1.2 - strong nuclear force
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
what is the strong nuclear force?
the force holding the nuclear force, overcoming the electrostatic forces of repulsion from the protons of the same charge trying to split the nucleus
what holds the nucleus together?
the strong nuclear force
what must the strong nuclear force be greater than? why?
the electrostatic forces of repulsion within the nucleus otherwise the nucleus would split apart
why is the nuclei a stable isotope that does not disintegrate?
because of the strong nuclear force holding it together
what is the range of strong nuclear force?
3-4 femtometres (fm), ~ size of a small nucleus
what is the range of electrostatic force?
infinite that decreases as range increases
does the effect of the strong nuclear force change depending on the types of nucleon it’s working between?
no - it has the same effect between 2 protons, 2 neutrons, and a neutron and proton
is strong nuclear force an attractive or repulsion force?
attractive up until 0,5fm, at which point it becomes repulsive to prevent neutrons and protons from being pushed into each other
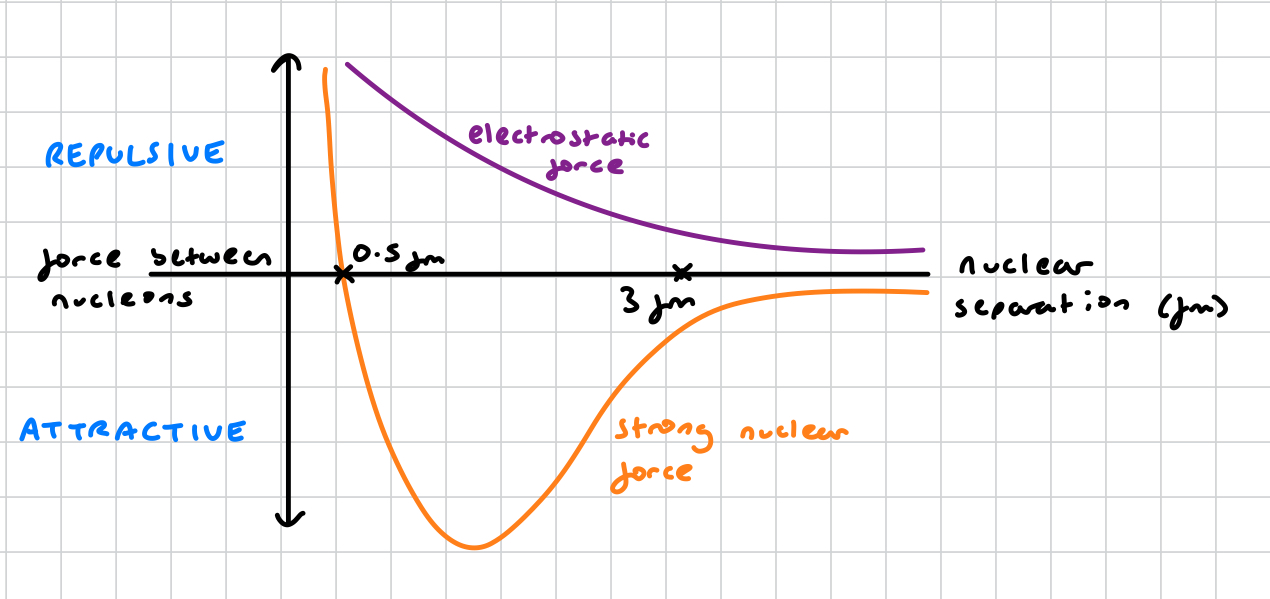
at which range does strong nuclear force become a repulsive force?
0.5fm
why does strong nuclear force become repulsive at 0.5fm?
to prevent nucleons being pushed into each other
define a stable nucleus
without an excess of energy and nucleons that it wants to emit because it cannot contain it
why are unstable nuclei radioactive?
because they cannot contain the excess energy / nucleons in their system
what does an unstable nucleus do?
release protons or neutrons to try and become stable
what is radiation?
the emission of energy and nucleons from an unstable nucleus in attempt to achieve stability
what are the 3 types of radiation in naturally occurring radioactive nuclei?
α, β, γ
what is a neutrino?
a subatomic particle with no mass or charge that carries the excess energy released in an interaction to conserve energy
which subatomic particle doesn’t interfere with the conservation rules and why?
neutrinos and antineutrinos since they have no mass or charge
what does a neutrino carry?
the excess energy released in an interaction
why does a neutrino carry the excess energy released in an interaction?
