The function and Structure of the Larynx
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
what is the function of the larynx?
guard the entrance of the trachea to prevent coarse material from entering
control passage of air in and out of trachea
act of swallowing
what is the structure of the larynx?
a musculo-cartilagenous organ
what are the components of the larynx?
laryngeal cartilage
laryngeal muscles
ligaments, membranes, and folds
glottic cleft
what is the location of the larynx in reference to the tongue?
caudal
what is the location of the larynx in reference to the trachea?
cranial
where can you palpate and access the larynx?
from the ventral neck (throat region)
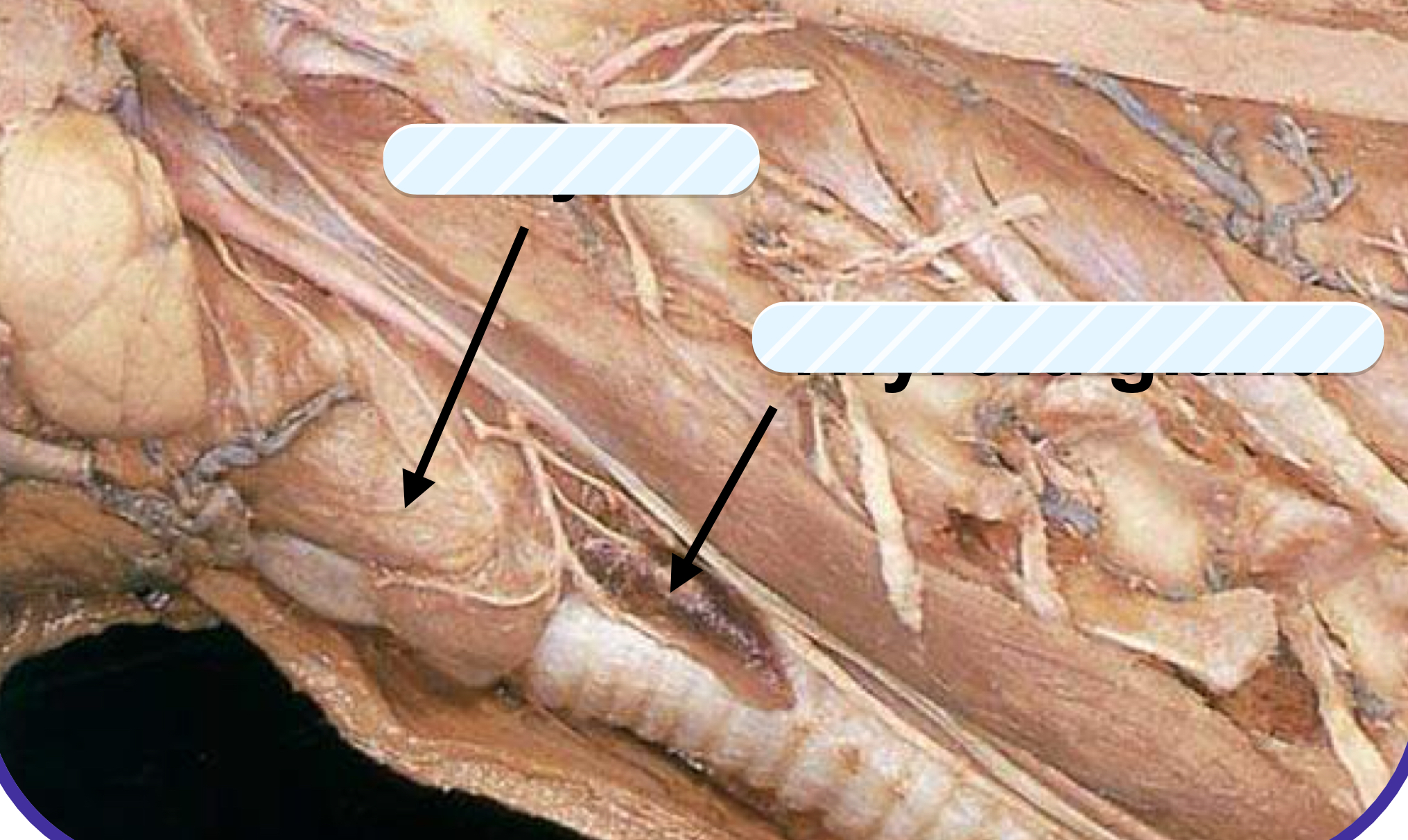
what structure is the arrow pointing to on the left?
larynx
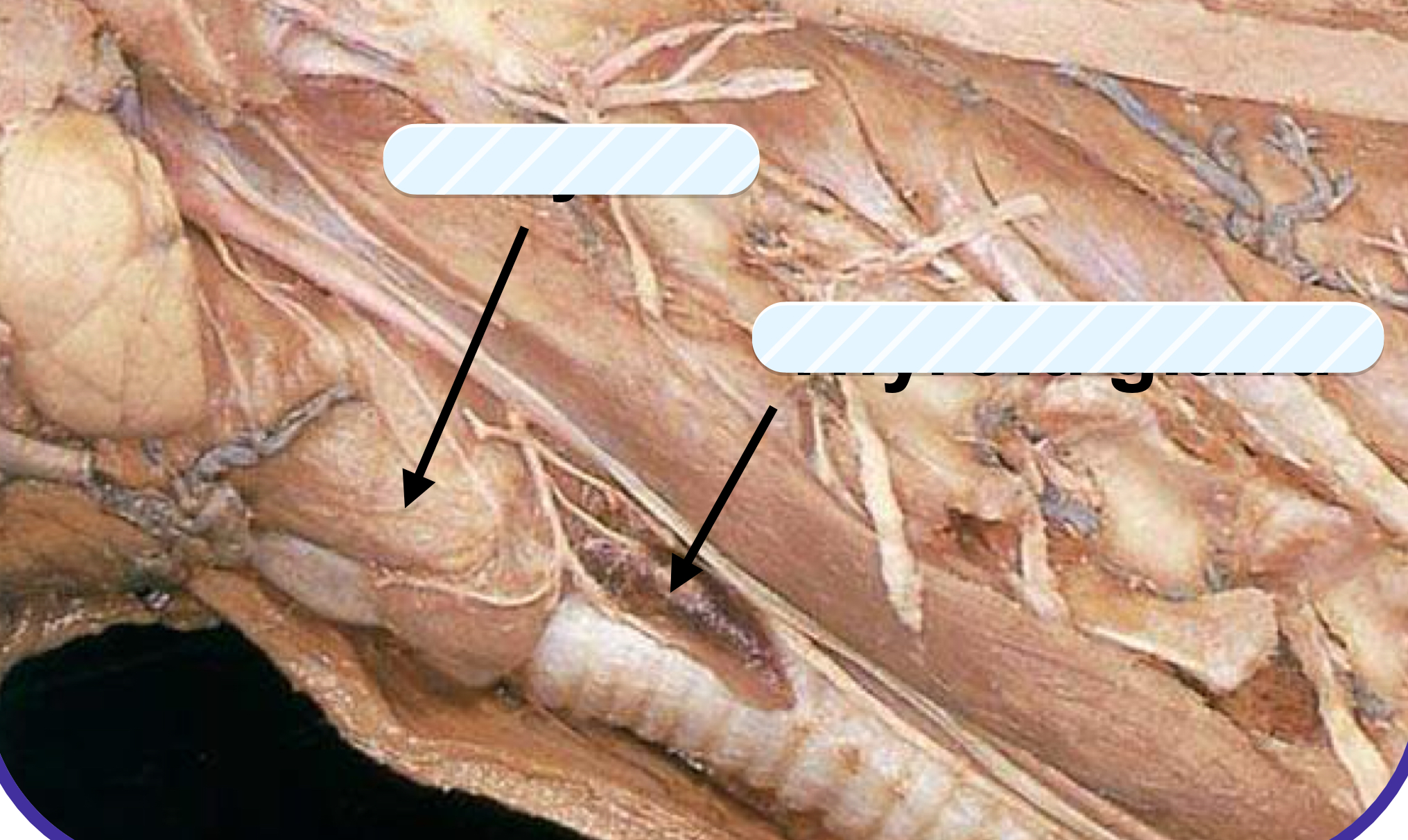
what structure is the arrow pointing to on the right?
thyroid gland
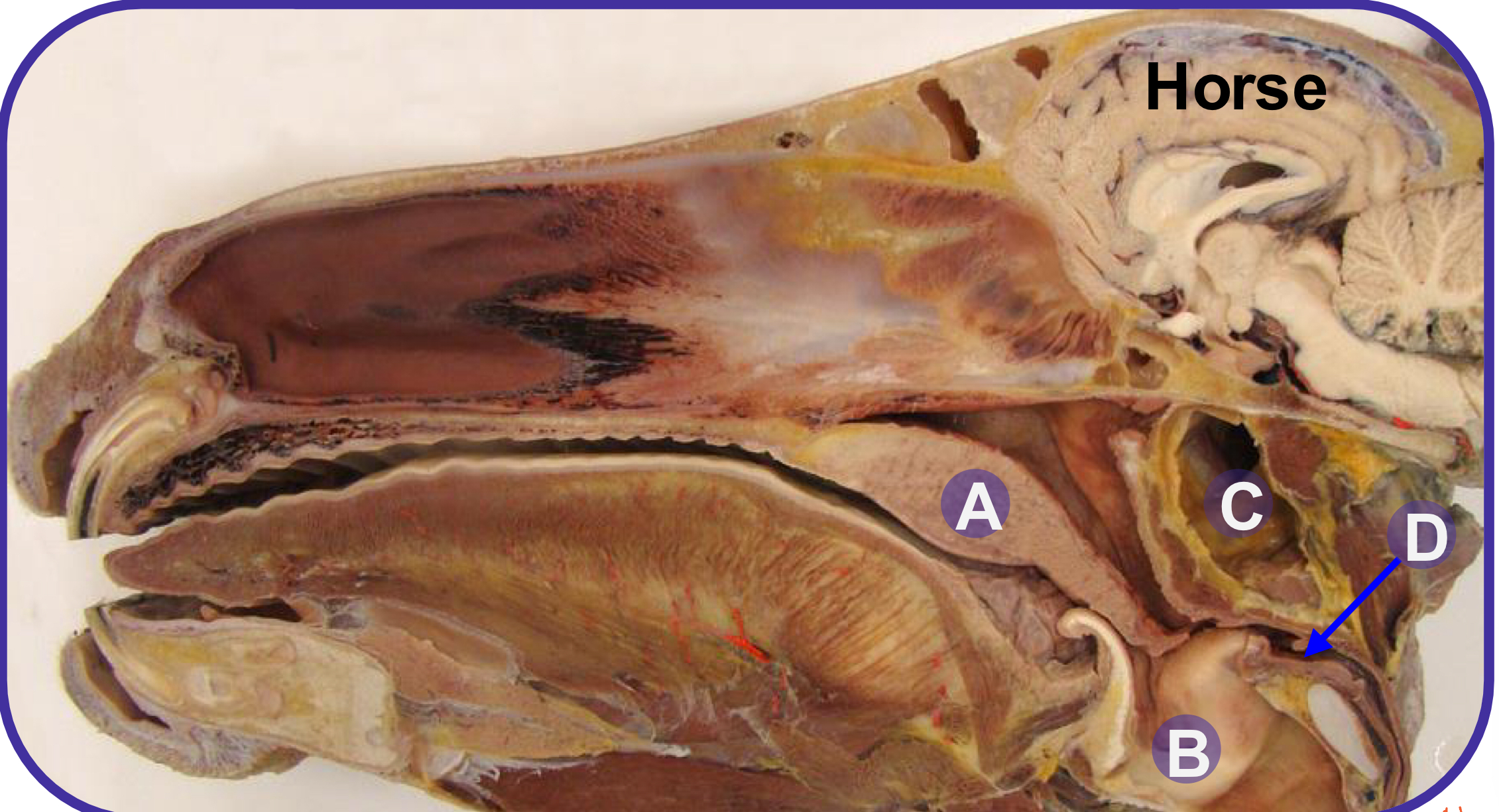
what structure is A?
