Nutrient Procurement and Gas Exchange in Plants and Animals
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
pH and particle size range that will have the most avalibility of nutrients
Ph: 6-7
particle size: smaller particles
Clay + organic compounds
have more SA for nutrients
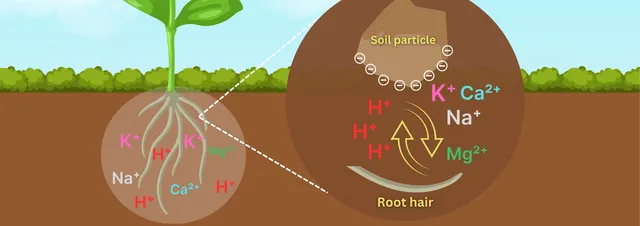
Cation Exchange
roots use cations such as H+ and release them into the soil so useful cations suchas K+, Ca+, and Mg+ leach into the roots
9 macro nutrients required in plants
Carbon (CO2)
Oxygen (CO2)
Hydrogen (H2O)
Nitrogen (NO3 -, NH4 +)
Potassium (K +)
Calcium (Ca 2+)
Magnesium (Mg 2+)
Phosphorus (H3PO4 -, HPO4 2-)
Sulfur (SO4 2-)
macro nutrients that form organic compounds for plant’s structure
Carbon (CO2)
Oxygen (CO2)
Hydrogen (H2O)
Nitrogen (NO3 -, NH4 +)
Magnesium (Mg 2+)
Phosphorus (H3PO4 -, HPO4 2-)
macronutrient that contributes the most to a plants growth
Nitrogen
how is atmospheric nitrogen made avalible to plants
nitrogen cycle
nitrogen cycle
N2 is taken into the soil via nitrogen-fixing bacteria and converted to ammonia (NH3)
The ammonia becomes ammonium (NH4 +) via ammonifying bacteria (can be sent to the roots) or by gaining a H+ from the soil
Nitrifying bacteria turn ammonium into nitrite and then nitrate → can come from weathering of rocks too
Nitrate is then sent to the roots or denitrifying bacteria, which recycle it and put nitrogen back into the atmosphere
humus
decomposing dead organic material
mycorrhizae
symbiotic relationship between plants and fungi. The fungus extends the roots of the plant, improving nutrient and water uptake. Fungus then gets carbohydrates from photosynthesis.
nutrient rec for plants
Calcium
Phosphorus
Sulfer
what are root nodules in Legumes
specialized swellings on plant roots that house Rhizobia bacteria, which form a symbiotic relationship with the legume plant
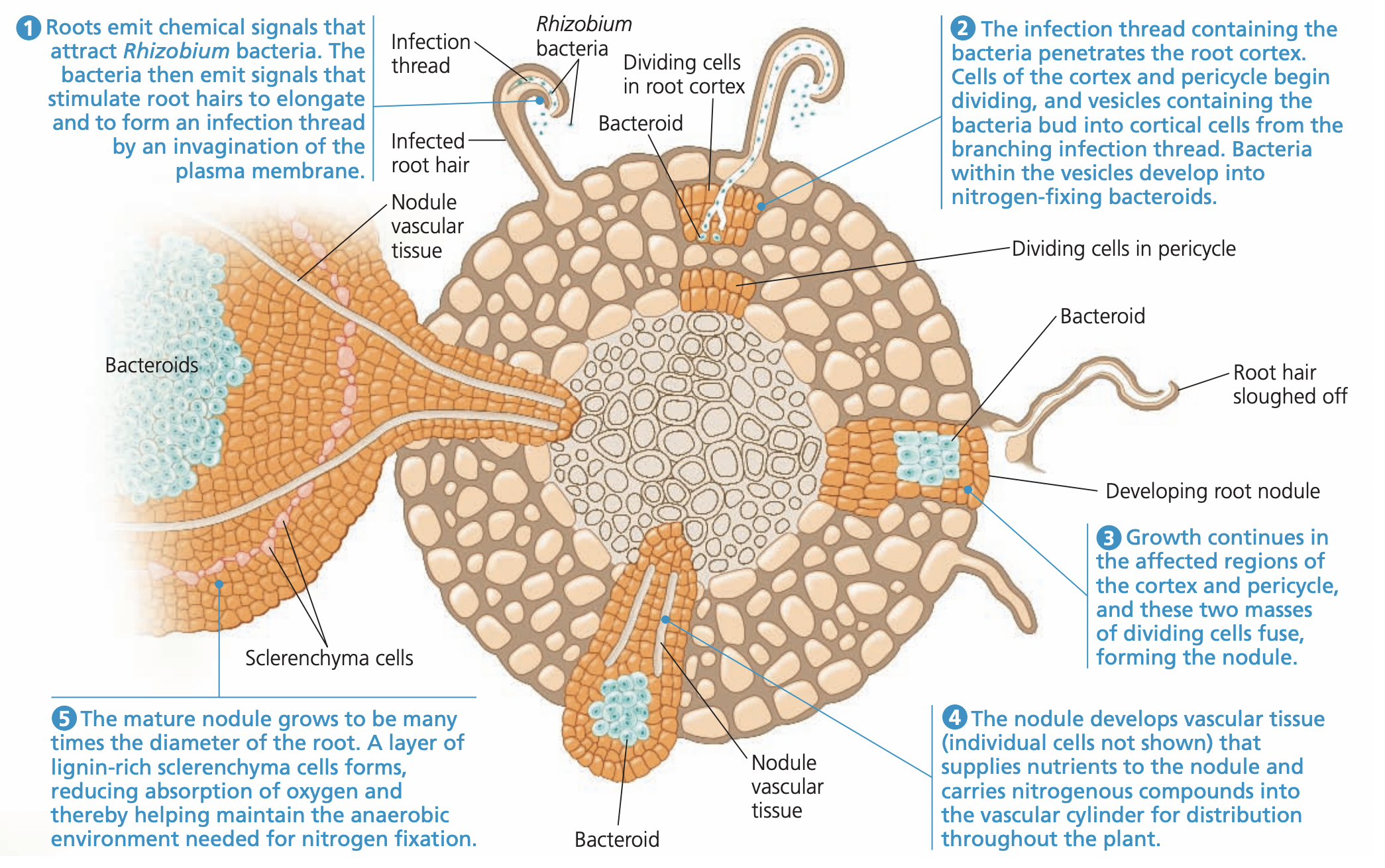
how are root nodules formed
roots emit a chemical signal to attract Rhizobium bacteria, Rhizobium bacteria release a chemical signal that makes the plant root grow an infection thread
The Rhizobium then enters the root cortex, and the pericycle and cortex cells begin dividing
growth from both types of cells intermesh into one growth
plants then develop vascular tissue to send the nodule nutrients
Nodule becomes large, and lignin-rich sclerenchyma cells form a ring around it to create an anaerobic environment for the bacteria to do nitrogen fixation
What do legumes get from their symbiosis with Rhizobium and vice versa
a reliable supply of nitrogen for the plant
carbohydrates and mineral nutrients
what is the role of root hairs in enhancing water and mineral absorption?
increases surface area
required nutrients for plants and animals
Ca
K
P
S
Mg
Cl
can the human body synthesize all amino acids
No, humans can only synthesize half of the 20 total AAs and must obtain the remaining essential amino acids from the diet
complete vs incomplete proteins
complete proteins contain all 9 essential AAs while incomplete lack one or more of the essential AAs
Are animal proteins complete or incomplete
complete, contain all 9 essential AAs
Vitamin definition
organic molecules that are required in the diet in small amounts
What is the function of the water-soluble vitamins?
