A/P CH.12-13
5.0(1)Studied by 46 people
Card Sorting
1/192
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:58 PM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
193 Terms
1
New cards
Axon
- Sends nerve impulses towards another neruron, muscle fiberl, or gland cell,
- Connects to cell by axon hill lock
- Either is myelanted or unmyelenated
- Connects to cell by axon hill lock
- Either is myelanted or unmyelenated
2
New cards
Axon Hilllock
- Triangular area of the cell body
3
New cards
Axon Terminals
- Axons and axon collaterals conduct action potentials along their full lengths to end in many fine branches
4
New cards
Cell Body
- Contains nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm that includes typical cellular organelles
5
New cards
Dendrites
- Are the reciving portion of neurons
6
New cards
Endoneurium
Covers myelinated and unmyelinated axons
7
New cards
Epineurium
-Surrounds the whole nerve
8
New cards
Fascicle
- Bundle of nerve fibers
9
New cards
Myelin sheath
-Multilayerd lipid and protein covering around and some axons that insulate them and increases the speed of the nerve impulse conduction
10
New cards
Neurofibril (of Ranvier)
- are bundles of neurofilaments that extend into the dendrites and axon, and provide internal support to them.
11
New cards
Neurolemmocyte (Schwann Cell)
-PNS
- Line all 4 venticles of the brain as well as the central canal of the spinal cord
- These cell form the cerebrospinal fluid and their cilia move the CSF through the ventricles
- Line all 4 venticles of the brain as well as the central canal of the spinal cord
- These cell form the cerebrospinal fluid and their cilia move the CSF through the ventricles
12
New cards
Nissl bodies
- synthesis and segregation of proteins.
- Subcellular structures found in nerve cell bodies and DENDRITES. They consist of granular endoplasmic reticulum
- Subcellular structures found in nerve cell bodies and DENDRITES. They consist of granular endoplasmic reticulum
13
New cards
Nucleaus of the Neuron
- the central area where all the neuronal protein synthesis takes place
- contains the genetic material that helps in the ribosomal RNA synthesis process.
- to guide the axon hillock that generates the impulses throughout the axon.
- contains the genetic material that helps in the ribosomal RNA synthesis process.
- to guide the axon hillock that generates the impulses throughout the axon.
14
New cards
Perinerium
Surrounds each fasicle
15
New cards
Synaptic End Bulbs
- Towards the end of the axon terminal, closest to the muscle fiber, the tip of the axon terminal enlarges and becomes known as the synaptic end bulb.
- It is the synaptic end bulb of the motor neuron that comprises the neuromuscular junction.
- the neurotransmitter is released into a small space, the synaptic cleft.
- It is the synaptic end bulb of the motor neuron that comprises the neuromuscular junction.
- the neurotransmitter is released into a small space, the synaptic cleft.
16
New cards
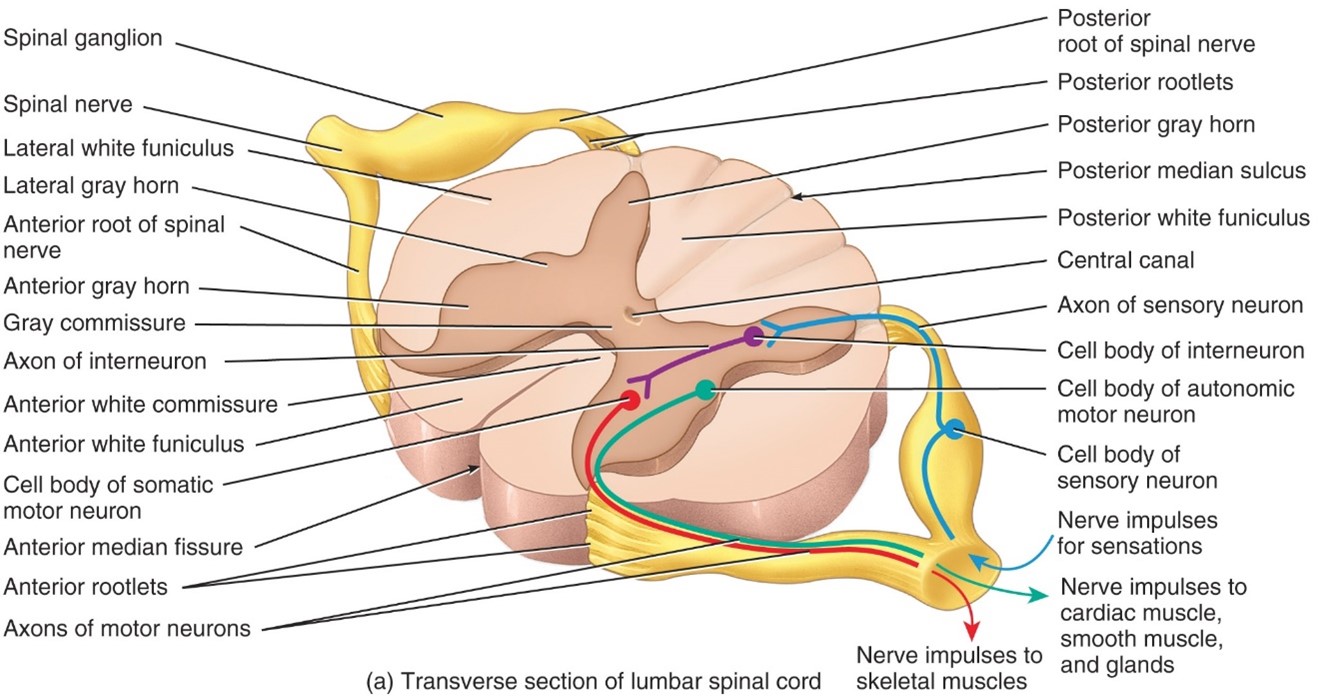
Anterior (Ventral) Horn
-Anterior, Somatic motor neuron cell bodies
17
New cards
Anterior (Ventral) Median Fissure
- Anterior median fissure, wide deep groove on anterior surface of spinal cord
18
New cards
How many pairs of nerves in spinal cord?
31 pairs:
-8 Cervical
-12 Throacic
-5 Lumbar
-5 Sacral
-1 Coccygeal
-8 Cervical
-12 Throacic
-5 Lumbar
-5 Sacral
-1 Coccygeal
19
New cards
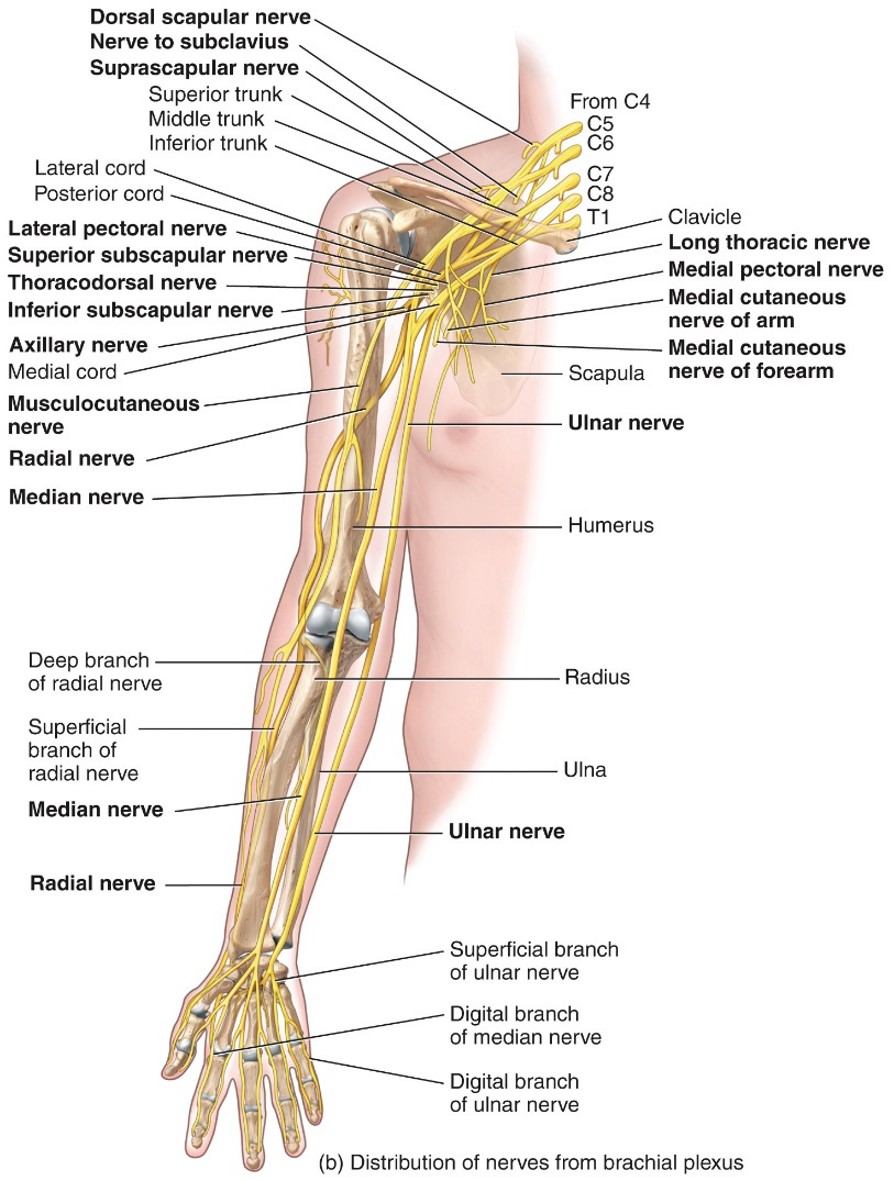
Brachail Plexus
- Provides almost the entire nerve supply to the shoulders and upper limbs
- Formed from anterior rami of C5-T1
- Main nerves are:
-- Axillary (Deltoid) C5-C6
-- Median (Flexor muscles of forearm) C5-T1
-- Musculocutaneous (Bicep brachii/Brachiallis) C5-C7
-- Radial (Tricep brachii/ extensor of forearm) C5-T1
-- Ulnar (flexor carpi ulnaris/ muscle of hand) C8-T1
- Formed from anterior rami of C5-T1
- Main nerves are:
-- Axillary (Deltoid) C5-C6
-- Median (Flexor muscles of forearm) C5-T1
-- Musculocutaneous (Bicep brachii/Brachiallis) C5-C7
-- Radial (Tricep brachii/ extensor of forearm) C5-T1
-- Ulnar (flexor carpi ulnaris/ muscle of hand) C8-T1
20
New cards
Cauda Equina
- Nerve roots arising from the inferior portion of the spinal crd continue inferiorly as a group
21
New cards
Central Canal
- Center of gray commissure and contains cerebrospinal fluid
22
New cards
Cervical Enlargement
- C3 to T1
- Designates the location of nuclei for the upper extremitiies
- Designates the location of nuclei for the upper extremitiies
23
New cards
Cervical Plexus
- Supplies the skin and muscles of the head, neck, superior portion of the shoulders and chest, and diaphragm
- Formed from anterior rami
- C1- C5
- Imporant nevre is the PHRENIC nerve
-- Which innervates the diaphragm and is important for breathing
- Formed from anterior rami
- C1- C5
- Imporant nevre is the PHRENIC nerve
-- Which innervates the diaphragm and is important for breathing
24
New cards
Conus Medullaris
- Spinal cord is inferior to it
- between L1 and L2
- between L1 and L2
25
New cards
Gray Commisure
- Narrow bridge of gray matter that connects the right and left side of gray matter in the middle of the spinal cord
26
New cards
Gray Matter
- Contains unmyelinated axons, cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, and neruoglia
- Gray matter receives and integrates incoming and outgoing information to perform spinal reflexes
- Gray matter receives and integrates incoming and outgoing information to perform spinal reflexes
27
New cards
Lumbar Enlargement
- T9 to T12
- Contans nucei for the lower extremitites
- Contans nucei for the lower extremitites
28
New cards
Lumbar PLexus
-- Supplies skin, abdominal wall, genitalia, and parts of lower limbs
- Made up of anterior rami
- L1-L4
- Major nerves are:
-- Femoral L2-L4
--- Largest nerve, flexor muscles of hip joint and extensor muscles of knee joint, skin over anterior and medial aspect of thigh and medial side of leg and foot.
-- Obturator nerves L2-L4
---Adductor muscle of hip joint
- Made up of anterior rami
- L1-L4
- Major nerves are:
-- Femoral L2-L4
--- Largest nerve, flexor muscles of hip joint and extensor muscles of knee joint, skin over anterior and medial aspect of thigh and medial side of leg and foot.
