pdhpe core 2- body in motion
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:35 AM on 8/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
anatomy
the study of structures of the body and their relationships
2
New cards
the anatomical position
standing upright, facing forward, hands down by side, palms facing forward
3
New cards
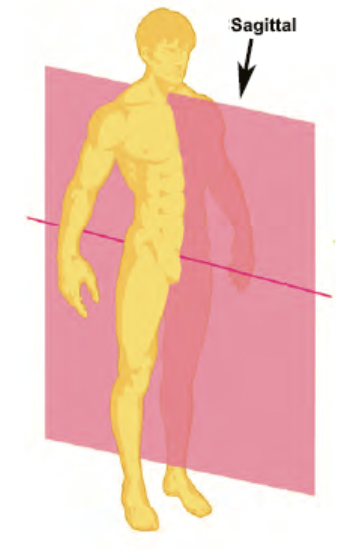
sagittal plane
vertical plane that divides the body into left and right
4
New cards
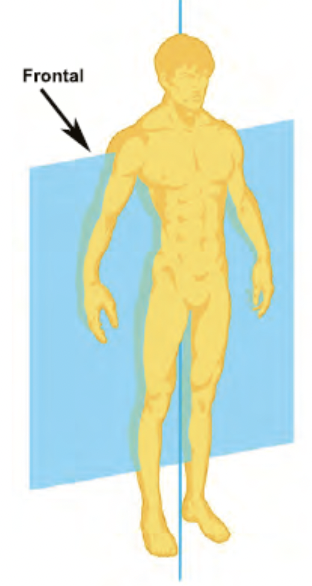
frontal plane
vertical plane that divides the body into front and back
5
New cards
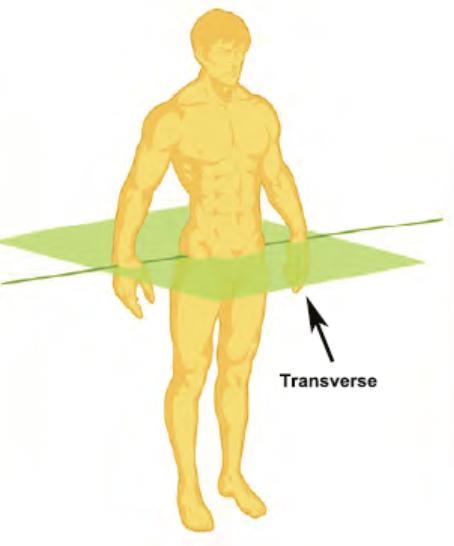
transverse plane
horizontal plane that divides the body into top and bottom
6
New cards
roles of the skeletal system
* **support** - bones provide a framework for the body
* **protection** - bones protect many internal organs from injury
* **movement** - skeletal muscles attach to bones; when muscles pull on bones they produce movement
* **storage of minerals** - bone tissue stores several minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus
* **blood cell reproduction** - red blood cells, white bloods cells and platelets are formed in bone marrow
* **storage of energy** - a secondary reserve of chemical energy is stored in the bone marrow
* **protection** - bones protect many internal organs from injury
* **movement** - skeletal muscles attach to bones; when muscles pull on bones they produce movement
* **storage of minerals** - bone tissue stores several minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus
* **blood cell reproduction** - red blood cells, white bloods cells and platelets are formed in bone marrow
* **storage of energy** - a secondary reserve of chemical energy is stored in the bone marrow
7
New cards
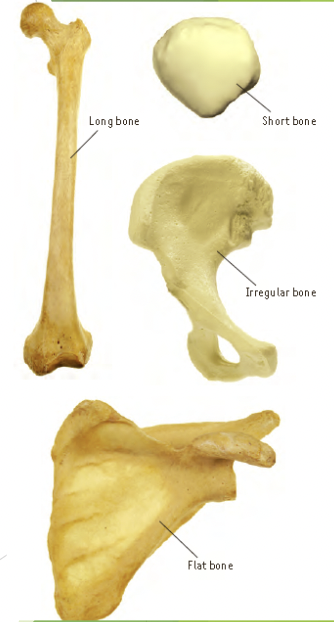
bones
* made up of compact bone and spongy bone
* there are four principal types of bone based on shape; long bones, short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones
* there are four principal types of bone based on shape; long bones, short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones
8
New cards
compact bone
contains few spaces and forms the external layer of all bones
9
New cards
spongy bone
contains marrow, which produces blood cells
10
New cards
long bones
* greater length and width and consist of a shaft; they consist mostly of compact bone encasing spongy bone
* eg. femur, tibia, fibula, phalanges, humerus, radius, ulna
* eg. femur, tibia, fibula, phalanges, humerus, radius, ulna
11
New cards
short bones
* somewhat cube-shaped, nearly equal in length and width
* spongy bone except for the surface, which is a thin layer of compact bone
* eg. carpals and tarsals
* spongy bone except for the surface, which is a thin layer of compact bone
* eg. carpals and tarsals
12
New cards
flat bones
* generally thin and composed of two thin plates of compact bone encasing spongy bone
* eg. cranial bones, sternum, ribs, scapula
* eg. cranial bones, sternum, ribs, scapula
13
