TAMU MKTG 409 EXAM 1 (Ch. 1-5)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is Marketing?
The process of:
-Creating, distributing, promoting, and pricing goods, services, and ideas
-To facilitate satisfying exchange relationships with customers
-To develop and maintain favorable relationships with stakeholders in a dynamic environment
Components of Strategic marketing
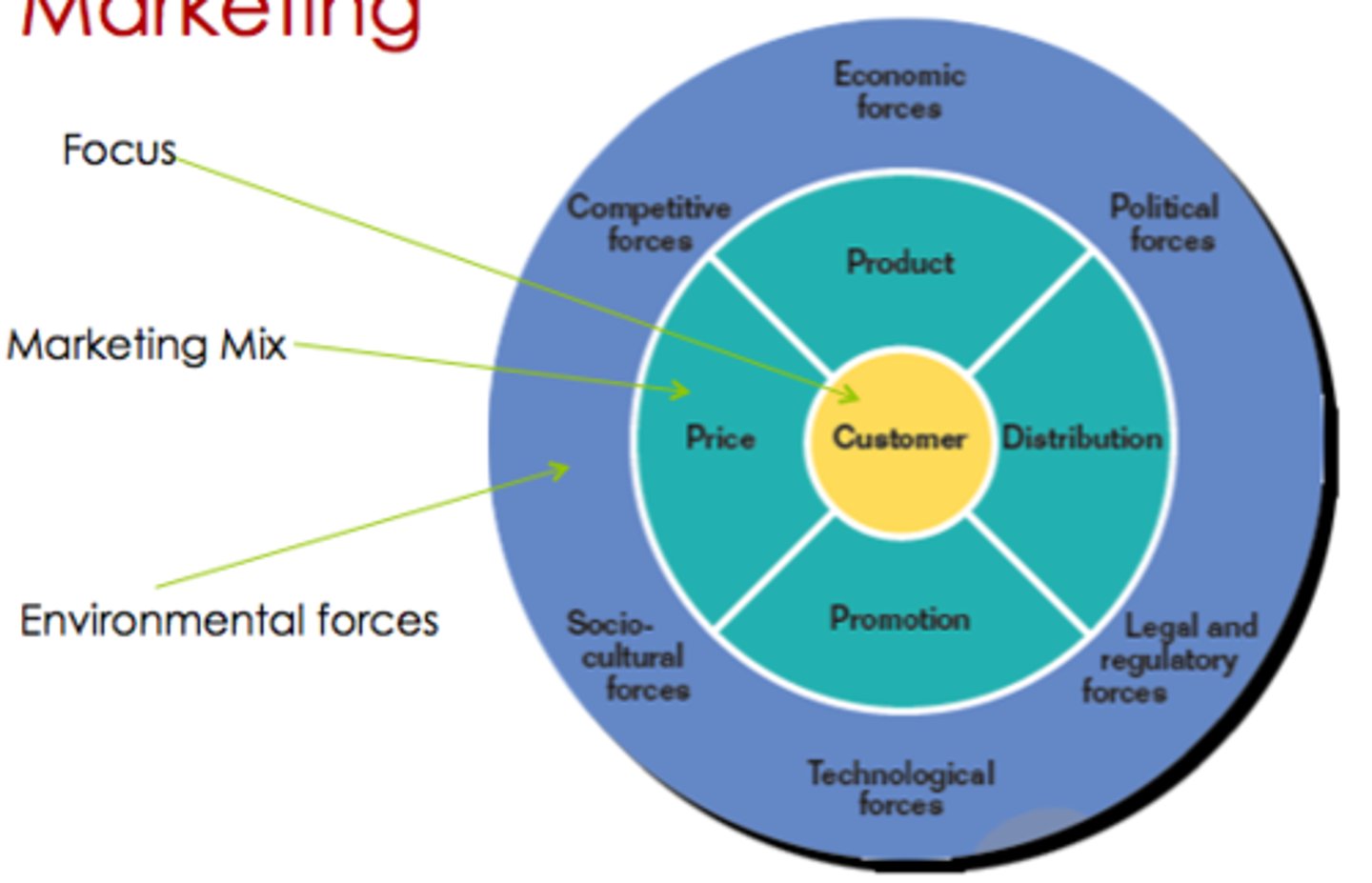
Marketing focuses on what?
