Key Concepts in Ecosystem Dynamics and Interactions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
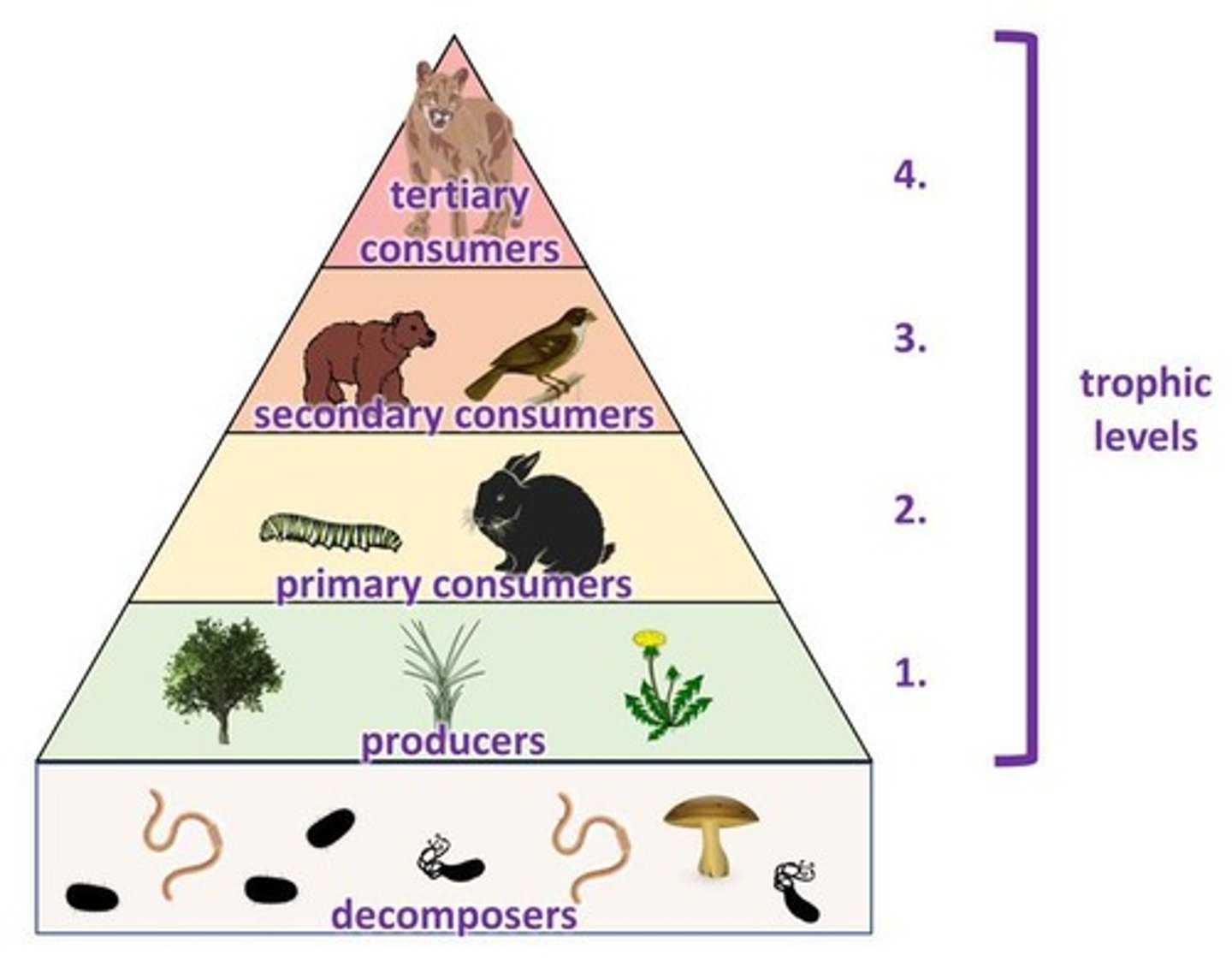
TROPHIC LEVEL
hierarchical levels in an ecosystem
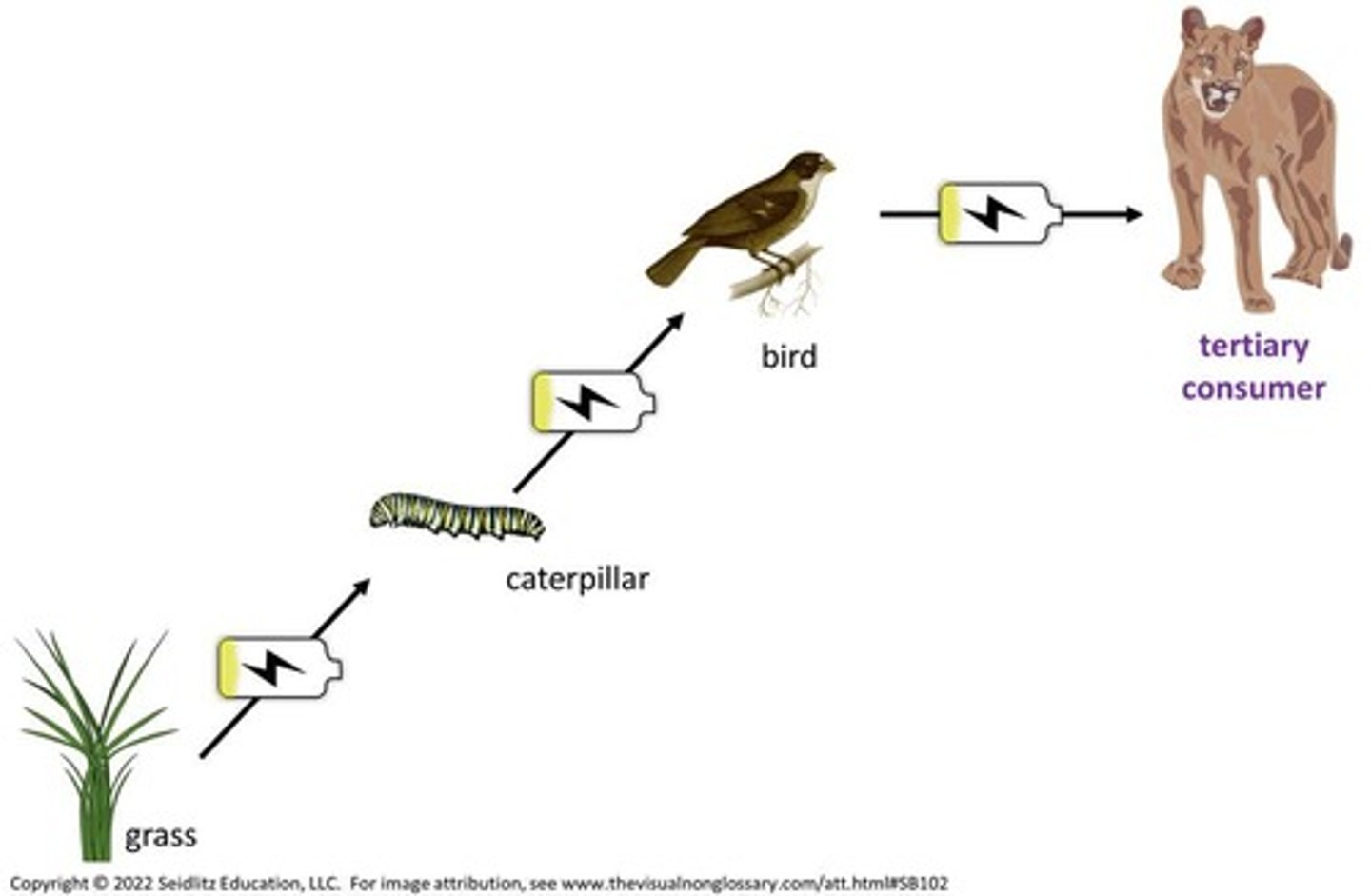