-- Obturator nerves L2-L4
---Adductor muscle of hip joint
29
New cards
Posterior (Dorsal) Horn
- Posterior, Contain neuron cell bodies that receive impulses from sensory neurons
30
New cards
Postererior Medial Sulcus (Fissure)
- Posterior median sulcus, a narraw groove
31
New cards
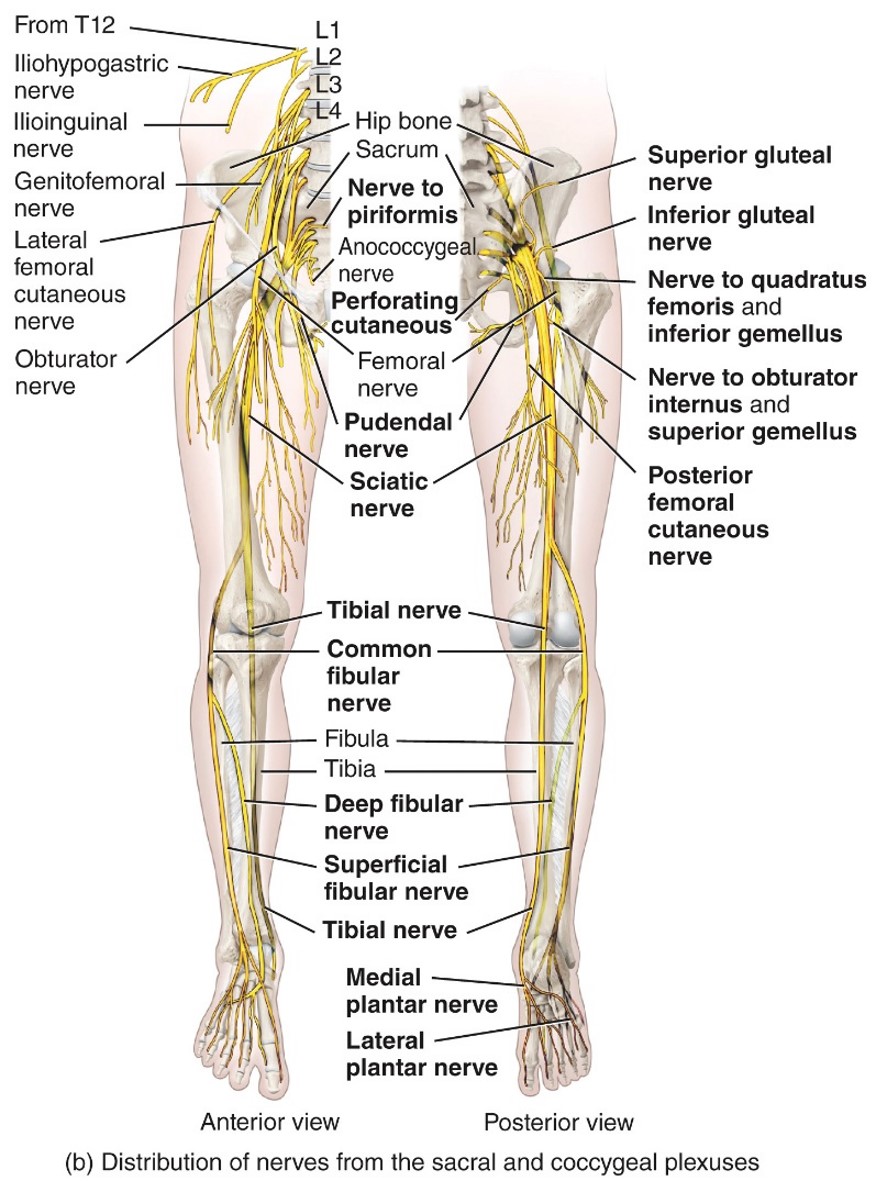
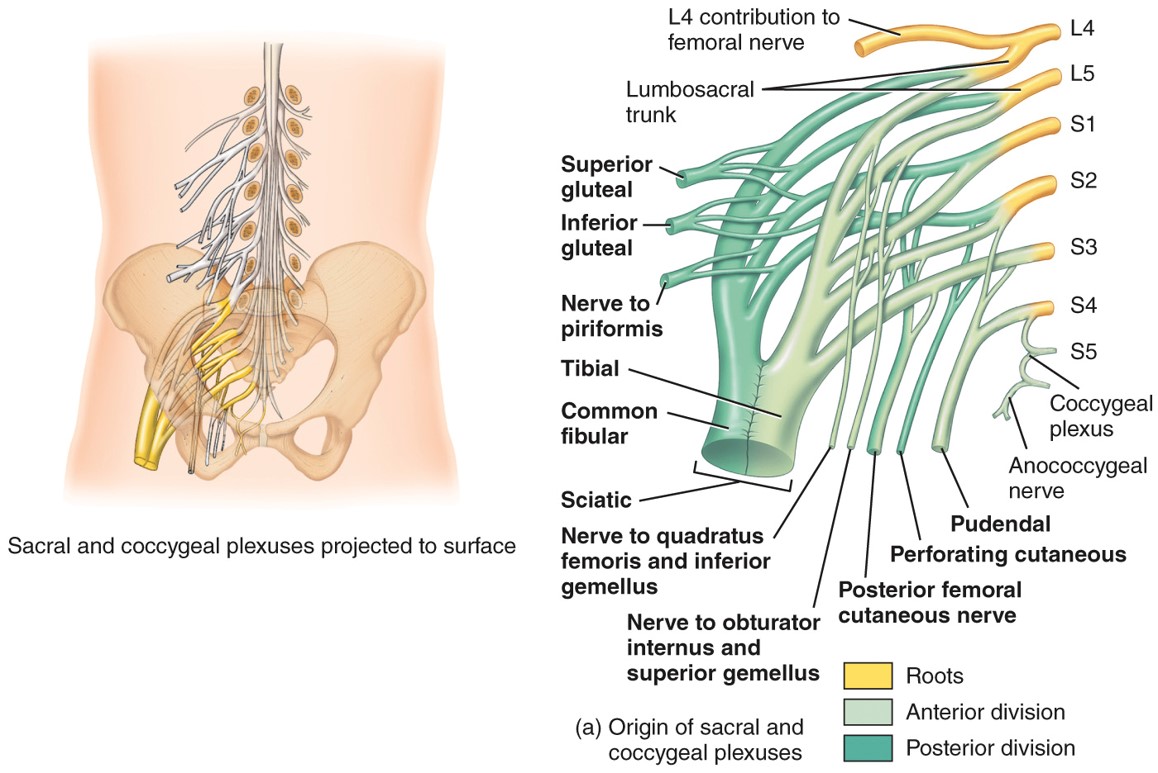
Sacral Plexus
-L4 to S4
-Formed from the anterior rami
- supllies lower limbs and glutes
-Formed from the anterior rami
- supllies lower limbs and glutes
32
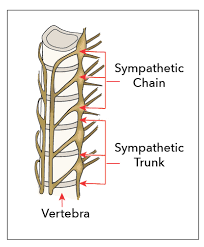
New cards
Symphatic Trunk
- a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx
33
New cards
White Matter
- Made up of myelinated axons
- White matter tacts conduct nerve impulses to and from the brain
- White matter tacts conduct nerve impulses to and from the brain
34
New cards
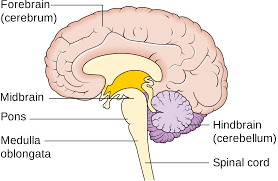
Medula Oblongata
he connection between the brainstem and the spinal cord
35
New cards
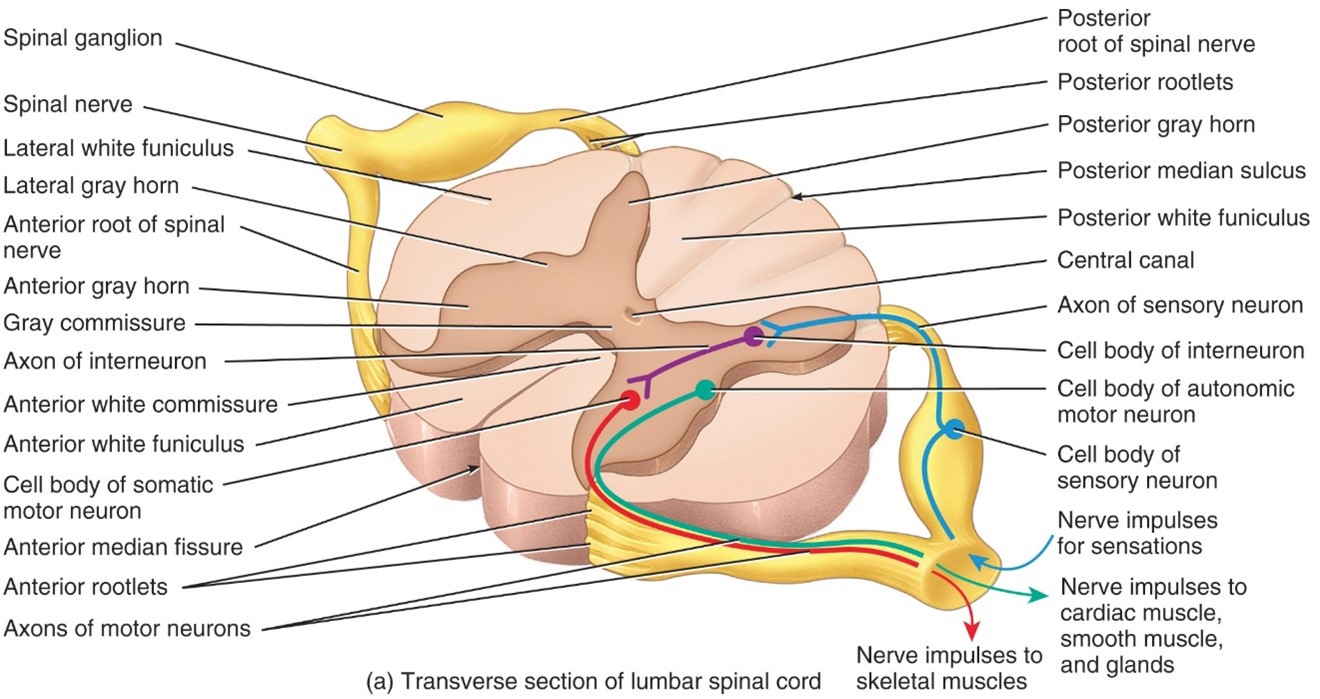
Anterior Root
- Carry motor responses
- Down the CNS to muscles, nerves, glands
- Down the CNS to muscles, nerves, glands
36
New cards
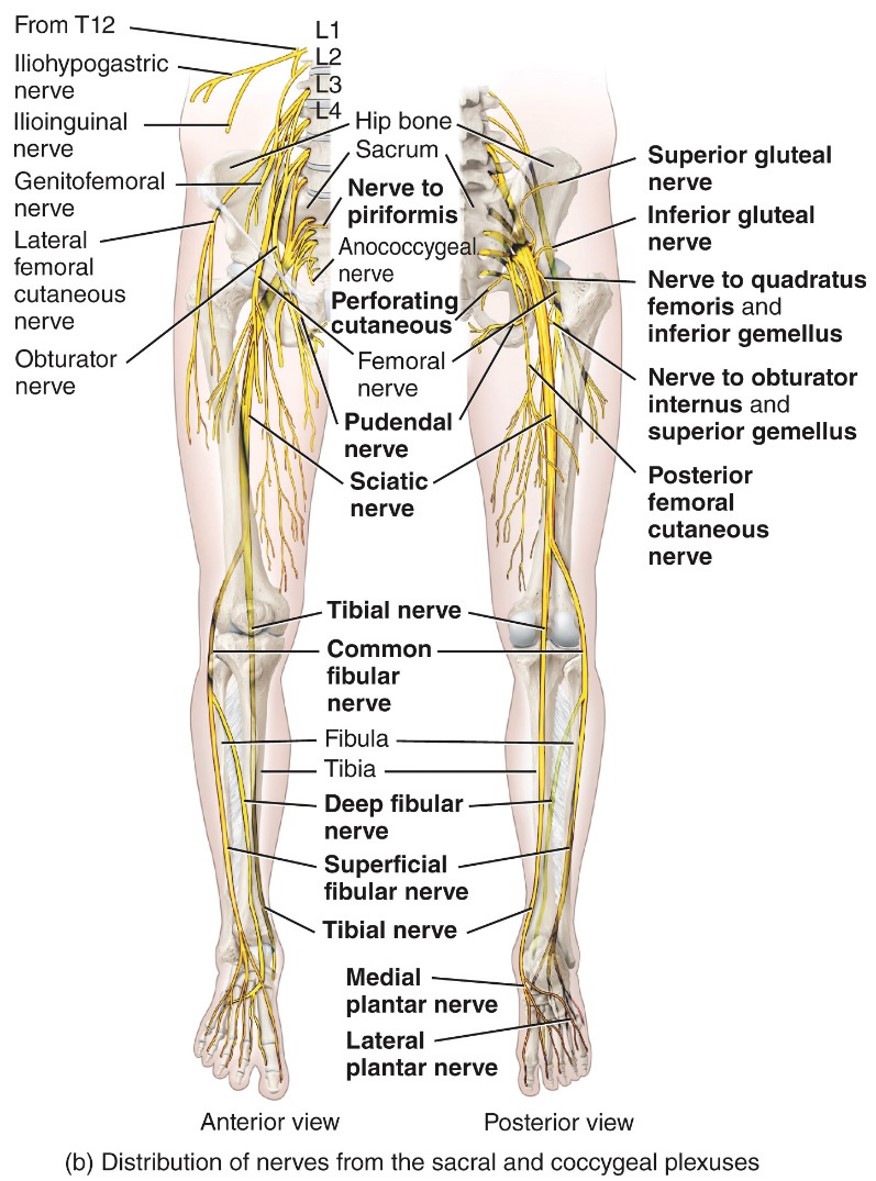
Common Fibular nerve
- Sacral Plexus
- L4-S2
- Fibularis longus muscle,
- tibialis anterior,
- extensor digitorumlongus
- L4-S2
- Fibularis longus muscle,
- tibialis anterior,
- extensor digitorumlongus
37
New cards
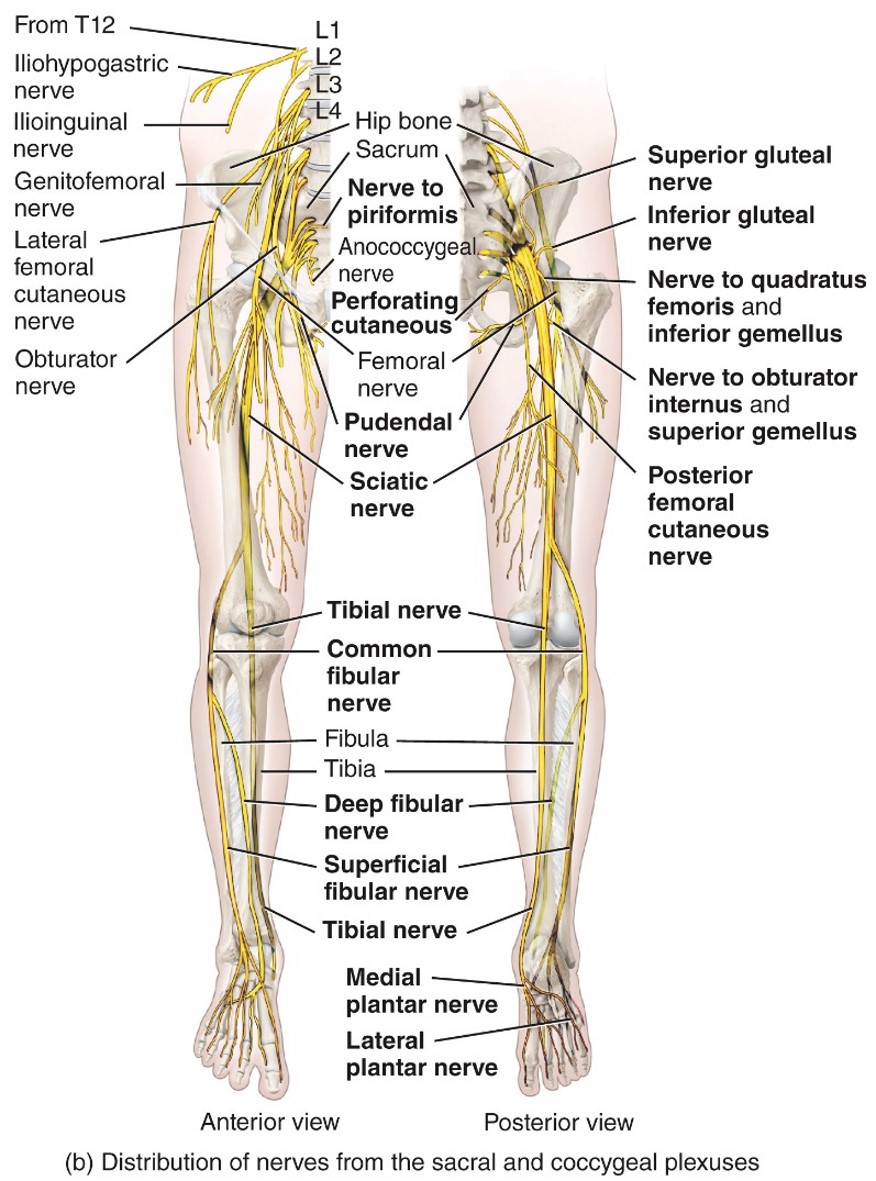
Femoral Nevre
- Lumbar Plexus
- L2-L4
- Iliopsoas
-quadriceps femoris
-sartoris
- pectineus
- L2-L4
- Iliopsoas
-quadriceps femoris
-sartoris
- pectineus
38
New cards
Orbturartor Nerve
- Lumbar plexus
- L2-L4
- Adductor longus
- Adductor brevis
- Aductor magnus,
- Gracilis
- L2-L4
- Adductor longus
- Adductor brevis
- Aductor magnus,
- Gracilis
39
New cards
Median Nerve
- Brachial Plexus
- C5-T1
- Muscle of anterior forearm
- Muscle of hand
- C5-T1
- Muscle of anterior forearm
- Muscle of hand
40
New cards
Musculocutaneous Nerve
- Brachial Plexus
- C5-C7
Bicep Brachii
- Brachialis
- C5-C7
Bicep Brachii
- Brachialis
41
New cards
Posterior Root
-Carries sensory fibers
- Up the CNS
- Up the CNS
42
New cards
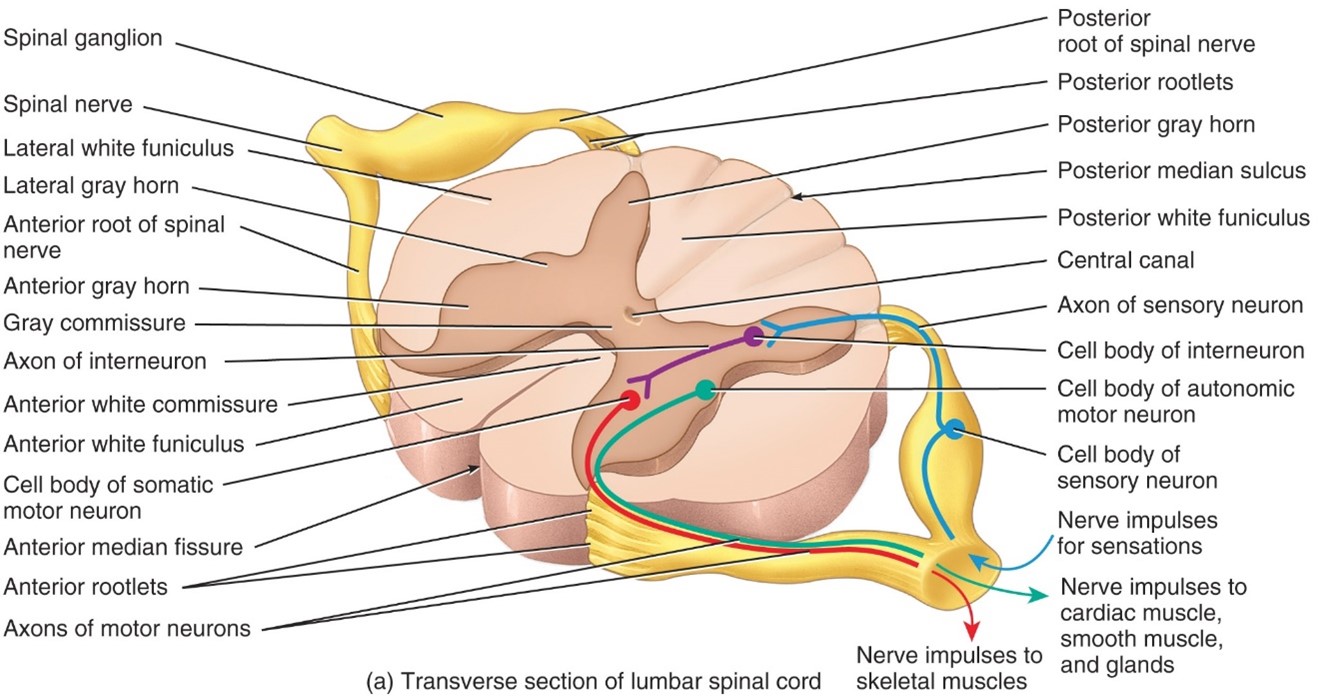
Posterior Root Ganglion
- Consist of sensory neuron cell bodies that synapse onto interneuron and motot neuron cell bodies
43
New cards
Radial Nerve
- Part of brachail plexus
- C5-T1
-Tricep brachii
- Extensor on forearm
- C5-T1
-Tricep brachii
- Extensor on forearm
44
New cards
Scaitic Nerve
- Sacral Plexus
- L4-S3
- Moves Bicep femoris
- Semimembraneous and semitendinosus
- Breaks up into tibial and common fibular nerve