New cards
irregular bones
* have complex shapes
* vary in the amount of spongy and compact bone
* eg. vertebrae, some facial bones
* vary in the amount of spongy and compact bone
* eg. vertebrae, some facial bones
14
New cards
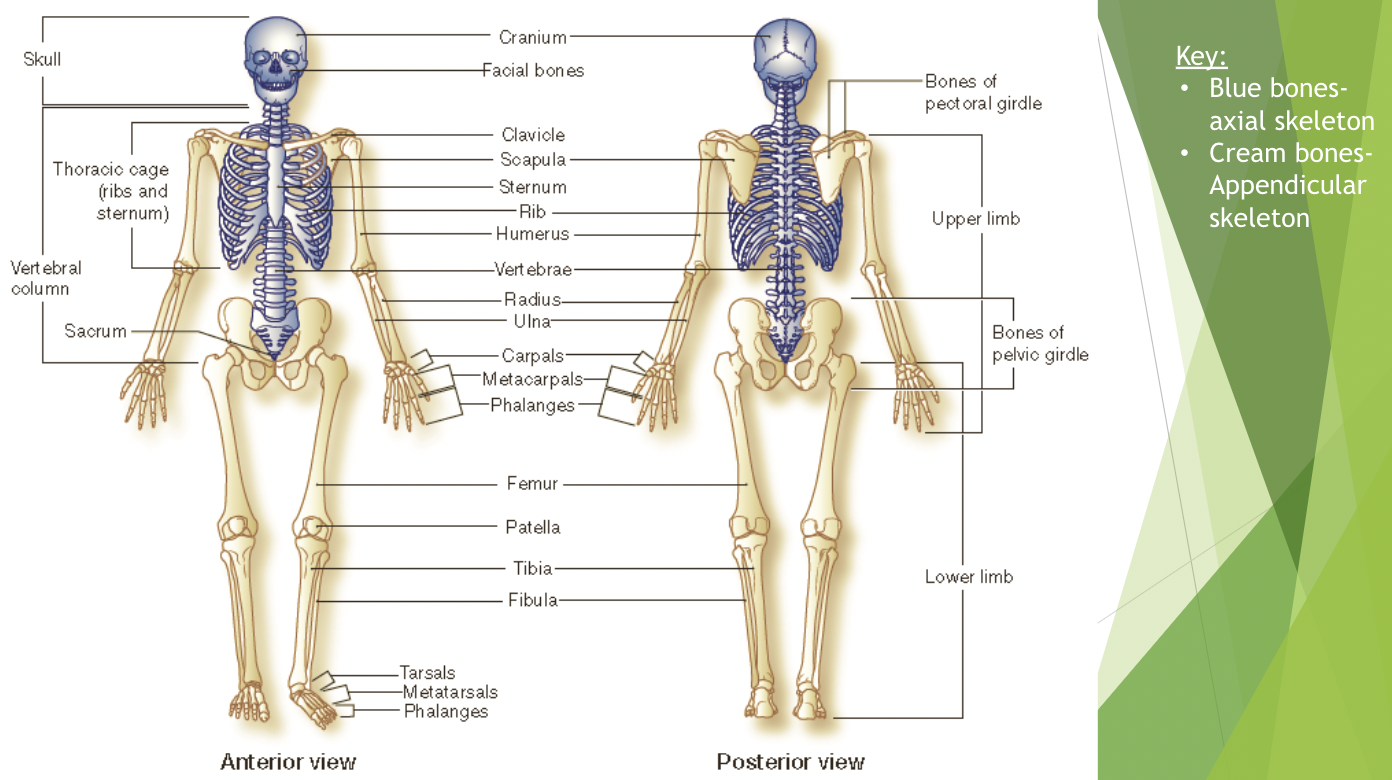
major bones involved in movement
the adult skeleton consists of 206 bones grouped into two divisions; the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton
15
New cards
axial skeleton
* the bones of the axial skeleton lie around the axis
* skull bones, breastbone, ribs, bones of the backbone
* skull bones, breastbone, ribs, bones of the backbone
16
New cards
appendicular skeleton
* contains the bones of the upper and lower limbs plus the girdles that connect the extremities to the axial skeleton
17
New cards
superior
toward the head
18
New cards
inferior
away from the head
19
New cards
anterior
nearer to the front of the body
20
New cards
posterior
nearer to the back of the body
21
New cards
medial
nearer to the midline of the body
22
New cards
lateral
further from the midline of the body
23
New cards
proximal
nearer to the attachment of an extremity
24
New cards
distal
further from the attachment of an extremity
25
New cards
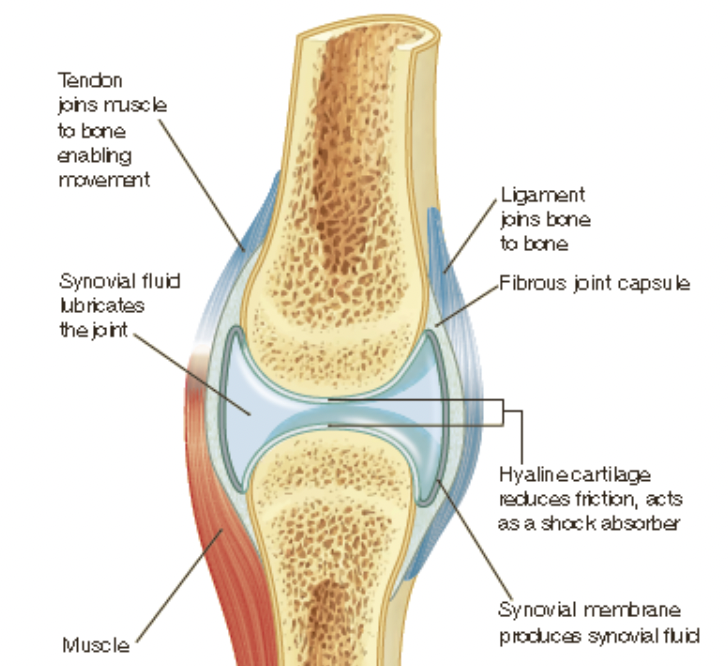
synovial joints
* freely movable joint
* most joints in the body are synovial joints
* most joints in the body are synovial joints
26
New cards
articular cartilage
covers the end of the bone providing cushioning and reducing friction during movement
27
New cards
synovial cavity
space that separates the two articulating bones
28
New cards
ligaments
join bone to bone
29
New cards
synovial fluid
acts as a lubricant with the synovial cavity
30
New cards
joint capsule
encloses the cavity and contains the fluid
31
New cards
fibrous capsule
encloses the bones and synovial cavity
32
New cards
synovial membrane
secretes fluid into the joint
33
New cards
meniscus
inward growing cartilage that absorbs shock, pressure, and enhances stability
34
New cards
bursae
saclike structures that are strategically placed to alleviate friction
35
New cards
tendon
join muscle to bone
36
New cards
types of synovial joints
* gliding joint
* hinge joint
* saddle joint
* ellipsoidal/conyloid joint
* ball-and-socket joint
* pivot joint
* hinge joint
* saddle joint
* ellipsoidal/conyloid joint
* ball-and-socket joint
* pivot joint
37
New cards
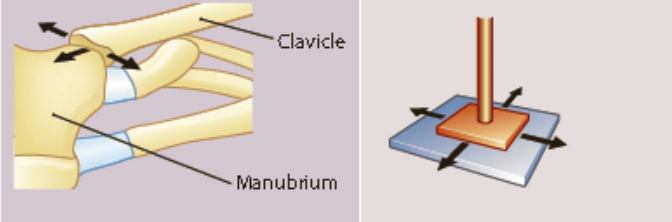
gliding joint
* side to side
* back and forth
* eg. carpals, tarsals, vertebrae
* back and forth
* eg. carpals, tarsals, vertebrae
38
New cards
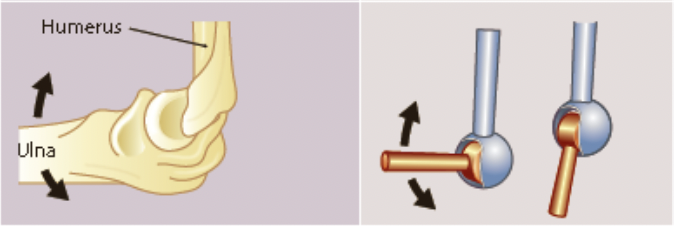
hinge joint
* the convex surface of one bone fits into the concave surface of another
* movement is in a single direction allowing flexion and extension
* eg. knee, elbow, ankle
* movement is in a single direction allowing flexion and extension
* eg. knee, elbow, ankle
39
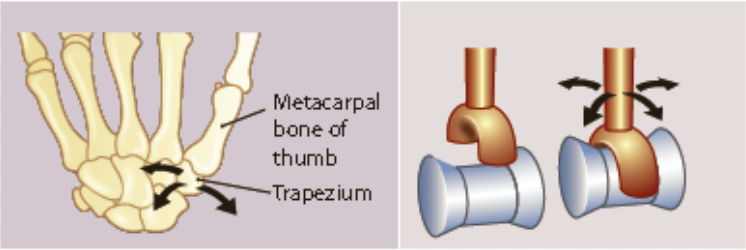
New cards
saddle joint
* one bone is saddle-shaped while the other bone is shaped like a rider
* side to side
