L5 Natural selection
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What was the idea of special creation of organisms?
- states species didnt change
- each species was separately created
- earth and life are young
What is descent with modification?
- States species change over time
- Species derive from common ancestors
- Earth and life are old
What did Carolus Linnaeus state?
• Species are immutable (unchanging)
• Fits with Genesis
• No evidence for an alternative explanation
What is Lamarckism?
• 1809 "Philosophie Zoologique"
• 3 elements
1. Fact
2. Course
3. Need
• Inheritance of acquired characteristics
Why was Lamarckism wrong?
• Confusion between physiology and evolution
• Evolution towards perfection
eg. he suggested that giraffes necks had stretched over time
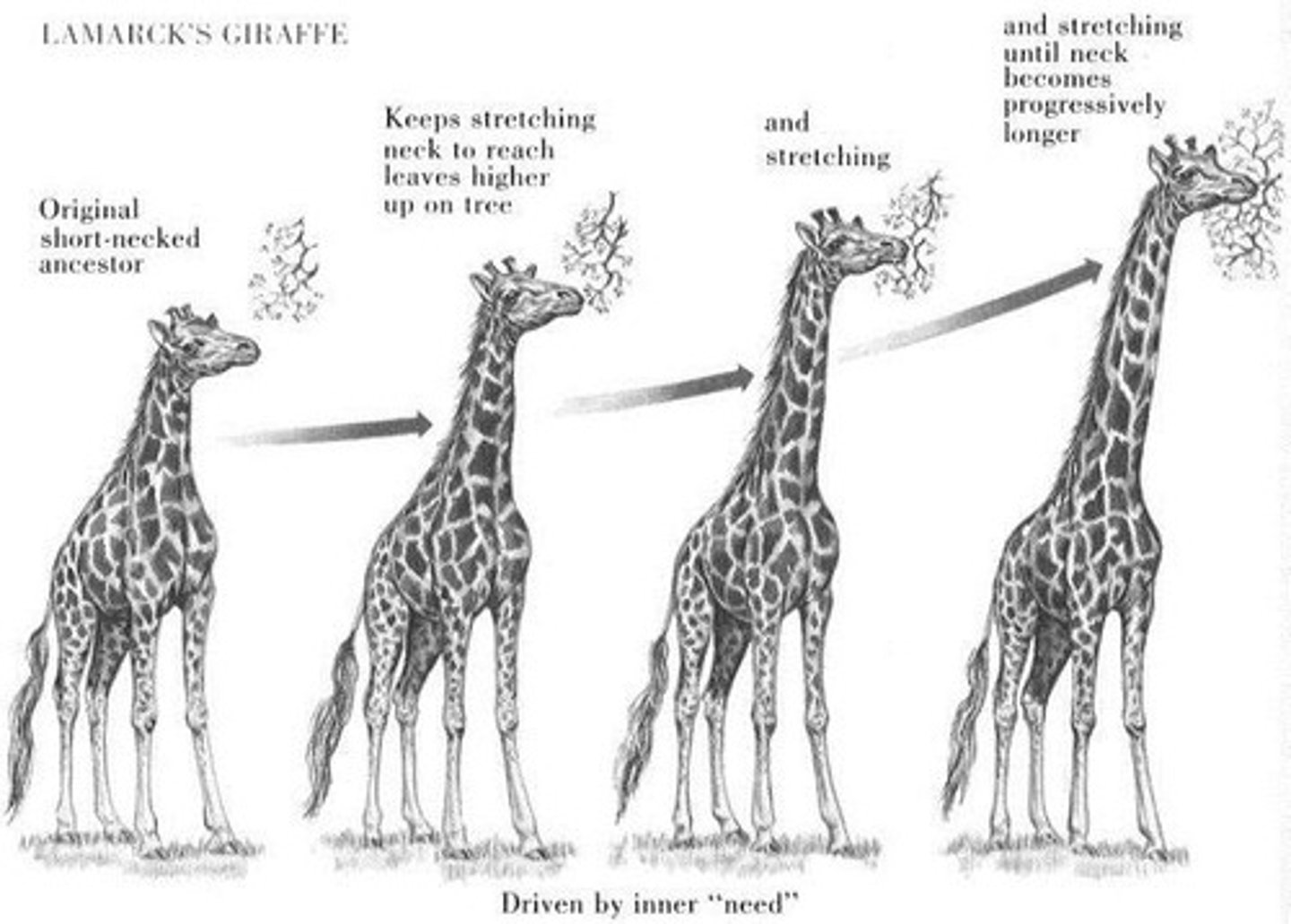
What was correct about Lamarckism?