- L4-S3
- Moves Bicep femoris
- Semimembraneous and semitendinosus
- Breaks up into tibial and common fibular nerve
45
New cards
Tibial Nerve
- Sacral plexes
-L4-S3
- Gastronemius,
- soleus
- tibialis posterior
- flexor digitorum longus
- plantaris
- flexor hallucis longus
-L4-S3
- Gastronemius,
- soleus
- tibialis posterior
- flexor digitorum longus
- plantaris
- flexor hallucis longus
46
New cards
Ulnar Nerve
- Brachial Plexus
-C8-T1
- Muscles of anterior forearm
-C8-T1
- Muscles of anterior forearm
47
New cards
Phrenic
- Cervical Plexus
- C3-C5
- Diaphragm
- C3-C5
- Diaphragm
48
New cards
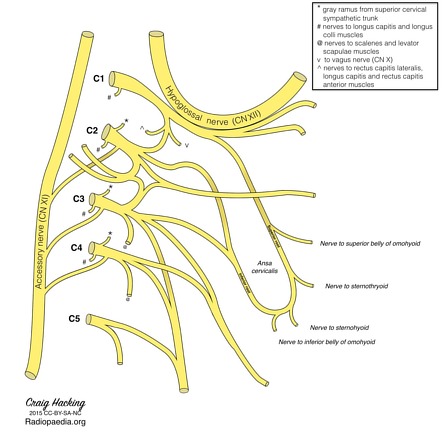
Ansa Cervicals
a neural loop in the neck formed by connecting the superior root from the cervical spinal nerves (C1–2) and the inferior root descending from C2–C3
49
New cards
Superior root of ansa cervicals
- created by the first cervical nerve (C1).
50
New cards
Inferior root of ansa cervicals
- comprised of nerve fibers arising from ventral rami of C2–C3.
- These two branches join in the anterior wall of the carotid sheath and form a neural loop.
-The ansa cervicalis almost always travels anterior to the internal jugular vein [2].
- These two branches join in the anterior wall of the carotid sheath and form a neural loop.
-The ansa cervicalis almost always travels anterior to the internal jugular vein [2].
![- comprised of nerve fibers arising from ventral rami of C2–C3.
- These two branches join in the anterior wall of the carotid sheath and form a neural loop.
-The ansa cervicalis almost always travels anterior to the internal jugular vein [2].](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/164143257491484899dd4dd47fec4666.jpeg)
51
New cards
Sensory Nerves (Chart)
- Input
- Receptors
- To feel
- Up the CNS
- Ascending
- Posterior/Back/Dorsal
-Pre-ganglionic
- Afferent
- Receptors
- To feel
- Up the CNS
- Ascending
- Posterior/Back/Dorsal
-Pre-ganglionic
- Afferent
52
New cards
Motor Nerves (Chart)
- Output
- Effectors
- To feel
- Down the CNS
- Descending
- Anterior/Front/Ventral
- Post-ganglionic
- Efferent
- Effectors
- To feel
- Down the CNS
- Descending
- Anterior/Front/Ventral
- Post-ganglionic
- Efferent
53
New cards
--- 2 main sundivisions of nervous sysyetem---
54
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Includes the Brain and spinal cord
55
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PSN)
Includes cranial nerves, spinal nerves & their branches, ganglia, and sensory receptors
56
New cards
---Organization of PNS---
57
New cards
Somatic Nervous system
- Conveys output from the CNS to the skeletal muscles only.