FOOD CHAIN
links species by their feeding relationships; 1 way flow of energy
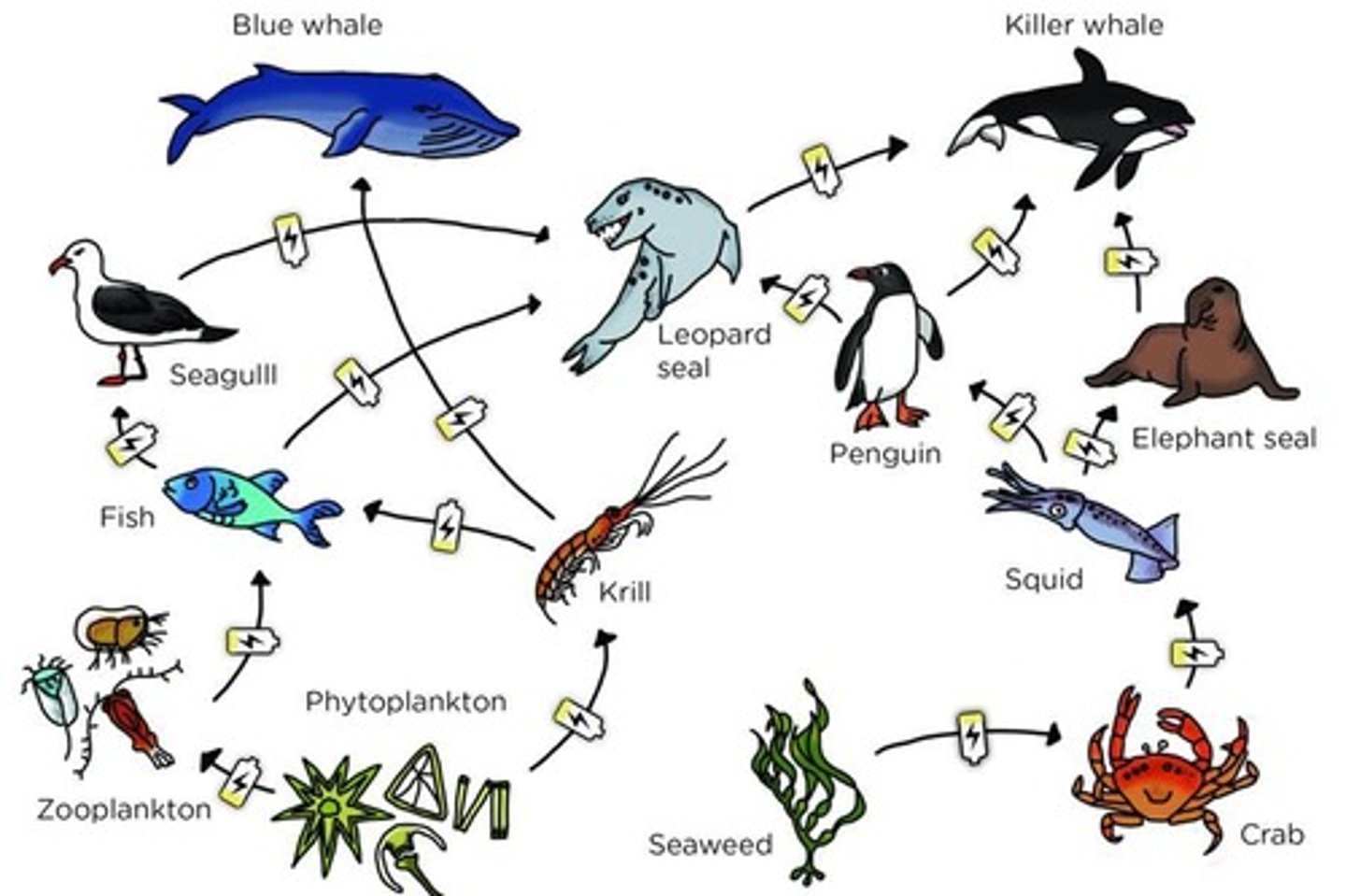
FOOD WEB
network of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationships among the various organisms in an ecosystem