Species do evolve
Is evolution goal orientated?
No, and it does not lead to perfectly adapted organisms
What evidence shows that evolution is not goal orientated?
Left recurrent laryngeal nerve
Mammalian larynx
in humans it loops round aorta
Which if we could choose its not a good idea for it to loop around
but we originally got this because of the anatomy of when we were fish
How is evolution shaped by natural selection?
Many processes shape evolution but only natural selection has a systematic tendency to build up the elaborate functions that are needed to maintain reproductive success (fitness)→ leads to adaptation
• Natural selection is the inevitable consequence of inherited variations in fitness
What is the definition of natural selection?
Any consistent difference in fitness (reproductive success) among phenotypically (genetically) different biological unit (individual, genotype, gene) within a population
What was Darwins idea?
• Darwin: preservation of favourable variations and the rejection of unfavourable variations
• The fitness of an individual is defined as the relative contribution of its genotype to the next generation relative to the contributions of other genotypes and is determined by the number of offspring it manages to rear successfully aka Darwinian fitness
What does natural selection depend on according to Darwin?
Inherited variation in fitness
What were Darwins 4 premises of natural selection?
1. Organisms are variable
2. At least some variation is heritable
3. A pair of parents produces more than just 2 offspring
4. Population size is generally stable → Differential survival →Differential reproduction
What is an Example of selection in response to an environmental pressure?
Variation in chilli spice
Hot chillies result in hot chillies etc
Predator can eat some of the chillies but only eats the mild ones, so over time only the hot ones are left, so there is a loss in mild chillies so the population gets hotter
