Pelvis, Sacrum, Coccyx and Hip Joint - Vocabulary Flashcards
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms related to the sacrum, coccyx, pelvis, hip joint anatomy, ligaments, and associated muscles as described in the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Sacrum
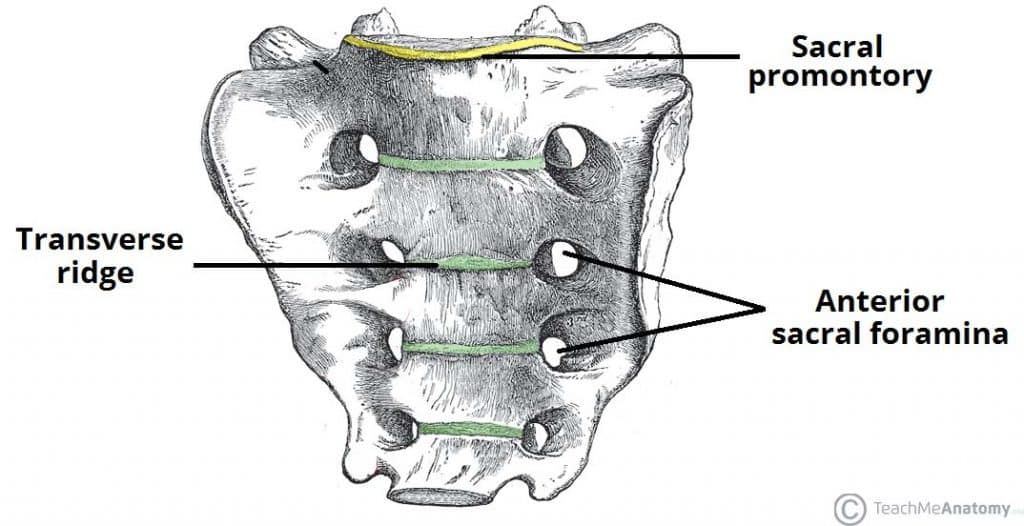
Triangular bone formed by fusion of five sacral segments; features include median, intermediate, and lateral crests; anterior and posterior sacral foramina; sacral promontory; participates in weight transfer to the pelvis via the sacroiliac joints.
Median sacral crest
Midline ridge on the posterior aspect of the sacrum formed by fused spinous processes.
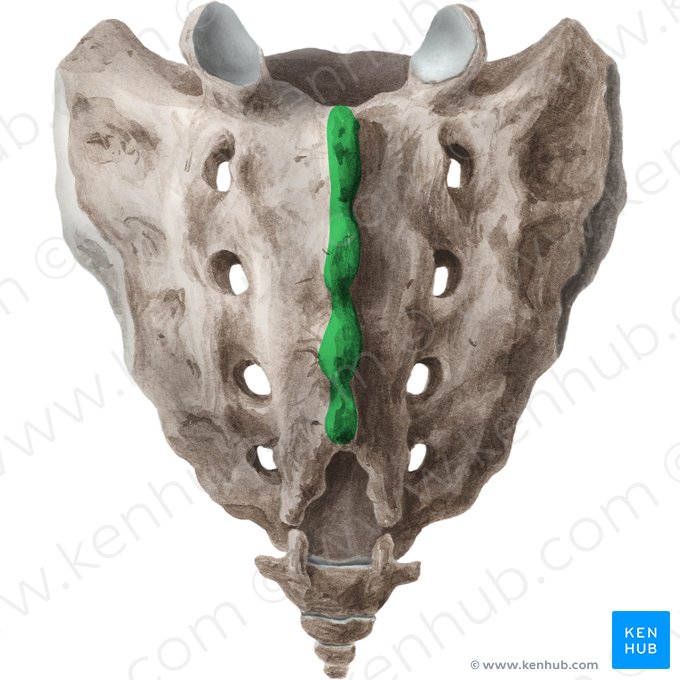
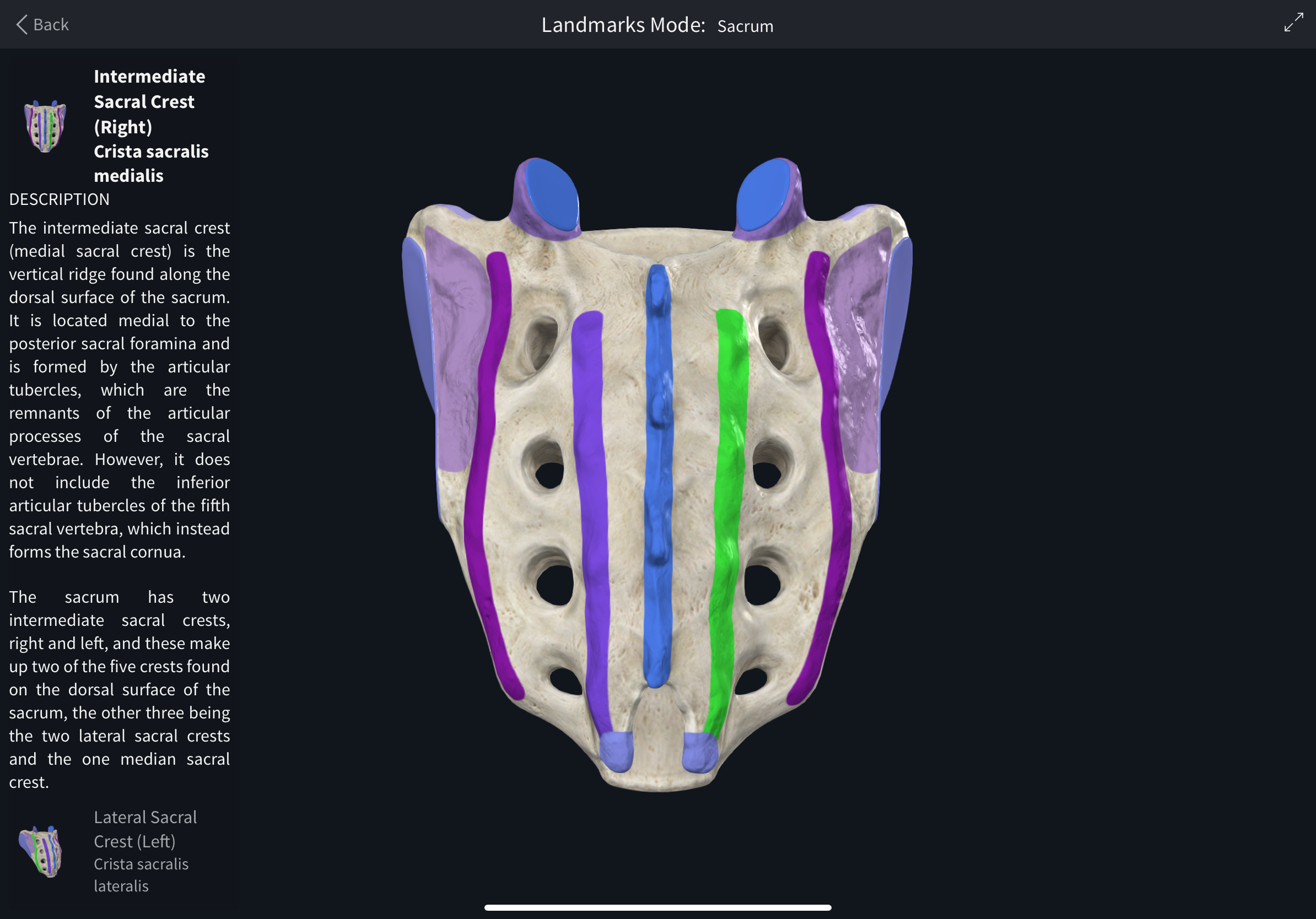
Intermediate sacral crest
Posterior crest formed by fused sacral articular processes.
