16. IGCSE Biology: Reproduction
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
asexual reproduction
a process resulting in the production of genetically
identical offspring from one parent
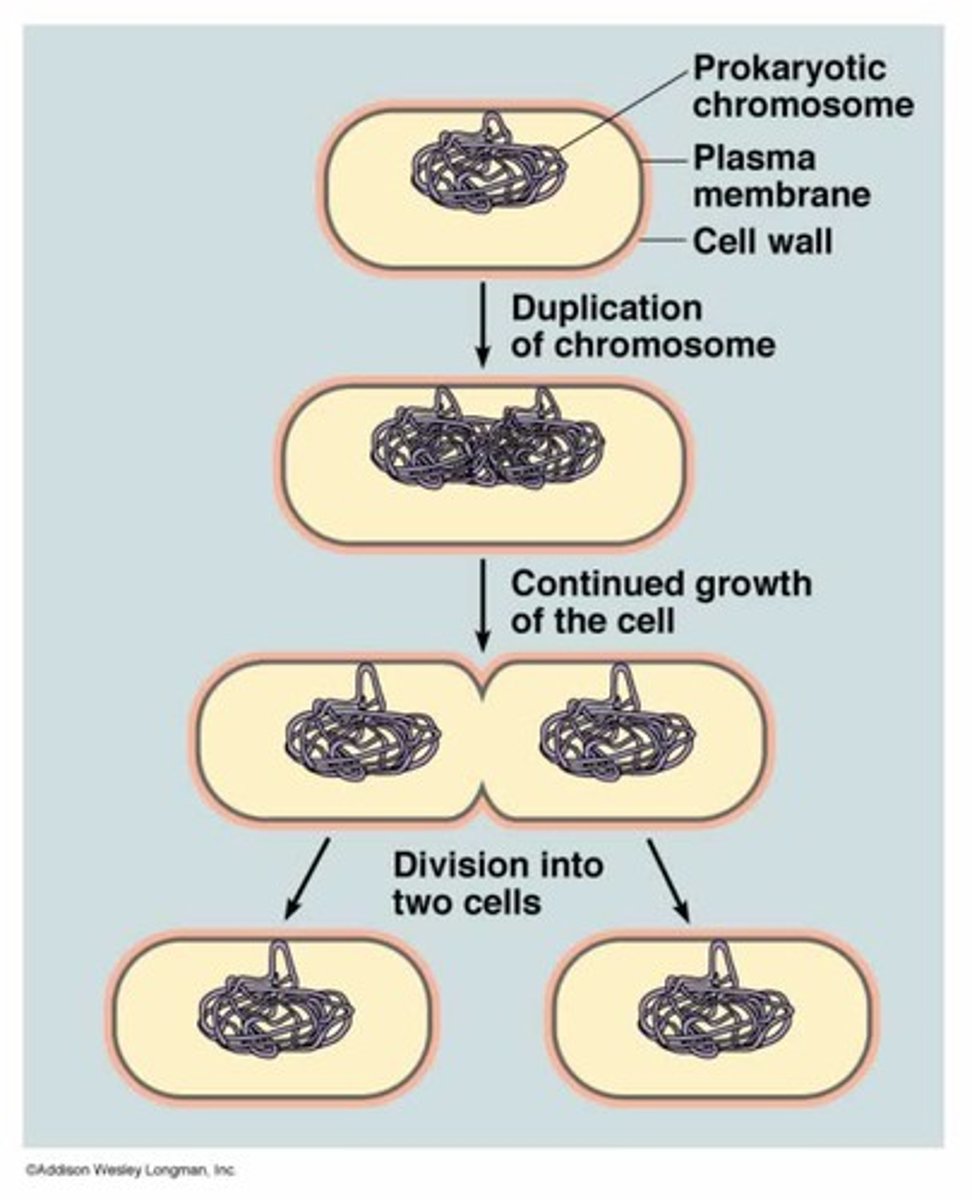
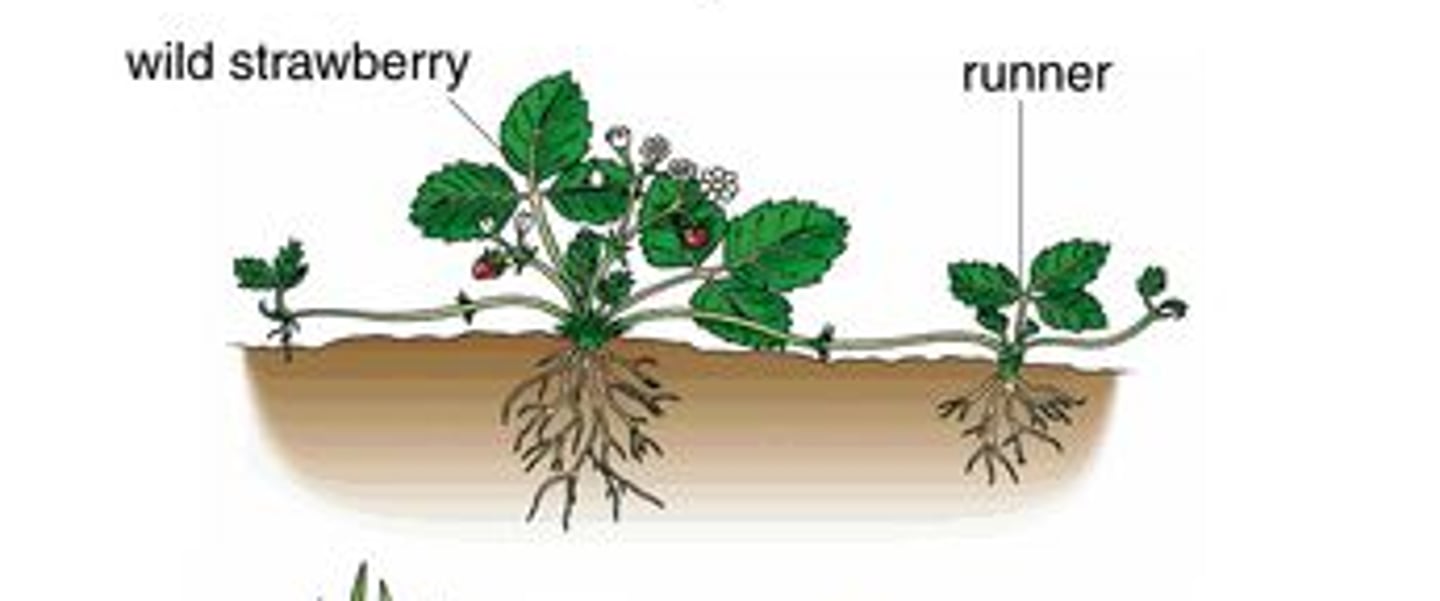
examples of asexual reproduction
- Binary fission in bacteria
- Spore production in fungi
- Tuber formation in potatoes
advantage of asexual reproduction
- produce many individual rapidly
disadvantage of asexual reproduction
- lack genetic variation to defend against diseases and environmental changes
sexual reproduction
a process involving the fusion of the nuclei of two gametes (sex cells) to form a zygote and the production of offspring that are genetically different from each other
fertilisation
the fusion of gamete nuclei
gametes
A haploid cell such as an egg or sperm. Gametes unite during sexual reproduction to produce a diploid zygote.
zygote
Diploid cell formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg.
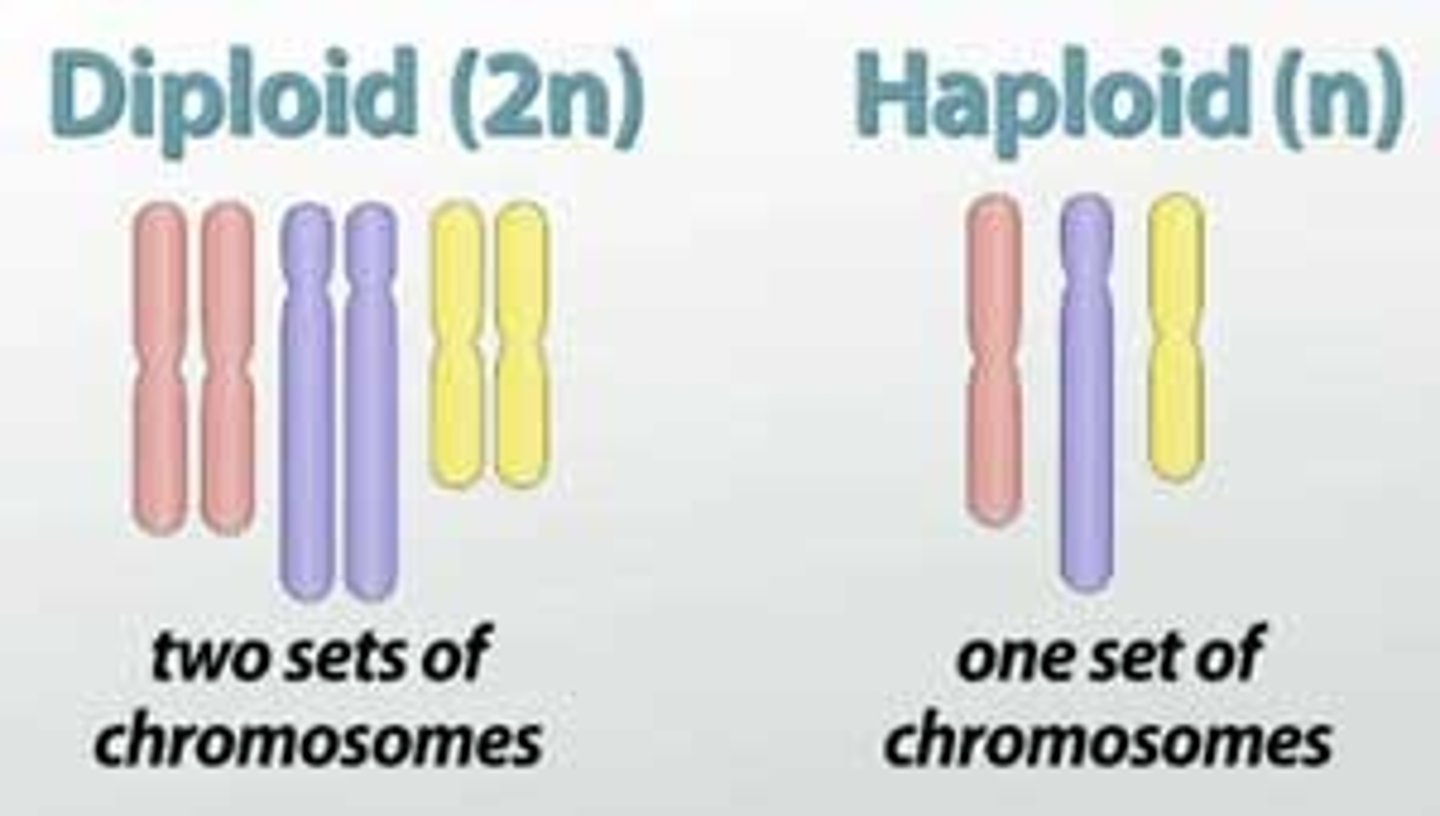
Haploid and Diploid
haploid contains half the number of chromosomes
advantage of sexual reproduction
more variation in the next generation
disadvantage of sexual reproduction
Slower process, need two parents
insect-pollinated flower
Flowers with brightly-coloured petals are usually insect-pollinated flowers. Insects carry pollen from one flower to another.
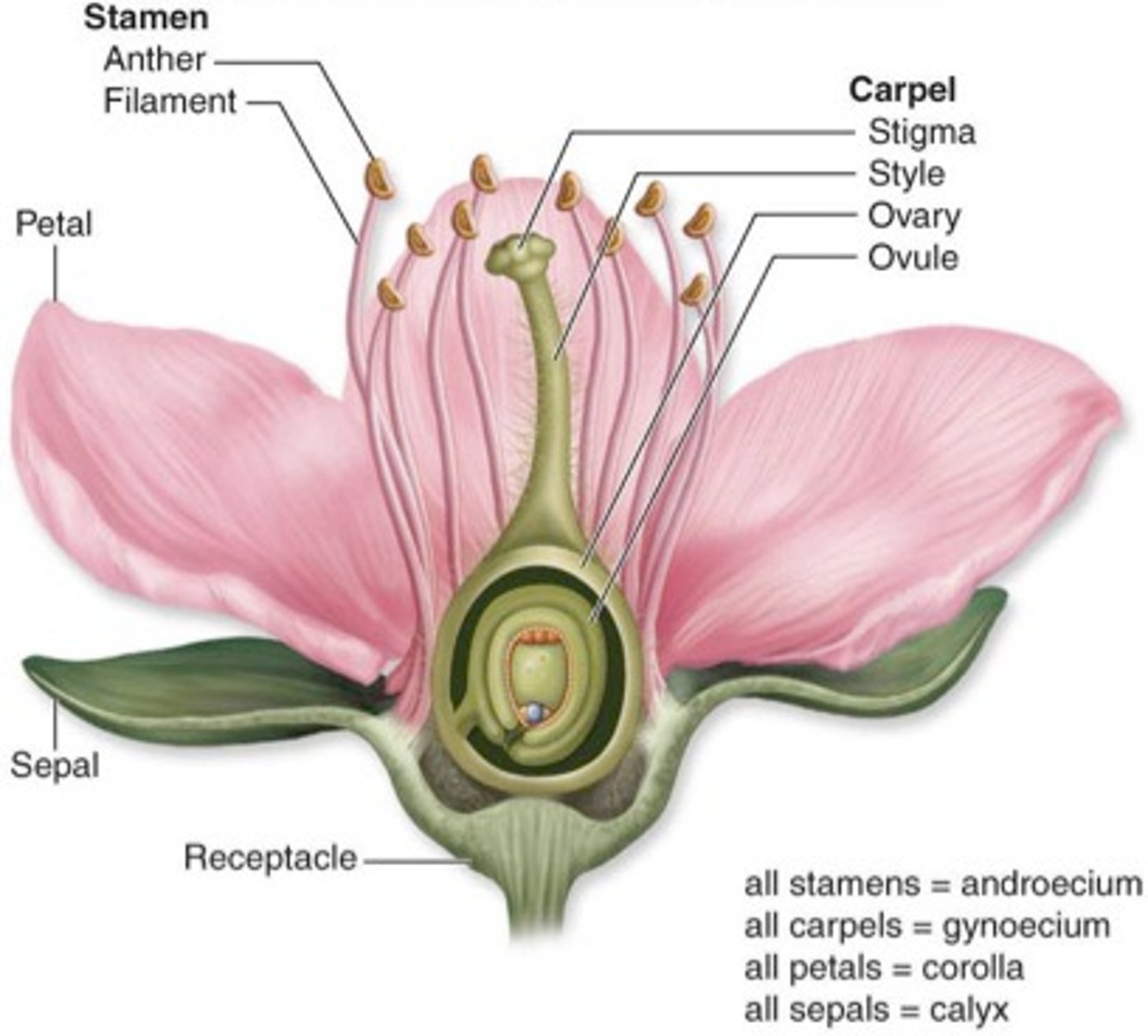
sepals
Leaflike parts that cover and protect the flower bud

petals
bright color and scented to attract pollinators.

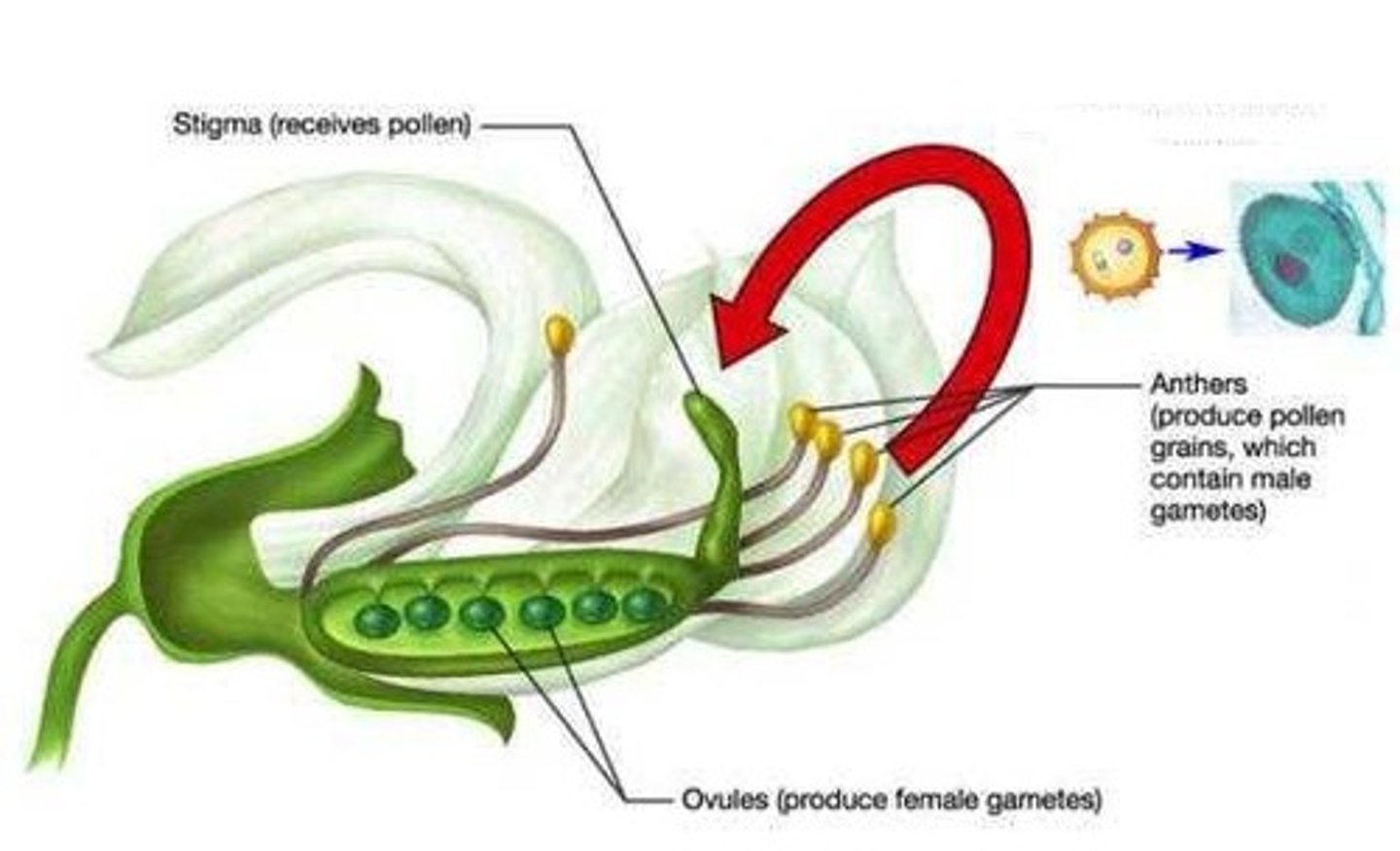
anthers
Produces the male sex cells (pollen)
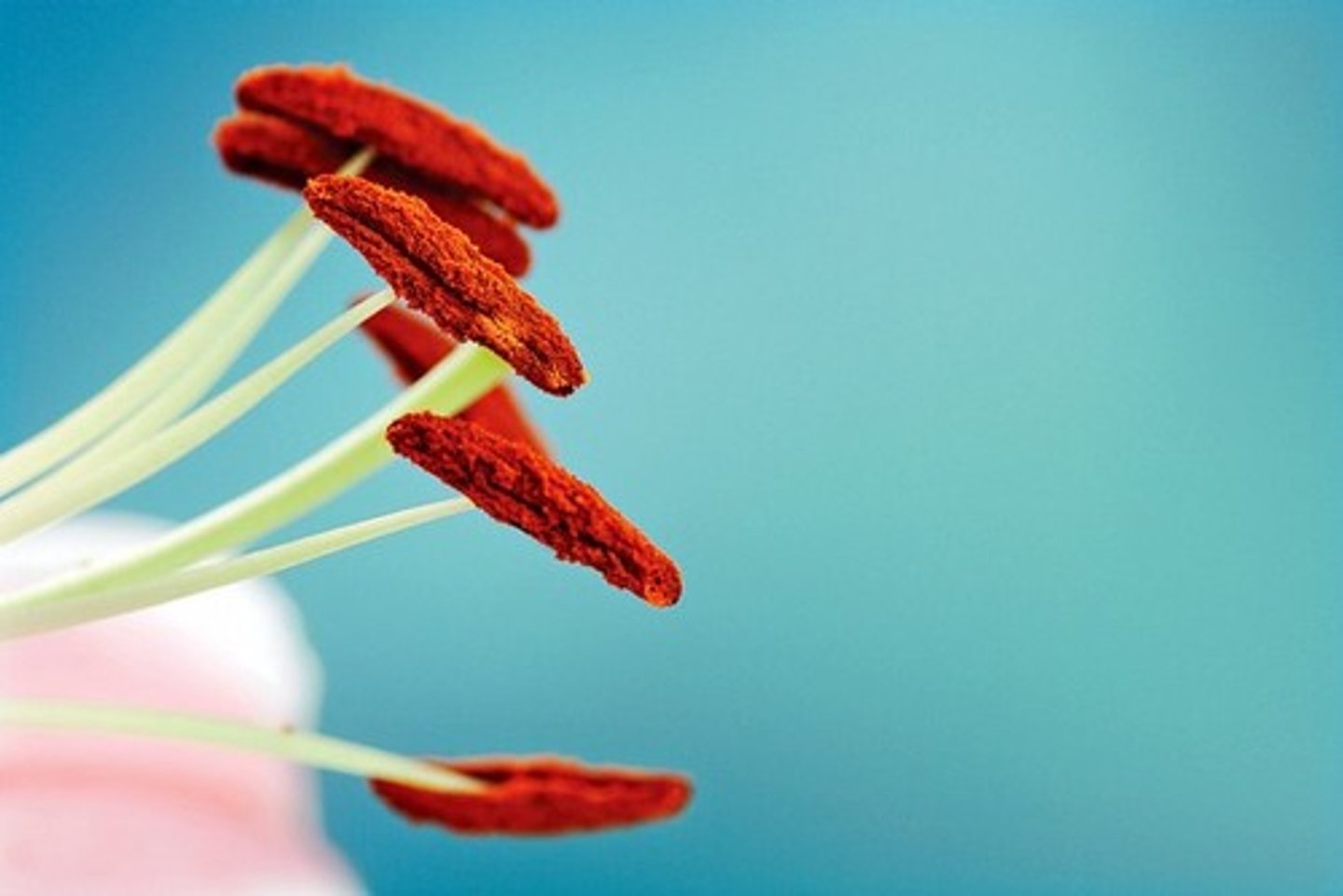

stigmas
The top of the female part of the flower, which collects pollen grains
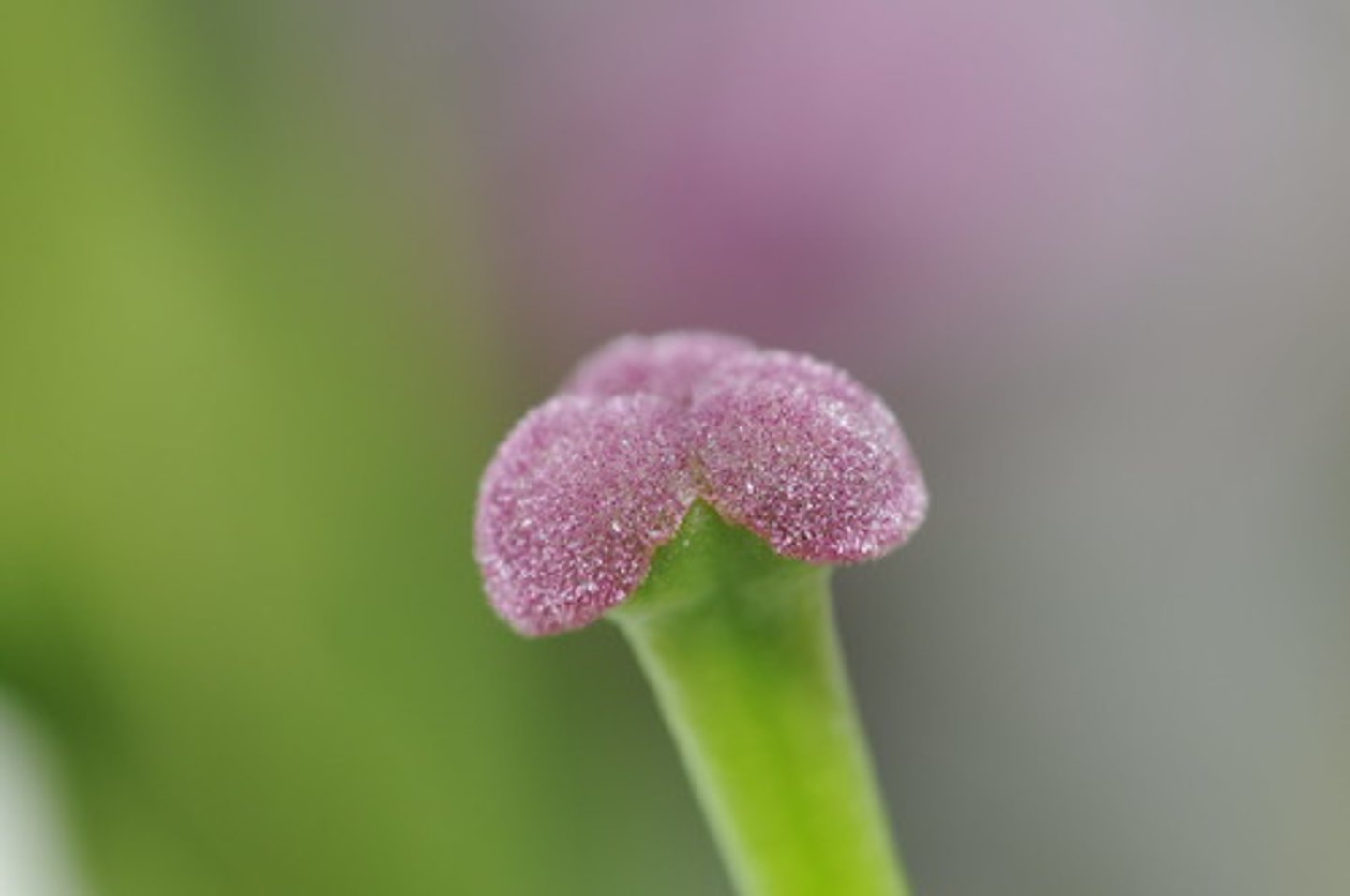

ovaries (plant)
Produces the female sex cells (contained in the ovules)
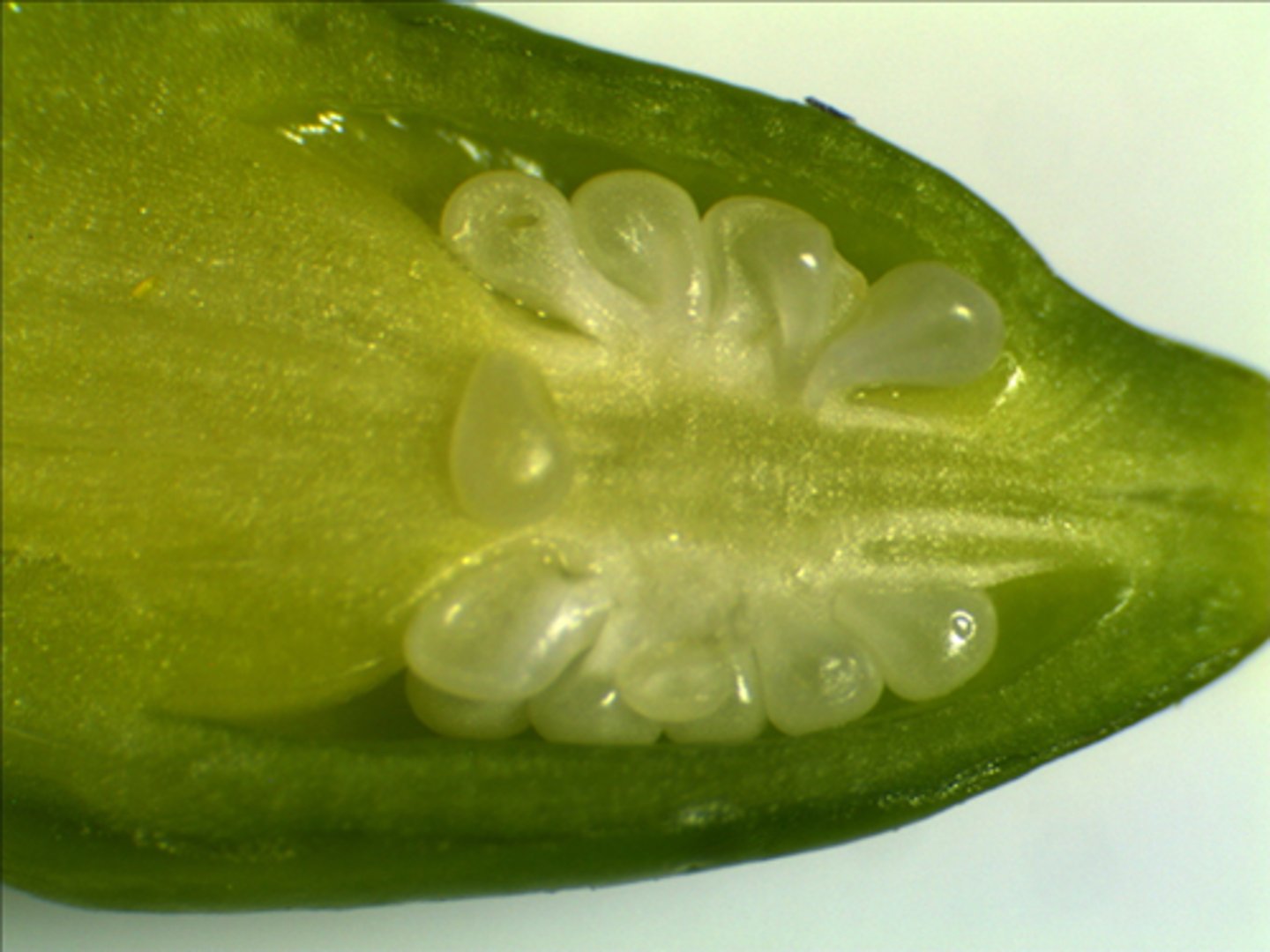

wind-pollinated flower
they have small petals, and their stamens and stigmas hang outside the flower.
pollen grains of insect-pollinated flowers
produce smaller quantities of spiky, sticky pollen to attach to insects
pollen grains of wind-pollinated flowers
produce large quantities of light, smooth pollen to be carried by the wind
pollination
transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma
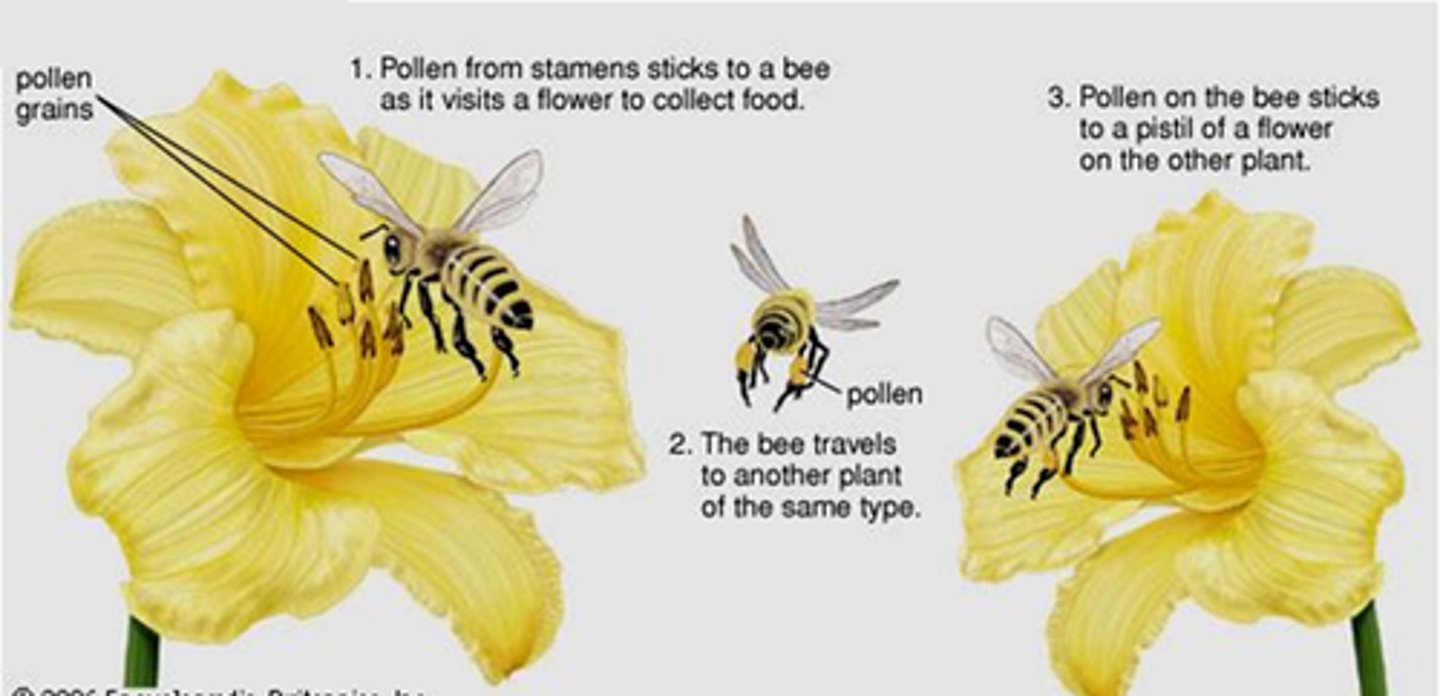

self-pollination
the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or different flower on the same plant
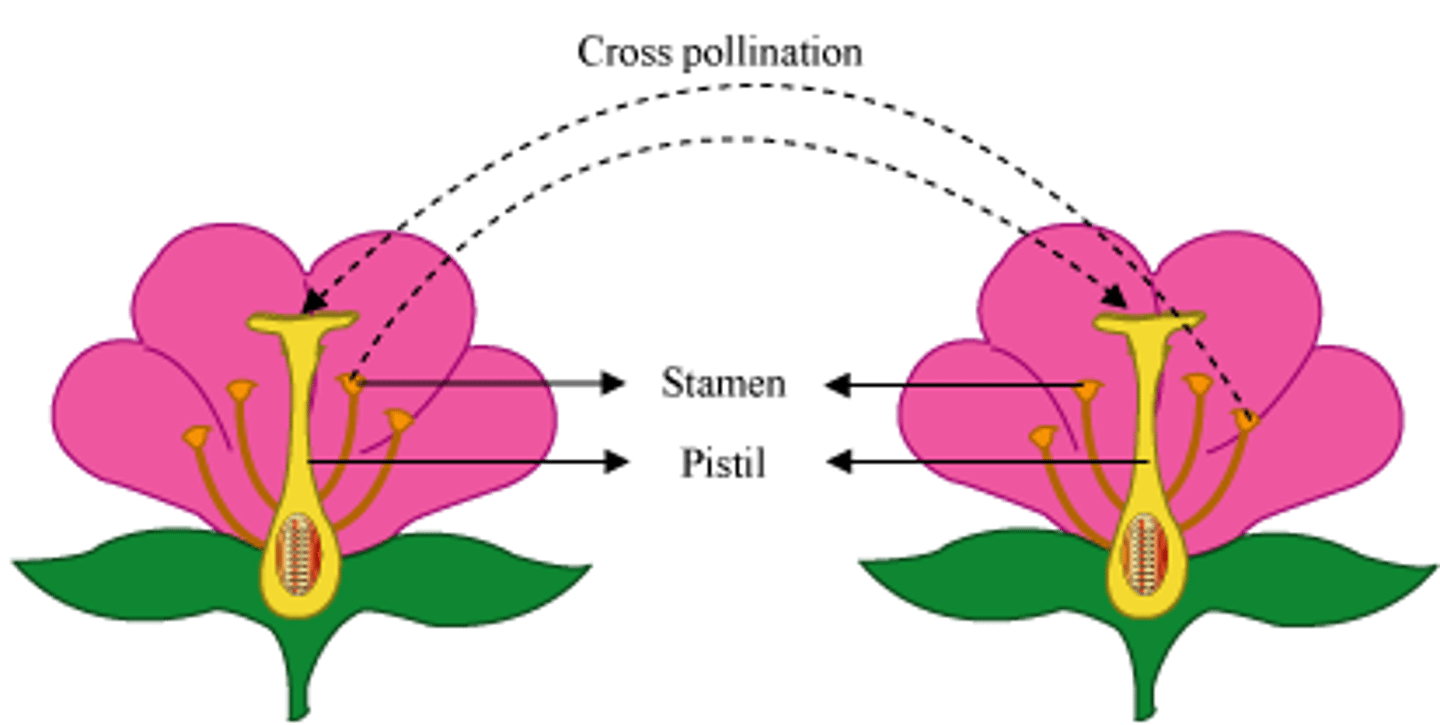
cross-pollination
transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of a flower on a different plant of the same species
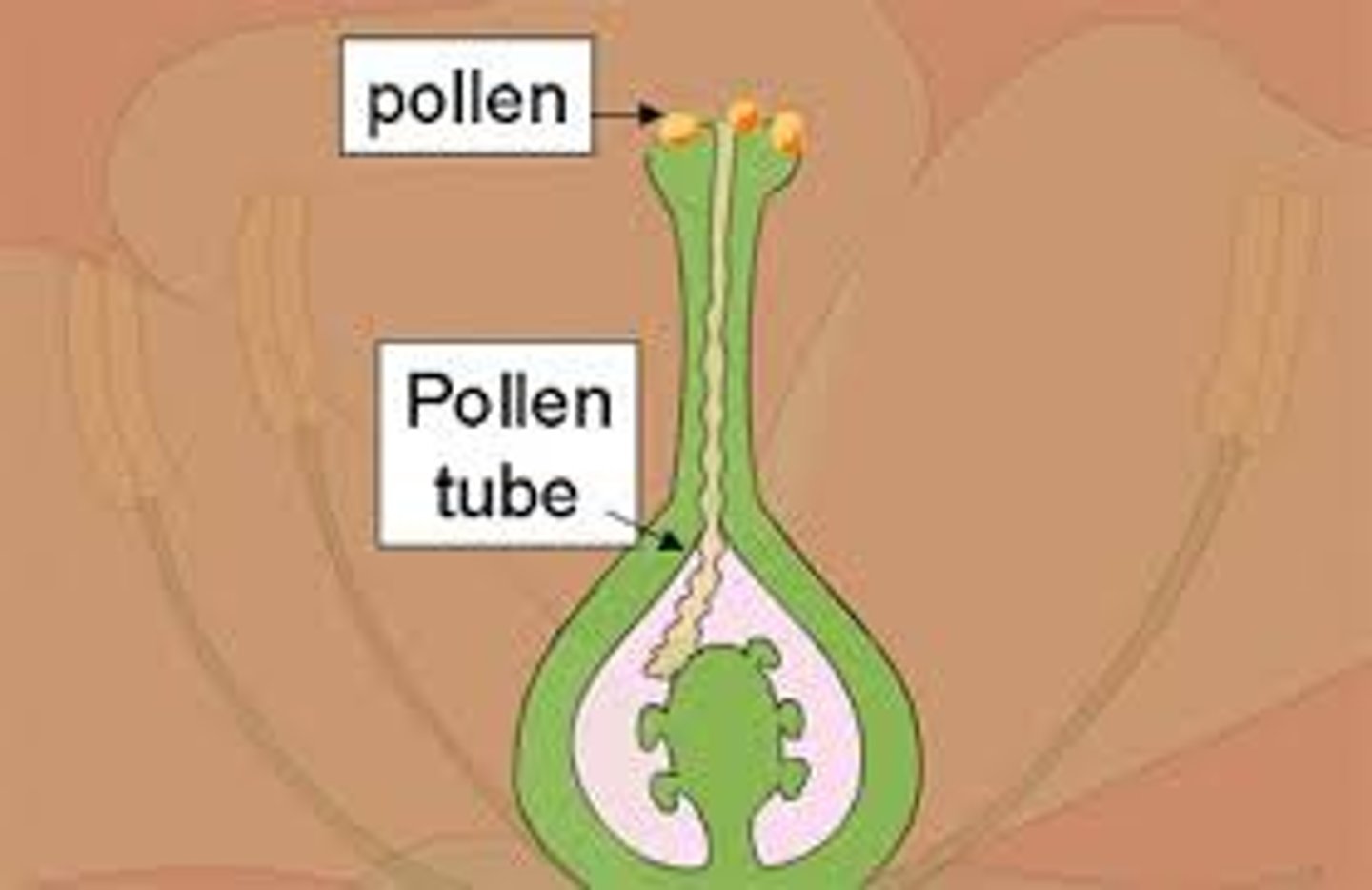
pollen tube
A tube that forms after germination of the pollen grain and that functions in the delivery of sperm to the ovule.
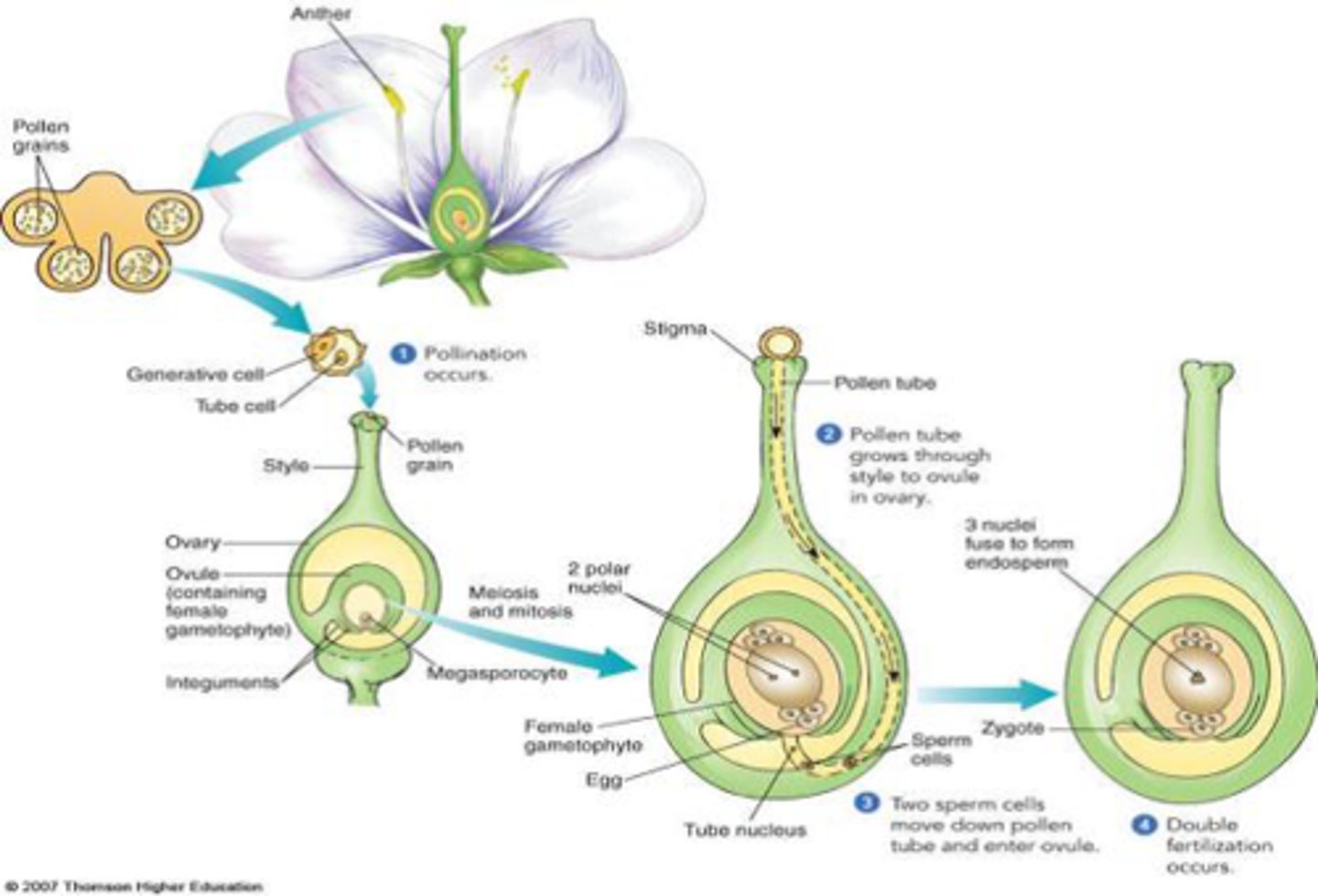
Plant fertilisation
- Pollen grain land on ripe stigma
- pollen grain form pollen tube that grows down the style to the ovary
- pollen tube gains nutrients from style
- pollen tube carries male gamete nucleus. - Gamete enters ovule through micropyle. - - Male gamete fuses with the female to form a zygote
environmental conditions that affect germination of seeds
- requirement for water
- oxygen
- suitable temperature
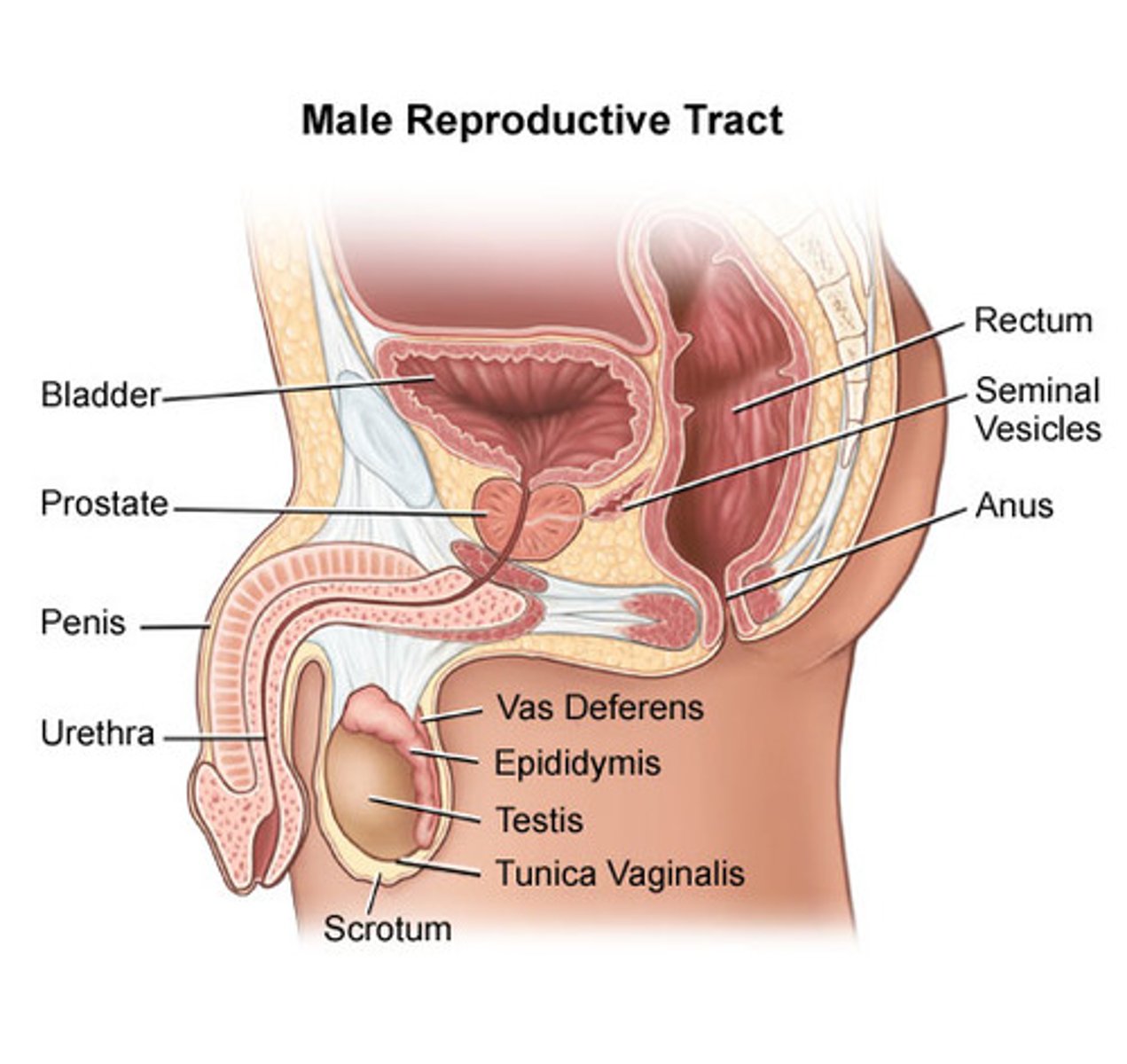
Male reproductive system
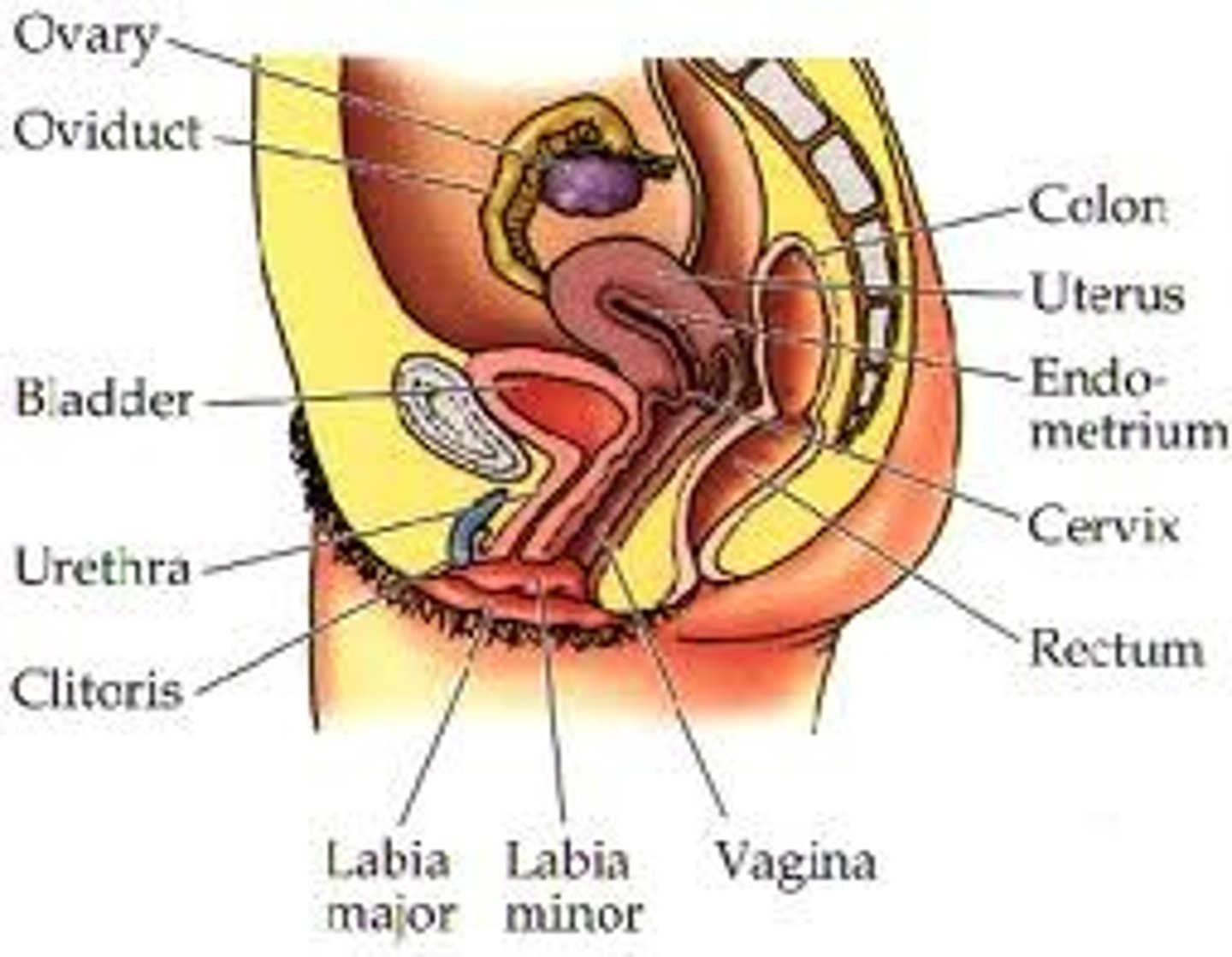
Female reproductive system
testes
Produces male gametes (sperm) and hormone testosterone
scrotum
Allows testes to be kept in cool enviroment to be stored and develop
sperm ducts
Connects to urethra to allow semen to move out of penis to vagina during sexual intercourse
prostate gland
Produces mucus and sugars for sperm cells to swim in and use the sugar for respiration to move
urethra
Allows urine to move out of body
penis
Male reproductive organ, contains duct for transfer of sperm
ovaries
Contains undeveloped egg cells
-produce oestrogen and progesterone
oviducts
Moves matured egg cell to uterus for implantation by peristalsis and beating of cilia
uterus
Place where fertilised egg cell is implanted
cervix
Ring of muscle
vagina
Muscular tube where penis is inserted during sexual intercourse for fertilisation to occur
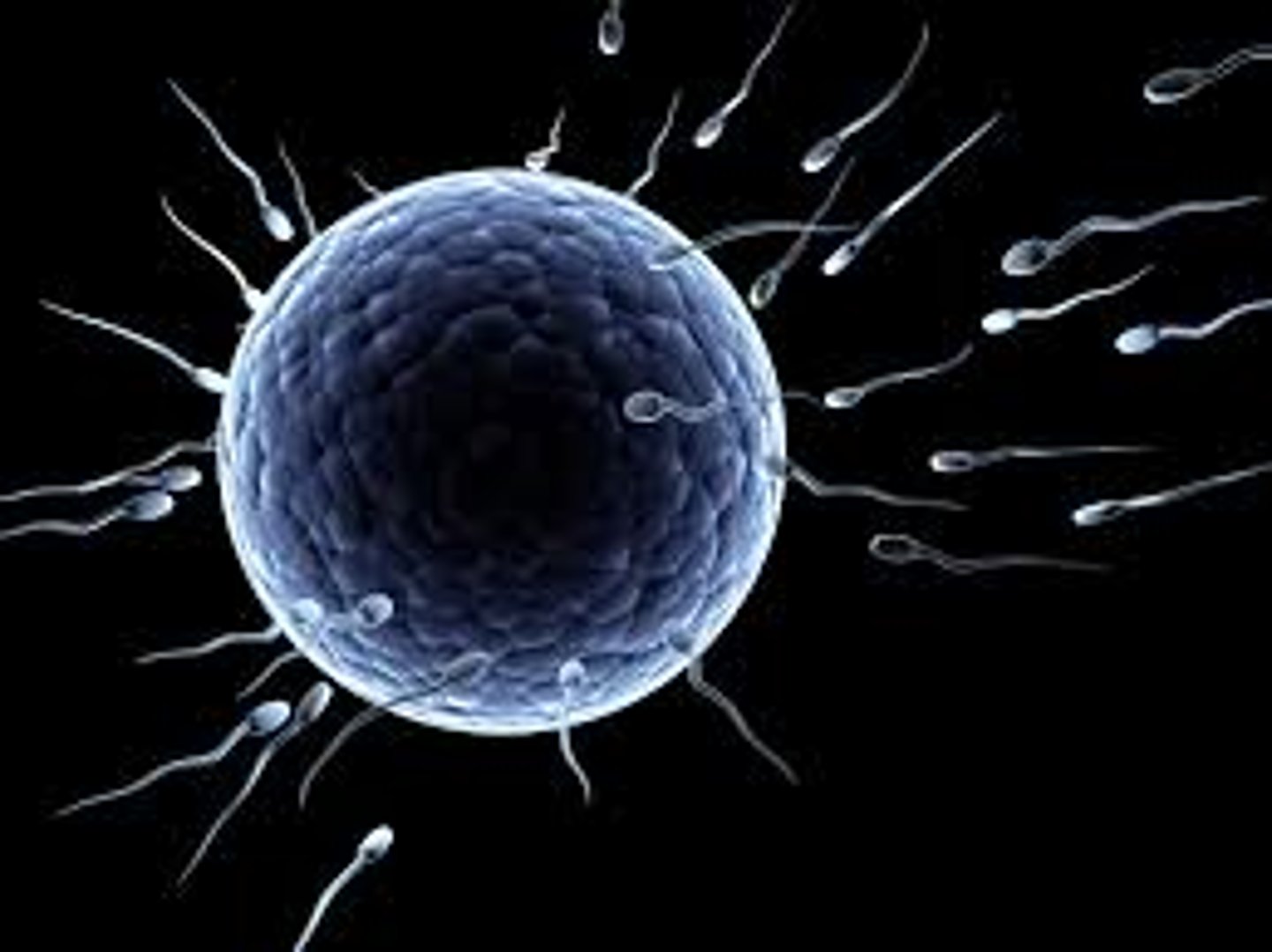
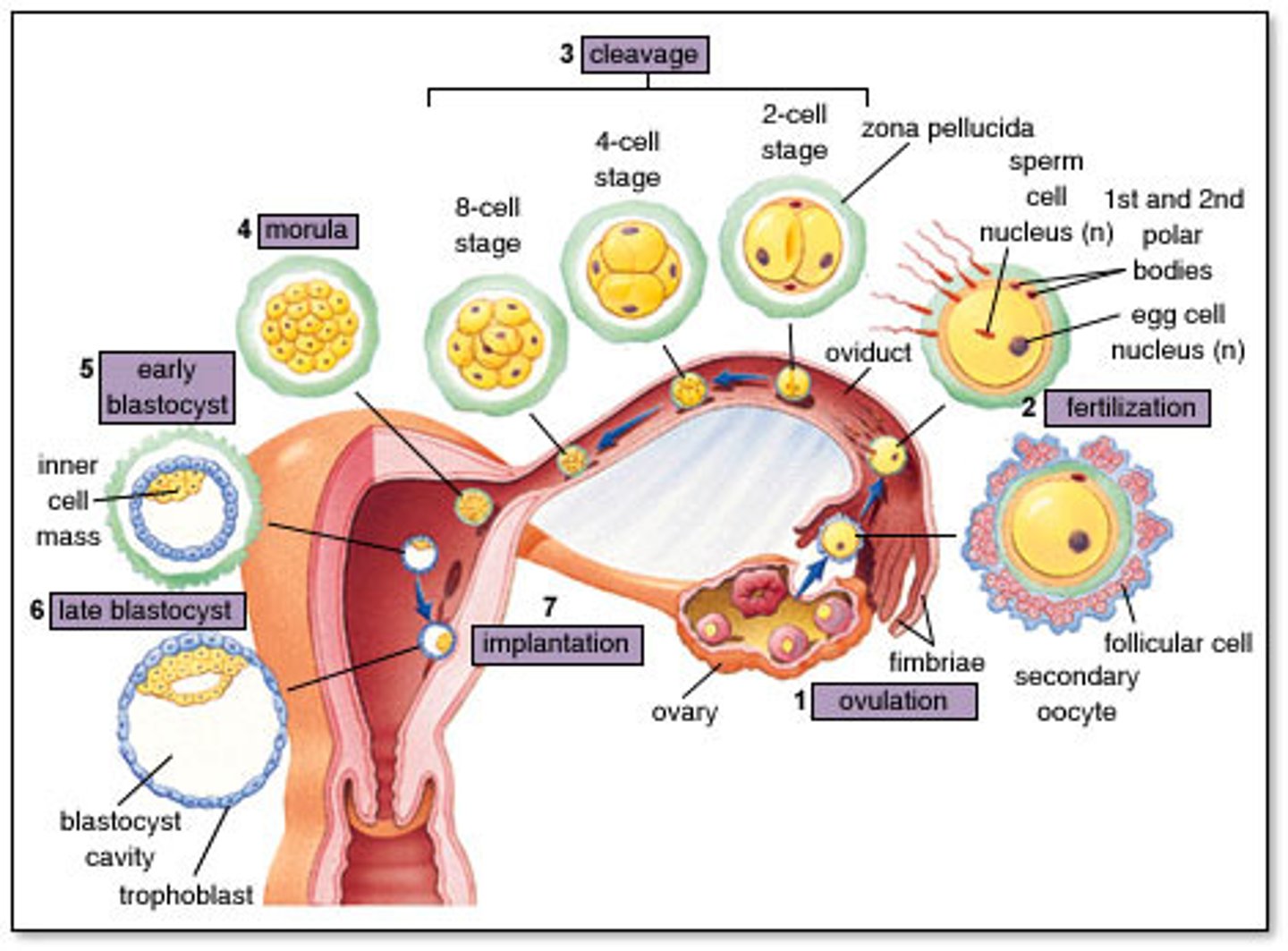
Human fetilisation
the fusion of the nuclei from a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (egg cell/ovum)
adaptive features of sperm
flagellum - helps it move fast
enzymes in the acrosome - help it penetrate the egg cell membrane
middle section - packed with mitochondria for energy
adaptive features of egg cells
energy stores - large amount if cytoplasm
jelly coat - changes at fertilisation
Implantation of zygote
the zygote forms an embryo which is a ball of cells that implants into the wall of the uterus
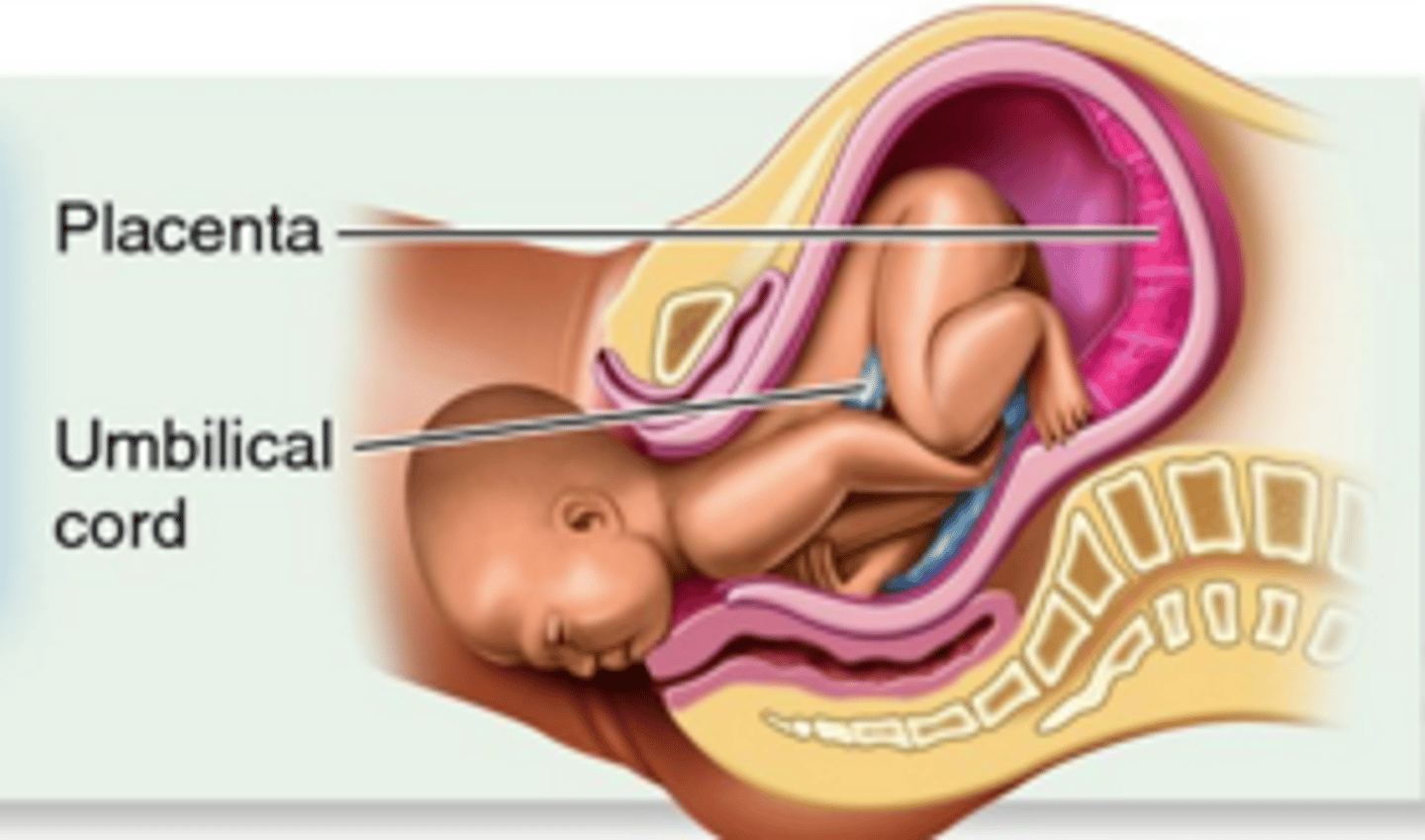
functions of the umbilical cord
Contains artery and vein that carry fetal blood to the placenta
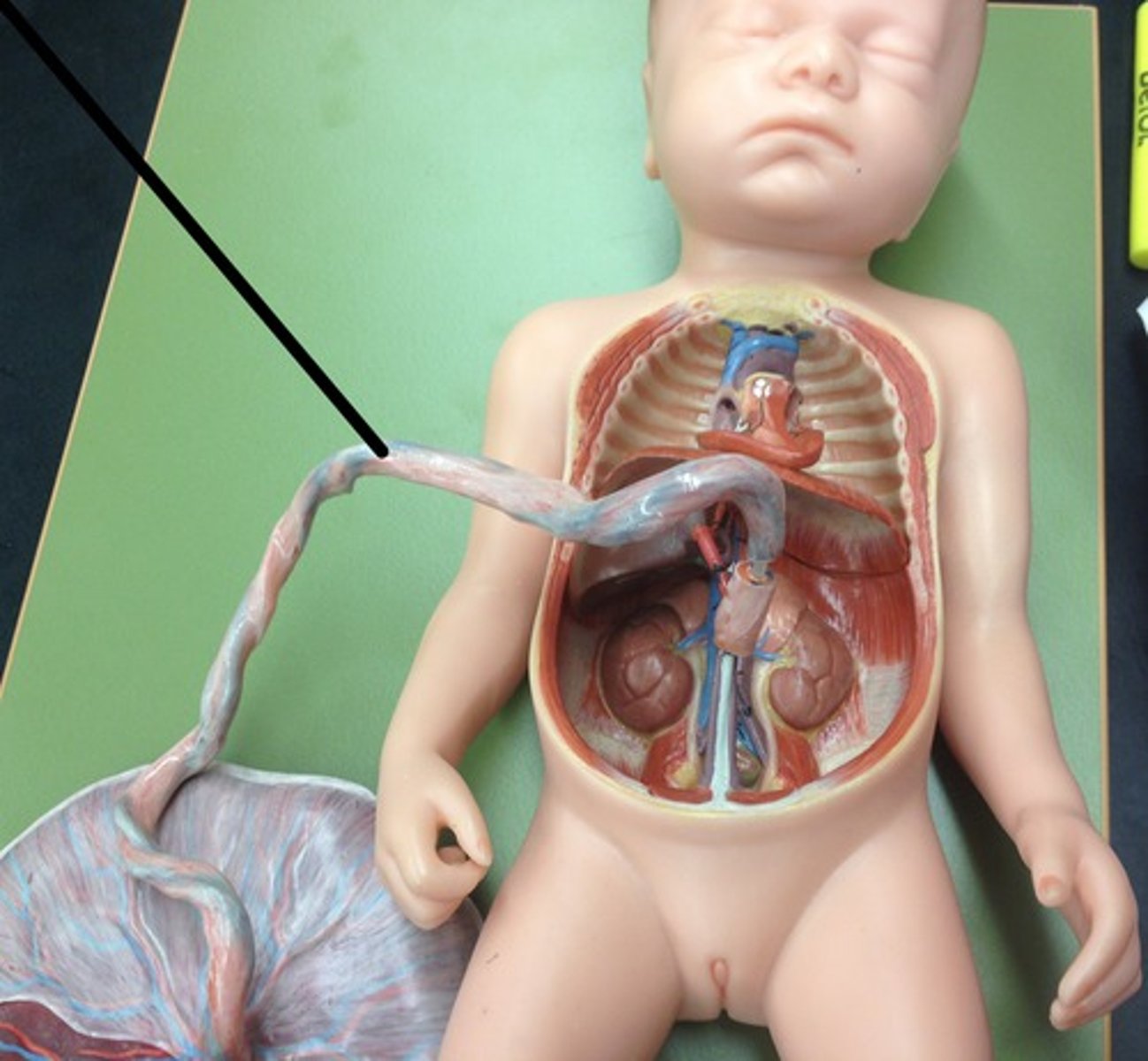
functions of placenta
-Separates mother's blood from fetus as both may have different blood types
-Prevents mother's blood with high pressure from damaging delicate blood vessels of fetus
-Allows for diffusion of oxygen and food molecules
functions of amniotic sac
Contains the amniotic fluid
functions of amniotic fluid
Maintains constant temperature for fetus and prevents mechanical damage
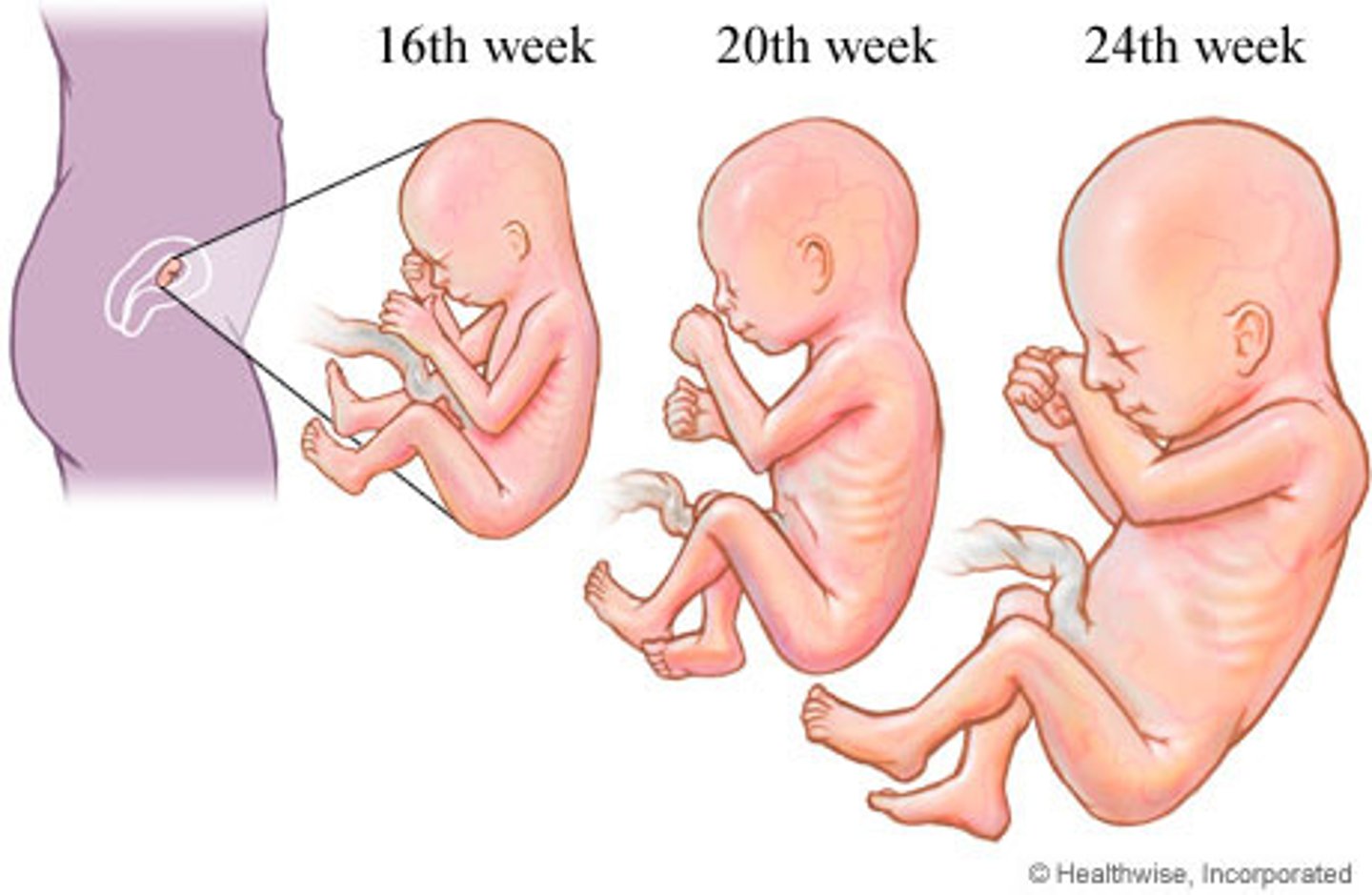
growth and development of fetus
increasing complexity in the early stages and increasing size towards the end of pregnancy
advantages of breast-feeding
-Contains antibodies from mother for passive immunity
-Form bonds between mother and child
-Is nutritious for baby
ante-natal care of pregnant women
special dietary needs and the harm from smoking and alcohol consumption
labour and birth
- breaking of the amniotic sac
- contraction of the muscles in the uterus
wall
- dilation of the cervix
- passage through the vagina
- tying and cutting the umbilical cord
- delivery of the afterbirth
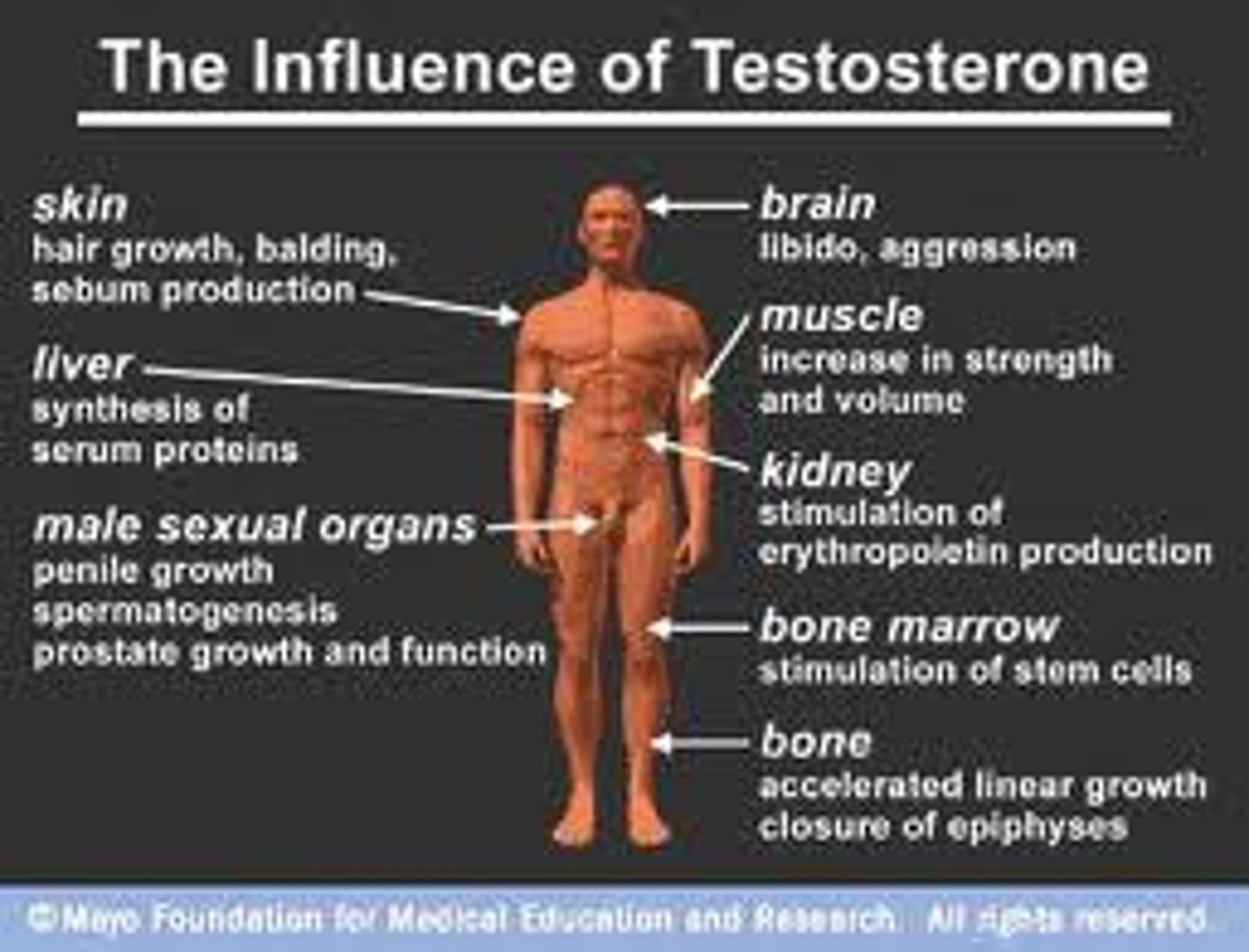
roles of testosterone
Stimulates change in male body during puberty
-Muscle growth
-Facial hair
-Increase in height
roles of oestrogen
Stimulate development of sex organs and secondary sexual characteristics
-Increase in hip size
-Breast develop
-Menstrual cycle starts
the sites of production of oestrogen and progesterone in the menstrual cycle and in pregnancy
-Follicle cell secrete oestrogen
-After matured egg cell is released the follicle cell turns into a yellow body that secretes progesterone
-During pregnancy oestrogen is produced by the ovaries and progesterone is produced by the placenta
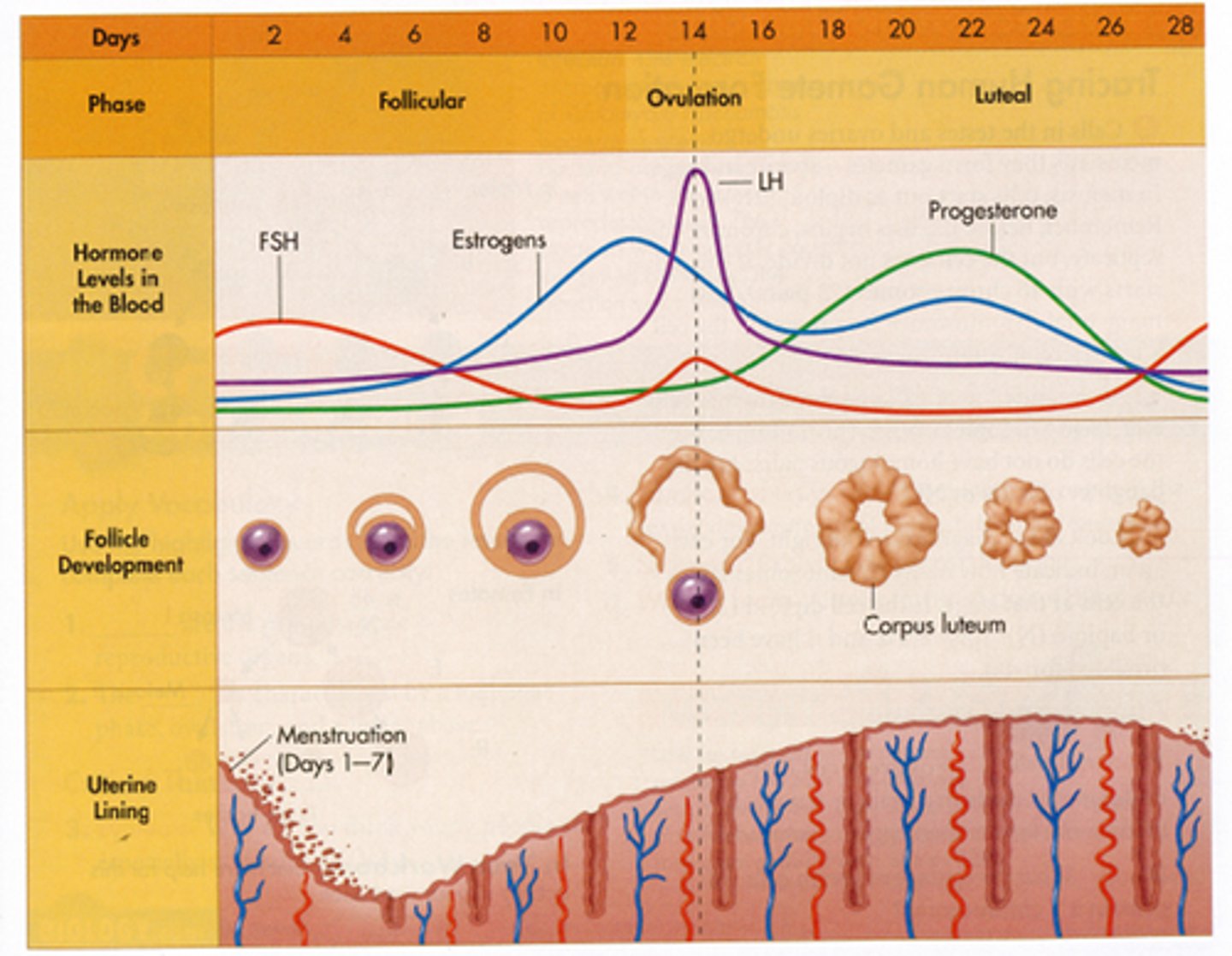
Describe the menstrual cycle
- FSH is produced by the pituitary gland to mature egg cell
- Cells in follicle produce oestrogen to allow thickening of uterus lining and stops pituitary gland from producing more FSH
- Pituitary gland then produces LH to stimulate release of egg cell (ovulation)
- Follicle cell to turn into corpus luteum.
- Corpus luteum produces progesterone that maintains thickening of uterus lining
- If no implantation occurs the egg cell dies and lining of uterus lining breaks down and is lost during menstruation
role of hormones in controlling the menstrual cycle and pregnancy
oestrogen - Causes thickening of the uterus lining
progesterone -Maintains the thickness of uterus lining for implantation
FSH
Stimulates development of follicle cell
LH
Stimulate follicle cells to form yellow body and to release matured egg cell
Natural methods of birth control
abstinence, monitoring
body temperature and cervical mucus

Chemical methods in birth control
IUD, IUS, contraceptive pill, implant and injection
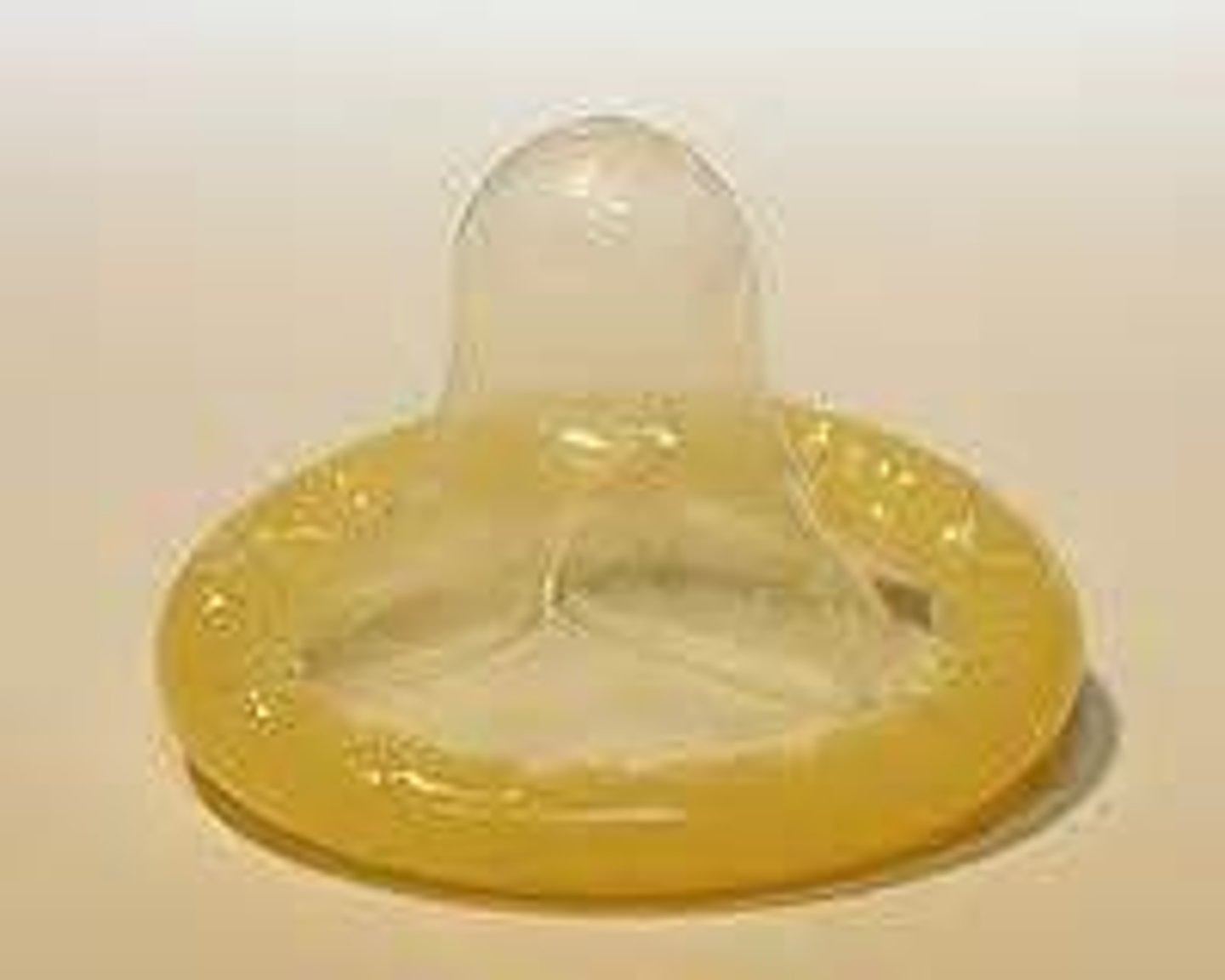
barrier methods in birth control
condom, femidom, diaphragm

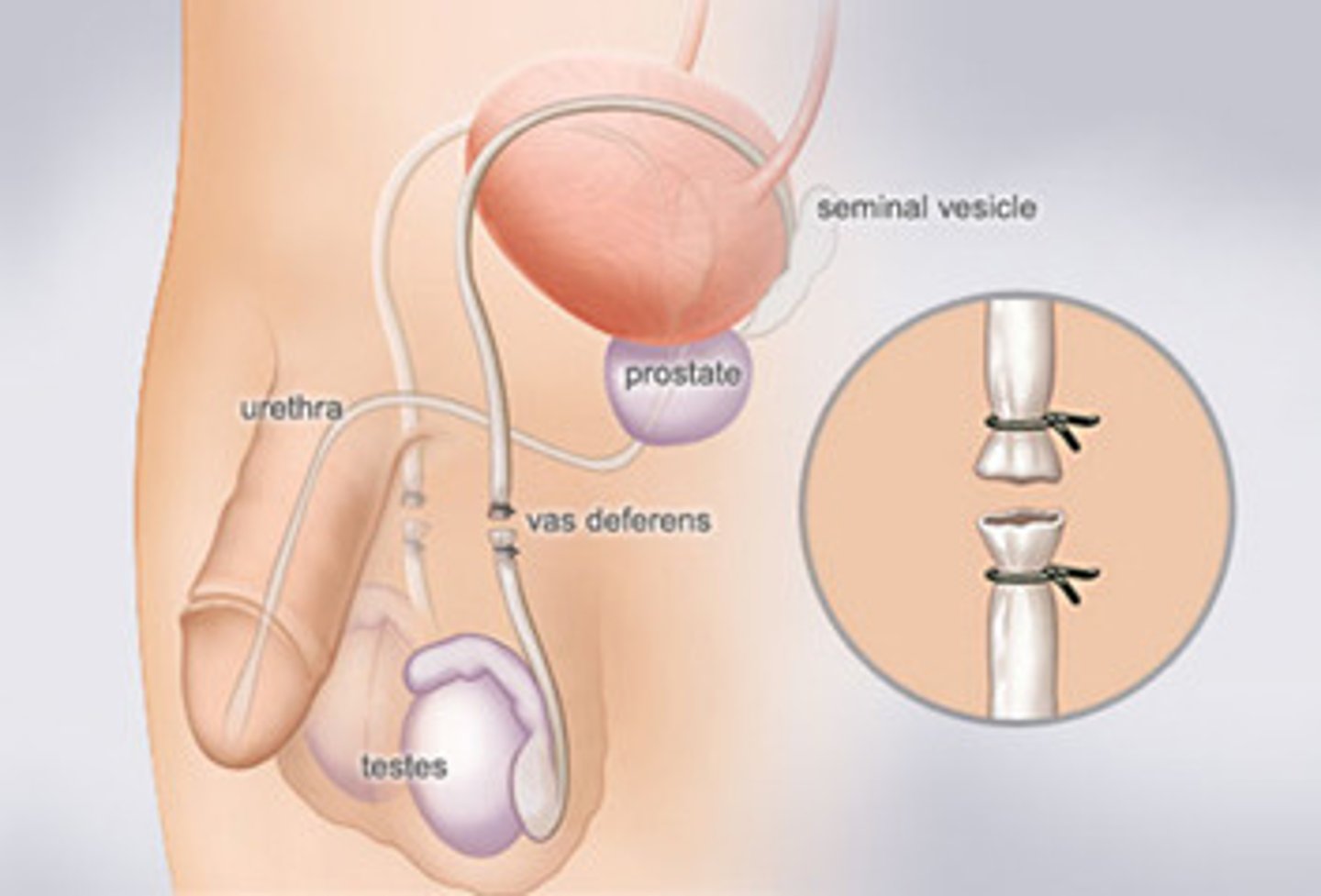
surgical methods in birth control
vasectomy and female sterilisation
artificial insemination (AI)
Semen is collected from a man and inserted directly into the woman's uterus via fine plastic tube

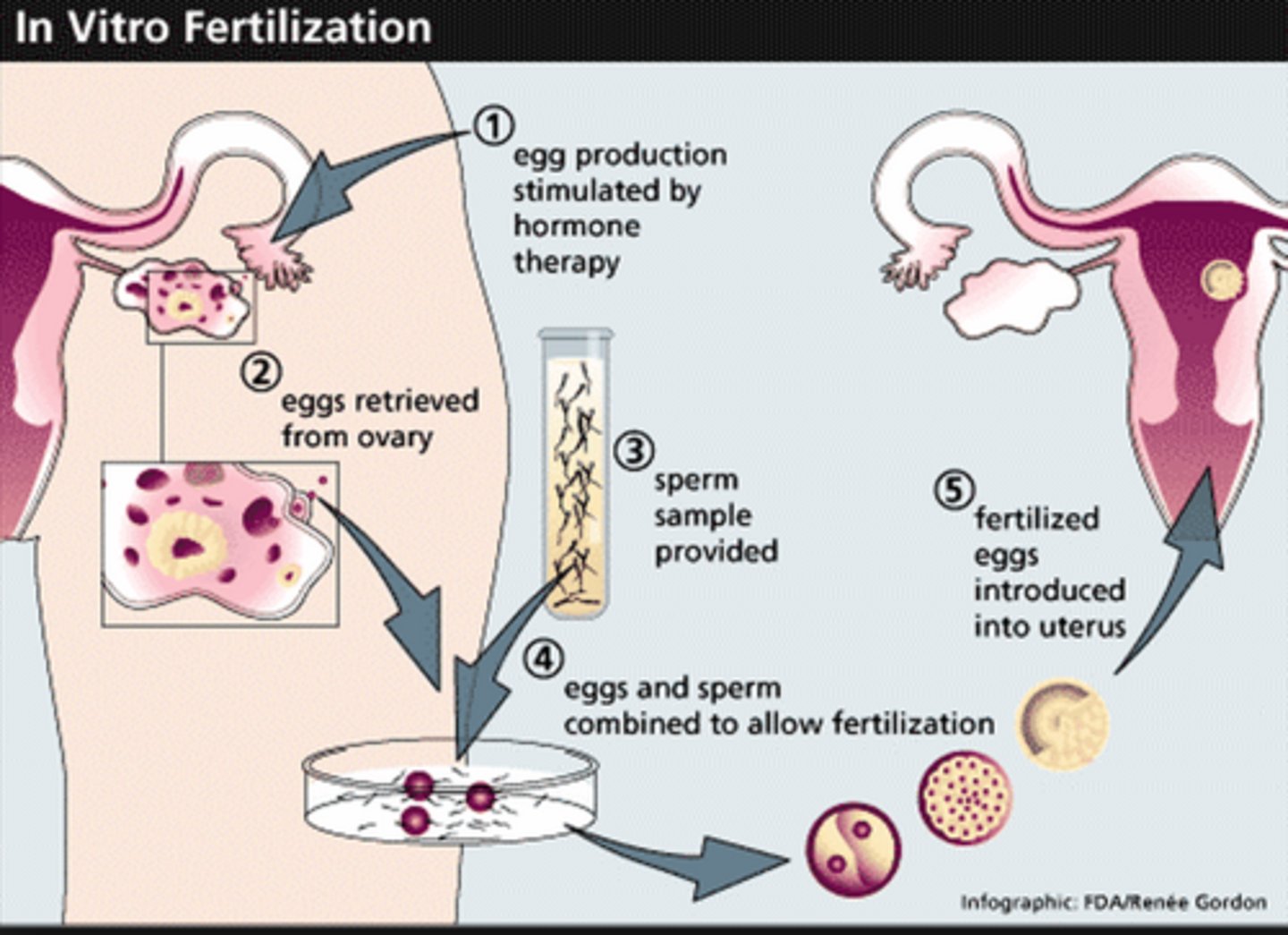
in vitro fertilisation (IVF)
- Woman takes hormone drugs containing FSH to develop follicle cells to mature
- needle is used to extract matured egg cells and combine externally with sperm cells
- the fertilised eggs is then placed into the uterus for implantation.
the use of hormones in contraception and fertility treatments
Contains hormones such as progesterone and oestrogen that inhibit the production of FSH thus ovaries do not mature and ovulation does not occur
social implications of contraception and fertility treatments
Is expensive, is not a 100% guarantee that contraceptive or fertility treatment will work
sexually transmitted infection (STI)
an infection that is transmitted via body fluids
through sexual contact
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
An STI charaterized by decreased lymphocyte numbers and reduced ability to produce antibodies

how the spread of STIs is controlled
-Use of condoms during sexual intercourse
-Free needle exchange scheme to reduce use of shared needles among drug users
-Careful screening of blood used for transfusions
methods of transmission of HIV
-Unprotected sexual intercourse with carrier
-Sharing or exchange of blood with carrier
AIDS
Immune system disease caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) which over a period of years weakens the capacity of the immune system
