Chapter 16: Signaling Pathways That Control Gene Expression in BE 359
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
cell surface, signal transduction
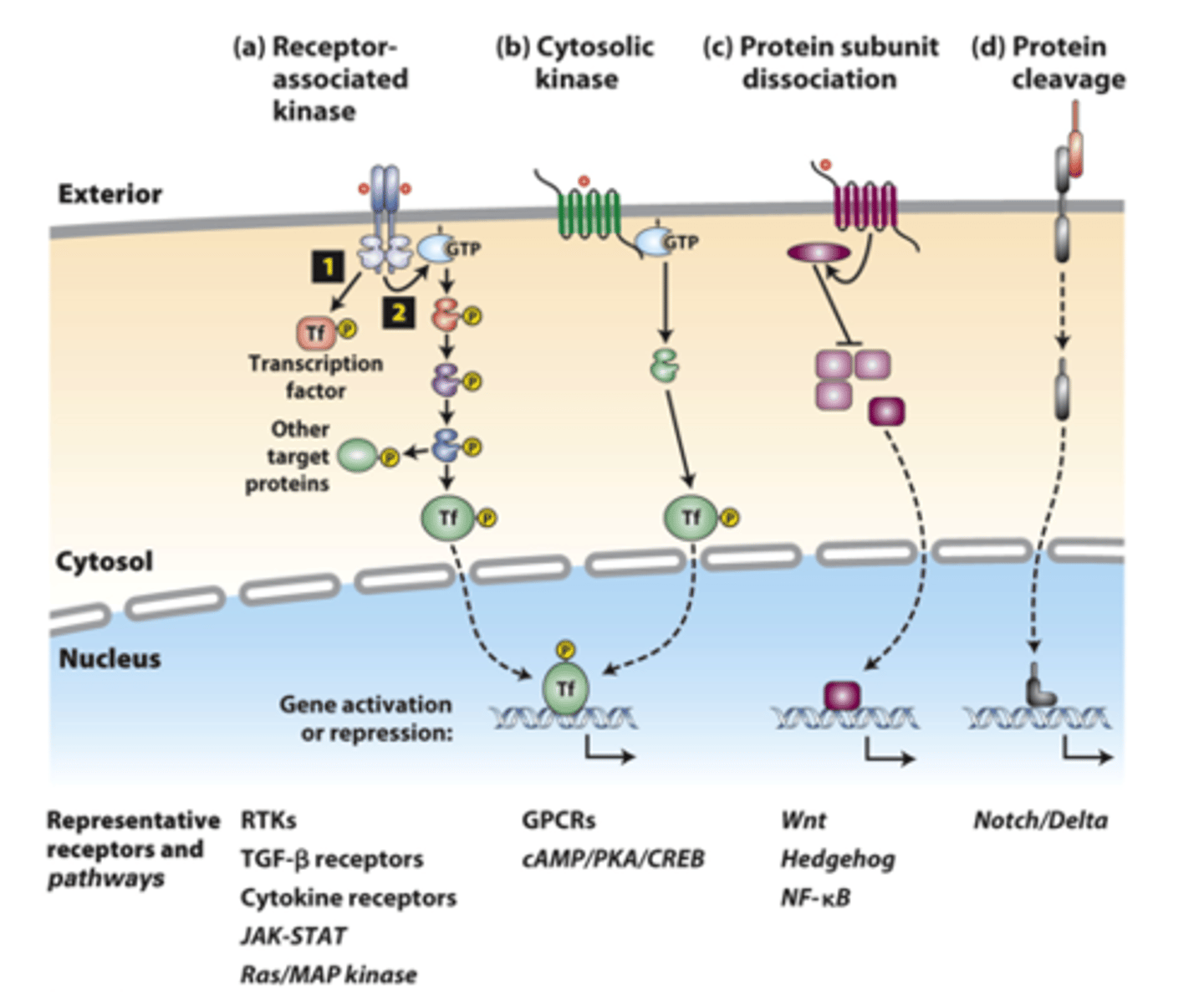
several common types of _______-__________ receptors and ___________ ____________ pathways
evolutionarily
_______________ conserved signaling pathways can induce cell-specific effects
cytosolic domains
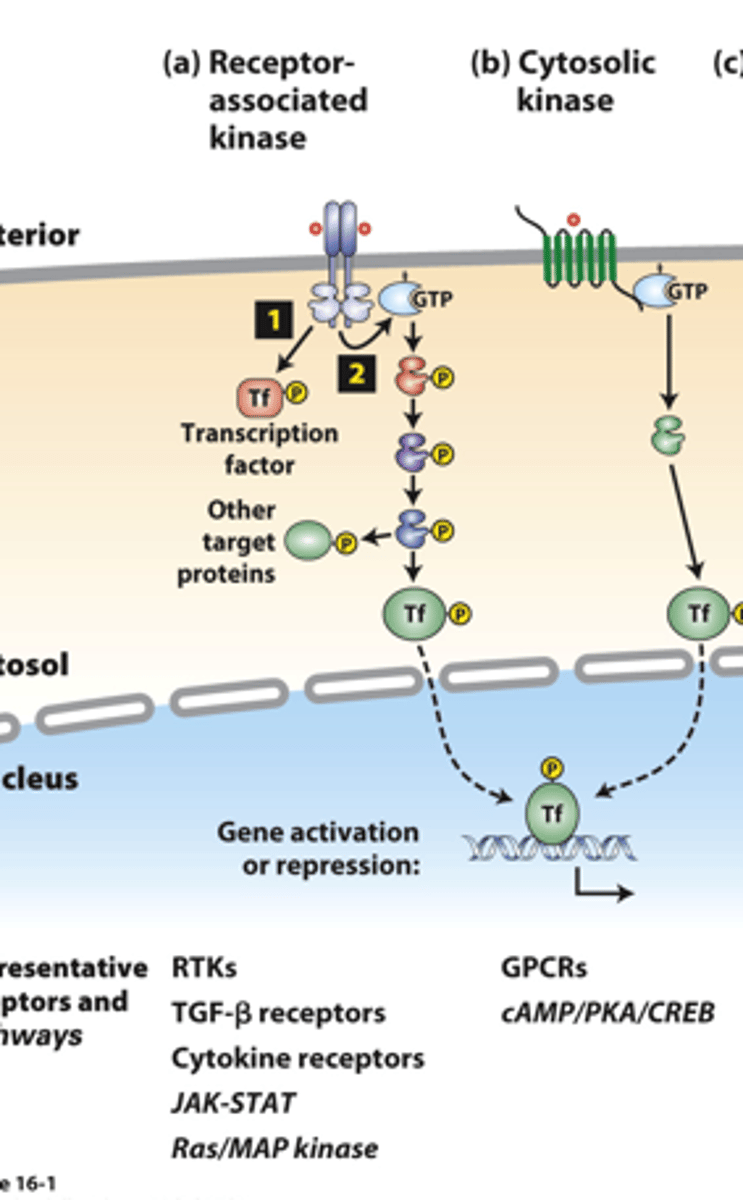
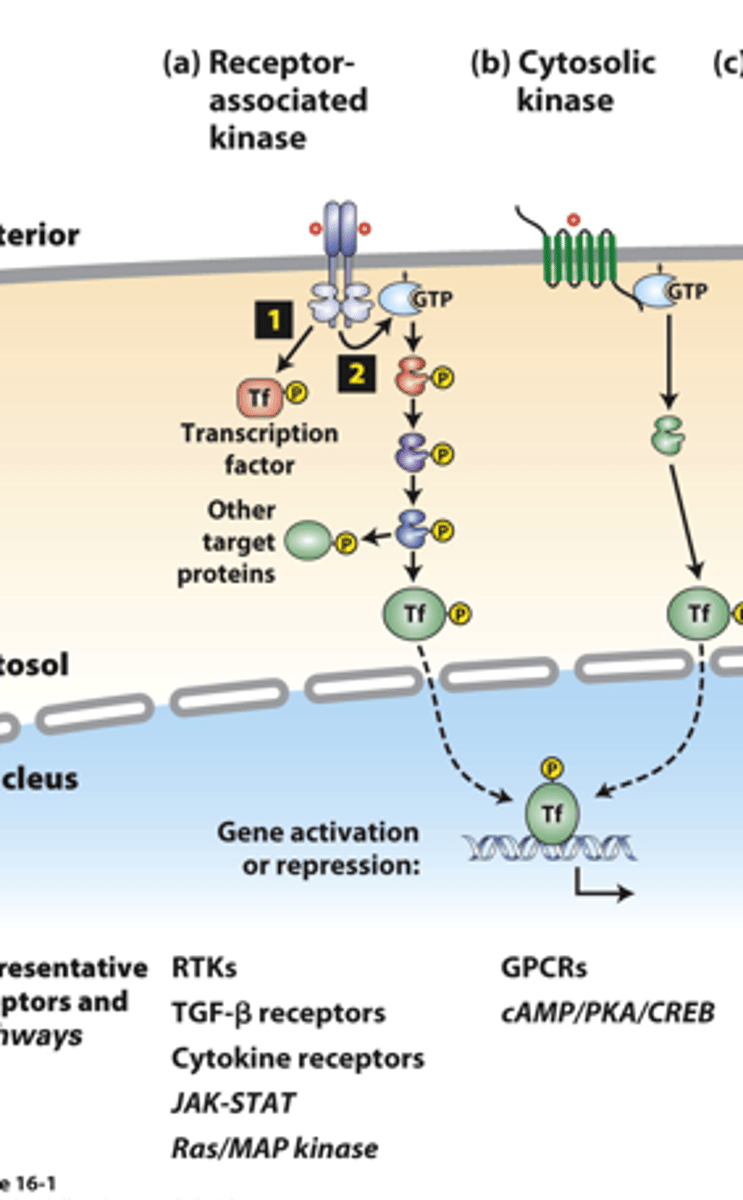
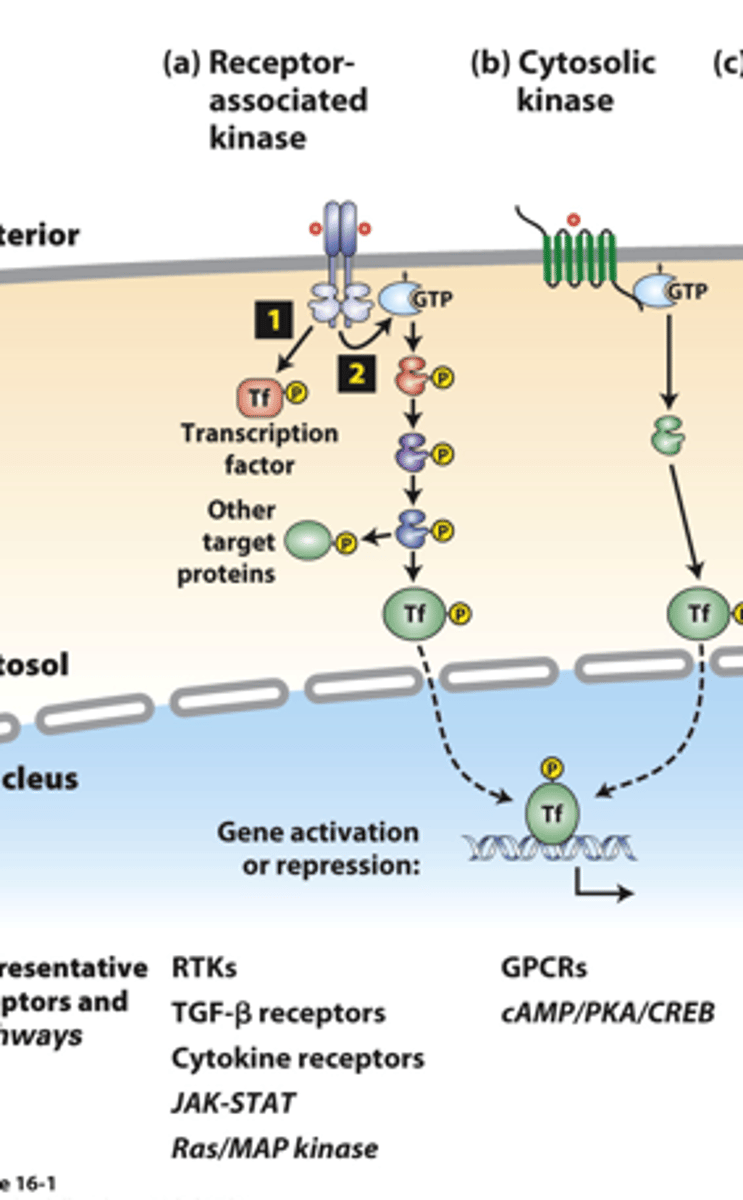
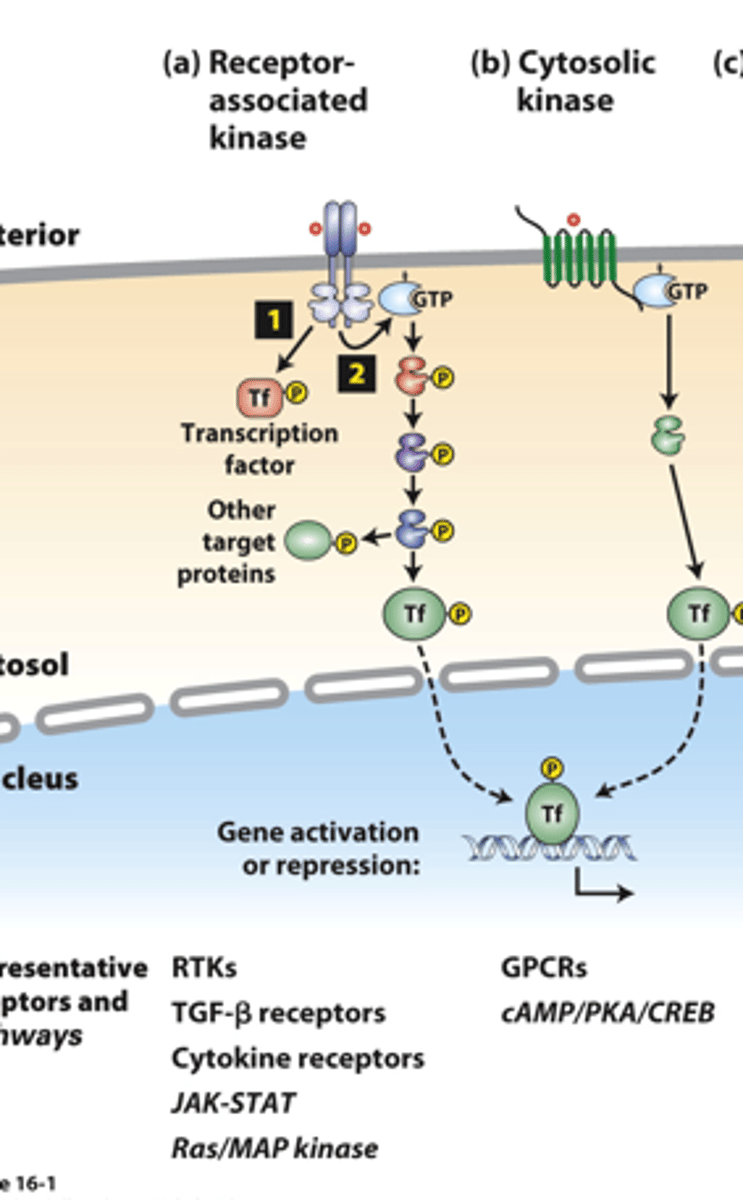
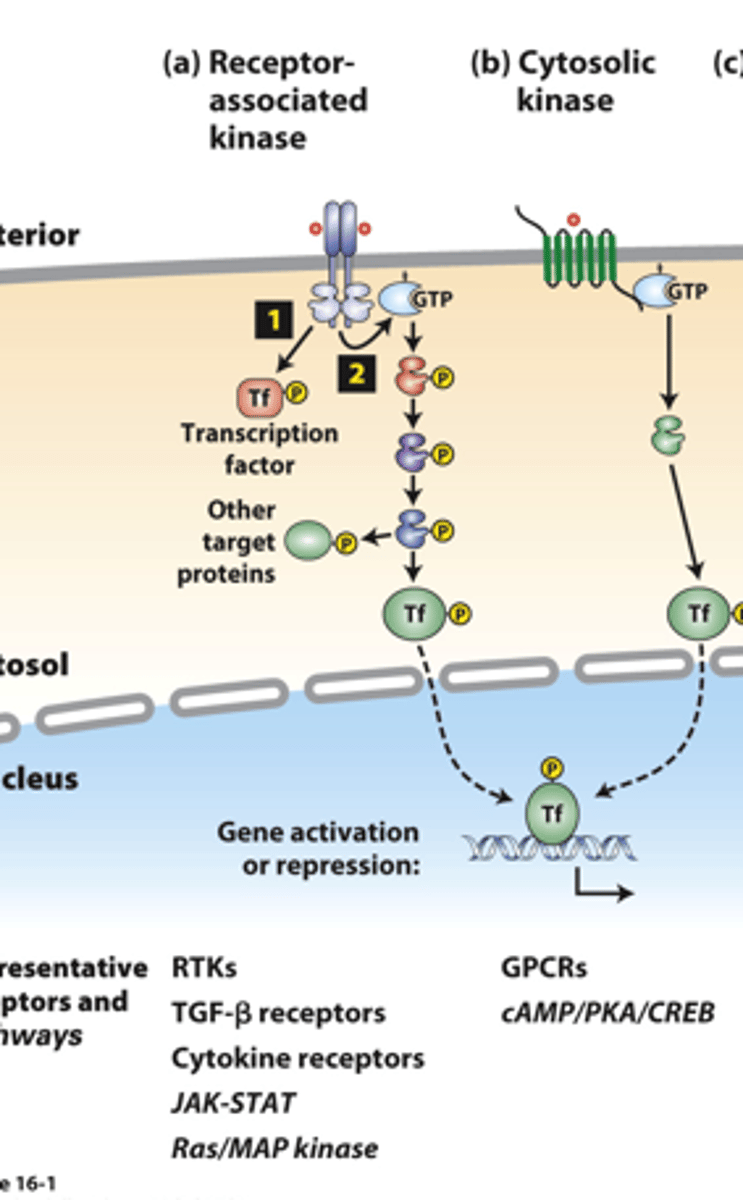
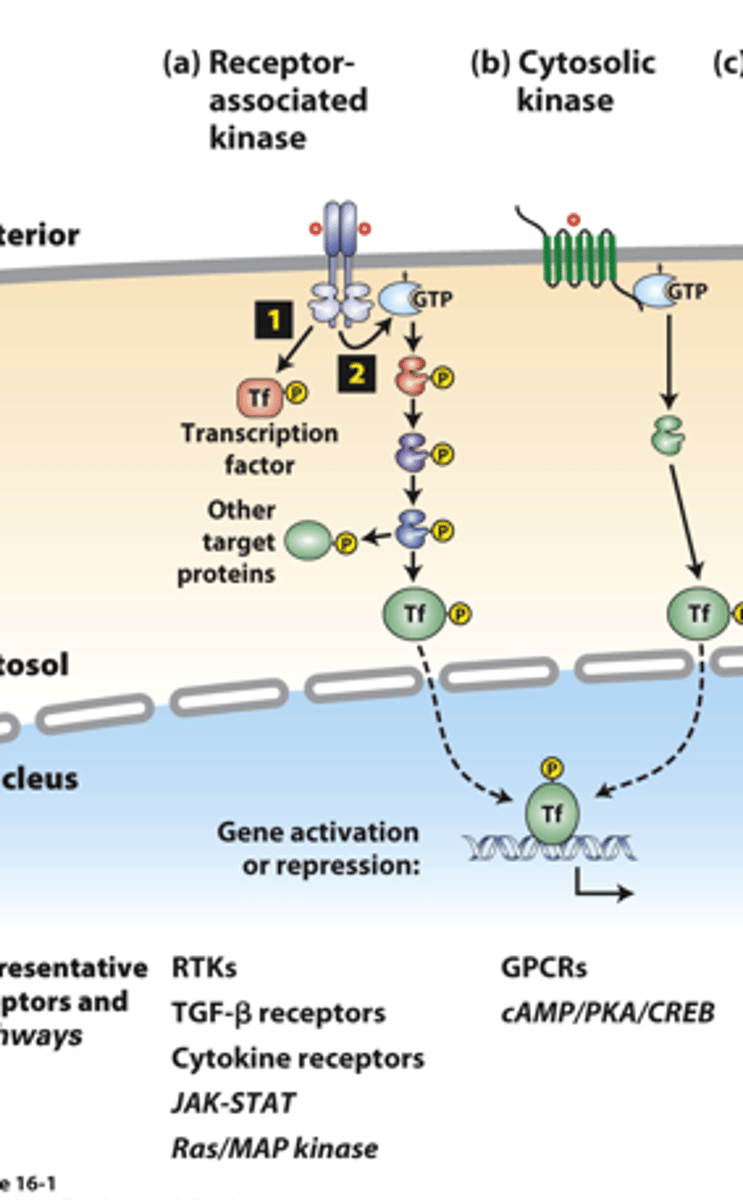
receptor associated kinases: many receptor __________ ___________ are protein kinases or tightly associate with a cytosolic kinase
ligand
receptor associated kinases: (1) __________ binding causes receptor dimerization which activates kinase activity
directly
receptor-associated kinases: (1) kinases ___________ phosphorylate and activate transcription factors or other signaling proteins
