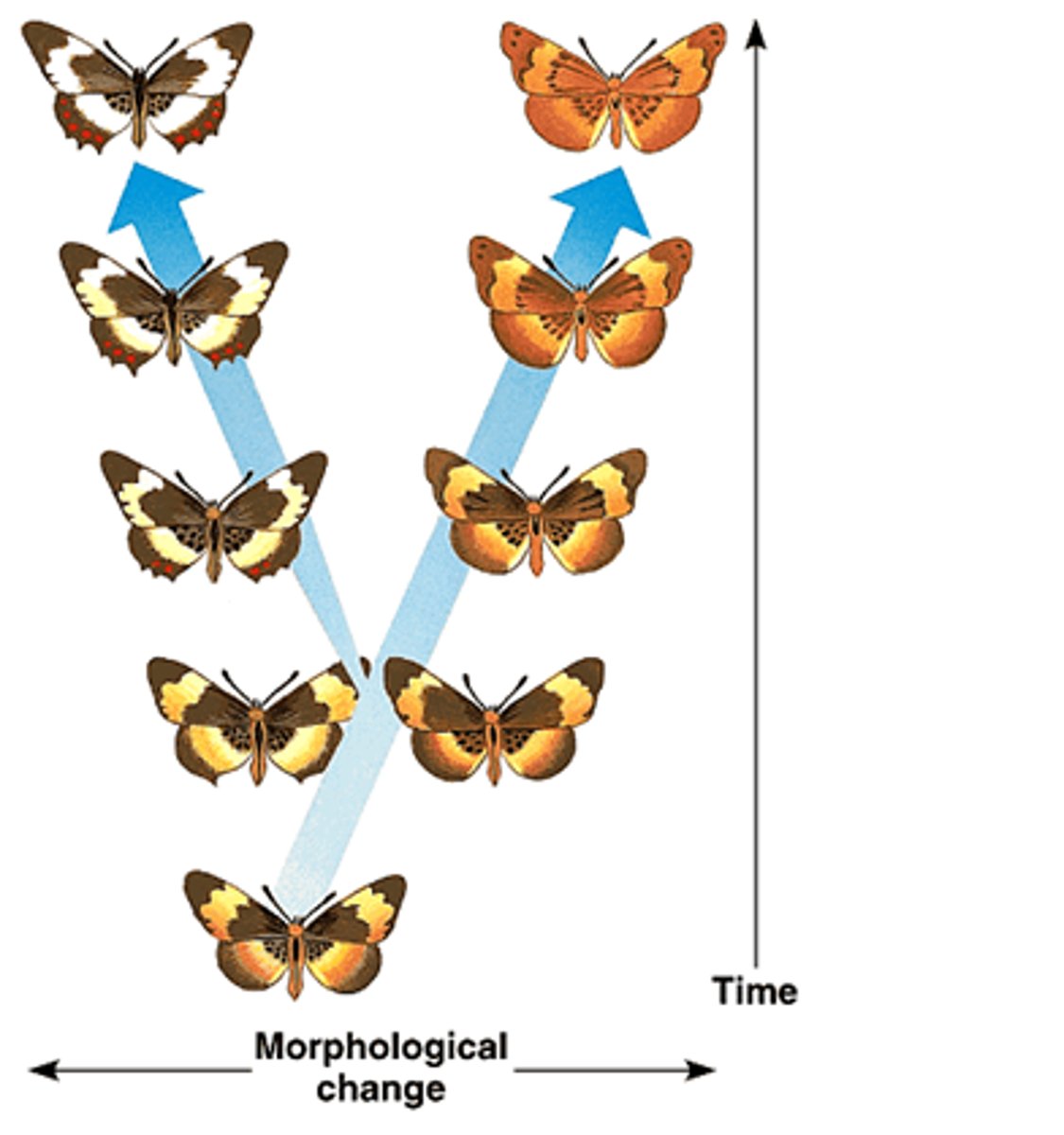
Gradual/Gradualism
under modest selection and genetic variation, ancestor disappears (e.g., hemoglobin changes in bar-headed geese)
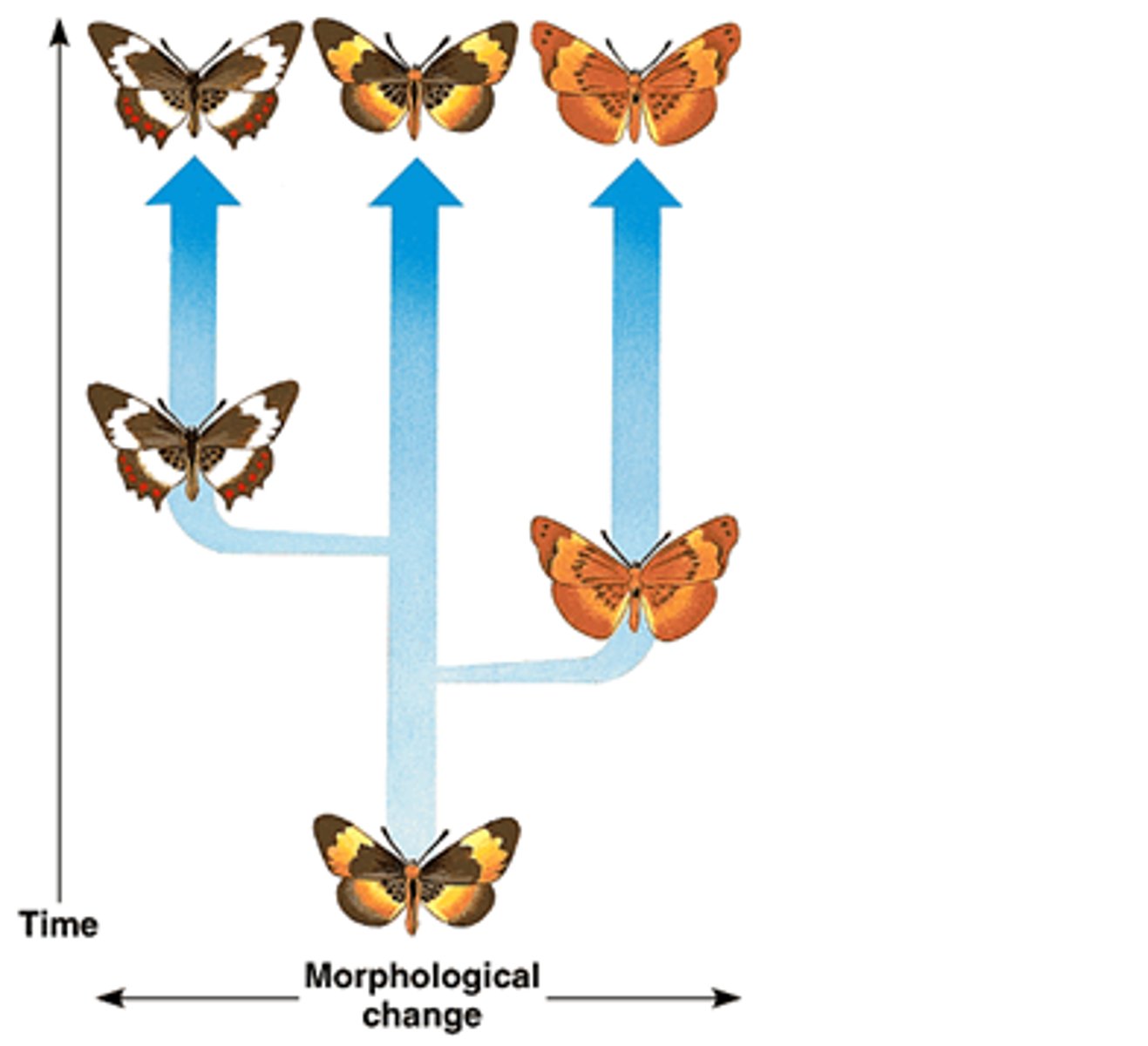
Punctuated Equilibrium
rapid change then stasis, lineage splitting