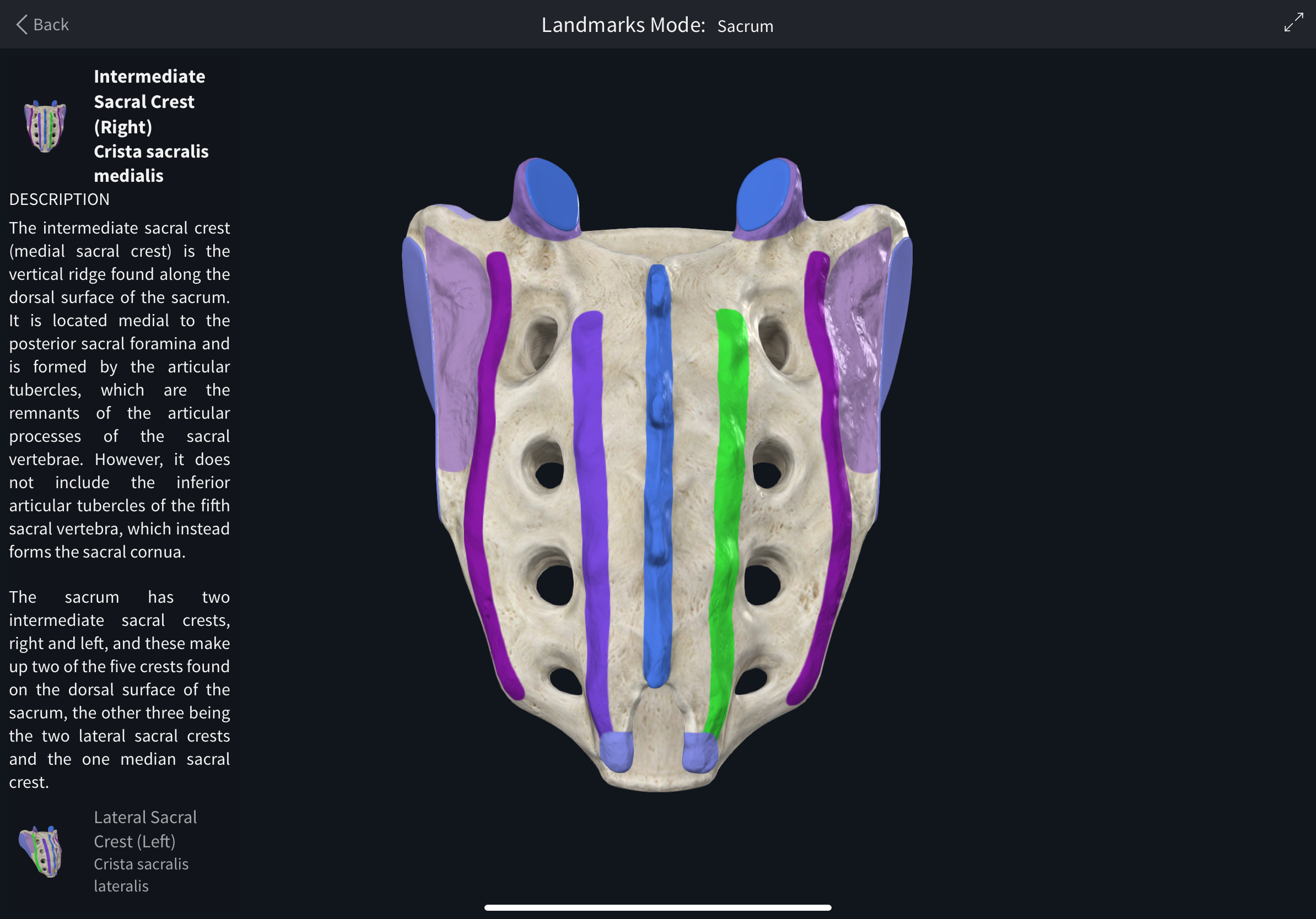
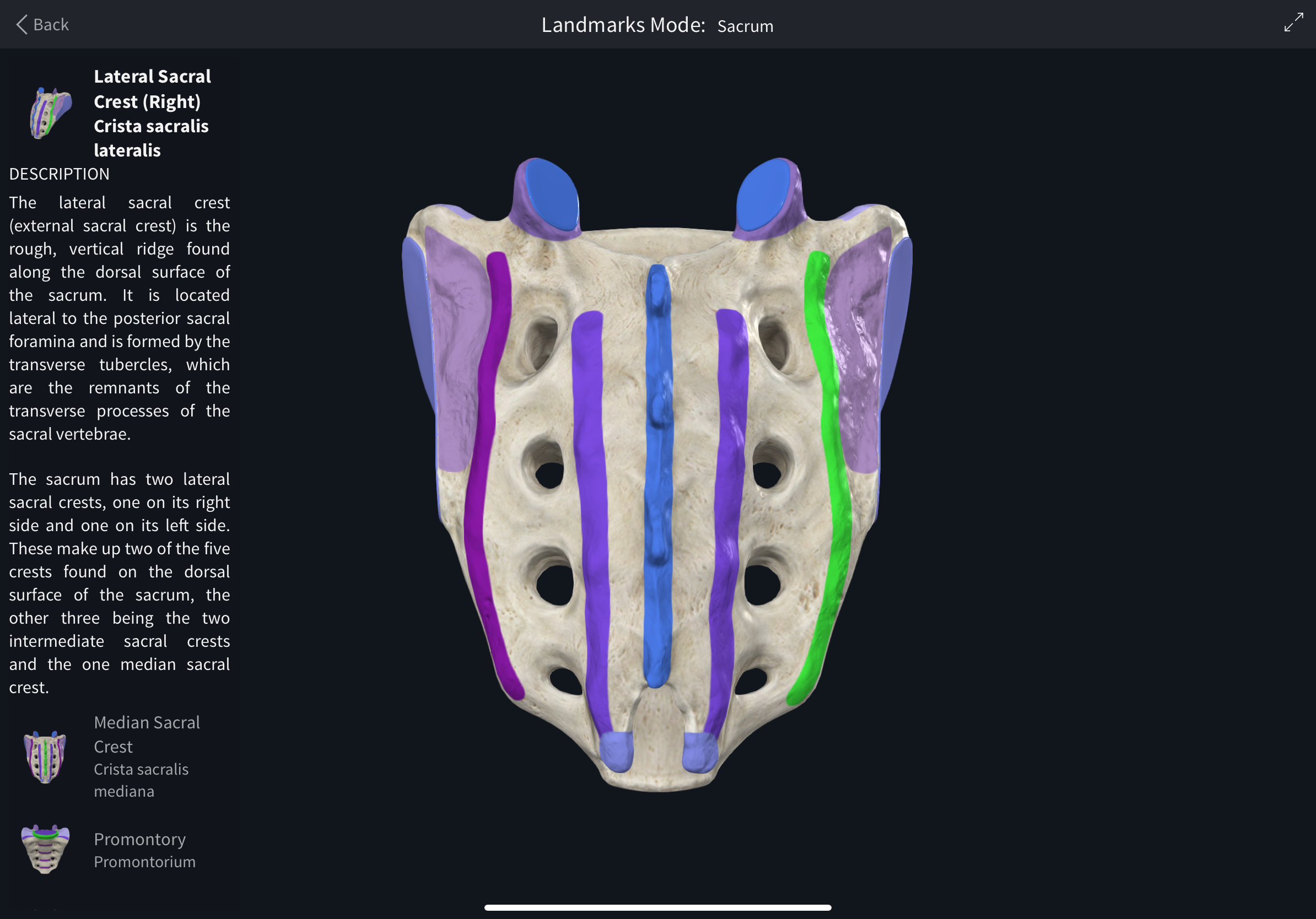
Lateral sacral crests
Posterior crests formed by fused sacral transverse processes.
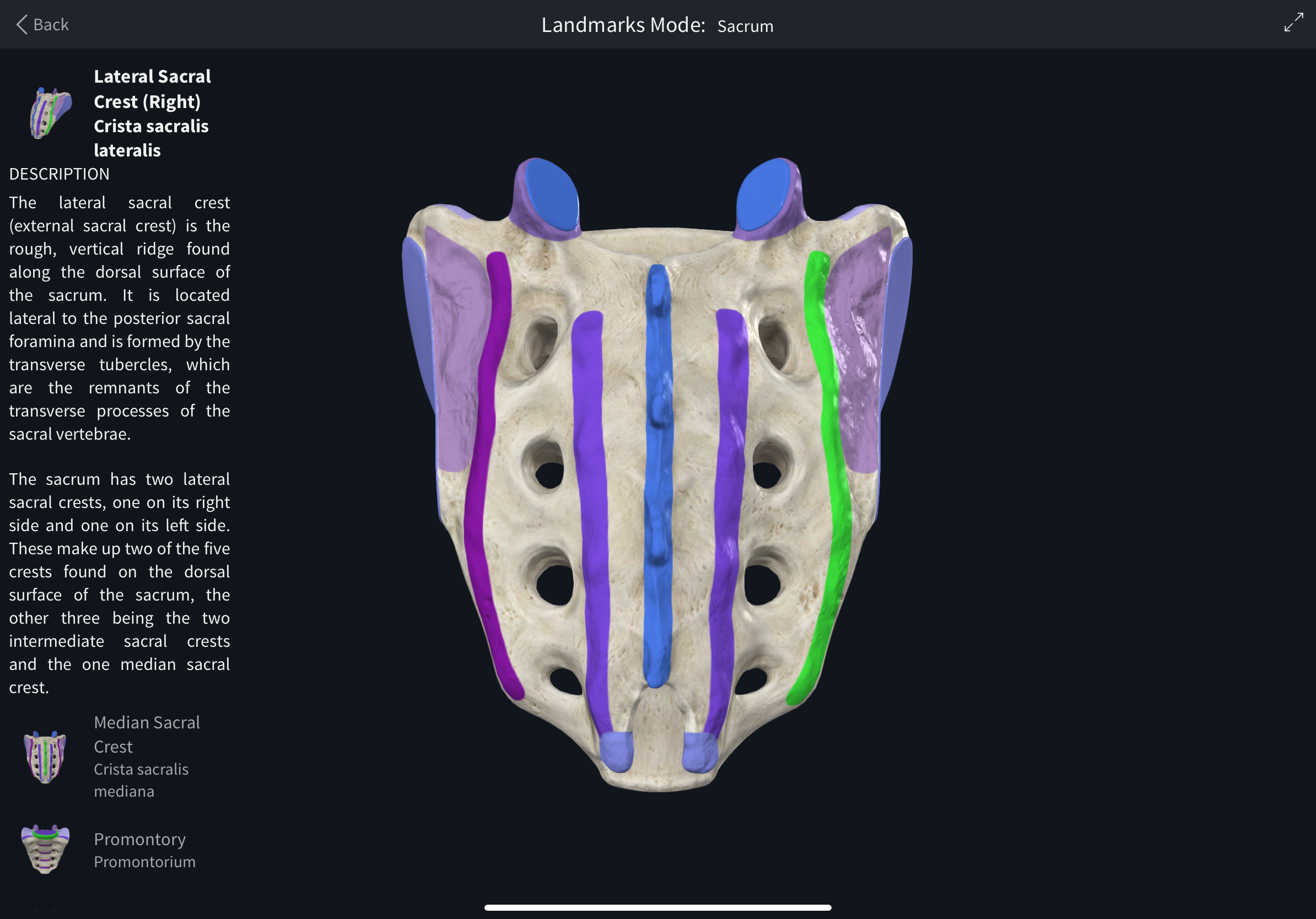
