judiciary !
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
role of s.c
final court of appeal
interprets constitution through judicial review
creates legal precedents
protects rights, liberties and principles set out in const
checks power of exec and congress
SUPREME COURT IS INDEPENDENT
lifetime appointments - tenure
appointment process- ensures vetted by both exec and congress- non partisan
salary protections- in const- protect economic manipulation
limited impeachment and removal- high threshold so judges arent subject to arbitrary dismissal
control over case selection- manage workload and choose without external pressure
judicial review
seperation powers- cant hold position in congress or exec
judicial restraint
encourage judges to limit own power stick to const
obergefell v hodges- roberts criticized majority and not explicitly state sin const
NFIB v sebelius- upheld affordable care act- upheld restraint by avoiding broad ruling which lead to detabilise power
SUPREME COURT ISN’T INDEPENDENT
candidates are appointed and confirmed based on political agendas
there has been executive criticisms of court decisions
court is being used by pressure groups to change laws
court is increasingly involved in political debates
bush v gore 2000 directly involved courts in political process
many justices have worked in political sphere or clear connections to political parties
appointment process
vacancy occurs
short list is drawn up w advice from judiciary committee, white house staff, justice department
short list are background checked by FBI
candidates interviewed by president
public announcement
rating given by ABA standing committee on federal judiciary
hearings held by senate judiciary committee
senate judiciary committee votes on whether to recommend further action
senate debates
floor vote in senate
strengths of appointment process
thorough vetting into past and qual
involves check and balances
promote diversity
lifetime tenure ensures ideoendence
demoratic
weaknesses of appointment process
politicisation by president-
politicisation by senate- used to be confirmed w overhwleming suppport- scalia 1986 98-0- all now party lines - merrick garland
unpredictable vacancies- obama 2 in 8 years - trump 3 In 4 years
less qualififed candidates due to political compromises
extremely partisan
reasons why pres chooses candidates
ideological alignment - barrett
liklehood for nomination -jackson appealed to moderates and progressives
legal qual and experience - kagan first female solicitor general
demographic considerations - jackson- rcial diversity women
current composition and needs of the court - barrett 48 young age - long term influence
conservative justices
originalist- republican- limit abortion and affirm action
chief justice john roberts- bush
samuel alito- bush- confirmation close reflecting partisan
clarence thomas- bush - intense deabte- sexual assual allegations- narrow margin
neil gorsuch- trump- refusal obama- cons titlt
brett kavanaugh- trump- sexual assualt, public scrutiny- slimmest margin in history
amy coney barrett- trump- soldiifed cons- days before election
liberal justices
champion abortion, liberties, affirm action
living constitutionalist
sonia sotomayor- obama- first latina- vocal advocacy civil rights and criminal jsutice reform- step diversity
