Class 11-Proteins pt2. Dietary Protein and Health
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What do protein requirements depend on? (4)
Age
Stage of life
Special conditions/requirements
Protein quality
what happens if energy requirements after some time?
If energy requirements are not met, then amino acids will be catabolized to provide energy
What is the effect of decreasing energy intake from adequate to inadequate on nitrogen balance?
will be in a catabolic state
what is EAR g/kg/d requirements for infants
infants = 1.75 g/kg/d
what is EAR g/kg/d requirements for children 2-5
children 2-5=-1.2-3g/kg/d
what is EAR g/kg/d requirements for children 10-12
children 10-12= 1g/kg/d
what is EAR g/kg/d requirements for adults
adults 18+= 0/5-0.7g/kg/d
amino acids are ‘wasted’ when:
1. Energy is lacking
2. Protein is overabundant
3. An amino acid is oversupplied
in supplement form
4. The quality of the diet’s protein
is too low
What are DRI for adults 18+ (sedentary) MvsF, what percent of total cals (AMDR) is recommended vs WHO
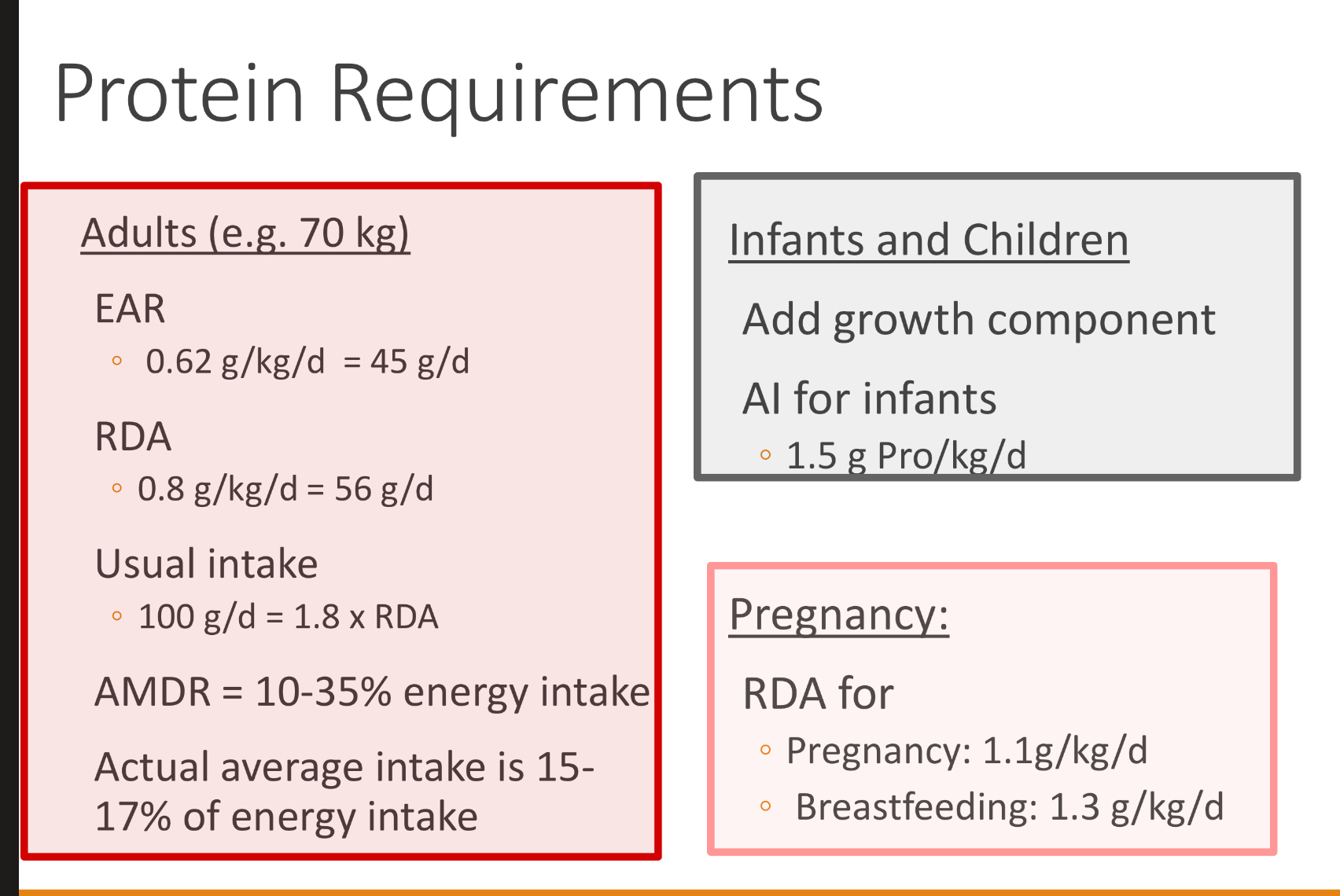
DRI:
0.8 grams of protein/kg/day…(based on sedentary individuals)
• 46 g /d women and 56g/d men
• ~ 10-35% of total calories (AMDR) vs WHO: 10-15% kcal from Protein
!Must also ensure consumption of adequate energy daily!
what are EAR, RDA and AMDR protein requirements for 1. Adults 2. Infants+children 3.Pregnant women
current research suggested x g/kg a. day for adults over 40, then 65+ to prevent xxx
current research suggested 1-1.2 g/kg a. day for adults over 40, then 1-1.2 for adults 65+ to prevent SARCOPENIA
why does liver disease affect protein needs
reduced gluconeogenesis from amino acids
liver can’t detoxify ammonia efficiently → ammonia (NH₃) and ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) build up in the blood.
This condition = hyperammonemia, which is toxic to the brain and can cause hepatic encephalopathy (confusion, drowsiness, coma).
The liver may also fail to make enough plasma proteins → leading to low albumin and edema.
SO :plant proteins or branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs: leucine, isoleucine, valine) are emphasized, since they are metabolized more in muscle than in the liver.
why does kidney disease affect protein needs
Kidney disease
• Decreased renal function
• Increased risk of kidney
stones
• Unable to filter
• Protein requirements depend on Stage of kidney failure
metabolites build up:
Urea (Blood Urea Nitrogen, BUN) → main nitrogenous waste from amino acid breakdown.
Creatinine → from muscle creatine phosphate metabolism.
Ammonia (NH₃ / NH₄⁺) → to a lesser degree compared to liver disease.
Other nitrogenous compounds (uric acid, guanidino compounds).
sarcopenia
degenerative loss of skeletal muscle mass, strength, ability .Major cause of disability + loss pf independent in older adults
the body’s response to protein depends on (3):
body’s state of health
other nutrients & energy taken w protein
protein quality
protein quality is based on these two things:
digestibility —> dependent on the source and food eaten w it
Source of protein (the AA composition) —> animal vs plant, need 9 EAA
what happens when AA is limited or insufficient..
protein synthesis is slowed
for protein digestibility, how are different proteins digested?
animal proteins—> most easily digested >90%
soy+legume proteins —→ >90%
plant proteins —> 70-90%
xxx heat improves digestibility; yy heat may impair digestibility
moist heat improves digestibility; dry heat may impair digestibility
what does PDCAAS represent? what is it used for?
=PROTEIN DIGESTIBILITY-CORRECTED AA SCORE (tested with rats)
PDCAAS represents the yield of protein that is 100% bioavailable
used by DRI and to calculator USA’s % DV for proteins
eg if PDCAAS is 0.8 and total protein is 10 g, then yield is 8 g of complete pro
what is DIAAS
Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) - pig models
E=Expressed as the percent of the dietary requirement (considering ileal digestibility) for each essential amino acid met by ingestion of 0.66 g of the test protein/(kg·day)
The lowest DIAAS is considered the DIAAS of the test protein.
DIAAS scores for Animal proteins : milk, eggs, and beef > 100%;
Soy > 100%
Other vegetable proteins generally fall below 80%
More accurate the PDCAAS – as ileal digestibility and values for each aa may be
calculated, suggested for use by FAO
general protein (in grams) content reference for 1c milk, 1 slice bread, 1/2cvegetables , 1ozmeat or 1/2c legumes
1c milk= 8g
1 slice bread=3g
1/2c veg=2
1oz meat or 1/2c legumes=7g
when you limit AA for protein synthesis will
will Limits body’s ability to build new proteins that
require it!
