Edexcel A-Level Biology B - Core Practicals
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What is standard deviation?
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
What is a serial dilution?
used to obtain a series of solution whose concentrations differ by known amounts
Why do we measure initial rate of reaction?
Reaction can be controlled, as when reaction starts substrate concentration will decrease fast
What does catalase catalyse?
break down of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas
What does copper sulphate do to catalase?
acts as a non completive inhibitor slowing production of oxygen
What effect will higher concentrations of copper sulphate have on a downward displacement of water experiment, measuring oxygen produced from hydrogen peroxide and catalase?
higher concentrations will cause less oxygen production as copper sulphate inhibit the activity of catalase so less oxygen is broken down
What are the four factors that affect enzyme activity?
-enzyme concentration
-substrate concentration
-pH
-temperature
Why do higher trypsin concentrations cause the colorimeter to decrease in absorbance faster?
higher trypsin concentrations means more enzymes available making collisions with substrate more likely, this breaks down protein in milk, causing it to lose its white colour faster, therefore less light is absorbed by solution
How is a control set up in a practical measuring enzyme activity?
replace enzyme solution with distilled water or boiled enzyme solution
Outline the practical procedure used to measure the effect of enzyme concentration on enzyme activity, using trypsin and milk
1. Dilute stock solution of trypsin with distilled water to produce solutions with concentrations of 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6% and 0.8%.
2. Make a control by adding 2cm3 of trypsin solution and 2cm3 of distilled water. Use this to set the colorimeter absorbance to zero.
3. To another cuvette, add 2cm3 of milk suspension and 2cm3 of the stock trypsin solution. Mix, place in the colorimeter and measure absorbance at 15 second intervals for 5 minutes.
4. Rinse the cuvette with distilled water. Repeat step 3 at all trypsin concentrations
What conclusions can be made from the expect results of an experiment in which trypsin and milk is used to investigate the effect of enzyme concentration on enzyme activity
-Milk contains a white protein called casein which, when broken down, causes the milk to turn colourless. Trypsin is a protease enzyme which hydrolyses the casein.
-As concentration of trypsin increases, the number of enzyme-substrate complexes forming also increases because enzymes and substrates are more likely to collide. This means that the rate of reaction increases up to the optimum enzyme concentration.
-The rate plateaus at the point where all substrates occupy an active site. Increasing the enzyme concentration won't increase rate as substrate concentration is limiting the rate
What is a microscope?
device that produces magnified images of structures that are too small to see with the unaided eye
What is a stage micrometer?
a millimetre long ruler etched onto a slide. it has 100 divisions, each of 0.01mm or 10 micrometres. It is used to calibrate the eyepiece graticule
Lower number means better microscope resolution, True or False
True
What does EPU stand for?
Eyepiece unit
What stain is used when observing a vascular bundle in a stem?
toluidine blue O
Why should a slide be touched with a paper towel before examining?
to absorb excess water
Outlie how to use a light microscope to observe and measure vascular bundles
1. Calibrate the eyepiece graticule by placing both on the stage and lining up the divisions of the stage micrometer (which have a known length) with the divisions of the eyepiece graticule (for which the length is unknown) to calculate the length of one division of the graticule.
2. Cut transverse sections of plant stem (on the white tile using a razor, wet to reduce friction) as thinly as possible. Select the two thinnest sections.
3. Mount one section in water on a microscope slide. Lower the cover slip down carefully onto the slide. Make sure there are no air bubbles in the slide which may distort the image.
4. Add toluidine blue O stain to the other and leave for three minutes, then mount in water on another microscope slide and add the cover slip.
5. Place under a microscope and set the objective lens on the lowest magnification, then use the coarse adjustment knob to move the lens down to just above the slide.
6. Use the fine adjustment knob to carefully re-adjust the focus until the image is clear (can use a higher magnification if needed).