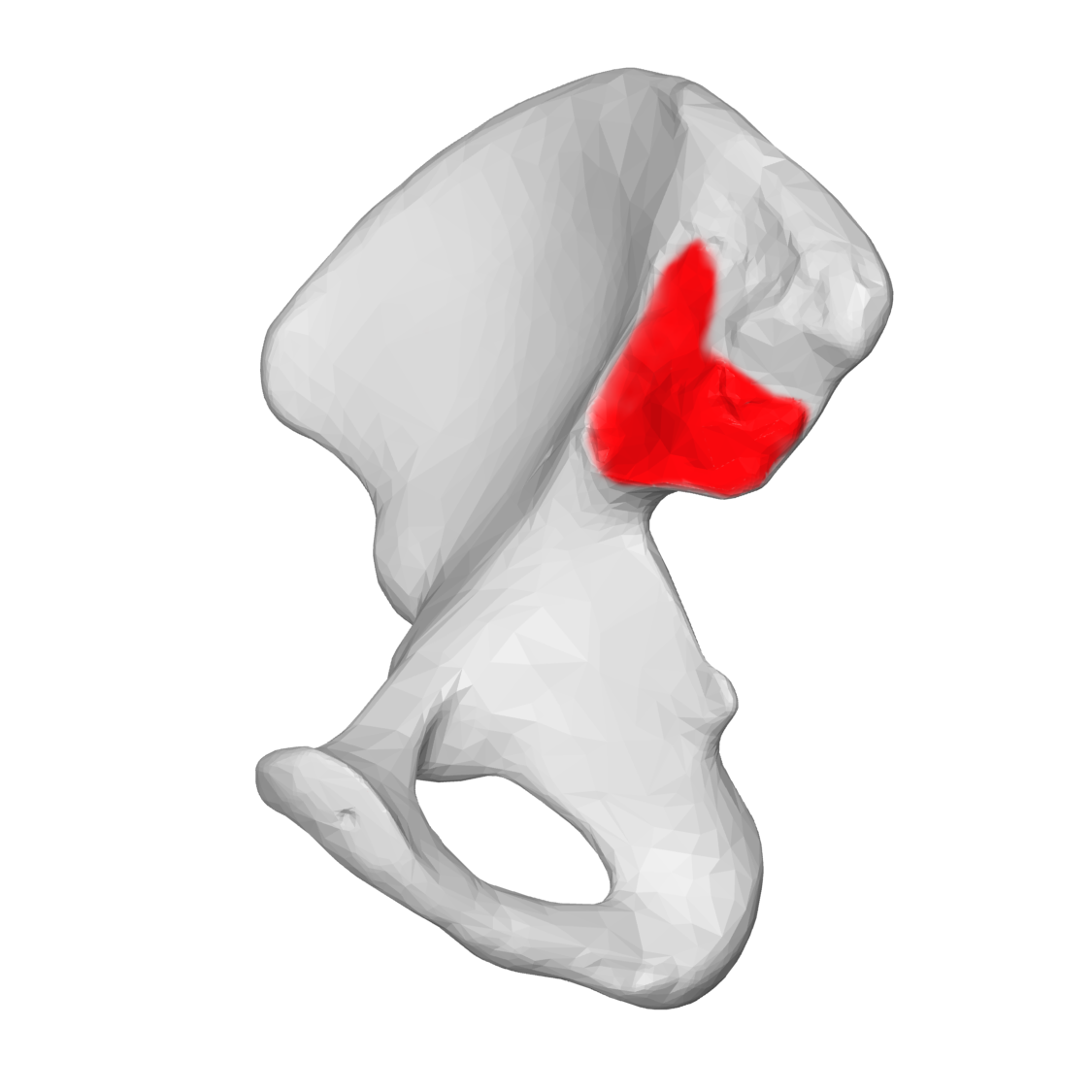
Auricular surface
Articular surface on the sacral ala for the sacroiliac joint, usually with hyaline cartilage.
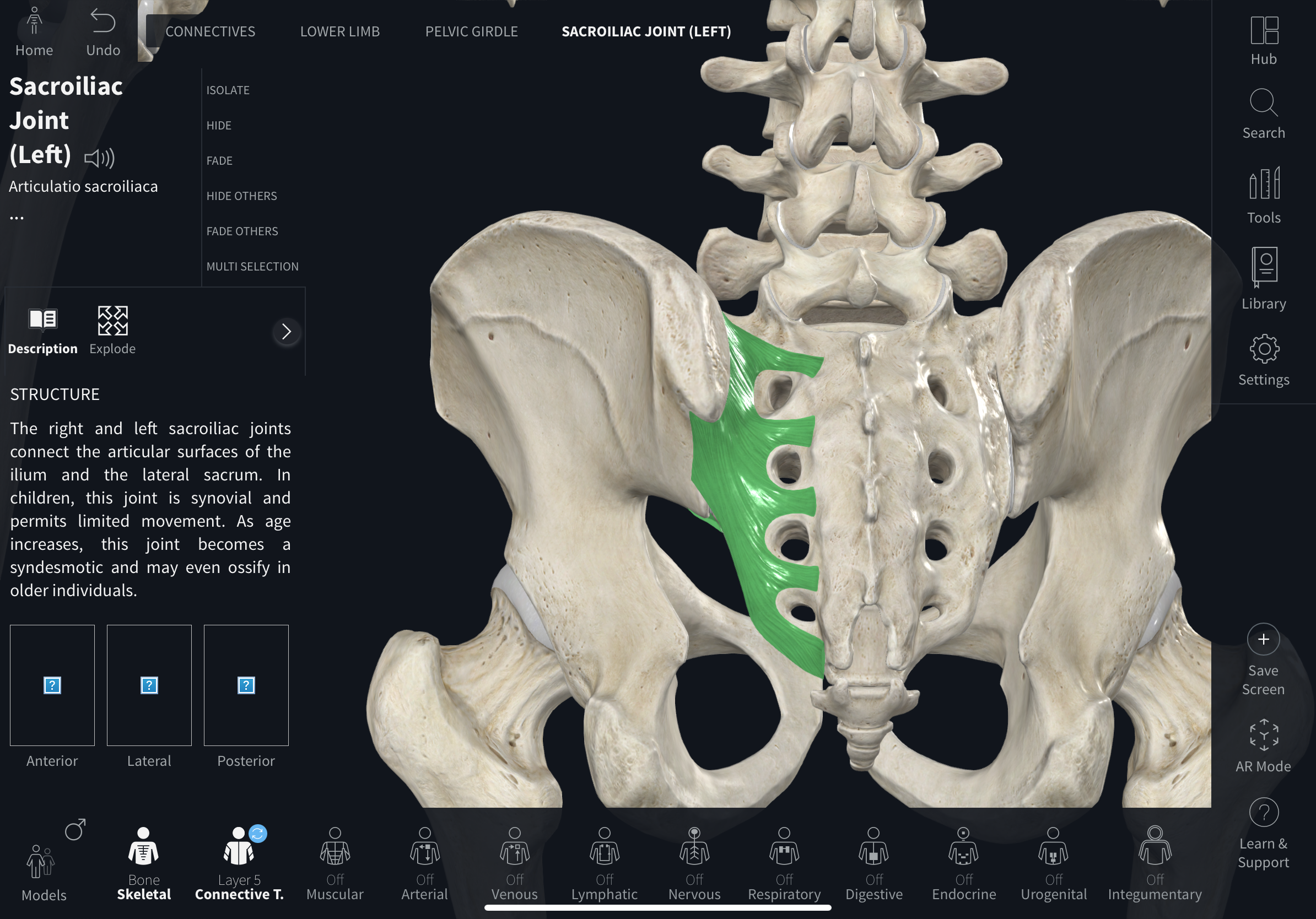
Sacroiliac joint
Joint between the sacrum and ilium; composed of a synovial anterior part and a fibrous posterior part; typically immovable but allows weight transfer to the hip via ligaments.
Sacral foramina
Anterior sacral foramina (ventral rami) and posterior sacral foramina (dorsal rami) for exiting nerves.
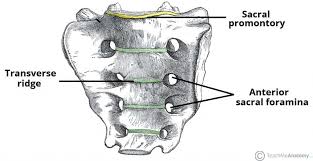
Sacral promontory
Forward-projecting part of the first sacral vertebral body; marks the pelvic brim.
Coccyx
Tailbone; typically 3–5 fused coccygeal segments; highly variable; articulates with the sacrum via the sacrococcygeal joint; muscles attach here and mobility decreases with age.
Bony pelvis
Pelvic skeleton formed by two hip bones, the sacrum, and the coccyx; includes sacroiliac joints and pubic symphysis.
Pubic symphysis
Symphysis joint between the two pubic bones; fibrocartilaginous disc with superior and inferior pubic ligaments.
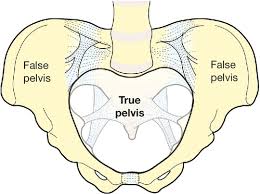
True pelvis
Pelvic space that contains pelvic viscera; bounded by the pelvic brim; inlet and outlet; separates from the false pelvis by the brim.
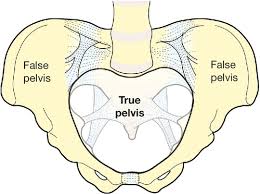
False pelvis
Portion of the pelvis above the pelvic brim, part of the abdomen.
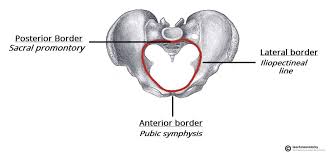
Pelvic brim
Line separating true and false pelvis; includes pubic crest, pectineal line, and arcuate line.
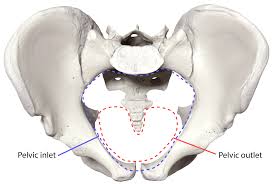
Pelvic inlet
Superior opening of the true pelvis guarded by the pelvic brim.
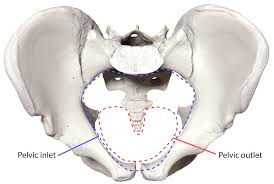
Pelvic outlet
Inferior opening of the true pelvis.
Pubic crest
Ridge on the pubis forming part of the pelvic brim.
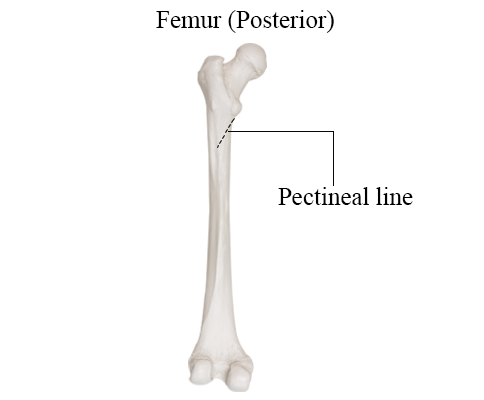
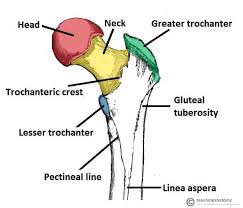
Pectineal line (femur)
Ridge on the proximal femur just below the lesser trochanter; attachment for the pectineus.
Intertrochanteric line
Anterior line on the femur between the greater and lesser trochanters; junction for the fibrous capsule.
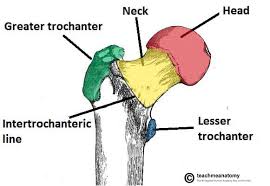
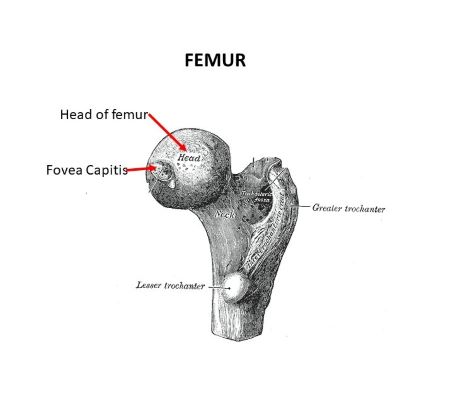
Greater trochanter
Large lateral prominence at the proximal femur; attachment for the gluteal muscles (medius/minimus).
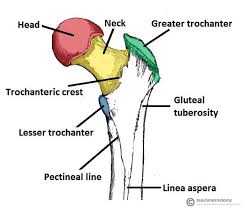
Lesser trochanter
Smaller posteromedial projection on the proximal femur; insertion for the iliopsoas.
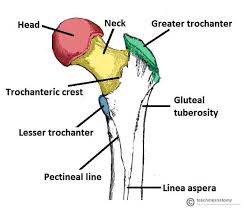
Gluteal tuberosity
Roughened area on the posterior femur just below the gluteus maximus insertion.
Linea aspera
Rough vertical ridge on the posterior surface of the femoral shaft; has a lateral and a medial lip.
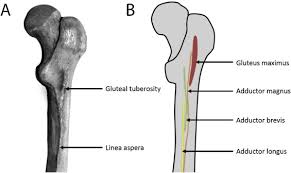
Spiral line
Continuation of the lateral lip of the linea aspera toward the femoral neck; part of the proximal femur
’s attachment pattern.
Fovea capitis (fovea)
Small pit in the femoral head where the ligamentum teres attaches.
Ligamentum teres (ligament of the head of femur)
Ligament connecting the femoral head to the acetabulum; not a major stabilizer in adults; transmits a vessel to the head during childhood.
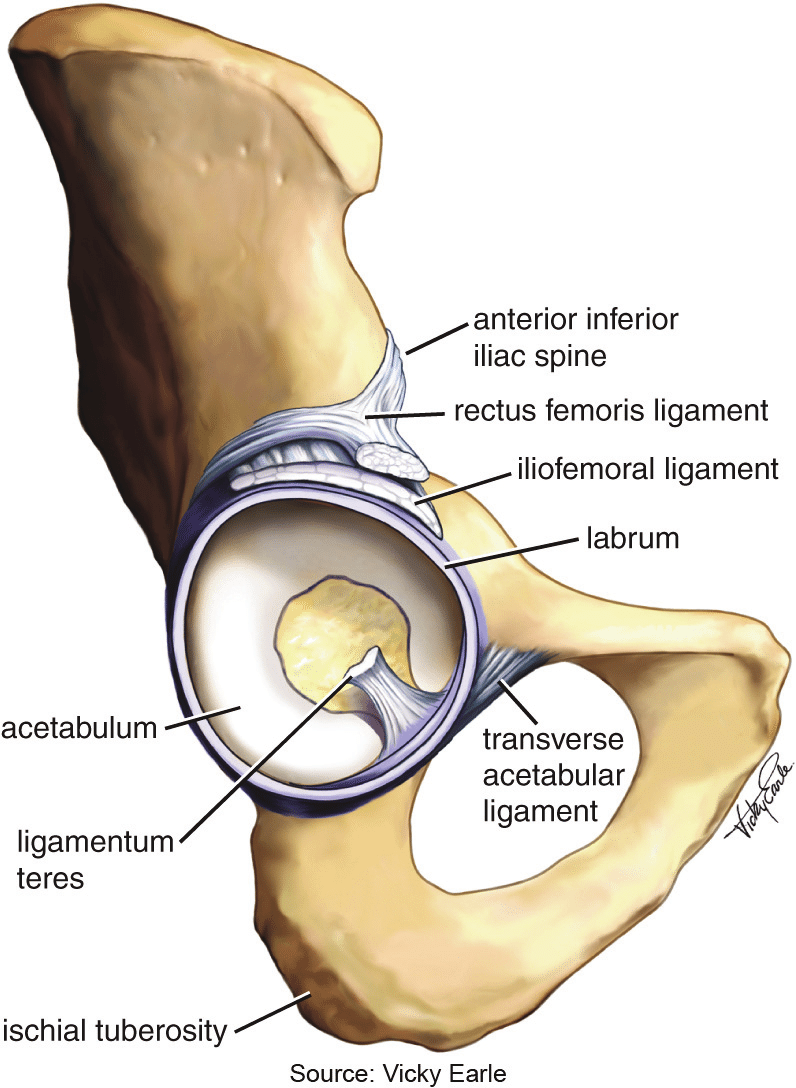
Transverse acetabular ligament
Bridge across the acetabular notch; completes the acetabular rim and serves as an attachment for the acetabular labrum.
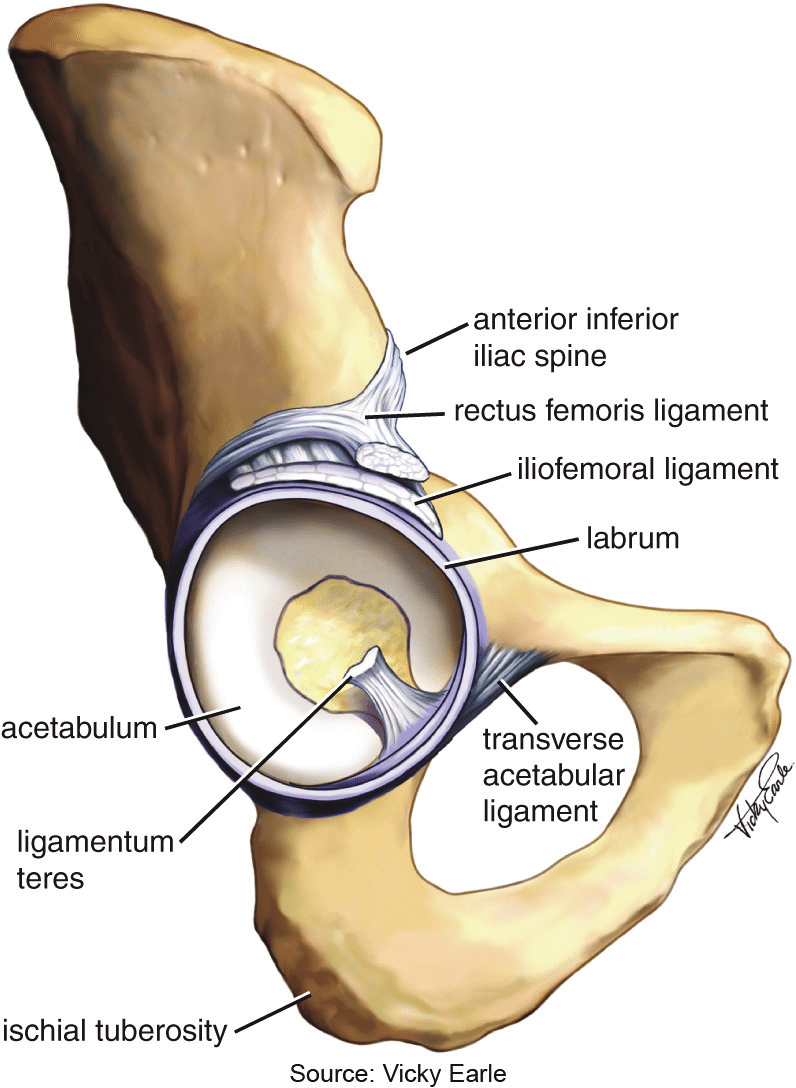
Acetabular labrum
Fibrocartilaginous rim that deepens the acetabulum and enhances joint stability; continuous with the transverse acetabular ligament.