Customers
Customers
-Purchasers of the products that organizations develop, promote, distribute, and price
-Focal point of all marketing activities
Target Market
A specific group of customers on whom an organization focuses its marketing efforts
Marketing Mix Variables
Marketing is more than simply advertising or selling a product it involves:
-Developing and managing a product
-Making the product available in the right place
-Pricing the product at an acceptable level for buyers
-Communicating information to help customers determine if the product will satisfy their needs
Marketing mix
Four marketing activities that a firm can control to meet the needs of customers within its target market
-There is a limit to how much these variables can be controlled
The 4 Marketing activities
1. Product
2. Distribution
3. Promotion
4. Price
Marketers must:
Aim to create and maintain the right mix of elements to satisfy customers in the target market
-Collect detailed and up-to-date information on:
Their target market
Consumer preferences
Competitors in order to develop the marketing mix
Product can be:
-Good—a physical entity that you can touch
-Service—the application of human and mechanical efforts to people or objects to provide intangible benefits to customers
-Idea—concept, philosophy, image, or issue
PRODUCT VARIABLE
Product Variable
Includes the creation or modification of brand names and packaging
-May also include decisions regarding warranty and repair services
Product variable decisions and activities directly impact the creation of products that meet customers' needs and wants
Distribution Variable
-Make products available in quantities desired to as many target market customers as possible
While minimizing these three costs:
1. Inventory
2. Transportation
3. Storage
-To satisfy customers, products must be available at the right time and in convenient locations
Marketing managers may:
-Select/motivate intermediaries (wholesalers and retailers)
-Establish/maintain inventory control procedures
-Develop/manage transportation and storage systems
DISTRIBUTION VARIABLE
How has internet impacted distribution?
-Making it faster and more wide-spread
-Netflix uses digital distribution that allows consumers to stream movies right off its website.
Promotion Variable
Relates to activities used to inform individuals or groups about the organization and its products
-Aim to increase public awareness of the organization and of new or existing products
-Educate customers about product features
-Urge people to take a stance on a political or social issue
-Help sustain interest in established products
Price Variable
Relates to decisions and actions associated with establishing pricing objectives and policies and determining product prices
