cerebral cortex and hippocampus
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
where is the hippocampus located
in the medial temporal lobe of cerebral cortex
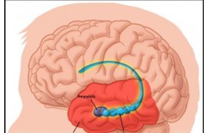
what is the function of hippocampus
consolidates info from short term memory into long term memory
spatial navigation
what is associated with damage of the hippocampus
memory impairment
disorientation
which disorders develop from damage of hippocampus
Alzheimer’s disease
depression
bipolar
what happens in the cerebral cortex
information is processed
what are the 2 parts of cerebral cortex
neocortex (larger)
allocortex (smaller)
true or false: areas of cerebral cortex are primary sites of seizures and epilepsy
true
[neocortex / allocortex] is mature part with 6 distinct layers of neuronal cells
[neocortex / allocortex] has less than 6 layers of neuronal cells and includes olfactory cortex and hippocampus
[neocortex
/ allocortex] is mature part with 6 distinct layers of neuronal cellsincludes all 4 lobes
[
neocortex /allocortex] has less than 6 layers of neuronal cells and includes olfactory cortex and hippocampus
what occurs in the neocortex
experience reaches conscious
many memories are stored
complex responses are planned
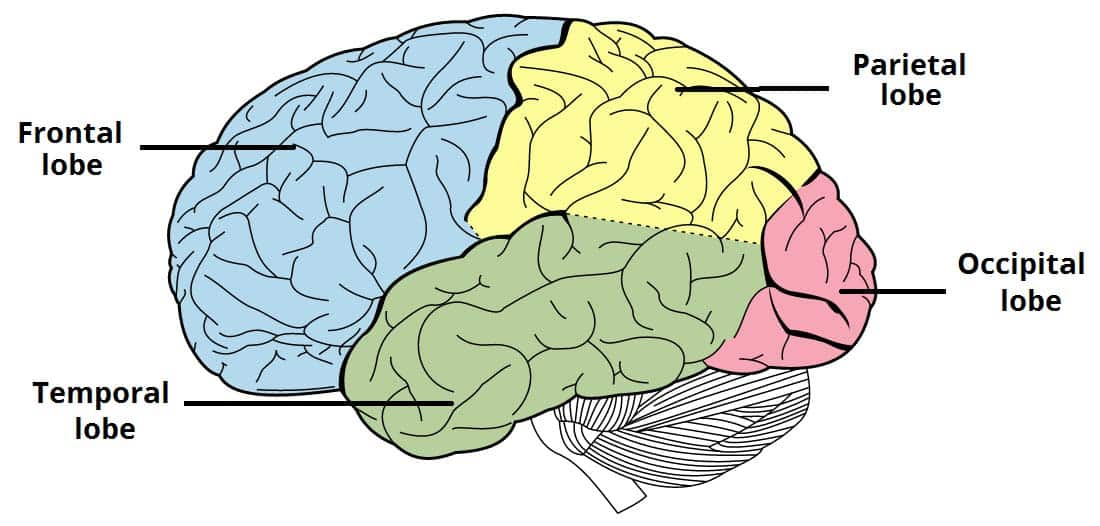
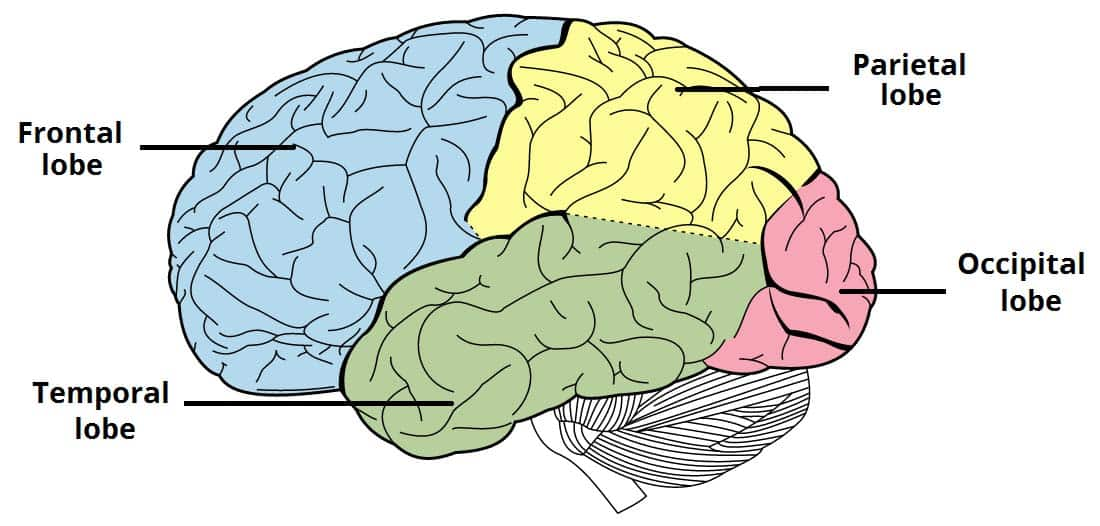
what 4 layers are the neocortex divided into
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
temporal lobe
occipital lobe
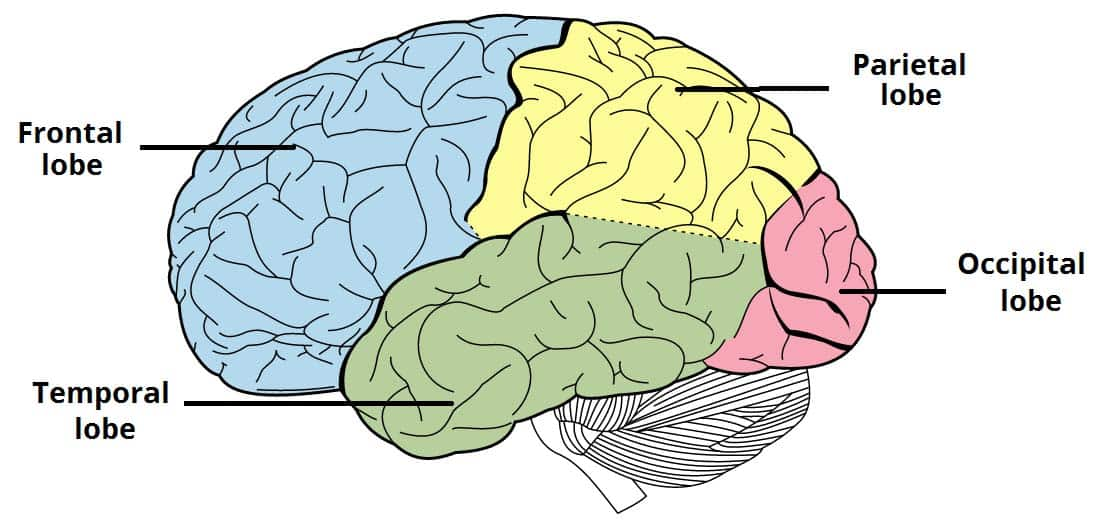
where is the frontal lobe located
front-most region of the cerebral cortex, behind the forehead
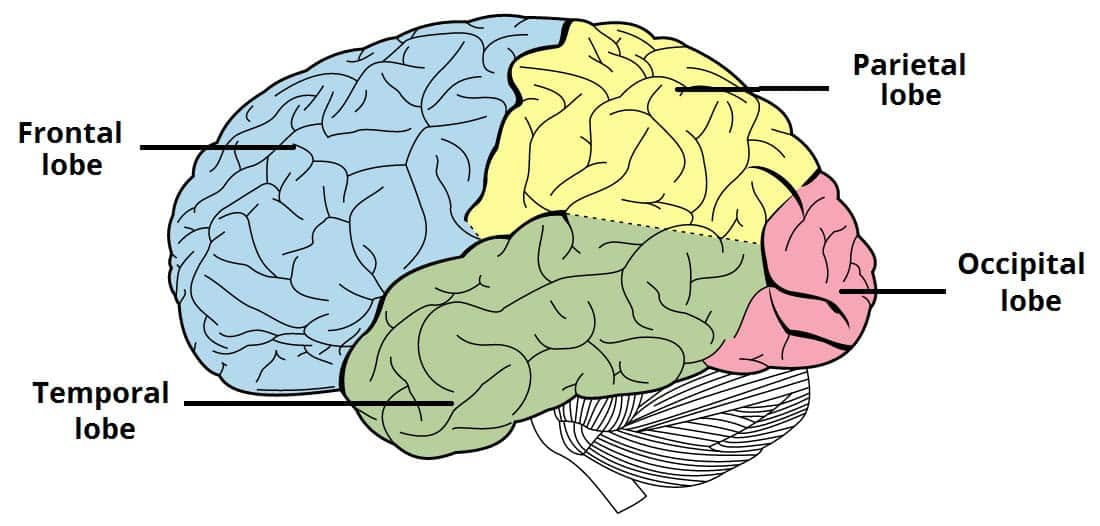
main functions of frontal lobe
movement
decision making
planning
problem solving
personality expression
main regions of frontal lobe
prefrontal cortex
promotor area
motor area
what does the prefrontal cortex do
manages personality, complex thinking, planning, and social behavior
what is the role of the premotor and motor areas
control and execute voluntary movements
what happens if the frontal lobe is damaged
problems with movement, speech, learning motor skills, and altered body image
