Vertebrate Physiology - Ch 5
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Function of the Nervous System
Acquire sensory information and generate adaptive response
What does adaptive mean in regards to the nervous system?
An appropriate response to a stimulus
What are the two forms of structural organization in the vertebrate nervous system?
Central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What sets apart the CNS from the PNS?
The CNS is encased in bone, the PNS is everything else
What organs are part of the CNS?
Brain, spinal cord, retina
Why is the retina a part of the CNS?
It develops from the middle part of the brain and extends outside the skull
What organs are a part of the PNS?
Nerve fibers
What does the afferent division of the PNS do?
Carries information from the peripheria (sensors) to the CNS
What does the efferent division of the PNS do?
Transmits instructions from CNS to effector organs
Two parts of efferent division
Sematic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
What does the sematic nervous system do?
Drives motor neurons that drive skeletal muscles
Two parts of the autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
How is information moved around the body via the nervous system?
Afferent division receives/carries division to CNS → CNS proccesses information and generates response → Efferent division carries information from CNS to effector organs
What are the three classes of neurons?
Afferent, efferent, and interneurons
What are the four parts of an afferent neuron?
1) Sensory receptor → peripheral end
2) Peripheral axon → extends from receptor to cell body
3) Cell body → dorsal root ganglion outside CNS
4) Central axon → extends from cell body into spinal cord
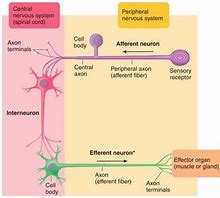
What are the three parts of efferent neurons?
1) Dendrites → in CNS
2) Cell body → in CNS
3) Axon → projects to effector organ
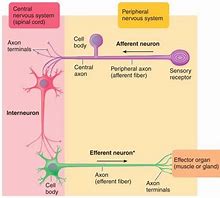
Where are interneurons found?
Within CNS
What do interneurons do?
Integrate peripheral responses to peripheral information
What do glial cells (neuroglia) do?
Maintain composition of ECF surrounding neurons;
Modulate synaptic function;
Prove myelin
What’s the most numerous type of glial cell?
Astrocytes
The processes on an astrocyte ___
Radiate out
What do the foot processes of astrocytes do?
Induce formation of blood-brain barrier → protect brain
What do astrocytes do?
Help recycle neurotransmitters and regulate contents of extracellular compostion
What do astrocytes take in and then release when recycling neurotransmitters?
Take in glutamate and send back glutamine
What do microglia do?
Conduct phagocytosis
What activates microglia to engage in phagocytosis?
Cytokines
What do ependymal cells do?
Line cavities of CNS and produce cerebral spinal fluid
What are the four types of glial cells?
Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells
What are the different glial cells derived from?
All derived from neural endoderm
What does the autonomic nervous system do?
Regulates visceral activities
Ex) Circulation, digestion, thermoregulation, pupil size
Dual innervation
Innervated by both parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve fibers
Ex) Most visceral (hollow) organs
What’s an example of the SNS found in mammals?
Sympathetic trunk lies aside spinal cord
*Sandwich filling
What’s an example of a PSNS in mammals?
Parasympathetic fibers extend from either side of spinal cord
*Bread of sandwich
What does the SNS handle?
Preparation for hard physical activity in emergenty situations
Ex) Fight or flight
What happens to the body during fight or flight?
Heart rate increases; respiratory airways open; glycogen/fat stores broken down; blood vessels that supply skeletal muscle dilate; pupils dilate
Why do respiratory airways open during fight or flight?
Increase oxygen intake → need for final electron acceptor
Why do blood vessels connecting to the skeletal muscles dilate?
Increase blood flow → more oxygen → more glucose
Why do pupils dialte during fight or flight?
Capture more light → improves distance vision
What does the PNS do?
“Housekeeping” during relaxation: digestion and emptying bladder
Automnomic pathway consists of a _____
Two-neuron chain
What are the two neurons of the autonomic pathway?
Preganglionic and posganglionic fibers
Where are preganglionic fibers in the autonomic pathway?
Extend from CNS to autonomic ganglion
→ Short
Where are postganglionic fibers in the autonomic pathway?
Innervate effector organs
→ Long
Where are sympathetic nerve fibers found?
Thoracic and lumbar spinal cord
Where are sympathetic ganglia found?
Form chain alongside spinal cord
Where are parasympathetic nerve fibers found?
Arise from cranial (brain) and sacral spinal cord
Where are parasympathetic ganglia found?
In or near effector organs
What do sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic fibers both release?
Acetylcholine
What do parasympathetic postganglionic fibers release?
Acetylcholine → cholinergic fibers
What do sympathetic postganglionic fibers release?
Norepinephrine (NE) → adrenergic fibers
Terminal branches of postganglionic fibers have ____ for diffuse release of neurotransmitters
Varicosities
What are the diffeent types of nervous system receptors?
Nicotinic acetylcholine, muscarinic acetylcholine, and adrenergic receptors
Where are nicotinic ACh receptors located?
On postganglionic cell bodies in autonomic ganglia
What types of channels do nicotinic ACh receptors have?
Ligand-gated nonspecific cation channels
*Depolarization: More Na+ enters than K+ leaves
Where are muscarnins ACh receptors find?
On effector cells responsive to parasympathetic system
What do the five subtypes of muscarinic Ach receptors do?
Activate second messenger systems when ACh binds → multiple effects
What does GPCR stand for?
Gene protein coupled receptors
Where are adrenergic receptors located?
On effector cells
What type of proteins are adrenergic receptors?
GPCR
What do alpha 1 receptors do?
Bind to Ne → excitatory response
What do alpha 2 receptors do?
Bind to NE → inhibitory response
What do beta 1 receptors do?
Bind equally to E (epinephrie) and NE → excitatory response
What do beta 2 receptors do?
Bind to E → inhibitory response
Where are motor neuron cell bodies located?
In ventral horn of spinal cord or in brainstem
What do axon terminals release?
ACh
What controls skeletal muscles?
Motor regions of cortex, basal nuclei, cerebullum, brainstem
*Motor neurons final common pathway
Where is the primary motor cortex?
Posterior part of frontal lobe in front of central sulcus
What does the primary motor cortex do?
Skeletal muscles move body → controls opposite side
Function of the spinal cord
Transmits information between brain/body
Integrate reflex activity between afferent and efferent divisions
What are the three regions of gray matter?
Dorsal, lateral, ventral horn
What does the dorsal horn consist of?
Cell bodies of interneurons on which afferent neurons terminate
What does the lateral horn consists of?
Cell bodies of autonomic efferent nerve fibers
What does the ventral horn consist of?
Cell bodies of somatic efferent neurons
What is white matter?
Bundle of myelinated nerve fibers (tracts)
What do the ascending tracts of white matter do?
Transmit afferent signals to brain
What do descending tracts of white matter do?
Relay messages from brain to efferent neurons
Where are spinal nerves located?
Emerge from spinal cord
What kinds of nerve fibers do spinal nerves contain?
Afferent and efferent fibers
Afferent fivers enter spinal cord through ___
Dorsal root
Efferent fibers leave spinal through ___
Ventral root
Where are cell bodies of afferent neurons clustered?
Dorsal root ganglion
Where are the neuron synapses located in respect to the stretch reflex?
Afferent, sensory neuron synapses directly on efferent, motor neuron
Motor neuron activates skeletal muscles to contract to ____
Counteract stretch
Withdrawal reflex
Withdrawal of limb from painful stimulus
What are the two ways the withdrawal relfex work?
Excited afferent neurons → stimulate excitatory interneurons → stimulate efferent motor neurons → flexor muscles (polysynaptic reflex)
Excited afferent neurons → inhibitory interneurons → inhibit efferent neurons → extensor muscles (reciprocal innervation)
Where is the somatosensory cortex located?
Anterior part of parietal lobe behind central sulcus (post-central gyrus)
What does the somatosensory cortex handle?
Initial processing and perception of somasthetic and proprioceptive sensations;
Receives sensory information from opposite side of body
Somasthetic meaning
Body surface
Proprioceptive meaning
Body position