GTP binding
receptor-associated kinases: (2) many receptors also activate small ______-____________ "switch" proteins such as Ras
Ras
receptor-associated kinases: (2) the _______ signal transduction pathway and others activate a kinase cascade, in which one kinase phosphorylates and thus activates (or occasionally inhibits) the activity of multiple copies of another kinase for signal amplification
transcription factors
receptor-associated kinases: (2) G-protein pathway kinases phosphorylate multiple protein targets, including cell type-specific _________________ ___________
seven
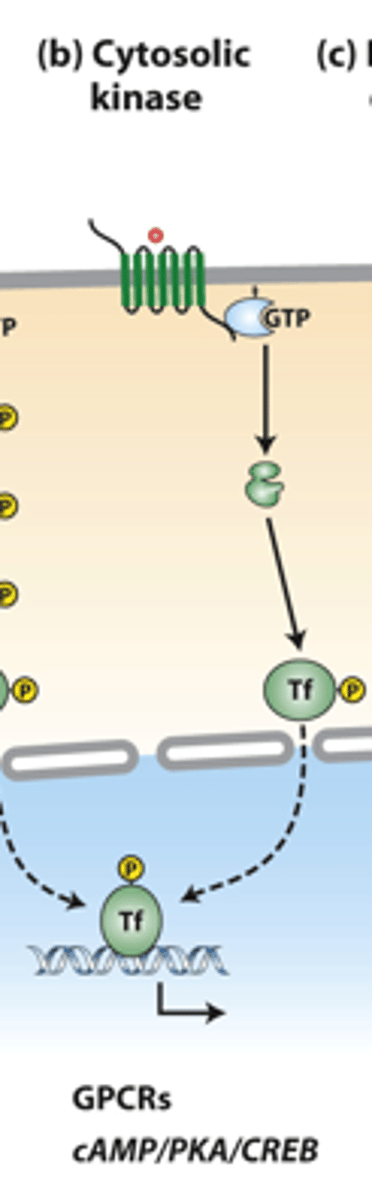
cytosolic kinases: ___________ membrane-spanning segments receptors activate GTP-binding Galpha proteins
kinases
cytosolic kinases: Galpha-GTP activates specific ___________ or other signaling proteins
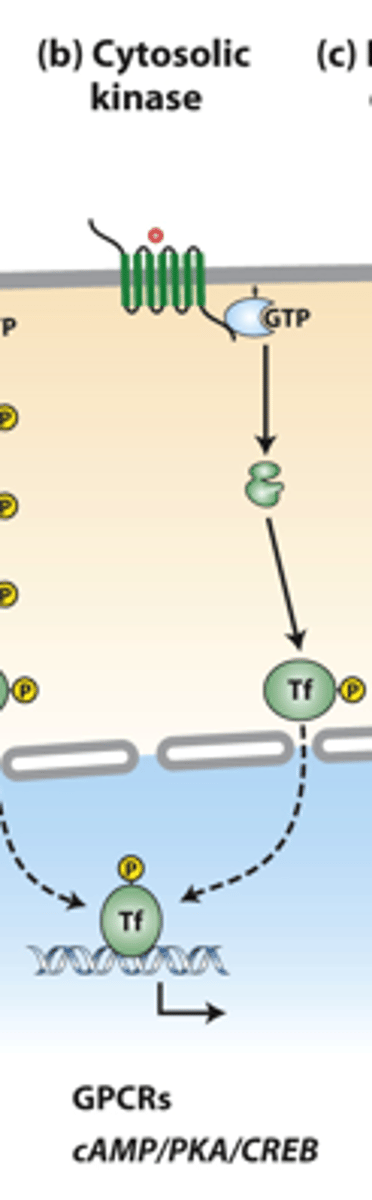
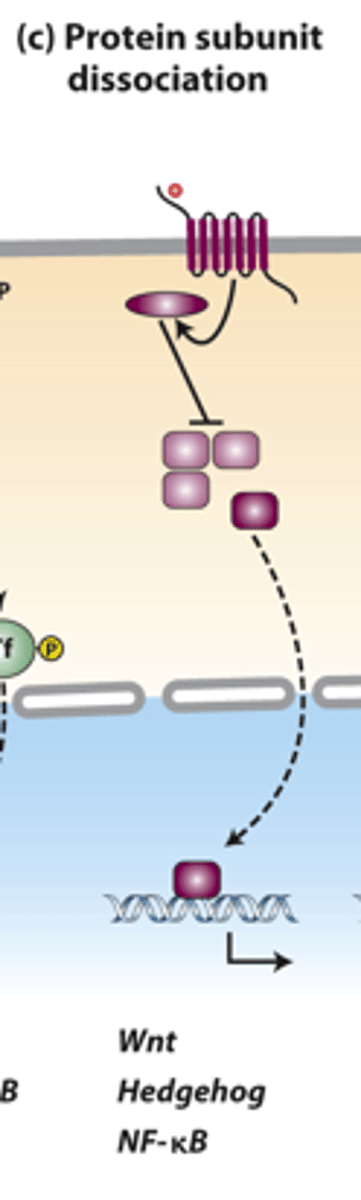
disassembly