to conserve energy in the reaction
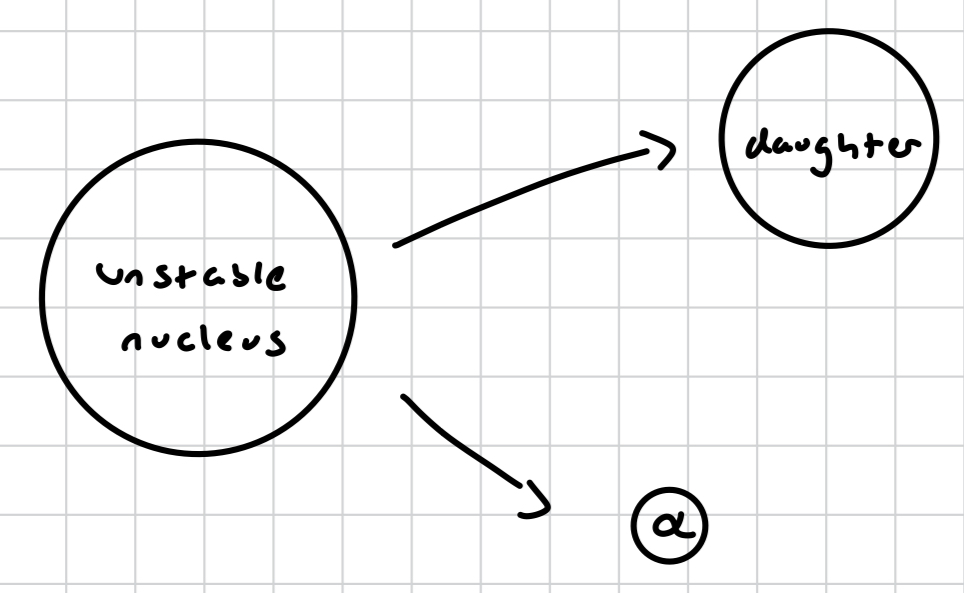
alpha radiation
alpha particle released
what is the general equation for alpha radiation?
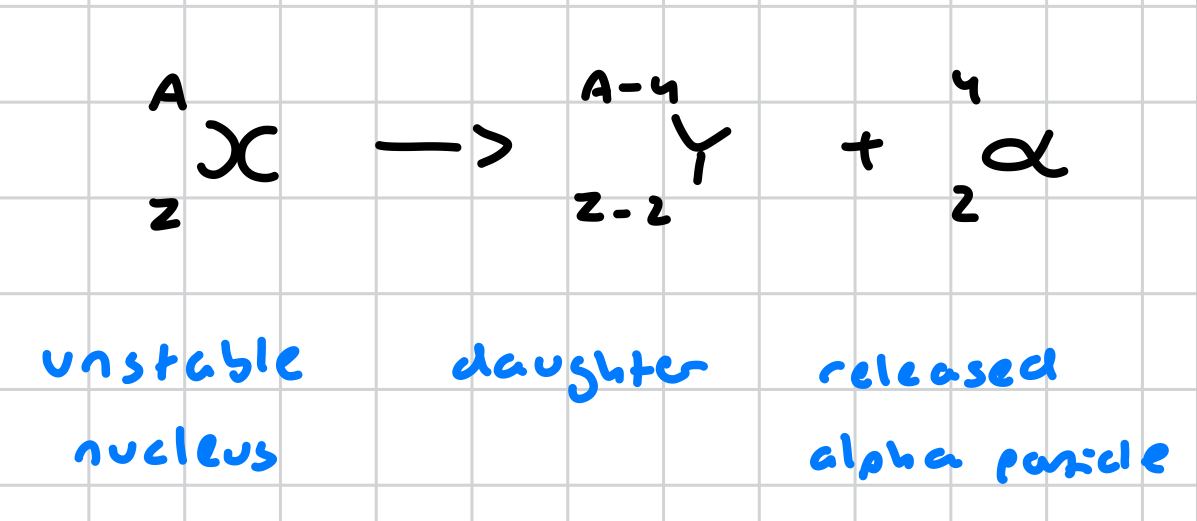
what is an alpha particle?
