5.1 Nitrogen Metabolism
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Find a rational explanation of why GTP inhibits glutamate dehydrogenase. Can we define it a feedback inhibition?
The product of glutamate dehydrogenase is α-ketoglutarate that is oxidized in the Krebs cycle to succinyl CoA. The latter undergoes substrate-level phosphorylation with synthesis of GTP. Accumulation of GTP means that glutamate metabolism is overcrowded and it is convenient to inhibit glutamate oxidation. Thus, this can be defined as a feedback inhibition.
Write the steps by which glutamine is converted to glucose
2×[(glutamine → glutamate → α-ketoglutarate → succinyl-CoA → succinate → fumarate → malate) in mitochondria → in cytosol (malate → oxaloacetate → P-enol-pyruvate → 2-P-glycerate → 3-P-glycerate → 1,3-bisP-glycerate → glyceraldehyde-P /dioxyacetone-P] → fructose-1,6 bisP → fructose-6-P → glucose-6-P → glucose)
Write the steps by which glutamine is converted to palmitate
Glutamine is converted to acetyl CoA through the Krebs cycle, malic enzyme and pyruvate dehydrogenase; we need therefore 8 glutamine molecules to form 8 acetyl CoA
8×[(glutamine → glutamate → α-ketoglutarate → succinyl-CoA → succinate → fumarate → malate → pyruvate → acetyl-CoA → citrate) in mitochondria → in cytosol (citrate → acetyl CoA] → → palmitate)
Lysine catabolism produces acetoacetyl CoA: explain why lysine is not a glucogenic amino acid
Acetoacetyl CoA can be converted to acetoacetate, to acetyl CoA, or to HMG CoA and mevalonate. None of these compounds in mammals can be converted into pyruvate or any other glucogenic compound
Calculate the concentration of NH3 required to reverse the glutaminase reaction (ΔG° = - 14 kJ/mol) when the concentration of glutamine and of glutamate is 1 mM
ΔG = ΔG° + 6 log Keq
To invert the exergonic reaction the ΔG must become 0
0 = -14 + 6 log [(10-3) / (X)]
log X = 2.3
X = 150 M
The concentration of ammonia required to synthesize glutamine under the given conditions would be impossibly high
Which of the following is catalysed by an aminotransferase?
A. Glutamine → glutamate + NH3
B. Ornithine + carbamyl P → citrulline + Pi
C. Glutamate + pyruvate → α-ketoglutarate + alanine
D. Argininosuccinate → fumarate + arginine
c) Glutamate + pyruvate → α-ketoglutarate + alanine
Aminotransferases or transaminases catalyse the transfer of an amino group from an amino acid to a keto acid.
a) is catalysed by glutaminase, a hydrolase
b) is catalysed by ornithine carbamyl transferase
d) is catalysed by a lyase
In blood plasma, alanine and glutamine are present in concentrations higher than those of any other amino acid. Describe why.
In peripheral tissues such as muscle, alanine is synthesized from pyruvate through transamination. Alanine is released into the bloodstream and transported to the liver, where it undergoes reverse transamination back to pyruvate.
Glutamine is synthesized in peripheral tissues from glutamate and ammonia, catalysed by glutamine synthase.
They are both the amino acids used as carriers of amino groups from peripheral tissues to liver.
Methionine can be synthetized by methylation of homocysteine. Why is methionine considered anyway an essential amino acid?
Homocysteine is a product of methylation reaction using S-adenosyl methionine as methyl donor. Thus, to form homocysteine we need methionine anyway. On the other hand, there is no reaction in humans to convert glucose metabolites to methionine.
Describe the steps by which glycerol can be used to synthesize alanine.
Glycerol → glycerol-P → dioxyacetone-P → glyceraldehyde-P → 1,3-bisP-glycerate → 3-P-glycerate → 2P-glycerate → phosphoenolpyruvate → pyruvate → alanine
Which of these is a substrate of ribonucleotide reductase?
a) AMP
b) ADP
c) ATP
d) dADP
b) ADP
Only ribonucleotides diphosphates can be used by ribonucleotide reductase to make deoxy ribonucleotide diphosphates.