soft palate
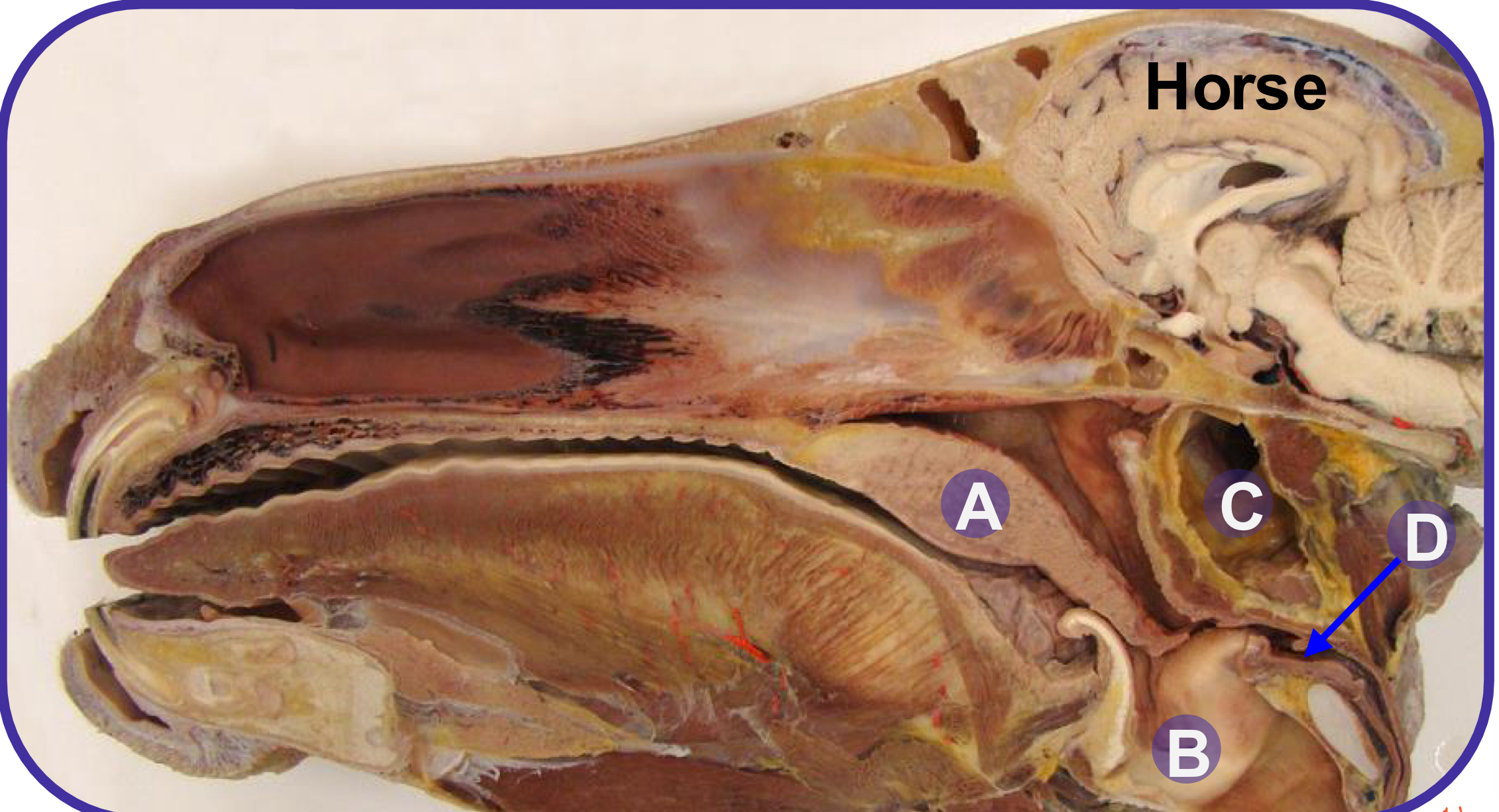
what structure is B?
larynx
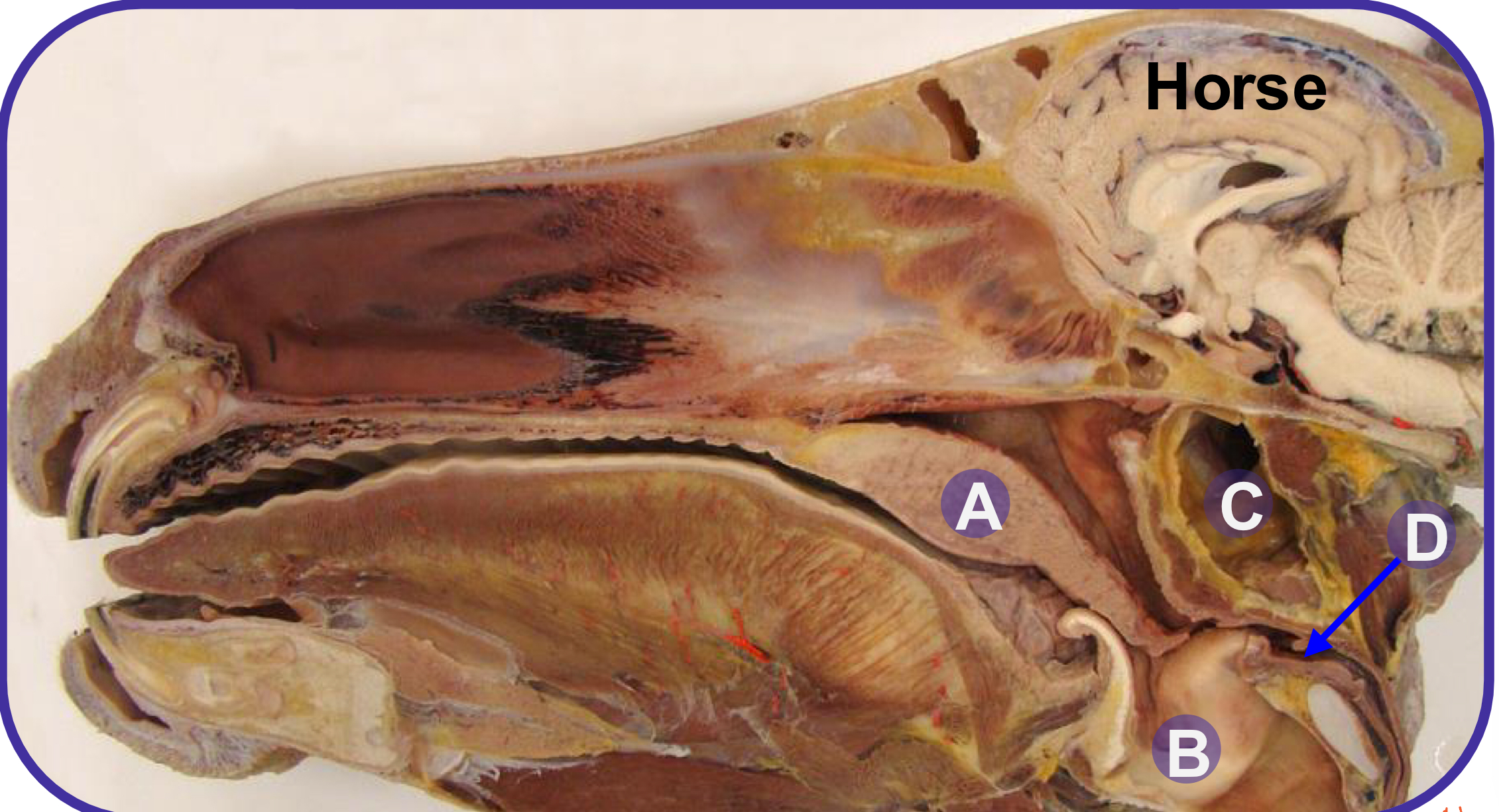
what structure is C?
guttural pouch
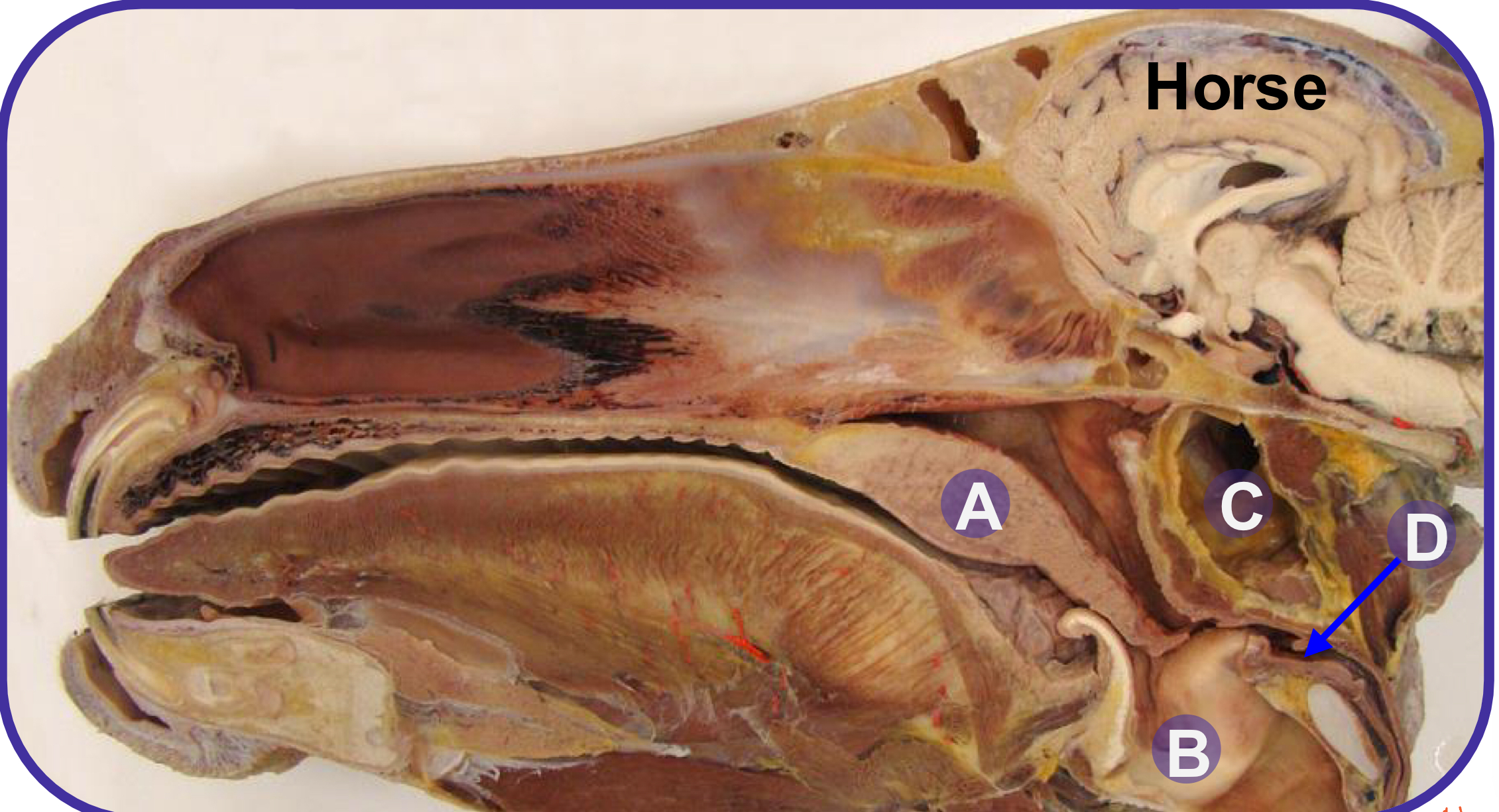
what structure is D?
laryngopharynx
what is the only paired cartilage in the larynx?
arytenoid cartilage
what is the only cartilage of the larynx that is completely closed and creates a ring structure?
cricoid cartilage
in the dog at the ventral aspect, what happens with the thyroid cartilage?
it is completely fused lamina from left and right side
what is the shape of the thyroid cartilage?