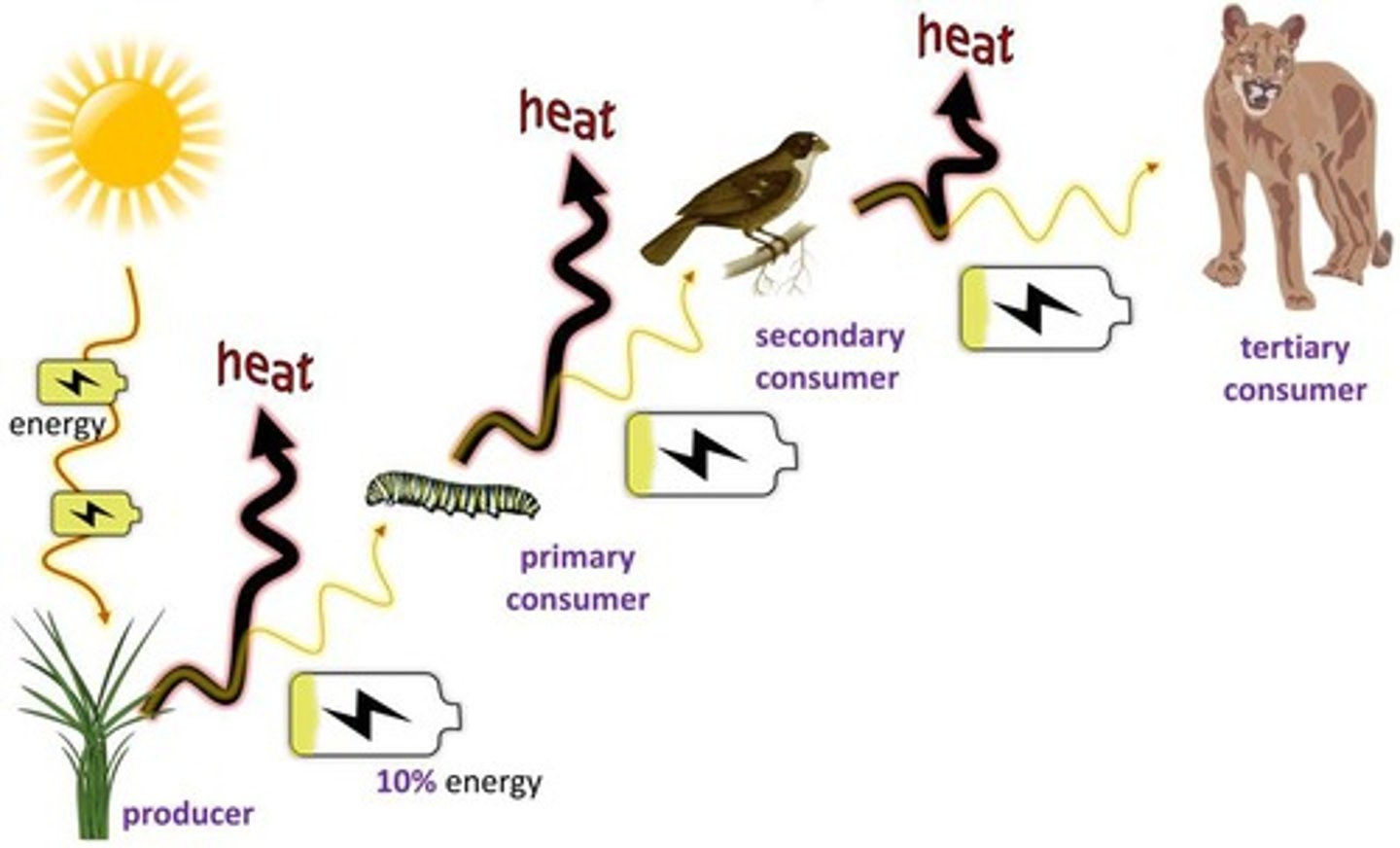
10% RULE
Only 10% of the total energy produced at each trophic level is available to the next level. The amount of energy passed on reduces as you go up.