Which of these are substrates of thymidylate synthase?
a. UMP and methyl FH4
b. dUMP and methyl FH4
c. dUDP and methylene FH4
d. dUMP and methylene FH4
e. UMP and methylene FH4
d) dUMP and methylene FH4
The methyl group in thymidylic acid is formed by reduction of the methylene group of methylene FH4 with resulting oxidation of FH4 to FH2.
Fill the spaces with dots with the words listed below.
Proline is a ___ amino acid. It is converted to ___ that follows the ___ until ___. The latter is translocated to the ___, where is oxidized to ___. The latter reaction provides ___ that is required for reduction of ___ to ___.
Cytosol, 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, glucogenic, glutamate, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, Krebs cycle, malate, NADH, oxaloacetate.
Proline is a glucogenic amino acid. It is converted to glutamate that follows the Krebs cycle until malate . The latter is translocated to the cytosol, where is oxidized to oxaloacetate. The latter reaction provides NADH that is required for reduction of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
Fill the spaces with dots with the words listed below.
In the synthesis ___ of purine nucleotides, synthesis of ___ requires several amino acids. ___ 3 and 9 derive from ___, ___ 4 and 5 and ___ 7 from ___, ___ 1 from ___. Finally ___ 2 and 8 derive from 1C units coming from β-carbon of ___.
Aspartate, carbons, carbons, de novo, glutamine, glycine, inosine, monophosphate, nitrogen, nitrogen, nitrogens, serine.
In the synthesis de novo of purine nucleotides, synthesis of inosine monophosphate requires several amino acids. Nitrogens 3 and 9 derive from glutamine, carbons 4 and 5 and nitrogen 7 from glycine, nitrogen 1 from aspartate. Finally carbons 2 and 8 derive from 1C units coming from β-carbon of serine.
Construct a figure using all of the following terms. Some may be used more than once.
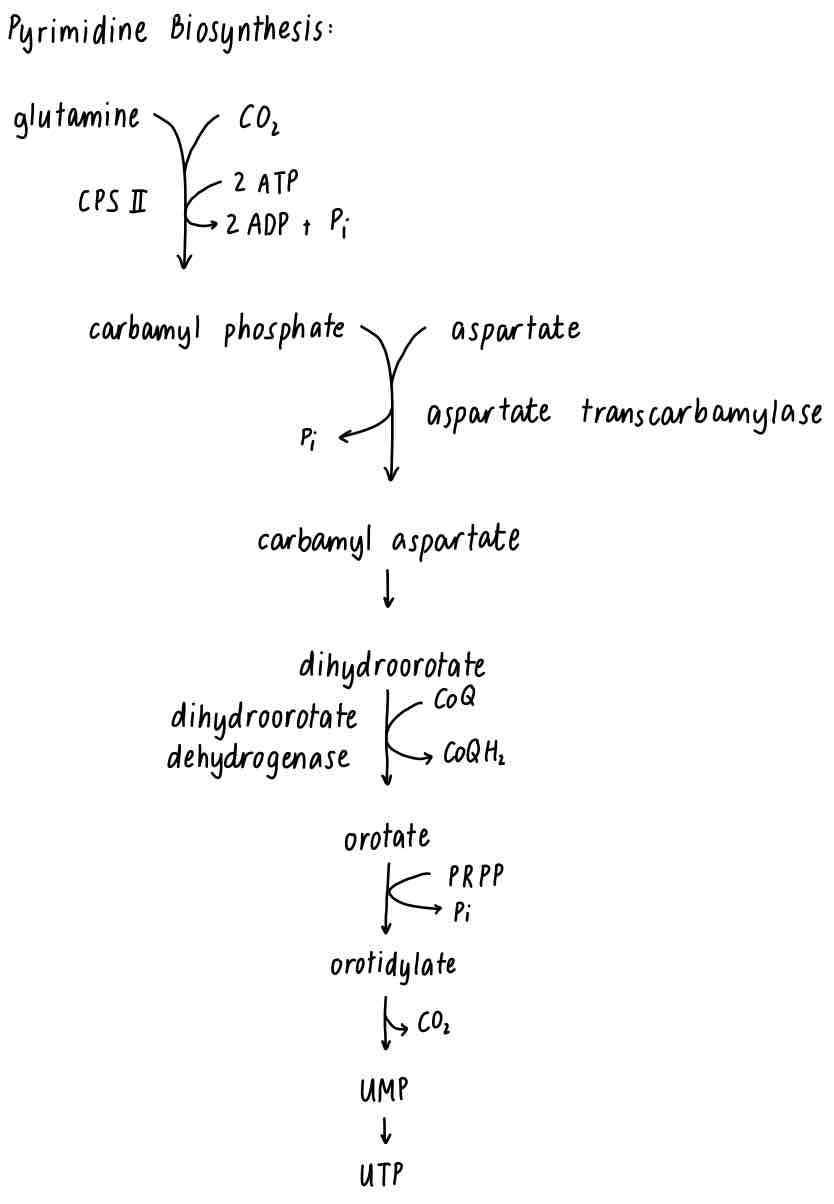
ADP, aspartate, aspartate transcarbamylase, ATP, carbamyl aspartate, carbamyl phosphate, CO2, CoQ, CoQH2, CPS II, CTP, dihydroorotate, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, glutamine, orotate, orotidylate, PPi, PRPP, UMP, UTP
Construct a figure using all of the following terms. Some may be used more than once.
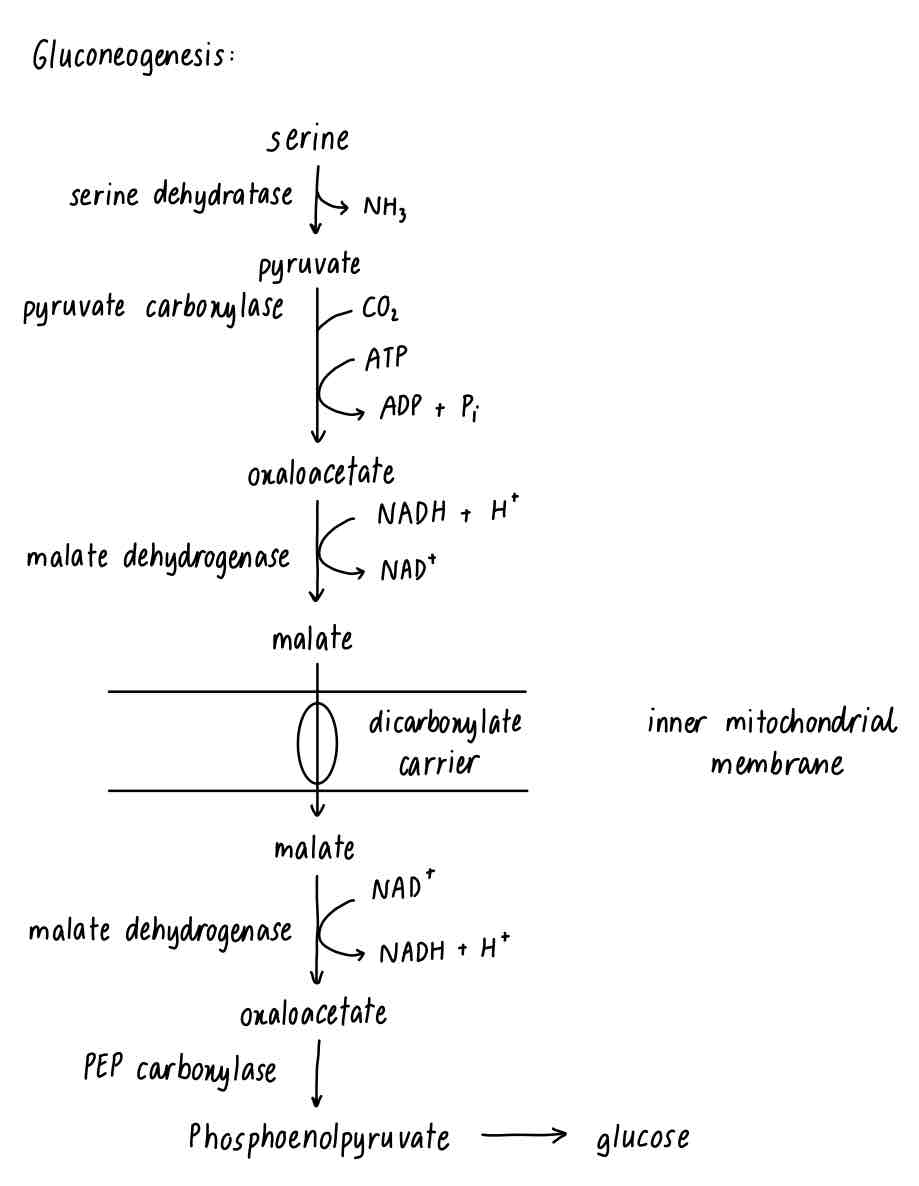
ADP, ATP, CO2, dicarboxylate carrier, glucose, inner mitochondrial membrane, malate, malate dehydrogenase, NAD+, NADH + H+, NH3, phosphoenolpyruvate, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, pyruvate, pyruvate carboxylase, serine, serine dehydratase.