protein subunit dissociation pathways: several signaling pathways cause _______________ of a multiprotein complex in the cytosol, which releases a transcription factor that translocates into the nucleus
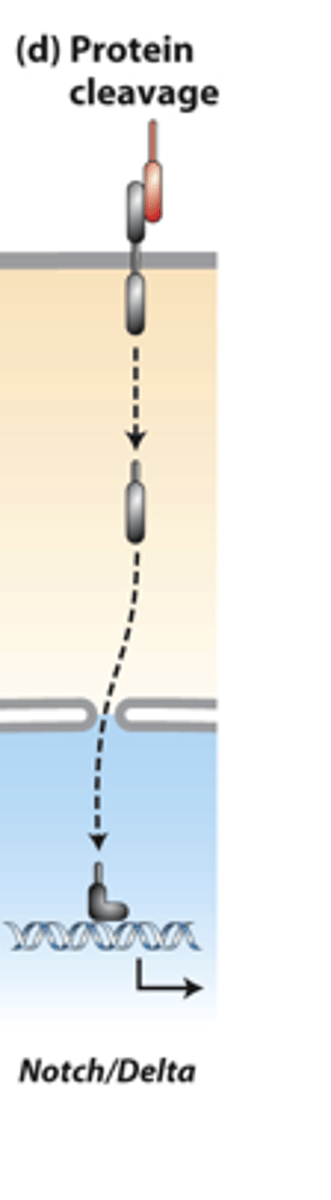
irreversible
protein cleavage pathways: ______________ signaling
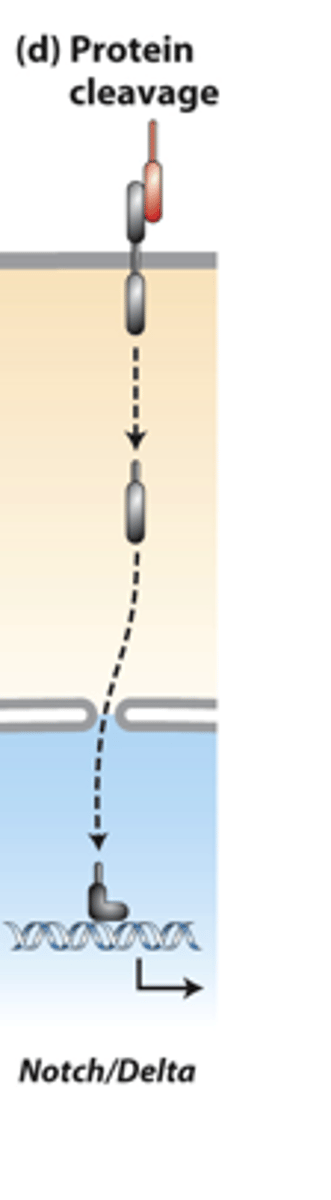
proteolytic cleavage
protein cleavage pathways: _______________ ____________ of a receptor releases an active transcription factor
binding, epigenetic, master
Induction of a particular gene by a transcription factor depends not only on ___________ sites for the factor, but also on the gene's _____________ state and on the presence of ____________ transcription factors and other nuclear proteins
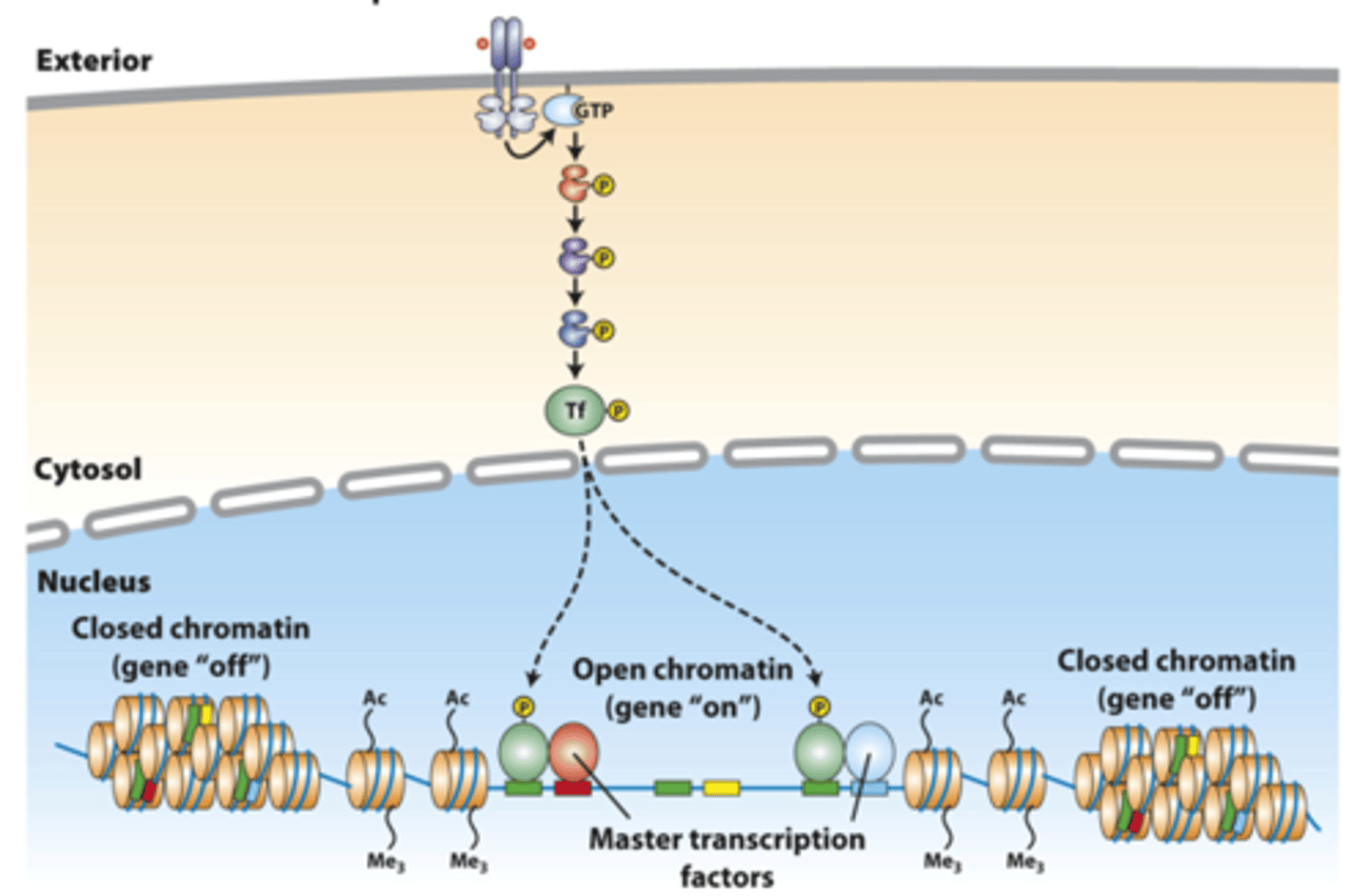
activation
____________ of a signaling pathway can induce cell-specific effects
open chromatin
activation of a signaling pathway can induce cell-specific effects: an activated transcription factor can bind to multiple chromosomal DNA sites such