PRODUCER/AUTOTROPH
an organism that can make its own food
CONSUMER/HETEROTROPH
an organism that acquires energy by feeding on other organisms
DETRITIVORE
organism that feeds on plant and animal remains and other dead matter
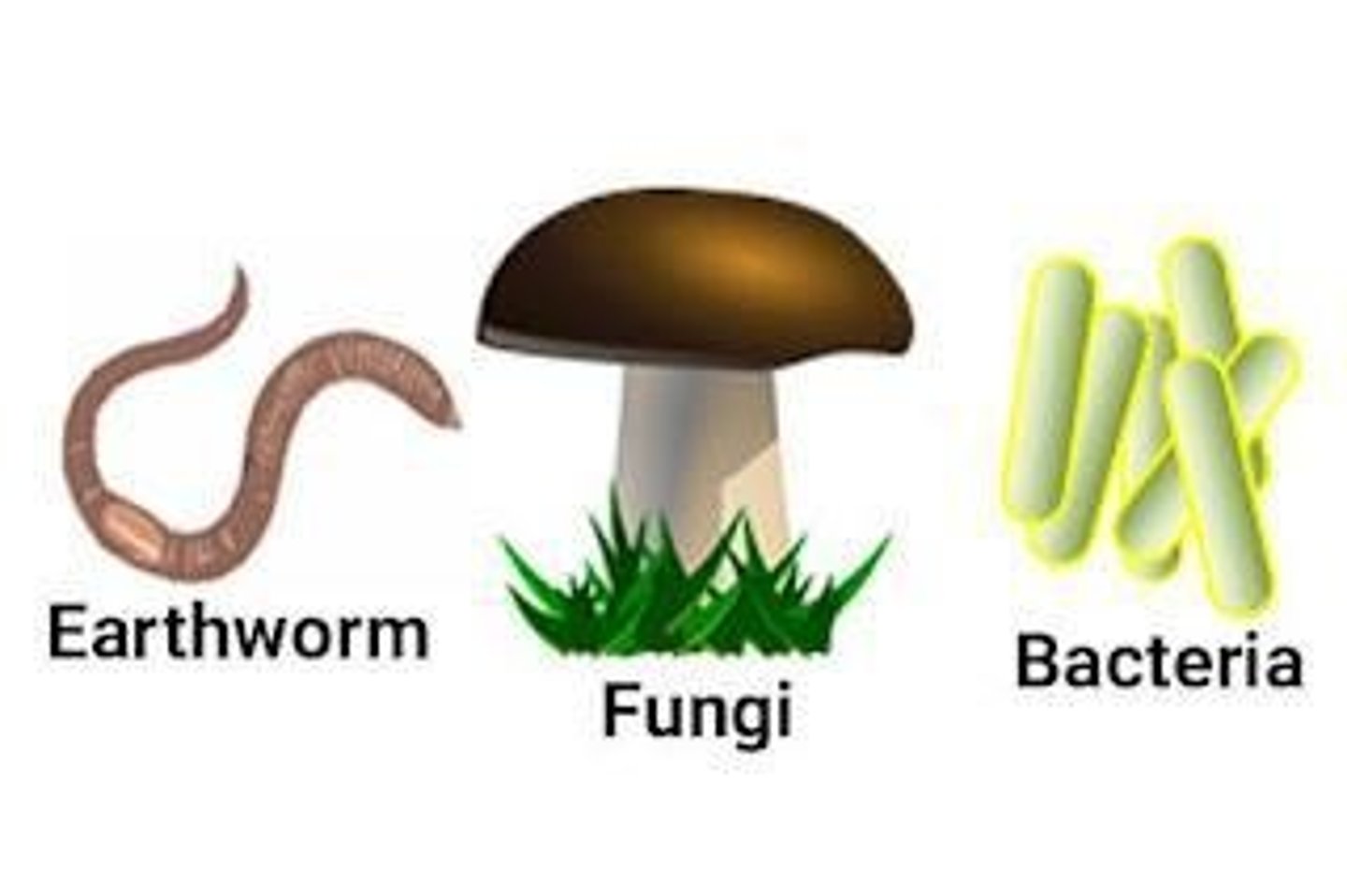
DECOMPOSER
an organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms
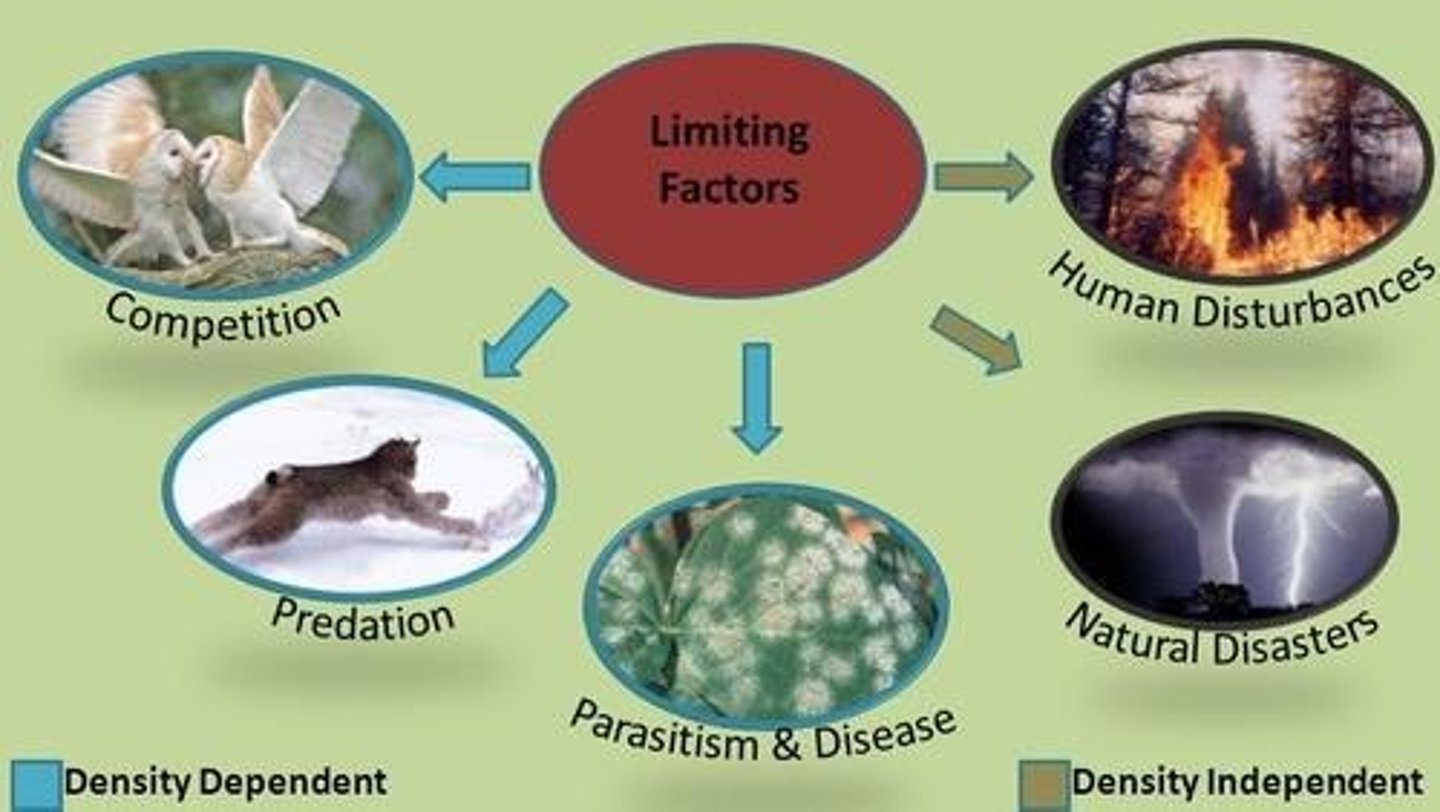
LIMITING FACTOR
factors that have great effects on limiting population growth
SYMBIOSIS
A close relationship between two species that benefits at least one of the species.
