Wood KU ARCH626 BTECH 1
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Hardwoods
Broadleaf, Deciduous, Walnut (take longer to grow)
Softwoods
Coniferous, Evergreen, Pine (grow fast)
4 Areas of a Tree
Trunk, Root Plate, Critical Root Zone, Total Root Zone
Dripline
Area under the canopy of a tree, avoid disturbing soil within this area
Annual Growth Rings
Become the grain of wood, show age of wood
Sapwood
the living part of the tree on exterior which still has sap
Heartwood
inner of tree, denser wood, no sap, oldest part of the tree
FSC
Forest Stewardship Council. Promulgates sustainable forestry standards
Wood stores ______
CO2
Steps to Seasoning Lumber
Green Lumber, Milled Lumber, Rough Sawn Lumber, Moisture Content, Drying (seasoning), Surfacing
Pressure Treated Lumber
Allows wood to withstand weather, animals, bugs, and rot by forcing chemicals into the wood
Common Wood
Lower quality, has knots and imperfections, can warp
Premium Wood
Higher quality, less imperfections
Example of Modified Wood
Acetylated Wood
Acetylated Wood
Basically add vinegar/acid to wood, it changes molecularly, becomes water/rot resistant
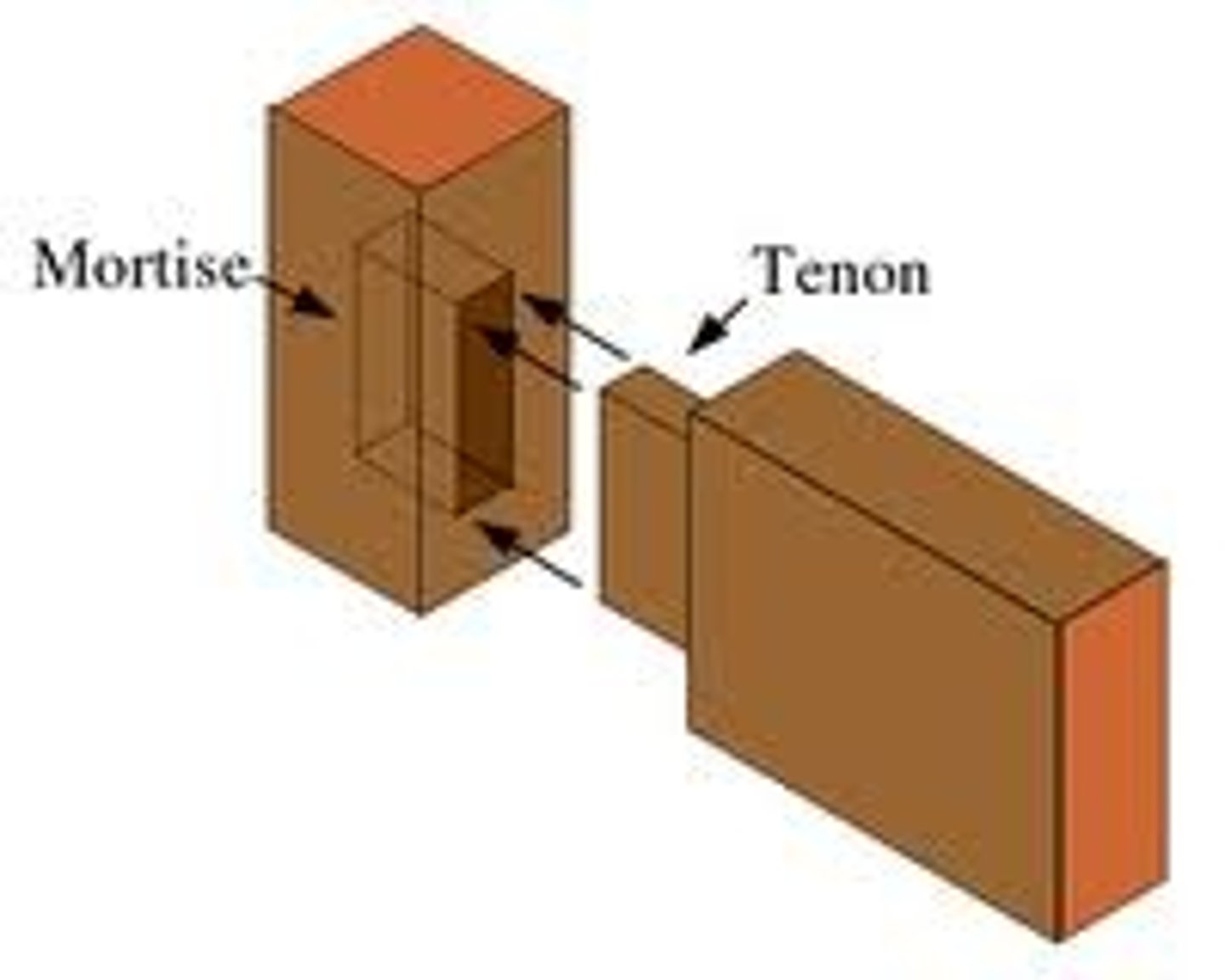
Mortise and Tenon
Older style of wood joining
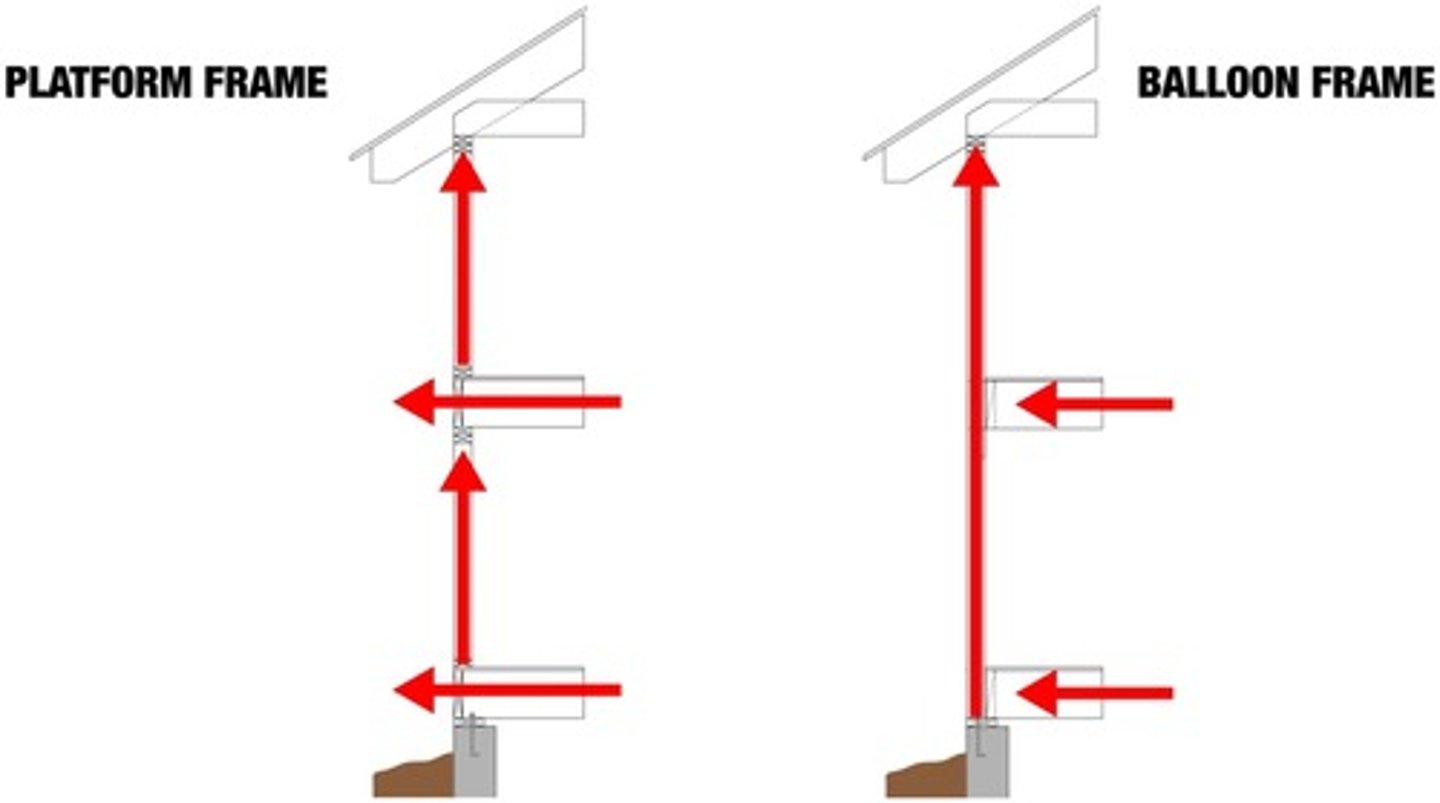
Balloon Framing
Studs are continuous all the way to the roof
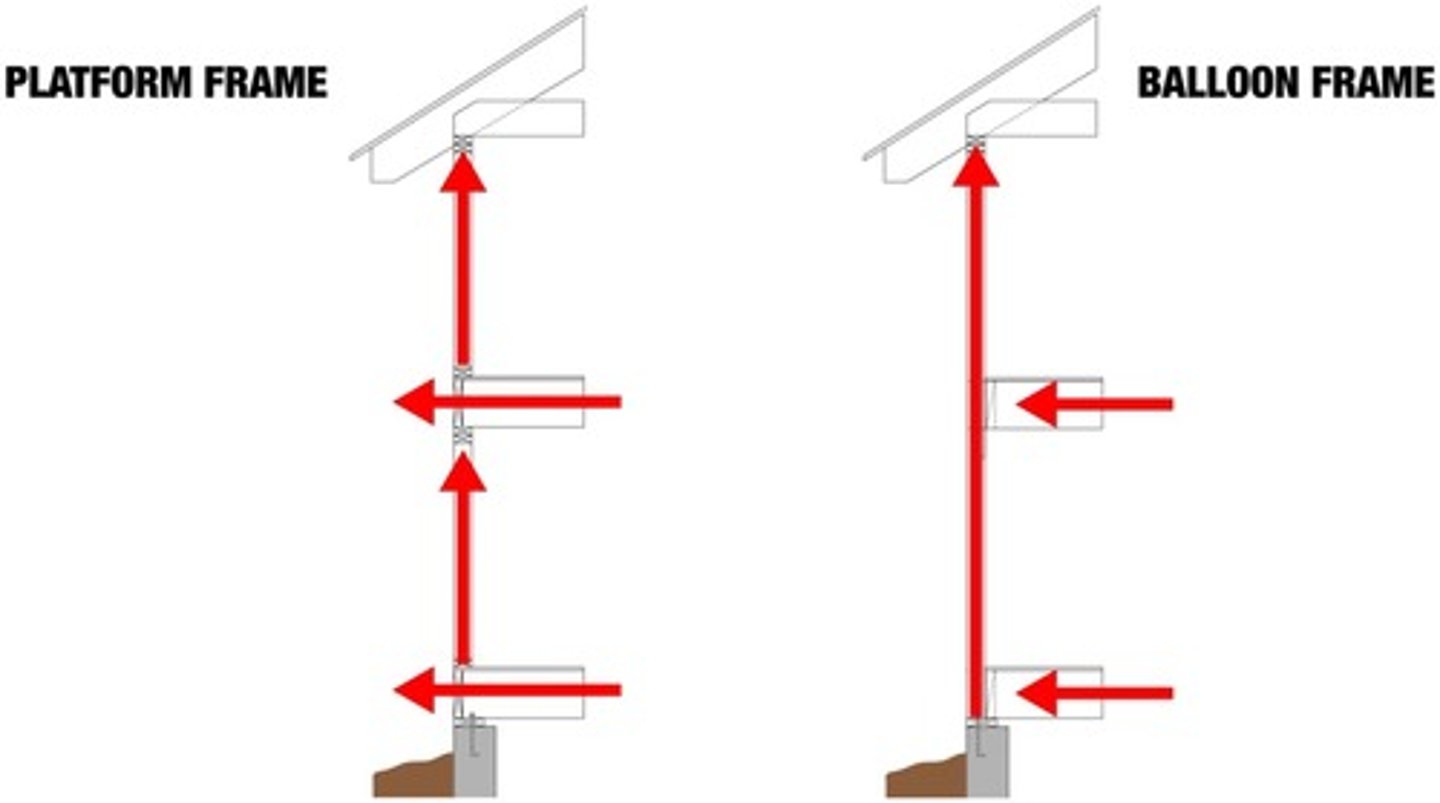
Platform Framing
The floor plates create separation in the studs vertically, 1st floor --> studs --> 2nd floor --> studs
5 Construction Types
Type I, Type II, Type III, Type IV, Type V
Type I Construction Type
Fire-Resistive Construction. non-combustible structure and partitions.
(ex) Skyscrapers:
Tall office or residential buildings that are designed to withstand fires for extended periods. They typically have reinforced concrete or steel frames, concrete or masonry walls, and fire-resistant materials throughout.
Type II Construction Type
Non-Combustible Construction: Fire restrictive, non combustible structure, with one hour fire rated partitions
(ex) Warehouse:
A large, industrial building used for storage, manufacturing, or distribution. These structures often have steel frames, metal roof and wall panels, and minimal wood components.
Type III Construction Type
Ordinary Construction: Fire resistive exterior walls
(ex) Apartment Buildings:
Multi-story apartment buildings are constructed with wooden structural elements, such as wood framing and wooden floors, but with fire-resistant materials and construction techniques applied to increase fire safety.
Type IV Construction Type
Heavy timber: slow burning
(ex) Barn:
Traditional barns constructed primarily with large wooden timbers and posts. Heavy timber construction relies on the thickness and density of the wood for fire resistance.
Type V Construction Type
Wood-Framed Construction: Platform framing
(ex) Single-Family Homes:
Most residential houses are built using wood framing, making them an example of Type V construction. While these homes have wooden structural elements, modern building codes often require fire-resistant materials in key areas like walls and roofs for improved safety.