Acetabulum
Deep socket formed by the ilium, ischium, and pubis; contains the lunate surface for the femoral head and the acetabular notch bridged by the transverse acetabular ligament; labrum deepens the socket.
Zona orbicularis
Circular fibers of the hip capsule that encircle the neck of the femur and help stabilize the joint.
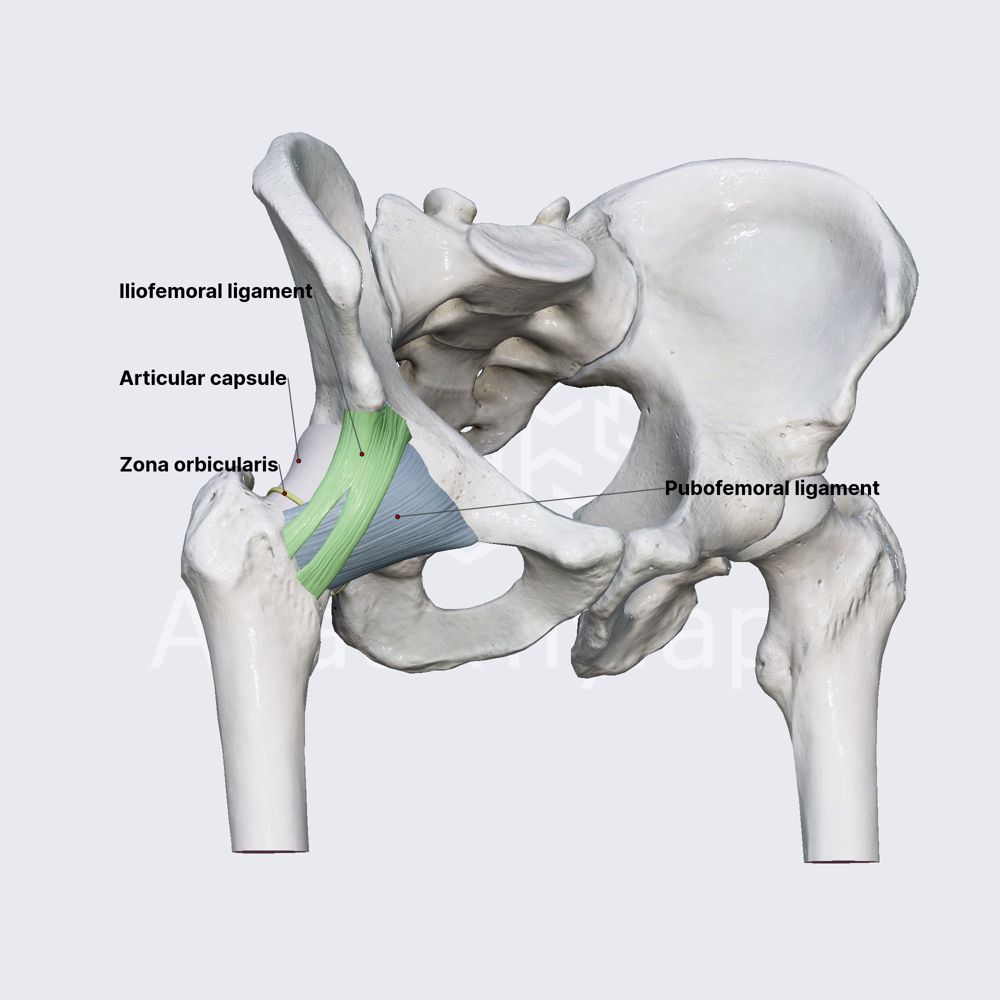
Hip joint capsule
Fibrous capsule surrounding the femoral head and neck; anterior attachment to the intertrochanteric line; posterior fibers wind around the neck and are relatively lax.
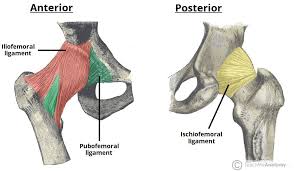
Iliofemoral ligament
Y-shaped anterior ligament from the ilium to the femur; one of the strongest ligaments; limits overextension.
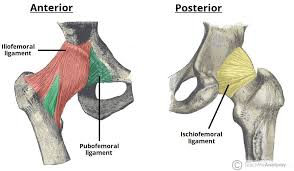
Pubofemoral ligament
Ligament reinforcing the anterior inferior capsule; tightest with abduction to prevent overabduction.
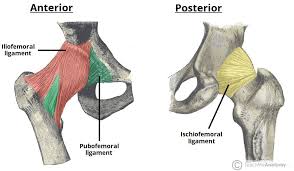
Ischiofemoral ligament
Posterior capsule ligament; becomes taut with medial (internal) rotation and helps stabilize the hip.
Piriformis
Pear-shaped deep lateral rotator; origin from the anterior sacrum; exits through the greater sciatic foramen to insert near the greater trochanter.
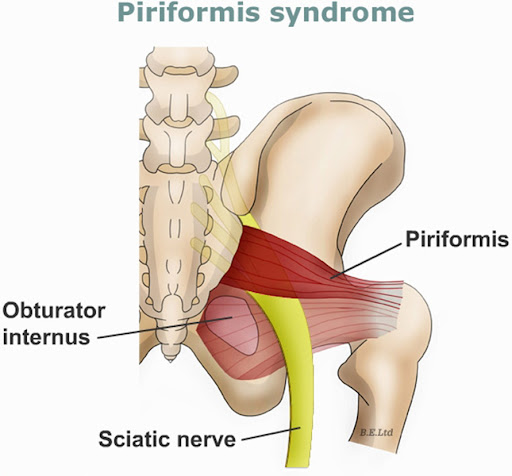
Obturator internus
Lateral rotator; originates around the obturator membrane/foramen; passes through the lesser sciatic foramen; inserts on the greater trochanter (via the trochanteric fossa).
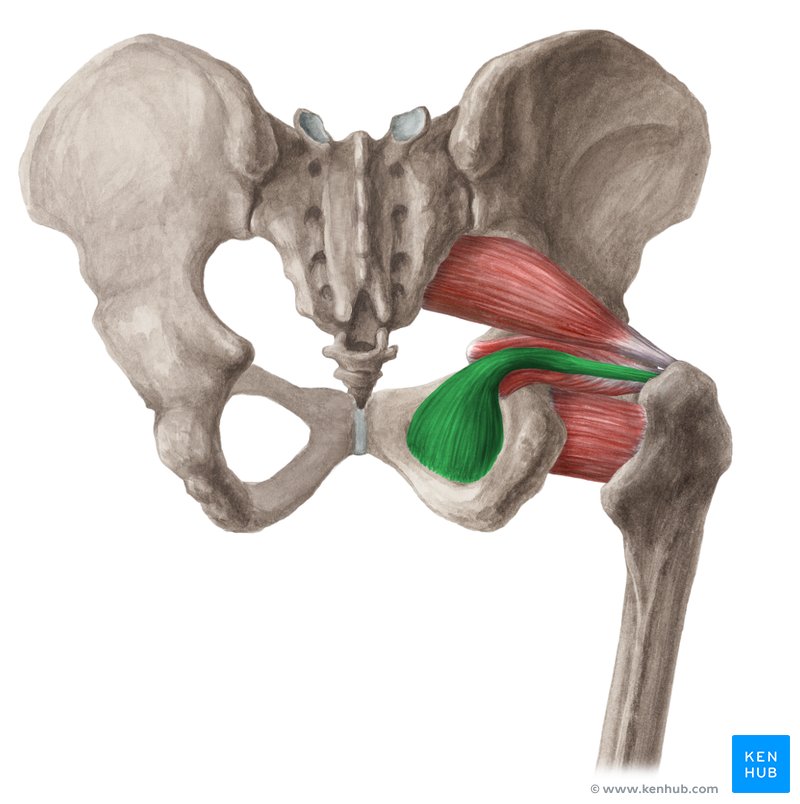
Obturator externus
Lateral rotator; originates around the obturator membrane; passes to the proximal femur and inserts near the greater trochanter.
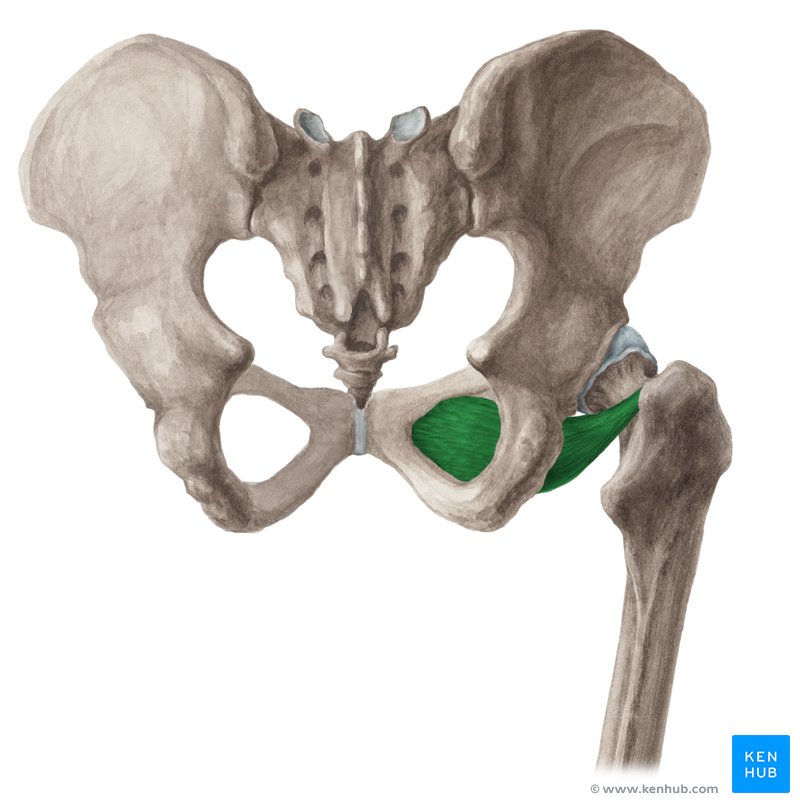
Gemellus superior
Small lateral rotator; originates from the ischial spine; inserts at the greater trochanter.
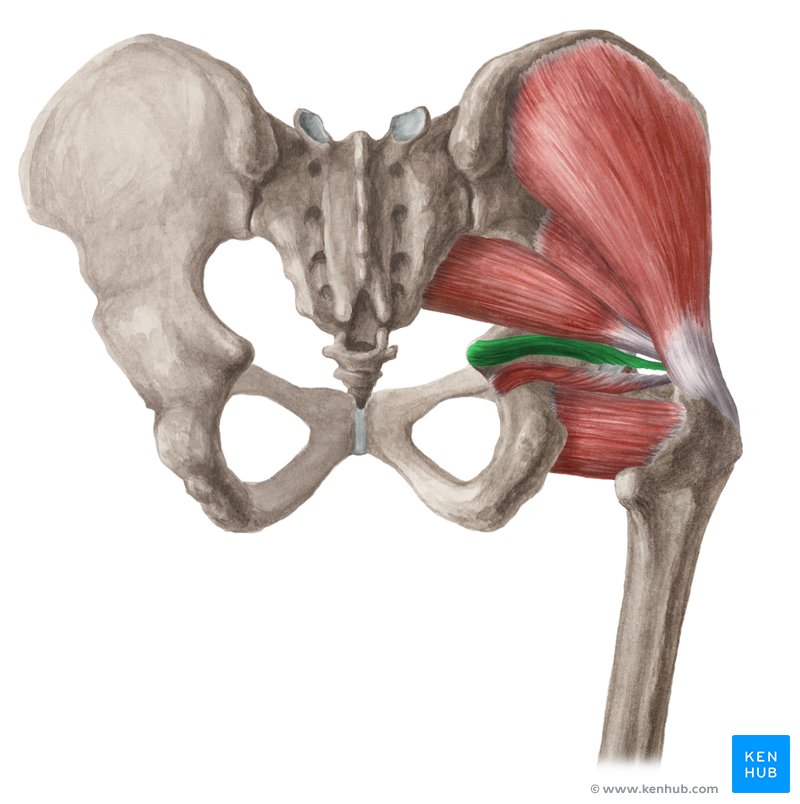
Gemellus inferior
Small lateral rotator; originates from the ischial tuberosity; inserts at the greater trochanter.