Lesson 6: Mitochondria
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Mitochondria
the organelles providing the energy (ATP) the cell requires for its activity
How big are Ribosomes in Mitochondria
70S
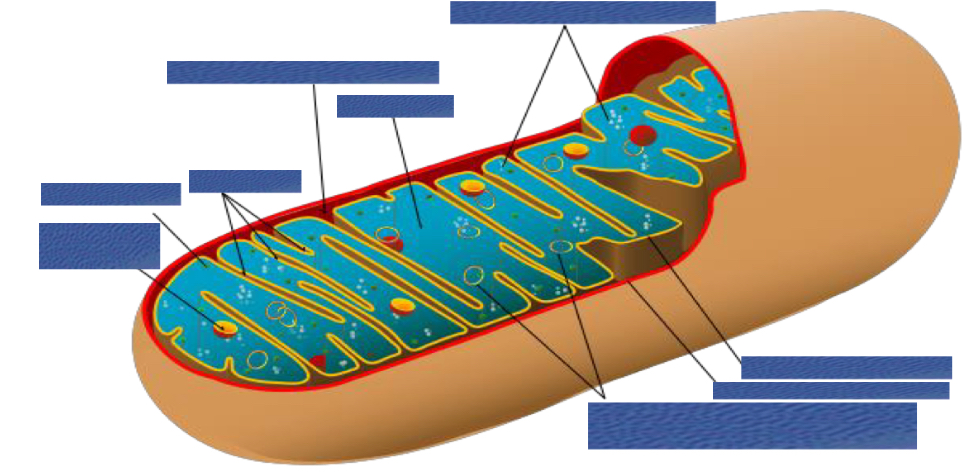
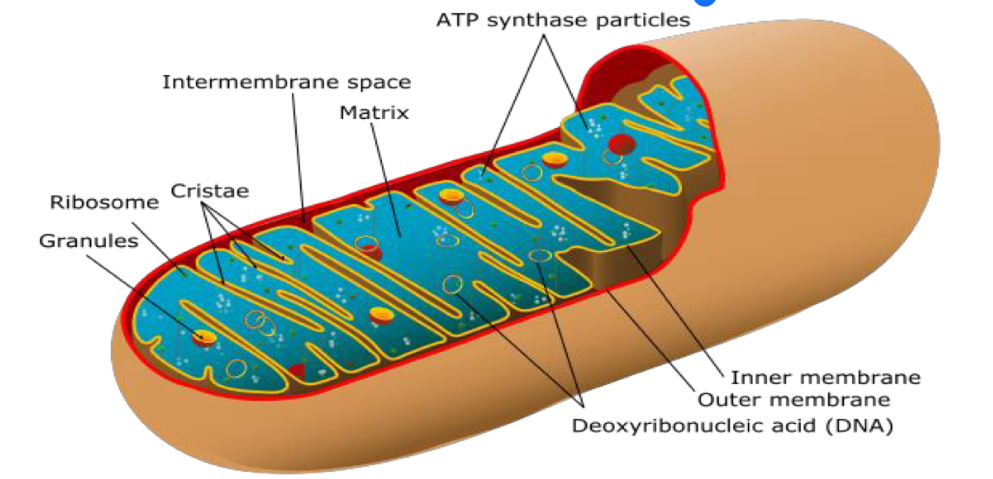
In which shape is the DNA inside of the Mitochondria
Circle shape
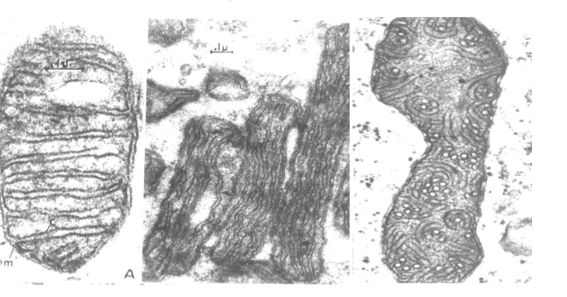
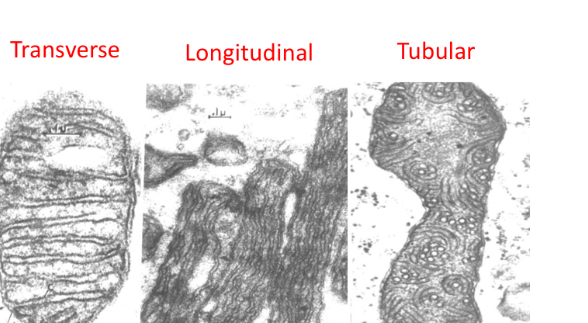
Types of cristae
General characteristics
-present in animal, plant and fungi cells
-large Size
-battery of enzymes and coenzymes tightly coordinated
that makes possible this metabolic and energetic function
Outer membrane
40% lipids / 60% proteins
Less cholesterol
-highly permeable
-Porins: hydroponics channel proteins
Intermembrane space
Similar to cytosol
Inner membrane
20% lipids/ 80% proteins
Almost impermeable → important for proton gradient
-many phospholipids
-no cholestrol
Proteins: components electron transport chain, ATP synthase, specific Transporters
Functions
-ATP production in cristae: Respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation
-cell survival
-apoptosis
Biogenesis
Can’t be produced only divided from other
Where are the proteins of mitochondria synthesised and how much percent do they self synthesize
By cytoplasmic ribosomes Encoded by nuclear DNA
Only 1%
Where does MtDNA come from
Only mother
Mitochondrial diseases
Can only come from mother
Endosymtbiotic theory
Mitochondria were first in prokaryotes than 2 organisms established symbiotic relationship.
Then both both divided and mitochondria became part component.
Facts that support the theory
-70S ribosomes
-mtDNA similar to prokaryotic
-prokaryotic protein synthesis inhibitors