elena kagan- obama- lack experience but solciitor general- confirmed by majority
kentanji jackson- first black women- biden- extensive legal experience - strong liberal voice
living constitution theory
still living and therefore open to new interpretations
loose constructionist give greater interpretations and go beyond words
framers kept it vague to allow it to evolve
role is to modernise s.c
liberal
orginalists theory
should only consider original intentions of the framers
a dead document not open to interpretations
strict constituionalist approach to stick closely to original consittution
courts role is to maintain 1788 beliefs to modern america
cons
power of judicial review
marbury v madison 1803
interpret meaning of constitution
strike down gov actions
strike down legislation
strike down state laws and actions
effectively amend constitution
power of judicial review is controversial
no expressley stated in constitution
s.c granted itself the power in madbury v madison 1803 and fletcher v peck 1810
undermines principle separation powers
gives too much power to unelected and unaccountable judges
some justices generally liberals have been criticised for judicial activism- interpret constitution in a new way ‘legislating from the bench
cons justices practice judicial restraint- avoiding overturning legal precedents
landmark rulings
- brown v board education topeka- 1954- right student not segregated by race
- griswold v connecticut- 1965- right to use contraceptives within marriage
-miranda v arizona - 1966- 5th amendment right when questioned by police
-loving v virginia- 1967- state laws on interracial marriage declared unconstitutional
- roe v wade - 1973- right to an abortion in first 2 trimesters
- obergefell v hodges- 2015- right of same sex marriage
- express v zarda - 2020- right of employees not discriminated for sexual orientation
judgements advanced liberal values
civil rights act
obergefell v hodges
roe v wade
zarda v altitude express- cannot be discriminated based on sexual orientation- follows from bostock v clayton county
use 14th amendment in riley v california extend to digital
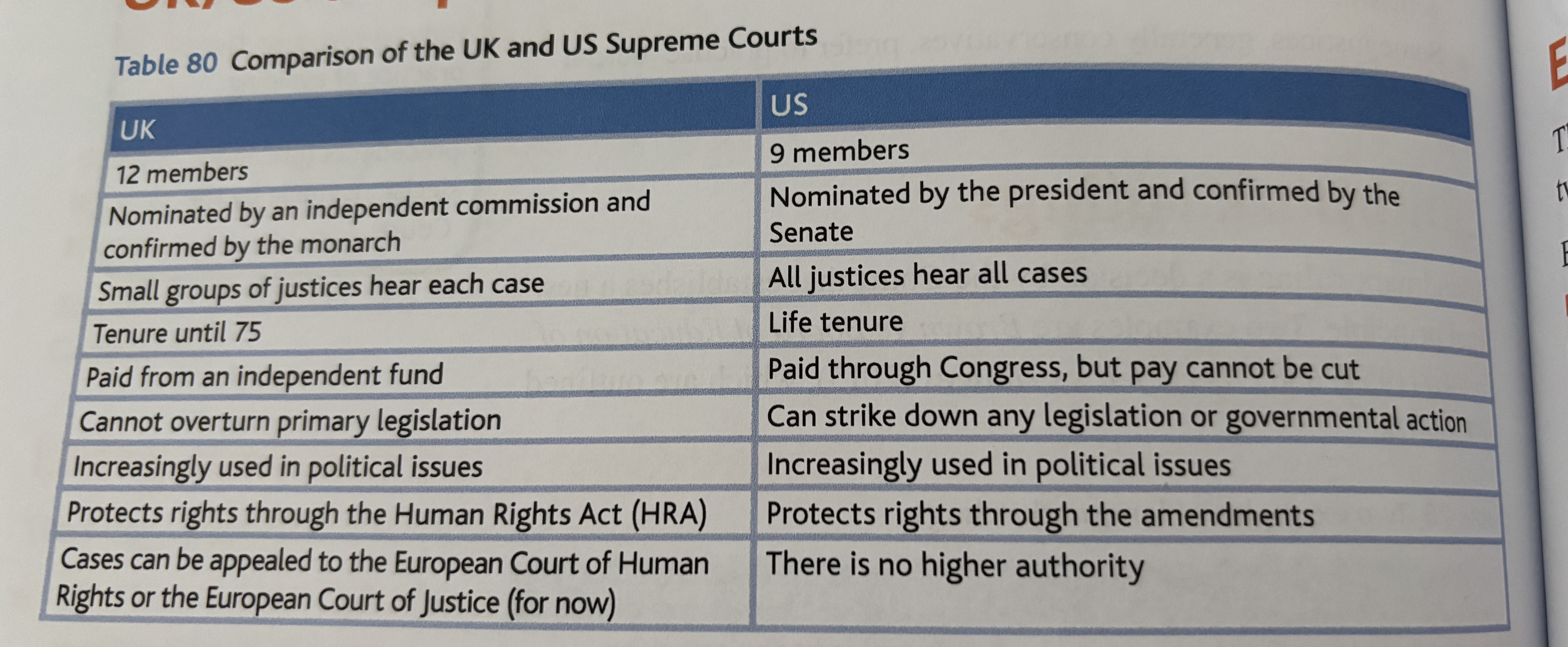
uk v us
Explain and analyse three criticisms of the Supreme Court
P1- lack of democratic accountability- unelected- bush v gore decision 2000- lifetime appointments remove incentives for justices to align with public opinion.- structure can be seen as undemocratic and disconnected from voter influence.
P2-politicization - barrett 2020 viewed as heavily partisan- Court’s rulings reflect ideological biases rather than impartial legal reasoning.- erosion of courts independence- appoitnment process
P3- judicial overreach- create laws not interpret them- roe v wade 1973 criticized for bypassing legislative process- undermines seperation of powers- bush v gore- gave self judicial review
Explain and analyse three ways in which judicial independence is maintained
P1- life tenure- ensures that judges are not swayed by political pressure or fear of losing their position, as seen in landmark rulings like Brown v. Board of Education (1954), which desegregated schools despite opposition.- enables judges to make impartial rulings without fear of retaliation.