7. Observe and draw the stem.
8. Measure the size of the stem diameter and vascular bundle using the calibrated eyepiece graticule.
What is the name of the pigment in beetroot?
betalain
State two factors that affect the permeability of cell membranes
-temperature
-concentration of solvents
How is beetroot used to measure the permeability of cell membranes?
the higher the permeability, the more red pigment leaks out to the surrounding solution within a given time. A colorimeter can be sued to determine the absorbance, hence concentration of pigment
Outline the procedure to investigate the effect of temperature on the permeability of the cell membrane
1. cut beetroot into 8 identical cylinders using a cork borer and rinse to clean off any pigment as a result
2. place each cylinder in a test tube with 10ml of distilled water. 3. place each test tube in a water baths ranging from 30-80C. Leave for 20 minutes
4. Remove test tubes from water and remove cylinders from test tubes. Decant liquid into clean test tube.
5 Calibrate colorimeter with distilled water. Filter each sample into cuvette using filter paper
5. Measure absorbance for each solution. A higher absorbance indicates a higher pigment concentration, and a hence more permeable membrane
When beetroot samples are put in different temperatures of water, intensity of colour of water increases with higher temperatures. Why?
higher temperatures disrupt the phospholipid bilayer, as there's more kinetic energy moving molecules around, making membrane more permeable, so pigment can move out of beetroot easier. Above 40 membrane proteins denature at high temperature disrupts bonds between R groups, creating even more gaps for pigment to escape through
When beetroot samples placed in higher concentrations of ethanol, intensity of the colour of the solution increases, why?
ethanol causes the membrane to be disrupted
-this is due to phospholipids dissolving in ethanol
-membrane proteins denatured by ethanol
-disruption of the vacuole membrane
-betalain / pigment can escape from the cell / vacuole when the membrane is disrupted
What is meant by plasmolysis?
where the protoplasm of the plant cell begins to shrink away from the plant cell
What is incipient plasmolysis?
-where the water potential of the cytoplasm is the same as the solution
-the point at which plasmolysis just begins to occur
-when 50% of cells in a tissue are plasmolysed
Outline a method that could be used to determine the water potential of onion cells
1. transfer a small set volume of each mineral salt solution into a watch glass. Place one of the sections of onion tissue into the watch glass and leave for 20 minutes
2. remove each section using forceps. Mount in a drop of the corresponding solution on a microscopic slide and cover with a coverslip
3. Observe 25 cells and make a note of how many are plasmolysed
Why do higher concentrations of sucrose cause more cells in an onions epidermis to be plasmolysed?
higher concentration of sucrose means higher concentration of solute, therefore more water bound to solute as hydration shell, decreasing solute potential and therefore water potential, so water diffuses out of cell causing cell membranes to break from cell wall
What is the mitotic index?
the ratio between the number of cells in mitosis in a tissue and the total number of observed cells
Outline the procedure to prepare a root tip slide
1. Warm 1M HCl to 60°C in a water bath.
2. Cut a root tip using a scalpel and add to the HCl. Leave for 5 minutes.
3. Remove from HCl and wash with distilled water and dry.
4. Cut the tip of the root tip sample and place on a slide. Macerate with needle to spread out cells
5. Add a few drops of acetic orcein to make chromosomes visible
Why do root tips need to be submerged in hydrochloric acid before observing?
breaks down pectin in middle lamella that glues cells together, softens tissue
What stain is used to observe mitosis?
acetic orcein
Why are root tips gently squashed?
-produces layer that is one cell thick
-performed gently so cells not ruptured and coverslip is not damaged
What is a pollen tube?
an outgrowth of the inner wall of a pollen grain, digests its way through the tissue of the stigma and style of the carpel. by using digestive enzymes
What structure controls the production of digestive enzymes in the pollen tube?
pollen tube nucleus
Why happens to pollen tube length with increased sucrose concentation?
pollen tube length increases as sucrose provides source of carbon, after optimum sucrose concentration is reached, pollen tube length becomes inhibited
Why should a coverslip not be used when observing pollen tubes?
to allow oxygen to reach pollen tube
Outline a method for observing the effect of different concentrations of sucrose on pollen tube growth
1. Dilute the stock sucrose solution to several set concentrations (e.g. 0.1M, 0.3M, 0.5M, 0.7M, 0.9M).
2. Place a moist piece of filter paper into a petri dish to form a humid chamber.
3. Put a few drops of sucrose solution and an equal volume of mineral salt medium onto a clean microscope slide.
4. Use a mounted needle to rub the anther of the flowers so they shed some pollen onto the microscope slide. Don't add a coverslip to prevent the conditions becoming anoxic.
5. Place the slides into the petri dish until it is time to observe them.
6. Start the stop clock. Place the slides under the microscope and use a calibrated eyepiece graticule to measure pollen tube growth.
Why does HCl diffuse into smaller agar cubes quicker?
smaller cubes have a greater SA:Vol ratio and therefore there is less diffusion distance, so time to diffuse is quicker
What ethical considerations must be made when dissecting insects?
benefits in advancing knowledge must be balanced against potential harm to living thing, it is important to derive the maximum possible learning benefit from dissection
Outline how to dissect a locust
1. pin down head an abdomen using pins
2. remove limbs starting with legs
3. elevate the wings, remove the outer part and then the inner part
4. using forceps and scalpel make incisions on both sides of the abdominal wall, remove abdominal wall
5. flood specimen with water, the gas exchange system/tracheoles should float, it will be a silvery-white colour
6. draw diagram of dissected locust
How do you work out stomatal density?
count number of stomata under microscope and work out area of view under the microscope
What effect does light have on transpiration?
increases rate of transpiration as photosynthesis can occur during the day therefore stomata are open more to let CO2 in
What is a potometer?
a device that can measure the rate of water uptake as a leafy stem transpires, measured by movement of air bubble along ruler
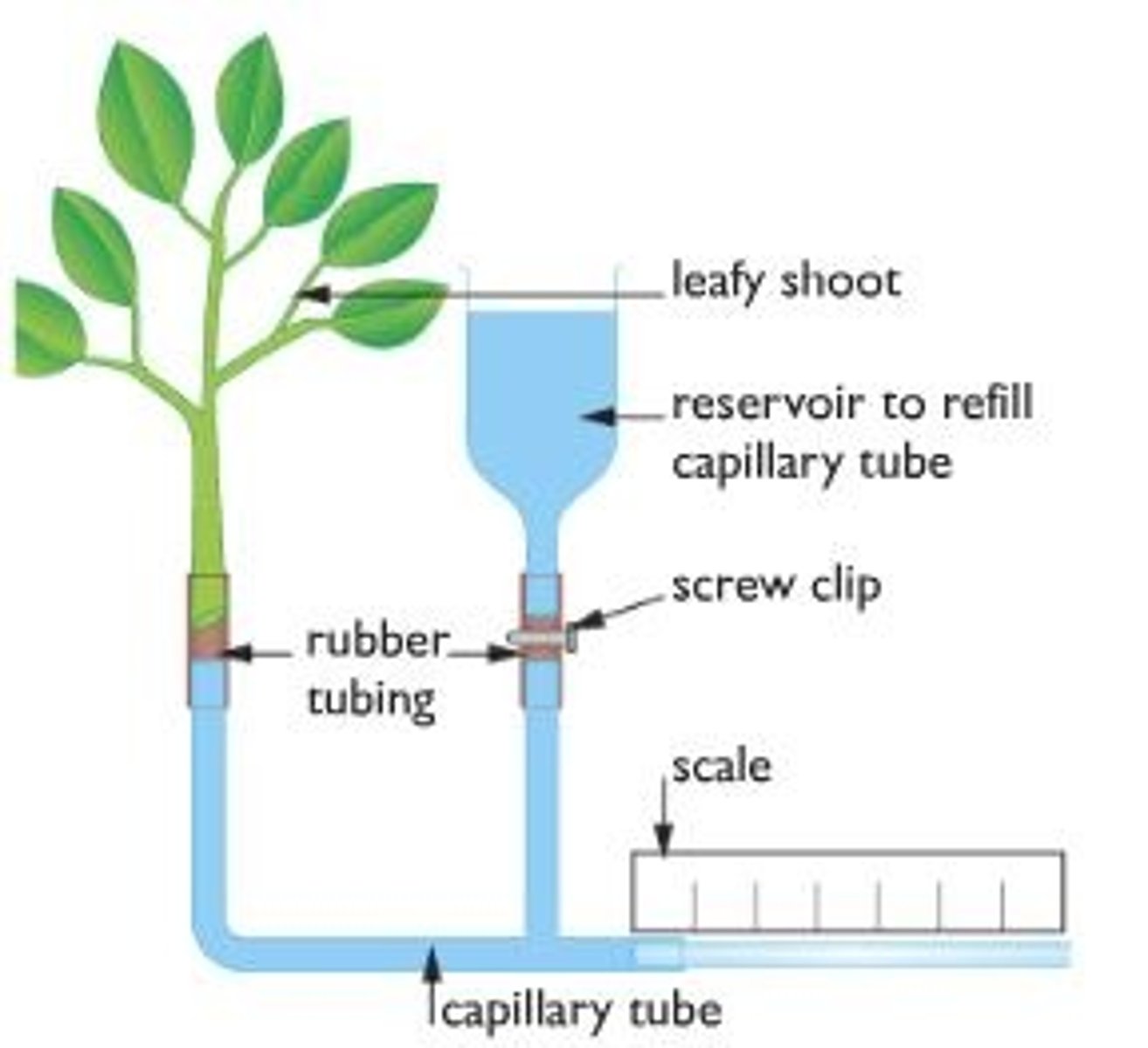
Why should plant stem be cut under water after placing in potometer?
prevents air bubbles from entering plant and disrupting continuous column of water allowing for potometer to be connected to leaves
Why must leaves be dried before starting the rate of transpiration experiment?
water on leaves will prevent transpiration as there is no diffusion gradient as stomata covered by water
How could a potometer experiment be modified to make a comparison between the water loss in upper and lower surfaces of the leaves?
-cover one surface of leaf with Vaseline to prevent transpiration on that side
-measure volume of water taken up in 5 minutes
-switch to other side by removing Vaseline or use different shoot with SAME surface area.
-repeat for each surface and compare results
-keep other variables controlled e.g. temperature
-repeats, calculate mean and standard deviation
Why does exercise increase heart rate?
as you exercise, your body requires more energy, therefore your heart needs to pump more blood in order to deliver these nutrients (oxygen and food) to all of the cells of the body.
Describe how a respirometer work
it is a chamber connected to a capillary tube with a drop of dye. As the organism in the chamber respires and uses oxygen, the pressure decreases and the liquid moves in the capillary
What is the control for a respirometer practical?
organism replaced with inert object of the same mass
How do you find the volume of oxygen consumed using a respirometer?
-place a fixed mass of soda lime at bottom of boiling tube with the organism
-figure out how far red dye moves
-use the formula volume = distance x πr2
1. Assemble the respirometer.
2. Add 5g of one organism to the boiling tube and replace the bung.
3. Place a drop of coloured manometer fluid in the open end of the respirometer. Use a syringe to draw the fluid as far from the respirometer as possible and record its starting position.
4. Close the tap. Start the stop clock.
5. After five minutes, open the tap. Record the end position of the coloured liquid.
6. Repeat the process for the other organism.
How can the volume of carbon dioxide produced be found using a respirometer?
-perform two sets, one with soda lime and one without. Find the volume of gas produced in a given time
-volume of carbon dioxide produced = volume from experiment 2 - volume from experiment 1
How is the rate of respiration calculated using data from the respirometer?
rate = volume of oxygen used/ mass/ time
What are the control variables in the respirometer practical?
-mass of organism
-time
-temperature
-mass of soda lime
-apparatus must be airtight, and replace air between each set up
Justify how would you set up a respirometer to measure the rate of anaerobic respiration in yeast?
-in boiling tube put 5 cm3 of yeast
-5 cm3 of glucose solution so yeast has supply of glucose for respiration
-thin later of vegetable oil to provide barrier to oxygen
-draw coloured liquid to the end of the tube as the coloured liquid will move away as CO2 is produced
What are the type of pigments found in chloroplasts?
Primary pigments and accessory pigments:
-carotene (orange)
-phaeophytin (grey)
-xanthophyll (yellow)
-chlorophyll a (blue-green)
-chlorophyll b (yellow-green)
What is the purpose of having accessory pigments?
plants have additional pigments (besides chlorophyll) so they can gather energy from more wavelengths of light
Why is sodium hydrogen carbonate added to pondweed in a beaker when measuring the effect of different wavelengths of light on photosynthesis?
provides pondweed with a source of carbon dioxide
Outline an investigation to find the effects of different wavelengths on the rate of photosynthesis
1. place piece of pondweed in a beaker of water
2. cover one side of beaker with aluminium foil so that light can only enter the beaker from the other side
3. add half a spatula of sodium hydrogen carbonate to water and leave for 5 minutes
4. position bench lamp close to beaker with a colourless filter between the lamp and beaker. This will be a white light control. Allow pondweed to adjust for 5 minutes.
5. fill the capillary tubing of the photosynthometer with water
6. place funnel end of tubing into beaker of water and add the pondweed, positioning it with the cut end at the top in the funnel opening.
7. as bubbles of oxygen begin to form and pass into the capillary tube, start the stop clock. After suitable time draw up any oxygen produced into syringe. Record volume of gas produced
8. Replace the filter with another filter or a different colour and leave for five minutes
9. Refill capillary tube using syringe and then begin recording again
What are the control variables when investigating the effect of wavelength of light on photosynthesis?
-light intensity
-temperature
-amount of sodium hydrogen carbonate
-time allowed for gas collection
What is the purpose of chromatography?
to separate different components in a sample.
State the factors affecting the rate of migration of different pigments
-solubility
-affinity for the paper
-mass
What is the formula for Rf value?
Rf value = Distance travelled by substance / Distance travelled by solvent
What is the purpose of finding the Rf value of a pigment?
-experimental Rf value can be compared to Rf value in a data base to identify the pigment
-the standard value should be using the paper and the solvent
Outline the procedure of using chromatography to separate photosynthetic pigments
1. Draw a pencil line 1cm above the bottom of the filter paper
2. Add some acetone and use the mortar and pestle to grind up leaf sample and release pigments
3. use capillary tube to transfer pigment onto pencil line
4 suspend paper in solvent (e.g. acetone) so that level of liquid does not lie above pencil line and leave until solvent has run up to top of paper
5. remove paper from solvent and draw a pencil line marking where the solvent moved up to
6. calculate Rf value for each spot
How can a colorimeter be used to measure the rate of growth in microorganisms?
as microorganisms increase in solution, the turbidity of the solution increases, less light passes through and absorbance increases
How is the growth rate of microorganisms measured using a colorimeter?
transfer a sample from the microorganism culture to the cuvette at intervals, or use a data logger to continuously monitor absorbance
As the age of the culture increases, how does the absorbance vary?
the absorbance increases to a maximum, then remains constant
How can a cell count be found from yeast?
1. stain yeast suspension with methylene blue and a view in the haemocytometer to find the cell density.
2. multiply cell density by total volume for cell count
Outline aseptic technique
-wipe down surfaces with an antibacterial cleaner both before and after the experiment
-use a Bunsen burner in the workspace so that convection current draw microbes away from culture
-flame wire loop before using to transfer bacteria
-flame the neck of any bottles before use to prevent bacteria from entering the vessel (air moves outwards so unwanted organisms don't move in)
-keep all vessels containing bacteria open for the minimum amount of time
-close windows and doors to limit air currents
What is the purpose of streak plating?
-bacteria spread out on nutrient agar plate so that distinct colonies can be seen
-these colonies can then be grown on clean agar plate to produce non contaminated samples of one species of bacteria
-colonies can be identified as a particular species of bacteria via indicators such as size, colour or shape of colony
How can different colonies on an agar plate be distinguished from each other?
different colonies will have different size, shape, colour and texture
Outline the procedure for isolating a particular species of bacteria
1. dip sterile inoculating loop into the mixed culture
2. make streaks on the agar plate using the inoculating loop
3. incubate the agar plate for 24 hours
4. take a sample of different colonies and streak them on different agar plates and incubate again for 24 hours
Why should the lid of the petri dish not be taped all the way round?
to allow oxygen to enter, preventing conditions from becoming anoxic
Outline how to Gram stain bacteria
-crystal violet stain added to culture, stain then poured off and excess stain is washed off with water after 10-60 seconds
-iodine solution used to cover smear for 10-60 seconds
-iodine solution poured off and rinsed off with water
-slide the rinsed with ethanol to break down outer lipopolysaccharide membrane
-slide flooded with red safranin counter stain
-culture observed under microscope
What is the role of gibberellin during germination?
-it is secreted by the embryo
-diffuses to aleurone layer of the endosperm
-stimulates production of amylase which hydrolyses starch to maltose, providing seed with food
How is the effect of gibberellin concentration on amylase production investigated?
1. dilute gibberellic acid to produce several concentrations
2. cut seeds in half and only used the endosperm (remove the embryo)
3. dip in sodium hypochlorite solution and wash with sterile water several times
4. place seeds in each gibberellin solution and leave for 12-48 hours
5. place seeds in petri dish and starch agar and incubate for 24-48 hours
6. pour iodine solution onto plates and measure clearance zones
What does the zone of inhibition show?
clear zone indicates starch that has been digested/hydrolysed by the amylase. The larger the zone of inhibition, the higher the amylase concentration
Why do seeds need to be placed in sodium hypochlorite (bleach) solution before experiments?
sterilises seeds/kills any microorganisms
What is the effect of gibberellic acid concentration on amylase production?
increasing gibberellin concentration increases the area of the clear zone, indicating an increased production of amylase and more starch hydrolysed
What are common sources of error for the gibberellin practical?
existing gibberellin and amylase contents of seed may be different
What are the control variables in the gibberellin practicals?
-time allowed to soak in gibberellin
-time left on starch agar plate
-source/age of seeds
-temperature incubated at
How is percentage cover calculated?
-use a quadrat with squares.
-count how many squares the required species is present in
-only count a square is more than half of the square is covered
-divide this by total number of squares available
-multiply by 100 to convert to percentage
Outline how you would investigate the effect of different sampling methods on estimates of the size of a population
1. choose an area to take samples from and use two tape measures to create a set of axis which coordinates can be read
2. use a random number generator to generate 10 sets of random coordinates
3. place smaller quadrat at each of the coordinates (placing the bottom left corner on the coordinate)
4. record the percentage cover of the chosen species
5. record the abundance of each species within quadrat
6. record how many pins touch the chose species (or if frame quadrat count how many intersection points contain species underneath)
7. repeat steps 3-6 with larger quadrat
8. to determine if there is a significant difference between percentage cover or density for each sampling method, use the t test
How can the results of an investigation be used to determine if there is a significant difference between two means?
statistical test e.g. students t test
What is an interrupted belt transect?
the quadrat is placed at uniform intervals along the tape measure
What is a point quadrat?
a horizontal bar with ten pin holes supported by two legs. Pins can be dropped through the hole, and whatever species the pin touches is recorded.
Explain how quadrant sampling should be carried out
1. Quadrats placed at random
2. Method of random number sampling
3. Other control variables considered - removes bias
List abiotic factors
temperature, precipitation, humidity, wind, nutrient availability, soil type, sunlight, rainfall
Outline how you could investigate the effects of light intensity on the distribution of a species
1. choose area with clear light intensity gradient
2. lay down 20m tape from area with shade to area that's more in light
3. choose species that changes in abundance along tape
4. place quadrat at 0m mark
5. measure light intensity at 0m mark at ground level
6. record abundance of chosen species by counting how many are present in quadrat and record in a table
7. repeat steps 4-6 every 2 meters along tape until all of tape is used up
8. create two more transects to have repeats
How can light intensity be measured?
light meter
How can temperature be measured?
thermometer - carefully push bulb end into soil and wait until a steady reading is obtained.
How can soil pH be measured?
pH meter (possibly with a glass electrode?)
What is a null hypothesis?
states that two variables are not related.
How can a colorimeter be used to collect valid data?
-use same light intensity
-use red filter
-use cuvette which is clean/no scratches
-use control with water
-use same concentration of chloroplasts
Describe how a microscope should be used to observe specimens using the high powered lens
-Locate specimen by using low power objective lens
-focus using low or medium power objective lens before using high power
-only use fine focus with high power lens