- Its motot responses can be be consciously controlled, the action of the PNS is VOLUNTARY
- Its motot responses can be be consciously controlled, the action of the PNS is VOLUNTARY
58
New cards
Autonomic Nervous sytem
- Conveys output from the CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscles, and glands
- Motor resposnses can be consciously controlled, the action of the PNS is Voluntary
- Motor resposnses can be consciously controlled, the action of the PNS is Voluntary
59
New cards
Enteric Nervous System
- Network of over 100 million neurons confined to the wall of the digestive canal
- Helps regulate the activity of smooth muscles and glands
- Functions independtly, but communicates with branches of ANS
- Helps regulate the activity of smooth muscles and glands
- Functions independtly, but communicates with branches of ANS
60
New cards
---Histology of Nervous tissue----
61
New cards
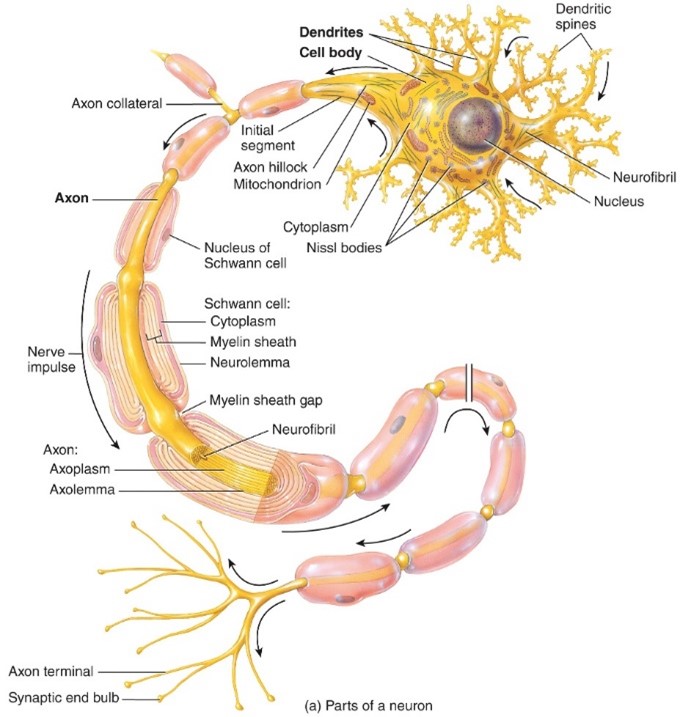
Nuerons
- Electrically Excitable
- Cellular structure
- Nerve impulses is called an action potential
- Cellular structure
- Nerve impulses is called an action potential
62
New cards
Neurolgia
- Not electrically Excitable
- Make up about half of the volume of the nervous system
- Can multiply and divide
- 6 kind total ( 4 in CNS, 2 in PNS)
- Glue that holds nervous tissue together
- Make up about half of the volume of the nervous system
- Can multiply and divide
- 6 kind total ( 4 in CNS, 2 in PNS)
- Glue that holds nervous tissue together
63
New cards
--- Explanation of Neuron Cell---
64
New cards
Cell Body
- Contains nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm that includes typical cellular organelles
65
New cards
Dendrites
- Are the reciving portion of neurons
66
New cards
Axon
-Sends nerve impulses towards another neruron, muscle fiberl, or gland cell,