events; influenced by generation time, selection intensity, and regulatory genes
Extinction
when a species dies out forever; occurs at a consistent rate with variations across clades

Mass Extinction
many more species than normal go extinct globally in a short geological time
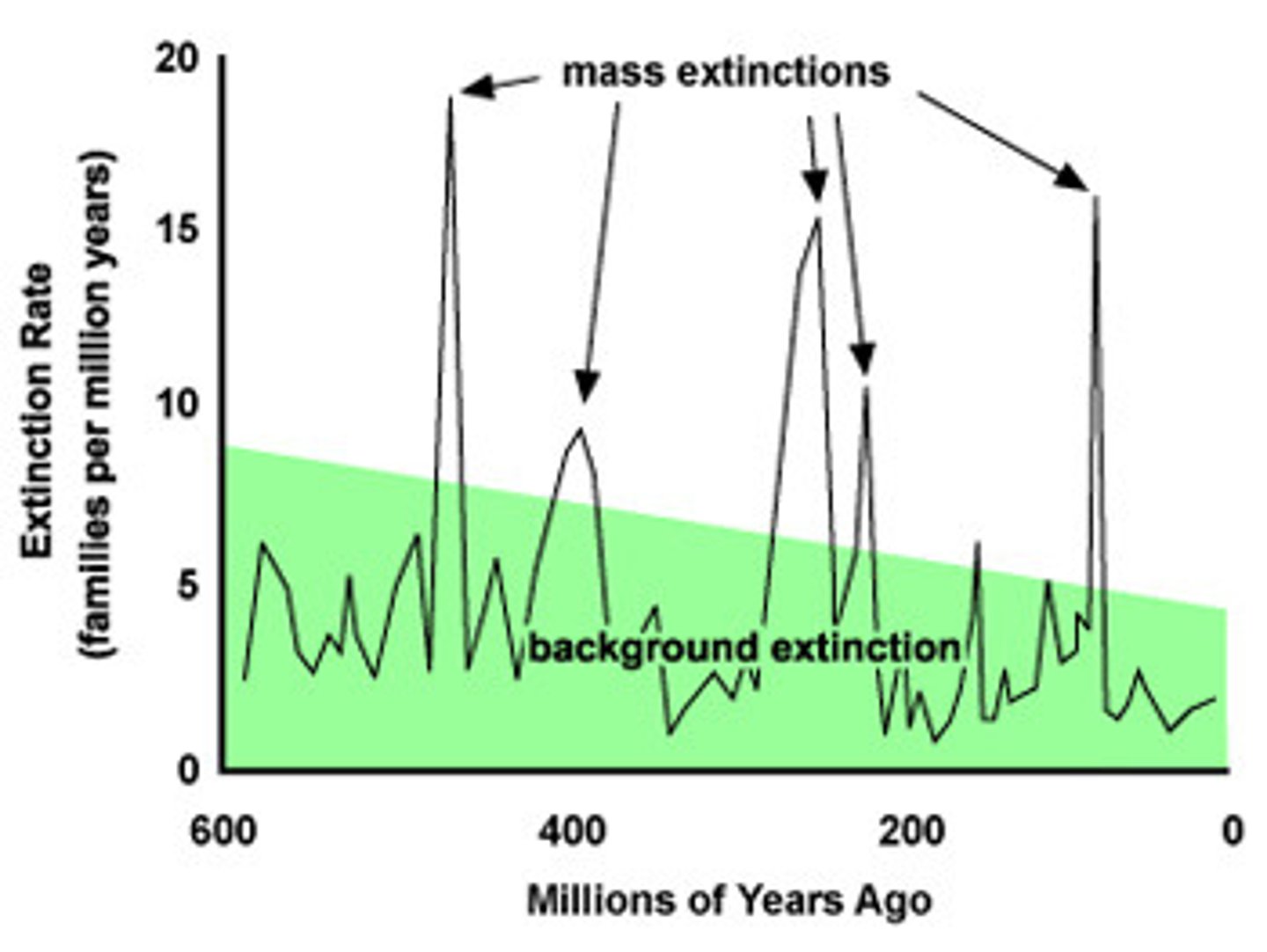
Permo-Triassic Extinction
biggest extinction event; over 50% species lost due to increased CO2 and anoxia from volcanism

KT Extinction
cretaceous-Tertiary extinction event; 65 million years ago, leading to dinosaur extinction and loss of 3/4 of plant and animal species
