Legal - Unit4Aos1
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
The Crown
Federal representative of the monarch: Governor-General (appointed by King on PM’s advice)
State representative of the monarch: Governor (appointed by King on Premier’s advice)
Key functions: grant royal assent to Bills, prorogue parliament, dissolve both houses (double dissolution), chair Executive Council, approve delegated legislation
Parliament
All elected representatives plus the Crown
Passes statute law (Acts)
Supreme law-maker except in constitutional cases
Bicameral: composed of two houses (Lower and Upper)
Government
Party or coalition with majority in the lower house
Runs the country and administers law
Executive authority
Commonwealth Parliament structure
Crown: Governor-General
Lower House: House of Representatives (150 members, 3-year term)
Upper House: Senate (76 members; 6 states × 12 + 2 territories × 2, 6-year staggered terms)
Leader: Prime Minister
Victorian Parliament structure
Crown: Governor
Lower House: Legislative Assembly (88 members, 4-year fixed terms)
Upper House: Legislative Council (40 members, 8 regions × 5 members, 4-year fixed terms)
Leader: Premier
Roles of lower houses
Decide government (majority forms government)
Provide representative government (electorate views, petitions, question ministers)
Assist responsible government
Scrutinise government (debates, question time)
Control government spending (money bills originate here)
Roles of upper houses
Review, amend, reject bills from lower house
Represent states/regions equally (not population)
Use proportional representation encouraging diversity
Hold government accountable, review rushed legislation
Law-making powers

Section 109 (Constitution)
Commonwealth law prevails over state law when inconsistent in concurrent powers
Only as far as the inconsistency
Ensures national consistency and Commonwealth supremacy
Tasmanian Dams case (1983)
Commonwealth used external affairs power (s51(xxix)) to stop dam construction
Expanded Commonwealth power to legislate on international treaty matters
Example of High Court broad interpretation affecting federal-state powers
Factor’s affecting parliament’s ability to make law
Bicameral structure: review, scrutiny, hostile Senate may block government agenda
International pressures: treaties may mandate law changes
Representative nature: parliamentarians respond to public opinion, may avoid unpopular laws
Checks on parliament by the Constitution
High Court: hears constitutional cases, can declare laws ultra vires (invalid), implies rights
Separation of Powers: legislature (makes laws), executive (administers), judiciary (interprets) balance power
Senate/upper house reviews government and legislation
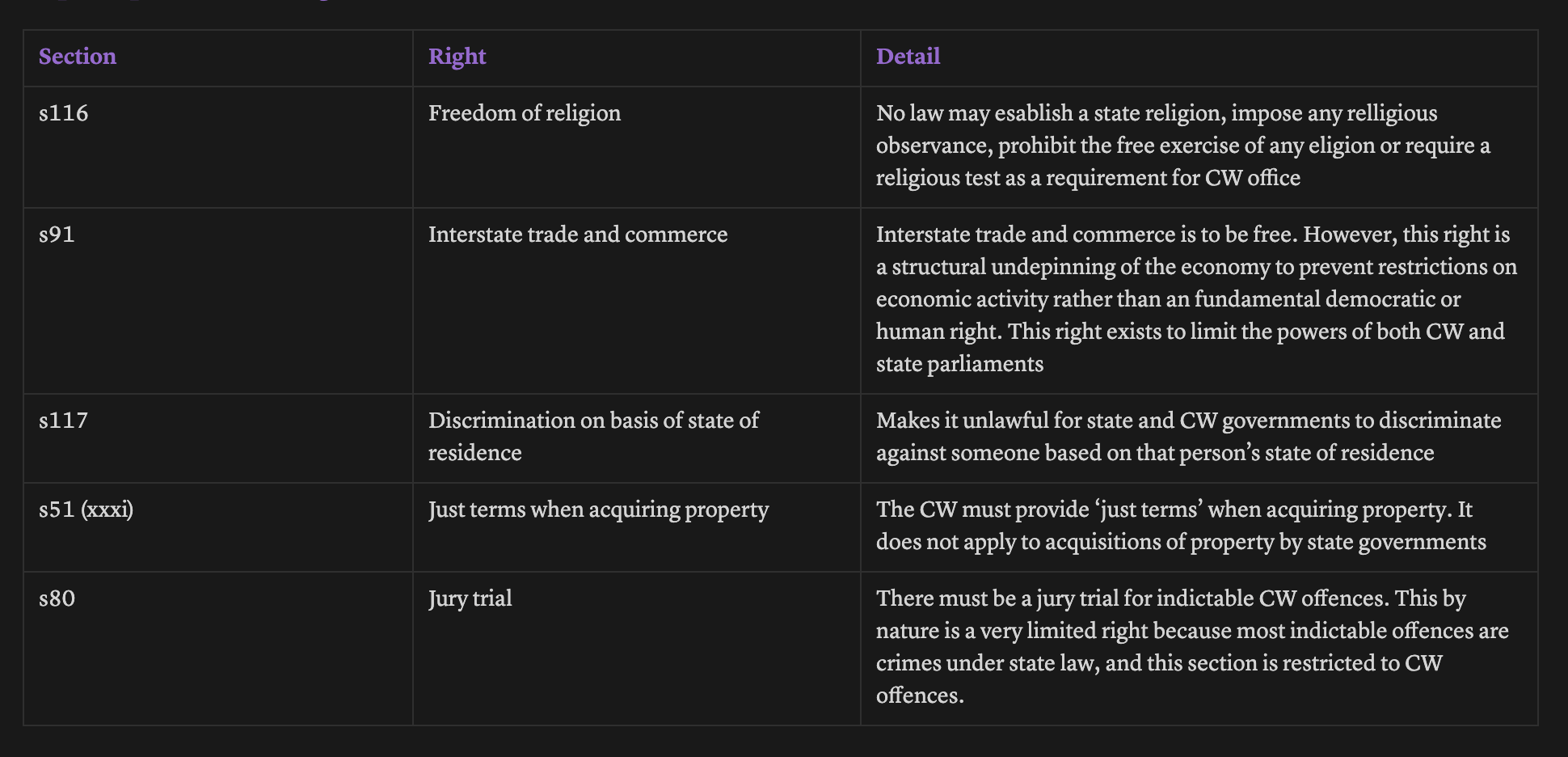
Express rights (entrenched in Constitution)
Statutory interpretation
Judges interpret and apply legislation's words when applied to cases
Interpretation decisions bind lower courts
Parliament can codify (adopt) or abrogate (override) judicial interpretations
Examples: Deing v Tarola (regulated weapon), Re Kevin (marriage/gender), McBain (state/federal clash)
Doctrine of precedent
Stare decisis: stand by decided cases (binding precedent)
Ratio decidendi: binding legal principle behind decision
Obiter dictum: persuasive comments, not binding
Overruling: superior court reverses previous decision
Reversing: same case, different outcome on appeal
Distinguishing: case facts different, so precedent not followed
Disapproving: judge disagrees but cannot overrule, signals need for law change
Factors affecting courts making law
Bound by precedent
Judicial conservatism vs. activism
Costs and delays in bringing cases
Requirement for standing (must be affected)
Relationship between courts and parliament
Parliament is supreme but subject to Constitution/High Court
Courts reactive and case-dependent
Parliament can codify court decisions or abrogate common law
Together they provide checks and balances in law-making