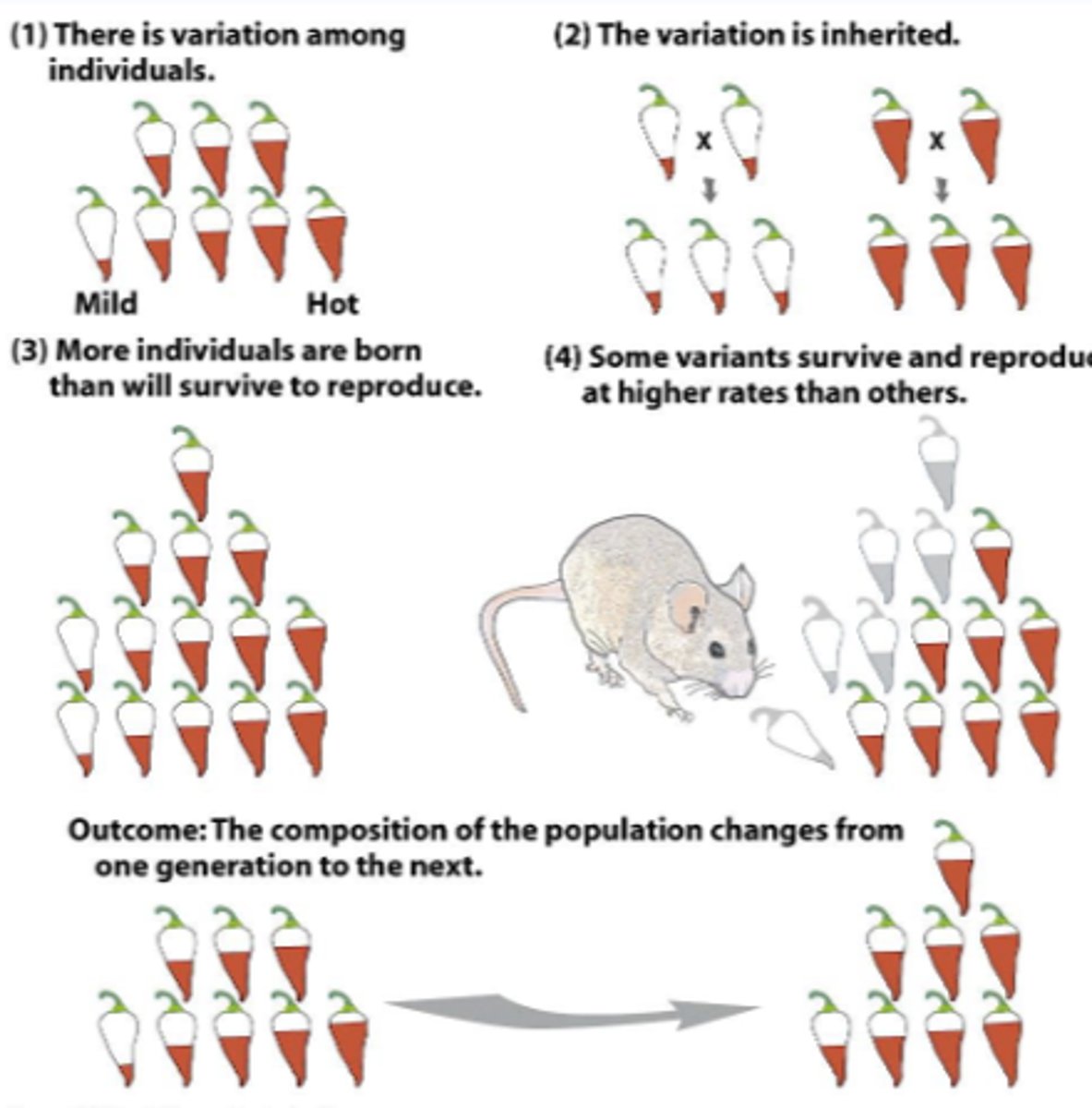
What does natural selection do to the fitness of genotypes?
• Selection increases the frequency of "fit" genotypes
Over time adaptive evolution
It increases mean fitness
What factors can effect the increase in fitness caused by natural selection?
• Mutation, migration, drift and recombination decrease mean fitness
• Natural selection is therefore the only process that causes adaptation
• However, other processes may facilitate natural selection
What is an adaptation?
'An adaptation' is a phenotypic trait moulded by natural selection. The trait could be physiological, behavioural, developmental or morphological, or it could be a life history trait
What is adaptation?
'Adaptation' is a process of evolution in which traits in a population are modified by natural selection to meet better the challenges presented by the local environment
What is evolution?
Evolution = Change in allele frequencies over time
What does natural selection result in over time?
evolution
What are the 2 conditions in which natural selection will result in evolution?
1. Variation in lifetime reproductive success
2. Trait variation must be heritable
• Environmental variation (provides selection pressures) →adaptive radiation
What was the idea of Darwins finches?
They famously evolved to have different beaks which are suited to different food types
Darwin's work with finches helped him understand how species can change over time through natural selection
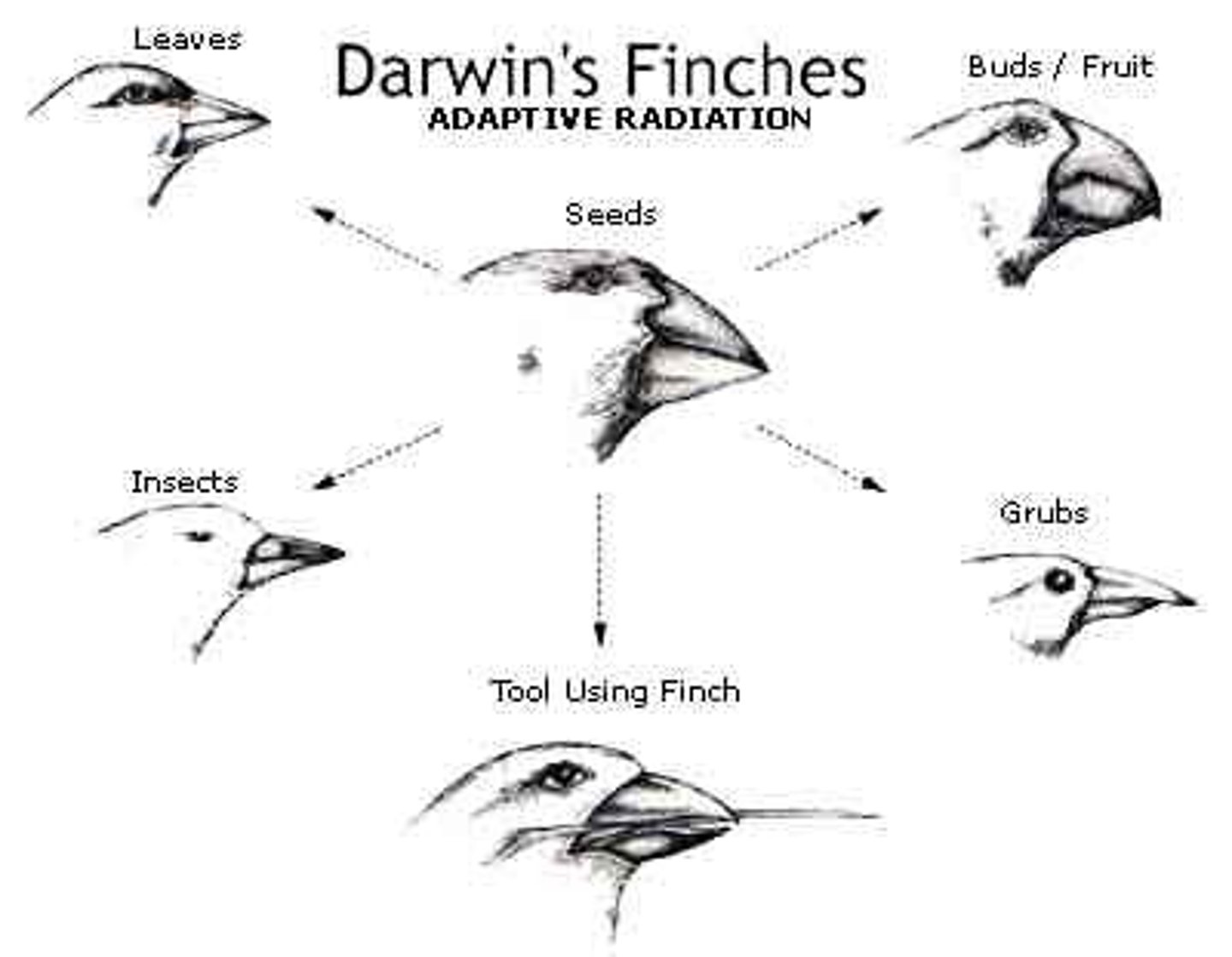
What are different modes of selection?
1. Directional
2. Disruptive
3. Stabilising
4. balancing
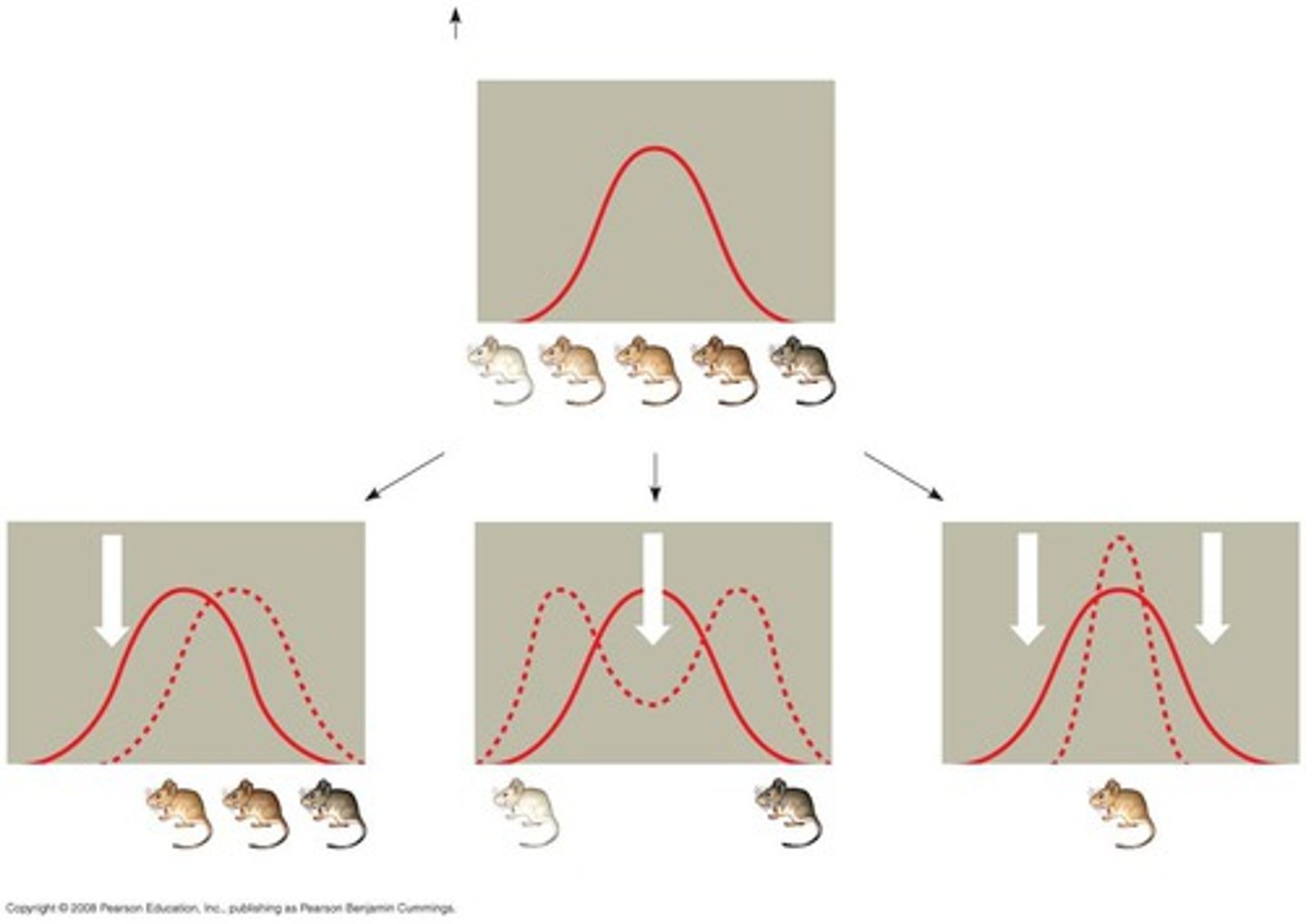
What is directional selection?
favours individuals at one end of the phenotypic range
invasion of a new trait
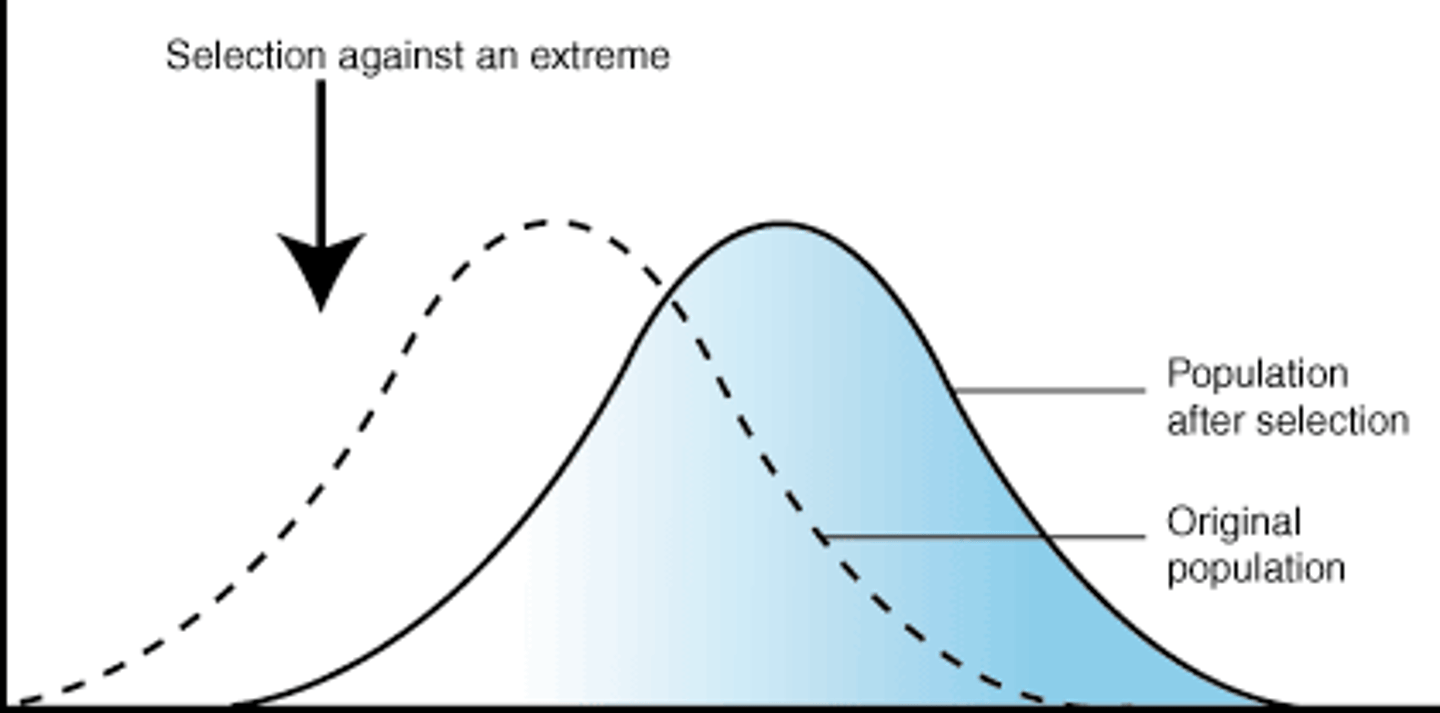
What is disruptive selection?
favours individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
Can cause adaptive radiation
eg. overdominance
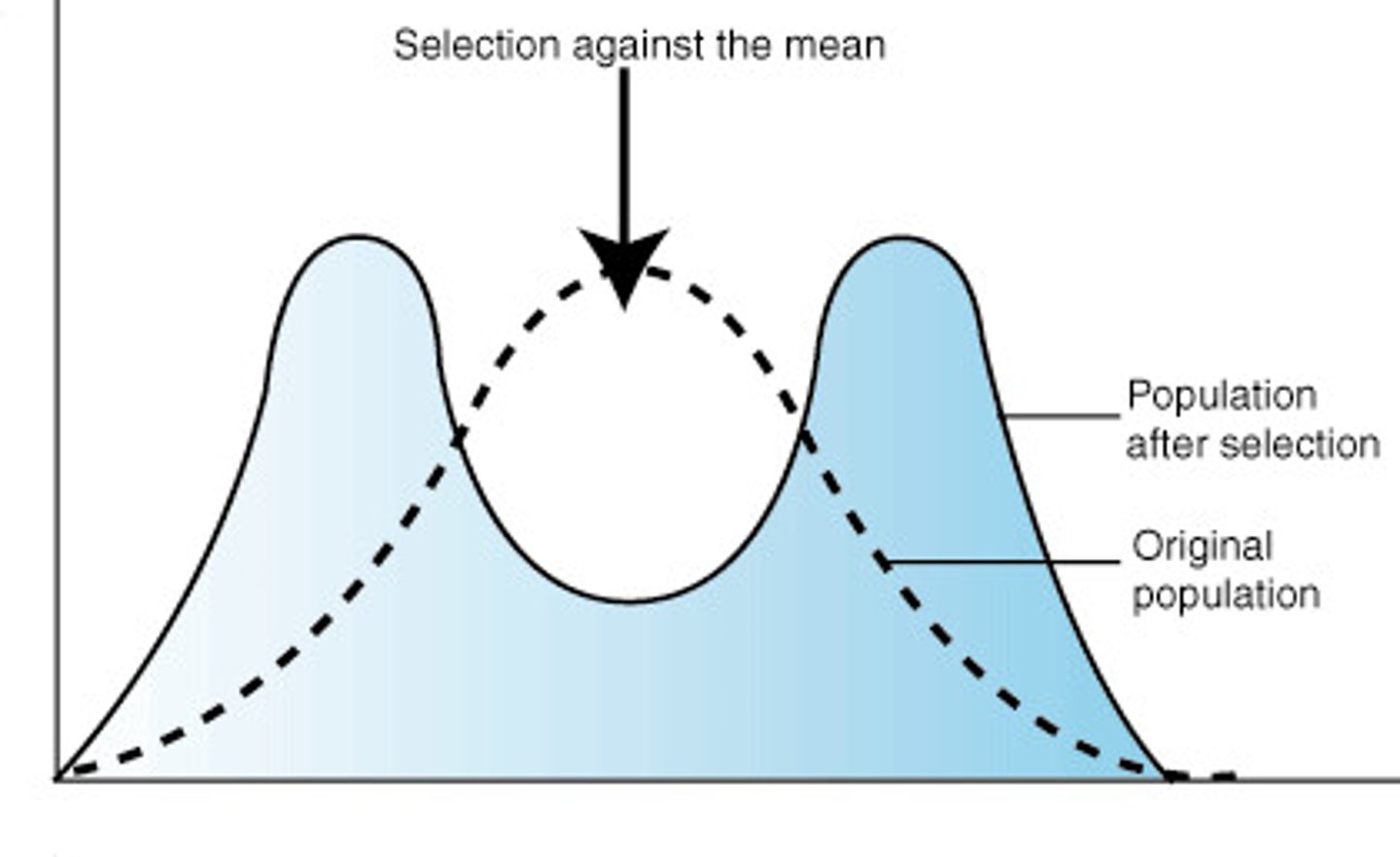
What is stabilising selection?
selection favouring average individuals
No evolution
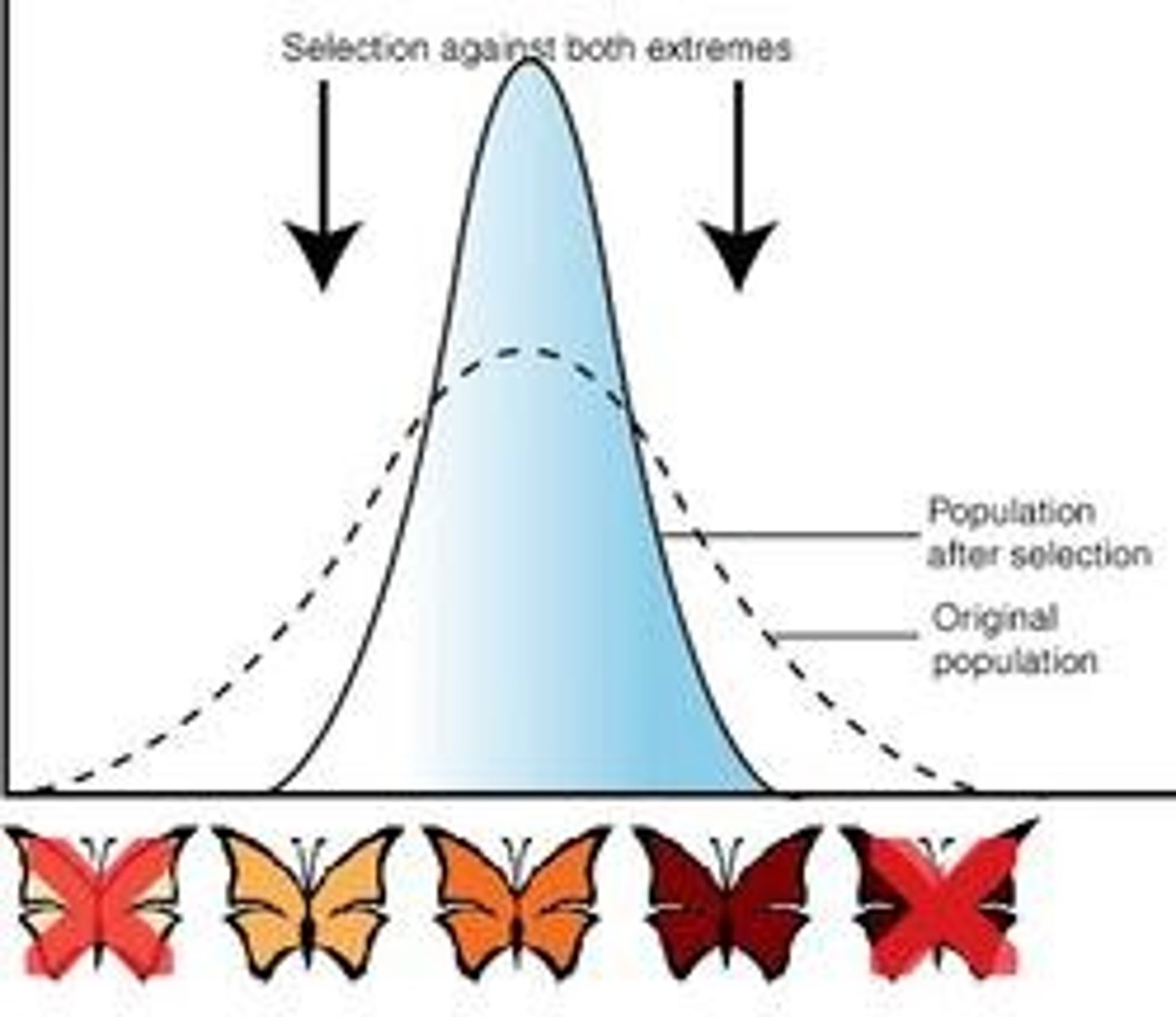
What are types of directional selection?
- Purifying selection = directional selection against deleterious mutations
- Truncation selection = allows only those with highest trait values to reproduce
What is balancing selection?
selection that maintains polymorphism (e.g. over dominance and frequency-dependent selection)