Terms of Refrence + Topography
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is anatomy
study of internal and external structures and their physical relationships
Why is precise vocabulary important in anatomy
to avoid miscommunication that could harm patients
define tissue
a group of cells that perform a similar function
what is an organ
group of tissues functioning together
what is organ system
a group of organs working together
what makes up an organism
sum of all cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems
name the four tissue types
connective
epithelial
muscle
nerve
what are the functions of epithelial tissue
lining, protection, secretion, absorption, diffusion
what the three types of muscle tissue
skeletal (voluntary),
cardiac (heart, spontaneous contraction),
smooth (involuntary, intestines and blood vessels)
what are examples of connective tissue
bone, cartilage, fat, blood
what is the role of nerve tissue?
transmits electrical impulses (brain, spinal cord, nerves)
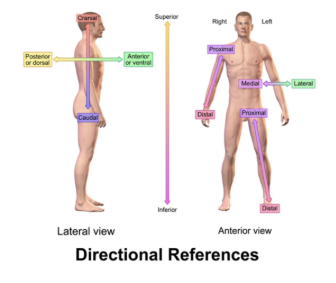
what is the normal anatomical position?
standing, facing forward, palms forward
name two anterior (front) anatomical landmarks
mid clavicular line, midaxillary line
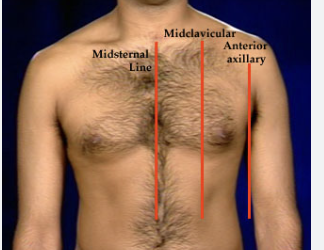
name two posterior (back) anatomical landmarks
mid-spinal line, mid-scapular line
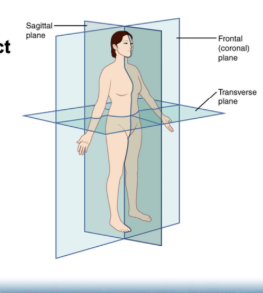
what are the three anatomical planes?
frontal/coronal plane (slice front/back vertically)
sagittal/mid-sagittal (slice in half, = left/right)
transverse (slice horizontally = upper,lower)
define medial vs lateral
medial = toward midline
lateral = away from midlinede
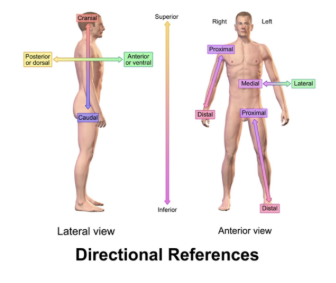
define superior(cranial) and inferior (caudal)
superior = toward head
inferior = toward feet
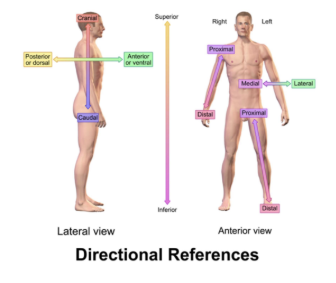
define anterior and posterior
anterior = front
posterior = back
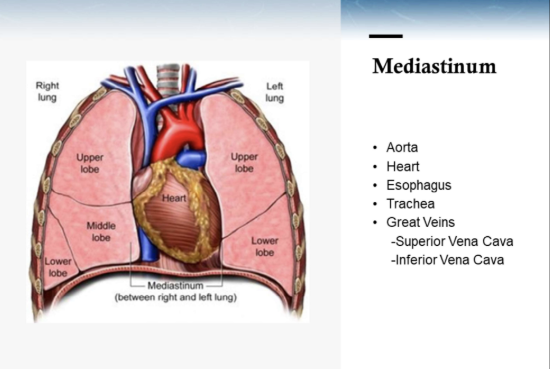
name structures in the mediastinum
heart, aorta, esophagus, trachea, great veins (superior vena cava, inferior vena cava
name the four abdominal quadrants
right upper, right lower,
left upper, left lower
what does brachial refer to
arm, near bicep
what does carpal refer to
wristw
what does femoral refer to
thigh
what does pedal refer to?
foot
where is carotid pulse
in the neck
what does supine mean?
lying on the backwhat
what does prone mean?
lying face downw
what is fowlers position
sitting upright at various angles
what is trendelenberg position
laying, feet higher than the head
what are the pulse landmarks used for
to assess rate, rhythm, and quality
where are pulse landmarks usually located?
close to the skin and near bone