- Connects to cell by axon hill lock
- Either is myelanted or unmyelenated
- Connects to cell by axon hill lock
- Either is myelanted or unmyelenated
67
New cards
---Structural Classification of nuerons---
68
New cards
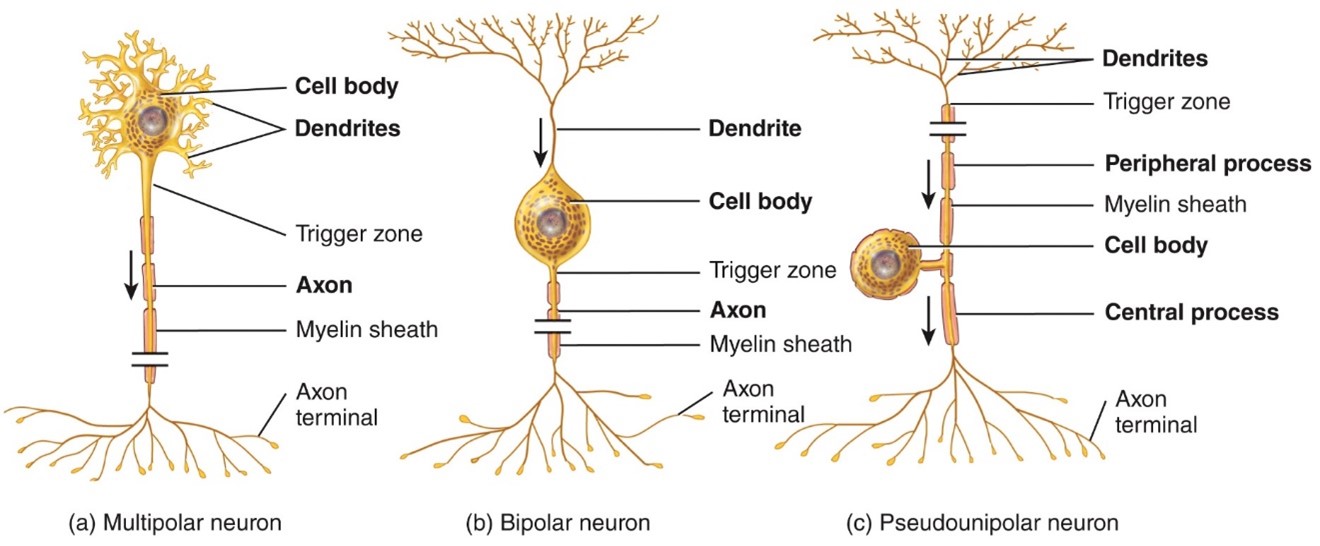
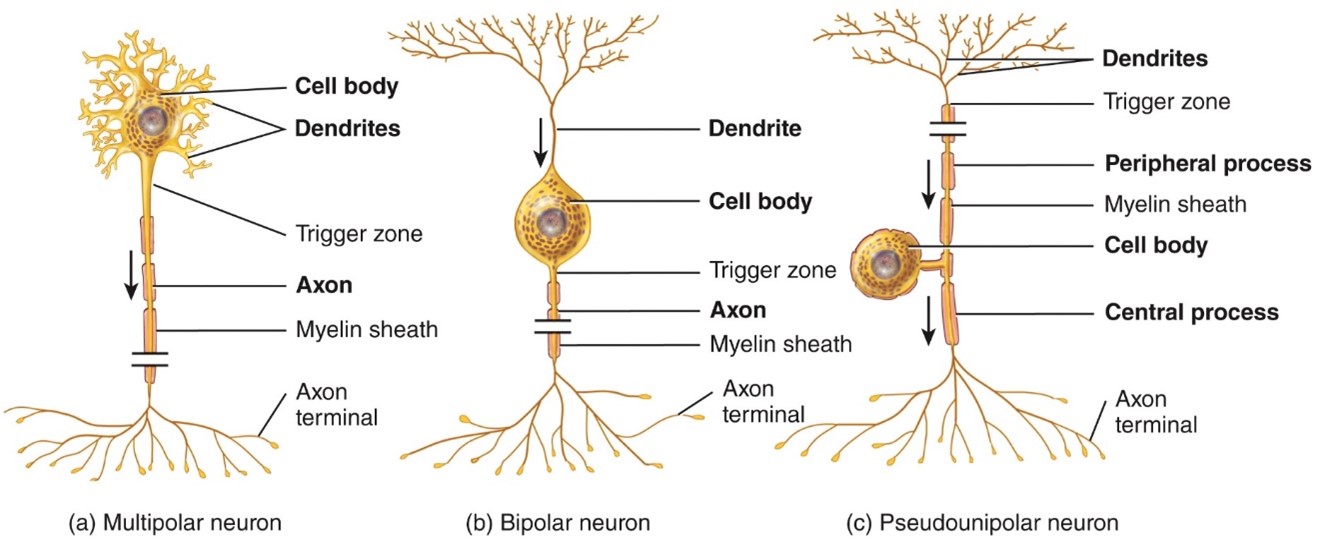
Multipolar Neurons
- Usually have several dendrites and 1 axon
- Most neurons in the brain and spinal cord are this type, As well as motot neurons
- Most neurons in the brain and spinal cord are this type, As well as motot neurons
69
New cards
Bipolar neurons
- Have 1 main dendrite and 1 axon
- Found in the retina of the eye
- Found in the retina of the eye
70
New cards
Unipolar neurons
- Have dendrites and 1 axon that are fused together to form a continues process from the cell body
- Found in sensory ganglia
- Found in sensory ganglia
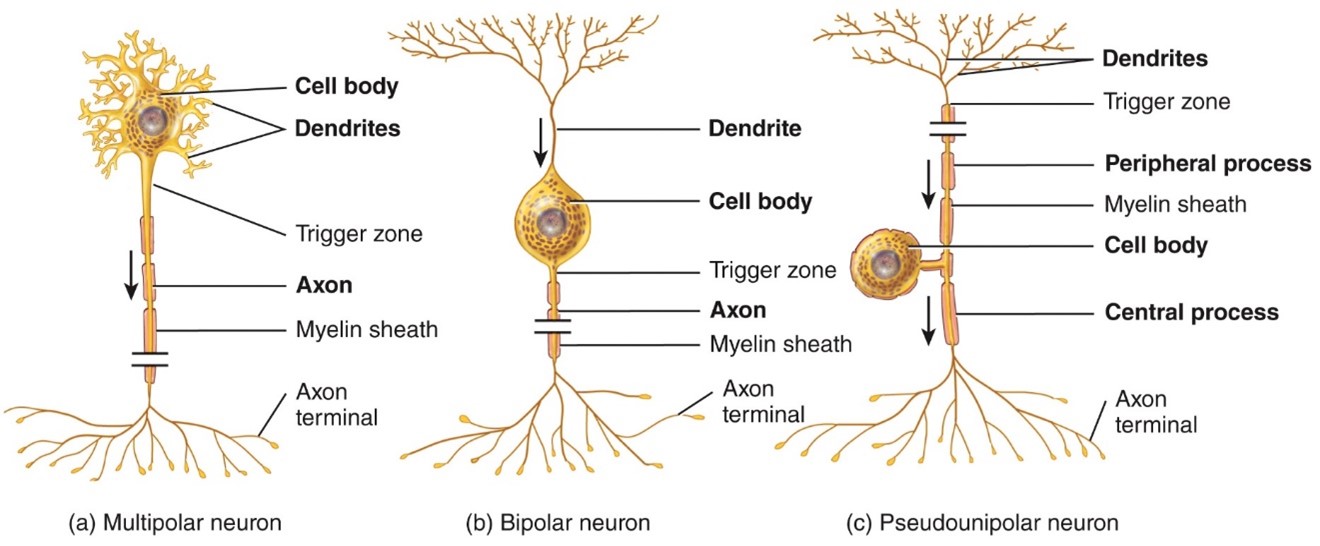
71
New cards
---Functional Classification---
72
New cards
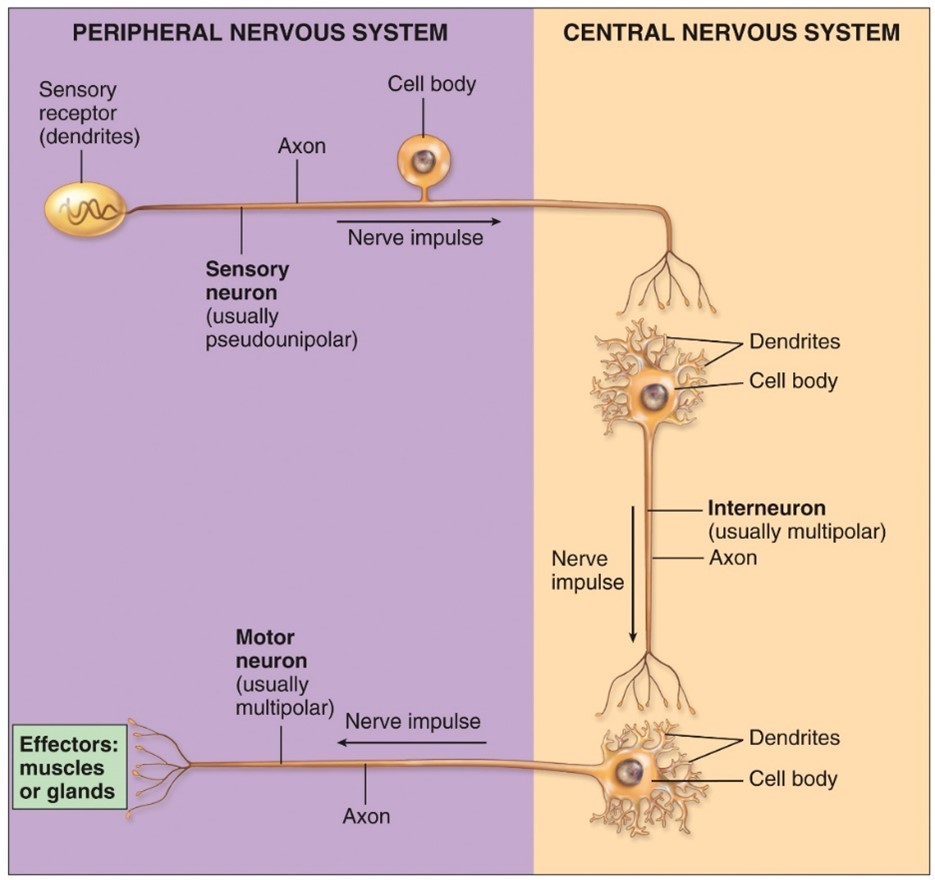
Sensory or afferent neruons
-Conveys information to the CNS
-unipolar
-unipolar
73
New cards
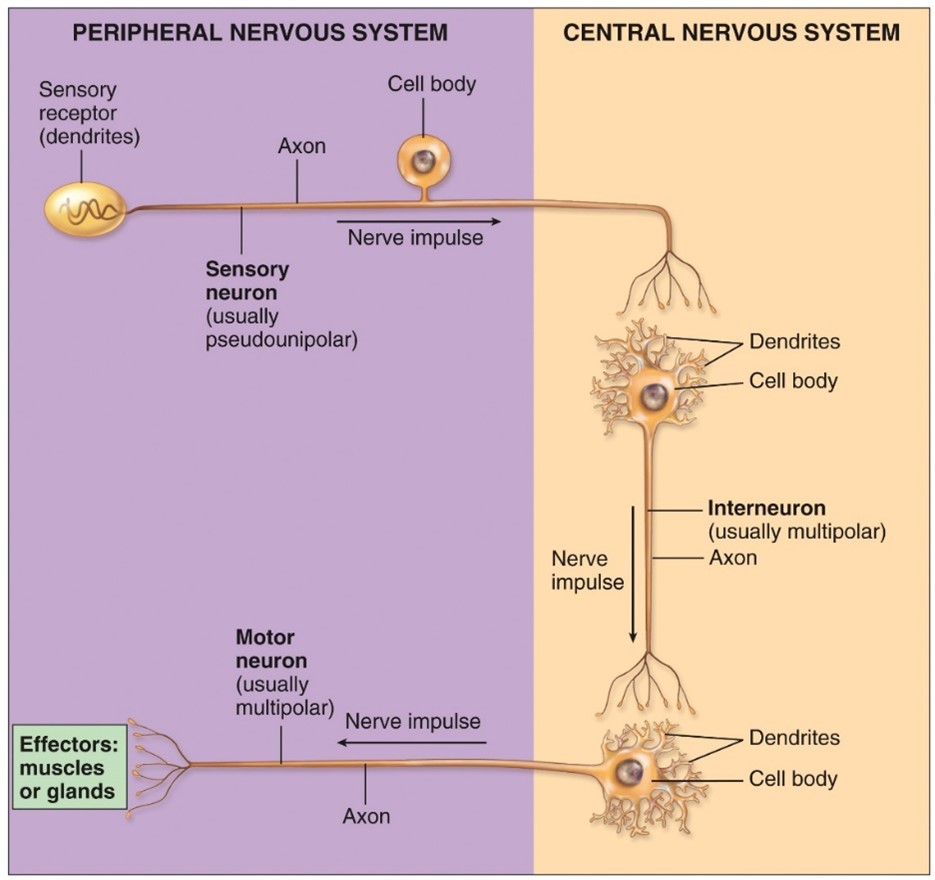
Motor of efferent neurons
Conveys action potential from the CNS
- Multi Polar
- Multi Polar
74
New cards
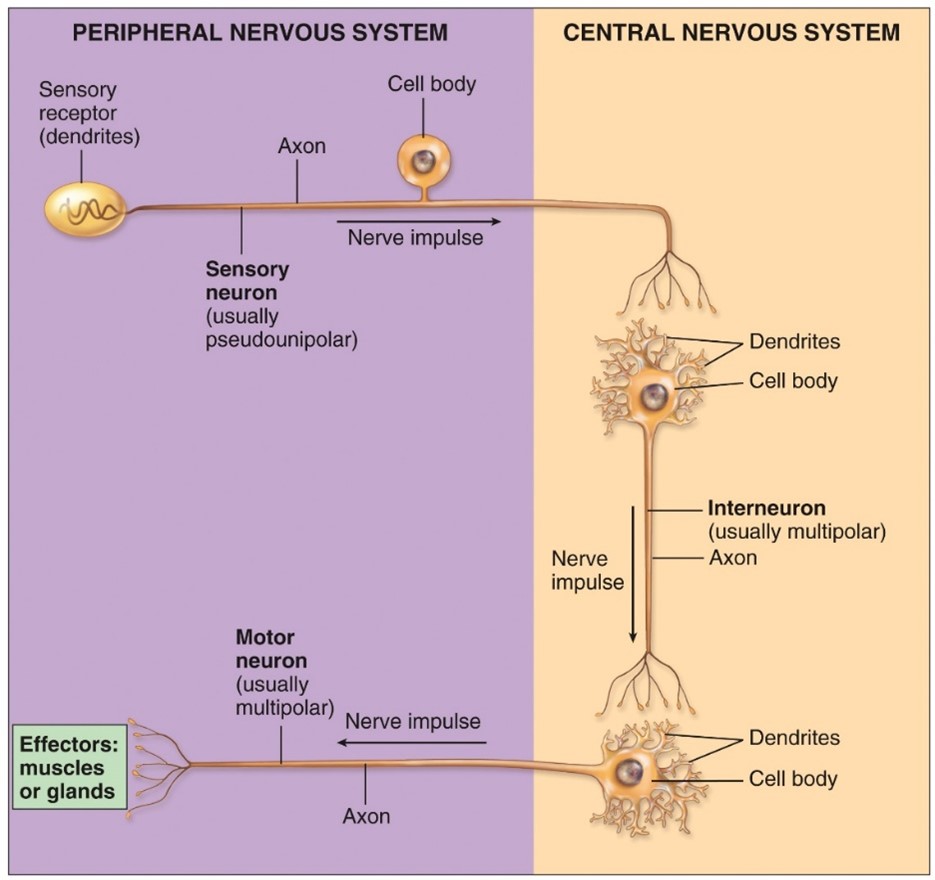
Interneruons or association neurons
-Process sensory information and elict motor resposnes
- Multi polar
- Multi polar
75
New cards
---Types of Neuroglia---
76
New cards
Neuroglia
Glue that holds nervous tissue together
77
New cards
Astrocytes
- CNS
- Have many process that make them look star shaped
- Wrap around and cover neurons and blood vessels to support them
- Guide neurons during development and control the composition of the chemical enviroment
- Have many process that make them look star shaped
- Wrap around and cover neurons and blood vessels to support them
- Guide neurons during development and control the composition of the chemical enviroment
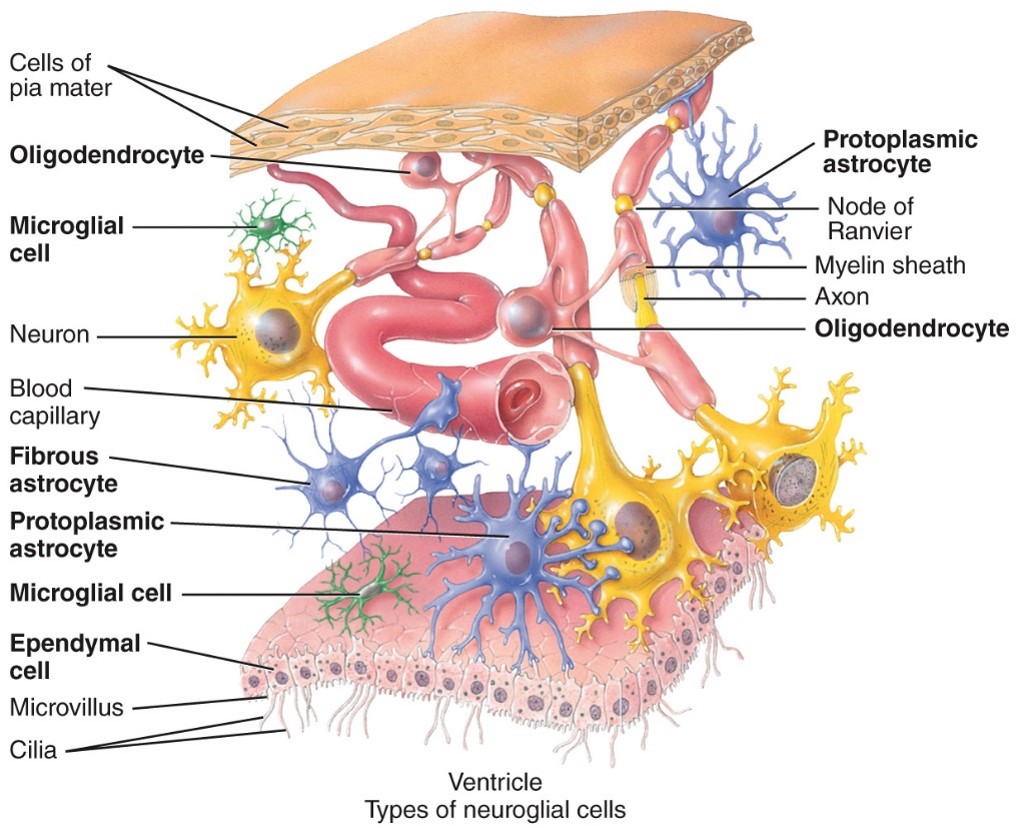
78
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
-CNS
- Support the CNS neurons and have the process that form myelin sheaths around axons to increase speed of nerve impulses
- Support the CNS neurons and have the process that form myelin sheaths around axons to increase speed of nerve impulses
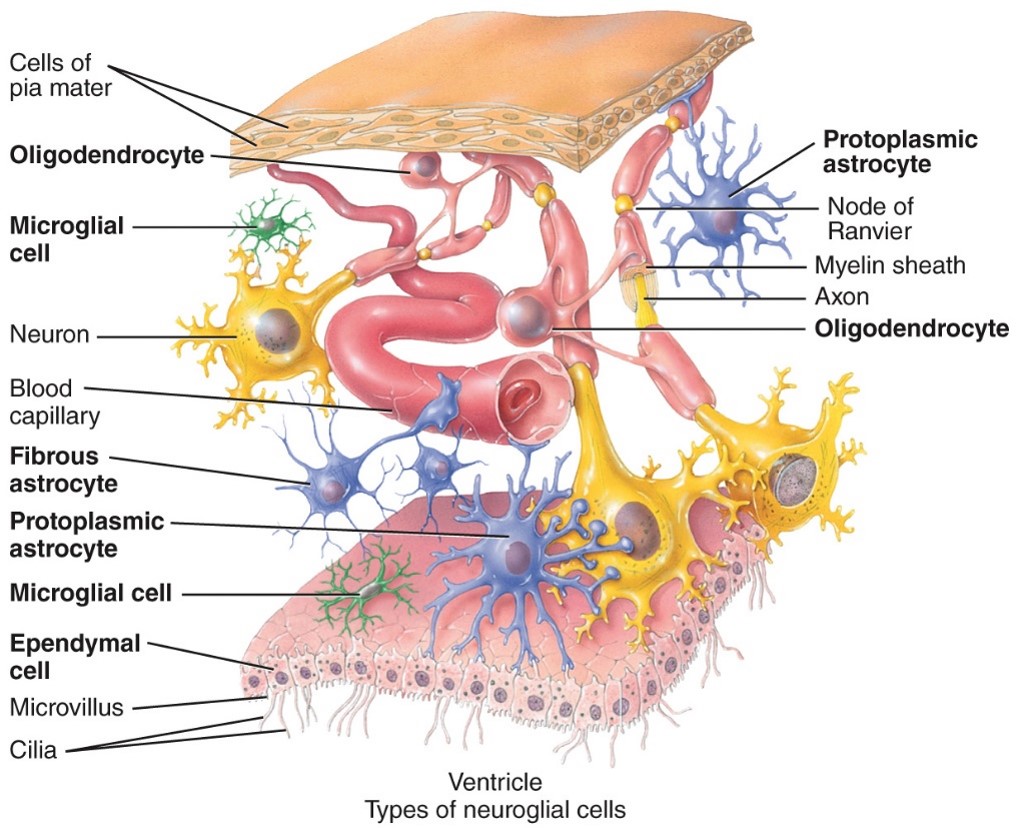
79
New cards
Microglia
- CNS
- Are the phagocytes of the CNS that engulf debris, necrotic tissue and invading bacteria or virus
- Are the phagocytes of the CNS that engulf debris, necrotic tissue and invading bacteria or virus
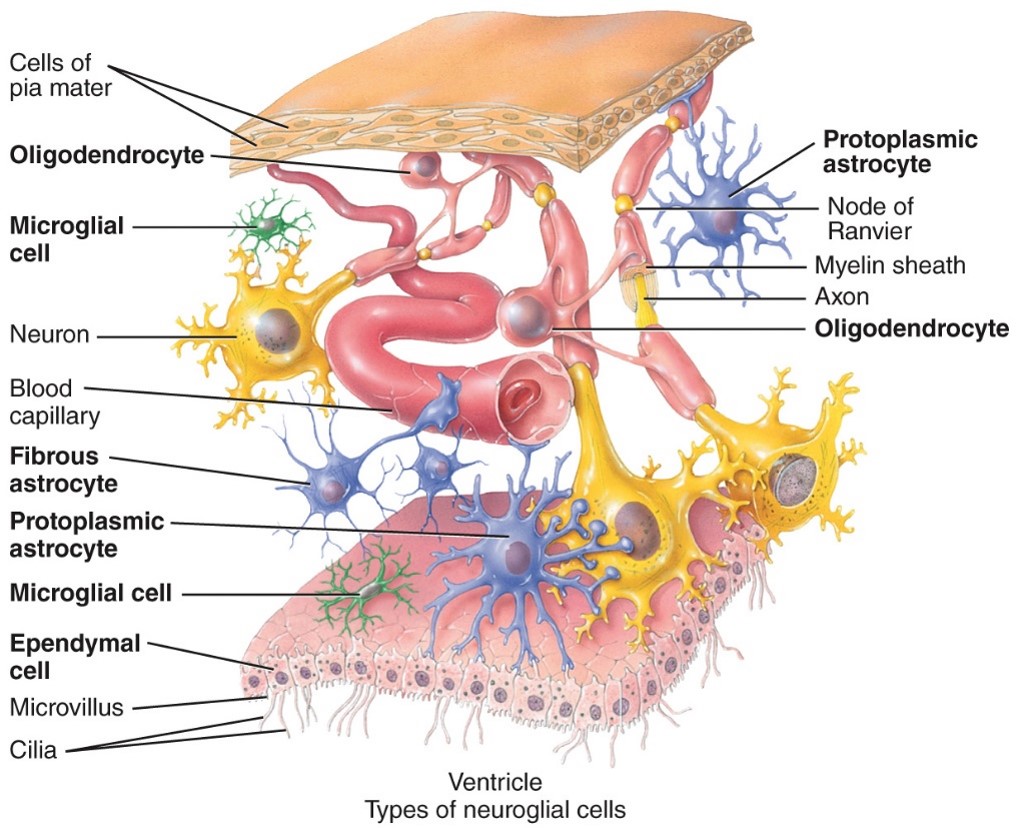
80
New cards
Ependymal cells
- CNS
- Lines all 4 ventricles of the brain as well as the central canal of the spinal cord
- Lines all 4 ventricles of the brain as well as the central canal of the spinal cord
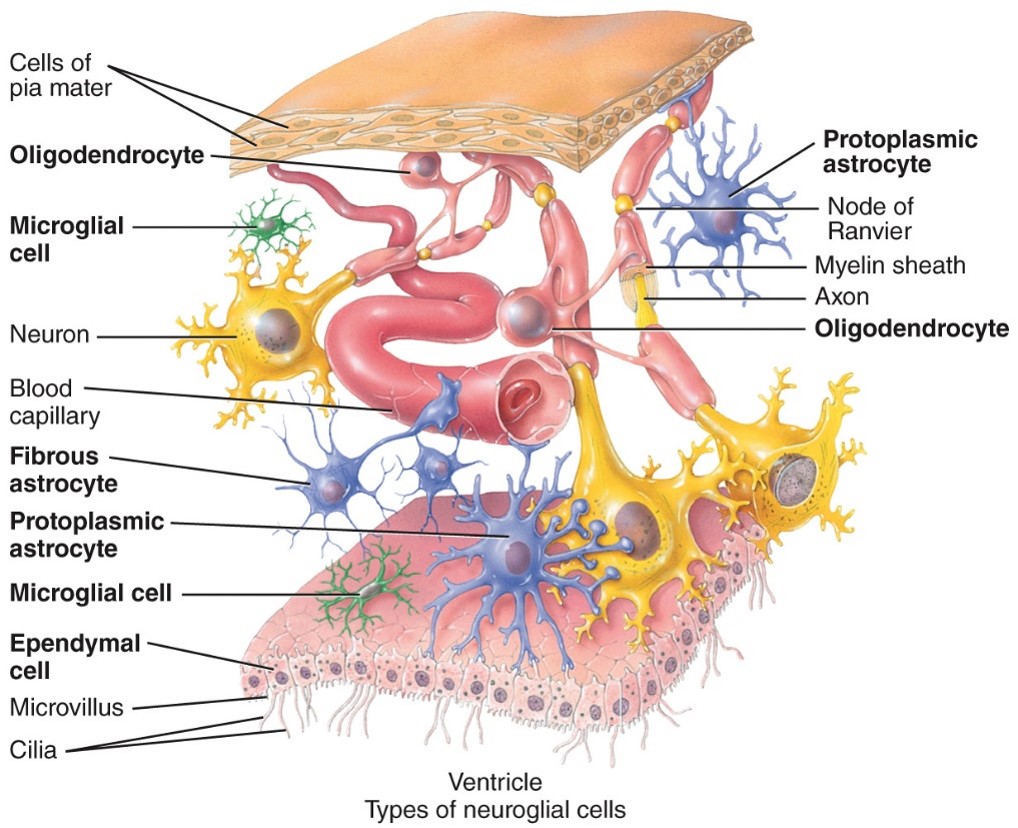
81
New cards
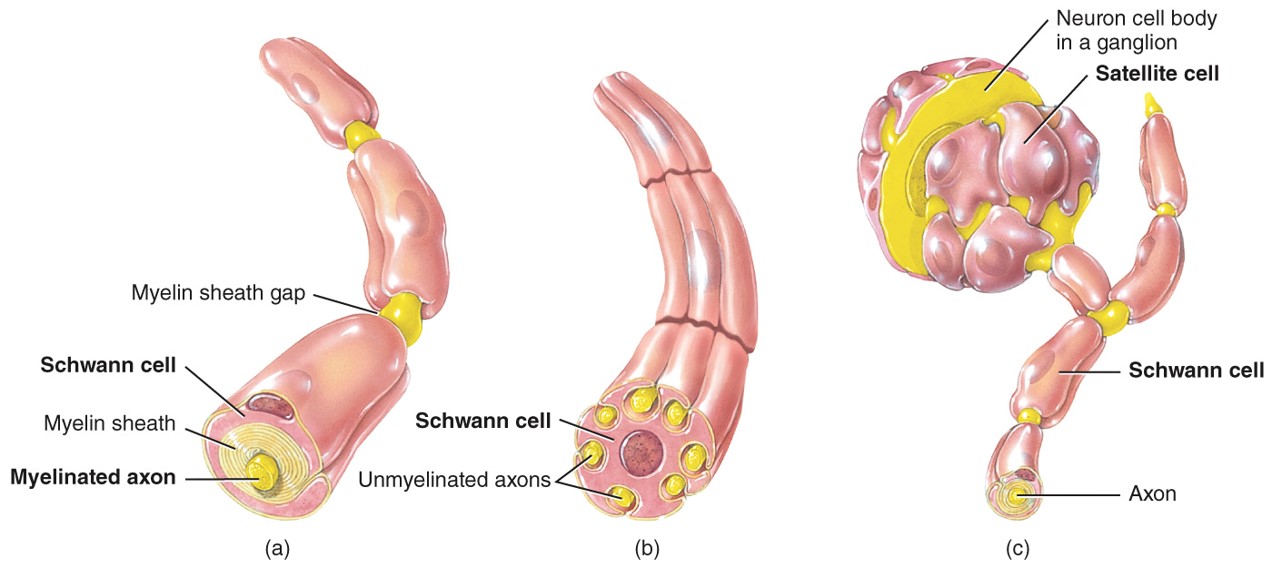
Schwann Cells
-PNS
- o Flattened cells that wrap around the axons in the PNS
o Many Schwann cells form the myelin sheath around one axon.
- o Flattened cells that wrap around the axons in the PNS
o Many Schwann cells form the myelin sheath around one axon.
82
New cards
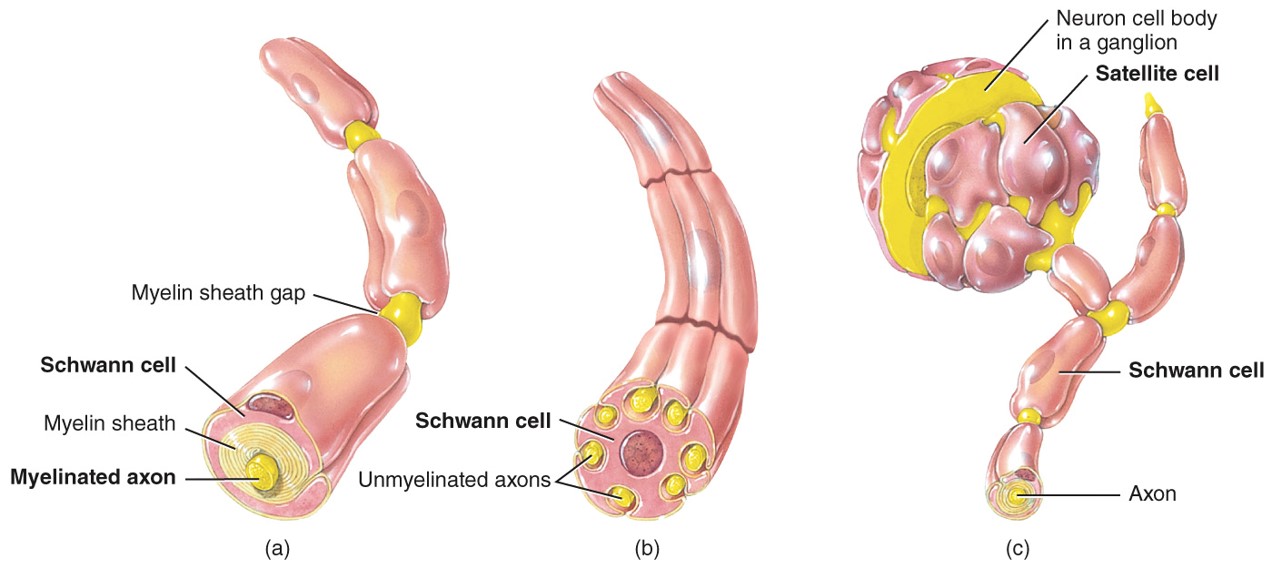
Satellite Cells
-PNS
-Have process that are flattend and surrounded sensory neruron cell bodies located in the ganglia in the PNS
-They give support to these neurons and regulate their chemical enviroment
-Have process that are flattend and surrounded sensory neruron cell bodies located in the ganglia in the PNS
-They give support to these neurons and regulate their chemical enviroment
83
New cards
---Myelanation/ 2 types of axons---
84
New cards
Myelin sheath
-Multilayerd lipid and protein covering around and some axons that insulate them and increases the speed of the nerve impulse conduction
85
New cards
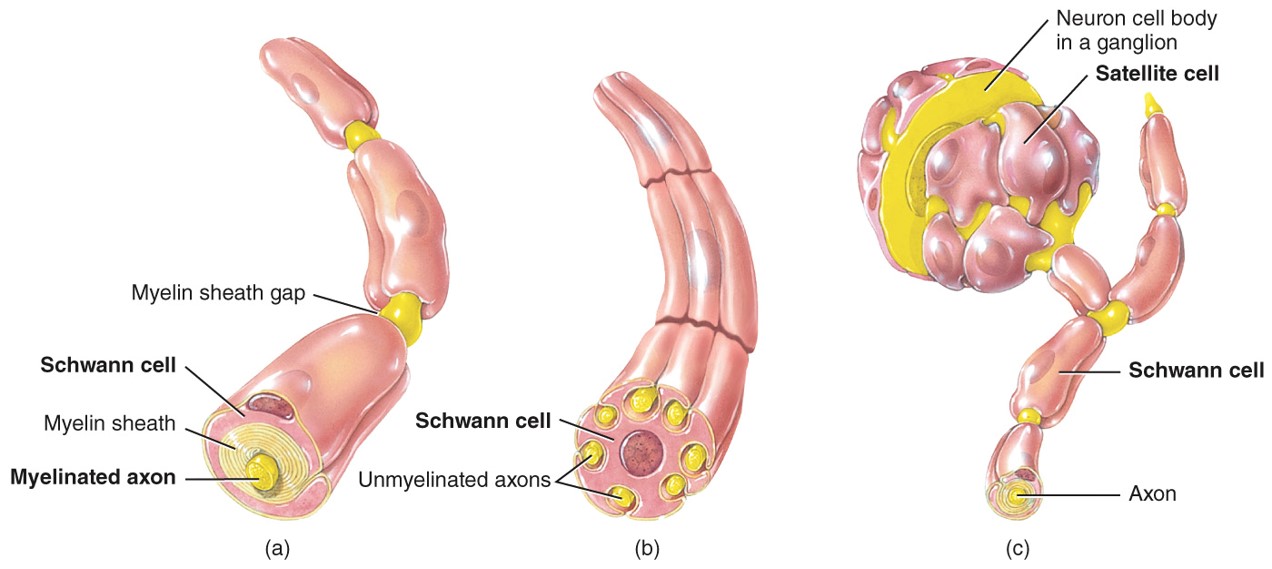
Unmyelinated
- Axons witouth myelin sheath
- Make up gray matter
- Make up gray matter
86
New cards
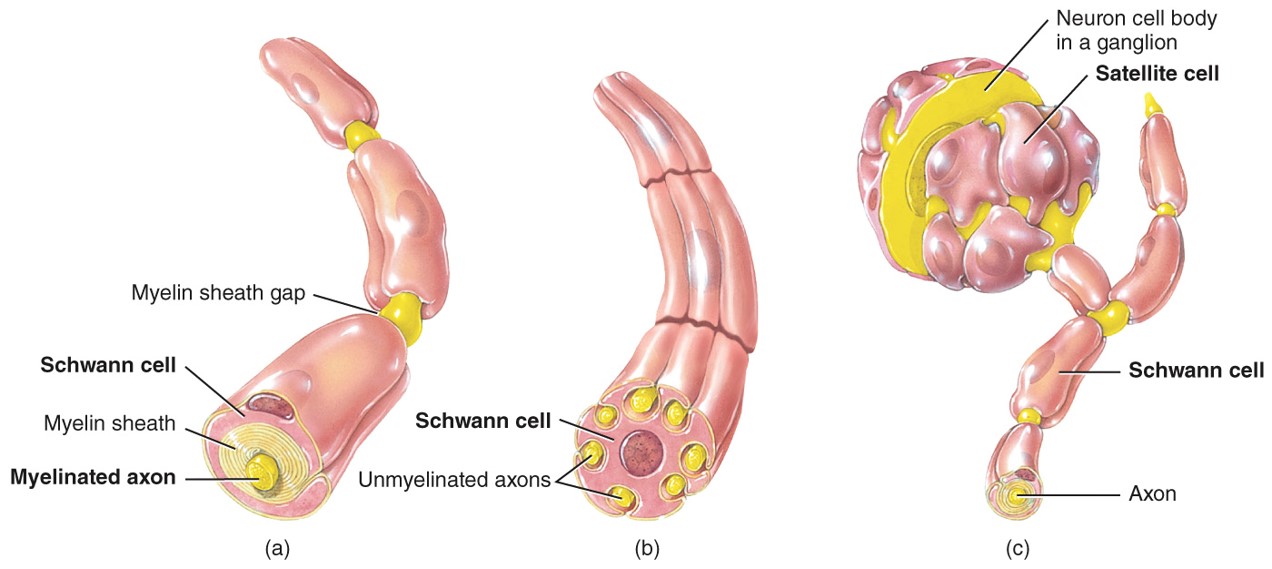
Myelinated
- Axons with a myelin sheath
- Make up white matter
- Make up white matter
87
New cards
which 2 types of neuroglia produce myelin sheathS
- Schwannn Cells (PNS)
- Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
- Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
88
New cards
---Gray and White matter---
89
New cards
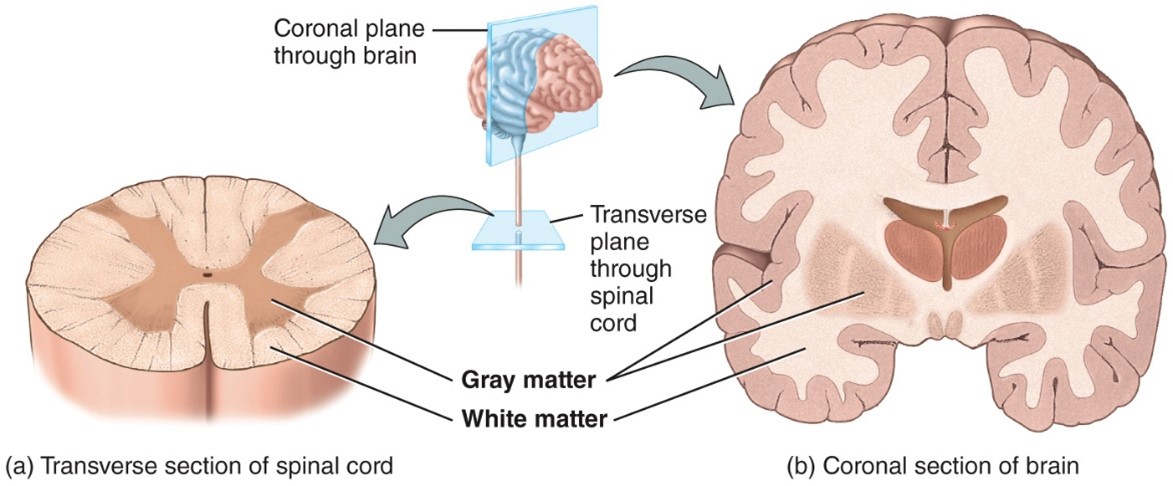
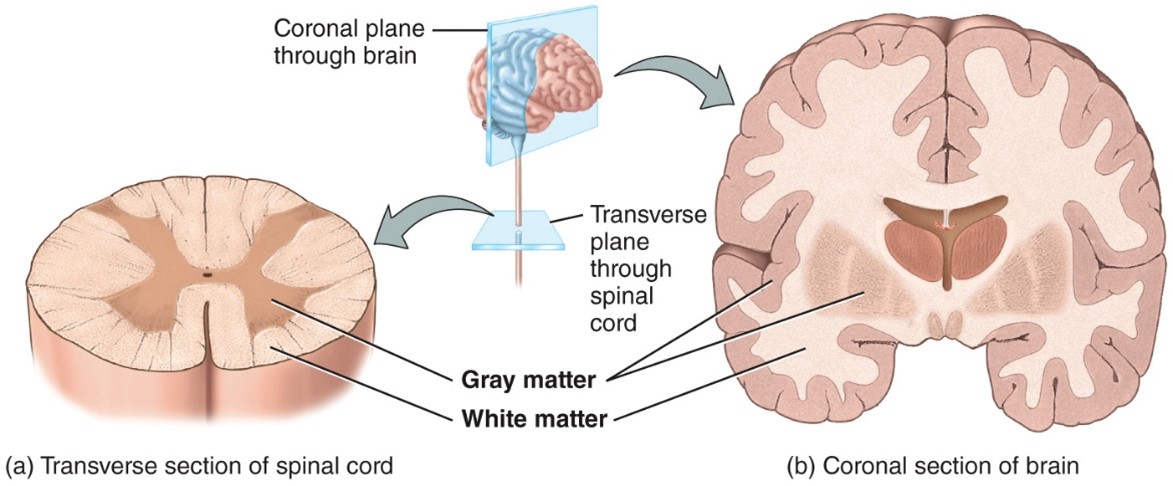
Gray matter
- Contains unmyelinated axons, cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, and neruoglia
- Gray matter receives and integrates incoming and outgoing information to perform spinal reflexes
- Gray matter receives and integrates incoming and outgoing information to perform spinal reflexes
90
New cards
White matter
- Made up of myelinated axons
- White matter tacts conduct nerve impulses to and from the brain
- White matter tacts conduct nerve impulses to and from the brain
91
New cards
---Physiology-Electrical signals in neurons: 2 types---
92
New cards
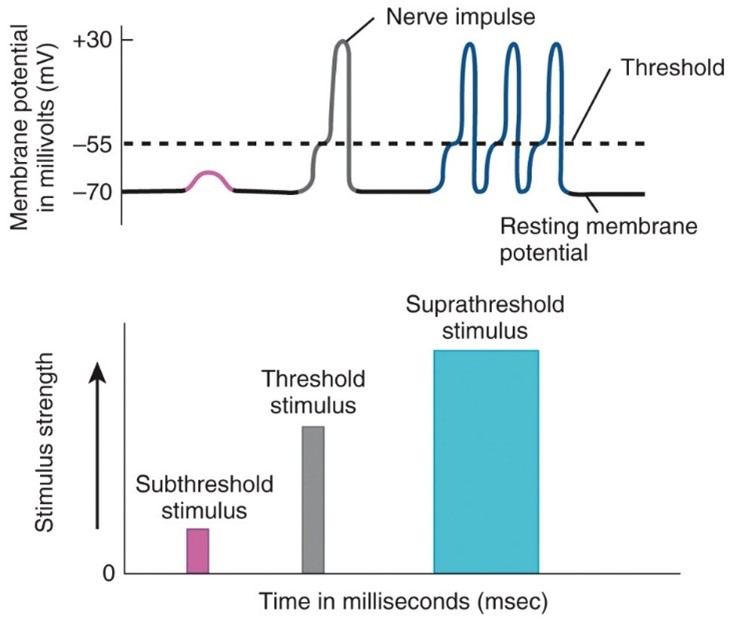
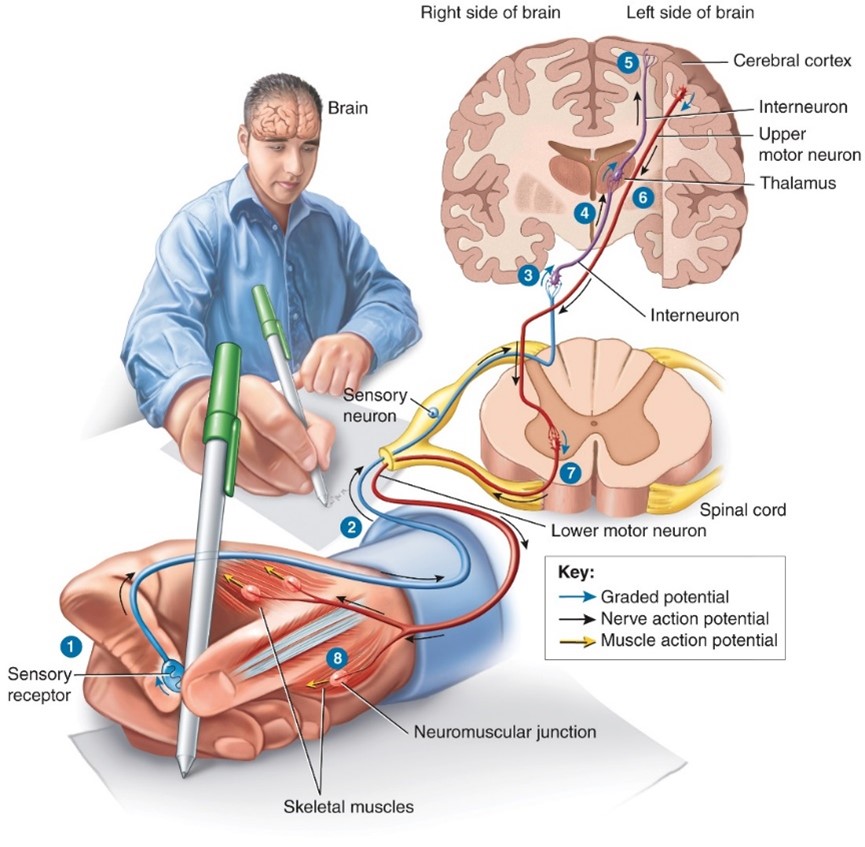
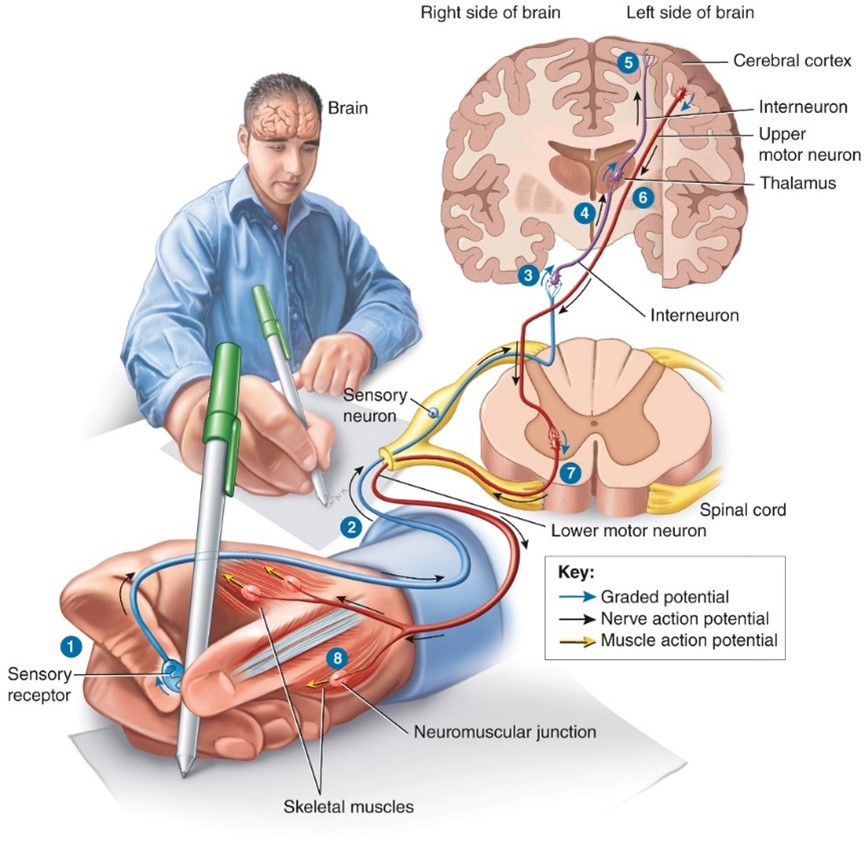
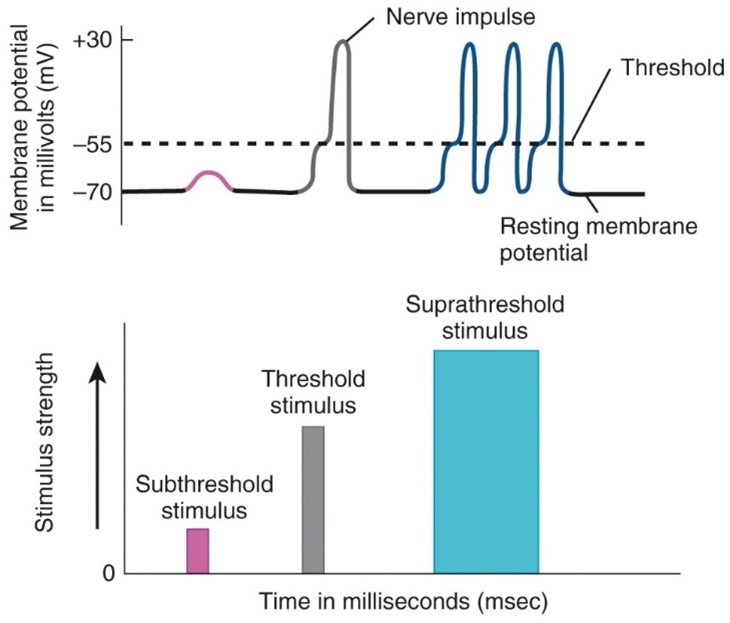
Action Potential
- membrane potential and resting membrane potential
- Communicate over SHORT and LONG distances
occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body.
- Communicate over SHORT and LONG distances
occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body.
93
New cards
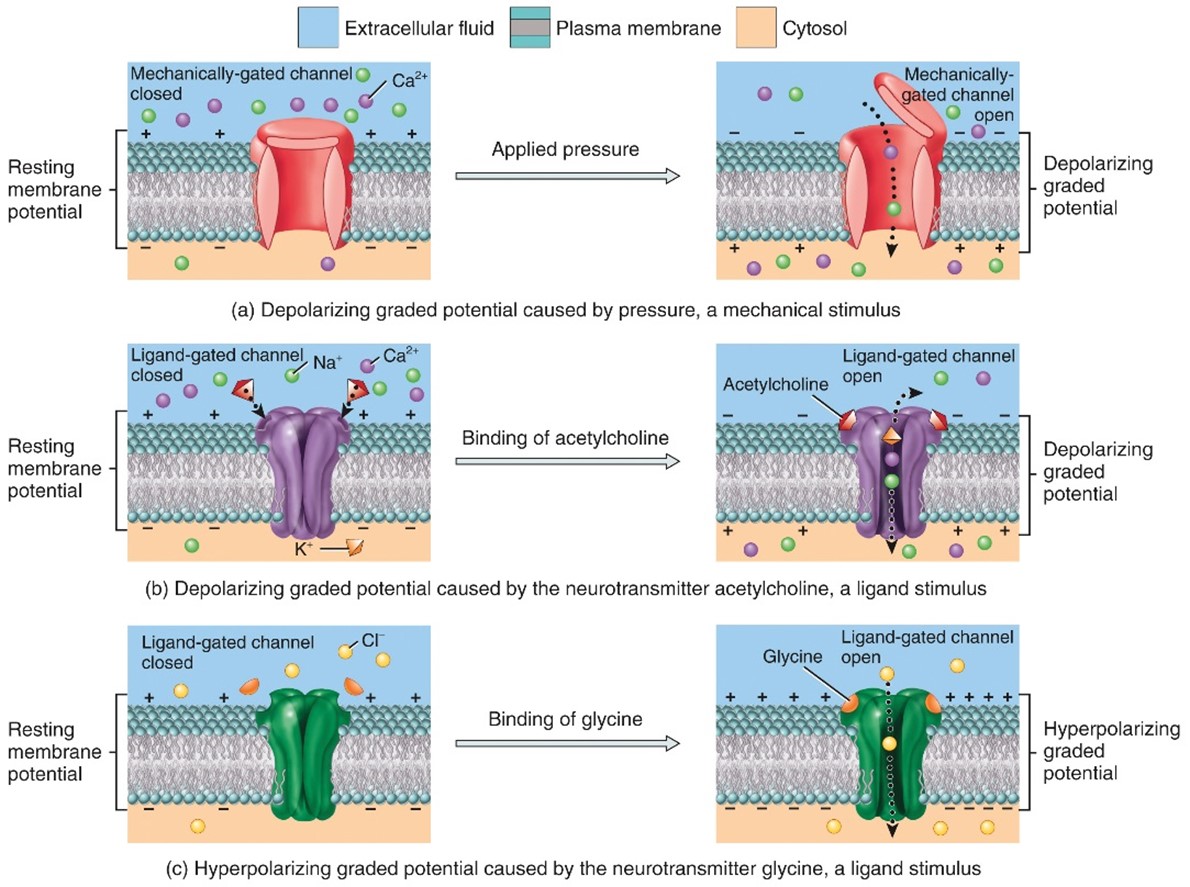
Graded potentials
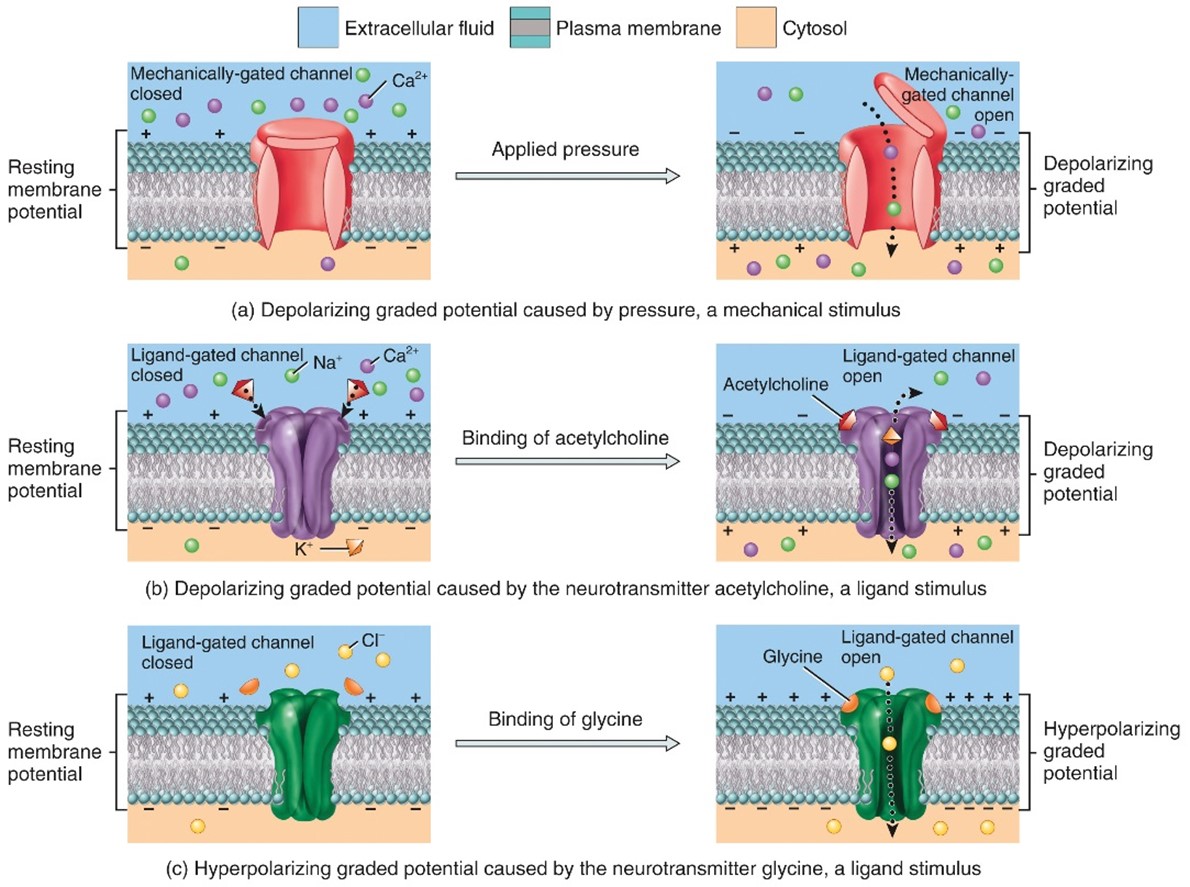
- A graded potential occurs in response to the opening of a mechanically-gated or ligand-gated ion channel
- Allow communications over SHORT distances only
- Allow communications over SHORT distances only
94
New cards
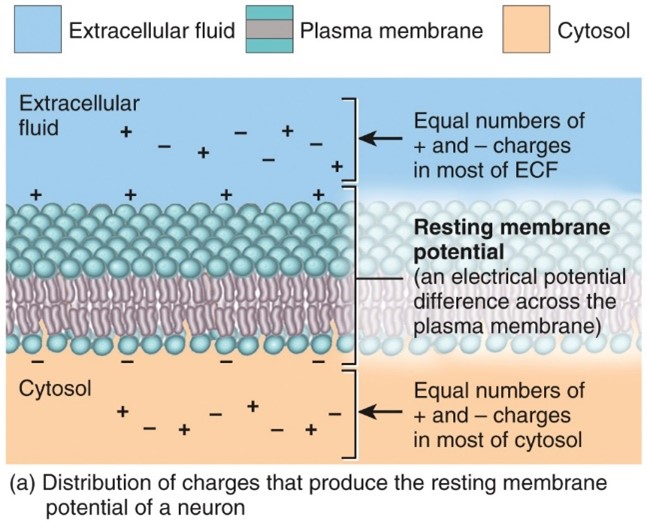
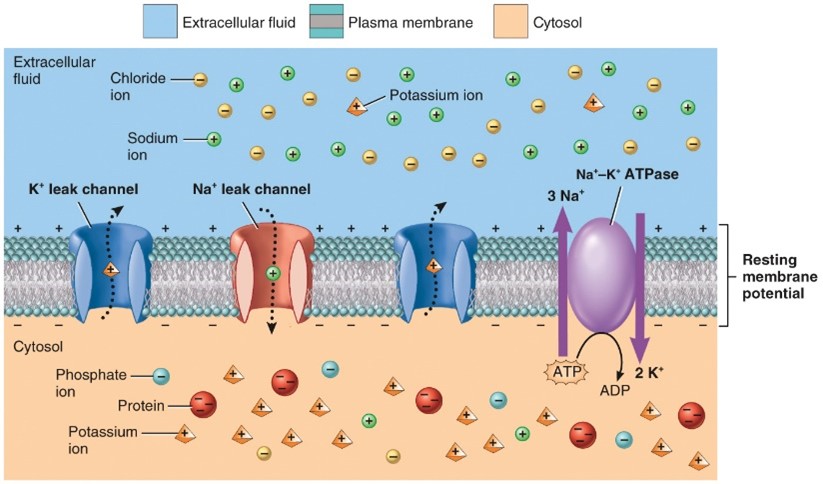
Resting Membrane potential
- Unequal distribution of ions across the plasma membrane and the selective permeability of the neuron’s membrane to N a+ and K+
- Most anions cannot leave the cell
- N a+/K+ pumps
- Most anions cannot leave the cell
- N a+/K+ pumps
95
New cards
---2 types of Graded Potentials---
96
New cards
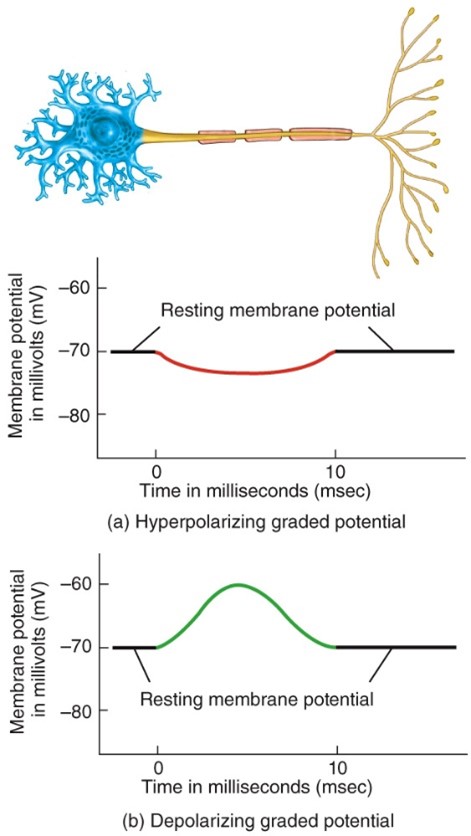
Hyperpolarizing graded potential
- When the response makes the membrane more polarized (inside more negative)
97
New cards
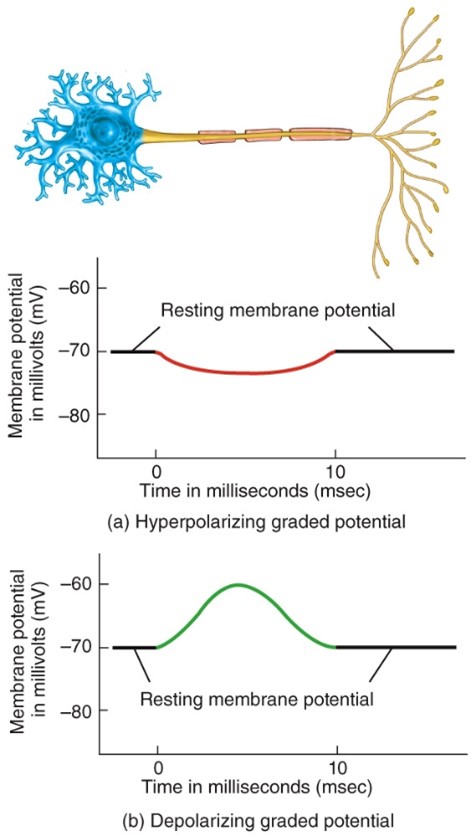
Depolarizing graded potential
- When the response makes the membrane less polarized (inside less negative)
98
New cards
---Generation of action potential: 3 phases---
99
New cards
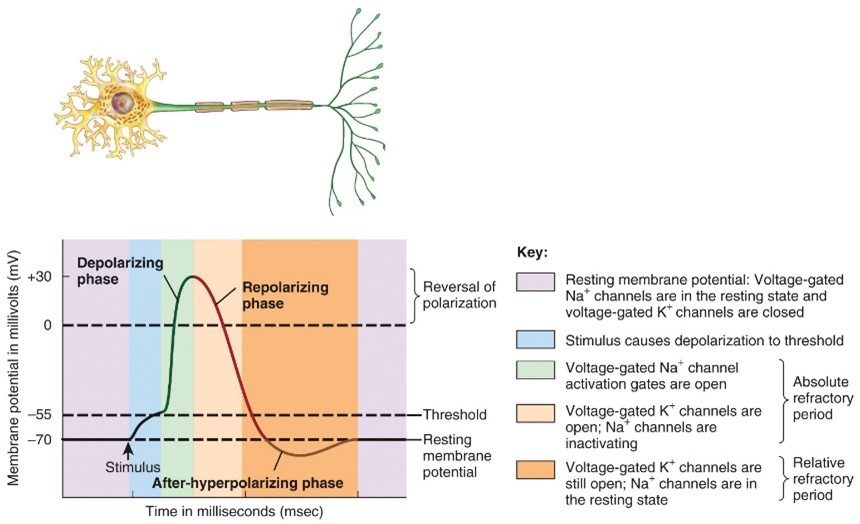
Depolarzing phase
- Excitation
- The negative membrane potential becomes less negative, reaches zero, and then become positive.
- The negative membrane potential becomes less negative, reaches zero, and then become positive.
100
New cards
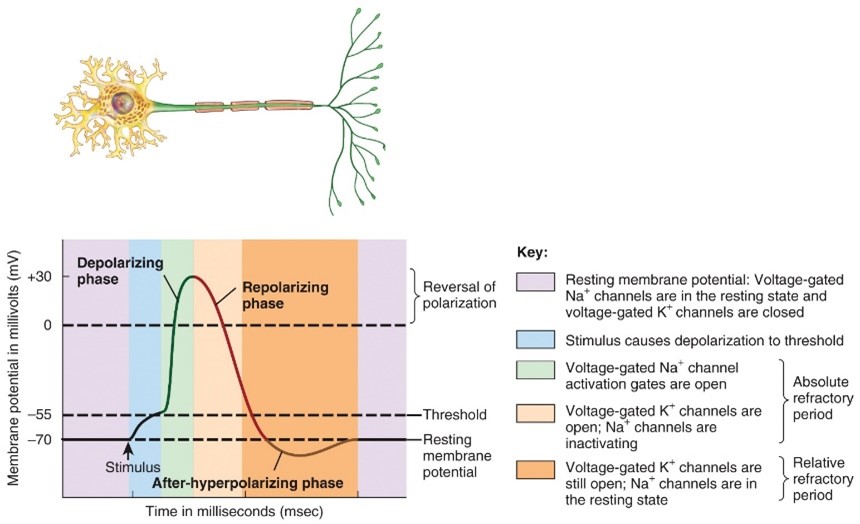
Repolarizing Phase
- Relaxation
The membrane potential is restored to the resting state of -70 mv
The membrane potential is restored to the resting state of -70 mv