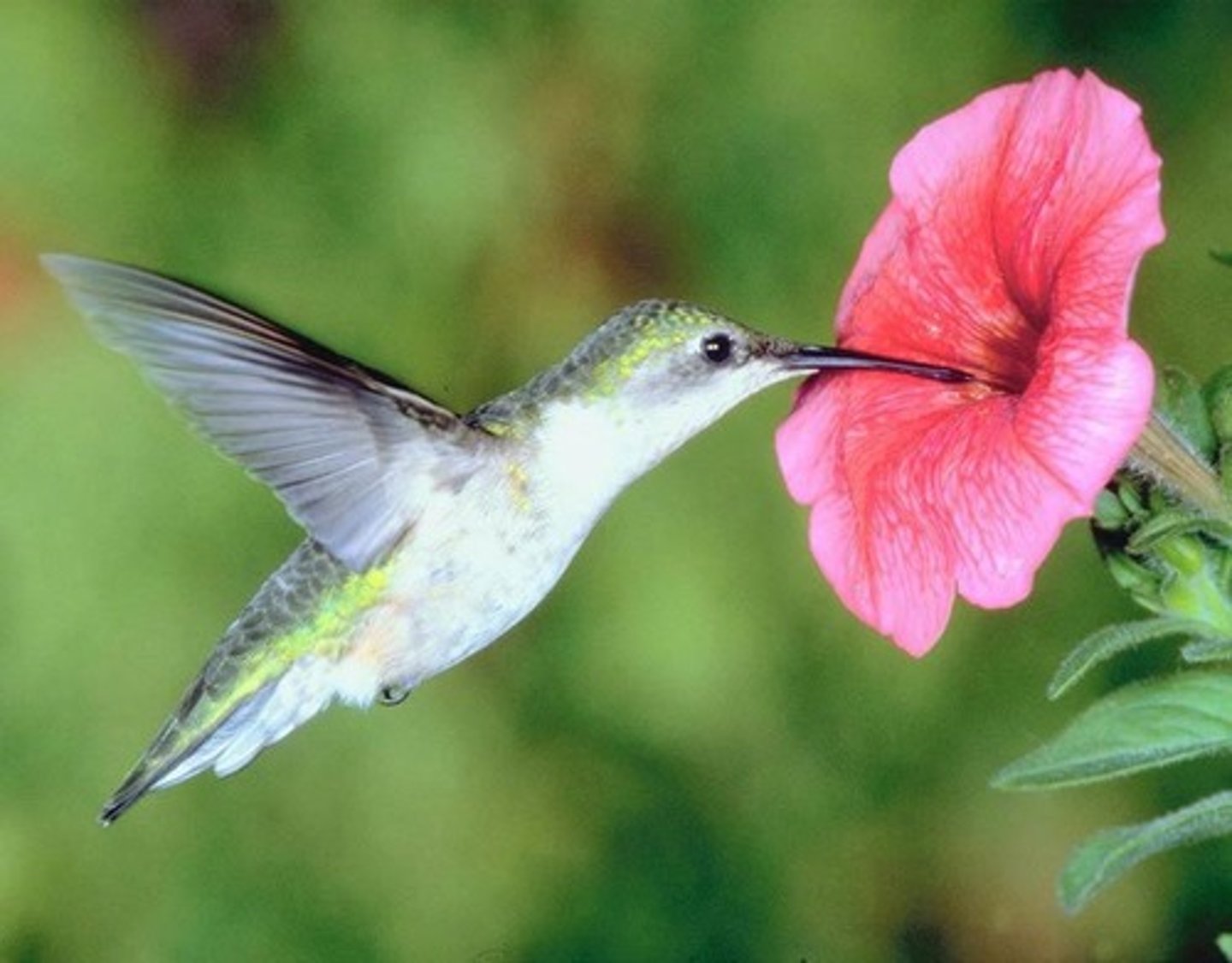
MUTUALISM
relationship between two species in which both species benefit

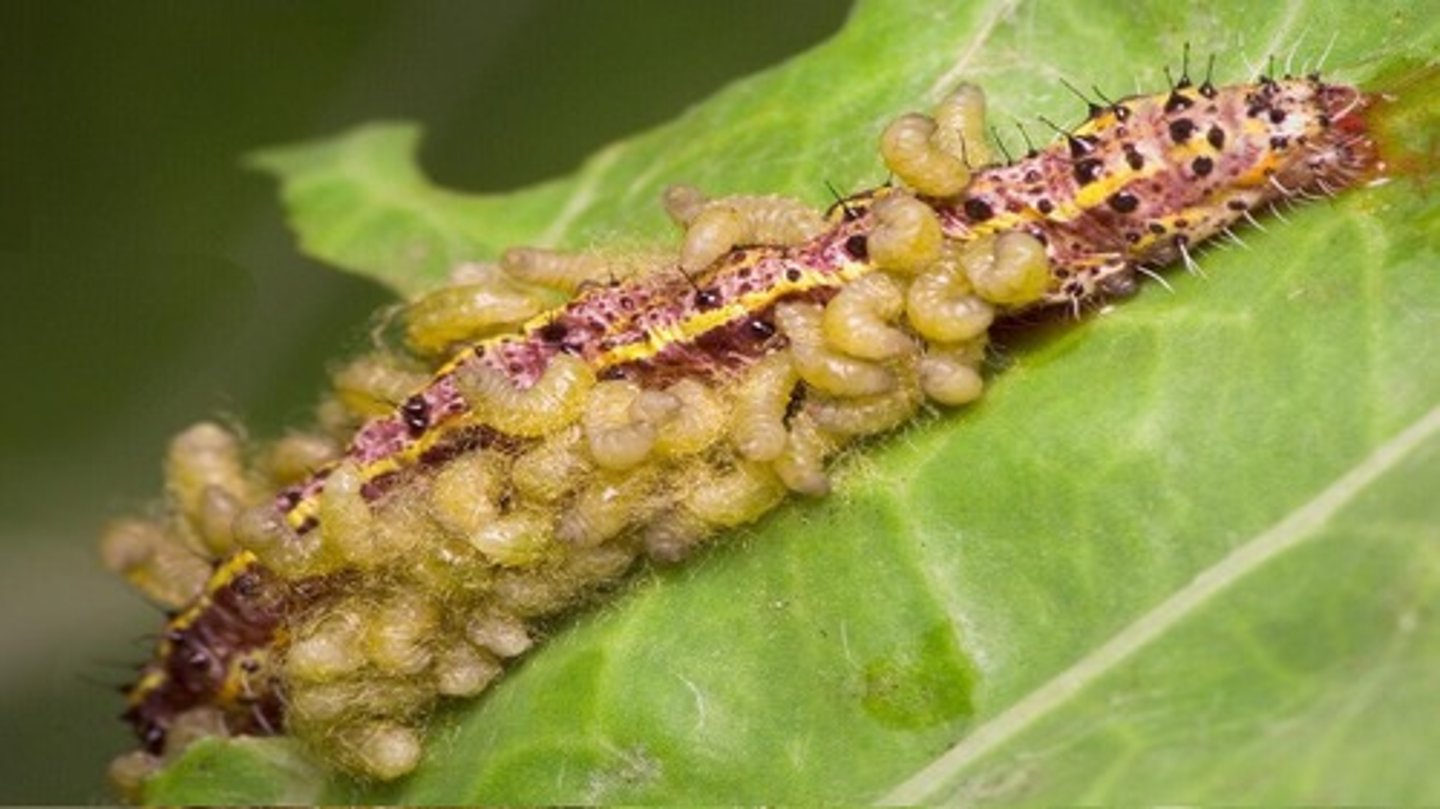
PARASITISM
relationship between two organisms where one benefits and the other is harmed

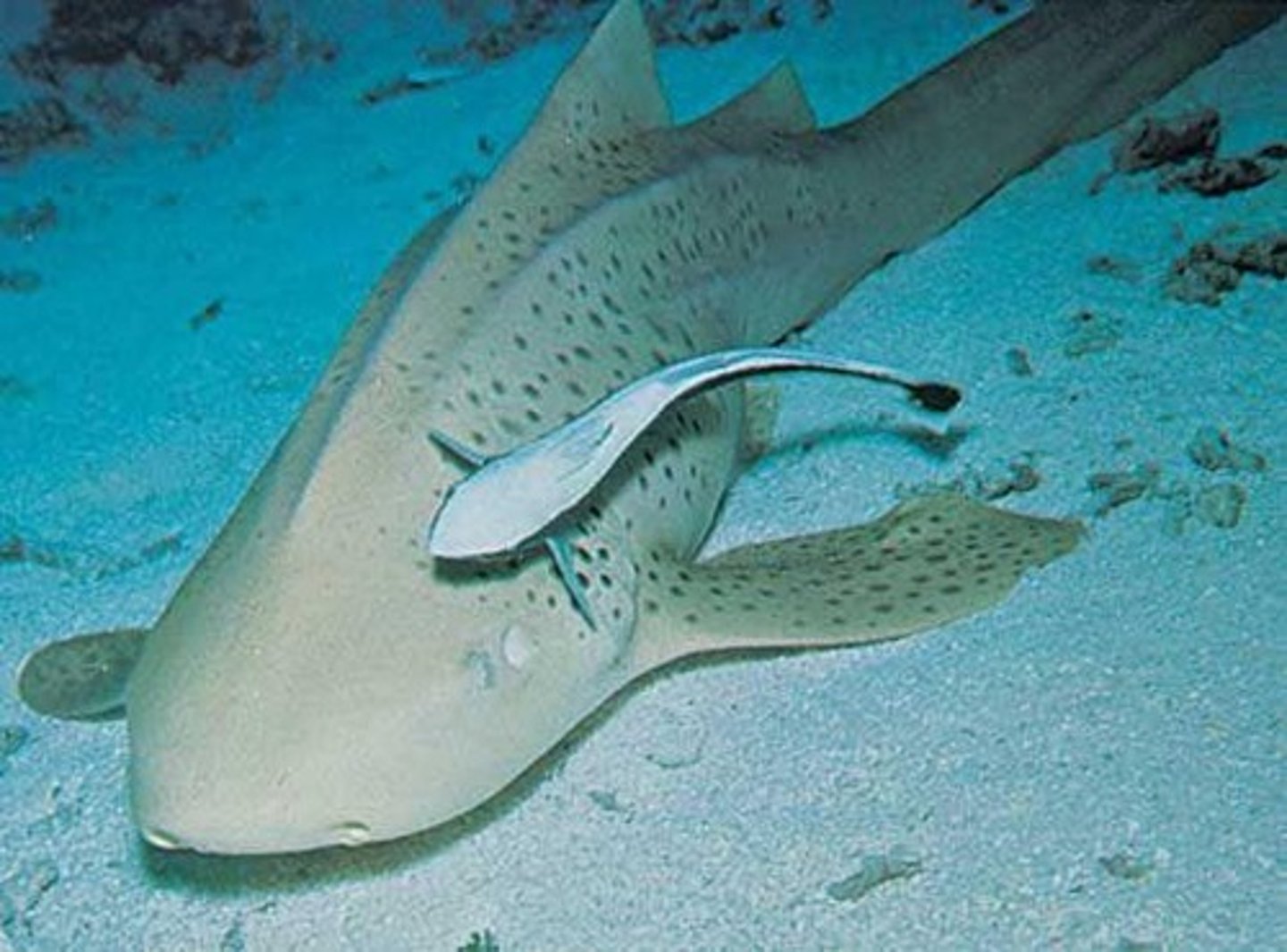
COMMENSALISM
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected

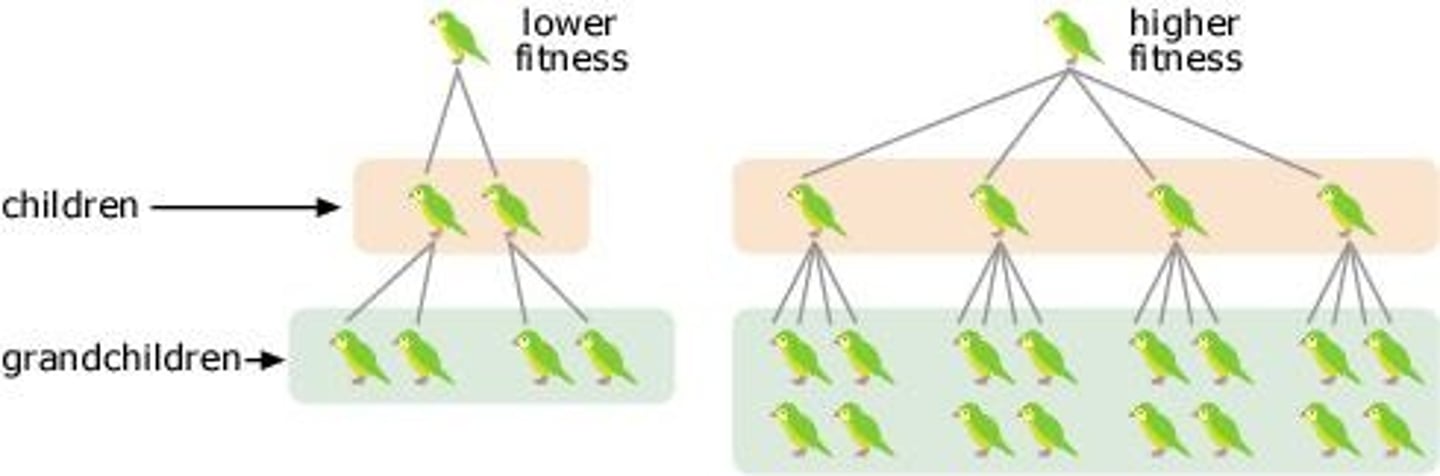