which cognitive disorders are linked to the frontal lobe
autism
ADHD
depression
main function of parietal lobe
processing sensory info from skin, muscle, joints and internal organs
spatial awareness
understanding where things are in space
what important area does parietal lobe contain
Somatosensory Area, which receives signals from the Somatosensory Thalamus
what can damage to the parietal lobe cause
difficulty recognising or locating objects body parts or events
which cognitive disorders are associated with parietal lobe dysfunction
ADHD
Alzheimer’s disease
what does temporal lobe contain
Auditory Area, which processes sounds from the Auditory Thalamus
main functions of temporal lobe
processing sound
understanding lang
supporting memory and learning
what happens when the temporal lobe is damaged
problems with speech comprehension, memory, recognition, and perception
which disorders are linked to temporal lobe dysfunction
schizophrenia, early Alzheimer’s disease, and autism
where is the occipital lobe located
back of the brain, behind the parietal and temporal lobes
main function of occipital lobe
processing visual information from the Visual Cortex, which receives input from the Visual Thalamus
what happens if the occipital lobe is damaged
vision problems like blindness or colour confusion
motion perception issues
which disorders are associated with occipital lobe abnormalities
schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, autism, and depression
what are association areas of cortex
regions that are not primary sensory regions (they do not receive direct input from the sensory thalamus), nor are they primary motor regions
main role of association area
to link sensory and motor information and support higher cognitive functions like planning, memory, and understanding the environment
which association area is involved in motivation
frontal cortex
what is the role of the premotor cortex (association area)
helps to plan movements before they are carried out
which area helps us understand our body’s relationship with the world
parietal cortex
which brain region helps generate new episodic memories (events and places)
temporal lobes
what is the limbic system
network of interconnected brain regions involved in emotion, motivation, and memory
which structures make up the limbic system
Cingulate Gyrus, Amygdala, Hippocampus, and Nucleus Accumbens
main function of limbic system
to regulate emotional responses and feelings, linking emotion to memory and motivation
which brain regions are mainly involved in movement control
Motor Cortex (Precentral Gyrus), Basal Ganglia, and Cerebellum
how do these movement control regions communicate with the body
they send instructions to motoneurones in the spinal cord (for limbs and trunk) and motor nuclei in the brainstem (for head and neck movements like speech and swallowing)
what do motoneurones do
activate muscle contractions that produce movement
what is the corticospinal tract
main output pathway from the motor cortex to the spinal cord that carries motor commands
where do corticospinal tract fibers cross over (decussate)
in the brainstem just before entering the cervical spinal cord, causing the left cortex to control the right side of the body and vice versa
why is the corticospinal tract important
fastest descending motor system, essential for fine, precise movements
what is the function of cerebral white matter
allows extensive communication between cortical areas, and between the cortex, brainstem, and spinal cord via myelinated axon fibers
what are the four main types of white matter fibers
Tracts – connect distant brain/spinal areas.
Commissures – connect right and left hemispheres (e.g., Corpus Callosum).
Association fibers – connect areas within the same hemisphere.
Projection fibers – connect cortex with lower brain regions and spinal cord.
what does cerebral gray matter consist of
Cerebral cortex
Basal ganglia nuclei
Basal forebrain nuclei
Other nuclei (clusters of neuronal cell bodies)
what’s the main difference between gray and white matter
Gray matter = neuron cell bodies (processing areas)
White matter = myelinated axon fibers (communication pathways)