* back and forth
* eg. the thumb
* side to side
* back and forth
* eg. the thumb
40
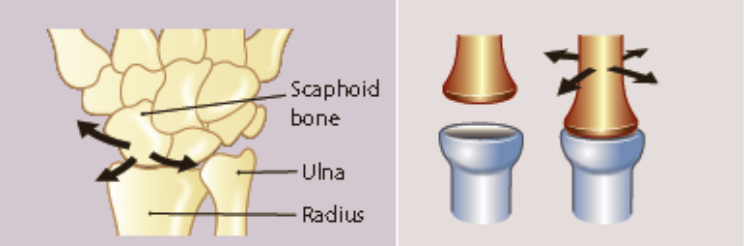
New cards
ellipsoidal/condyloid joint
* an oval shaped bone fits into an elliptical cavity of another bone
* side to side
* back and forth
* eg. the joint at the wrist
* side to side
* back and forth
* eg. the joint at the wrist
41
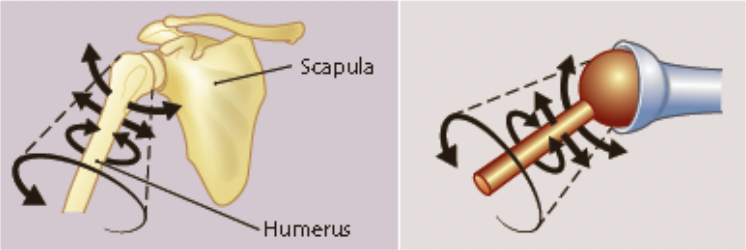
New cards
ball-and-socket joint
* consists of a ball-like surface that fits into a cuplike depression of another
* flexion and extension
* adduction and abduction
* rotation
* eg. the hip and the shoulder
* the shoulder also allows circumuction
* flexion and extension
* adduction and abduction
* rotation
* eg. the hip and the shoulder
* the shoulder also allows circumuction
42
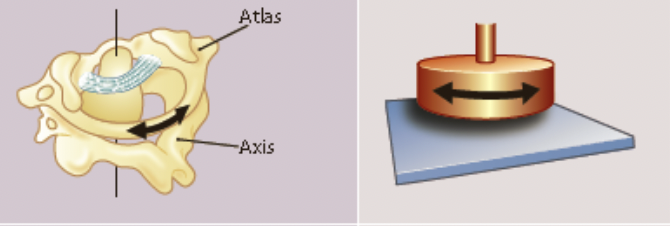
New cards
pivot joint
* a rounded surface of one bone articulates with a ring formed partly by another
* primary movement is rotation
* eg. the atlas of the neck rotating
* primary movement is rotation
* eg. the atlas of the neck rotating
43
New cards
flexion
movement as the joint reduces the angle between the bones
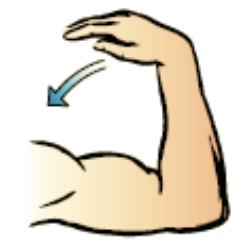
44
New cards
extension
movement at the joint increases the angle between the bones
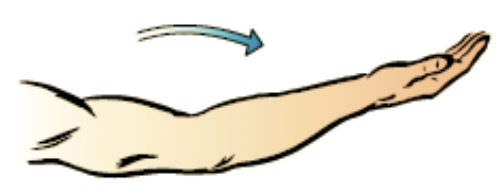
45
New cards
hyperextension and hyperflexion
makes the joint go beyond its normal range of motion
46
New cards
circumduction
the distal end of the body moves in a circle
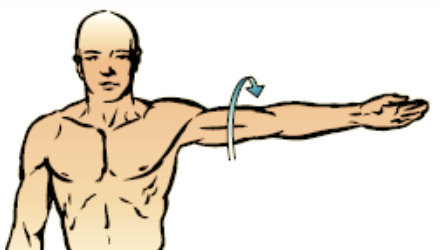
47
New cards
rotation
the movement of a bone around its axis
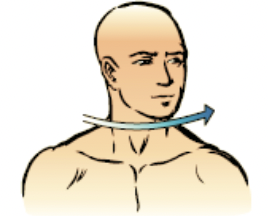
48
New cards
abduction
movement of a bone away from the midline of the body
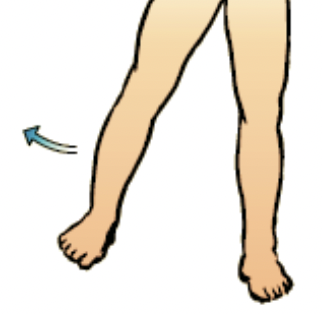
49
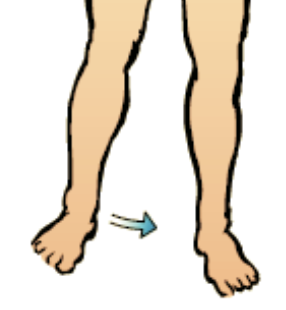
New cards
adduction
movement of a bone towards the midline of the body
50
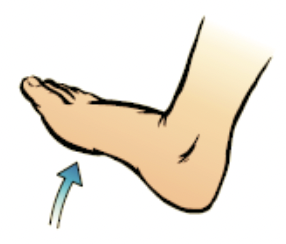
New cards
dorsiflexion
the foot flexes towards the skin
51
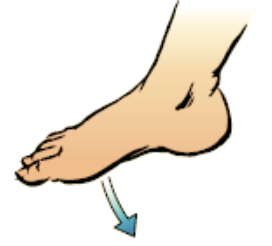
New cards
plantarflexion
the foot points down to the ground
52
New cards
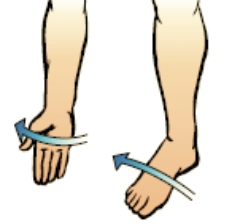
supination
movement of the forearm in which the palm is turned anteriorly
53
New cards
pronation
movement of the forearm in which the palm is turned posteriorly
54
New cards
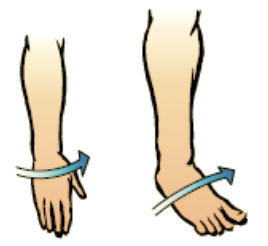
inversion
movement of the sole of the foot inward

55
New cards
eversion
movement of the sole of the foot outward

56
New cards
types of muscle tissue
* skeletal muscle tissue
* cardiac muscle tissue
* smooth muscle tissue
* cardiac muscle tissue
* smooth muscle tissue
57
New cards
skeletal muscle tissue
* attached primarily to bones
* striated due to its alternating dark and light bands
* a voluntary muscle
* striated due to its alternating dark and light bands
* a voluntary muscle
58
New cards
cardiac muscle tissue
* forms most of the heart
* striated, but involuntary
* striated, but involuntary
59
New cards
smooth muscle tissue
* located in the walls of hollow internal structures, such as the intestines
* smooth in appearance, often involuntary
* smooth in appearance, often involuntary
60
New cards
skeletal muscles
* produce movement by exerting force on tendons, which in turn pull on bones or other structures
* most muscles cross at least one joint and are attached to the articulating bones that form the joint
* normally one bone is held in its original position, while the other bone moves during a contraction
* the attachment of the tendon at the stationary bone is called the origin, while the attachment at a movable bone is the insertion
* most muscles cross at least one joint and are attached to the articulating bones that form the joint
* normally one bone is held in its original position, while the other bone moves during a contraction
* the attachment of the tendon at the stationary bone is called the origin, while the attachment at a movable bone is the insertion
61
New cards
major muscles of the body
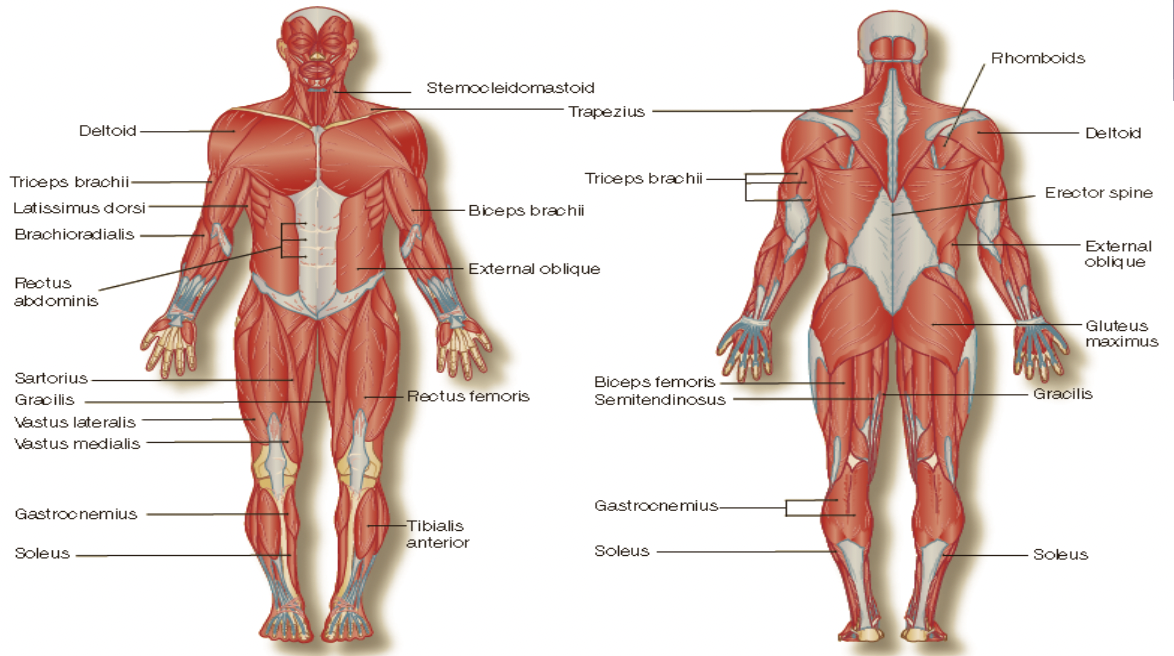
62
New cards
major muscles involved in movement
* most movement requires several muscles working together
* most skeletal muscles are therefore arranged in opposing pairs
* the muscle that causes the desired action is the prime mover or **agonist**
* while the agonist is contracting, its opposing partner is relaxing. the muscle relaxing is known as the **antagonist**
* most movements also include a synergist, which serves to stabilise the movement
* most skeletal muscles are therefore arranged in opposing pairs
* the muscle that causes the desired action is the prime mover or **agonist**
* while the agonist is contracting, its opposing partner is relaxing. the muscle relaxing is known as the **antagonist**
* most movements also include a synergist, which serves to stabilise the movement
63
New cards
types of muscle contraction
there are different types of contractions that muscles are capable of. the muscles will contract according to the need of the movement requires. there are two main types of contractions; isotonic and isometric
64
New cards
isotonic contractions
isotonic contractions occur when the muscle contracts (shortens) and lengthens to produce movement. there are two types of isotonic contractions; concentric contraction and eccentric contraction
65
New cards
concentric contraction
the muscle shortens during the contraction and pulls on another structure to produce movement (eg. flexion phase of bicep curl)
66
New cards
eccentric contraction
the muscle lengthens during the contraction. eccentric contractions result in more delayed onset muscle soreness than concentric contractions (eg. down phase of a push-up)
67
New cards
isometric contractions
occur when the muscle does not or cannot shorten, but the tension on the muscle increases. no movement is produces and the length of the *muscle* stays the same (eg. wall sit)
68
New cards
the respiratory system
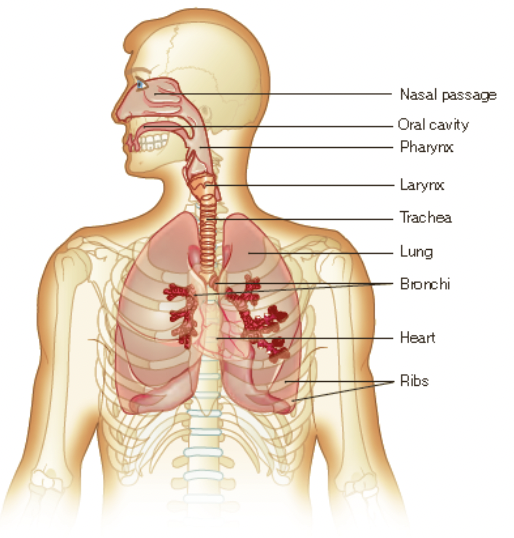
69
New cards
the nose
* has an external and internal portion
* the inside of both the external and internal nose is called the nasal cavity. it carries three functions;
* incoming air is warmed, moistened and filtered
* smell stimulus is received
* chambers modify speech sounds
* the inside of both the external and internal nose is called the nasal cavity. it carries three functions;
* incoming air is warmed, moistened and filtered
* smell stimulus is received
* chambers modify speech sounds
70
New cards
the pharynx
a passageway for both air and food
71
New cards
the larynx
* a short passageway that connects the pharynx to the trachea
* the epiglottis is responsible for directing food and air into the corresponding tubes
* it closes off the larynx ensuring food and liquids go to the oesophagus
* the epiglottis is responsible for directing food and air into the corresponding tubes
* it closes off the larynx ensuring food and liquids go to the oesophagus
72
New cards
trachea
a passageway for air
73
New cards
bronchi
* the trachea divides itself into the left and right bronchus
* these bronchi eventually branch into bronchioles
* this process resembles a tree trunk with its branches, the bronchial tree
* these bronchi eventually branch into bronchioles
* this process resembles a tree trunk with its branches, the bronchial tree
74
New cards
lungs
* paired organs within the thoracic activity
* each lung is divided into lobes, which receives the bronchi
* these eventually divide into alveoli, which are tiny air sacs
* the gas exchange takes place within the alveoli
* each lung is divided into lobes, which receives the bronchi
* these eventually divide into alveoli, which are tiny air sacs
* the gas exchange takes place within the alveoli
75
New cards
lung function
* the principle purpose of respiration is to supply the cells of the body with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide
* the three processes of this are;
* pulmonary ventilation
* external respiration
* internal respiration
* the three processes of this are;
* pulmonary ventilation
* external respiration
* internal respiration
76
New cards
pulmonary ventilation
* more commonly known as breathing
* this is the process by which gases are exchanged between the atmosphere and the human body, mainly the alveoli
* this is due to a pressure gradient
* this is the process by which gases are exchanged between the atmosphere and the human body, mainly the alveoli
* this is due to a pressure gradient
77
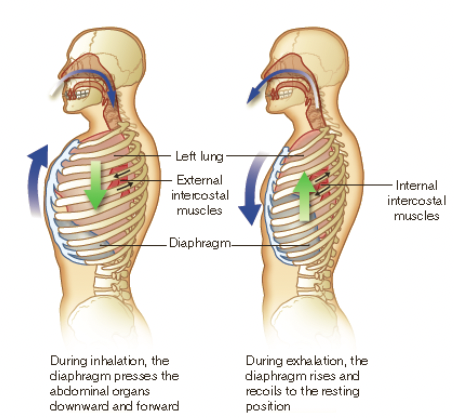
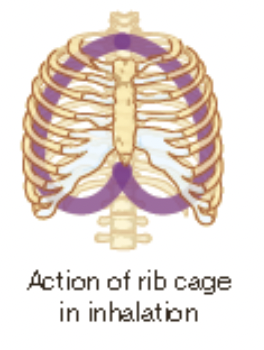
New cards
insipration (inhalation)
* for air to flow into the lungs, the size of the lungs needs to increase
* this occurs when the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract
* this pulls up the ribs upward and sternum forward and consequently the walls of the lungs are pulled outward
* this creates a pressure difference and air enters the lungs
* this occurs when the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract
* this pulls up the ribs upward and sternum forward and consequently the walls of the lungs are pulled outward
