Organic Chemistry IR Spectroscopy
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is spectrometry?
Measuring spectral components of a physical phenomenon in order to describe a physical property
What is spectroscopy?
Measuring how molecules interact with energy of the electromagnetic spectrum
What kind of form does electromagnetic energy come in?
This comes in wave form, the magnetic field points away and the electric field points up
What is the connection between wavelength length and energy?
As wavelength increases (longer wavelengths), energy decreases and as wavelength decreases (shorter wavelengths), energy increases
What is wave particle duality?
At small atomic scales, energy waves become all but the same as particles. Electromagnetic radiation becomes the same as a photon.
The electromagnetic spectrum and the size of the different wavelengths?
Gamma rays are the size of an atomic nucleus
X rays are the size of an atom
UV light is the size of a molecule
The visible light that we see is the size of cells
IR light is the size of a human
Microwave is the size of a building
What does it mean that energy is quantized?
The amount of energy that is put in must be enough to get to the second energy level. This exact amount of energy will be used to excite the molecules from a lower energy to a higher energy
What is the connection between the different amounts of energy that is used for different scenarios?
For electronic energy levels, or ultraviolet light, the amount of energy that is absorbed is incredibly high
For vibrational energy levels, or IR, the amount of energy that is absorbed is relatively low
For rotational energy levels, or NMR, the amount of energy absorbed is very small
what are bonding vibration modes?
this shows the infrared absorbance that is occuring when the energy of the measurement matches the energy needed to excite a bond vibration mode
different bonds will have different energies and thus different signals will be observed on the IR spectrum
what is hooke’s law?
this states that the IR absorption energy is related to the masses of the two atoms bonded as well as their bond strength
What factors influence IR signals?
Identity of atoms involved
hybridization will influence the energy they will absorb
number of bonds shared between the two atoms
strength of dipole that exists between the two atoms
what can IR spectrum information tell us?
This can tell us the presence or absence of a specific bond or this is known as the “diagnostic region”
where is the “diagnostic region” located on an IR?
This is located to the left of the 1500 mark
how do you convert wavelength to wavenumber?
this is accomplished by
What things will occur in the diagnostic region of the IR spectrum?
4,000-2700 = X-H
The triple bonds from C to C and C to N are also present
Double bonds are also present from C to C, C to N and C to O
Trends of IR signals relating to signal energy vs. number of bonds
The triple bonds between two carbons absorbs the most energy, about near 2100 and the C-C single bonds absorb the least energy
Trends of IR signals relating to signal energy vs. hybridization state
The sp hybridization states are the highest energy and the sp3 are the lowest energy with sp2 being in the middle
Trends of IR signals relating to signal intensity vs. polarization strength
The more polarized, the more absorbance and thus a stronger IR
what is the difference between strong vs. weak signals?
strong signals are very long, down the % transmittance
weak signals are about half way down, not quite as long as the strong signals
Examples of strong vs. weak signals?
strong signals: typical a C=O
weak signals: typically a C=C
What is an example of a maximum weak signal that will never show up?
Any molecule that has equal substitution will not have a dipole
Examples of broad vs sharp signals?
Broad signals are very fat
Narrow signals are very skinny
What is an example of a broad signal?
A good example of a broad signal is the OH band
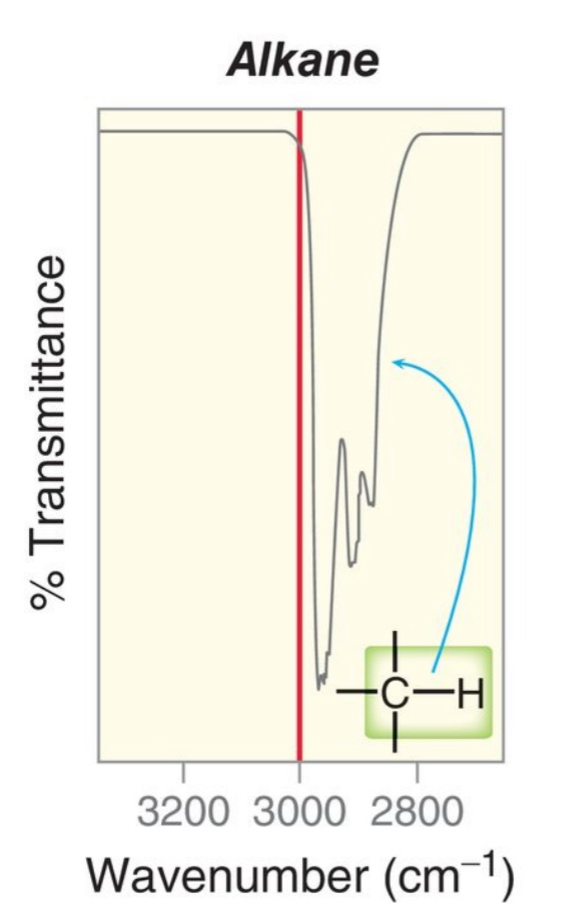
Example of Alkane C-H signals
There is a one 3000
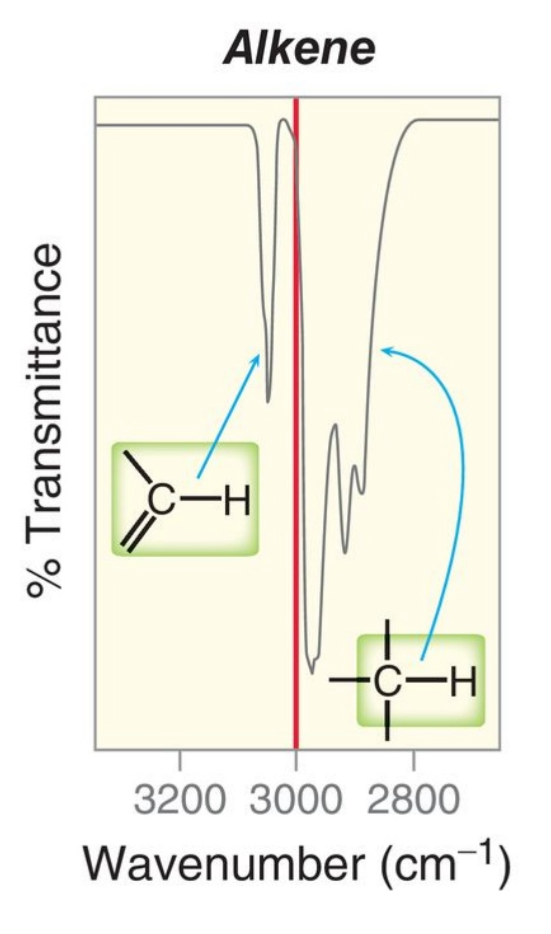
Examples of Alkene C-H signals
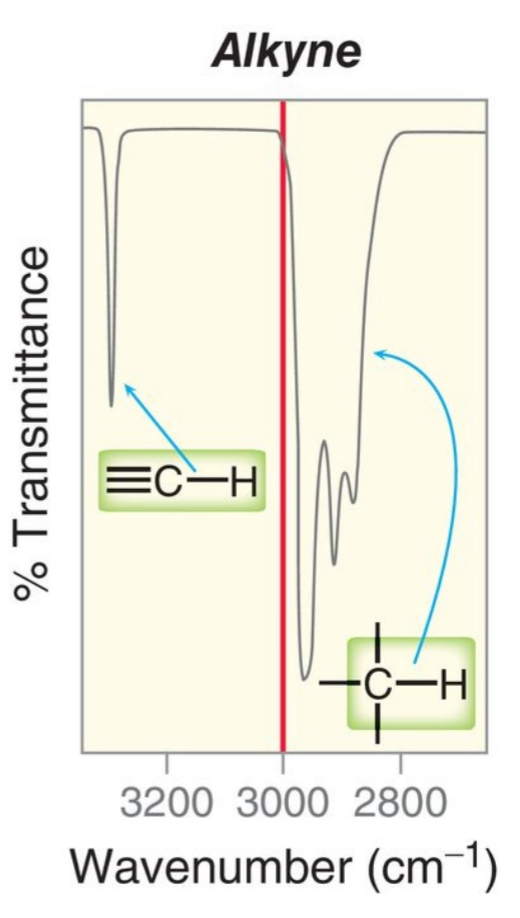
Examples of Alkyne C-H signals
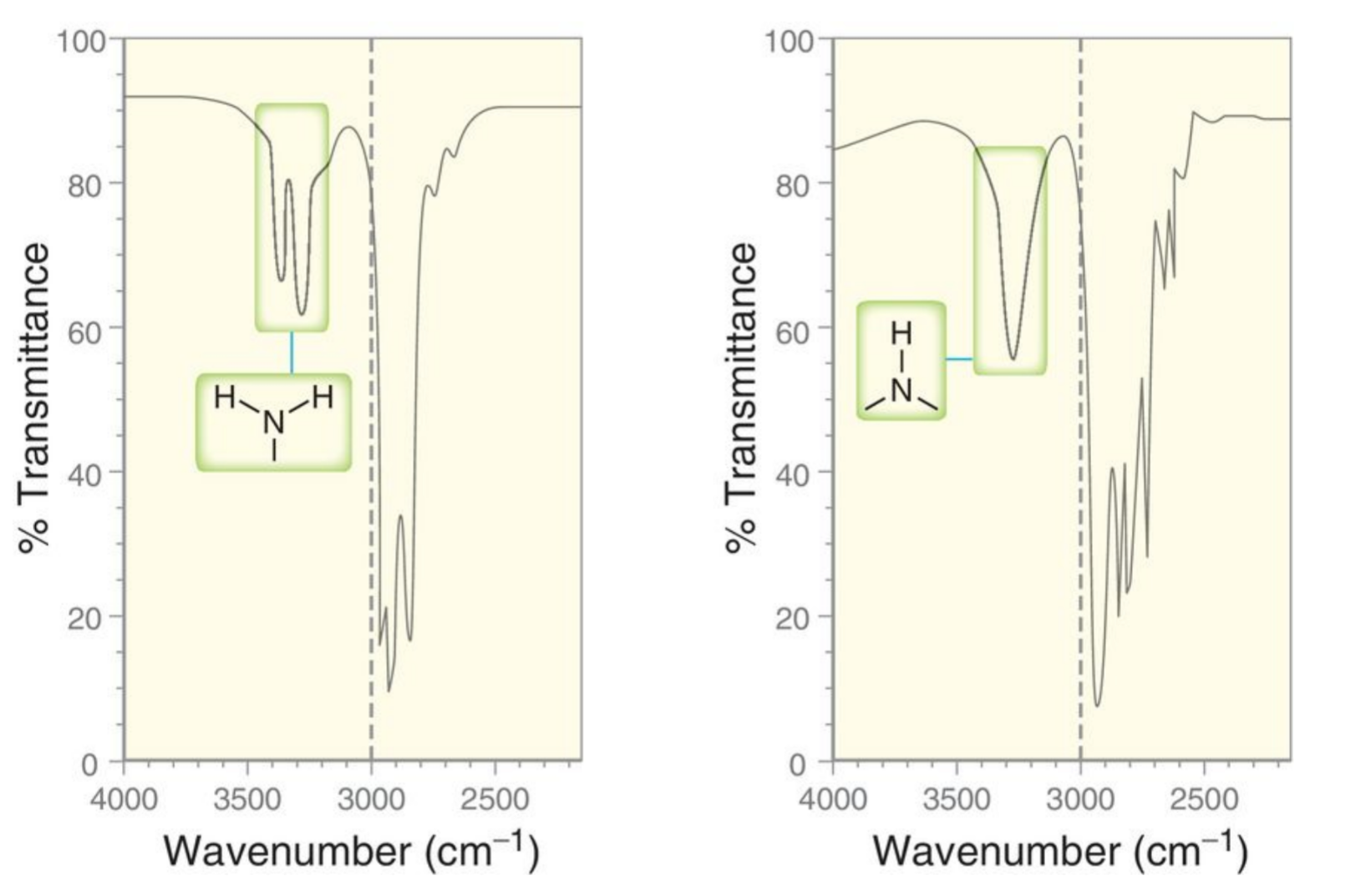
Two examples of N-H signals