A level Economics - Micro
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
Ceteris paribus definition?
All other influencing factors are held constant
Four factors of production?
Land, labour, capital, enterprise
What is land?
Natural physical inputs which are used up in production
What is labour?
The exertion (physical and mental) of workers
What are capital and consumer goods?
capital good - Used to make other goods, are not used up in production
consumer good - goods bought by individuals for personal consumption
What is an entrepreneur?
Takes risks and organises factors of production
What is a positive statement?
objective statements that can be tested and evaluated based on empirical evidence
can be proven to be true or false
What is a normative statement?
subjective statements that include opinions and personal beliefs
cannot be tested by empirical evidence
What is resource scarcity and the economic problem?
when demand for a resource is greater than the available supply
having unlimited wants and finite resources
What are the causes of resource scarcity?
demand-induced, supply-induced, structural scarcity, no effective substitutes
What is demand-induced resource scarcity?
high market demand for a scarce resource
can be due to fast growing populations, rising prosperity, advances in technologies and economies of scale
What is supply-induced resource scarcity?
supply of a resource is running out over time as extraction rates increase
What is structural scarcity?
due to mismanagement of the resource which leads to long term degradation of the resource
What is allocative efficiency?
resources have been allocated in the most efficient manner
demand = supply
social surplus is maximised
working at the social optimum
What is a non-renewable resource?
finite in supply, no mechanisms exist at present to replenish them
eg fossil fuels
What is a renewable resource?
replaceable over time
eg solar energy, oxygen
What is opportunity cost?
the benefit lost from the next best alternative
What is a PPF?
a production possibility frontier graphically demonstrates how much an economy can produce when all factors of production are fully and efficiently employed
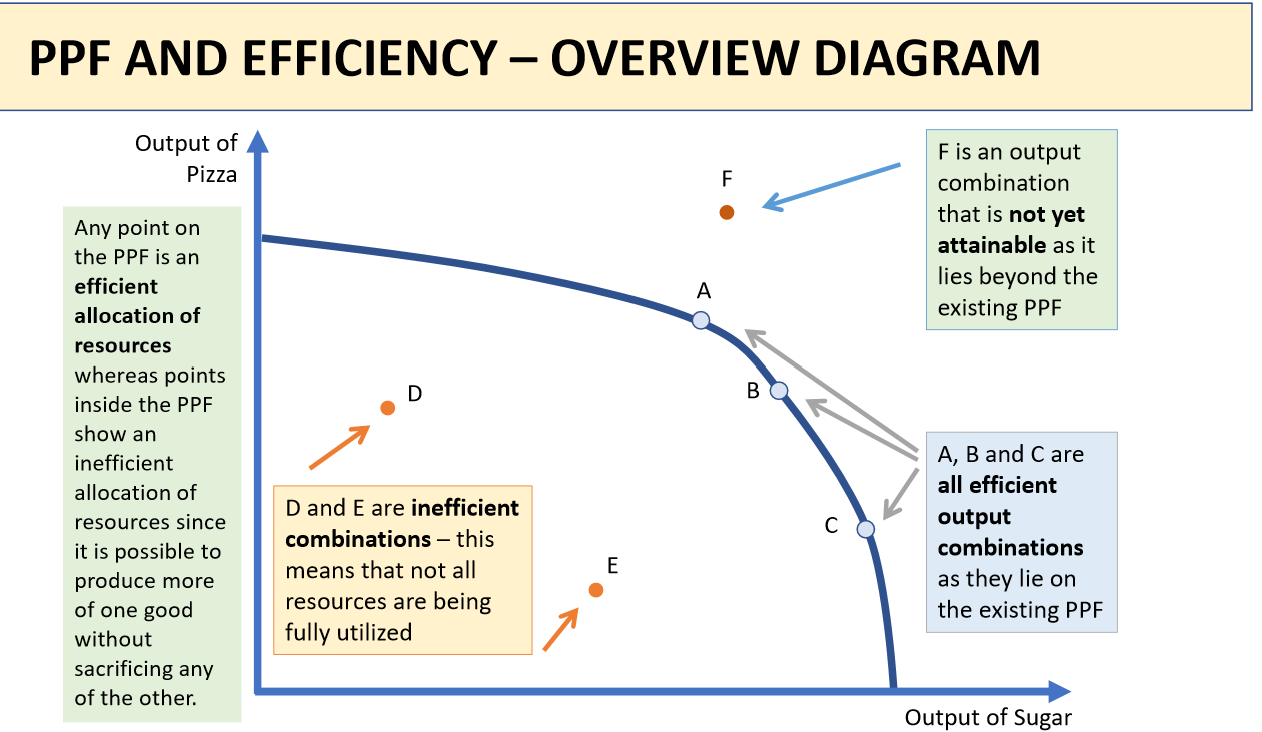
Explain the shape of the PPF curve?
arc that is concave to the origin
this is because the opportunity cost of expanding X measured in terms of lost units of Y is increasing
Why would a PPF be linear?
the marginal opportunity cost of switching resources between consumer and capital goods is constant - perfect factor substitutability of resources
When will a PPF shift outwards?
represents economic growth - allows the economy to produce more of both goods or to improve its production capabilities
due to: increase in natural resources, technological advancements, human capital development, or investment in capital
What do the points on, inside and outside the PPF mean?
any point on PPF = efficient allocation of resources
any point inside PPF = inefficient allocation of resources since it is possible to produce more of one good without sacrificing any of the other
any point outside the PPF = not yet attainable/sustainable with current resources
What is a value judgement?
evaluative processes based on an individual’s standards or priorities
What is specialisation?
The concentration of production on a limited range of goods or tasks, allowing for increased efficiency.
What is division of labour?
The splitting of the production process into different tasks, with each worker specializing in one task to increase productivity.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of division of labour?
Advantages: increased efficiency, economies of scale
Disadvantages: reduced job satisfaction, lower motivation, increased workplace absenteeism
What is the difference between production and productivity?
production - a measure of the value of the output of goods and services (eg GDP)
productivity - a measure of the efficiency of factors of production measured by output per person employed
What are the factors affecting productivity?
competition, technology, specialisation, training, demand
What is economies of scale?
the cost advantage experienced by a firm when it increases its level of output
What are the main functions of money?
medium of exchange (widely accepted), store of value (can save it), unit of account (standard value), standard of deferred payment (can owe it)
What is a free market economy?
economic decisions are primarily made by private individuals and firms
Advantages and disadvantages of a free market economy?
advantages: choice, profit motive, dynamic, risk is well rewarded, competition, efficiency
disadvantages: market failure, monopolies, potential loss of quality/ price, missing markets, inequality, sustainability
What did Friedrich Hayek believe?
pro free market
strong belief in the role and importance of the individual in an economy
he was highly critical of centralised planning, arguing that no government or authority could understand and control an economy effectively, leading to mistakes and inefficiencies
What did Adam Smith believe?
pro free market
came up with concept of the invisible hand - pricing mechanism that assume the markets would always return to equilibrium and allocate resources efficiently on their own
came up with the ideas of division of labour and competition
What is a command economy?
all economic decisions are made by the government or central authority
Advantages and disadvantages of a command economy?
advantages: less inequality, provision of public goods and services
disadvantages: lack of competition (reduces efficiency), no profit motive, narrow range of choice, inefficient resource allocation
What did Karl Marx believe?
pro command economy
he believed that in a free market, drive for profit would lead to exploitation of workers
he believed command economies would lead to equality and a classless society based on collective ownership and distribution according to need
What is a mixed economy?
both the private sector and the government play significant roles in economic decision making
most modern economies have mixed economic systems
What did John Maynard Keynes believe?
he debated with Hayek in the 1930s
he supported significant government intervention in the economy to stimulate growth whereas Hayek did not
What is a market?
places where buyers and sellers can meet to sell and purchase goods and services
What is demand?
the quantity of a good or service that consumers are able and willing to buy at a given price
What is the law of demand?
as price increases demand decreases
Why does the demand curve slope down?
substitution effect, income effect and diminishing marginal utility
What is the substitution effect?
substitutes are replacements for another product
a fall in the price of goods and services will lead to higher demand as some switch from other similar goods due to price
What is the income effect?
when the price of a product falls, consumers have more real purchasing power allowing them to purchase more of the product, leading to an increase in the quantity demanded
What is diminishing marginal utility?
as people consume more of a particular product, the additional satisfaction they derive from each additional unit decreases, meaning they are willing to pay less for each successive unit
What is a shift in the demand curve?
inward shift - less is demanded at each given price
outward shift - more is demanded at each given price
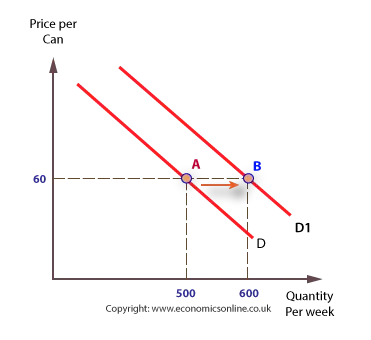
What are the factors that affect demand?
changes in:
price, weather, life style, tastes and preferences, seasonality, population, price of substitutes and complementary goods, advertisement, interest rates
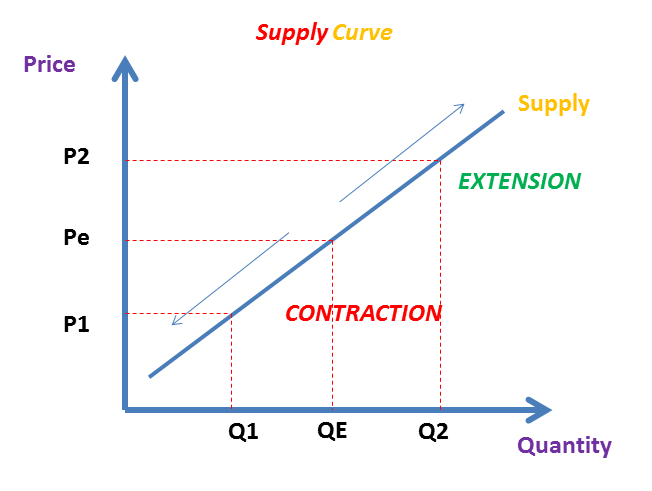
What causes movement along a demand curve?
changes in the market price of the product itself
higher price leads to contraction of demand
lower price leads to expansion of demand
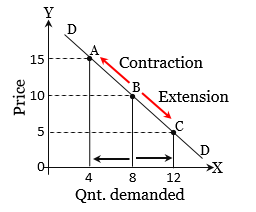
What are complementary goods?
goods that are joint in demand - if you buy one you are likely to buy the other
What is supply?
the amount firms are willing and able to produce at a given price
What is the law of supply?
as price increases firms will be willing to supply more
Why does the supply curve slope up?
firms are profit motivated
cost to produce each additional unit increases
What is a shift in the supply curve?
inward shift - less is supplied at each given price
outward shift - more is supplied at each given price
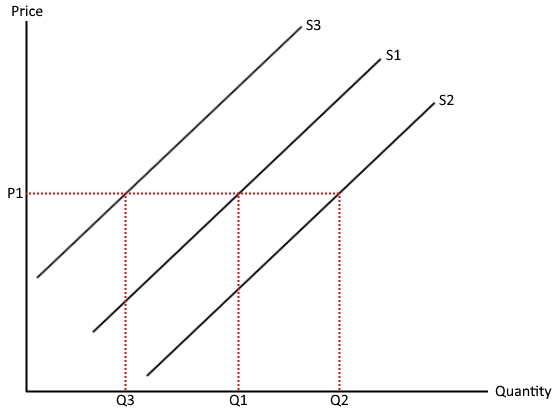
What causes a movement along a supply curve?
changes in the market price of the product itself
higher price leads to expansion of supply
lower price leads to contraction of supply
What are the reasons for a shift in supply?
PINTSWC
Productivity, indirect taxes, number of firms, technology, subsidies, weather, cost of production
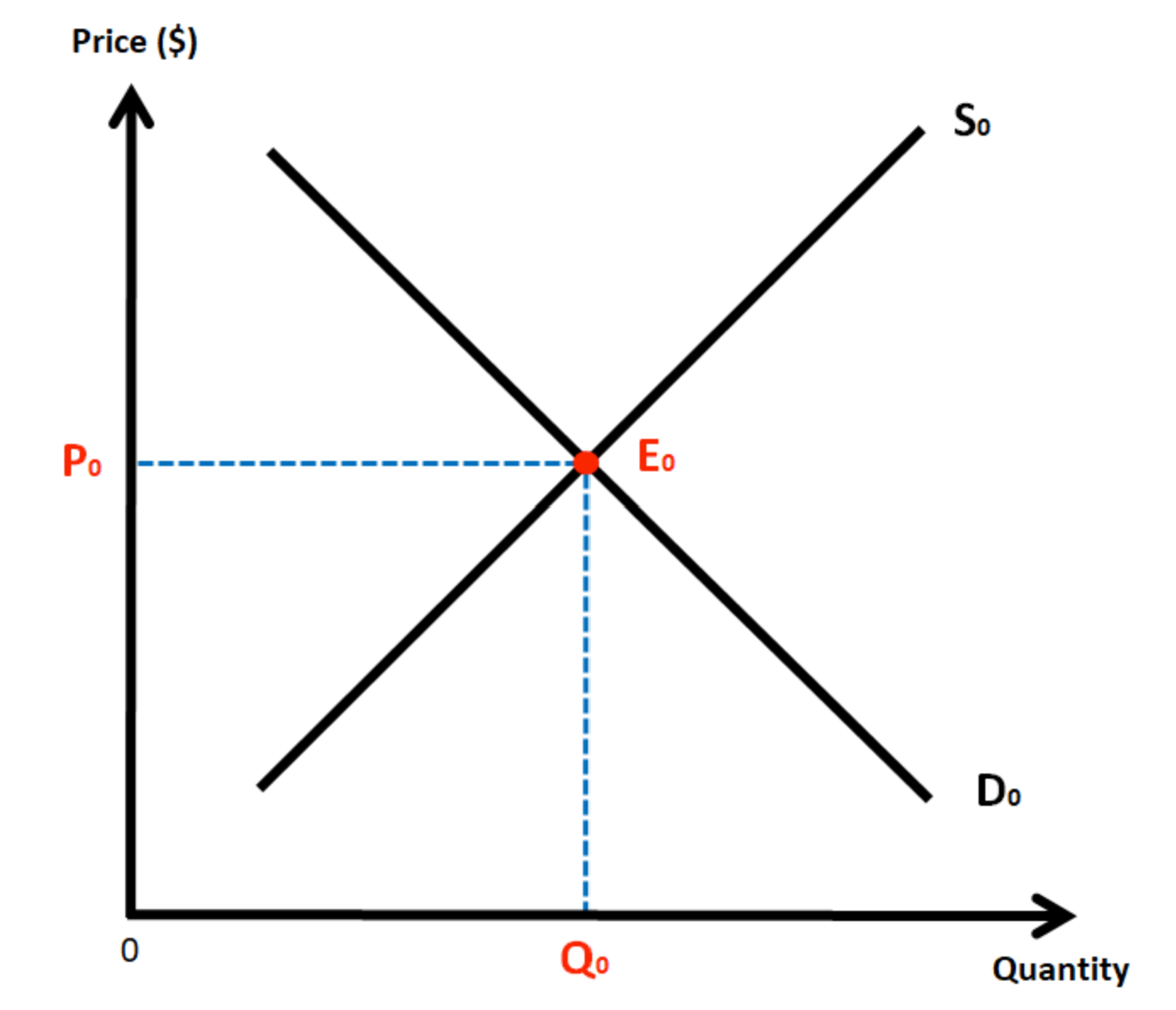
Demand and supply key diagram?
What is a subsidy?
A grant given to firms which lowers the cost of production
What is market equilibrium and the equilibrium point?
when supply and demand are equal leading to stability in prices and quantities exchanged
the point at which the supply and demand curve intersect is the equilibrium point
What is excess demand and excess supply?
excess supply - when supply is greater than demand
excess demand - when demand is greater than supply
How does the price mechanism work when there is a shift in demand?
increase in demand:
demand shifts right
excess demand
signals to producers (eg empty shelves)
producers increase price and increase supply
new market equilibrium is reached
decrease in demand:
demand shifts left
excess supply
signals to producers (eg too much stock)
producers decrease price and contract supply
new market equilibrium is reached
How does the price mechanism work when there is a shift in supply?
increase in supply:
supply shifts right
excess supply
price falls
incentive for consumers to increase demand
new market equilibrium is reached
decrease in supply:
supply shifts left
excess demand
price rises
incentive for consumers to reduce demand
new market equilibrium is reached
What is elasticity?
the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another
What is PED and formula?
price elasticity of demand measures responsiveness of demand to a change in the price of the good itself
PED = % change in QD / % change in P
Values for PED meaning?
0 - perfectly inelastic (d doesnt change when p changes)
0-1 - inelastic
1- unitary
>1- elastic (d responds more than proportionately to a change in p)
infinite - perfectly elastic
What are the factors that determine PED?
inelastic demand:
low percentage of income
necessity
few substitutes
short time frame
broad definition
difficult to switch between subs
habitual consumption (addiction)
peak demand
brand loyalty
opposites for elastic demand
How to draw a graph to represent PED?
inelastic demand - steep curve
elastic demand - shallow curve
perfectly inelastic - straight line vertically
perfectly elastic - straight line horizontally
What is the relationship between total revenue and PED?
change in revenue is greater for elastic goods than inelastic goods when the price changes
What is XED and the formula?
cross price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of demand for good X following a change in the price of good Y
XED = % change in QD of good X / % change in price of good Y
What does the XED value represent?
positive value - goods are substitutes
negative value - goods are complementary
value of 0 - goods are not related
the higher the absolute value the stronger the relationship between the 2 goods (strong/weak substitutes/complements)
What is YED and what is the formula?
income elasticity of demand measures the relationship between in change in quantity demanded for a good and a change in consumers’ real income
YED = % change in QD for X / % change in real income
YED values meaning?
positive - normal goods
negative - inferior goods
0-1 - necessities
1+ - luxury goods
What is an inferior good?
demand varies inversely to the economic cycle (demand rises in a recession)
e.g own-label beans
What is a normal good?
a good that experiences an increase in demand due to an increase in a consumer's income
e.g clothing
What is price elasticity of supply (PES) and equation?
measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied following a change in price
PES = %change is QS / % change in P
PES values
coefficient is always positive
0-1 = inelastic supply
1+ = elastic supply
What factors determine supply elasticity?
ease of factor substitution
availability of spare production capacity
stock levels
time frame
artificial limits eg quotas
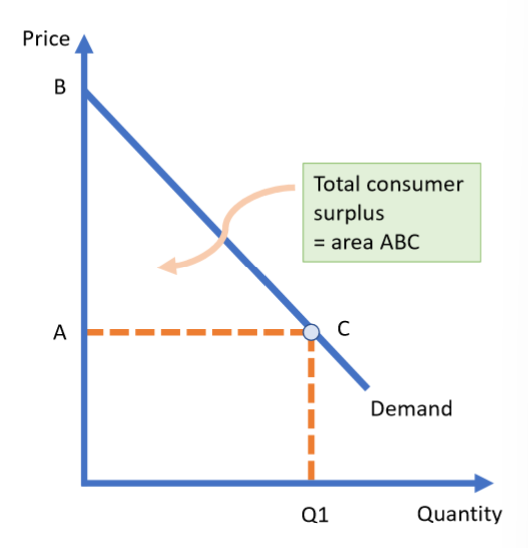
What is consumer surplus?
the difference between what consumers are willing and able to pay for a good or service (demand curve) and the total amount they do pay (price per unit x quantity)
How is consumer surplus shown on a graph?
area underneath the demand curve and above the market price
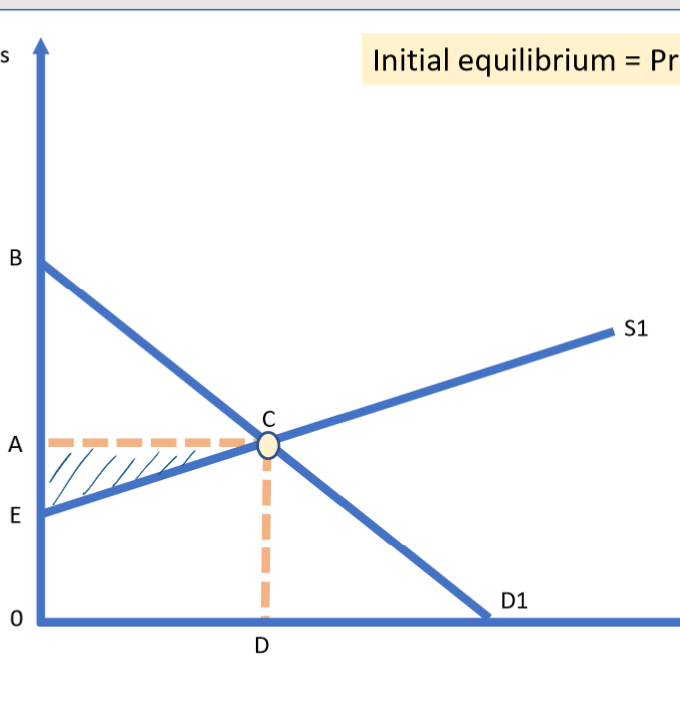
Changes in consumer surplus
when supply shifts in consumer surplus decreases (area is smaller)
when demand shifts out consumer surplus increases (area is bigger)
What is producer surplus?
the difference between the price producers are willing and able to supply at and the price they receive in the market
How is producer surplus shown on a graph?
the area above the supply curve and below the market price
What is social surplus?
consumer surplus + producer surplus
How do shifts impact overall surplus?
shifts out in both supply and demand curve lead to more welfare and increased overall surplus

How does PED impact consumer surplus?
when demand is inelastic there is a greater consumer surplus as there are some buyers willing to pay a very high price to continue consuming the product
What is the difference between a direct and indirect tax?
direct tax - tax on income
indirect tax - tax on expenditure
What is tax revenue and how do you calculate it?
revenue received by the government from the tax
tax per unit x quantity
What is producer revenue and how do you calculate it?
income from sales
price x quantity
What is consumer tax burden?
difference between the original market price and the new market price x quantity
What is producer tax burden?
tax revenue - consumer burden
What is the difference between a specific and Ad Valorem tax?
specific - fixed tax per unit regardless of price
ad valorem - tax which is a percentage of the price
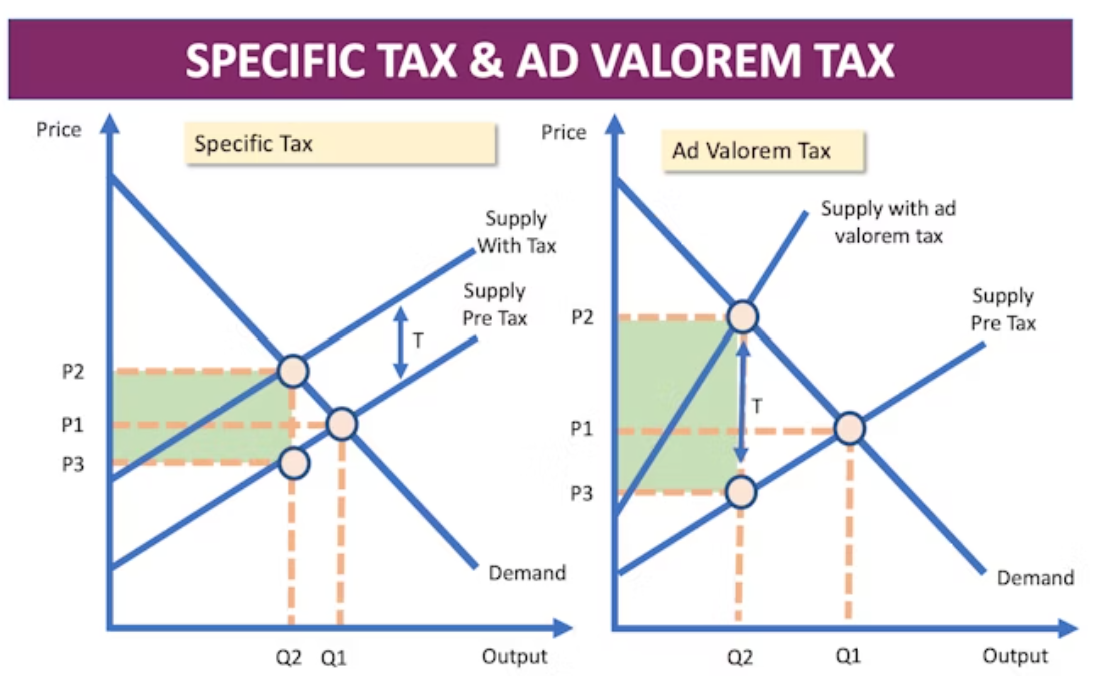
Why do we have taxes?
revenue source for government to fund public services etc
reduce income inequality
reduce consumption of demerit goods
help to address market failure
improve a country’s trade balance
What are excise duties?
indirect taxies levied on three major demerit goods: alcohol, tobacco and road fuels
What is a regressive tax?
a tax which takes a higher percentage of someone’s income from those on low incomes
Why would a a government give out subsidies?
encourage consumption of merit goods by increasing supply
to protect domestic industries from threat of foreign competition
maintain or increase revenues of producers
reduce costs of investment which will stimulate long term economic development in a country
What is the impact of a subsidy and diagram?
supply shifts out
price decreases
output increases
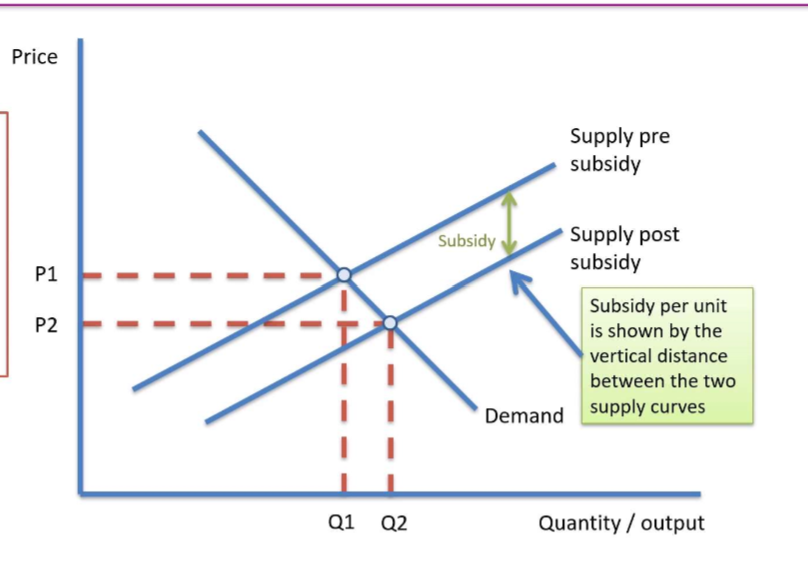
What is consumer and producer subsidy?
consumer subsidy - encourages consumers to purchase more of a particular good or service. affects demand but does not shift supply curve
producer subsidy - lower cost of production for the firm. shifts the supply curve
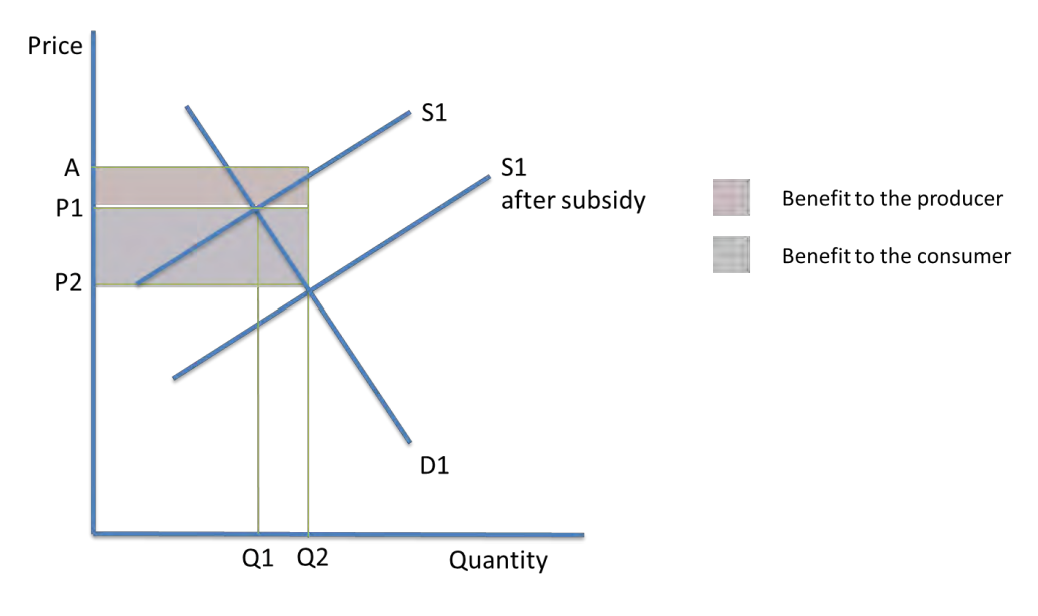
How can subsidy be calculated from a graph?
subsidy per unit: vertical difference between supply curves
consumer subsidy: area - diff between old and new price x output
producer subsidy: area - diff between old price and new equilibrium point x output
total subsidy: area of producer + consumer subsidy
What are three reasons consumers may not behave rationally?
habitual behaviour
weakness at computation
influence of other people’s behaviour
How does the influence of other people’s behaviour affect consumer decisions?
Consumers may follow social norms, influencers, trends, or peer pressure, leading to irrational decision-making and herd behaviour