* this creates a pressure difference and air enters the lungs
78
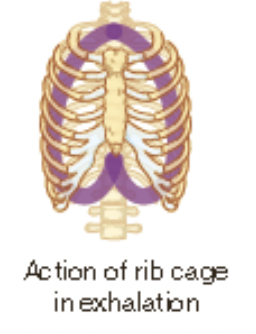
New cards
expiration (exhalation)
a passive process due to muscle recoil and surface tension
when the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, the ribs move downwards, the lungs decrease in size and the pressure gradient now causes air to exit the lungs
when the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, the ribs move downwards, the lungs decrease in size and the pressure gradient now causes air to exit the lungs
79
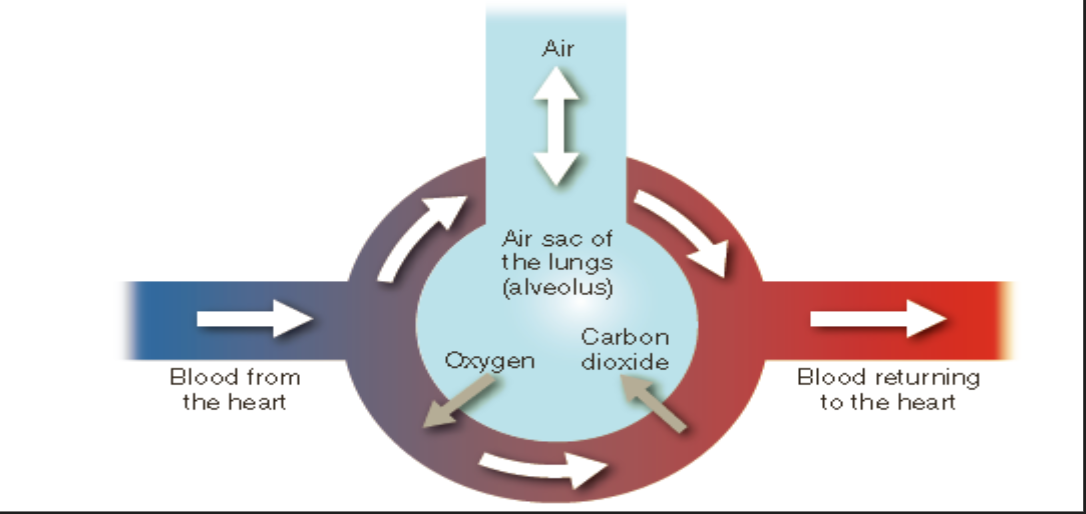
New cards
exchange of gases in the lungs
* wherever there is a difference in gases, Boyle’s Law suggests that these gases will move to achieve equilibrium
* the remaining two processes result in the exchange of gases;
* external (pulmonary) respiration
* internal (tissue) respiration
* the remaining two processes result in the exchange of gases;
* external (pulmonary) respiration
* internal (tissue) respiration
80
New cards
external (pulmonary) respiration
* the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli in the lungs and pulmonary blood capillaries
* results in deoxygenated blood becoming oxygenated blood
* deoxygenated blood in the lungs, oxygenated blood in the blood
* the exchange of gases occurs as the carbon dioxide moves into the lungs, while oxygen moves into the blood within the pulmonary cavities
* results in deoxygenated blood becoming oxygenated blood
* deoxygenated blood in the lungs, oxygenated blood in the blood
* the exchange of gases occurs as the carbon dioxide moves into the lungs, while oxygen moves into the blood within the pulmonary cavities
81
New cards
internal (tissue) respiration
* the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between blood capillaries and tissue cells
* results in deoxygenated blood becoming oxygenated blood
* oxygen in blood capillaries, carbon dioxide in tissue cells
* the exchange of gases occurs as the carbon dioxide moves into the blood capillaries, while oxygen moves into the tissue cells throughout the body
* at rest, only about 25% of the oxygen in the blood enters the cells
* the deoxygenated blood returns to the heart, where it begins the cycle again
* results in deoxygenated blood becoming oxygenated blood
* oxygen in blood capillaries, carbon dioxide in tissue cells
* the exchange of gases occurs as the carbon dioxide moves into the blood capillaries, while oxygen moves into the tissue cells throughout the body
* at rest, only about 25% of the oxygen in the blood enters the cells
* the deoxygenated blood returns to the heart, where it begins the cycle again
82
New cards
the circulatory system
includes the cardiovascular system and lymphatic system
83
New cards
cardiovascular aspects
* all cells in the body need;
* oxygen
* nutrients
* waste removed
* main structures involved within the system;
* heart
* blood
* blood vessels
* oxygen
* nutrients
* waste removed
* main structures involved within the system;
* heart
* blood
* blood vessels
84
New cards
components of blood
* blood is heavier, thicker and more viscous than water
* it makes up approximately 8% of total body weight
* the blood volume of an average-sized;
* male: 5-6 litres
* female: 4-5 litres
* blood has three functions within the body
* transportation
* regulation
* protection
* blood is composed of two portions;
* blood plasma (55%0)
* formed elements (45%)
* it makes up approximately 8% of total body weight
* the blood volume of an average-sized;
* male: 5-6 litres
* female: 4-5 litres
* blood has three functions within the body
* transportation
* regulation
* protection
* blood is composed of two portions;
* blood plasma (55%0)
* formed elements (45%)
85
New cards
transportation
* transports oxygen from the lungs to the cells and carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs
* also carries nutrients, heat, waste products and hormones
* also carries nutrients, heat, waste products and hormones
86
New cards
regulation
regulates pH levels throughout the body and adjusts body temperature
87
New cards
protection
* clotting protects against blood loss
* antibodies protect agains foreign toxins
* antibodies protect agains foreign toxins
88
New cards
blood plasma
* 55%
* a straw-coloured liquid that is mostly water
* also contains waste products, nutrients, vitamins, hormones and enzymes
* a straw-coloured liquid that is mostly water
* also contains waste products, nutrients, vitamins, hormones and enzymes
89
New cards
formed elements
* 45%
* red blood cells (erythocytes)
* white blood cells (leukocytes)
* platelets
* red blood cells (erythocytes)
* white blood cells (leukocytes)
* platelets
90
New cards
red blood cells (erythocytes)
* containing oxygen carrying haemoglobin
* highly specialised in oxygen transport
* live approx. 20 days, 4 m
* highly specialised in oxygen transport
* live approx. 20 days, 4 m
91
New cards
white blood cells (leukocytes)
responsible for fighting infections within the body
92
New cards
red blood cell : white blood cell ratio
700:1
93
New cards
platelets
help repair damaged blood vessels and promote blood clotting
94
New cards
structure/function of the heart, arteries, veins, capillaries
* the heart is about the size of a closed fist about two-thirds of it lies to the left of the body’s midline within the thoracic cavity
* the heart contains chambers and valves, which fulfil a role in ensuring the effective functioning of the heart, given that it can pump around 7000 litres of blood a day
* blood vessels form a closed system that transports blood to and from the heart
* the heart contains chambers and valves, which fulfil a role in ensuring the effective functioning of the heart, given that it can pump around 7000 litres of blood a day
* blood vessels form a closed system that transports blood to and from the heart
95
New cards
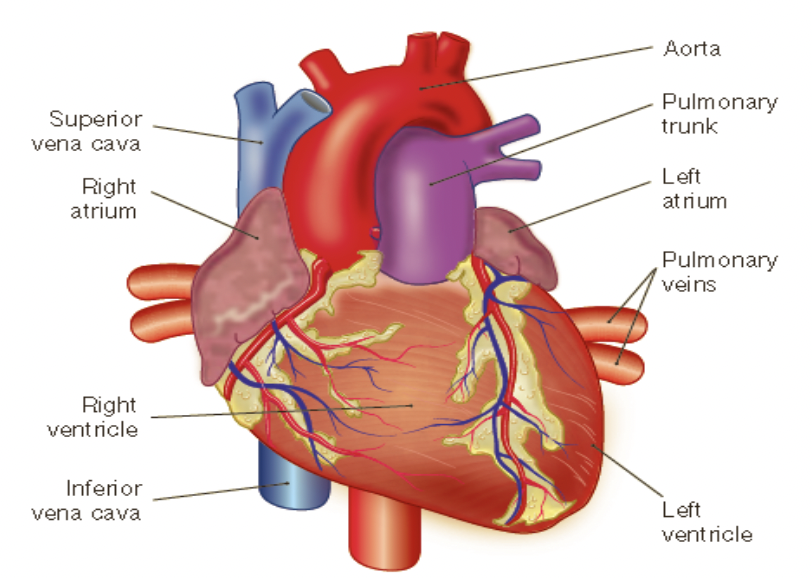
chambers of the heart
* the heart has four chambers;
* the two superior chambers are called the left and right atrium
* the two inferior chambers are called the left and right ventricles
* the two superior chambers are called the left and right atrium
* the two inferior chambers are called the left and right ventricles
96
New cards
atria
thin walled as they deliver blood to the ventricles
97
New cards
ventricles
* the right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs while the left ventricle pumps blood around the body
* thus, the wall of the left ventricle is 2-4 times as thick as the right ventricle
* thus, the wall of the left ventricle is 2-4 times as thick as the right ventricle
98
New cards
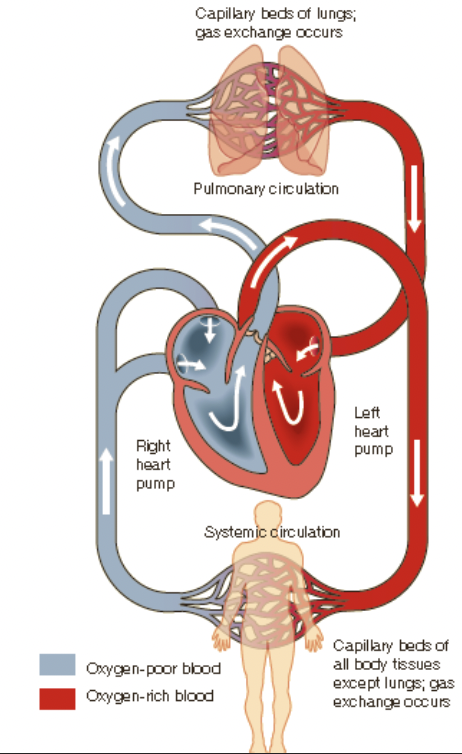
blood flow within the heart
* the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from various parts of the body via the superior and inferior vena cava
* from here, the blood travels to the right ventricle where it is pumped via the pulmonary **artery** to the lungs
* the gas exchange occurs within the lungs and the now oxygenated blood travels back via the pulmonary **vein** to the left atrium
* this oxygenated blood then travels to the left ventricle where it is pumped around the body via the aorta
* from here, the blood travels to the right ventricle where it is pumped via the pulmonary **artery** to the lungs
* the gas exchange occurs within the lungs and the now oxygenated blood travels back via the pulmonary **vein** to the left atrium
* this oxygenated blood then travels to the left ventricle where it is pumped around the body via the aorta
99
New cards
blood vessels
* arteries
* arteries carry blood away from the heart
* arteries have elasticity and contractility. allowing them to be effective in transporting blood around the body
* thick, muscular vessels
* become smaller as they divide and eventually branch into arterioles
* capillaries
* microscopic vessels that connect to arterioles and venules
* found near most cells in the body
* primary function: permit the exchange of nutrients and waste products
* veins
* carry blood to the heart
* their anatomy is very similar to that of an artery. only thinner in some instances
* veins gradually become larger and stem from the smaller vessels, called venules
* arteries carry blood away from the heart
* arteries have elasticity and contractility. allowing them to be effective in transporting blood around the body
* thick, muscular vessels
* become smaller as they divide and eventually branch into arterioles
* capillaries
* microscopic vessels that connect to arterioles and venules
* found near most cells in the body
* primary function: permit the exchange of nutrients and waste products
* veins
* carry blood to the heart
* their anatomy is very similar to that of an artery. only thinner in some instances
* veins gradually become larger and stem from the smaller vessels, called venules
100
New cards
the pulmonary artery exception
the pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood
the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood
the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood