tutorial 4: Western Blot Day 3 antibody-based protein detection
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
how does SDS bind to proteins
SDS strongly binds to the positively charged and the hydrophobic residues of proteins through its sulfate groups and alkyl chains, respectively
when SDS meets a protein what happens?
SDS’s hydrocarbon tail dissolves any hydrophobic
region of the protein, while the sulfate end breaks non-covalent ionic bonds. This causes the protein to lose its secondary and tertiary structure, and unfold
purpose of this lab/experiment
This lab will involve the extraction of cellular proteins form 2 different E. coli strains and identification of the Beta-galactosidase producing strain by means of SDS-PAGE and an anti-beta- galactosidase monoclonal antibody.
why are Polyvinylidene (PVDF) difluoride membranes widely used for immunoblotting techniques such as Western blots
PVDF membranes has high protein binding capacity
monoclonal antibodies
(mAbs)
are generated by identical B cells which are clones from a single
parent cell. This means that the monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity and only recognize the same epitope (antibody binding site) of an antigen (a substance that stimulates immune response).
Monoclonal antibodies are produced ex vivo using tissue-culture techniques
polyclonal antibodies
(pAbs) are mixture of heterogeneous which are usually produced by
different B cell clones in the body. They can recognize and bind to many different epitopes of a single antigen.Polyclonal antibodies are produced by injecting an immunogen into an animal
what is the secondary antibody in this experiment?
anti-mouse IgG alkaline-phosphatase (AP) conjugate.
This complex is an antibody which recognizes the mouse IgG antibody
and has the alkaline phosphatase enzyme covalently linked to it
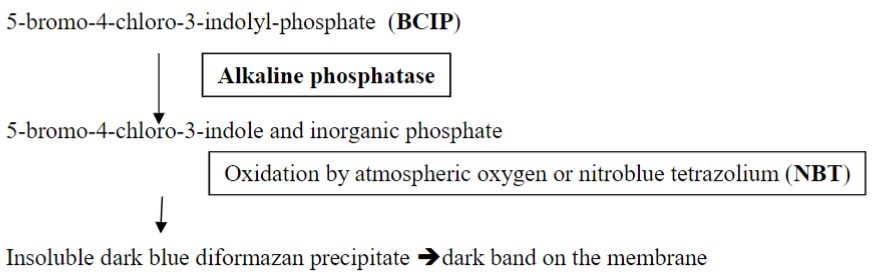
what will the protein-antibody-antibody-alkaline-phosphatase-complex react with?
BCIP (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-phosphate) which is a substrate of alkaline
phosphatase in conjunction with NBT (nitroblue tetrazolium) for the color detection of alkaline phosphatase activity (a purple-grey color on the filter).
BCIP (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-phosphate) is a substrate of alkaline phosphatase in conjunction with NBT (nitroblue tetrazolium)
what is TBST? what does it do?
tris (tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane)-buffered saline and Tween 20 (non-ionic
surfactant used as a detergent); a buffer for washing nitrocellulose membranes in Western Blotting.
Tween 20 is used as a washing agent in immunoassays. It prevents non-specific binding of other proteins (e.g. antibodies used in the detection system) to the surface of the membrane.