P2- protection from salary changes- gov are unable to exert influence through economic pressure, reinforcing impartiality in their rulings. For example, this measure is enshrined in Article III of the U.S. Constitution.- restricts political manipuation
P3- appointment process and safeguards- processes designed to assess legal expertise rather than political loyalty.- how fair and transparent appointment processes help maintain an independent judiciary
Explain and analyse the limits of the Supreme Court’s power
P1- dependence o other branches- Brown v. Board of Education (1954), which ordered school desegregation, resistance from Southern states delayed implementation until federal action, such as Eisenhower deploying troops to enforce integration in Little Rock, Arkansas.- Court’s authority can be limited by the willingness of other branches
P2- congressional power- Oregon v. Mitchell (1970), Congress passed the 26th Amendment, lowering the voting age to 18, overriding the Court's split decision.- legislative powers can curtail or reverse the Court’s influence.
P3- public opinion- influenced by societal attitudes and fears of losing legitimacy.- Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization (2022) reflect shifting public and political pressures on controversial issues. Justices may tailor decisions to avoid public backlash or maintain the Court's credibility.- public opinion indirectly influences
Explain and analyse the role of judicial restraint in the US judiciary.
P1-uphold seperation powers- Judges practicing restraint avoid striking down laws passed by Congress or executive actions unless there is a clear violation of the Constitution.- Burwell v. Hobby Lobby Stores (2014), the Court deferred to Congress’s decision on healthcare policy- Judicial restraint ensures that the judiciary respects the roles of the legislative and executive branches
P2-respect precedent- Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992), the Court upheld Roe v. Wade despite criticisms, following the principle of stare decisis.- encourages judicial consistency by respecting prior rulings and avoiding unnecessary disruption
P3- limit judicial activism- limits decisions based on opinion- Missouri v. Jenkins (1995), the Court displayed restraint by refusing to impose a solution to a desegregation issue, leaving the task to local authorities.- limits the judiciary’s power, ensuring it does not overreach by deciding cases that involve policy-making better left to elected officials.
Explain and analyse how the Supreme Court has shaped civil rights in the United States
P1- desegregation- brown v board- challenged institutional racism and paved the way for further desegregation in other public services- instrumental in advancing civil rights by challenging racial segregation and setting a legal precedent
P2- protect voting rights- Voting Rights Act of 1965- key to expanding access to voting for minorities.- however shelby county reduced this- role in both advancing and limiting civil rights, demonstrating its complex relationship
P3- same sex marriage- obergefell v hodges- ignificant shift toward equality for LGBTQ+- reinforced the Court's role in expanding civil rights protections for historically marginalized groups- equality under the law
Explain and analyse the significance of judicial review in the US political system
P1- uphold constitution- ensure that laws and executive actions comply with the U.S. Constitution- brown v baord used judicial review to overturn state laws that allowed racial segregation in public schools, emphasizing the importance of the Constitution's guarantees of equal protection. - uphold equality and integrity of const
P2- checks and balances- judicial review was crucial in United States v. Nixon (1974), where the Court forced President Nixon to comply with a subpoena for tapes related to the Watergate scandal- affirmed the principle that even the executive is not above the law, demonstrating the Court's role in maintaining checks and balances.
P3- influence public policy- interpreting the Constitution in ways that shape societal norms and political practices.- Roe v. Wade (1973), the Supreme Court’s decision to legalize abortion in all states through its interpretation of the right to privacy had a profound impact on U.S. politics and public policy- significant role of judicial review in not only interpreting the Constitution but also in influencing broader societal and political changes.