as gene enhancers in an "__________ _____________" conformation that has cell-specific master transcription factors other proteins bound to adjacent sites
on
open chromatin--gene _______
off
closed chromatin--gene _______
multiple
many genes are regulated by _____________ transcription factors activated or repressed by different intracellular signaling pathways that are activated by different extracellular signals
transforming growth factor beta
what does TGF-β stand for
transforming growth factor
the _____________ __________ ___________β (TGF-β) family of extracellular signaling molecules inhibits cell proliferation and regulates development
three
__________ types of TGF-β receptors activates Smads
smads
_________ interact with regulatory DNA sequences at sites adjacent to those occupied by cell-specific master transcription factors to induce target genes cell-specifically
smads
comprise a family of structurally similar proteins that are the main signal transducers for receptors of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-B) superfamily
transforming growth factor beta
critically important for regulating cell development and growth
transforming growth factor beta 1
the first TGF-β discovered, was found in a mutated pathway that promotes tumor metastasis
signaling
TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway, general mechanism: (1) a large family of conserved TGF-β _____________ molecules (secreted by virtually all cell types) activate
receptor tyrosine kinase
what does RTK stand for
kinase
TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway, general mechanism: (2) a large family TGF-β receptors with S/T __________ activity (on most cell types) that phosphorylate-activate
smad
TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway, general mechanism: (3) a conserved class of ______ transcription factors that regulate
pathways
TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway, general mechanism: (4) several growth and differentiation _____________
three
structure of a mature TGF-β dimer: ___________ monomer intrachain disulfide linkages (yellow) form a cystine knot domain
disulfide
structure of a mature TGF-β dimer: another ___________ bond (red) links the two monomers
transforming growth factor beta
____________________ ____________ __________ _________ is secreted as a latent TGF-β complex that binds to ECM until released as a free signaling molecule by extracellular proteases
three
how many TGF-β receptors activate the signaling pathway?
receptor
TGF-β receptors activate the signaling pathway, step 1a: In some cells, TGF-β binds to the type III TGF-β ____________ (RIII), which presents TGF-β to the type II receptor (RII)
RII
TGF-β receptors activate the signaling pathway, step 1b: In other cells, TGF-β binds directly to _______, a constitutively active kinase
ligand bound
TGF-β receptors activate the signaling pathway, step 2: ___________-_________ RII recruits and phosphorylates the juxtamembrane segment of the RI receptor, which does not directly bind TGF-β, releasing inhibition of RI kinase activity
nuclear localization signal
TGF-β receptors activate the signaling pathway, step 3: Activated RI phosphorylates Smad2 or Smad3 (Smad2/3), causing a conformational change that unmasks its ___________ __________________ __________ (NLS)
two
TGF-β receptors activate the signaling pathway, step 4: ________ phosphorylated Smad2/3 molecules bind to a co-Smad (Smad4) molecule (not phosphorylated) and to an importin, forming a large cytosolic complex
smad importin
TGF-β receptors activate the signaling pathway, step 5 and 6: the ________-__________ complex translocates into the nucleus where Ran∙GTP dissociates the importin
nuclear transcription
TGF-β receptors activate the signaling pathway, step 7: the Smad2/3/Smad4 complex associates with a _________ _______________ factor (e.g., TFE3) to form an activation complex that cooperatively binds to target gene regulatory sequences
gene transcription
TGF-β receptors activate the signaling pathway, step 8: activation complex recruits transcriptional co-activators and induces ________ ____________
target gene activation
complex activating plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) gene; similar complexes activate expression of genes encoding other extracellular-matrix proteins such as fibronectin
nuclear
TGF-𝛃/Smad signaling pathway inactivation, step 9: a __________ phosphatase dephosphorylates Smad2/3
cytosol
TGF-𝛃/Smad signaling pathway inactivation, step 10: dephosphorylated Smad2/3 recycles through a nuclear pore to the ____________, where it can be reactivated by another TGF-β receptor complex
tumors
many human ___________ contain inactivating mutations in either TGF-β receptors or Smad proteins and thus are resistant to TGF-β growth inhibition. Most human pancreatic cancers contain a deletion in the Smad4 gene
RTKs
transmembrane protein receptors that help cells interact with their neighbors in a tissue