a helium atom; 2 protons 2 neutrons
beta radiation
nucleus has a stable charge but an excess of neutrons
neutron becomes a proton (must happen to balance the number of nucleons), unbalancing the charge
beta and antineutrino emitted to balance charge
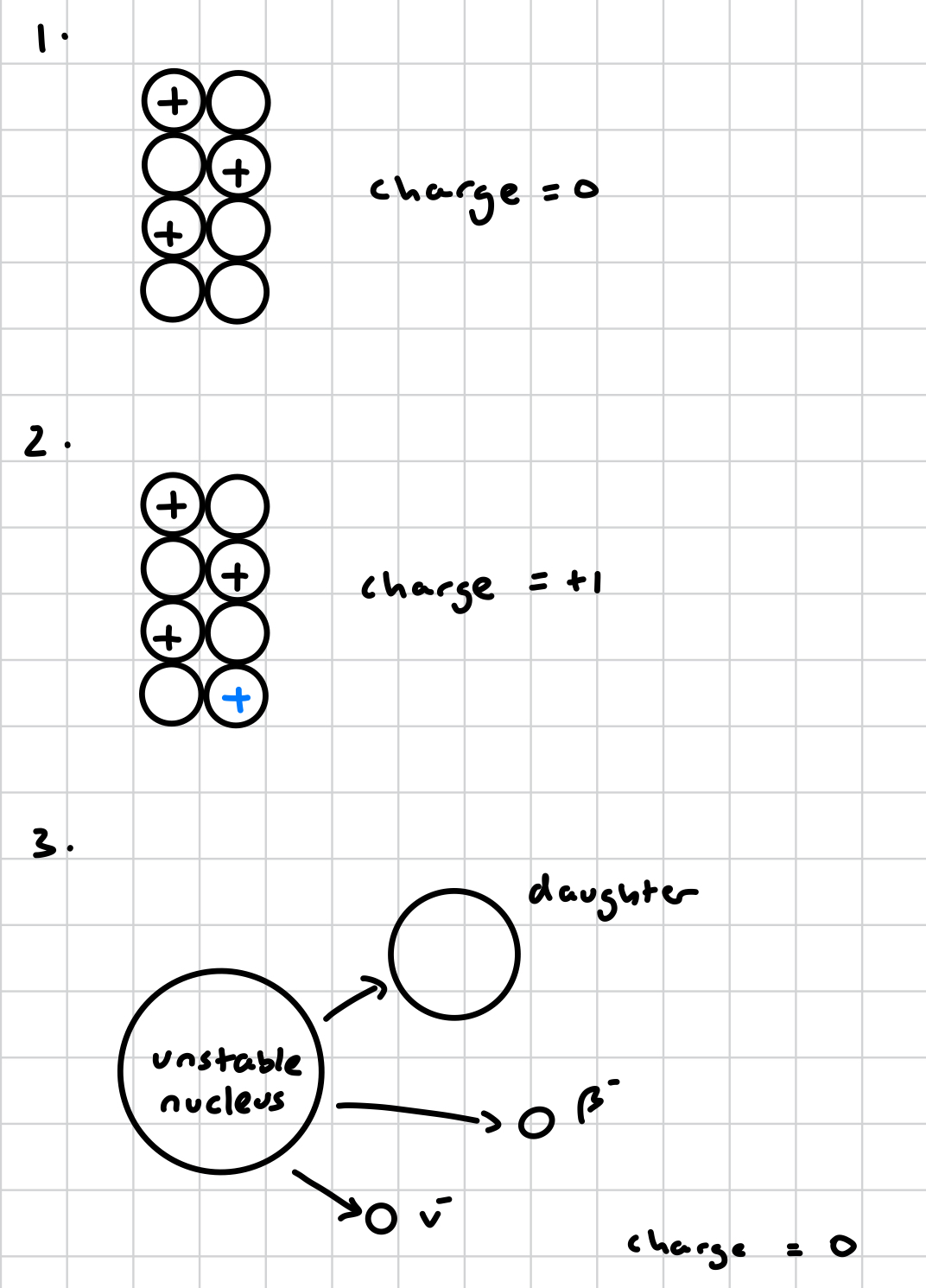
what is the general equation for beta radiation?
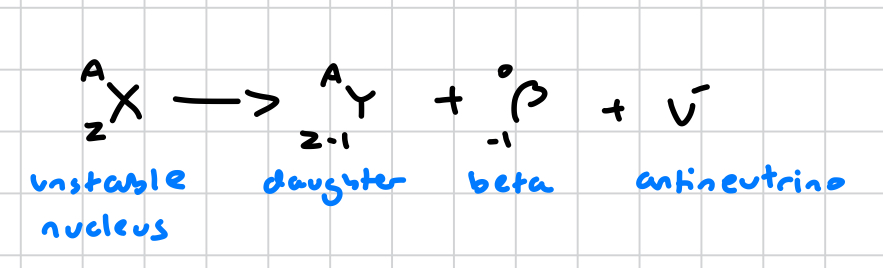
what is a beta particle?
a fast moving electron
in which type of unstable nucleus does beta radiation occur?
in a nucleus with a stable charge but excess neutrons
why does a neutron become a proton in beta radiation?
to balance the number of nucleons
what is the consequence of neutron turning to a proton in beta radiation?
the charge is unbalanced
what is emitted in beta radiation?
beta particle + anti-neutrino
why is a beta particle + anti-neutrino emitted in beta decay?
beta particle - to balance charge
antineutrino - carrying energy
what is the function of the beta particle in beta emission?
to balance charge
what is the function of the antineutrino in beta emission?
to carry energy
gamma radiation
em radiation emitted by unstable nucleus with too much energy following an alpha / beta emission
no mass or charge
what is the mass of gamma?
trick question STUPID FOOL !!!!! It has no mass because it’s a photon of em radiation IDIOT STUPID BITCH !!!!
what is the charge of gamma?
alas, it has no charge also STUPID LOSER FUCKING IDIOT because it is a photon of em radiation NOT. a charged particle
why doesn’t gamma radiation have a mass or charge?
because it is a photon of em radiation and not a (charged) particle
in which cases does gamma radiation occur?
following alpha / beta emission, in which the nucleus has a stable number of particles but an excess of energy, in which energy is emitted via the gamma photon


