VI Geography - Weather, Climate and Ecosystems
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Evidence for Climate Change
Sea-floor sediments - Indicate previous ocean temperatures
Ice Cores - CO2 Levels have fluctuated - Indicate previous gaseous composition of the atmoshphere
Lake Sediments - Pollen grains indicating the vegetation types from the past
Tree rings - the width of the annules vary depending on the temperature
Fossils - Indicates the plants and animals that were able to survive in the conditions
Glacial and Inter-Glacial periods - we have not entered one
Human Causes for Climate Change
Fossil Fuels - releases CO2 from the lithosphere into the atmosphere
Agriculture - cattle farming releasing methane
Deforestation - releasing CO2 from the biosphere into the atmosphere
Natural Causes for Climate Change
Solar output - measured using sunspots
Orbital changes - the ellipse of the earth’s orbit changes, so does the angle of the axis and it wobbles
Volcanic activity - emit clouds of dust and gas that reflect the short waves from the sun back out of the atmosphere, cooling the planet
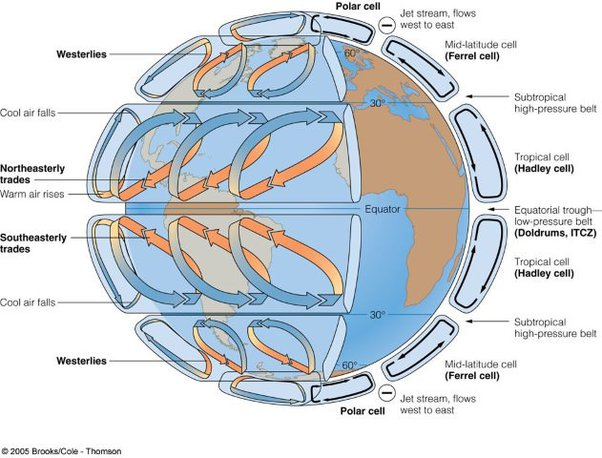
Global Circulation System (tri-cellular model)
Low Pressure Hazards and Formation
Tropical storms (Hurricane):
A strong upward movement of air draws water vapour up from the warm ocean surface
This evaporated air cools as it rises and condenses to form towering thunderstorm clouds
As the air condenses it releases heat which powers the storm and draws up more and more water from the ocean
Several small thunderstorms join to form a giant spinning storm
As the storm is carried across the ocean by the prevailing winds it continues to gather strength
The storm now develops an eye at its centre where air descends rapidly
On reaching land the storm’s energy supply is cut off and friction with the land slows it down
High Pressure Hazards and Causes
Droughts and Heat Waves:
Weather
Global Warming
El Nino
Overpopulation
Overcultivation
Overextraction
Deforestation
Distribution of: Low Pressure Storms
Found over warm oceans (27 degrees +) - the tropics
Form 5-15 degrees north and south of the equator as there is not enough ‘spin’ at the equator
The intense heat in tropical climates makes the air unstable causing air to rise rapidly
Distribution of: High Pressure Systems
Higher risk in:
LICs
Places with overpopulation
Places with hotter climates
Change overtime of: Low Pressure Systems
Form in the summer and autumn when sea temperatures are at their highest
Increased due to climate change
Change overtime of: High Pressure Systems
Increase in drought in the last 100 years due to climate change
Low Pressure System Case Study
What: Hurricane Matthew
Where: Caribbean, SE Coast of USA
When: October 2016
Consequences: Homelessness, Displacement, Separation of families, Death, Flooding, Destruction of property, Contaminated water (LICs),
Responses: Evacuation, Money donation from other countries and NGOs, Donation of resources from this places (LICs)
High Pressure System Case Study
What: California’s Drought and Wildfires
Where: California
When: 2012-2015
Causes: Jet stream that usually brings precipitation to California was too high up
Consequences: Lower precipitation → dry soils → wildfires, fires engulfed many homes, housed pipe bans, property damage, loss of crops, vegetation dies
Responses: Mass Evacuation
Factors that create Weather Variation in the UK
Latitude
Altitude (+ relief rainfall)
Ocean Currents - North Atlantic Drift (warm)
Continentality - land heats up and cools down quickly whereas water does so slowly
Air Masses
Distribution of Biomes (Tropical Rainforests, Tundra and Savanna)
Tropical Rainforests: Grow in a band around the equator where the equatorial climate is hot and wet.
Tundra: Found where Winters are cold and Summers are short (arctic areas)
Savanna: Found in regions that have a tropical semi-arid climate (above and below the equator)
Tropical Rainforests (Climate and Distinctive Features)
Climate: Hot and wet - humid
Distinctive Features: Hot climate and abundant rainfall allow for rapid plant growth and trees that can reach very high heights
Savannas (Climate and Distinctive Features)
Climate: Hot with wet and dry seasons
Distinctive Features: An open tree canopy (i.e., scattered trees) above a continuous tall grass understory
How humans impact the ecosystems of: Tropical Rainforests
Deforestation:
Exposes soil to erosion
Takes carbon dioxide out of the biosphere and then lithosphere contributing to global warming
Creates ecological islands - separating groups of animals from others
Nutrient cycles are broken
The use of heavy machinery damages shrubs → derives insects of food → disrupts the food chain
How humans impact the ecosystems of: Savanna
Desertification:
Slash and burn of trees → reduces evapotranspiration levels → reduces rainfall levels → reduces water for people who rely on rivers for water
The removal of vegetation → leaf litter can no longer fall into the soil → the nutrient cycle is broken → shrubs no longer replace nutrients or help to maintain a healthy soil structure by adding organic material to the soil
The destruction of the tree canopy → exposes the soil to rain splash erosion + during heavy rainfall the water flows over the surface of the ground in sheets, eroding all the organic material from the upper layers of the soil. On steeper slopes the power of the water picks up and carries soil particles and smaller rocks → it uses these to erode downwards into the soil in a process known as gulley erosion.
Sustainable Management of: Tropical Rainforests
Wildlife corridors - planting strips of forest to connect the remaining fragments of forest together. Allows animals to move freely from one area of forest to another without coming into conflict with people.
Buffer zones - encourages the local people to use the zone sustainably rather than just banning the usage of forests altogether - helps to make a living and educate people
Sustainable Management of: Savannas
Great Green Wall of Africa - involves planting a wall of native trees and shrubs across the width of Africa:
Increase biodiversity
Reduce soil erosion
Reduce time women spend collecting firewood
Grow medicinal plants
Diversify plant incomes
Improve soil fertility
Increase fodder for livestock
Provide shade for crops and increase their yield
Increase capability of coping with climate change
How humans affect small scale ecosystems in the UK: Studland Bay Sand Dunes
BBQs - Burns vegetation
Dog waste - fertilises the soil so unwanted plants also grow
Walking - tramples vegetation and kills it
Can be managed by: Land-use zoning, dog waste bins
Weather
Day to day conditions/changes in the atmosphere
Climate
Weather over a long period of time (30 years)
Affect of: Latitude on Temperature
Temperature: Greater curvature = Greater area of land to heat up
Affect of: Altitude on Temperature and Rainfall
Temperature: Density decreases as altitude increases.
Rainfall: Air is forced to rise over areas of high altitude causing relief rainfall
Affect of: Ocean Currents on Temperature and Rainfall
Temperature: Warm and cold ocean currents bring different temperatures
Rainfall: Brings in different pressure systems
Anticyclones
High pressure
Air sinks in the lower atmosphere
In the Summer: brings hot and sunny weather with light wind
In the Winter: Anticyclones cause cold weather including fog and frost
Depressions
Low Pressure
When a warm front meets a cold front
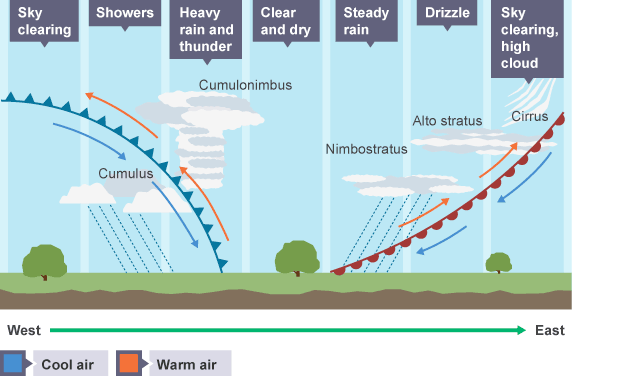
Air rising causes the formation of clouds, which brings rainfall. Depressions often move eastwards across the UK, bringing changeable weather as they travel.
There are usually frontal systems associated with depressions. The diagram below shows the changing weather that the warm and cold fronts bring as they move towards the east.
Urban micro-climates
The buildings and traffic in a large city influence the local climate - creates temperatures that are warmer than in the surrounding rural area.
Factors of: Urban micro-climates
Concrete, brick and tarmac all absorb heat from the Sun during the day. This heat is then radiated into the atmosphere during the evening and at night.
Buildings that are badly insulated lose heat energy, especially through roofs and windows. Heat is also created by cars and factories, which is lost to the air from exhausts and chimneys.
Tall buildings in a city affect local patterns of wind - act as a shelter so average wind speeds in cities are lower than in the surrounding countryside. However, rows of tall buildings can also funnel the wind into the canyon-like streets between them and cause high wind speeds. This may cause hazards for pedestrians and, in some extreme weather conditions, has led to the collapse of scaffolding.
During the summer months, the extra heat due to the urban heat island causes air to rise over larger cities - this can lead to convectional rainstorms.
Urban areas have 10 times the dust particles in the atmosphere than rural areas leading to higher amounts of rainfall - when water vapour condenses in the air to form water droplets it does so by attaching itself to a dust particle.