FITNESS
an organism's ability to pass its genetic material to its offspring
NICHE
an organism's particular role in an ecosystem
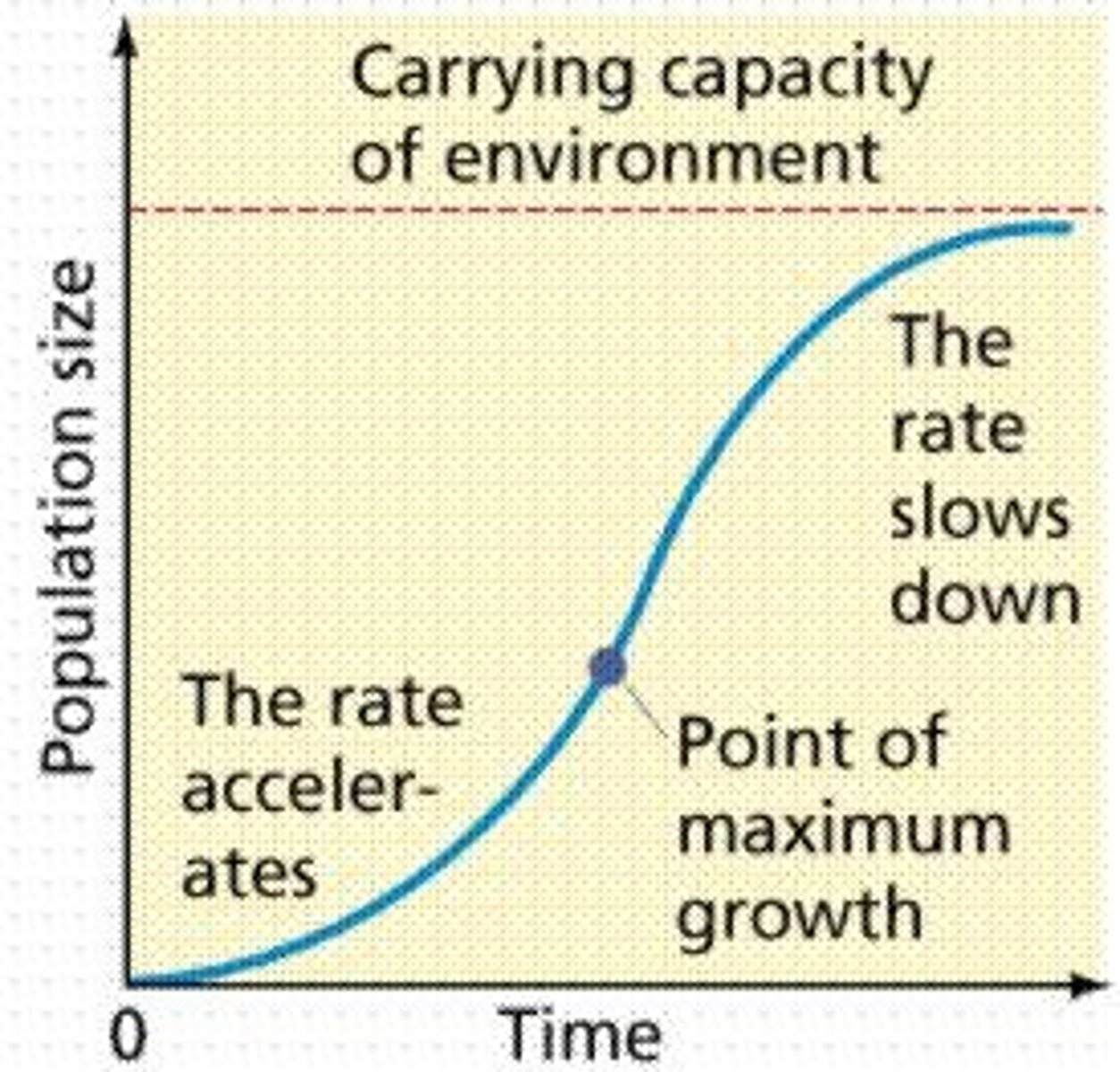
CARRYING CAPACITY
largest number of individuals that an environment can support
BIODIVERSITY
the variety of living things in an ecosystem
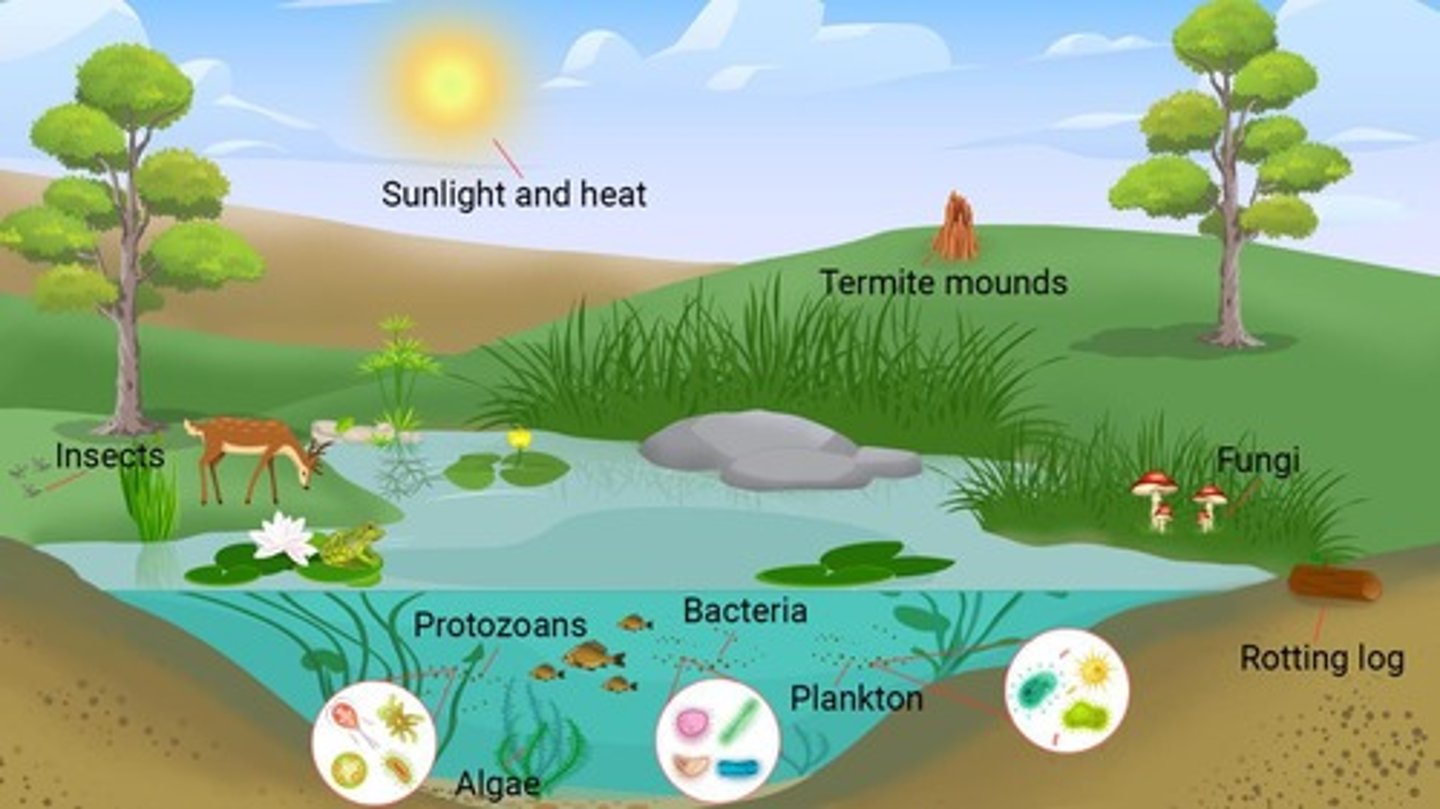
BIOTIC
factors that are living
ABIOTIC
factors that are non-living
ECOSYSTEM
all the communities in an area and the physical (abiotic) environment
COMPETITION
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
POPULATION DENSITY
number of individuals living in a defined space
ADAPTATION
An inherited trait that helps an organism to better survive and reproduce
WATER CYCLE
how water evaporates from the surface of the earth, rises into the atmosphere, cools and condenses into rain or snow in clouds, and falls again to the surface as precipitation
CARBON CYCLE
transfer of carbon from the atmosphere to living organisms, and return back to the atmosphere through respiration, decay of organisms and burning of fossil fuels
NITROGEN CYCLE
transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere