2.3 Molars, wisdome teeth etc
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is function of molars?
Main mastication
maintain vertical dimensions
Less aesthetic influence
What are the five surfaces of molars?
buccal
lingual
mesial
distal
occlusal
Maxillary molars - roots
Three roots - mesiobuccal, distobuccal and palatal (lingual)
Maxillary molars - Lingual View
Lingual surface is narrower at the cervical third
What are the two well-defined cusps of first maxillary molar?
First maxillary molar has two well-defined lingual cusps: larger mesiolingual cusp and smaller distolingual cusp. Small fifth cusp (Cusp of Carabelli) is often present on the mesiolingual cusp
Maxillary molars - Proximal view
Maxillary molar crowns are short and broad. Distal surface of the crown is narrower than the mesial
Maxillary molars - Occlusal view
The four cusps form a primary cusp triangle (Trigon), especially noticeable in three-cusp second molars
Mandibular molar - buccal view
These molars are wider mesiodistally than high cervico-occlusally
Mandibular first molar has the largest mesiodistal dimension of any tooth
Mandibular molar - Lingual view
Lingual cusps are slightly longer and more pointed than buccal cusps.
Roots are mesial and distal, with the mesial root being longer
Mandibular molar - Occlusal view
Mandibular molars have a rectangular occlusal surface with well-defined cusps
Why are wisdom teeth more difficult to clean and cause more problems?
Due to their posterior location, making them harder to clean and their wrinkled occlusal surface which makes them prone to decay
What are some traits of the third molars that make them different to the second and third molars?
Typically smaller than first and second molars
Often more bulbous crowns with smaller occlusal table
Roots shorter, frequently fused, and often curved distally
What are the shortest of all mandibular teeth?
Mandibular third molars
What is the shortest of all permanent teeth?
Maxillary third molars
What is the difference in the size of teeth between temporary and permanent teeth?
Temporary - smaller in size
Permanent - larger in size
What is the difference in enamel thickness between permanent and temporary teeth?
Temporary - thinner enamel (about 1mm)
Permanent - thicker enamel (about 2-3mm)
what is the difference in occlusal planes of permanent and temporary teeth?
Temporary - flat occlusal plane and prominent cervical ridges
Permanent - curved occlusal plane
Do permanent teeth or temporary teeth have mamelons and if so then on what teeth?
Temporary - no
Permanent - yes on incisors
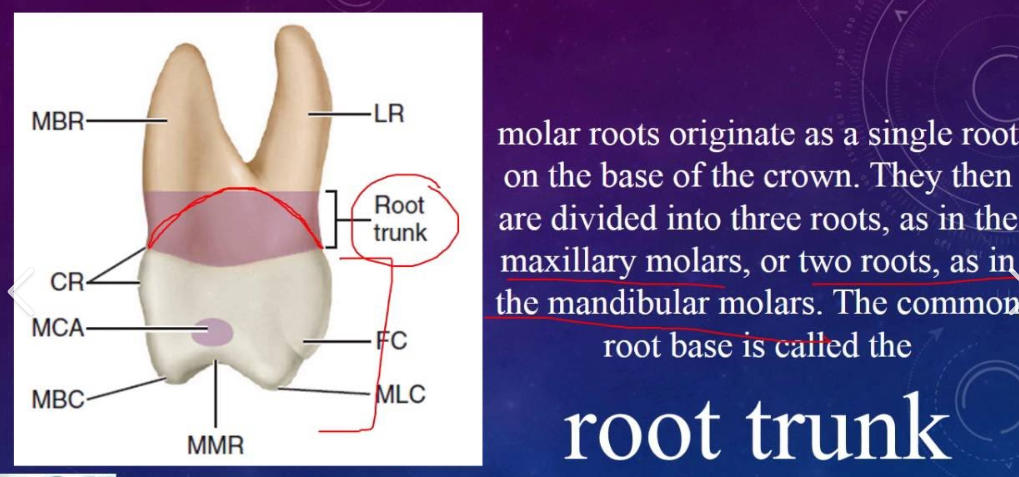
Compare the length, thickness, shape of roots and features of permanent and temporary teeth
Temporary - longer, slender with less rot trunk and the roots reabsorb during exfoliation (shedding)
Permanent - shorter, more bulbous, larger root trunks
Compare the size, thickness of dentin of temporary and permanent teeth
Temporary - Larger pulp chambers, thinner dentin (making teeth more prone to wear and decay)
Permanent - smaller pulp chamber, denser dentin
Compare the colour and mineralisation of temporary and permanent teeth
Temporary - whiter, less mineralized
Permanent - more mineralized, stronger enamel and dentin
What are the 4 types of teeth identification marks?
Angle mark (for incisors)
Segment Mark (Cusped Teeth)
Curvature Mark (all teeth)
Root mark (all teeth)
What is the Angle mark (for incisors)?
The angle between the incisal edge and mesial surface is sharp while the distal surface is more rounded
What is the Segment Mark (for cusped teeth)?
Mesial cusp ridge is shorter than the distal (except for upper first premolar)
What is Curvature mark (for all teeth)?
Mesial part of the crown is larger than the distal part
What is the Root Mark (all teeth)?
The root apex typically bends distally