7 - Heredity
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
a _____ is a distinct unit or sequence of genetic material that codes for a trait
gene
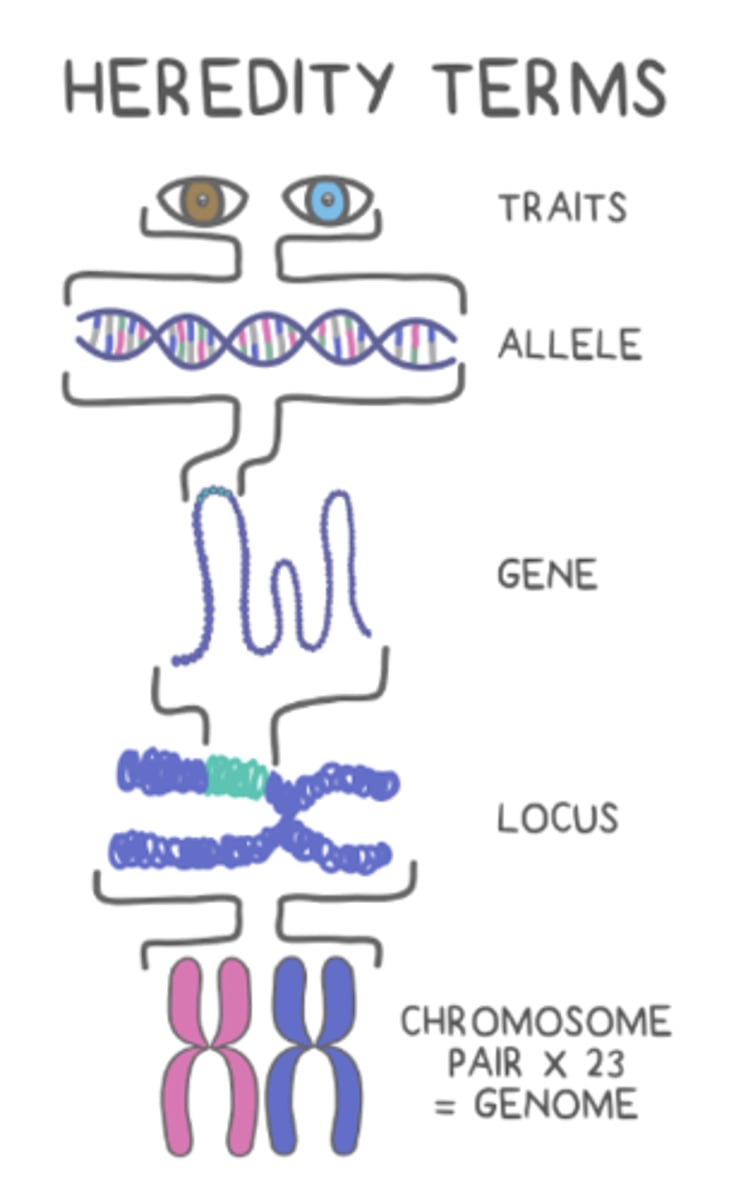
a _____ is the location of a gene on a chromosome
locus
an _____ is one variation of a gene that has different forms
E.g. brown or blue coded at the eye color gene locus
allele
a _____ allele is the 'normal' copy of an allele
wild type
a _____ allele has an altered DNA sequence that can affect a gene's phenotype
mutant
the _____ refers to the actual DNA sequence of a gene
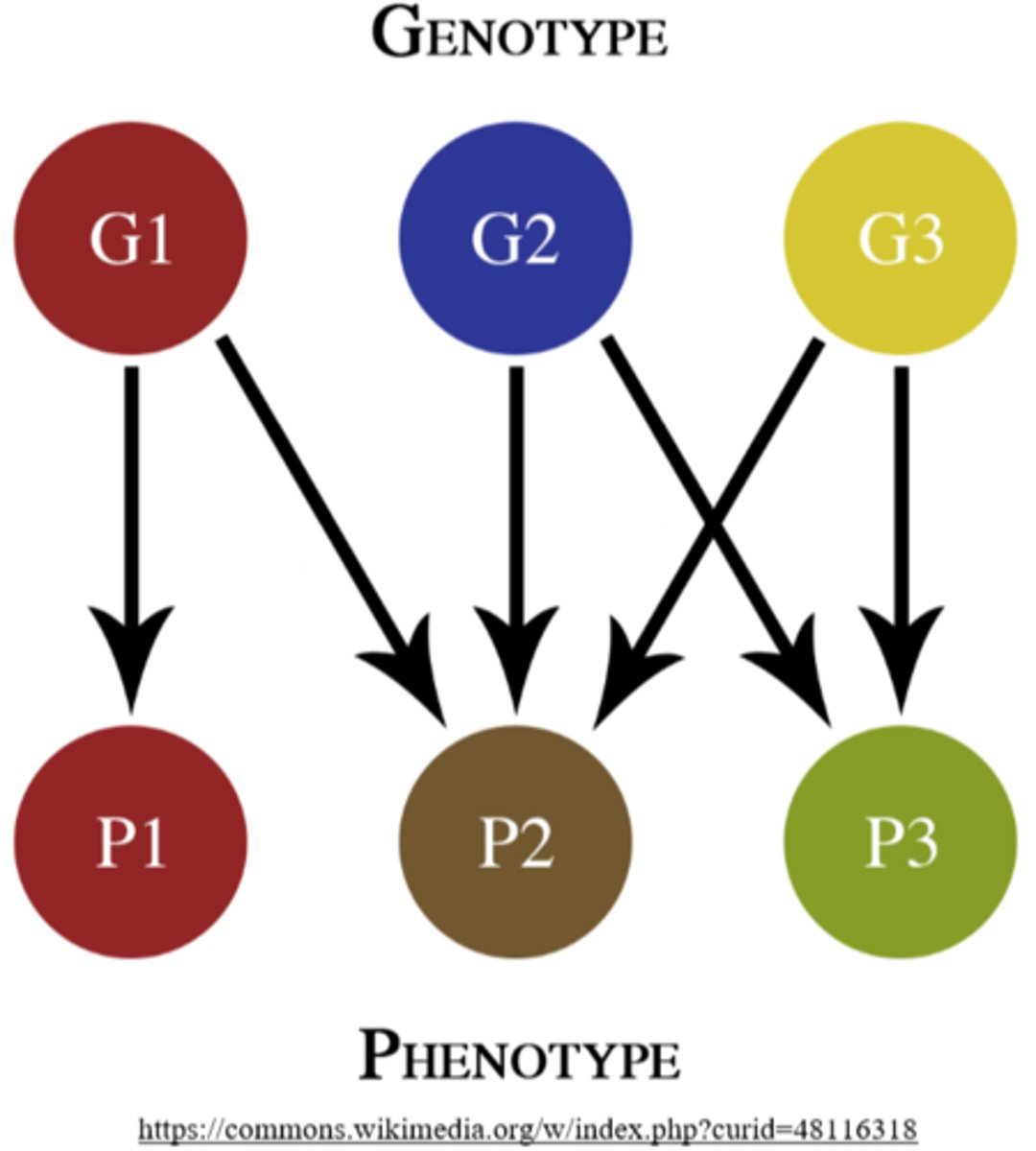
genotype
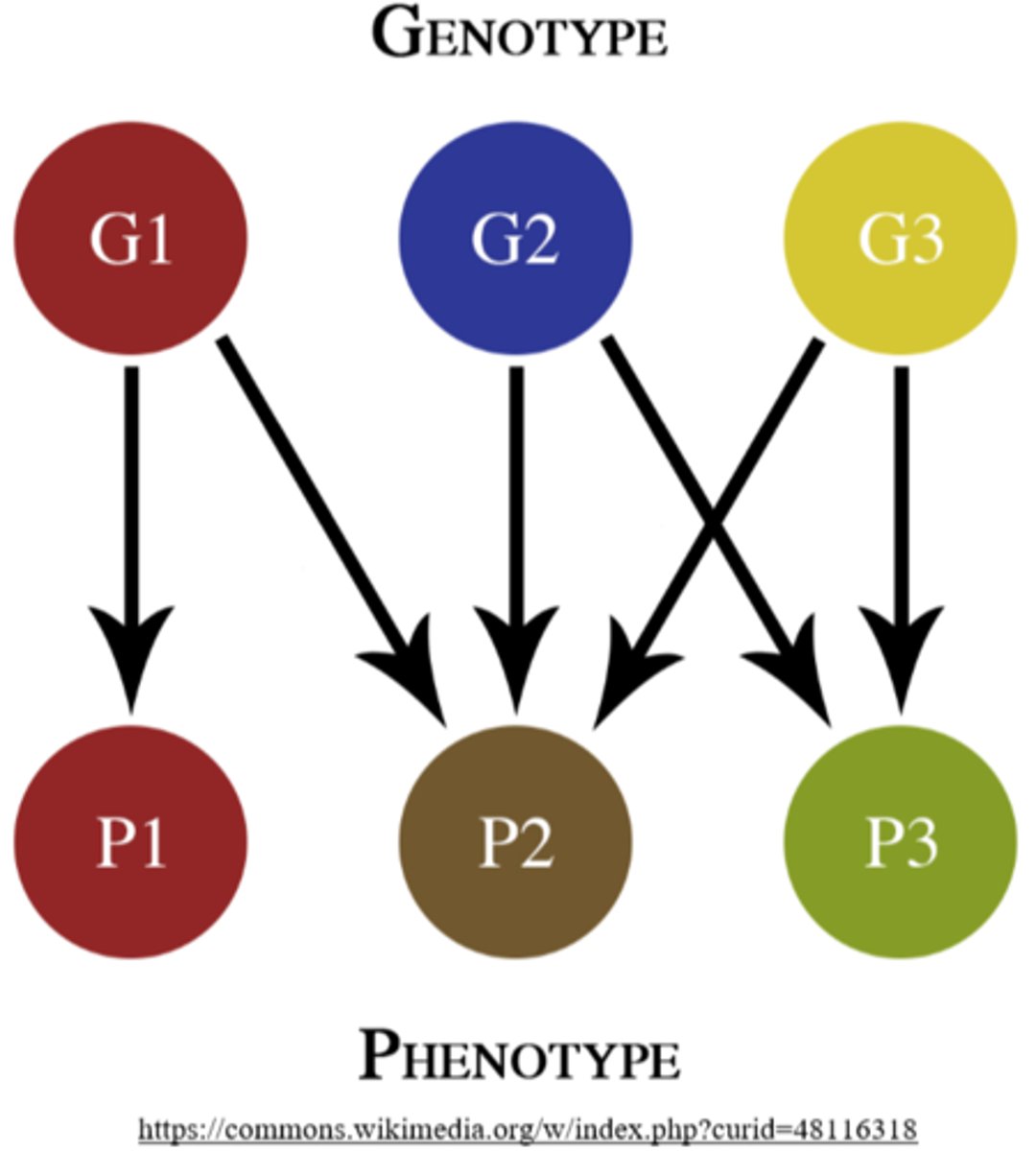
the _____ refers to the observable characteristics of a gene's expression
phenotype
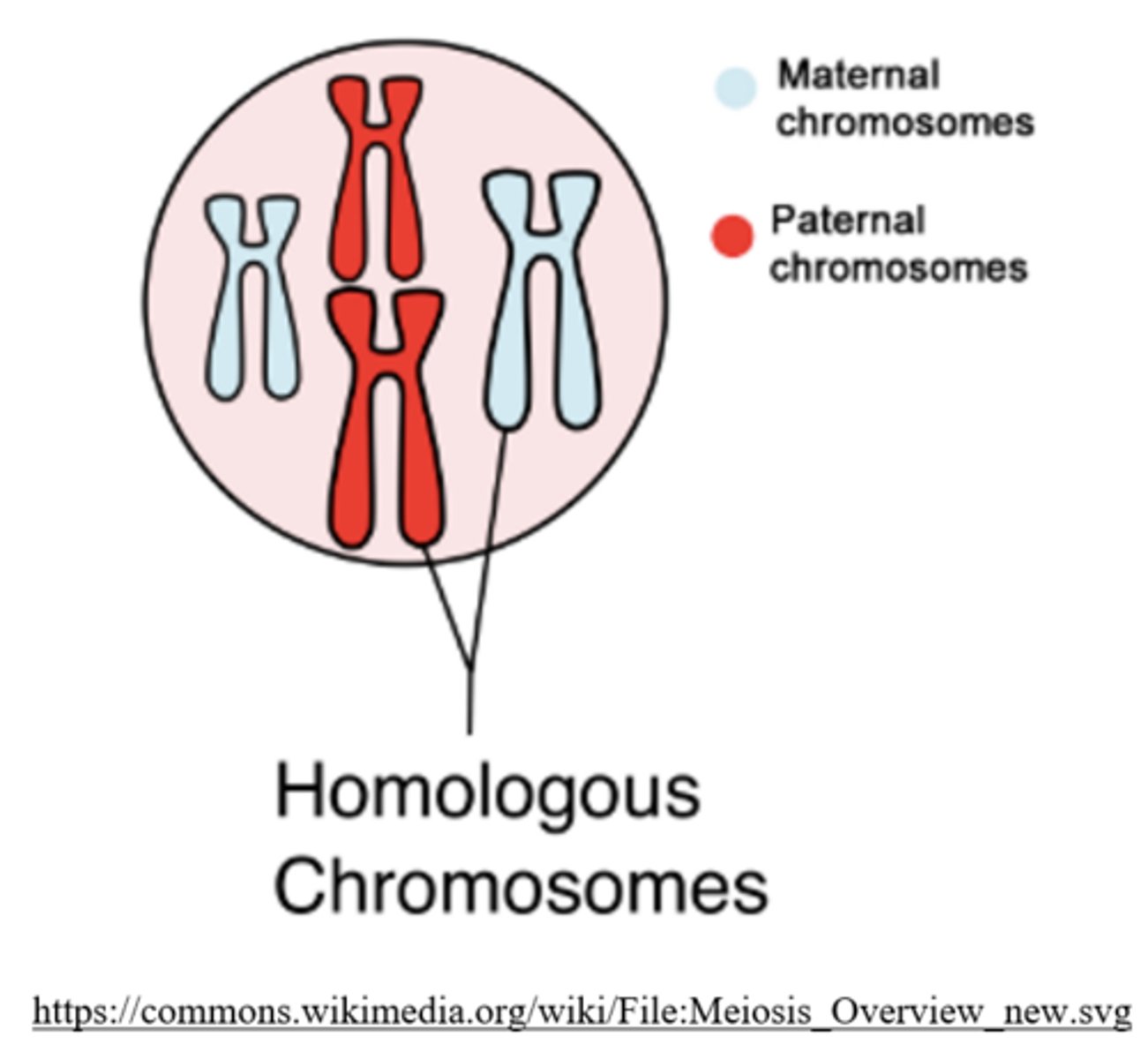
_____ are a pair of chromosomes (one maternal and one paternal) that contain all the same gene loci
homologous chromosomes
homologous chromosomes have the same gene loci, but they do not have to have the same _____
alleles
humans have 22 pairs of _____ chromosomes and 1 pair of _____ chromosomes
autosomal; sex

(True/False) the sex chromosomes of a female are homologous because they are XX (genotype)
true
(True/False) the sex chromosomes of a male are homologous because they are XY (genotype)
false
They are not homologous because men are hemizygous
an organism is considered to be _____ for a given gene if an identical allele is present on each homologous chromosome
homozygous
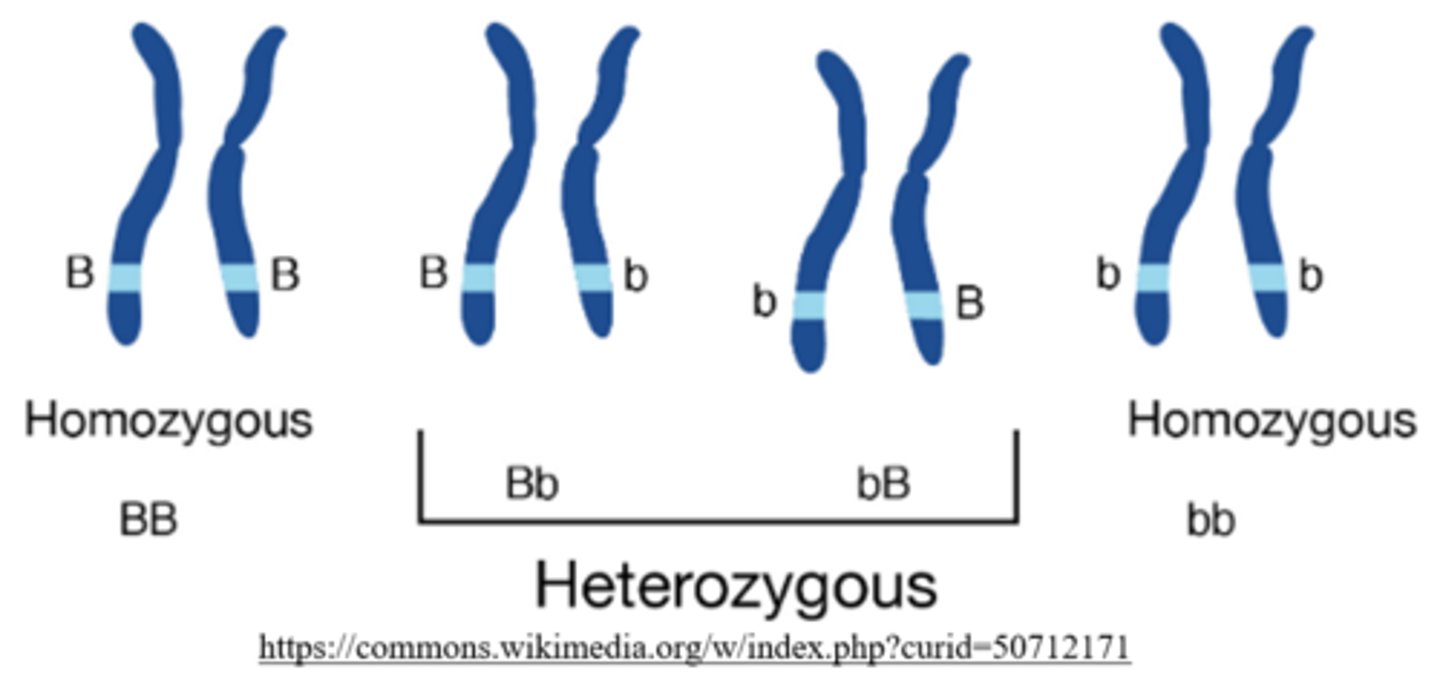
how many copies of the dominant allele do homozygous-dominant individuals carry?
2 (ex: BB)
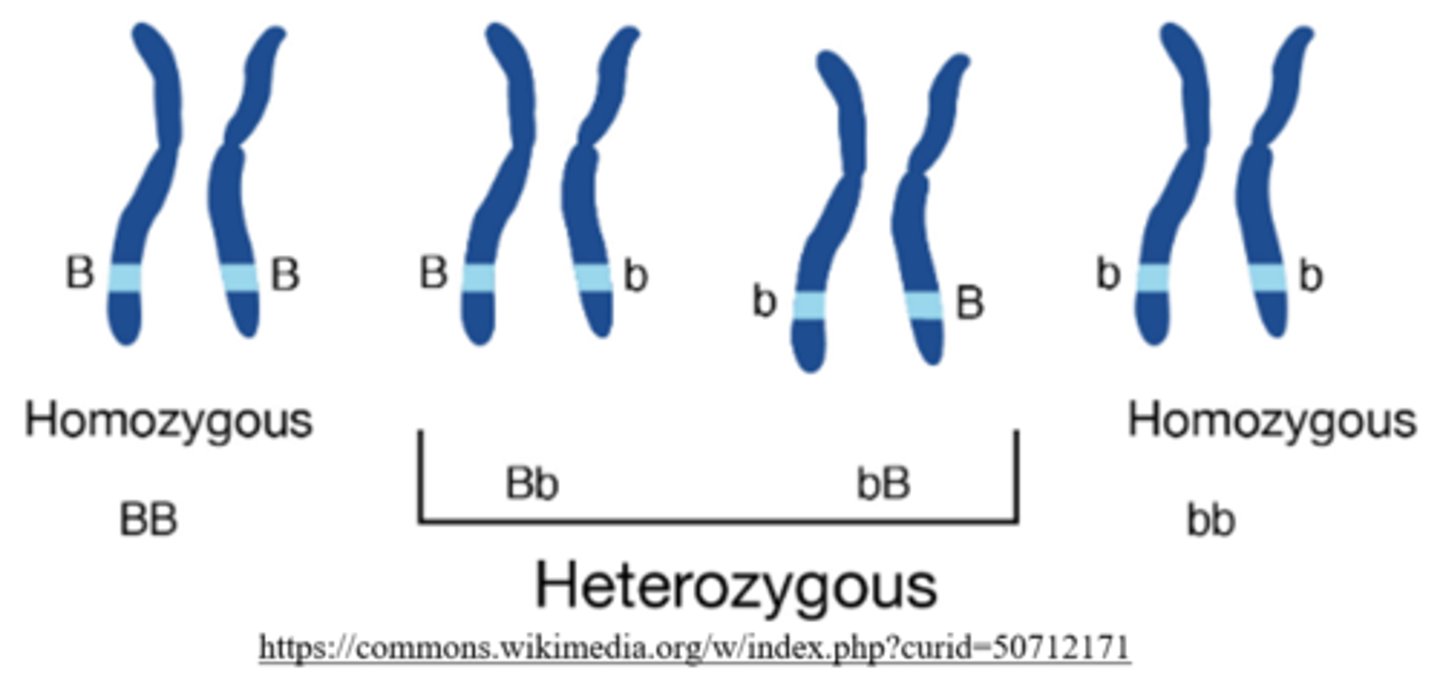
how many copies of the recessive allele do homozygous-dominant individuals carry?
0 (ex: BB)
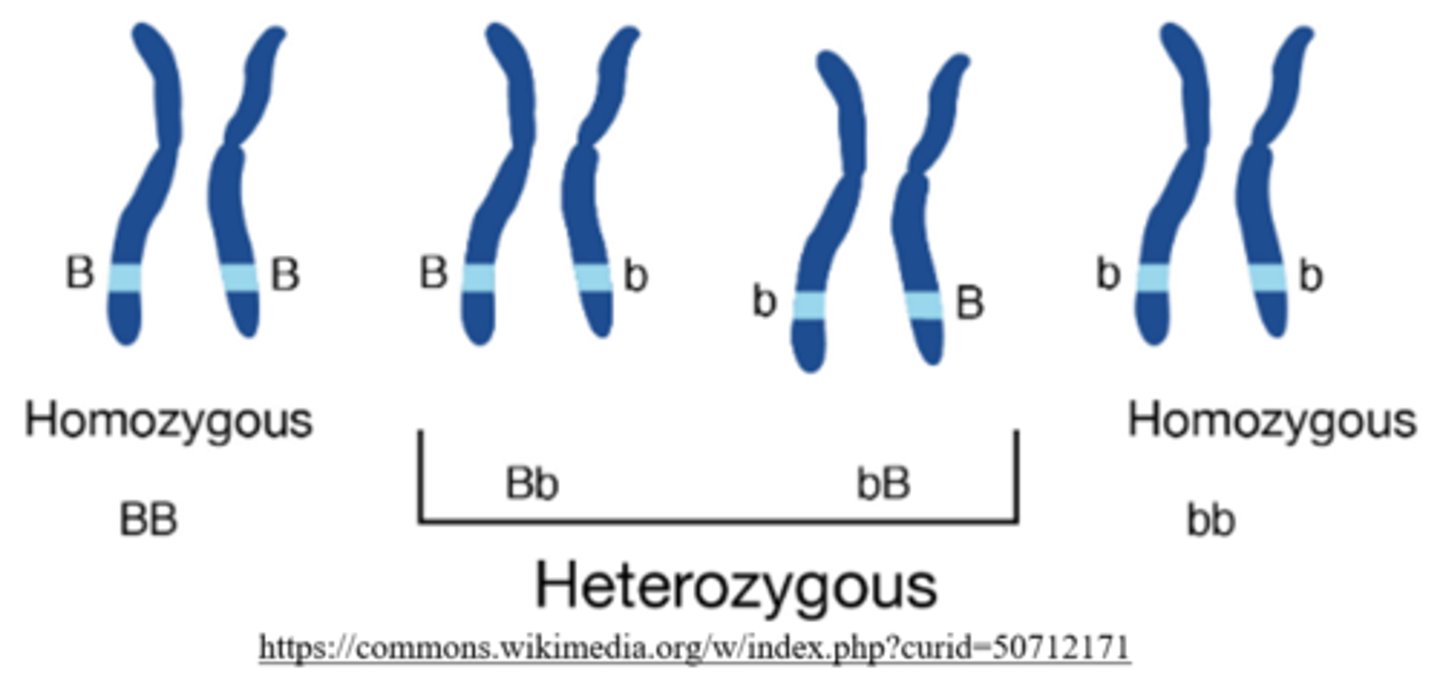
how many copies of the dominant allele do heterozygous individuals carry?
1 (ex: Bb)
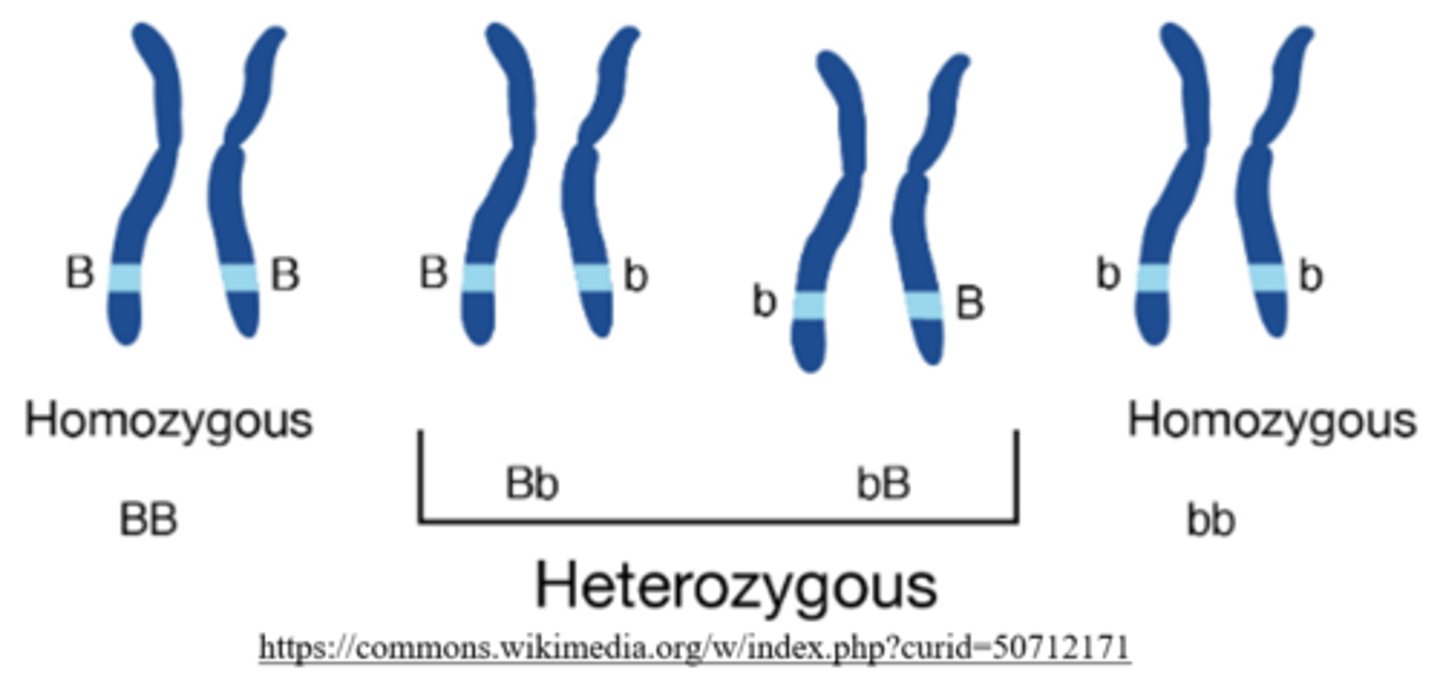
how many copies of the recessive allele do heterozygous individuals carry?
1 (ex: Bb)
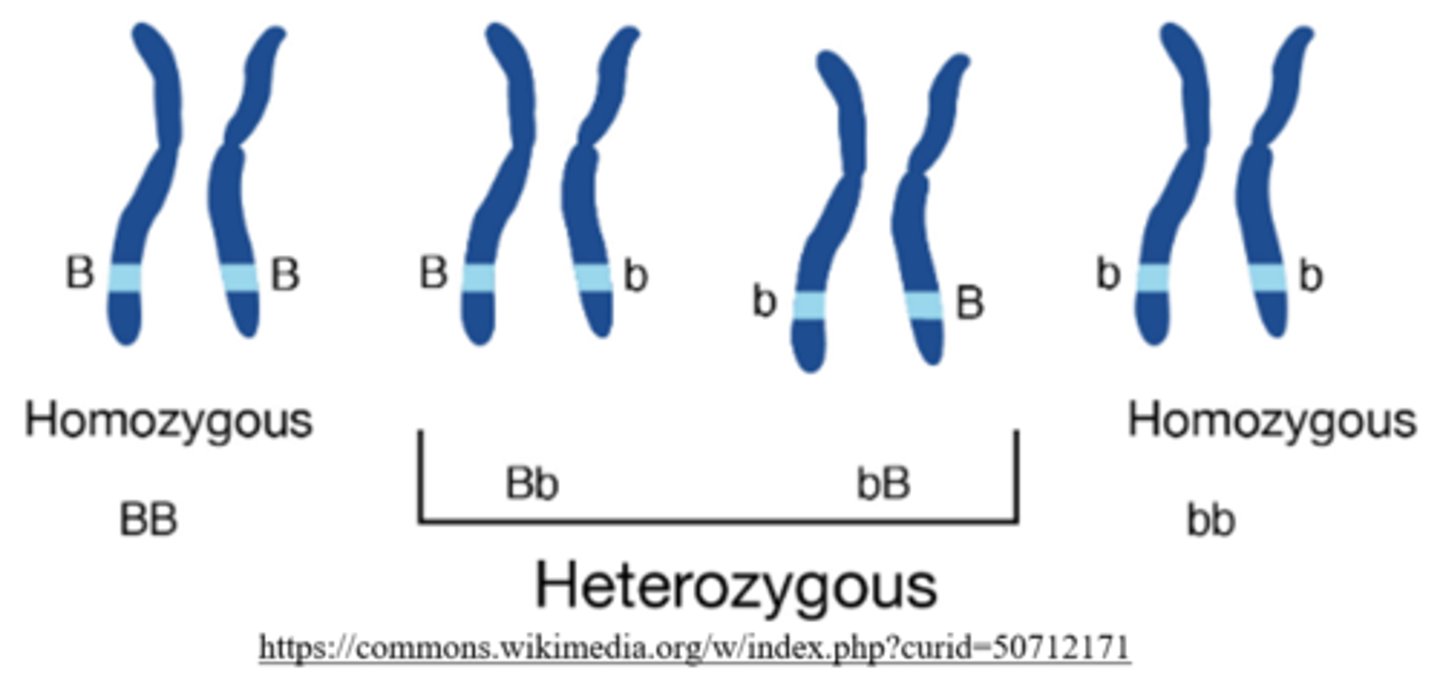
what is the phenotype of a heterozygous individual?
dominant
how many copies of the dominant allele do homozygous-recessive individuals carry?
0 (ex: bb)
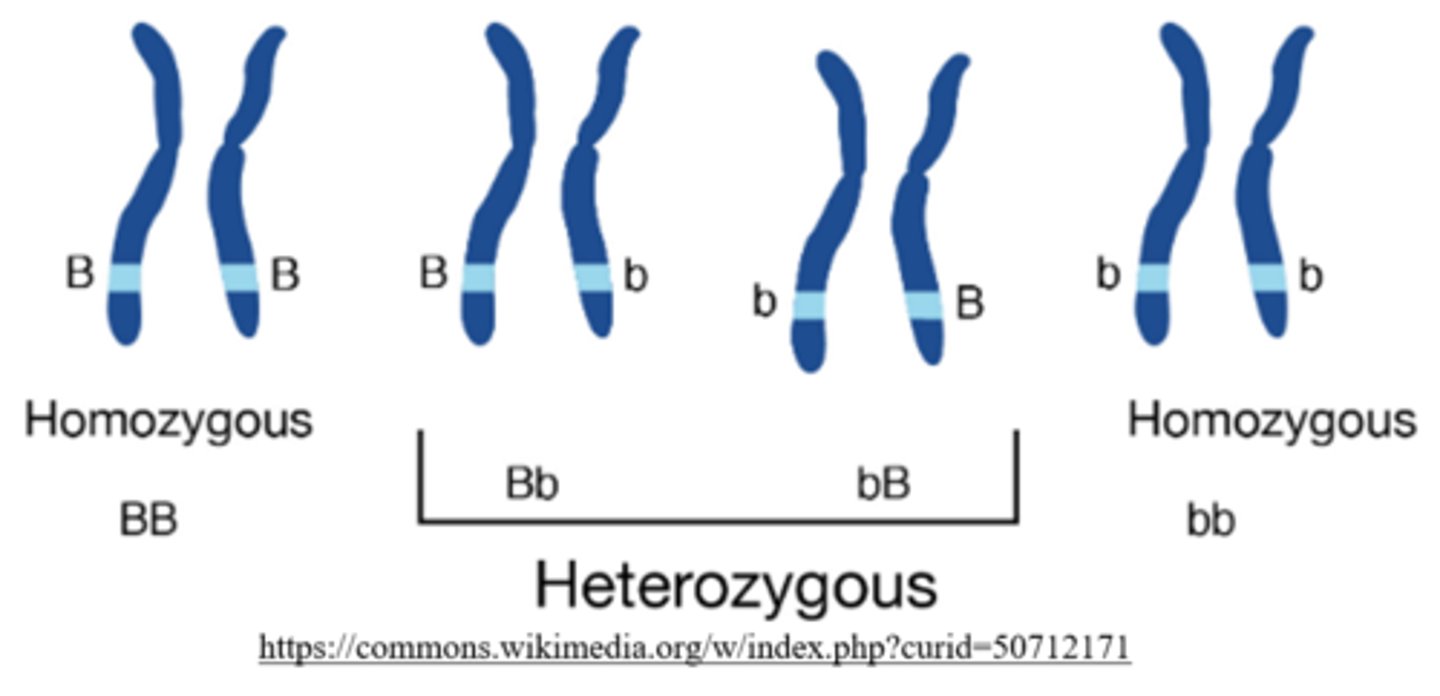
how many copies of the recessive allele do homozygous-recessive individuals carry?
2 (ex: bb)
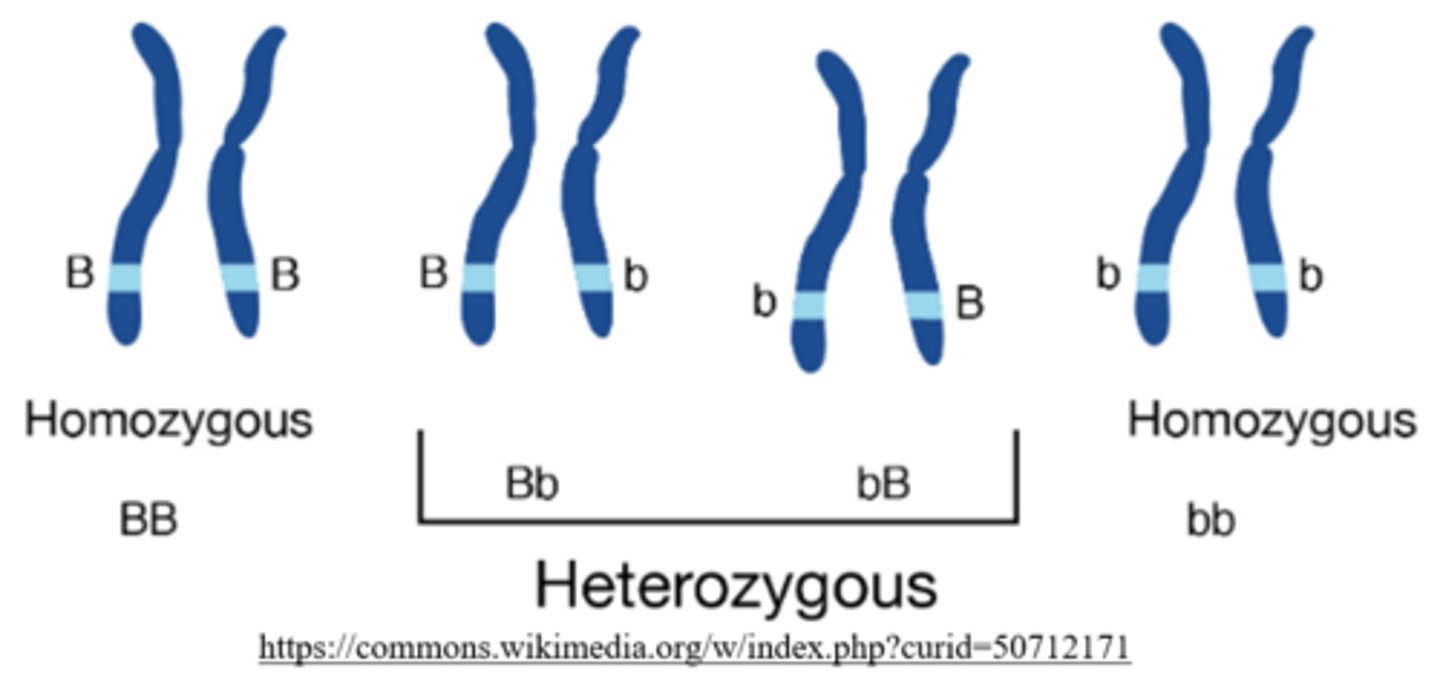
what is the phenotype of a homozygous-recessive individual?
recessive
_____ refers to the condition of having a single copy of a gene instead of 2
hemizygous
men have 2 different sex chromosomes (XY), so they are _____ for genes on each chromosome
hemizygous
the law of _____ says that homologous chromosomes separate during _____ (cell phase), so each parent only passes 1 of their alleles to their offspring
segregation; anaphase I of meiosis
the law of _____ says that 1 chromosome does not affect another as they separate during _____ (cell phase)
independent assortment; anaphase I of meiosis
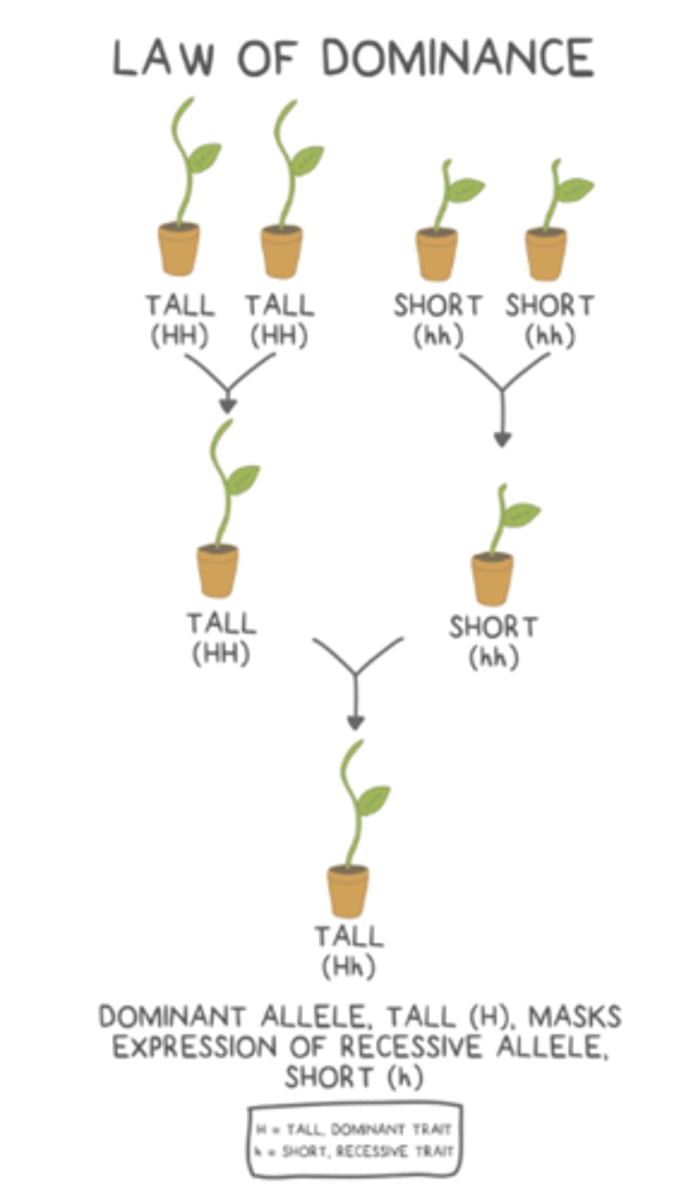
the law of dominance says that _____ alleles will mask the effect of _____ alleles
dominant; recessive
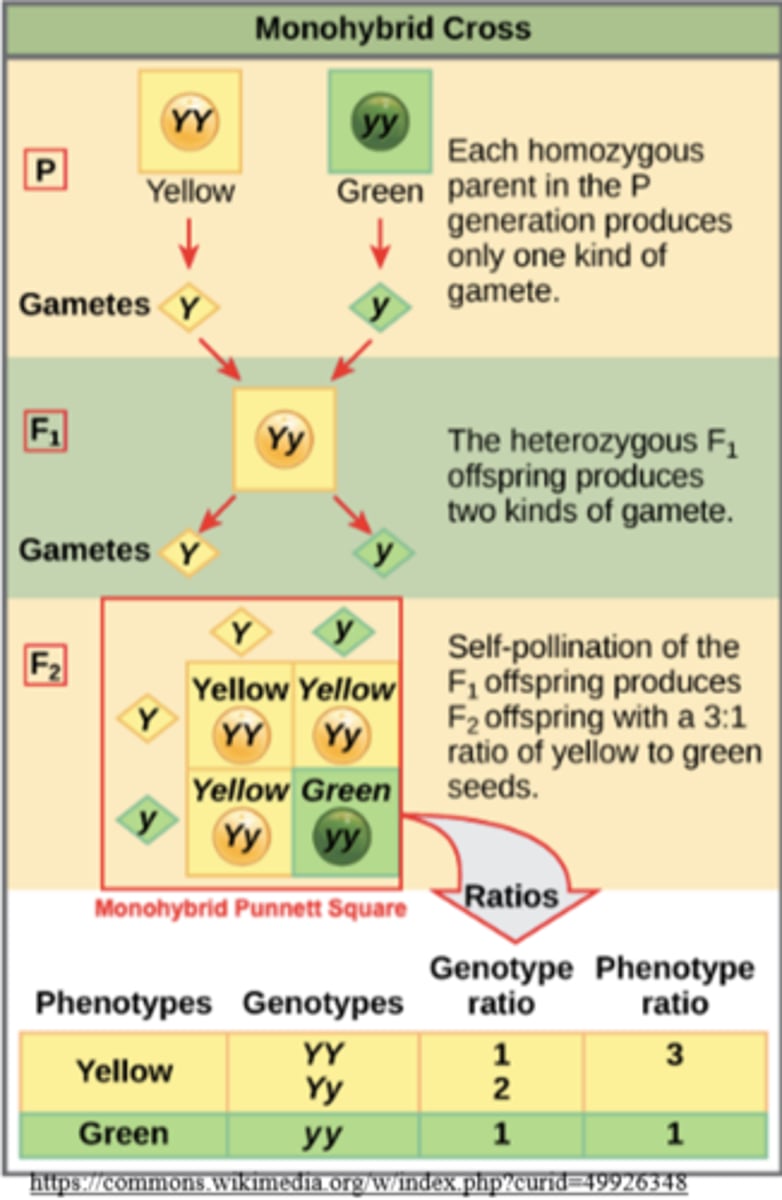
a monohybrid cross mates individuals that are _____ for _____ gene(s)
homozygous; a single
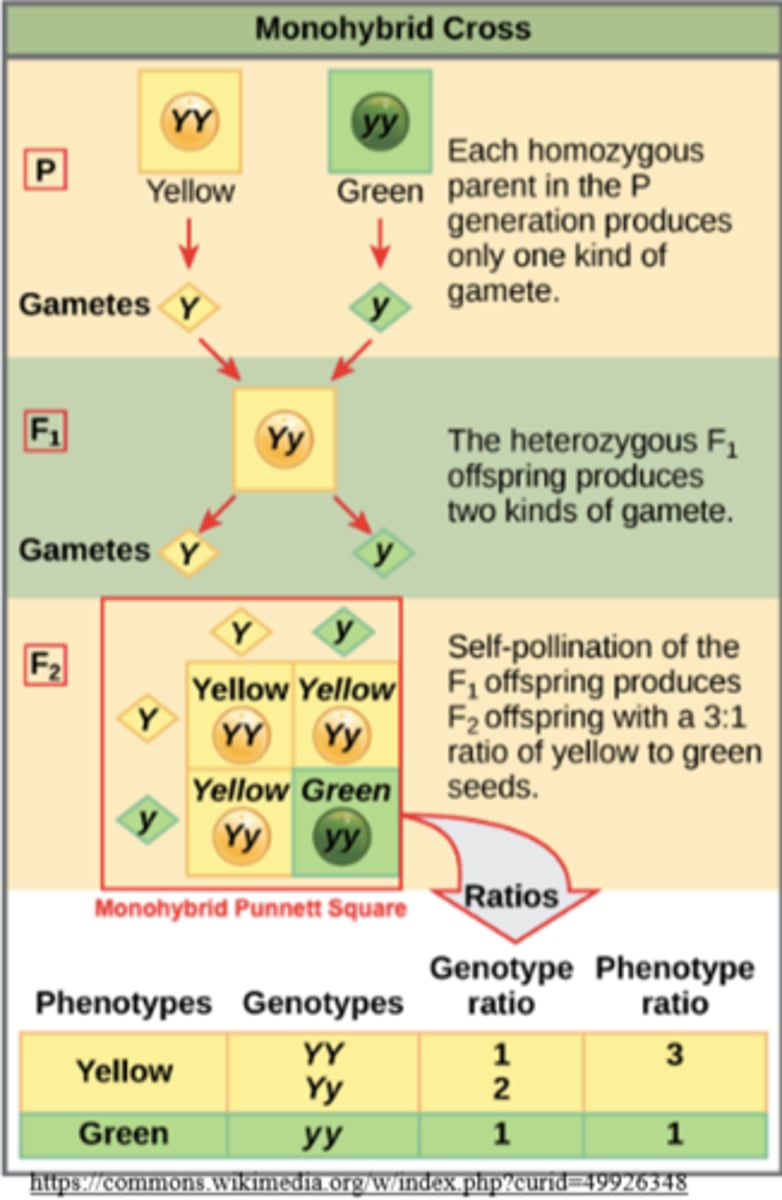
what is the phenotypic ratio for a monohybrid cross?
3:1
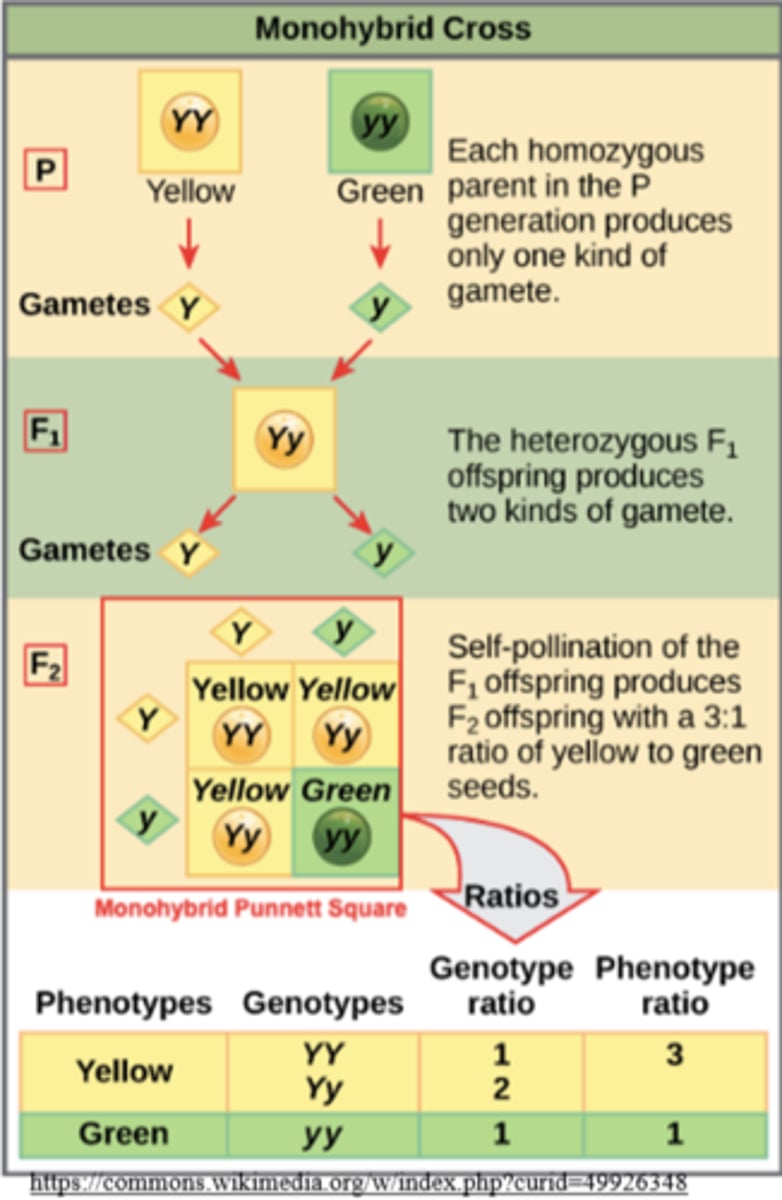
what is the genotypic ratio for a monohybrid cross?
1:2:1 for XX : Xx : xx
a dihybrid cross mates individuals that are _____ for _____ gene(s)
heterozygous; 2
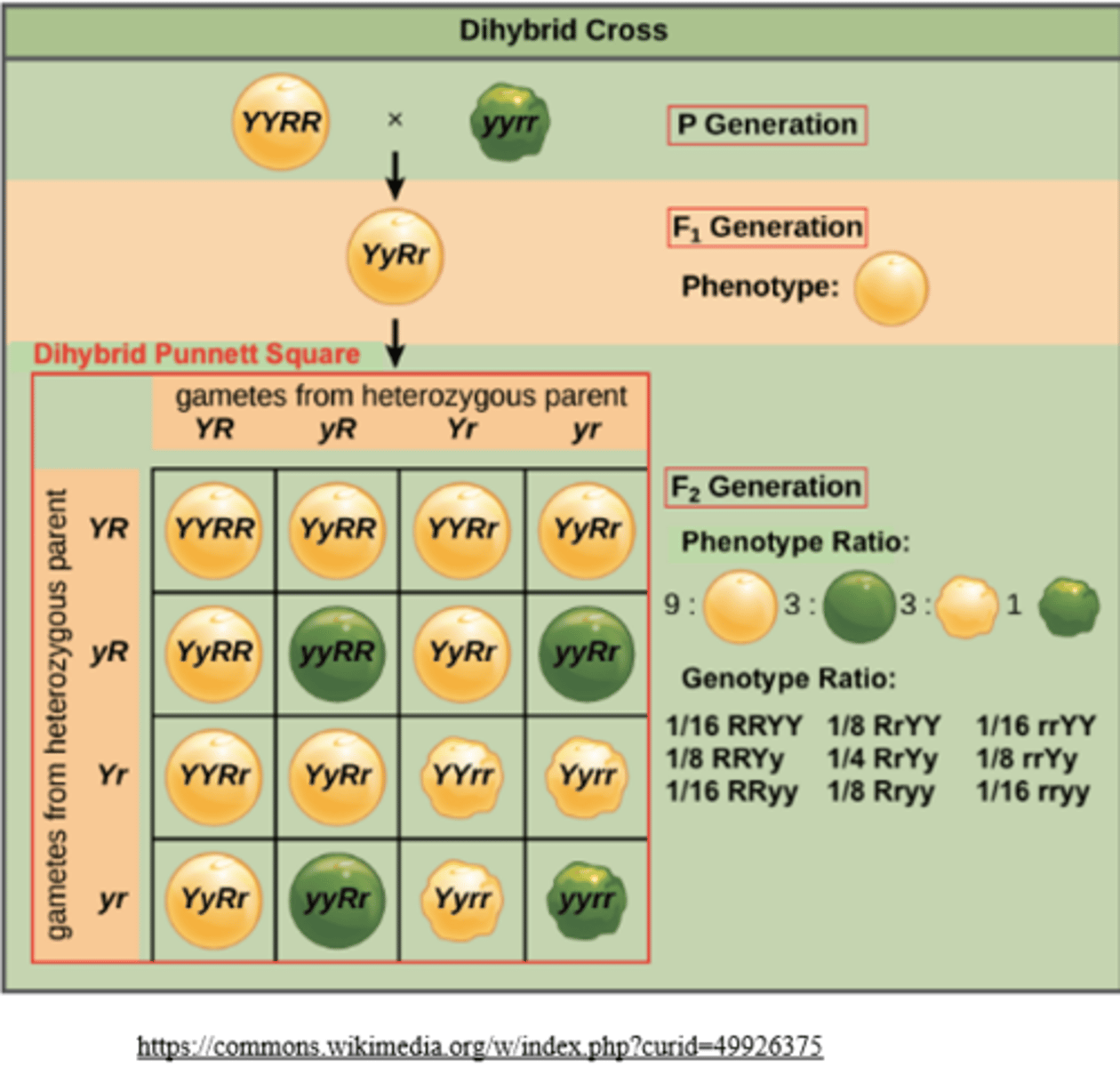
what is the phenotypic ratio of a dihybrid cross?
9:3:3:1
what is the label for the parental generation in a cross?
P = parental
what is the label for the first generation of offspring in a cross?
F1 = filial 1 hybrid = offspring of parental generation
what is the label for the second generation of offspring in a cross?
F2 = filial 2 hybrid = offspring of F1 generation
what are the three important single allele crosses?
homozygous x homozygous = 1/1 AA, Aa or aa
homozygous x heterozygous = 1⁄2 AA (or aa) and 1⁄2 Aa
heterozygous x heterozygous = 1⁄4 AA; 1⁄2 Aa; 1⁄4 aa (1:2:1 monohybrid ratio)
what is the simplest way to calculate the probability of a specific dihybrid cross?
multiply the heterozygous x heterozygous single allele cross probabilities together
(ex: Aabb = 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8)
in a dihybrid cross, gene loci must be on separate _____
chromosomes
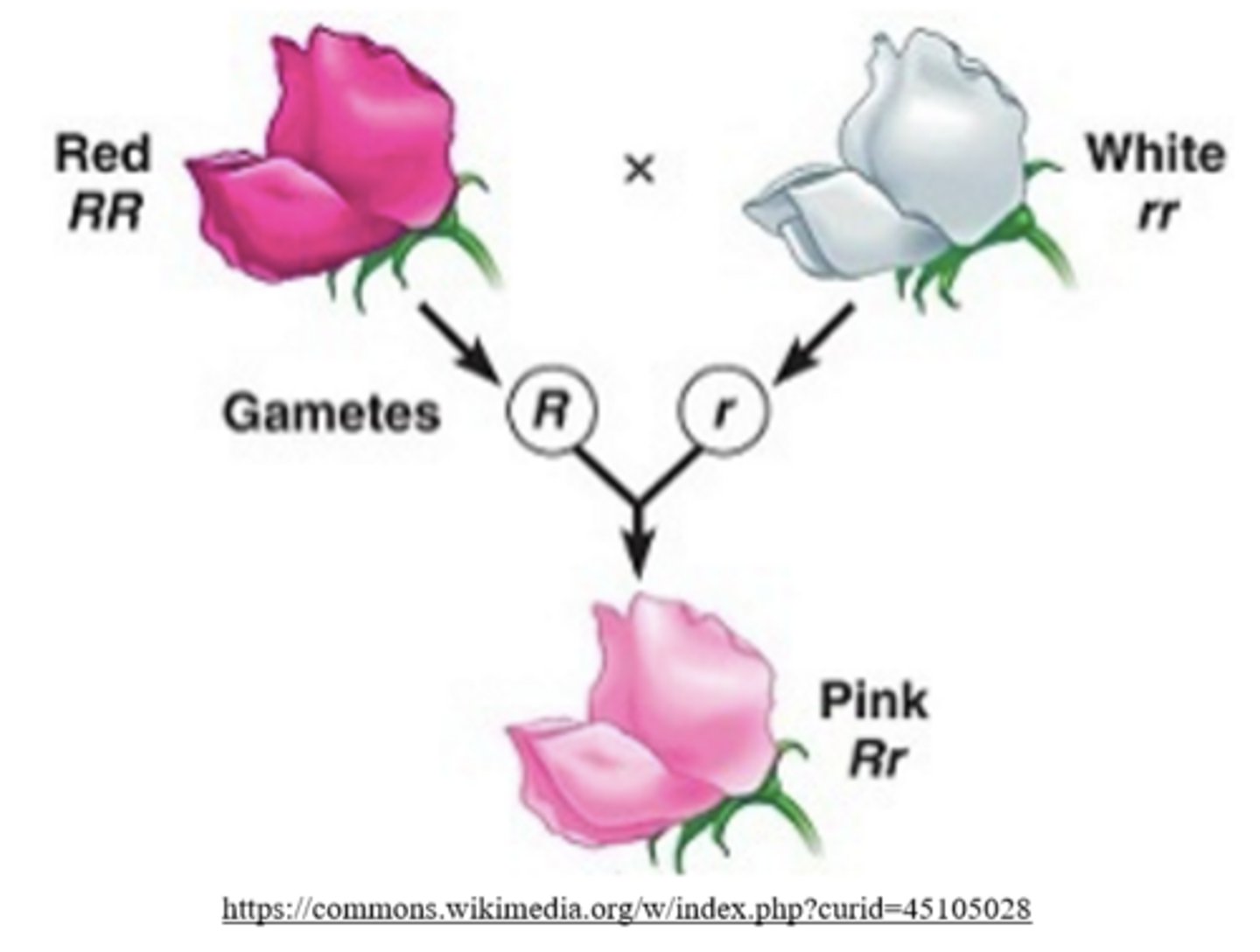
_____ is the pattern of inheritance in which the expression of alleles is blended, producing a unique heterozygous phenotype
incomplete dominance
Mnemonic: INcomplete dominance is the INtermediate
_____ is the pattern of inheritance in which both alleles (for the same gene) are completely expressed at the same time
codominance
Mnemonic: Codominance is NO dominance
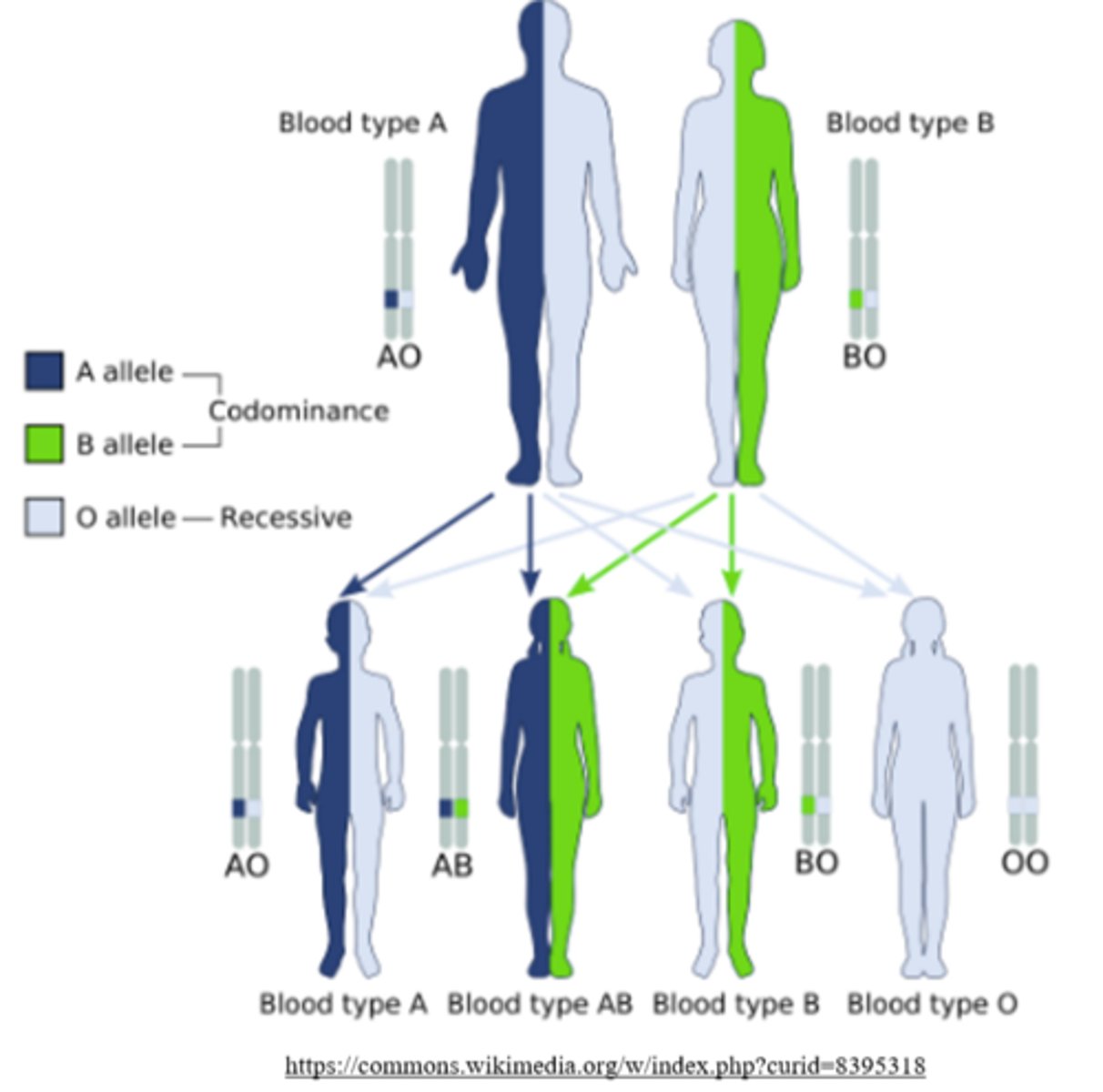
_____ is the pattern of inheritance in which more than two alleles exist for a given gene
multiple alleles
what is an example of multiple alleles in humans?
the ABO blood typing. A person can be type A, AB, B, or O
_____ is the pattern of inheritance in which 1 gene affects the phenotypic expression of a second, separate gene
epistasis
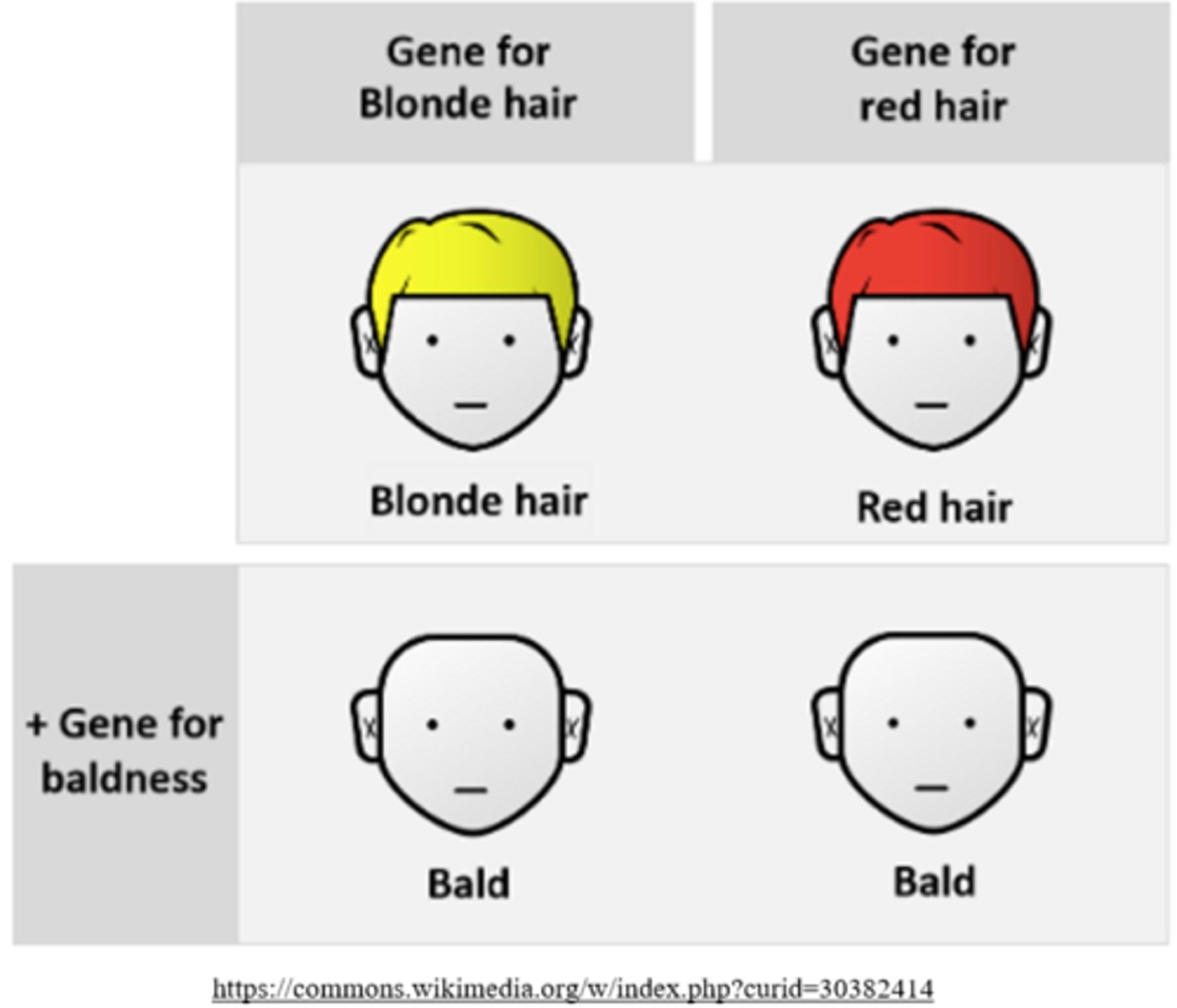
_____ is the pattern of inheritance in which a single gene has more than 1 phenotypic expression
pleiotropy
what is an example of pleiotropy in humans?
cystic fibrosis. A single gene will lead to the expression of different symptoms in different tissues
_____ is the pattern of inheritance in which multiple genes affect one phenotype with continuous variation
polygenic inheritance
(ex: height or skin color)
_____ genes are genes that reside on a sex chromosome
sex-linked
(ex: color blindness)
in _____, a specific allele is expressed (or not) depending on whether it is inherited from the mother or father
genomic imprinting
why is genomic imprinting distinct from sex-linked genes?
because the effect also occurs on autosomal chromosomes
_____ is the probability that an organism with a specific genotype will express the corresponding phenotype
penetrance
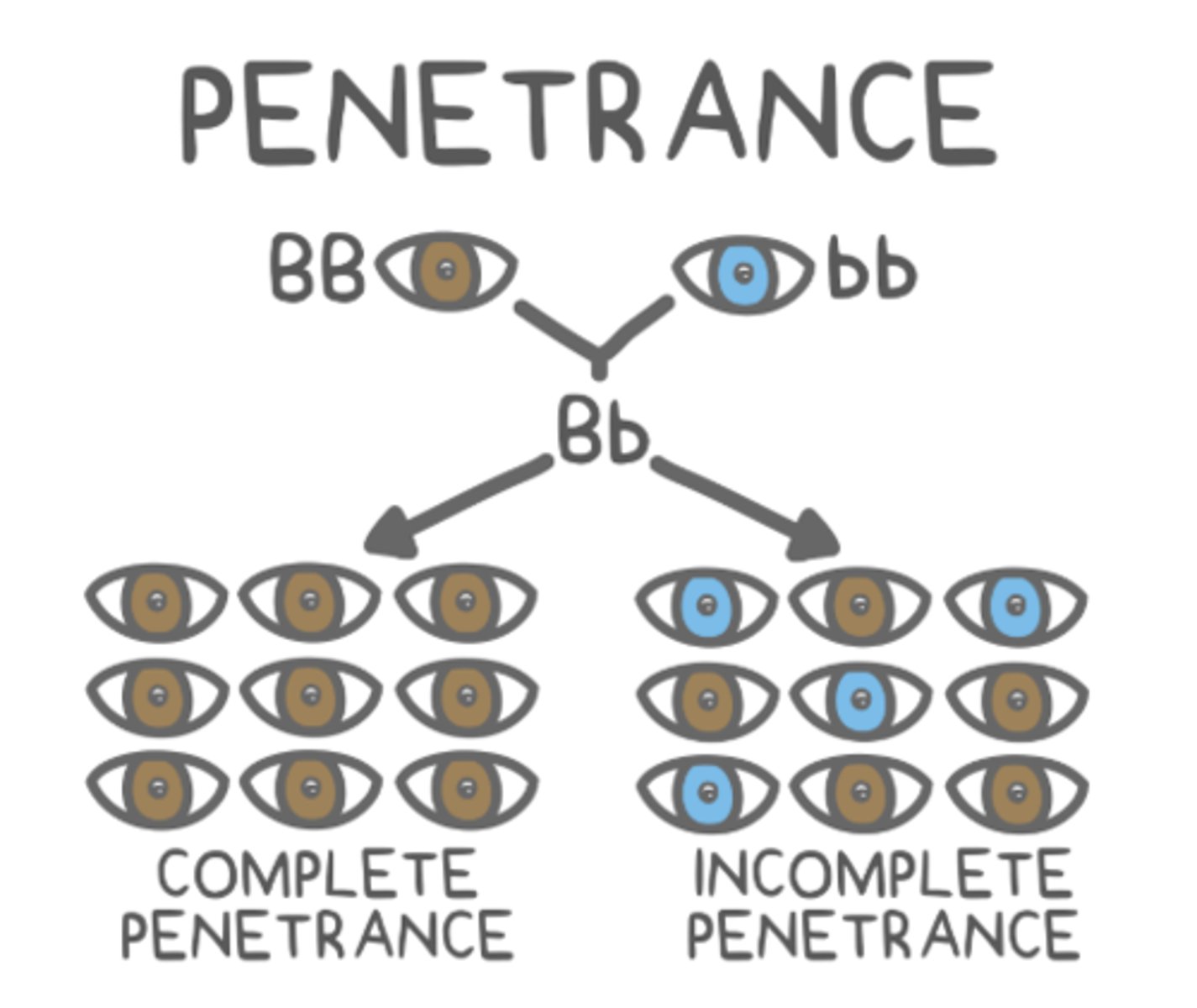
_____ means that 100% of individuals will express a phenotype that corresponds to their genotype
complete penetrance
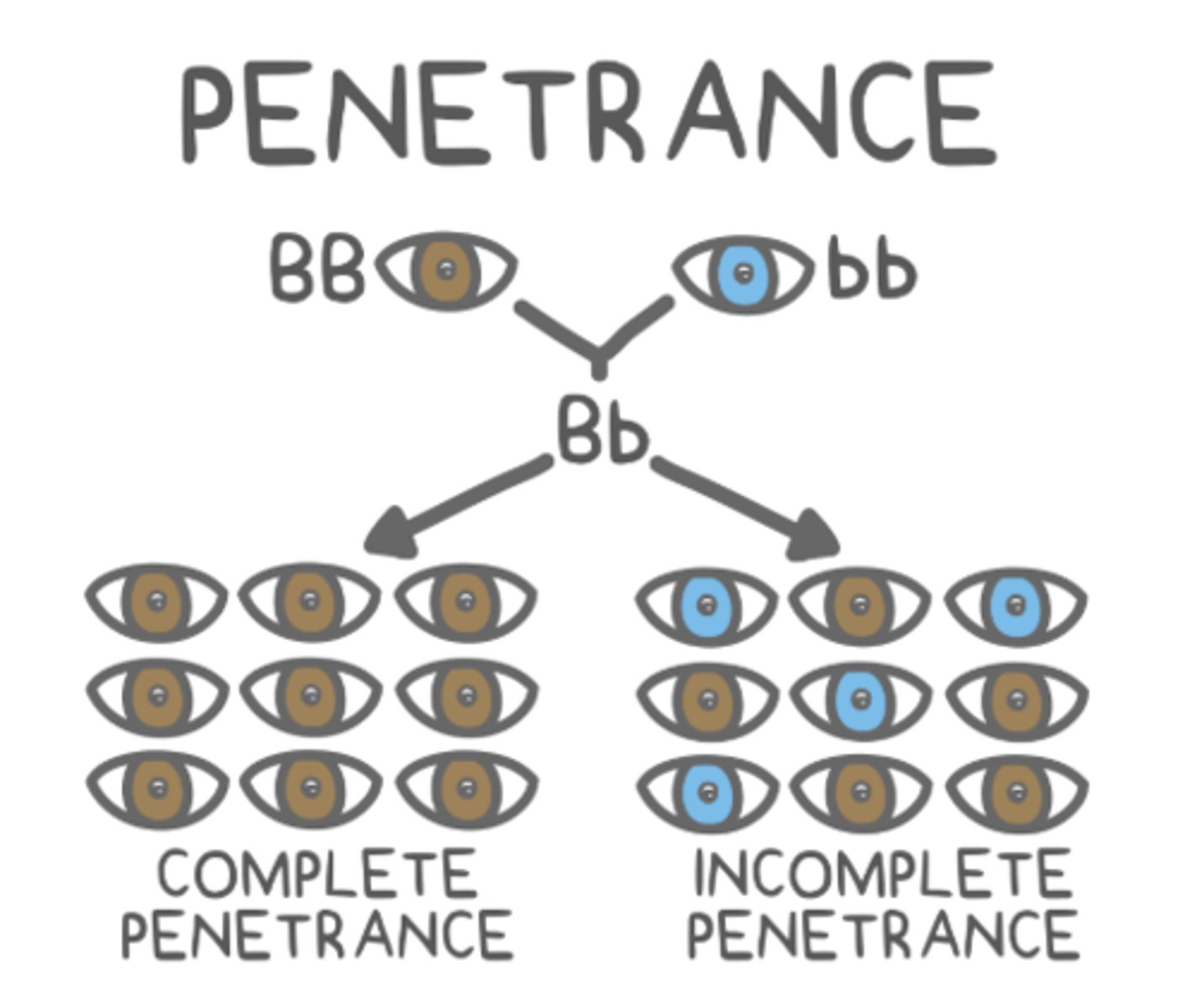
_____ means that less than 100% of individuals will express a phenotype that corresponds to their genotype
incomplete penetrance
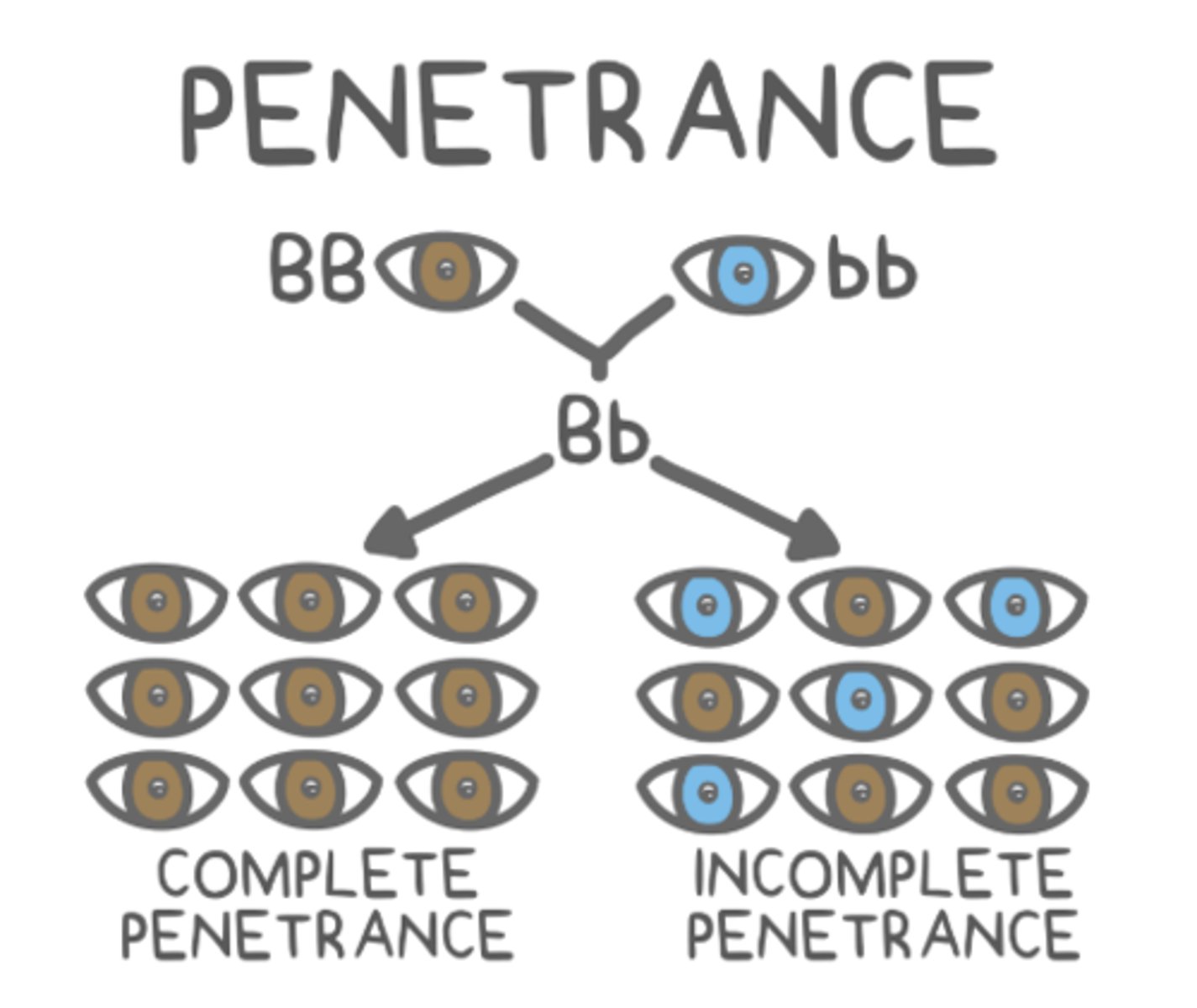
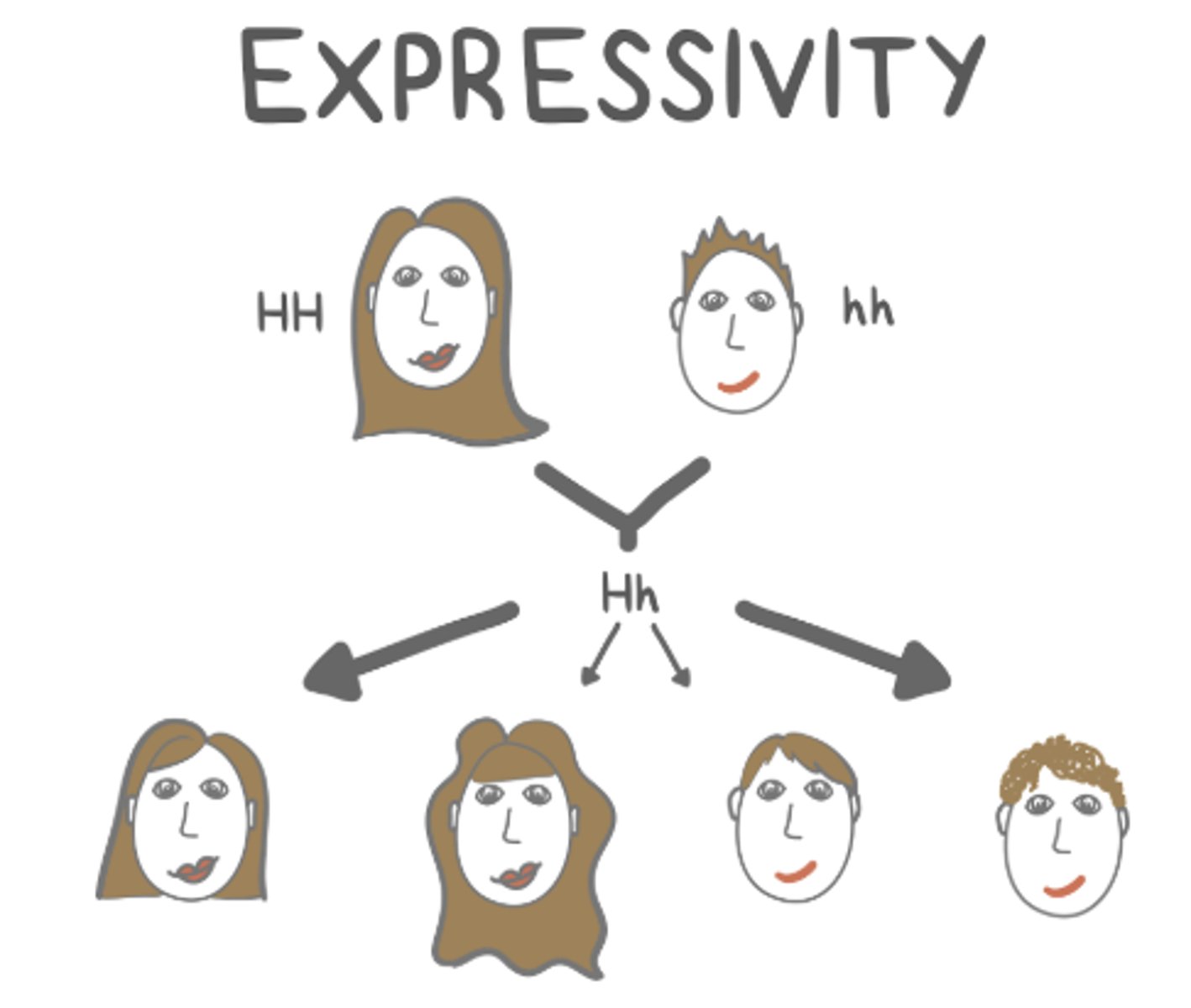
_____ describes the degree of expression of a certain phenotype for a given genotype
expressivity
(ex: differences in hairiness despite the same genotype)
during embryonic development in female mammals, 1 of 2 X chromosomes is inactivated - this is known as _____
X inactivation
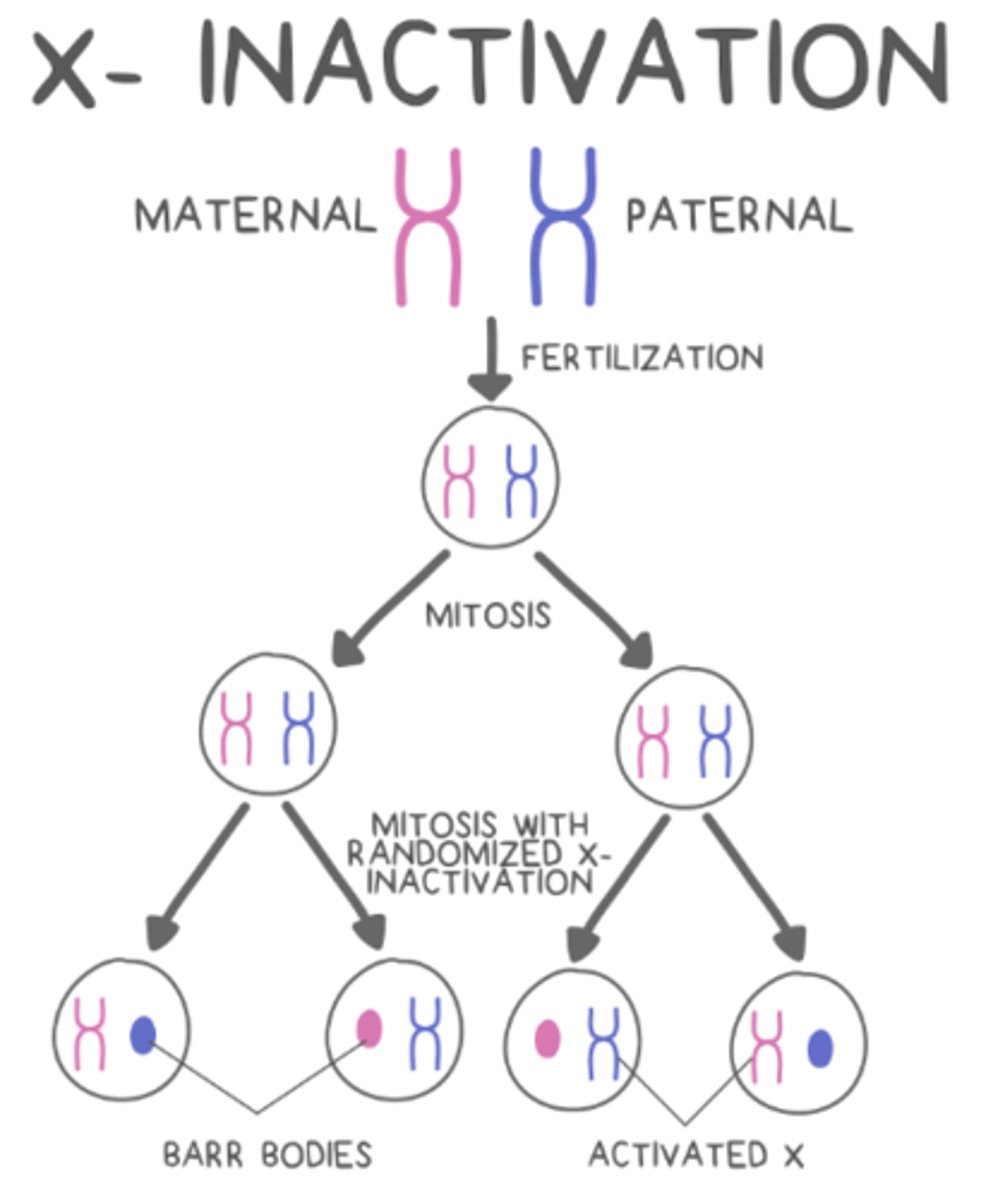
the X chromosome that does not uncoil due to X inactivation in female mammals is known as a _____
Barr body
_____ genes are 2 or more genes that reside close together on the same chromosome
linked
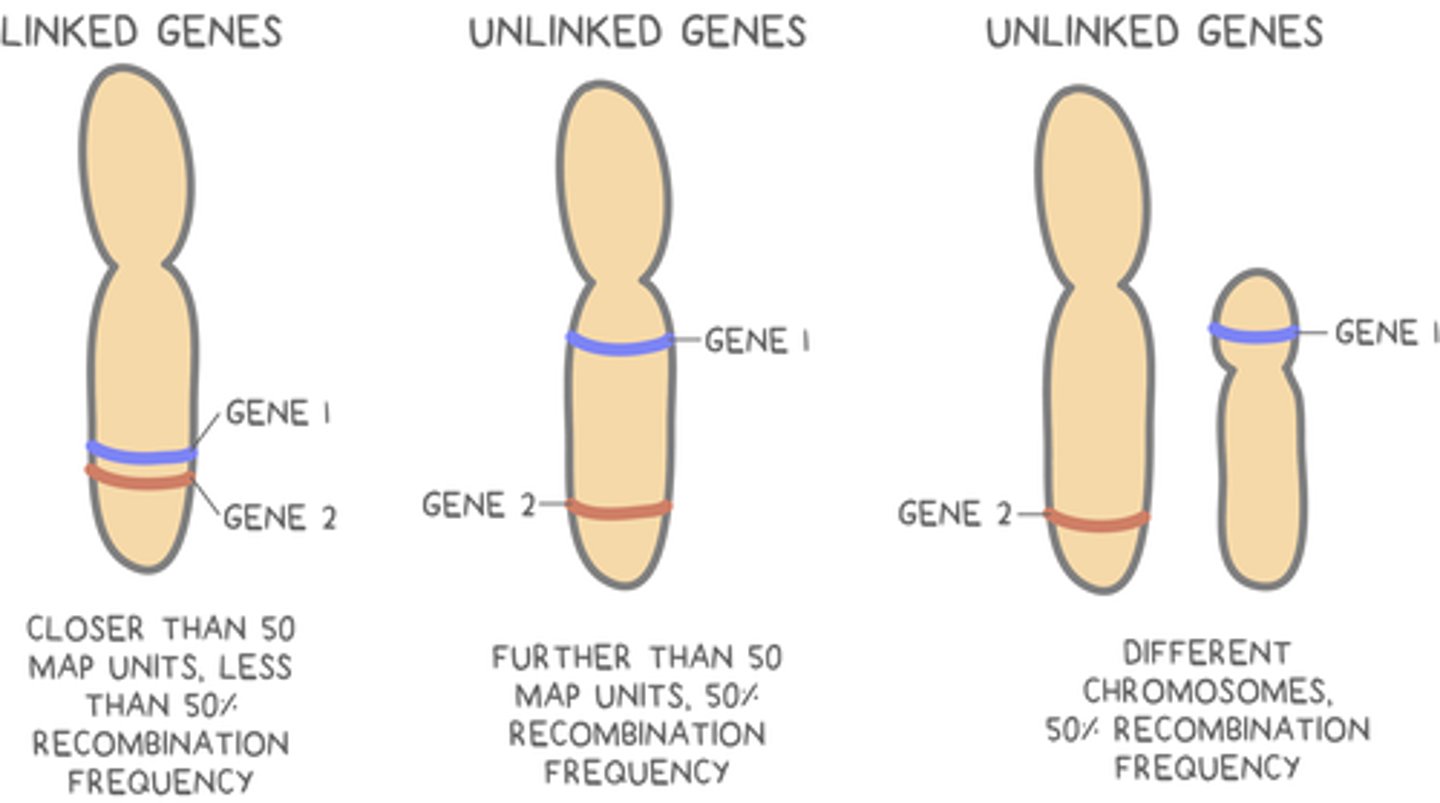
linked genes are _____ (less/more) likely to be separated by recombination during meiosis, and are _____ (less/more) likely to be inherited together
less; more
the failure of chromosome/chromatid separation during mitosis or meiosis is known as _____
nondisjunction
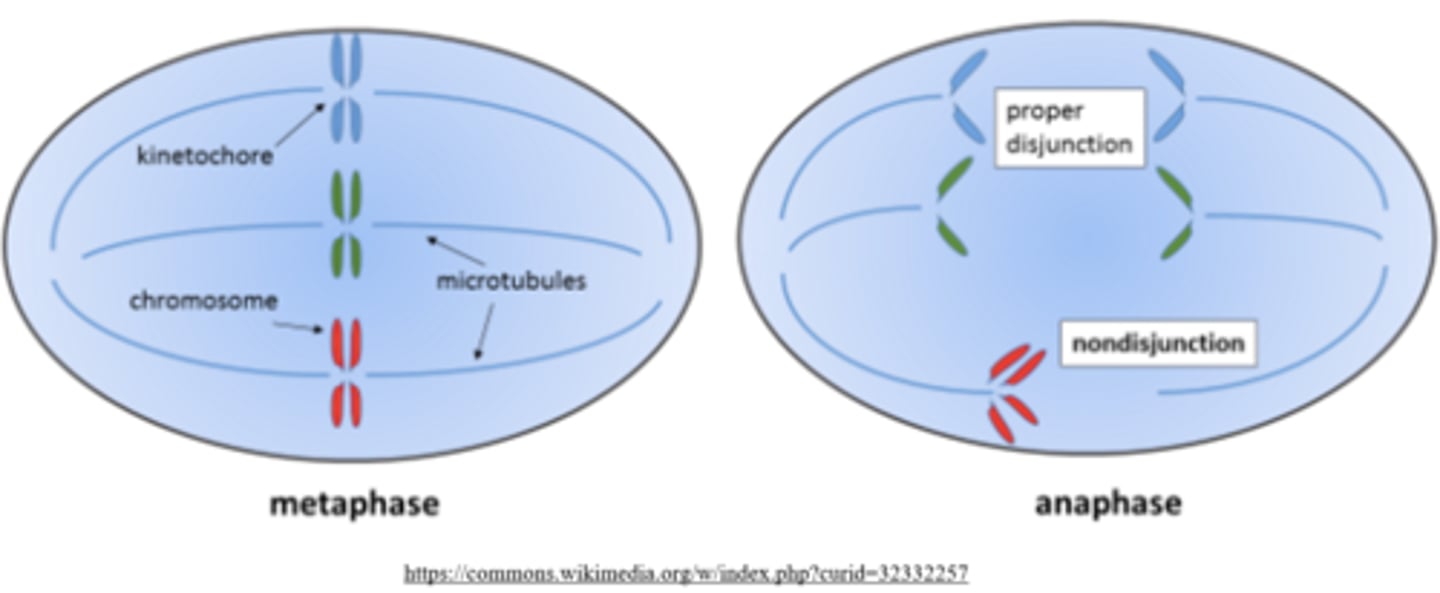
_____ nondisjunction can result in gametes with missing or extra chromosomes, creating _____
meiotic; aneuploidies
a(n) _____ is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, but it does not include a difference of 1 or more _____ of chromosomes
aneuploidy; complete sets
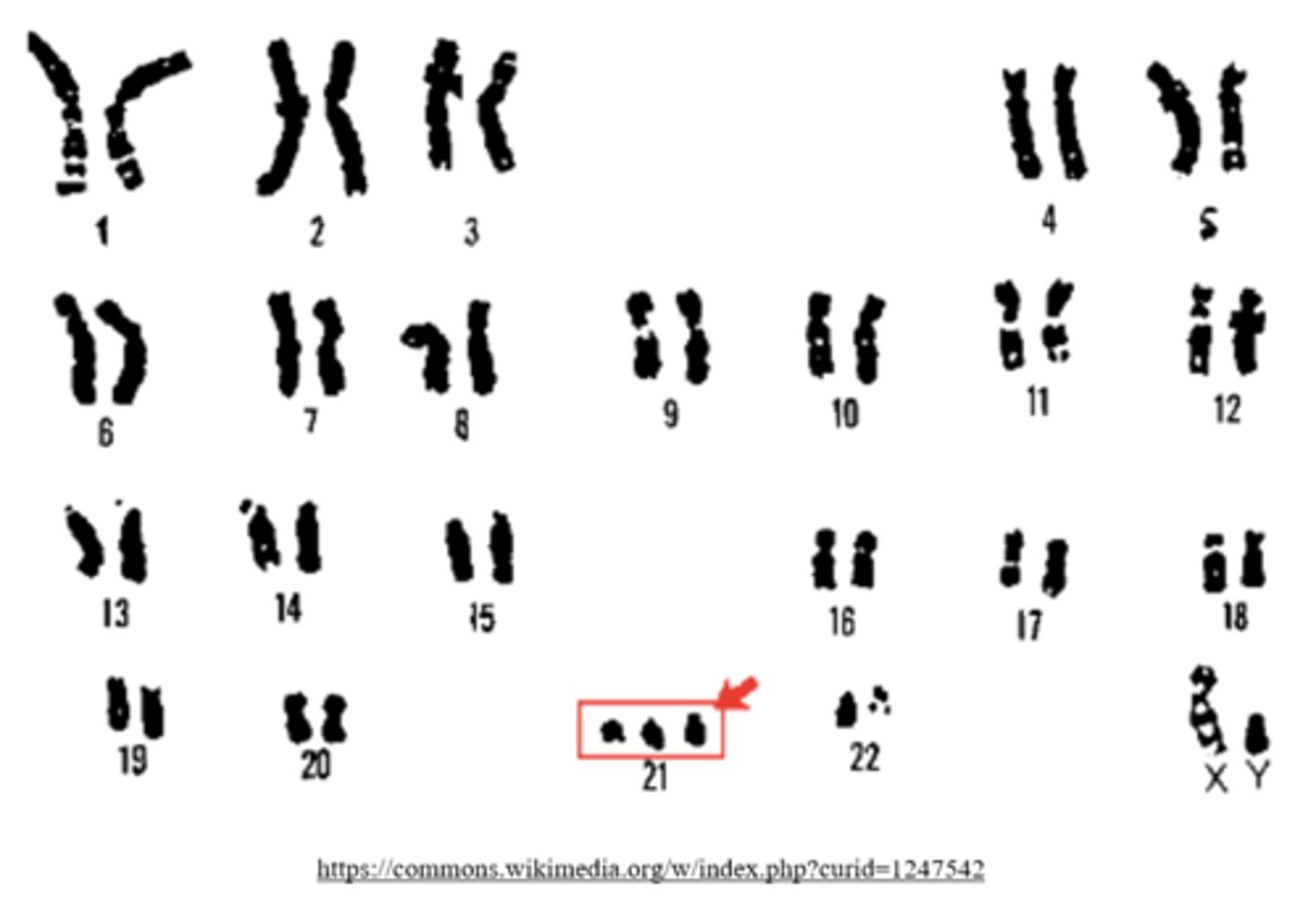
a _____ is an aneuploidy created by meiotic nondisjunction, where there are 3 copies of a chromosome
trisomy
(ex: trisomy 21 = Downs syndrome)
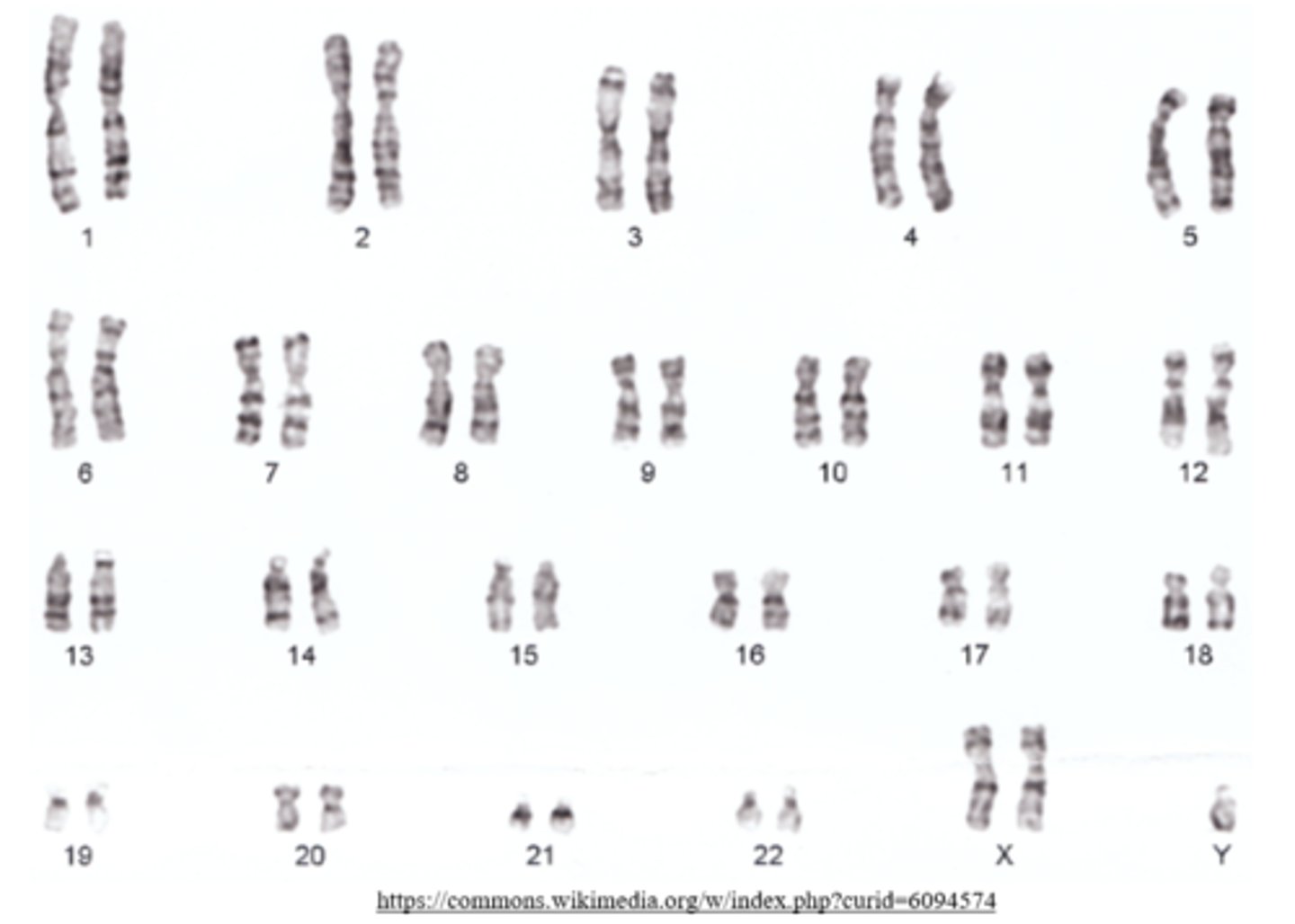
_____ is a sex chromosome trisomy resulting in XXY and sterility
Klinefelter syndrome
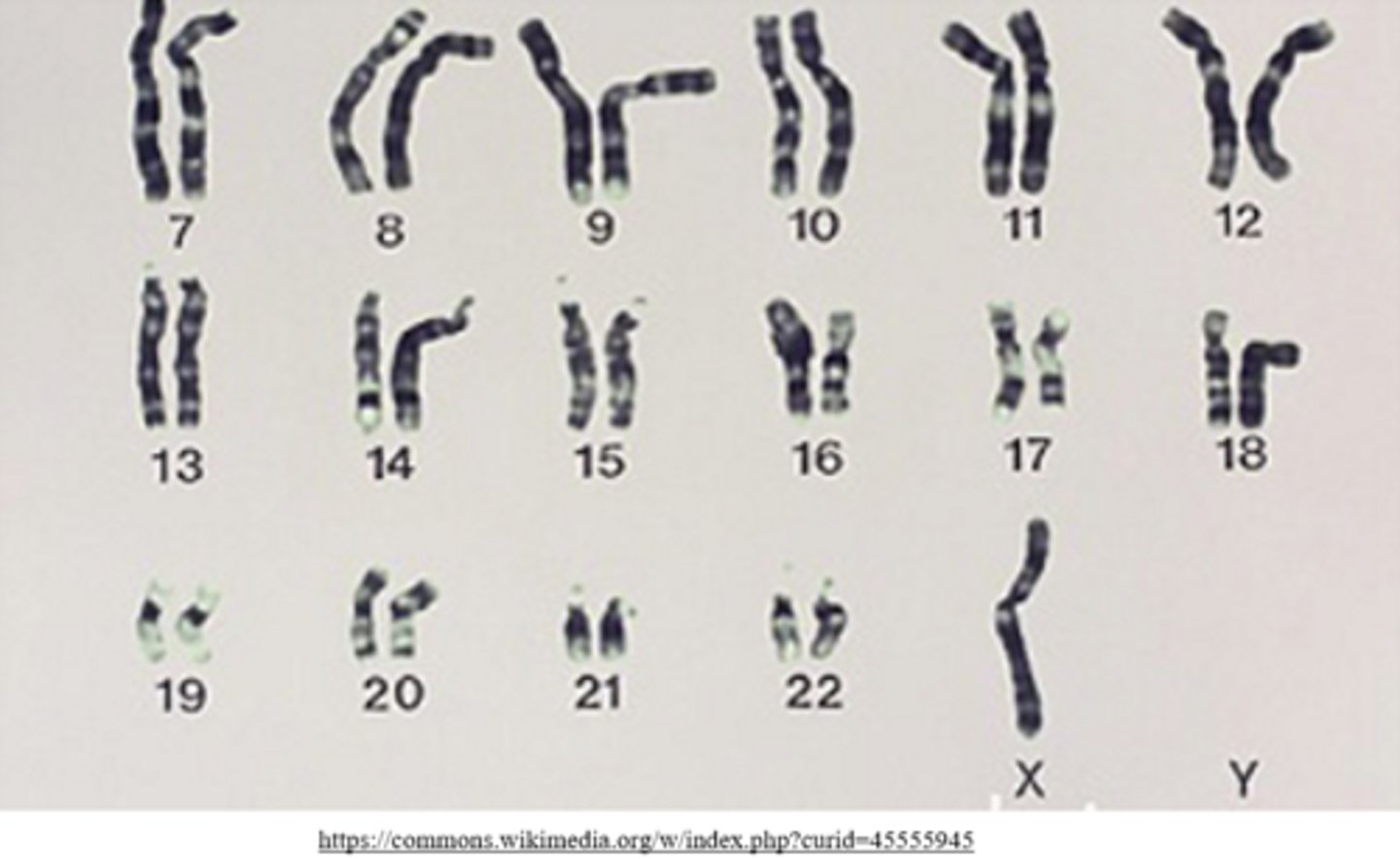
a _____ is an aneuploidy created by meiotic nondisjunction, where there is 1 copy of a chromosome
monosomy
(ex: monosomy X = Turner syndrome)
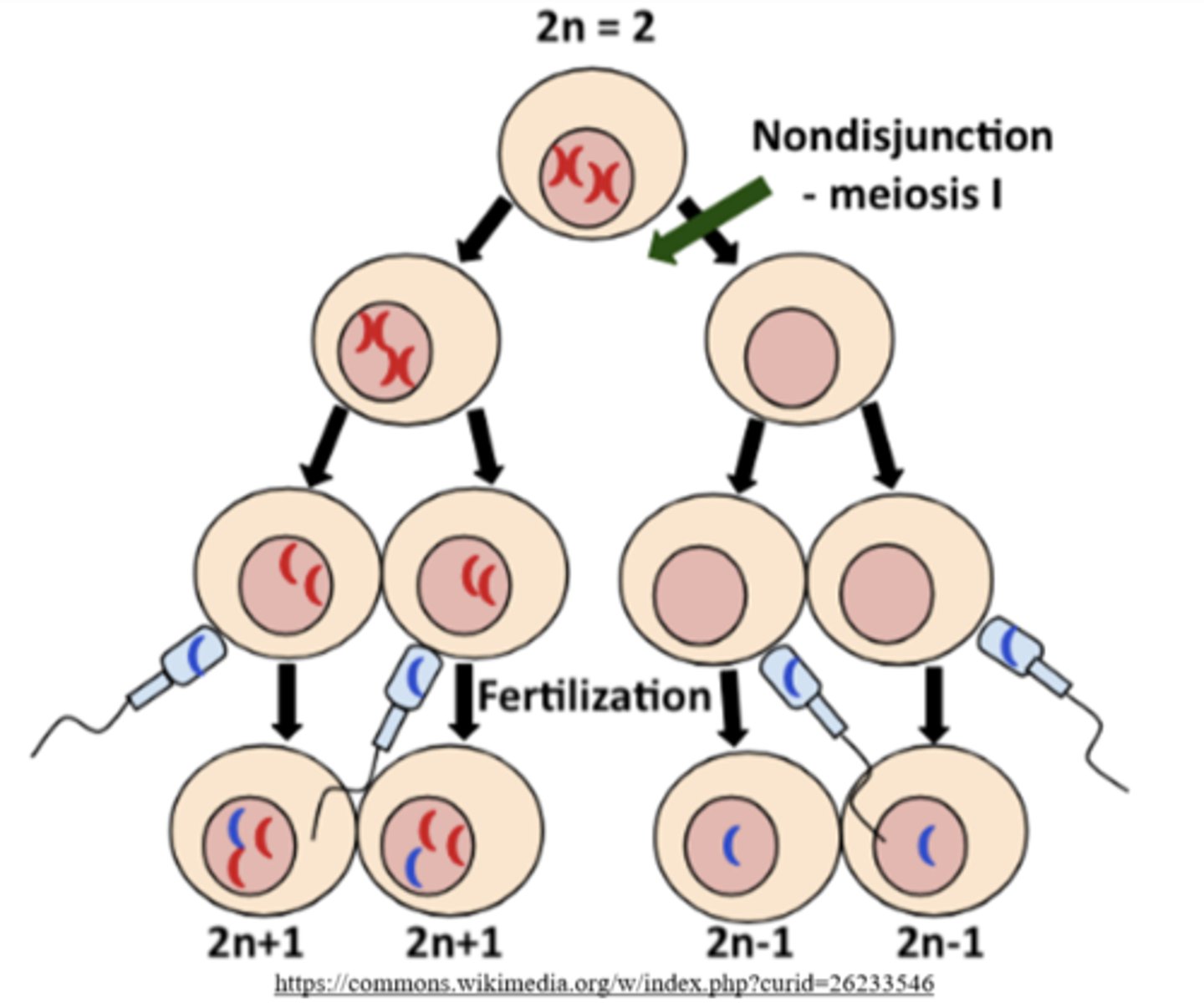
list the possible gametes of a meiosis I nondisjunction:
n+1, n+1, n-1, n-1
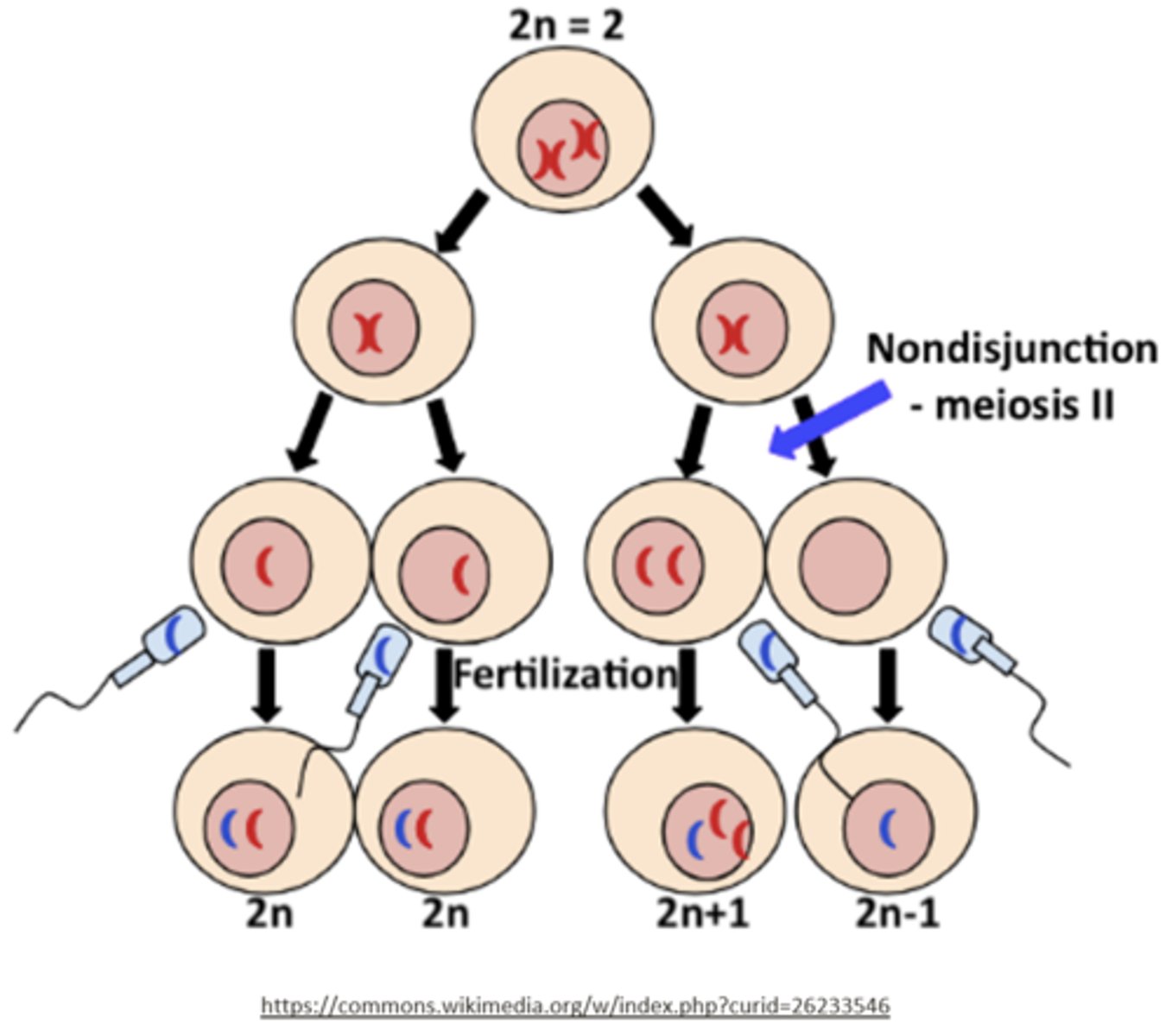
list the possible gametes of meiosis II nondisjunction:
n, n, n+1, n-1
a _____ is a mutation that causes a single nucleotide change
point mutation
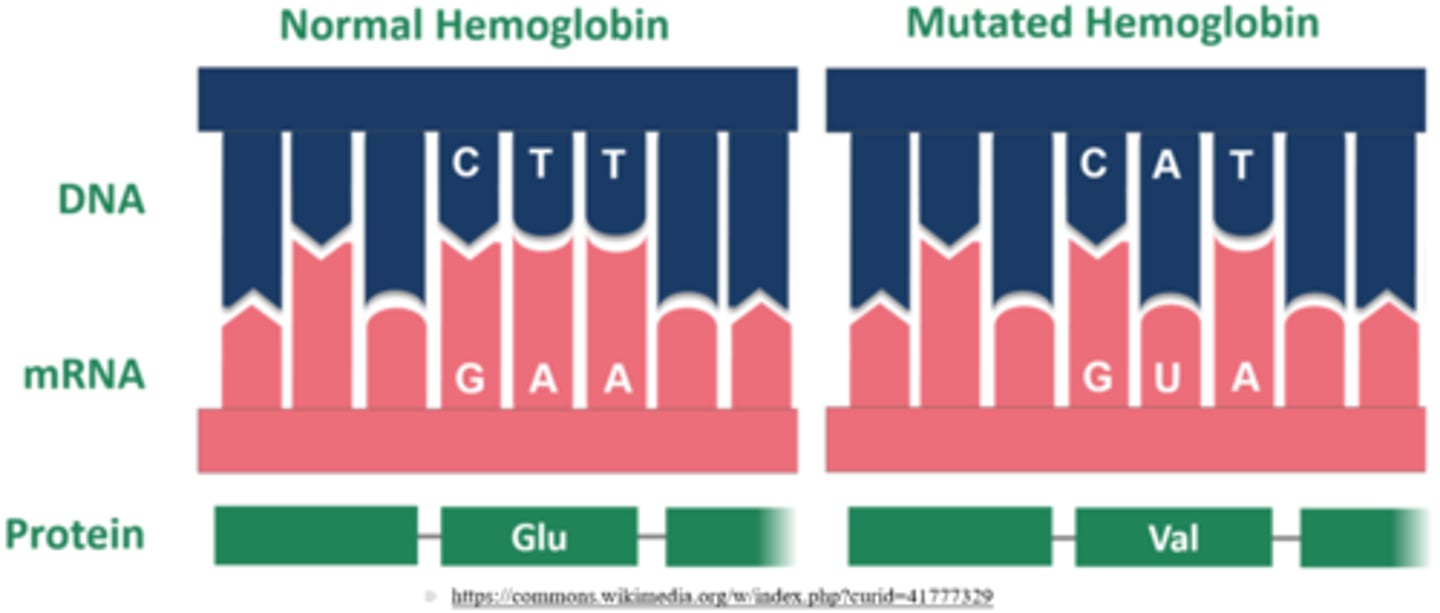
what are the 3 general types of mutations that can result in a point mutation?
substitution; insertion; deletion
a _____ mutation is the change of 1 nucleotide to a different nucleotide
substitution
an _____ mutation is the addition of a nucleotide
insertion
a _____ mutation is the removal of a nucleotide
deletion
a _____ results in the 'reading frame' of an RNA transcript being shifted, causing different amino acids to be translated and resulting in impaired protein structure
frameshift mutation
the insertion/deletion of nucleotides in multiples of _____ will not lead to a frameshift mutation
3
which types of mutations cause a frameshift mutation?
insertion and deletion
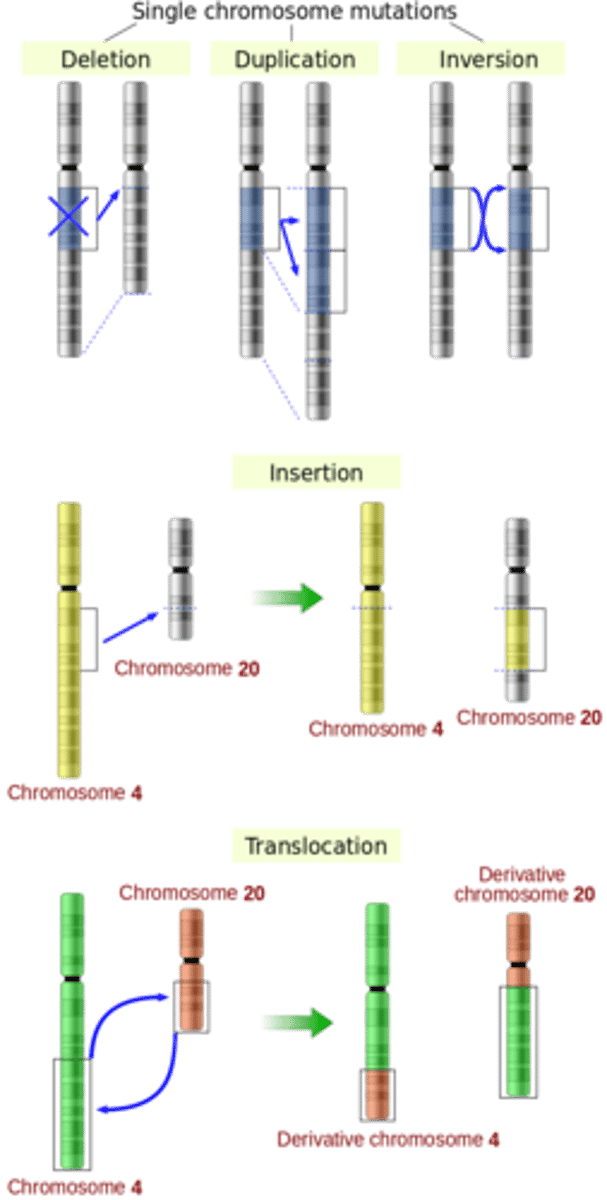
_____ involve changes to segments of DNA
chromosomal mutations
_____ occur when a chromosome segment is moved to another chromosome
translocations
_____ regulate normal cell growth/function (e.g. ras gene)
proto-oncogenes
if mutated, proto-oncogenes can become _____
oncogenes
how do mutated proto-oncogenes that become oncogenes cause cancer?
oncogenes cause dysregulation of cell growth and function
proto-oncogenes turn into cancerous oncogenes after a _____ mutation following the _____ hit hypothesis
gain-of-function, one
_____ (e.g. p53) help prevent uncontrolled cell growth
tumor suppressor genes
if tumor suppressor genes are mutated in a way that _____ their activity, they can contribute to the onset of cancer
decreases
tumor-suppressor genes becomes cancerous after _____ mutations following the _____ hit hypothesis
loss-of-function, two
_____ traits follow a dominant inheritance pattern on an autosome
autosomal dominant
if an autosomal dominant allele is inherited from _____ parent(s), the offspring will be affected
either
(GG, Gg are all "affected" by the dominant trait)
_____ traits follow a recessive inheritance pattern on an autosome
autosomal recessive
if an autosomal recessive allele is inherited from _____ parent(s), the offspring will be affected
both
_____ genetic disorders are carried on either the X or Y chromosome
sex-linked
_____ disorders are _____ genetic disorders characterized by a dominant allele on the X chromosome
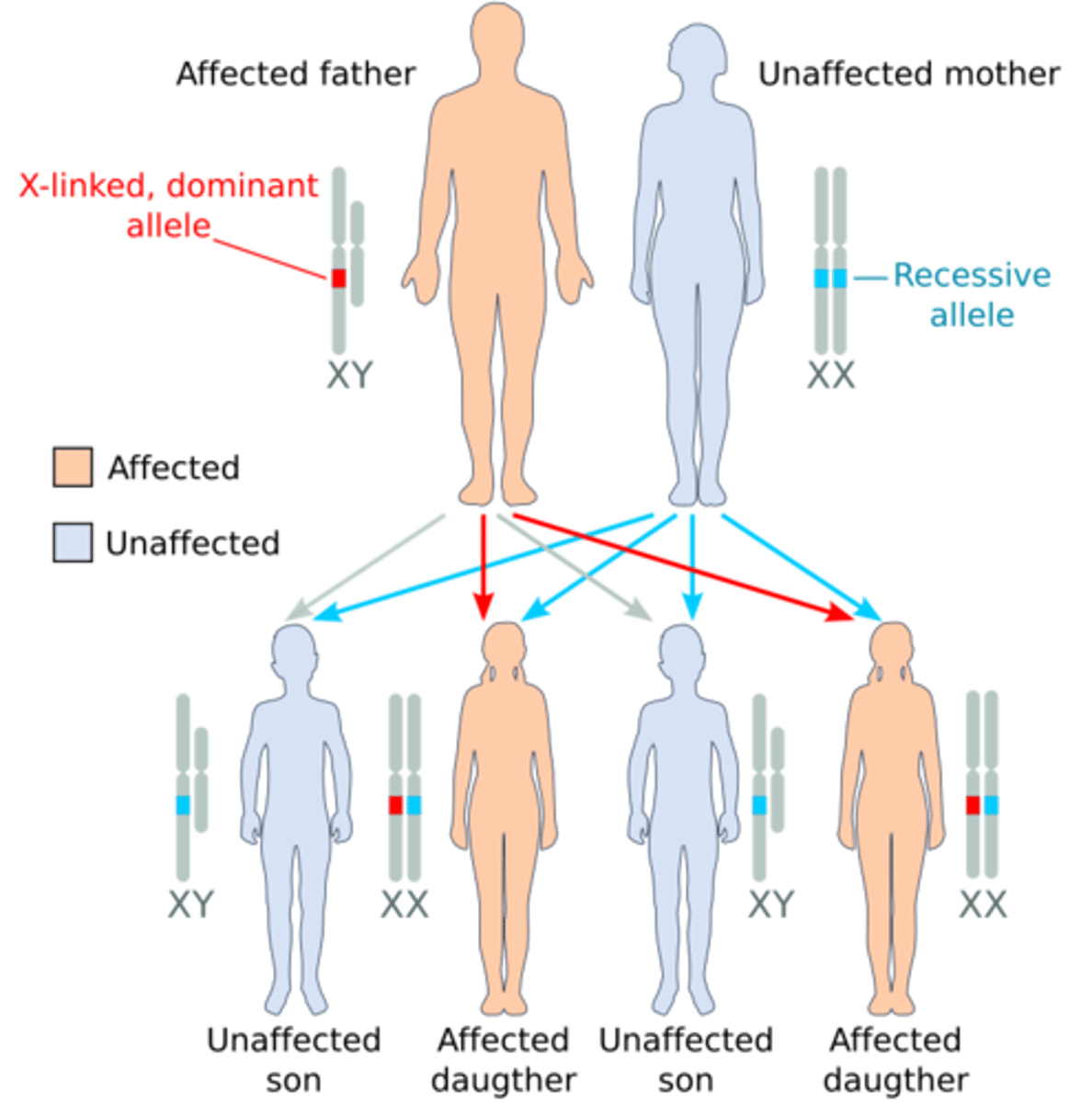
X linked dominant; sex-linked
if an X linked dominant allele is inherited from _____ parent(s), the offspring will be affected
either
(fathers must pass the Y chromosome to their son)
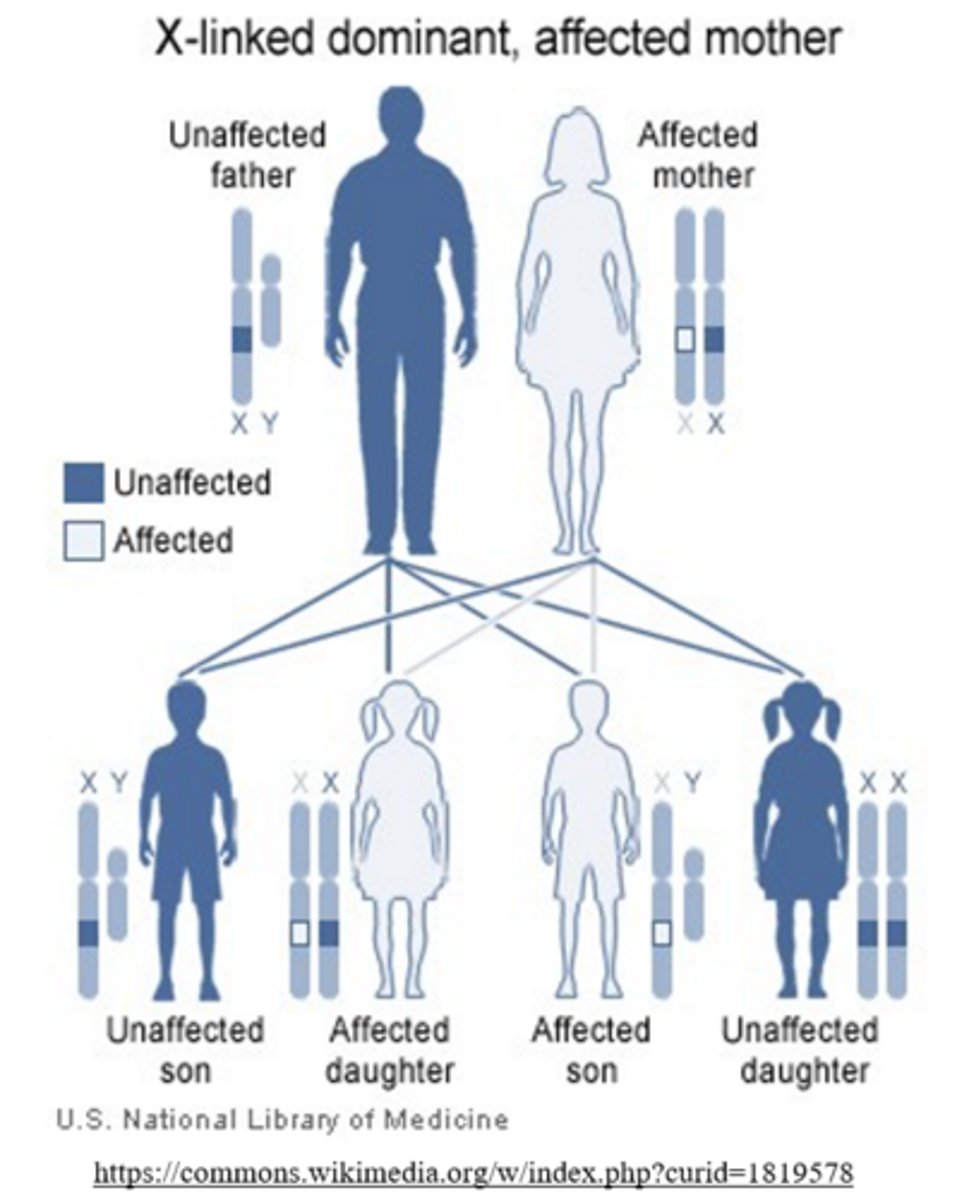
X linked dominant alleles cannot be passed from _____ to _____
father; son
(fathers must pass the Y chromosome to their son)
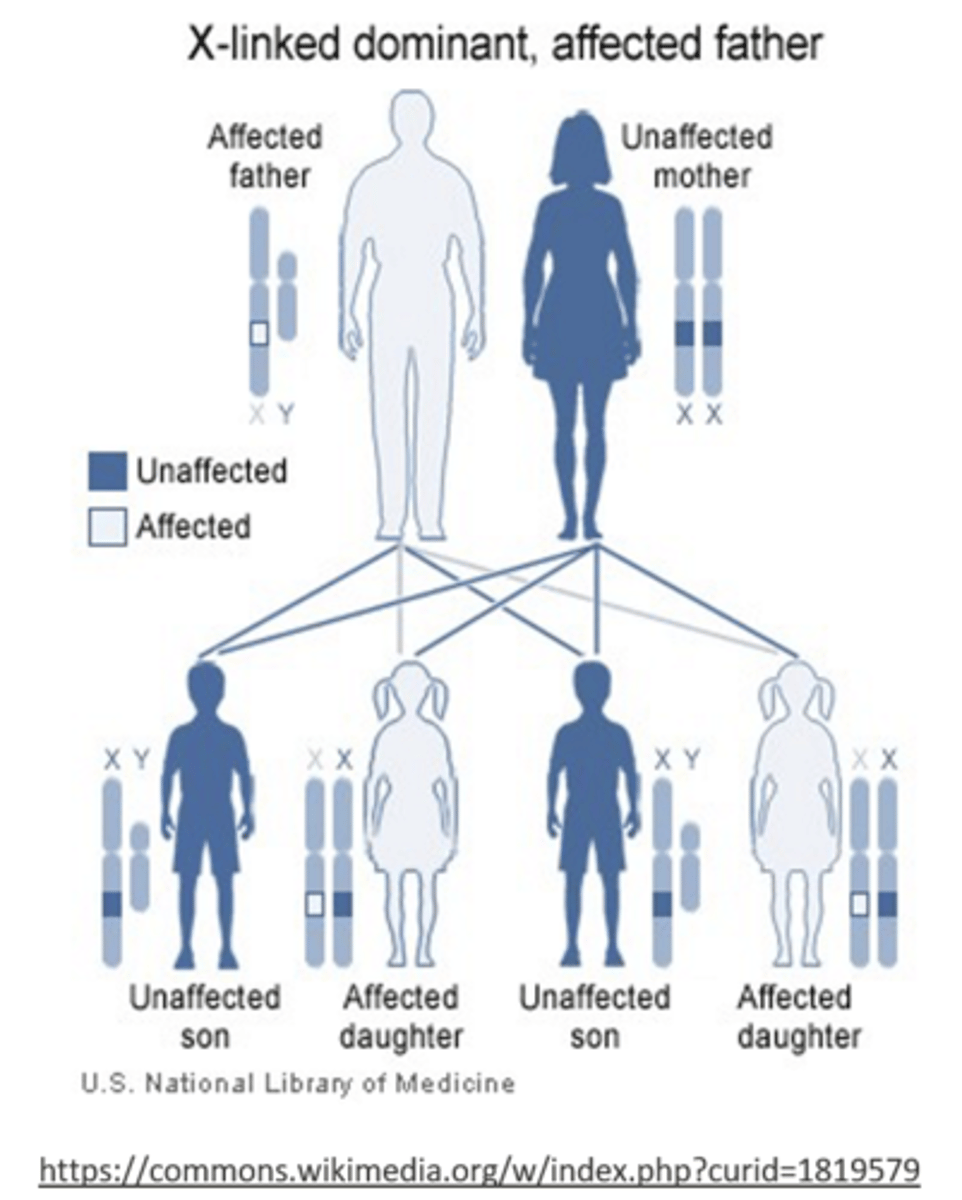
_____ disorders are _____ genetic disorders characterized by a recessive allele on the X chromosome
X linked recessive; sex-linked
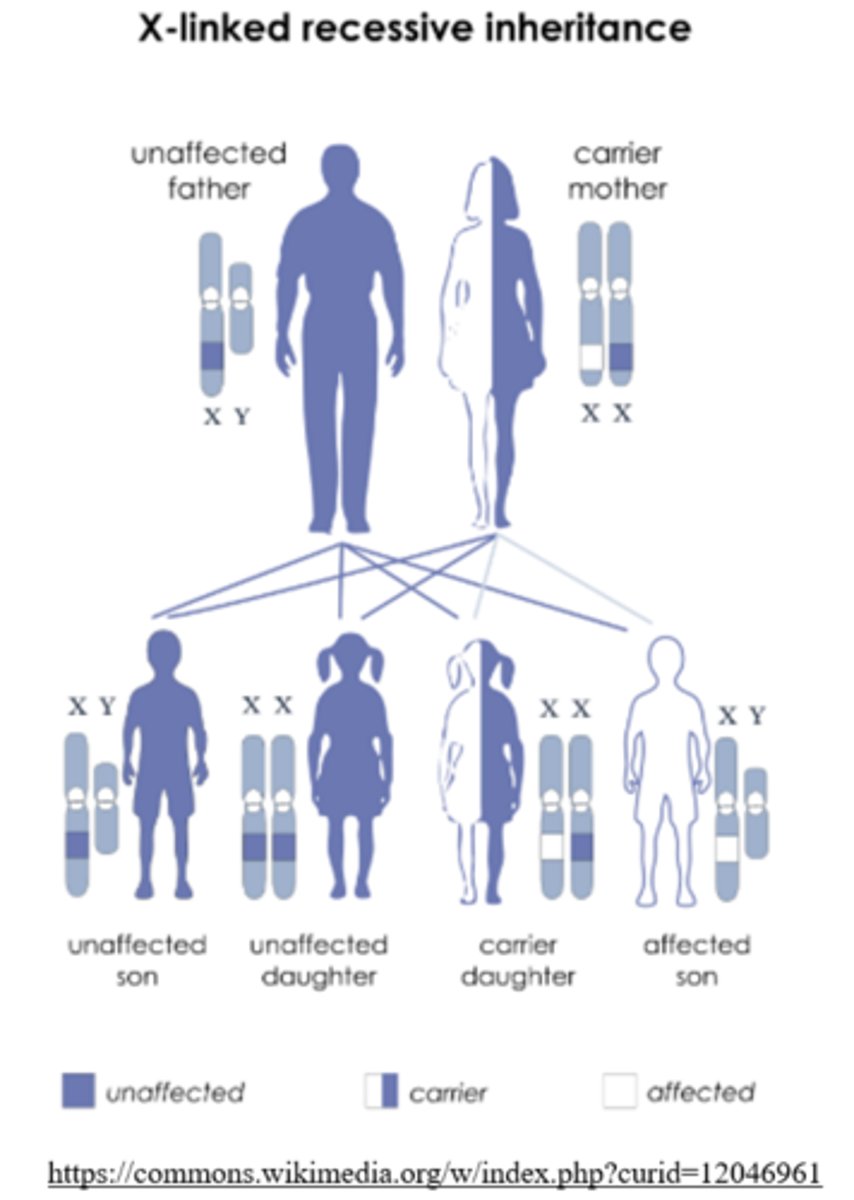
if a X linked recessive allele is inherited from _____ parent(s), the offspring will be affected
both
(fathers must pass the Y chromosome to their son)
X linked recessive alleles cannot be passed from _____ to _____
father; son
(fathers must pass the Y chromosome to their son)
_____ disorders are _____ genetic disorders characterized by an affected allele on the Y chromosome
Y linked; sex-linked
the Y chromosome is only present in men (1 copy), so alleles that cause Y linked disorders _______
are always expressed if they are inherited
Y linked disorders can only be passed from _____ to _____
father; son