Psych-module 22 & 23 memory: encoding, storage, retrieval
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is memory?
the persistence of learning over time through the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information
How do we measure memory retention?
recall: a measure of memory where the person retrieves information learned earlier as on a fill in the blank test
recognition: a measure of memory where the person identifies information previously learned as on a multiple choice test
relearning: a measure of memory that assesses the amount of time saved when learning material again
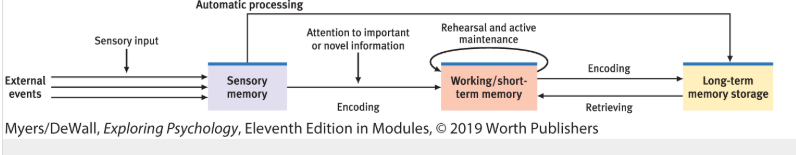
What are the three processes involved in the information processing model?
encoding
storage
retrieval
Connectionism information processing model
focuses on parallel processing which means the processing of multiple aspects of a problem simultaneously
ex. views memories as products of interconnected neural networks
What are the three memory processes in the Atkinson-Shiffrin model?
sensory memory
short-term memory
long-term memory
Sensory memory
The first step in recording to-be-remembered information
brief and fleeting
records sensory information
Short-term memory
The second step where we process information into short term memory
holds a few items briefly
30 seconds
quickly forgotten
ex. remembering a phone number just long enough to dial it
Long-term memory
the final step that occurs after we have encoded information
permanent and limitless storage
knowledge, skills, experience
used for later retrieval
Working memory
occurs during short-term memory and involves newer understanding of the short-term memory through conscious and active processing of the information that often involves updating the information
ex. these short-term memories can become long-term
ex. playing chess
Explicit memory
conscious
effortful processing
declarative memory
memory of facts and experiences
Implicit memory
“how to” memory
automatic processing
retention of learned skills
unconscious
nondeclarative memory
ex. how to ride a bike
Sensory memory
feeds our active working memory, recording momentary images of scenes or echoes of sounds through either iconic or echoic means
ex. occurs through the senses
Iconic memory
type of sensory memory
anything related to visual stimulation
lasting for less than a second
Echoic memory
type of sensory memory
anything related to auditory information
lasting for 30 seconds
What is the short-term memory capacity?
holds a few items briefly (such as the seven digits of a
phone number while dialing) before the information is stored or forgotten
Without distraction, how much information can we typically recall?
seven digits or about six letters or five words
Spacing effect
encoding is more effective when it is spread over time
Distributed practice
a method that produces better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice
ex. study is spread out over time
Massed practice
an ineffective method that produces speedy short-term learning and feelings of confidence
ex. cramming for an exam
Testing effect
enhanced memory occurs after retrieving, rather than simply re-reading information
What are the levels of processing information?
shallow processing
deep processing
Shallow processing
encodes on both a basic (word’s letters) and intermediate (word’s sound) level
involves repeating information
Deep processing
encodes semantically based on the word’s meaning
has better retention and involves understanding the information and making comparisons between concepts
Self-reference effect
the tendency for good recall of information we can relate too
What information do we encode more easily?
information that is meaningful or related to our experiences
Can we fill more information within our brains if we discard others?
no, long-term storage of memories is essentially limitless
How does the brain store memories?
the brain distributes the components of a memory across a network of locations in the brain
How are the brain cells involved in memories?
some of the cells that fired when we experienced something fire again when we recall it
What are the two explicit types of memory involved in memory storage?
episodic memory
semantic memory
Episodic memory
a type of explicit memory
memory of personally experienced events
ex. related to episodes within our life
Semantic memory
type of explicit memory
memory of facts and general knowledge
ex. not related to specific events i.e. how old you are
Hippocampus
registers and temporarily holds elements of explicit memories before moving them to other brain regions for long-term storage.
The cerebellum
plays important role in forming and storing implicit memories created by classical conditioning
Basal ganglia
brain structures involved in implicit memories like motor movement and formation of our procedural memories for skills
Infantile amnesia
we cannot remember any information from the first three years of our lives because our hippocampus was not fully developed
Flashbulb memories
clear memories of emotionally significant moments or events that occur via emotion triggered hormonal changes
ex. vivid and almost picture-like
Memory consolidation
neural storage of long-term memories
ex. the process by which short-term memories become long-term memories
Amygdala
the brain center that is triggered by excitement or stress to engage memory
ex. engaged by emotions
Which type of memories are generally shared by a generation?
flashbulb memories
Memories are held in storage by what?
web of associations
What are the best retrieval cues?
those that come from associations formed at the time a memory was encoded
Priming
activation, often unconsciously, of particular associations in memory
ex. dropping cues that prepare your brain to respond in a certain way
ex. hearing the word yellow and when asked to name some fruit, you say a banana
What are the different memories for retrieval cues?
context dependent
state dependent
Context dependent memory
involves improved recall of information when the context is the same for both encoding and retrieval
ex. context matches
State dependent memory
emotions that accompany good or bad events become retrieval cues
ex. you will remember information easier when you are experiencing the same emotions as you were when memory was formed
Mood congruent memory
the tendency to recall experiences that are the same as one’s current good or bad mood
ex. girlfriend remembers boyfriend cheating when she is in bad mood
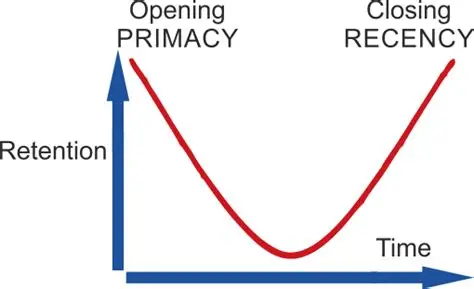
Serial position effect
our tendency to recall best the last (recency effect) and first (primacy effect) items within a list