“U” shaped
in the horse at the ventral aspect of the thyroid cartilage what is happening?
there is a gap between laminae
which cartilage of the larynx is related to the caudal edge of the soft palette?
epiglottic cartilage
which cartilage of the larynx has a rostral and caudal horn?
thyroid cartilage
describe the epiglottic cartilage in the horse
more curved
always over the caudal edge of soft palette (other than swallowing)
cuneiform processes
describe the thyroid cartilage of the horse
longer
prominent rostral and caudal horns
deep notch exists on caudal and ventral aspect
laminae are fused only cranially
describe the arytenoid cartilage of the horse
cuneiform process not present
list the laryngeal cartilages in the horse
epiglottic cartilage
thyroid cartilage
arytenoid cartilage
cricoid cartilage
which nerve provides nerve supply to most of the intrinsic muscles including cricoarytenoideus dorsalis muscle?
caudal laryngeal nerve
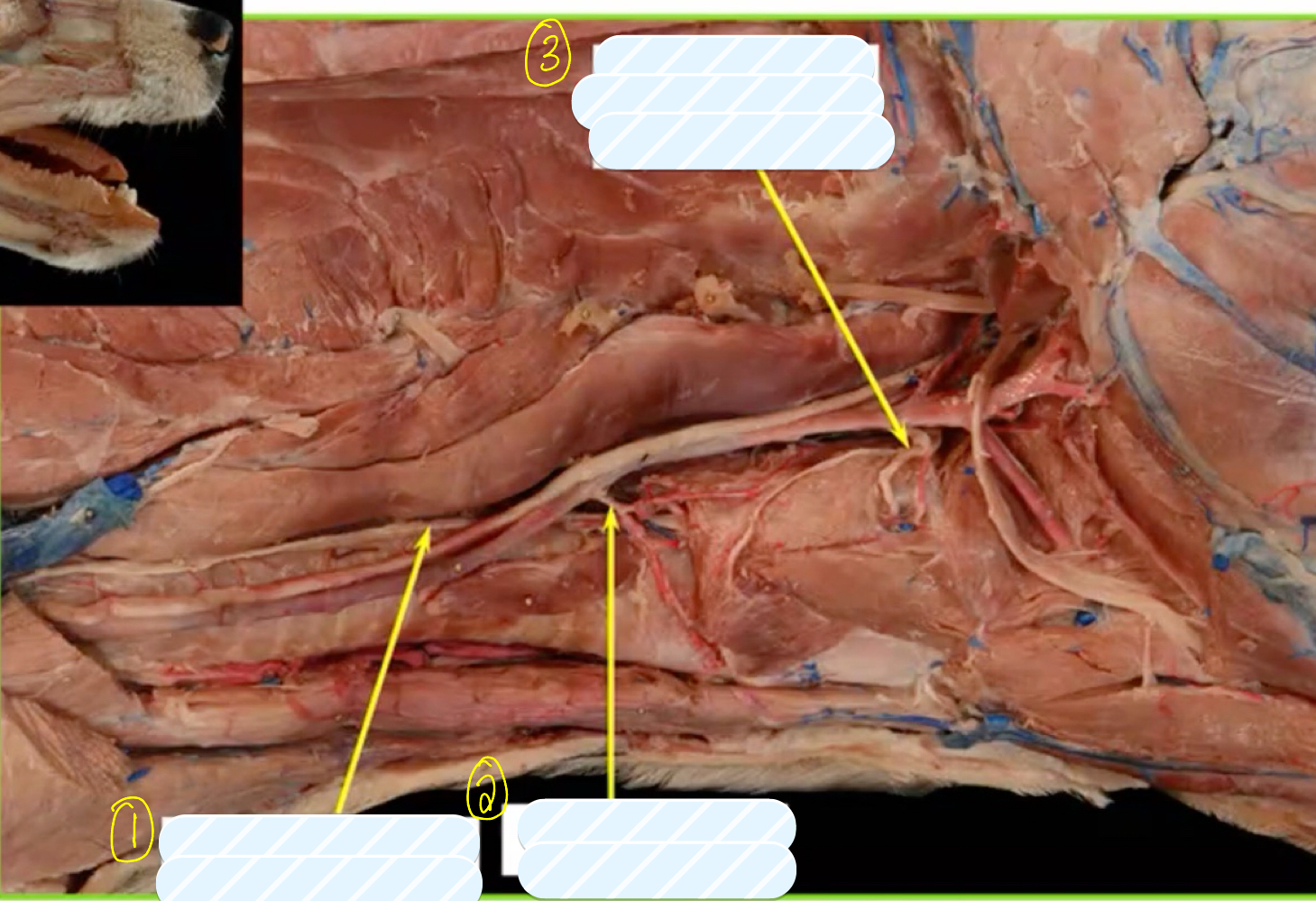
what is structure 1?
recurrent/caudal laryngeal nerve
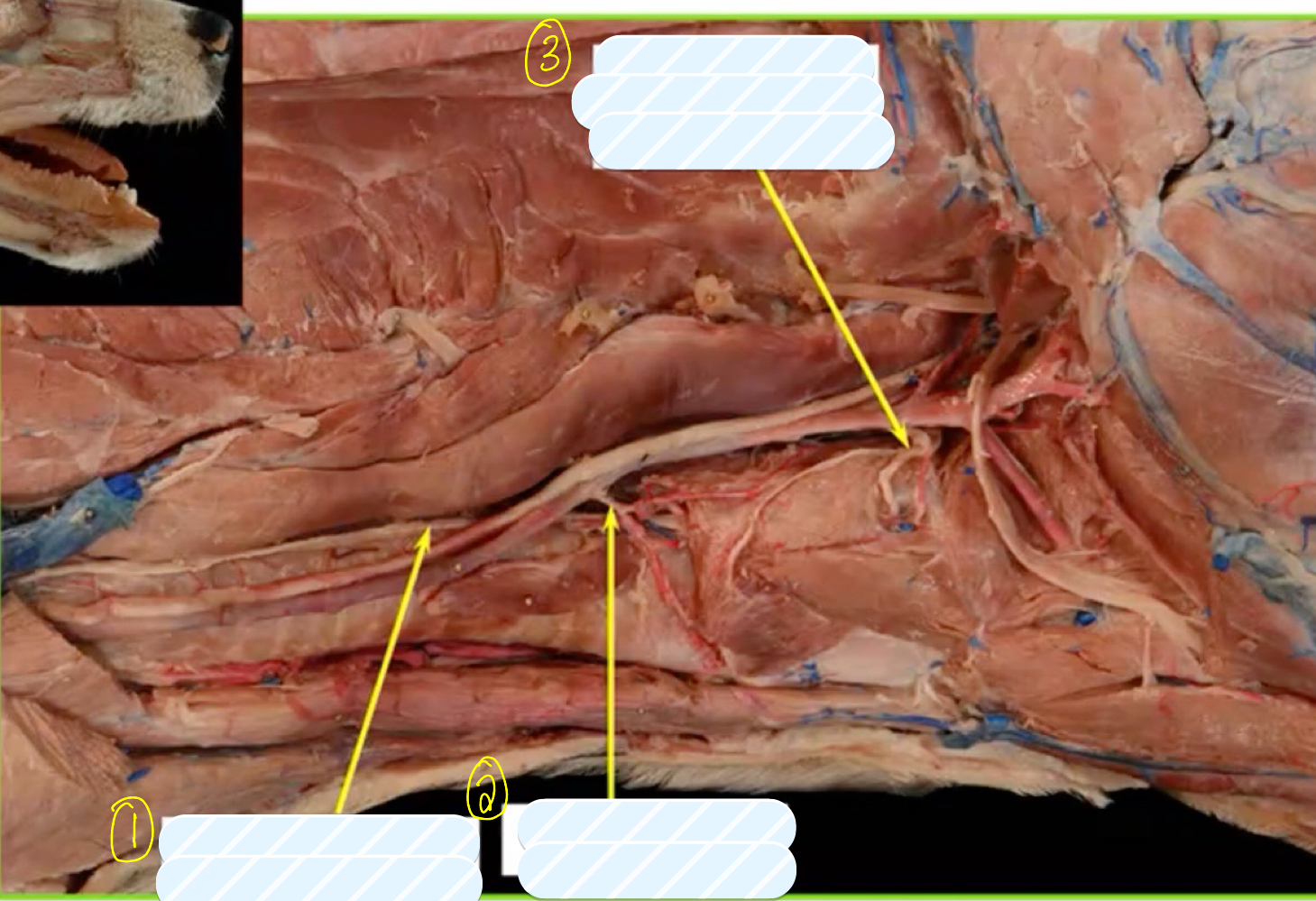
what is structure 2?
cranial thyroid artery
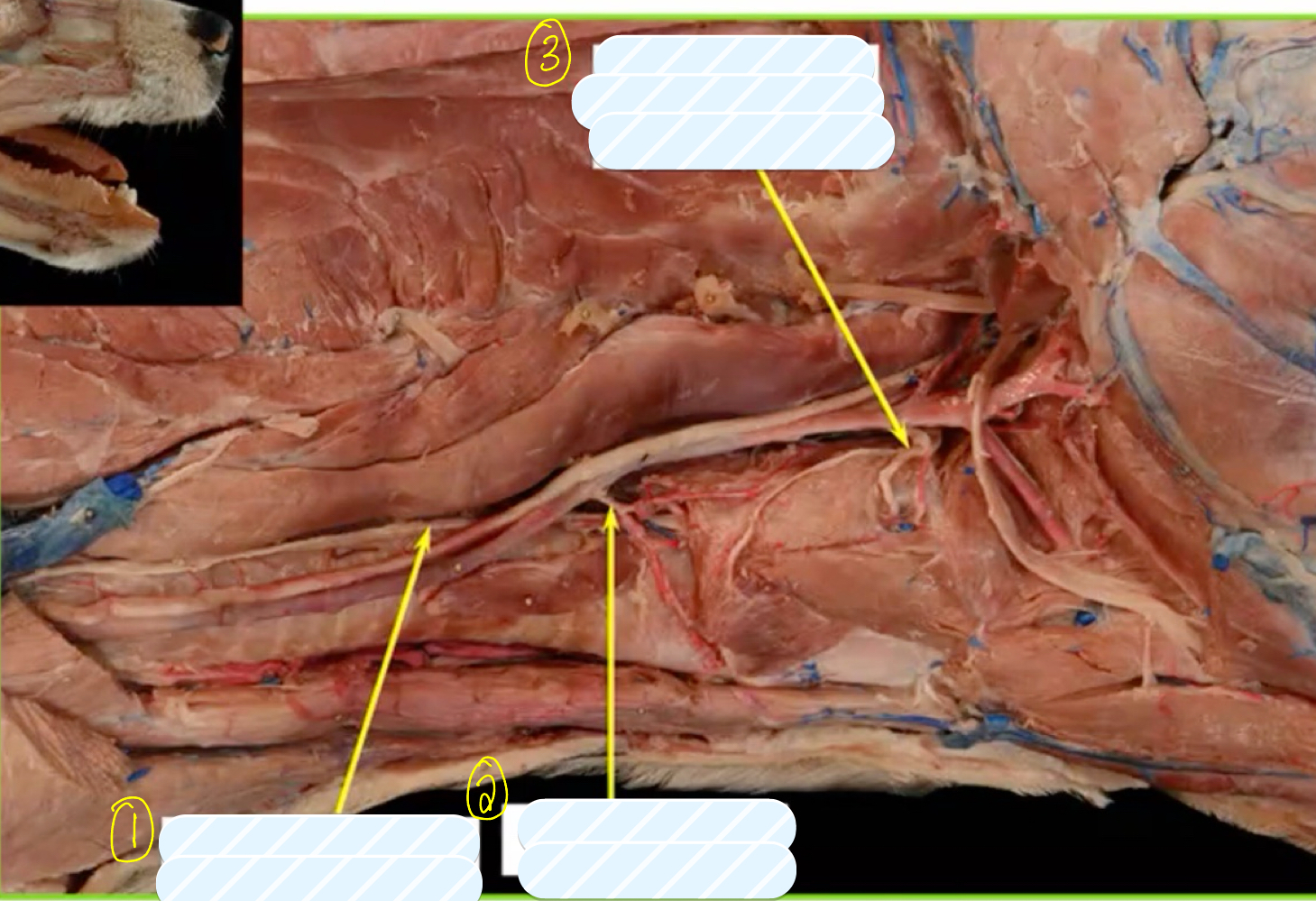
what is structure 3?
cranial laryngeal artery and nerve
what does the cranial laryngeal nerve innervate?
cricothryoideous muscle
what does the glossopharyngeal nerve innervate?
related to extrinsic muscles of the larynx via pharyngeal plexus
hypoid apparatus
set of bones that connect the larynx to the skull
what is the function of the hypoid apparatus?
support larynx
function like a spring to bring larynx back into place
support tongue
is the thyrohyoid bone paired or unpaired?
paired
where is the thyrohyroid bone located?
attached to rostral horn of thyroid cartilage
is the basihypoid bone paired or unpaired?
unpaired
where is the basihypoid bone located?
transversley oriented at the baseof the tongue, between the thyrohyoid bones.
what does the basihyoid bone have in the horse?
lingual process
is the ceratohyoid bone paired or unpaired?
paired
is the epihyoid bone paired or unpaired?
paired
the epihyoid bone in horses is
rudimentary
which bone of the hyoid apparatus makes contact with the skull?
stylohyoid bone
is the stylohyoid bone paired or unpaired?