Which metabolic pathway is shown by this figure?
Gluconeogenesis
Which of the following statements regarding pyrimidine biosynthesis is CORRECT?
a) Pyrimidine biosynthesis begins with PRPP
b) CTP inhibits aspartate transcarbamylase
c) UTP is not a precursor for CTP
d) Amino acids are not required
e) Carbamyl phosphate for pyrimidine biosynthesis is synthesized in mitochondria.
b) CTP inhibits aspartate transcarbamylase
a) False. PRPP reacts with already formed nucleotide (orotate)
b) True. ATC is an allosteric enzyme. CTP is a feedback inhibitor
c) False. UTP is the precursor of CTP
d) False. Glutamine and aspartate are required
e) False. CPS II is cytosolic
Only one statement concerning one-carbon metabolism is incorrect.
a) The major donor of 1C units is serine
b) The synthesis of TMP requires methylene FH4
c) Methylation of homocysteine requires B12 coenzyme
d) Formyl FH4 is required for pyrimidine biosynthesis
e) The formyl group has the oxidation level of formic acid
d) Formyl FH4 is required for pyrimidine biosynthesis
Formyl FH4 is not required for pyrimidine synthesis, but rather for purine synthesis
True or false? Concerning purine nucleotides biosynthesis. More than one answer is correct
a) We may state that C8 of purine nucleotides derives from β-carbon of serine
b) Nitrogen 1 of the purine ring derives from aspartate with formation of oxaloacetate
c) Two carbon atoms of the purine ring derive from glutamine
d) The first product of de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides is IMP
e) GMP is synthesized from AMP
f) PRPP is required for activation of the anomeric C of ribose-5-P
a) True. The formyl group that provides C8 derives from the β carbon of serine
b) False. N1 derives from aspartate with formation of fumarate
c) False. Two nitrogen atoms derive from glutamine
d) True
e) False. Both AMP and GMP are synthesized from IMP in separate pathways
f) True
True or false? Concerning haem catabolism. More than one answer is correct.
a) One product of haem oxygenase reaction is CO2
b) Bilirubin from reticulo-endothelial system circulates bound to albumin
c) Bilirubin conjugation with glucuronic acid takes place in the spleen
d) The bile secretion contains bilirubin diglucuronide
e) In jaundice originating from excessive haemolysis, plasma bilirubin is conjugated with glucuronic acid
a) False. It is carbon monoxide CO
b) True
c ) False. Conjugation takes place in the hepatocytes
d) True
e) False. This is pre-hepatic icterus in which bilirubin is bound to albumin
Only one answer is correct
a) Deamination of serine yields pyruvate and ammonia
b) Isoleucine is an only ketogenic amino acid
c) Valine enters the Krebs cycle at the level of oxaloacetate
d) Glutamate dehydrogenase catalyses an irreversible reaction
a) Deamination of serine yields pyruvate and ammonia
a) True
b) False. Isoleucine is both ketogenic (acetyl CoA) and glucogenic (propionyl CoA)
c) False. Valine enters the Krebs cycle at the level of succinyl CoA
d) False. The reaction is reversible
Concerning protein intracellular degradation:
a) It is inhibited during fasting
b) Inducible proteins are more stable than constitutive proteins
c) Ubiquitin binds the target protein by an isopeptide bond
d) Ubiquitinated proteins are degraded in the lysosomes
c) Ubiquitin binds the target protein by an isopeptide bond
a) False. During fasting cortisol stimulates protein degradation
b) False. Inducible proteins have very short lives
c) True. It binds with the side chain amino group of lysine
d) False. Ubiquitinated proteins are degraded in the proteasome
Concerning γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
a) It is obtained by deamination of glutamate
b) Its catabolism occurs via the Krebs cycle
c) Its ionotropic receptor opens Na+ channels
d) Its synthesis requires TPP
b) Its catabolism occurs via the Krebs cycle
a) False. GABA is formed by decarboxylation of glutamate
b) True. GABA transaminase generates succinic semialdehyde that is then oxidized to succinate
c) False. GABA A receptor opens Cl- channels
d) False. Requires pyridoxal P
. The 5-methyl group of thymine originates from
a) S-adenosylmethionine
b) Methyl tetrahydrofolate
c) Methylene tetrahydrofolate
d) Formyl tetrahydrofolate
c) Methylene tetrahydrofolate
Which of the following most accurately describes purine nucleotide biosynthesis?
a) PRPP → Glutamine → AMP → IMP
b) Glutamine → PRPP → AMP → IMP
c) PRPP → Glutamine → IMP → AMP
d) Glutamine → PRPP → IMP → AMP
c) PRPP → Glutamine → IMP → AMP
PRPP reacts with glutamine and the purine ring is built till formation of IMP. Then AMP is synthesized from IMP
Insert the missing intermediates
AMP → Adenosine → Inosine → ___ → ___ → Uric acid
Aspartate + ___ → carbamylaspartate → ___ → orotic acid
PRPP + adenine → ___ + ___
IMP + aspartate → adenylsuccinate → AMP + ___
Methyl FH4 + ___ → methionine + ___
dUMP + methylene FH4 → TMP + ___
Serine + FH4 → ___ + Methylene FH4
Nor-adrenaline + ___ → Adrenaline + ___
Hypoxanthine, xanthine
carbamyl phosphate, dihydroorotic acid
AMP, PPi
fumarate
homocysteine, FH4
FH2
Glycine
S-adenosyl methionine, S-adenosyl homocysteine
Which of these is not required for pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis?
a) Glutamine
b) Aspartate
c) NADPH
d) PRPP
c) NADPH
NADPH is not required. Glutamine is required for CPS II
During fasting
a) Urea synthesis is decreased because we do not eat any protein
b) Urea synthesis is increased because we consume tissue proteins
c) Urea synthesis is decreased for lack of ATP
d) Urea synthesis is decreased because we use amino acids for gluconeogenesis
b) Urea synthesis is increased because we consume tissue proteins
Tissue proteins are degraded and amino acids addressed to gluconeogenesis. To do this, amino acids are deaminated and ammonia is used for urea synthesis. Thus, d) is incorrect.
One of the following statements referred to humans is not correct
a) Alanine is not an essential amino acid because it can be synthesized from pyruvate
b) Aspartate is not an essential amino acid because it can be synthesized from oxaloacetate
c) Methionine is not an essential amino acid because it can be synthesized from homocysteine
d) Valine is an essential amino acid because we cannot synthesize it
c) Methionine is not an essential amino acid because it can be synthesised from homocysteine
It is true that methionine can be synthesized from homocysteine, but the latter can only originate from methionine.
One of these statements concerning histidine is not correct
a) It is not an essential amino acid
b) Its catabolism leads to glutamate
c) It is present in the active site of many enzymes
d) it is a glucogenic amino acid
a) It is not an essential amino acid
One of these statements is not correct
a) All aminoacids can be converted to acetyl CoA
b) Leucine is partly glucogenic
c) Phenylalanine is converted to tyrosine by hydroxylation
d) The β carbon of serine is a source of 1C units
b) Leucine is partly glucogenic
Leucine is only ketogenic
One of these statements is not correct
a) Haem synthesis depletes Krebs cycle intermediates
b) The source of nitrogen for haem is glycine
c) During haem catabolism the 4 pyrrole groups are separated from each other
d) Many reactions of haem biosynthesis take place in mitochondria
e) One product of haem oxygenase is carbon monoxide
c) During haem catabolism the 4 pyrrole groups are separated from each other
During haem catabolism only the bond between pyrrole rings A and B is broken. Bile pigments have a linear tetrapyrrolic structure
Which of these is NOT an intermediate of the urea cycle? More than one correct answer may apply.
a) Carbamyl phosphate
b) Carbamyl aspartate
c) Argininosuccinate
d) Methylmalonyl CoA
e) Citrullyl AMP
f) Citrulline
b) Carbamyl aspartate, d) Methylmalonyl CoA
b) is an intermediate of pyrimidine biosynthesis
d) is involved in the metabolism of propionyl CoA