◦ the AA present in the lowest amount relative to
the body’s need for it—> All others are present in excess and must be
degraded
what is the one exception of a animal-derived ‘high-quality’ food
gelatin, lacking all EAA
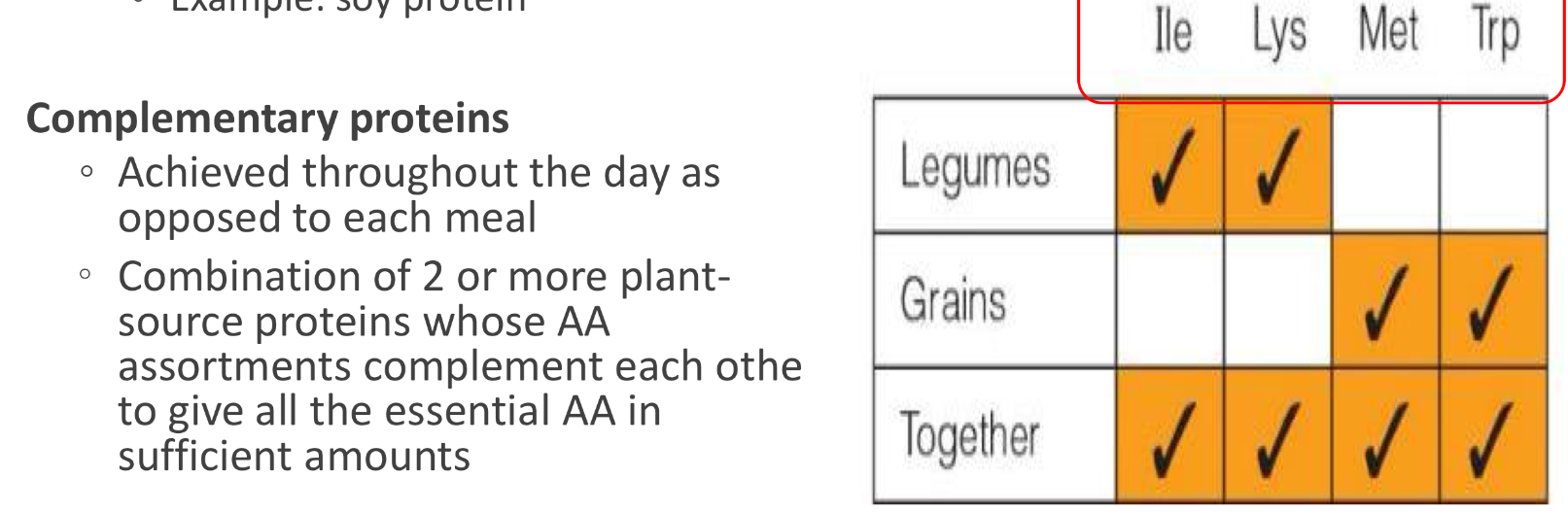
what is complementary protein pairing
what are 2 forms of energu/energy malnutrition
marasmus and kwashiorkor
Marasmus= (less then 2yrs old) severe malnutrition from total caloric and macronutrient deficiency, leading to wasting and a shriveled appearance.
Kwashiorkor (older infants 1-3yrs old) is primarily a protein deficiency with adequate, or near-adequate, calorie intake, causing significant fluid retention (edema), leading to swollen limbs and face.
The key differentiator is the presence of generalized edema in kwashiorkor, which is absent in marasmus.
too little protein can lead to..
learning deficiencies/shortnent attention span
sounded height
inc. rate of infections/illness
what happens with protein overconsumption ?
common with meats
Overconsumption (>AMDR)
• Extra calories, saturated fat and cholesterol
• Replacement of other food groups, lack of fiber, phytochemicals…
Health Risks
• Heart disease
• Kidney disease? Dehydration
• Adult bone loss
• Cancer
◦ Nitrogen excreted as urea (liver and kidney function)
◦ problem for infants esp. prematures, elderly..
protein needs are dependant on activity depending on..
intensity, duration, type
what are protein reccomendations for active adults, endurance, strength athletes
active athletes= 1-1.5g/kg
endurance=1.2-1.6g/kg
strength=1.6-1.8/kg
smokes and charred foods have high amounts of —-, how can we reduce this?
Charred foods have high amounts of heterocylic amines (HCA)
• Reduce charring by limit cooking at high temperatures (BBQ, pan frying,
broiling, etc)
• Use low temperature methods (steam, stew, roast)
• Marinate or add dressing
Leaner meats, poultry and seafood produce less HCAs at high heat