Explain and analyse how the Supreme Court acts as a check on the other branches of government
P1- legislative- strike down laws passed by Congress that violate the Constitution Marbury v madison- United States v. Lopez (1995), where the Court ruled that a federal law banning guns near schools exceeded Congress’s power under the Commerce Clause.- check the legislative branch by ensuring laws align with constitutional
P2- executive actions- judicial review was crucial in United States v. Nixon (1974), where the Court forced President Nixon to comply with a subpoena for tapes related to the Watergate scandal- trump action including many immigration policies havent been approved but trump continues to act however
P3- check exec appointment powers- NLRB v. Noel Canning (2014), the Court ruled that President Obama’s recess appointments to the National Labor Relations Board were unconstitutional because they violated the Senate’s power- president’s actions do not overstep the boundaries set by the Constitution
Explain and analyse the role of the Supreme Court in interpreting the Constitution
P1- judicial review- marbury v madison gave rights- roe v wade court interpreted in constitution extends womens rights- allows it to interpret the Constitution’s principles in response to evolving societal norms and issue
P2- expanding rights- brown v board education- interpreted the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment to declare that racial segregation in public schools was unconstitutional- the Court shapes American society by interpreting constitutional clauses
P3- adapting to modern contexts- obergefell v hodges- interpreted the Equal Protection Clause and the Due Process Clause of the 14th Amendment to legalize same-sex marriage nationwide, adapting constitutional principles to modern understandings of equality and marriage rights.- remains a living document
Explain and analyse three aspects of selection and appointment of Supreme Court justices
P1- presidential nomination- nominates a candidate based on their judicial philosophy, political ideology, and sometimes their legal qualifications- Trump barrett- driven to solidify conservative court- President plays a significant role in shaping the ideological direction of the Court
P2- senate confirmation- Senate Judiciary Committee, followed by a full Senate vote.- Senate refused to confirm Merrick Garland’s nomination in 2016 during President Obama’s final year in office- scrutinize a nominee’s qualifications, judicial record, and ideological leanings- Senate influences the selection of justices
P3- Political and Ideological Considerations- Presidents and Senators often seek nominees whose views align with their party’s agenda- ideological shift in the Court after President Trump appointed three justices, solidifying a conservative majority- process is not purely based on qualifications but is often deeply entangled with partisan politics
3 ways judicial review is important
ensures all gov action in line w const - safeguards rights
critical check on branches
allow const to evolve w societal changes
3 ways judicial review isnt important
not in const - gave to self- marbury v madfison
judicial overreach - bush v gore
relies heavily on subjected interpretation of judges
examples of appointment process
Kentanji brown jackson- scrutinised her past public defender role, ruling in child porn cases and defense of guantanamo bay detainees
amy coney barrett- criticised healthcare and abortion views - changes ideology of court- rushed hearrings
brett kavanaugh- - allegations sexual assualt highschool and college- division - 50-48 won- controversial
merrick garland- obama nomination- denied- great record- repub controlled senate- highlights issues politics
recent cases
reporductive rights- dobbs v jackson- overturn roe v wade
religious freedom- fulton v philadelphia- violated 1st amend when froze contract of catholic foster care for not allowing same sex couples- allows more religious expression - sides due to cons
voting rights- bronvich v dnc 2021- discard ballots cast outside of designated precinct- affects race- upheld voting laws - chnages to gerrynmandering
gun rights- new york state rife and pistol assoc v bruen 2022- ny restrictive gun permit law violated 2nd amen- expansive Interp 2nd amend
enviornemnt- sackett v enviorn protec agency 2023- chnages jurisdictaion over wetland- limit regukatory power over businesses
judicial activism
rulings suspected to be base don personal or political bias - broad interpretation, overturn precendent and expanding rigths further than const
examples of judicial axctivism
brown v topeka- bold chnage - active role in guaranteeing rights
miranda v arizona- courts willingness to actively intervene in cirminal jsutice
roe v wade- critics argue went beyond const- far reaching decision
district of columbia v heller 2008- coumbia band on andguns and need triger locks violated 2nd amend- expoanded gun rights too far
citizen united v fec 2010- overturned decades of campaign regulation - far reaching conseuqences
dobbs v jackson- reflected cons beliefs - dire consequences
shelby counter v holder- removed provisions voting rights act- gave states rihts- led to many ID laws
affirmative action ruling - student for fair admission v harvard- ruled affirmative action unconst- overturned numerous precedents- cons leaning
3/4 ways arguments for judicial activism
allows necessary adaptation- keep pace w changes
protects rights- safeguard againat policies
helps to fill legislative gaps- if laws fail to address specific issues - facebook v fuguid 2021- clarified definitions which original 1991 ruling couldnt
allows for correction of injsutices - brown v board education
¾ arguemnts against judicial activism
undermines sep powers and democracy- overreach
creates legal insatbility and unpredictability- undermines legal certainty- changing of precedents
encoursages bias and subjectivity- undermines impartiality- eroding public trust