maintaining bodily functions
energy production, red blood cell formation, DNA synthesis, immune function, collagen synthesis, and nervous system health
Is a vitamin for one organism necessarily a vitamin for another organism
No, a substance is only considered a vitamin for a particular species if that species cannot synthesize it
herbivore
only eats plants
carnivore
only eats meat
omnivore
can eat both
4 main feeding mechanisms
filter feeding
strain large quantities of small organisms
substrate feeders
animals that live in or on their food source
Fluid feeders
suck nutrient rich fluid from a living host
Bulk feeding
eating realitivly large pieces of food
intracellular digestion
When the cell breaks down its food using lysosomes in the cytoplasm
extracellular digestion
when a cell breaks down its food outside mechanically or with acid to make them into smaller absorbable pieces
what type of digestion do humans use
extracellular
4 stages of food processing
ingestion
digestion
absorbtion
elimination
qualities of a efficient digestive system
has a seperate entrance and exit and is made up of section that are specialiized for different functions
which type of digestion is more efficient and why
Extracellular digestion because it allows for a division of laborbetween different cells that will have a specialized role in the digestion
rule for all multicellular animals
gastrovascular cavity vs complete digestive tract
Gastrovascular cavity has only one opening and does all functions of food processing, while a complete digestive tract has two and specialized sections
Hydra sites of:
ingestion
digestion
absorbtion
elimination
ingestion: Mouth
Digestion: Gastrovascular Cavity
Absorption: Gastrodermis
Elimination: Mouth
Earthworms’ sites of:
ingestion
digestion
absorbtion
elimination
Ingestion: Mouth
sucked in with the muscular pharynx
digestion: muscular gizzard → intestines
absorption: intestines
elimination: Anus
Grasshopper sites of:
ingestion
digestion
absorption
elimination
Ingestion: Mouth
stored in the crop
digestion: Midgut
performed by the gastric Ceca
absorption: gastric Ceca
elimination: Anus
Bird sites of:
ingestion
digestion
absorption
elimination
ingestion: mouth
stored in the crop
digestion: stomach and gizzards → intestines
absorption: intestines
elimination: anus
mechanical digestion
the physical breakdown of food into smaller particles without changing its chemical composition
chemical digestion
the process of breaking down large, complex food molecules into smaller, simpler molecules that the body can absorb and use
Ph of the stomach
1.5 to 3.5
Why the stomach and small intestines are not digested by the enzymes they store and secrete
thick mucus lining
secretion of digestive protein in an inactive form so that they activated later in the highly acidic environment of the enzymes
how are the small intestines adapted for its function of digestion and absorption
large surface area
have vili and microvili
significant length
internal circular folds
hard palate
bony part of the roof of the mouth
soft palate
muscular part of the roof of the mouth
incisors
front teeth
pharynx
beggining of the esophagus and links the nasal cavity with the oral cavity
composed of:
nasopharynx
oropharynx
hypopharynx
epiglottis
flap of cartilage that covers the the trachea.
ensures that food goes down the esophagus
glottis
vocal cords
salivary glands
3 pairs
parotid
sublingual
submandibular
produce saliva
thyroid gland
A gland that produces T3 and T4, which are involved in regulating growth, metabolism, and development
esophagus
transport tube for food to the stomach
has an esophageal sphincter that closes when nothing is being consumed
liver
produces bile
pancreas
secreates:
hormones
insulin and glucagon
Enzymes for digestion
Trypsin (Proteins)
Lipase (Fats)
Amylase (Carbohydrates)
diaphragm
separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity
stomach
performs mechanical and chemical digestion and storage of food
how is glucose turned into maltose
the enzyme amylase breaks it into disacharides (maltose)
By what kind of reaction is a polymer of glucose broken down to glucose
hydrolysis
What is the enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of starch to glucose
Where is it formed
Where does it act
salivary and pancreatic amylase
formed in the mouth and the exocrine pancreas
mouth and small intestines
part of the circulatoary system where monosachoaiudes are absorbed
in the small intestines via the capillaries
Protein Digestion
proteins
pepsin
small polypeptides