paired
explain the stylohyoid bone in horses
very large and runs transverse in guttural pouch to divide pouch into lateral and medial component
explain the hyoid bone in case of ruminants
hyoid bone going to have an extension more rostrally where tongue is attached to basihyoid bone
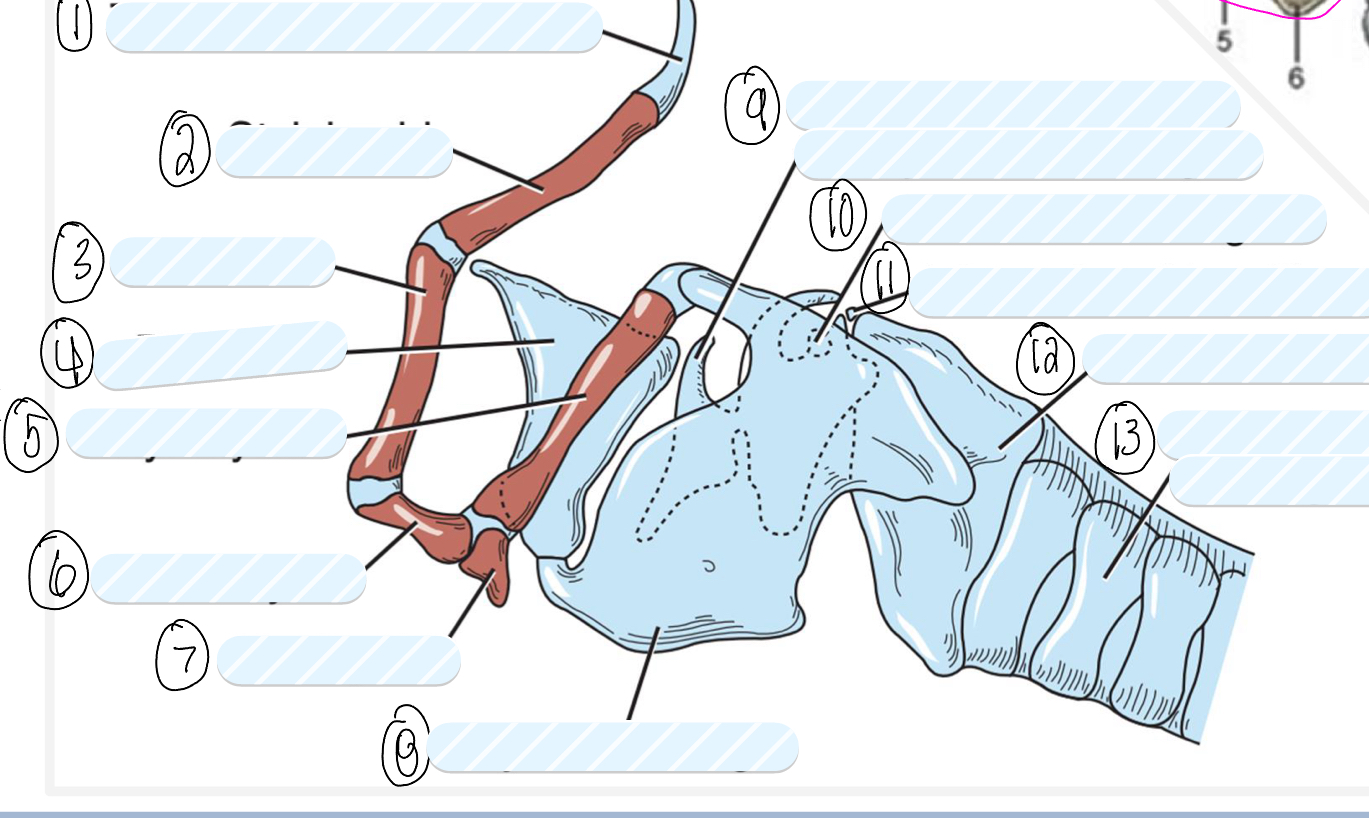
what is 1?
tympanohyoid cartilage
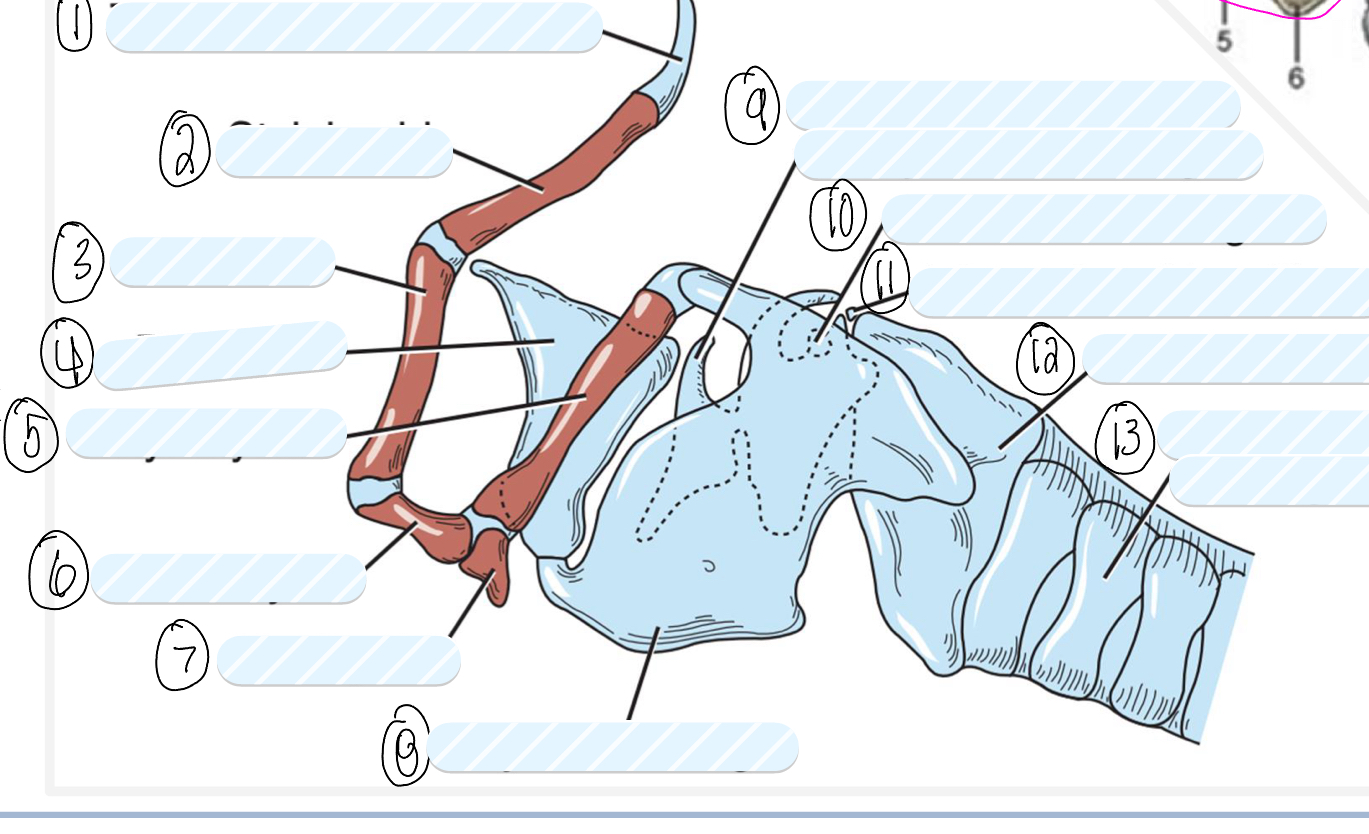
what is 2?
stylohyoid bone
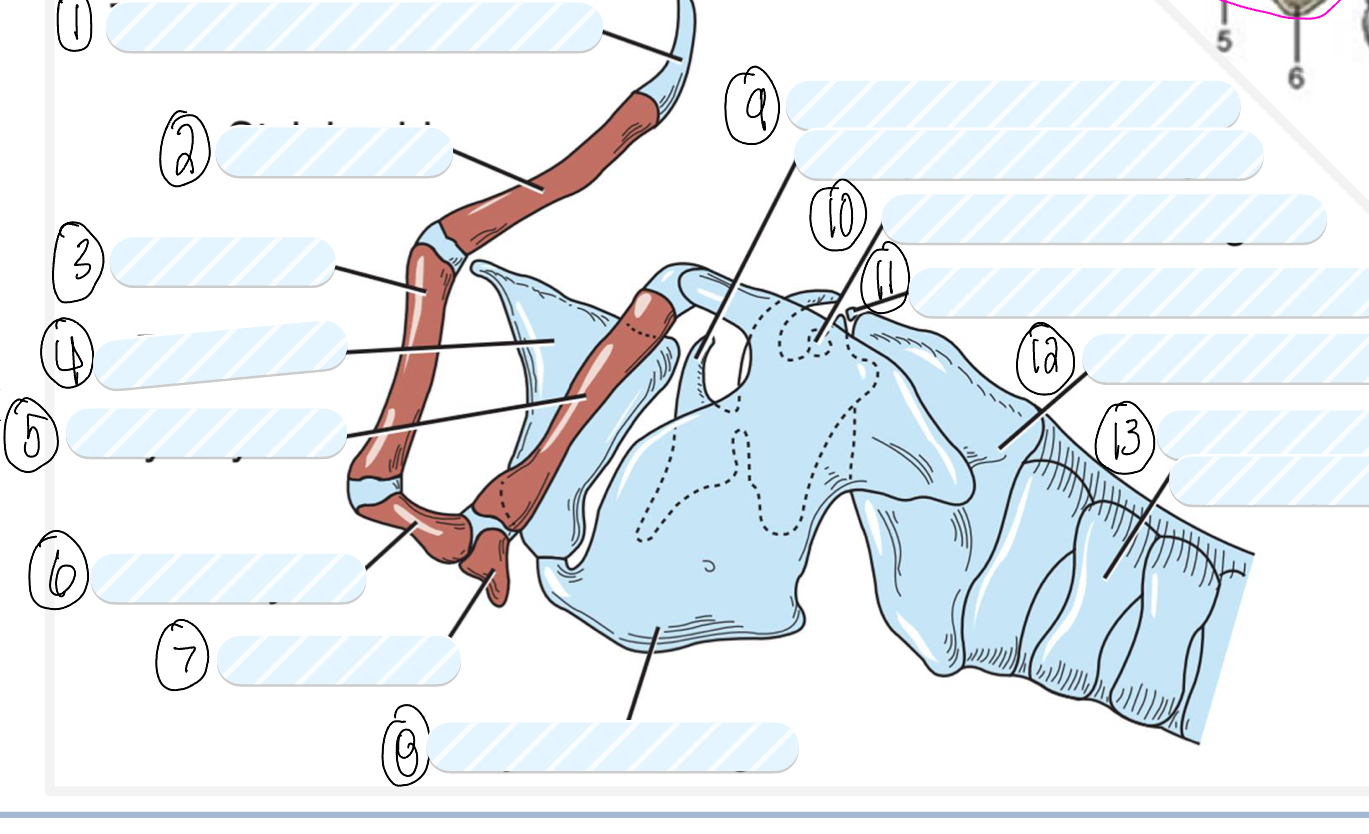
what is 3?
epihyoid
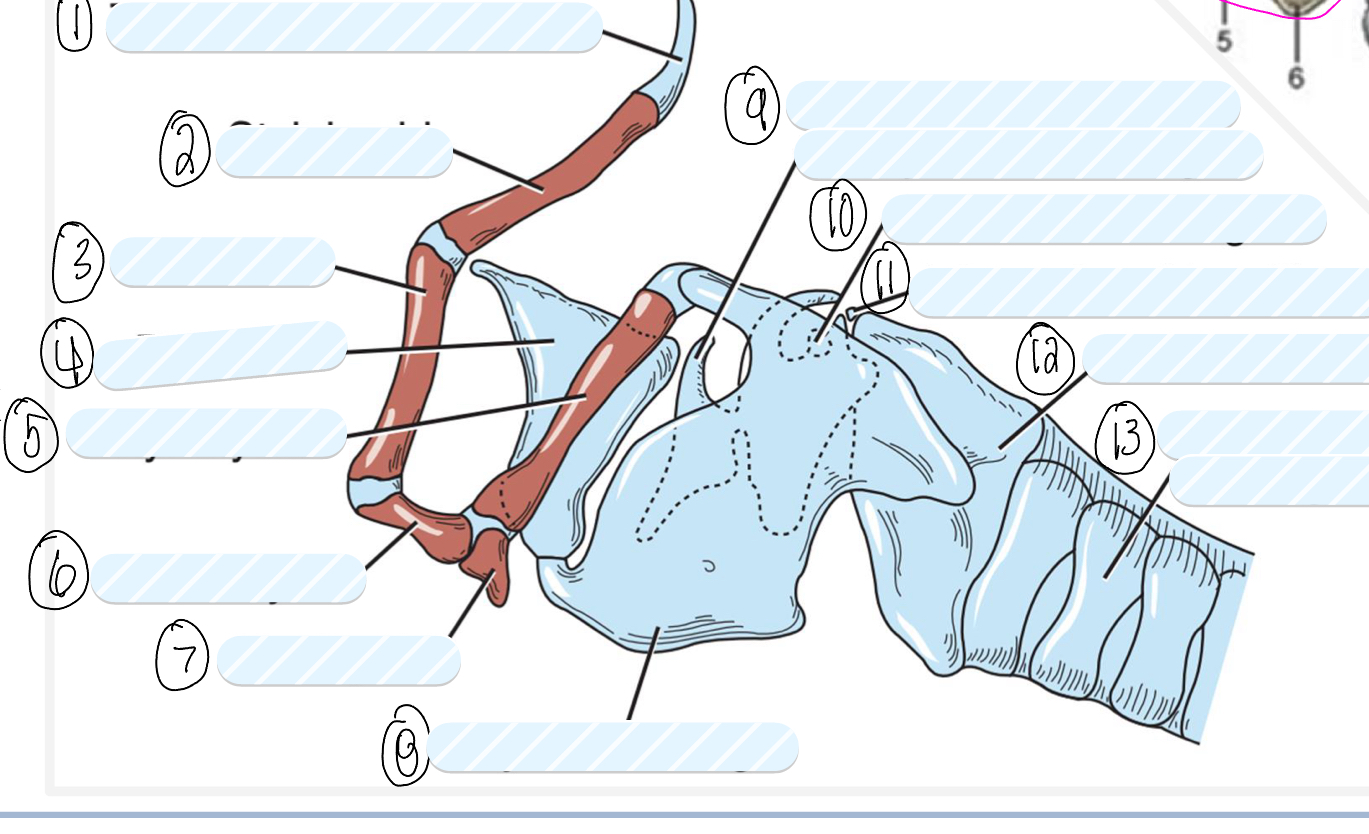
what is 4?
epiglottis
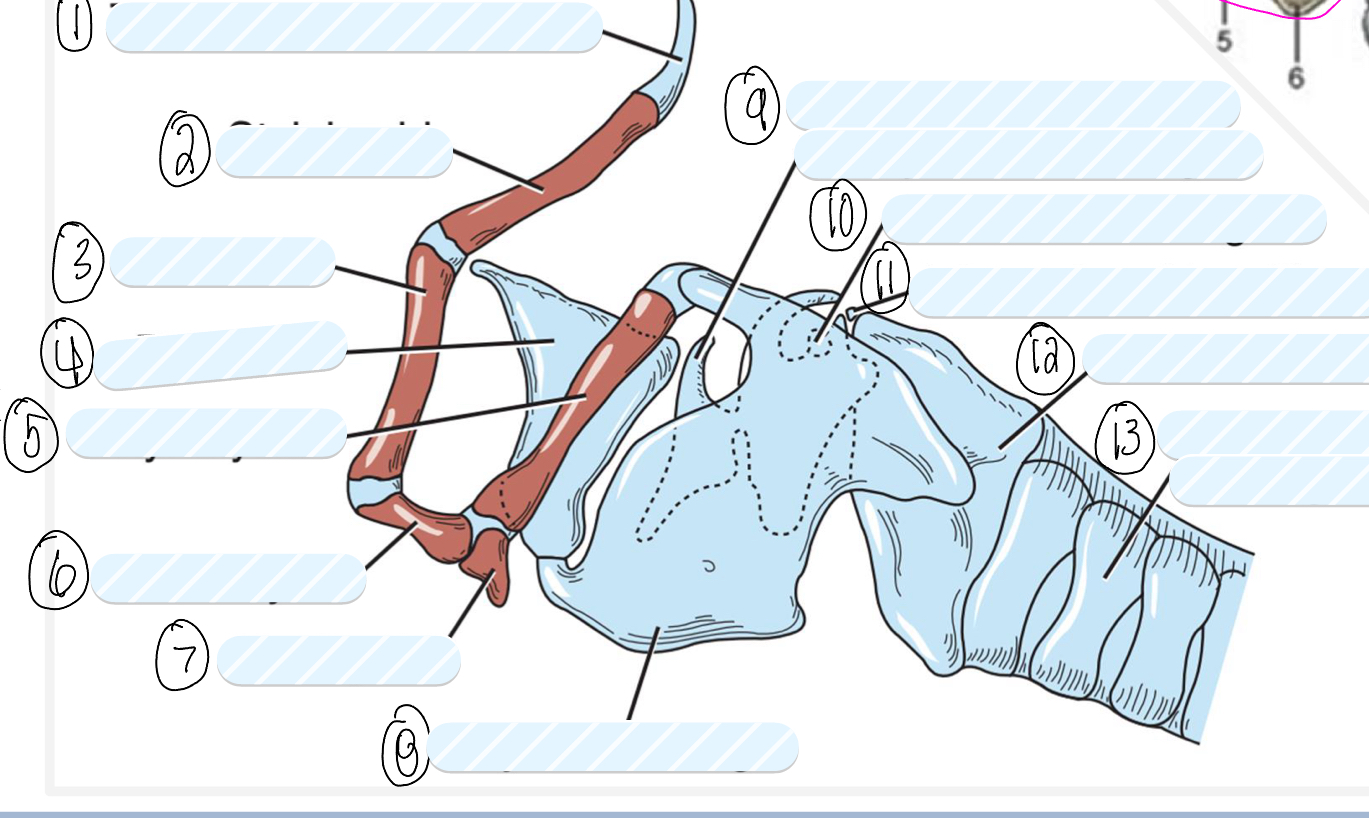
what is 5?
thyrohyoid
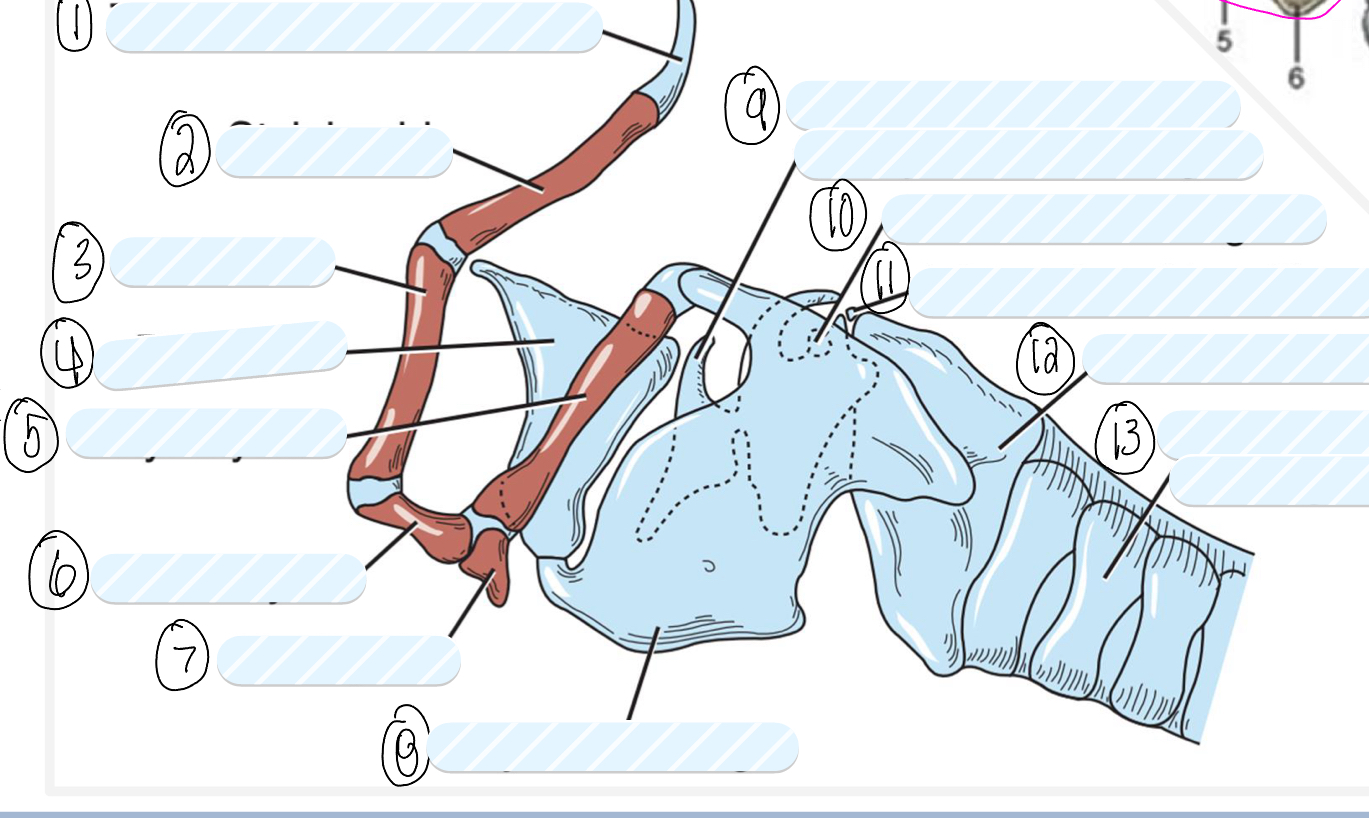
what is 6?
ceratohyoid
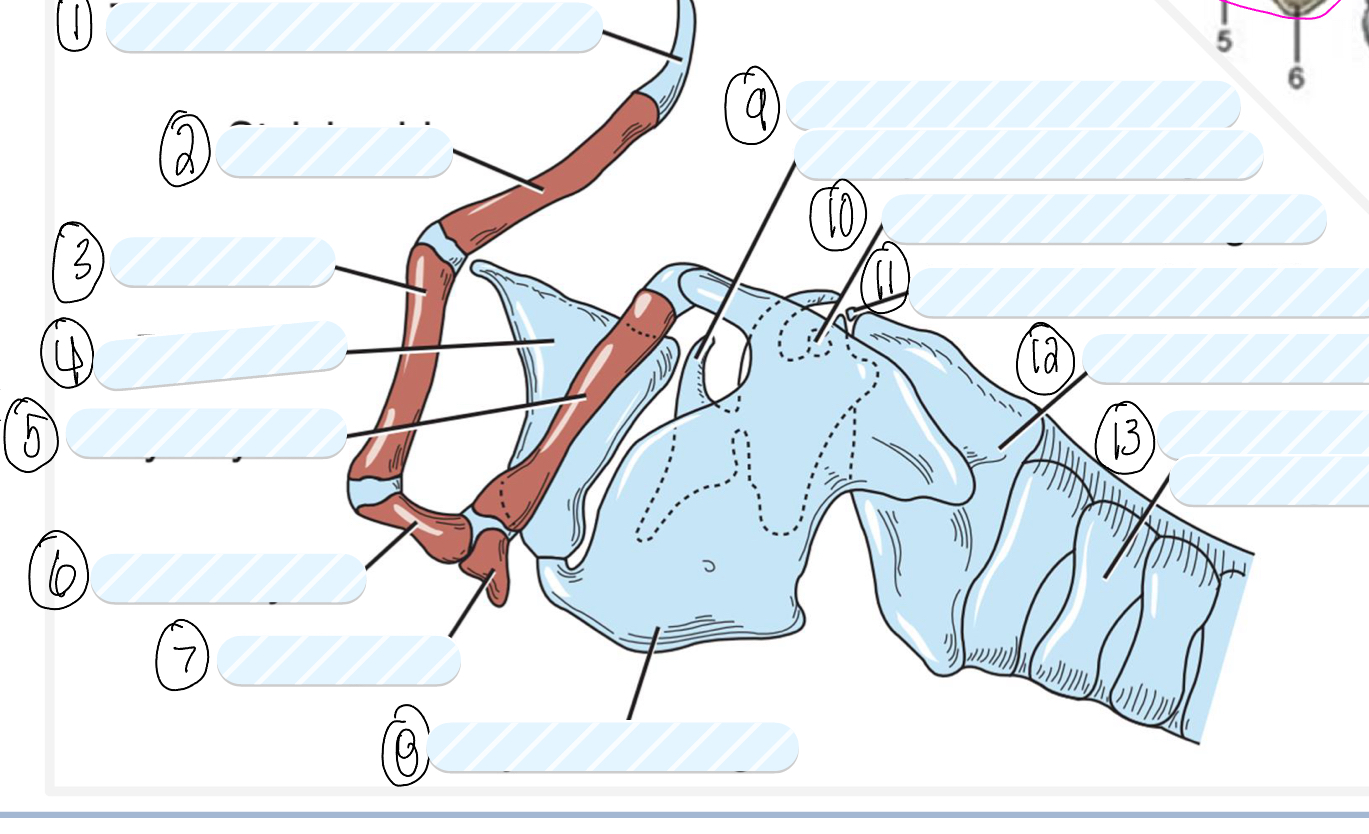
what is 7?
basihyoid
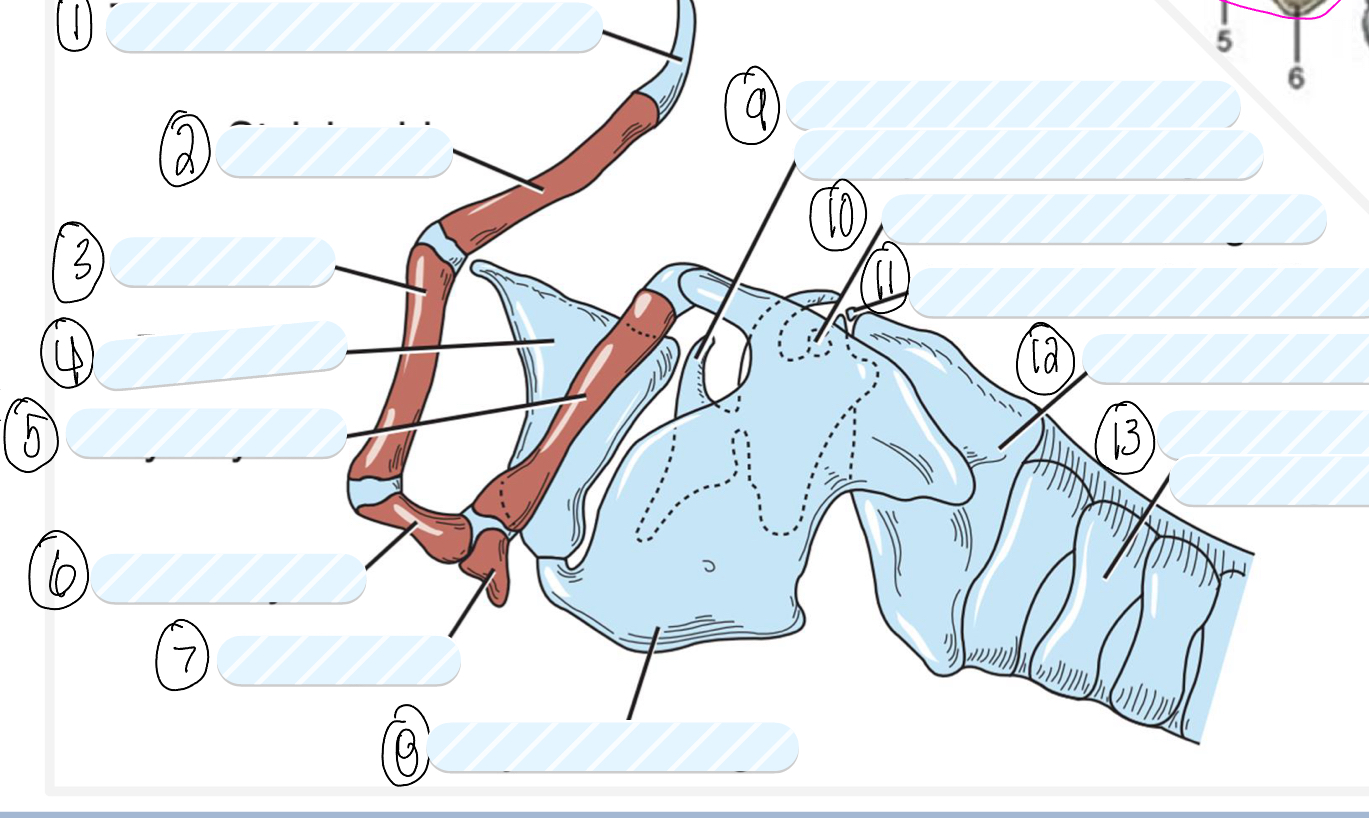
what is 8?
thyroid cartilage
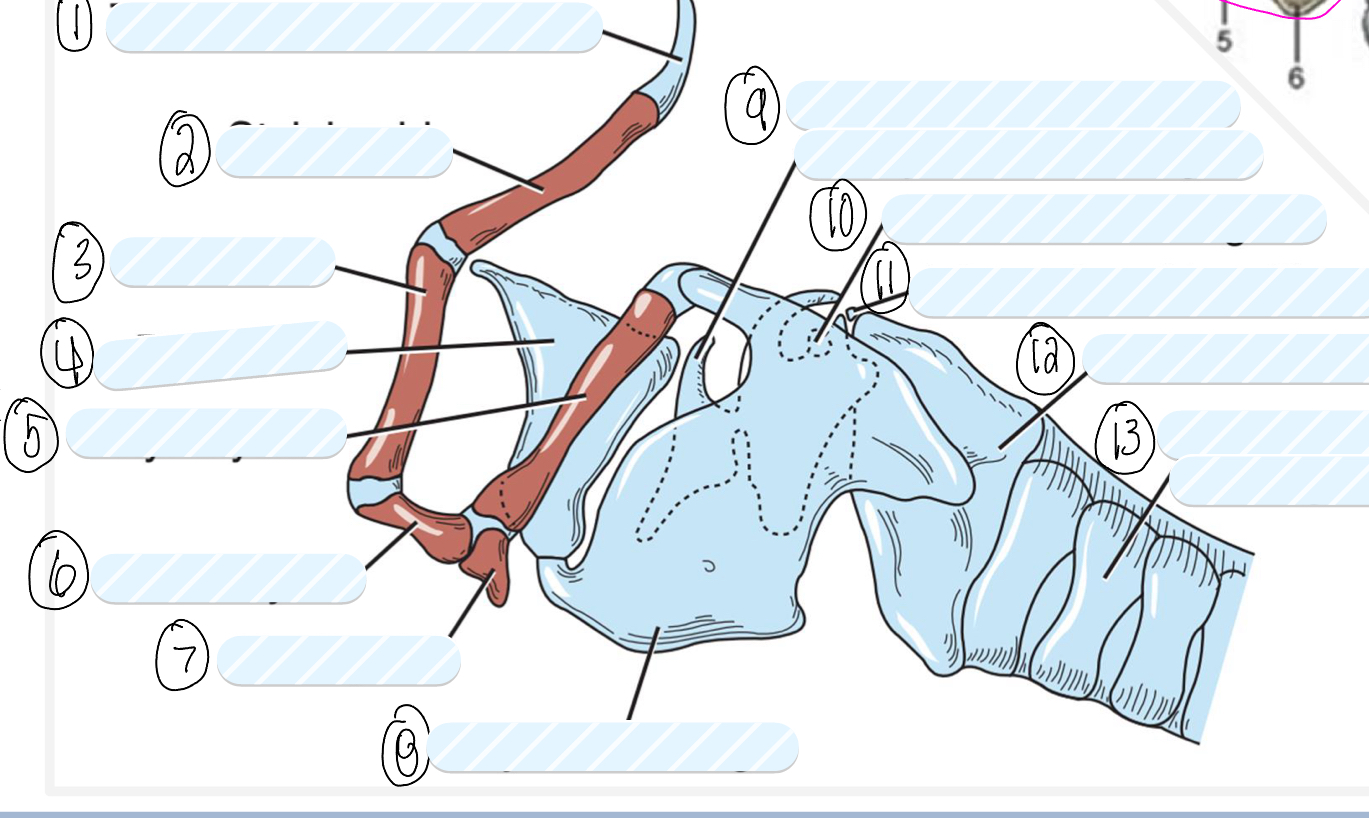
what is 9?
cuneiform process of arytenoid cartilage
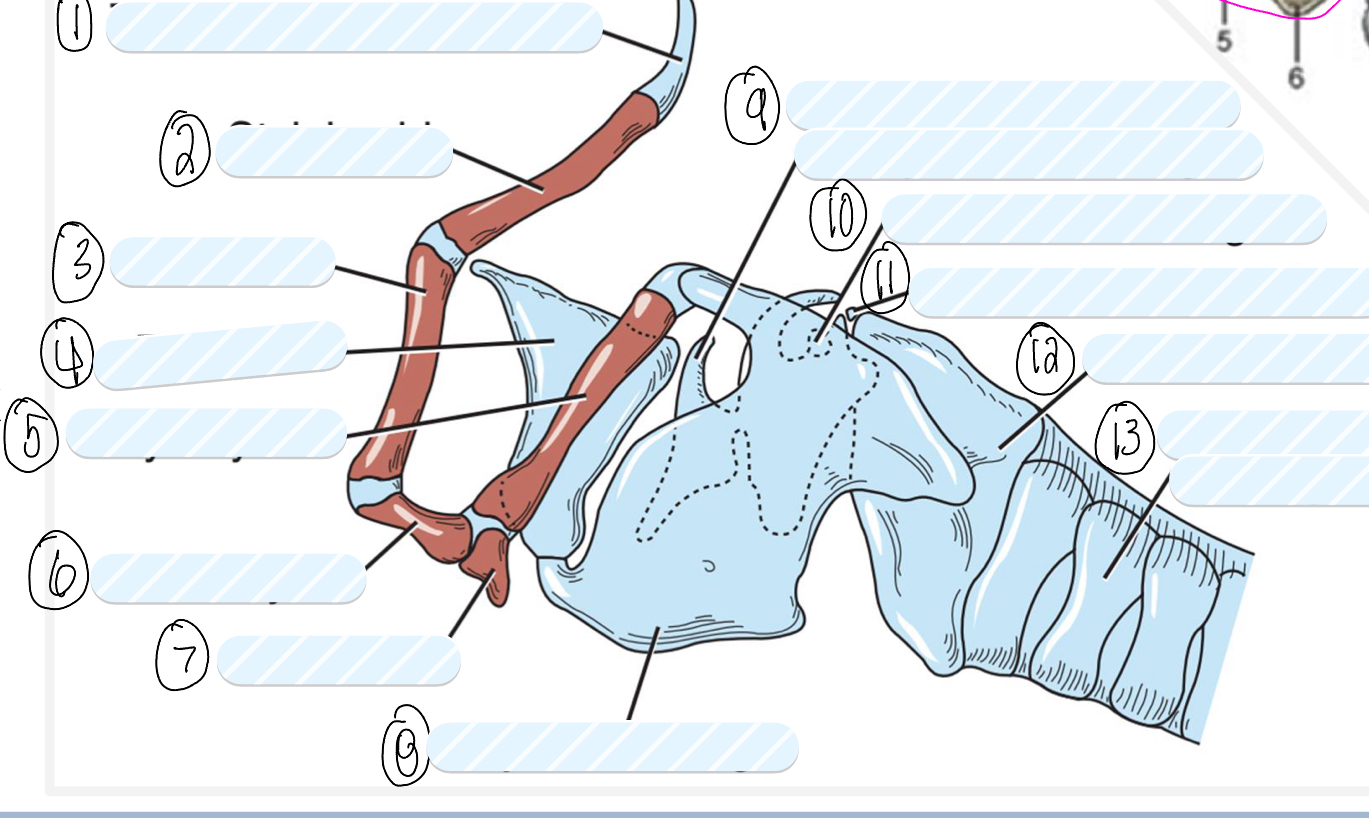
what is 10?
sesamoid cartilage
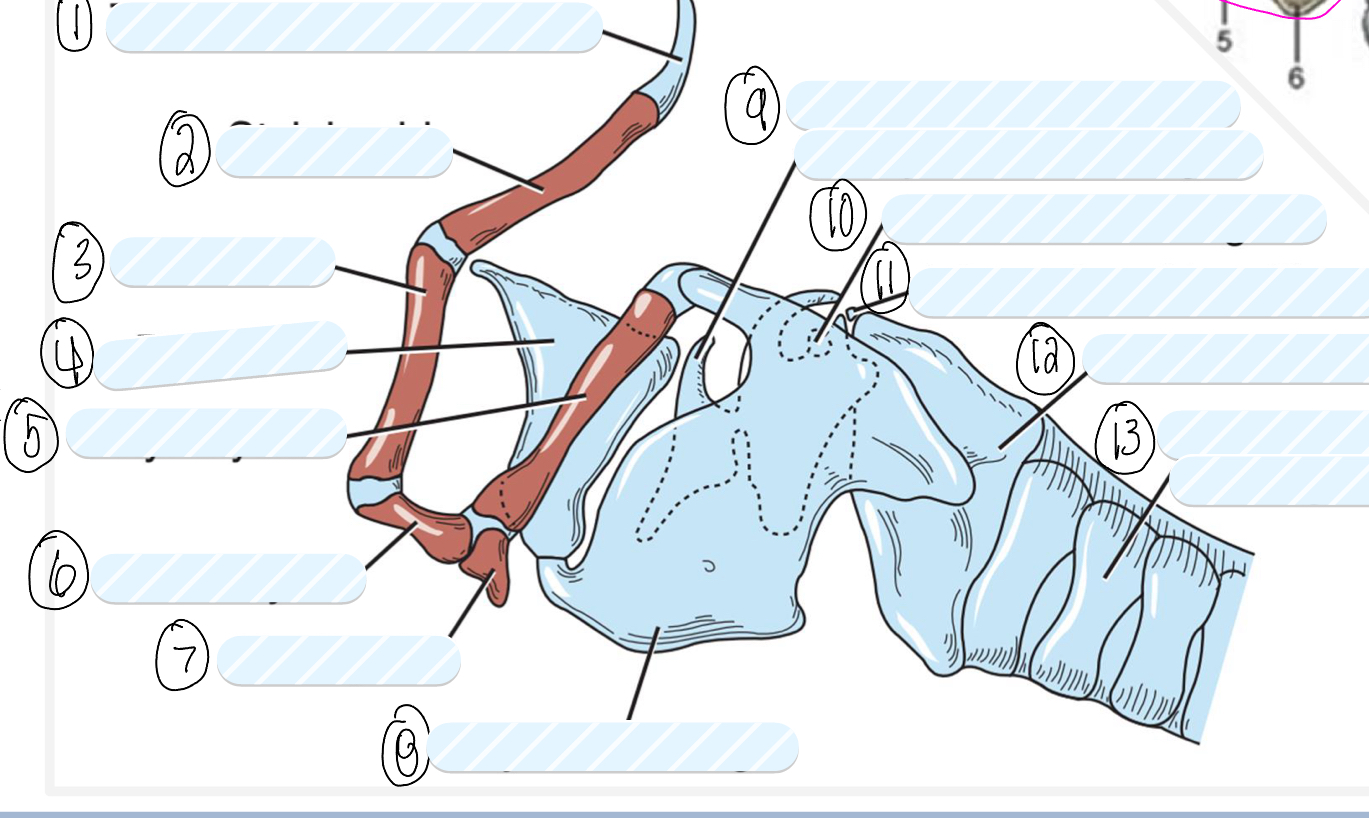
what is 11?
interarytenoid cartilage
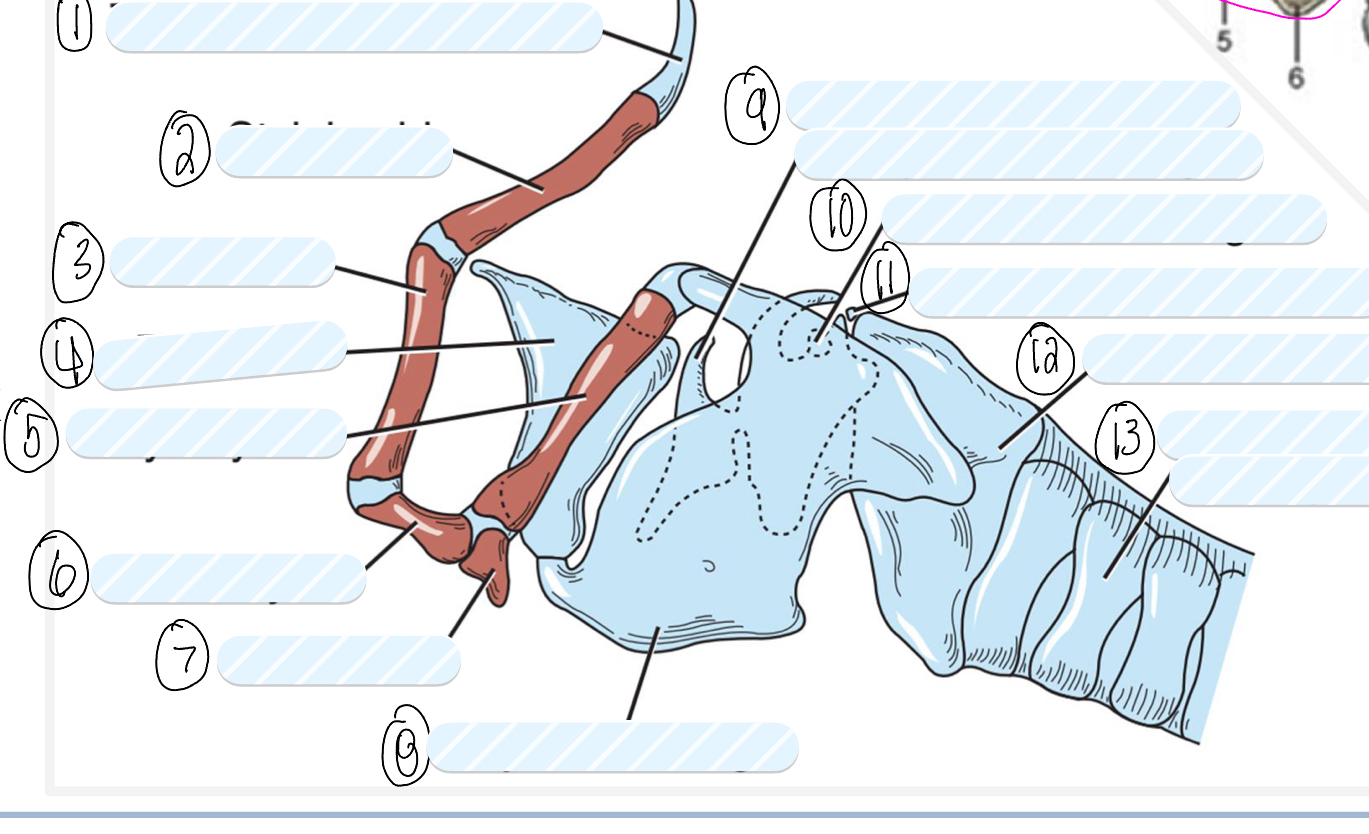
what is 12?
cricoid cartilage
which direction is the larynx pulled during contraction?
backwards
list the extrinsic muscles of the larynx
sternothyroideus muscle
thyrohyoideus muscle
hyoepiglotticus muscle
cricopharyngeus muscle
thyropharyndeus muscle
thyrohyoid articulation
thyrohyoid bone will attache to thyrohypoid cartilage
cricothyroid articulation
caudal horn of thyroid cartilage will attache with little lateral aspect of cricoid cartilage
cricoarytenoid articulation
caudal end of arytenoid cartilage will connect to cranial edge of cricoid cartilage
what is the function of the sternothyroideus muscle?
move larynx backward with cranial nerve 11
what is the function of the thyrohyoideus muscle?
move larynx forward (hypoglossal nerve (12))
what is the function of the hyoepiglotticus muscle?
move larynx forward (hypoglossal nerve (12))
what is the function of the cricopharyngeus muscle?
connect larynx and laryngopharynx
constricts laryngopharynx (vagus nerve + CN 12)
what is the function of the thyropharyngeus muscle?
constricts laryngopharynx and assists in swallowing (vagus nerve + CN 12)
connect larynx and laryngopharynx
what is the only muscle that ABDUCTS arytenoid cartilage and opens glottic cleft?
cricoarytenoid dorsalis
cricoarytenoideus lateralis
an adductor of the vocal processes and thus NARROWS the glottis
thyro-arytenoideus
associated with the vocal and vestibular folds
what clinical condition involves paralysis of the laryngeal muscles on the left/right side only?
laryngeal hemiplegia
what are clinical signs of aryepiglottic fold collapse?
exercise intolerance and noise with exercise
what leads to aryepiglottic fold collapse in horses?
negative pressure in upper airways lead to collapse
tissue between the epiglottis and larynx pulled into the airway
laryngeal hemiplegia
degeneration of laryngeal branch of vagus nerve leads to neurogenic atrophy of cricoarytenoideus dorsalis muscle
what side is more common in horses for laryngeal hemiplagia?
left
what is the longest nerve in the body?
laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve
dorsal displacement. of the soft palette is seen in which species?
horses
what occurs physiologically in dorsal displacement of the soft palette?
soft palette lies over the epiglottic cartilage blocking the laryngeal inlet and airways
what are the effects of dorsal displacement of the soft palette?
respiratory distress and performance issues
what is the arrangement of the soft palette in the dog?
caudal margin of the soft palette just makes contact with the epiglottic cartilage
what is the arrangement of the soft palette in the horse?
soft palette always lies beneath the epiglottic cartilage
what can horses not do, due to the arrangement of their soft palette?
emesis (vomit)
mouth breath (they are obligate nasal breathers)
what is it called if paralysis of the laryngeal muscle only occurs on one side?
laryngeal hemiplegia
what is it called if paralysis of the laryngeal muscle occurs on both side?
laryngeal paraplegia
what forms the glottic cleft?
media, side-by-side arrangement of arytenoid cartilages
what closes the glottic cleft?
adduction of the arytenoid cartilages
what is the glottic cleft important for?
closing the entrance to the trachea
normal smooth inspiration and expiration of breath
what opens the glottic cleft?
abduction of the arytenoid cartilage
what is the ONLY muscle that opens the glottic cleft?
cricoarytenoideus dorsalis
what are the components of the larygneal cavity?
vestibule
glottis
infraglottic space
what is the function of the laryngeal cavity?
receives sensory innervation from cranial and caudal (recurrent) laryngeal nerves
laryngeal ventricles
lateral extension/blind sacs of the lumen
what is not present in the cat in the laryngeal cavity?
left laryngeal ventricle
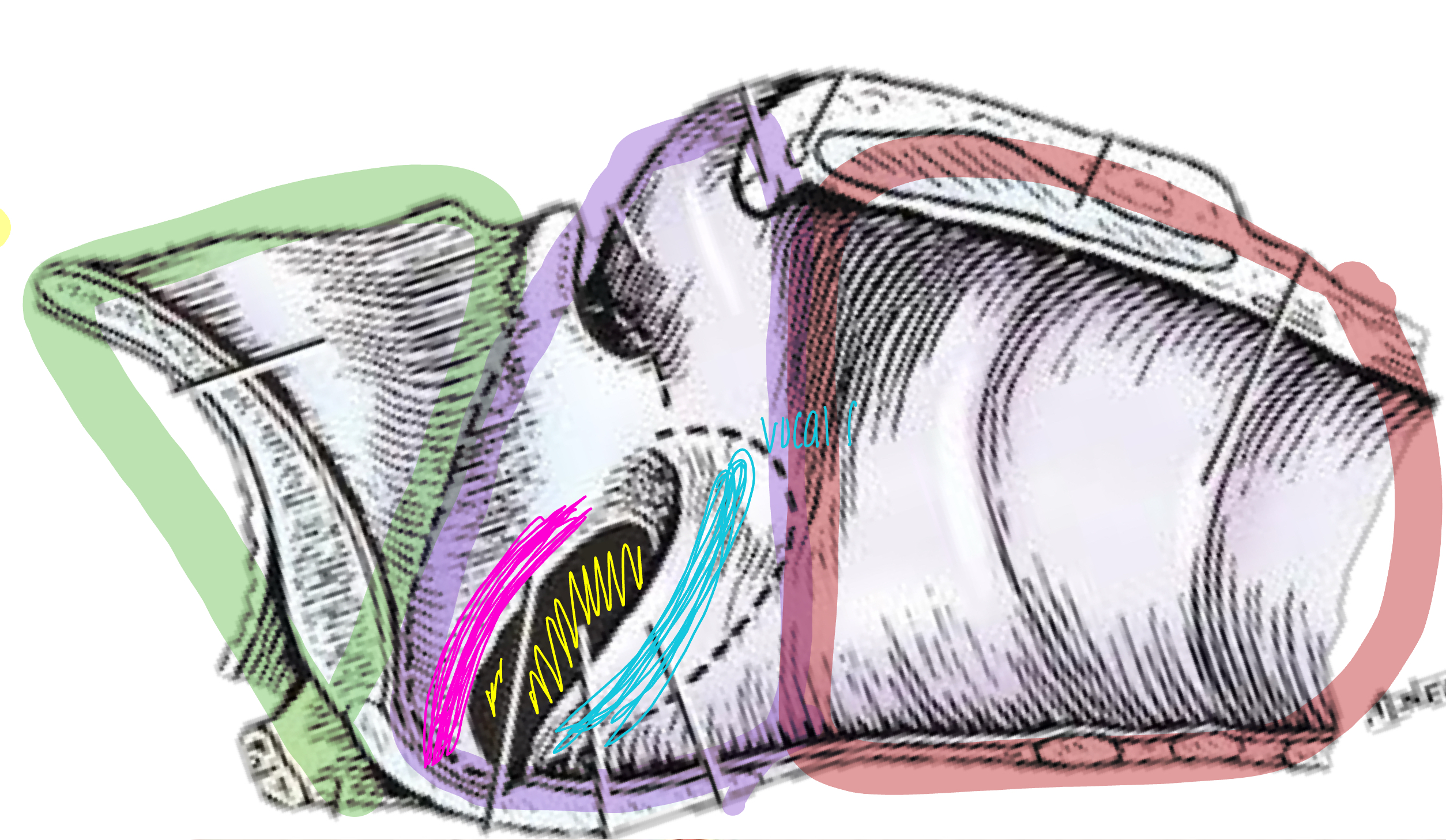
what is the green shaded area?
vestibule of laryngeal cavity
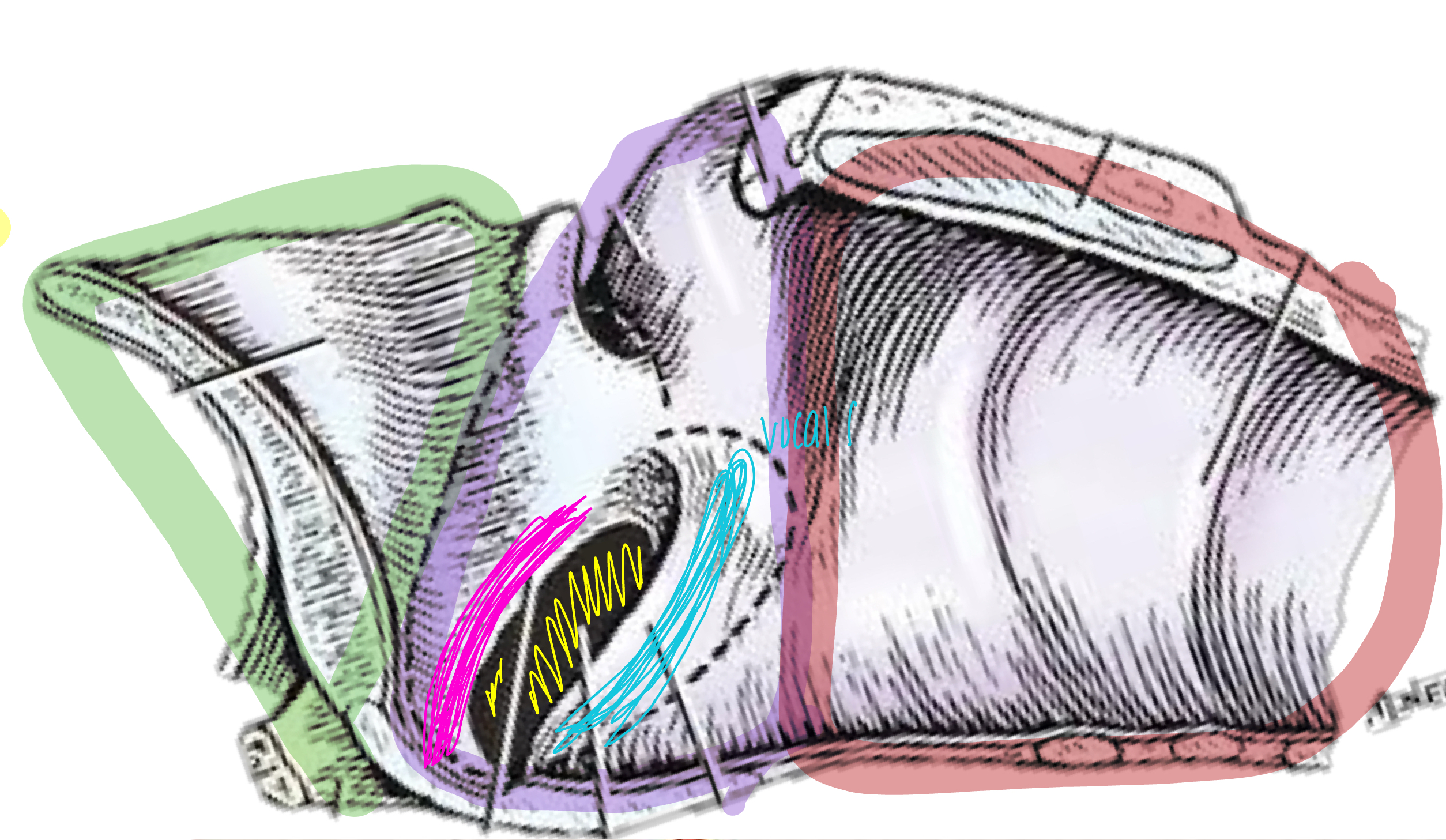
what is the purple shaded area?
glottis of laryngeal cavity
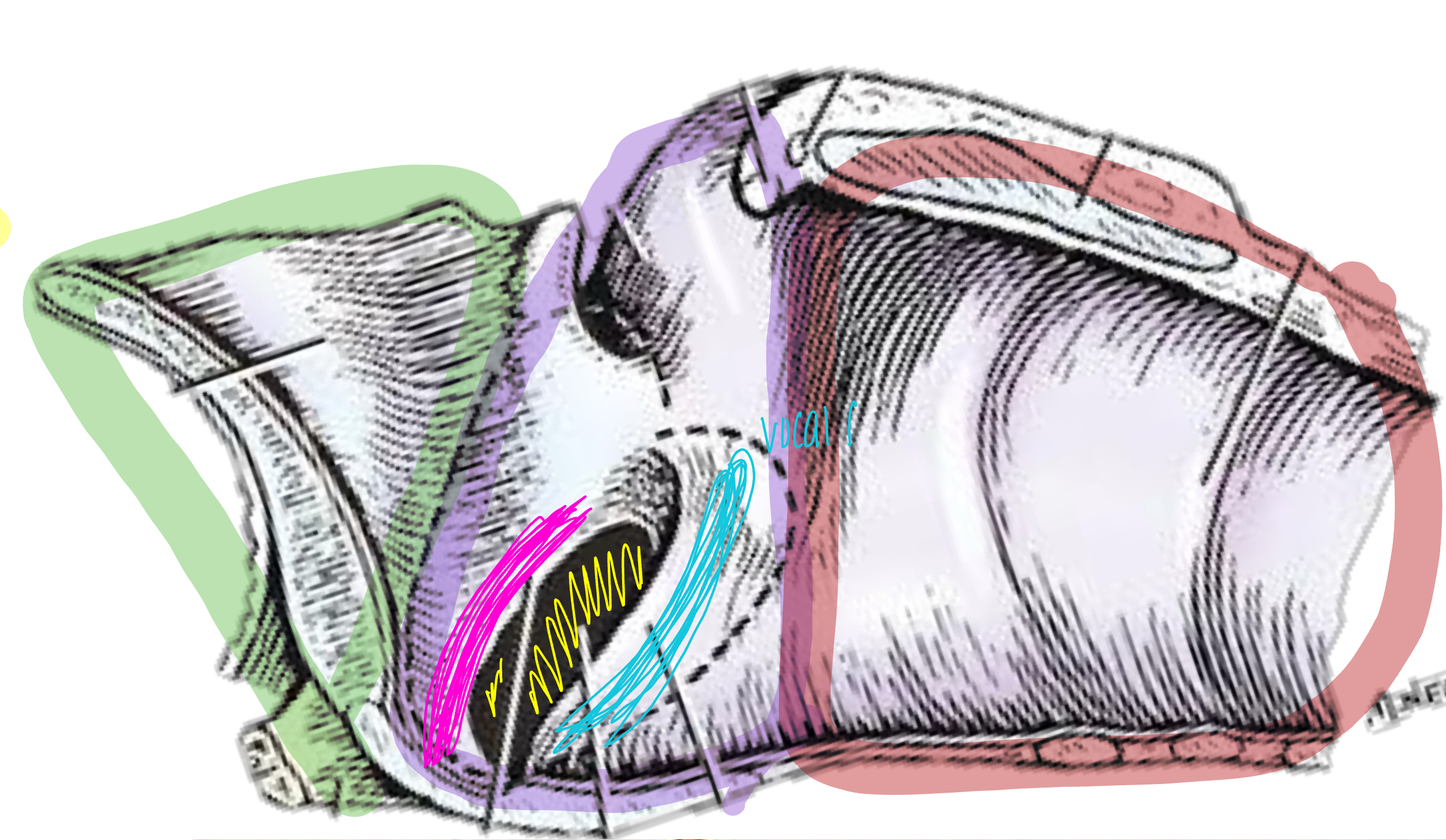
what is the pink line referring to?
vestibular fold of laryngeal cavity

what is the blue line referring to?
vocal fold
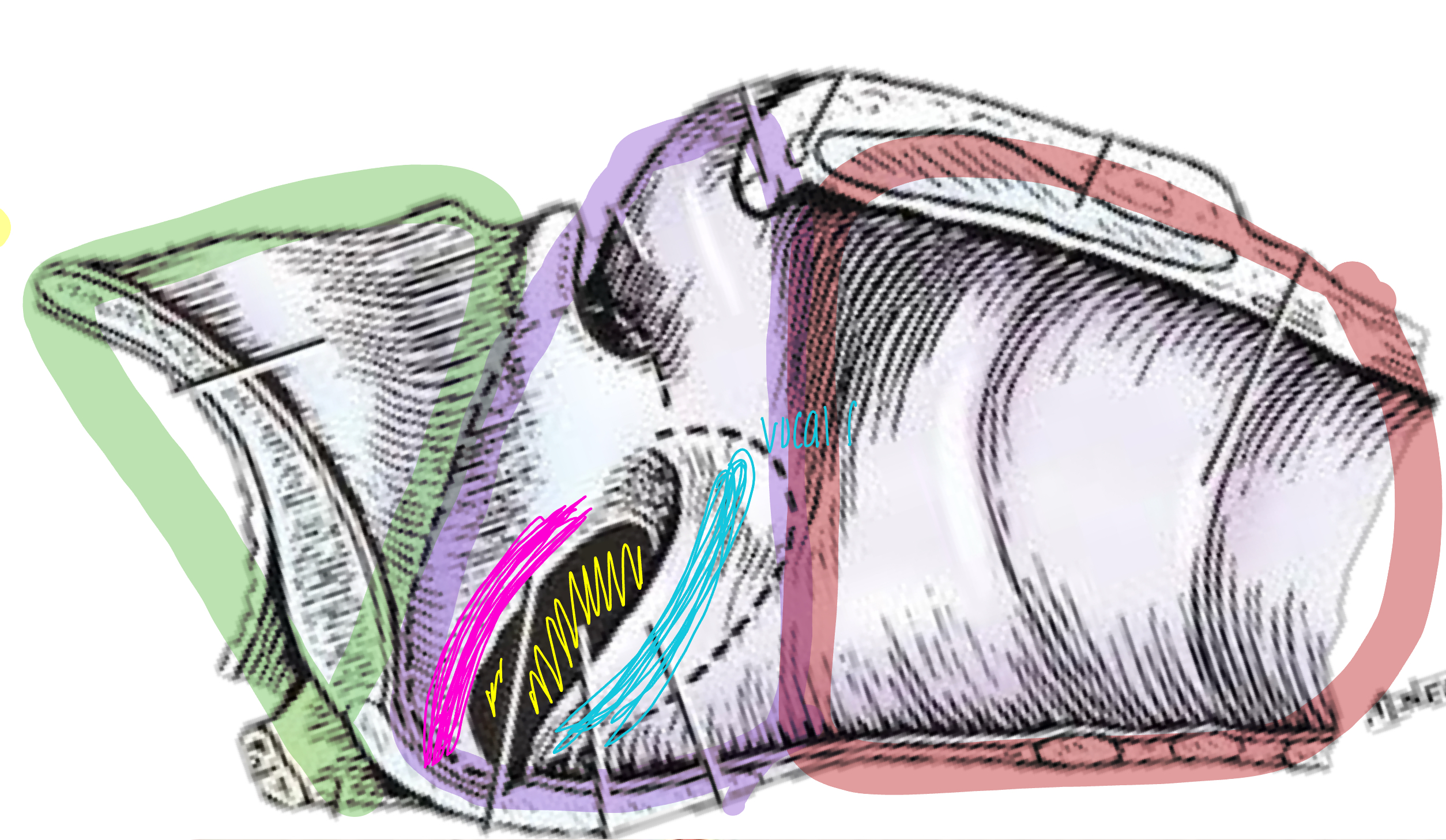
what is the red shaded area referring to?
infraglottic space
which opening can be closed by backward closing of the epiglottic cartilage?
aditus laryngis
what is the only laryngeal intrinsic muscle that is innervated by the cranial laryngeal nerve?
cricothyroid muscle