-Price is a critical component of the marketing mix as customers are concerned about value obtained in an exchange
-Price is often used as a competitive tool
-Intense price competition sometimes leads to price wars
Value
Value = Customer benefits - Customer costs
Value is a customer's subjective assessment of benefits relative to costs in determining the worth of a product
-Customer benefits include anything a buyer receives in an exchange
-Customer costs include anything a buyer must give up to obtain the benefits the product provides including cost, time, effort, and risk
How does Marketing Create Value?
-Value is a subjective assessment of benefits relative to costs
-Marketing has the ability to increase consumers' perceptions of a product's quality and social approval
Exchanges
Are the provision of transfer of goods, services, or ideas in return for something of value
Relationships with Customers
For an exchange to take place:
-Two or more parties must participate, and each must possess something of value that the other party desires
-The exchange should provide a benefit or satisfaction to both parties
-Each party must have confidence in the promise of the something of value held by the other
-To build trust, the parties to the exchange must meet expectations
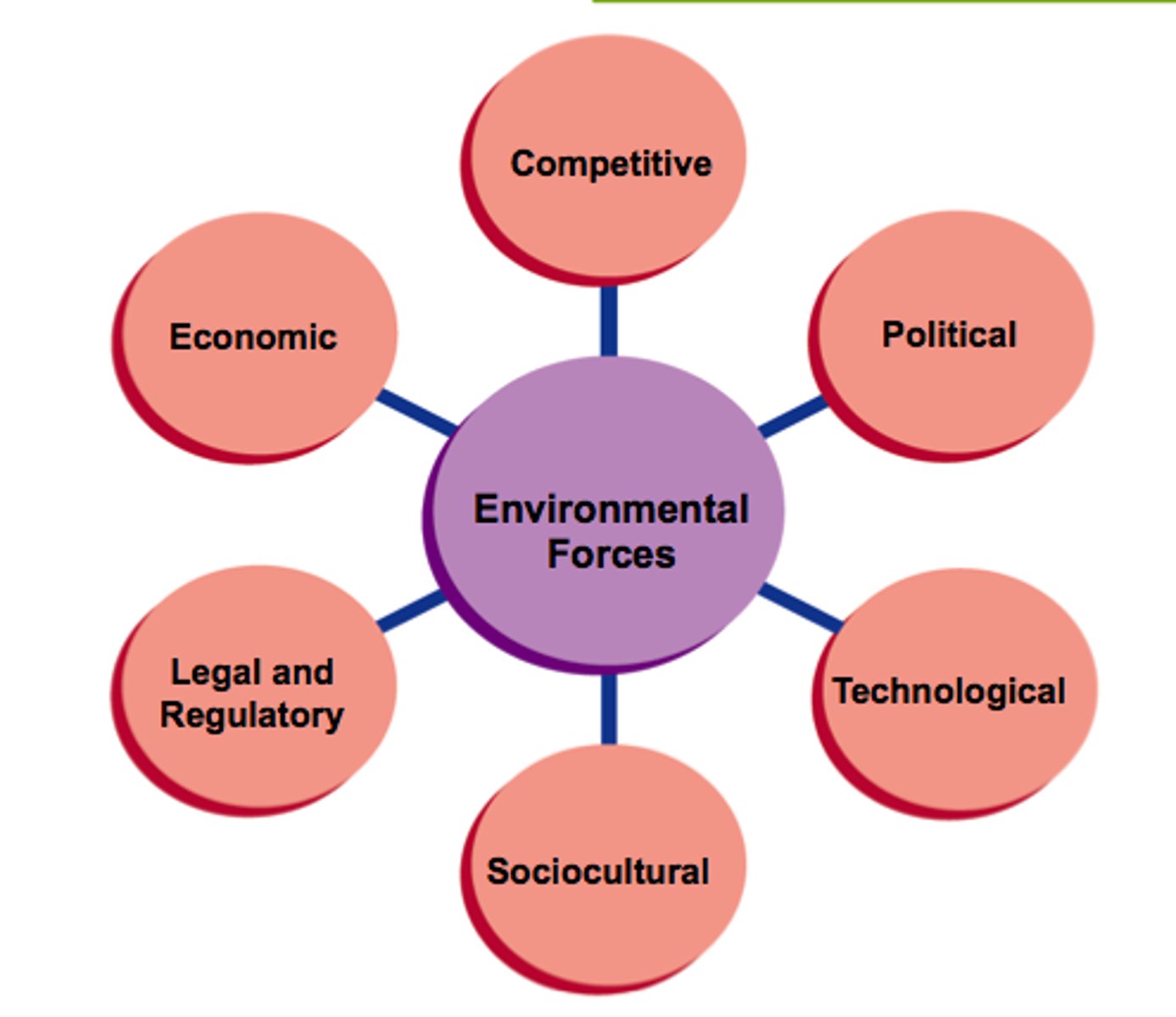
Marketing Environment
Is dynamic and includes the following forces:
-Competitive
-Economic
-Political
-Legal and regulatory
-Technological
-Sociocultural
These forces affect a marketer's ability to facilitate value-driven exchanges in three ways:
1. Influence customers by affecting their lifestyle, standards of living, and preferences and needs for products
2. Help to determine whether and how a marketing manager can perform certain marketing activities
3. May affect a marketing manager's decisions and actions by influencing buyers' reactions to the firm's marketing mix
Relationship marketing:
-Refers to long-term mutually beneficial buyer/seller relationships
-Focused on value enhancement through the creation of more satisfying exchanges
-Continually deepens the buyers trust
Increases the company's understanding of the customer's needs
-Through the use of e-marketing, companies can personalize customer relationships on a nearly one-on-one basis
Customer lifetime value
Predicts the net value (profit or loss) for the future relationship with a customer
What is strategic marketing management?
The process of planning, implementing, and evaluating the performance of marketing activities and strategies, both effectively and efficiently
Strategic planning:
Is the process of establishing an organizational mission and formulating goals, corporate strategy, marketing objectives, and marketing strategy
Components of the Strategic Planning Process
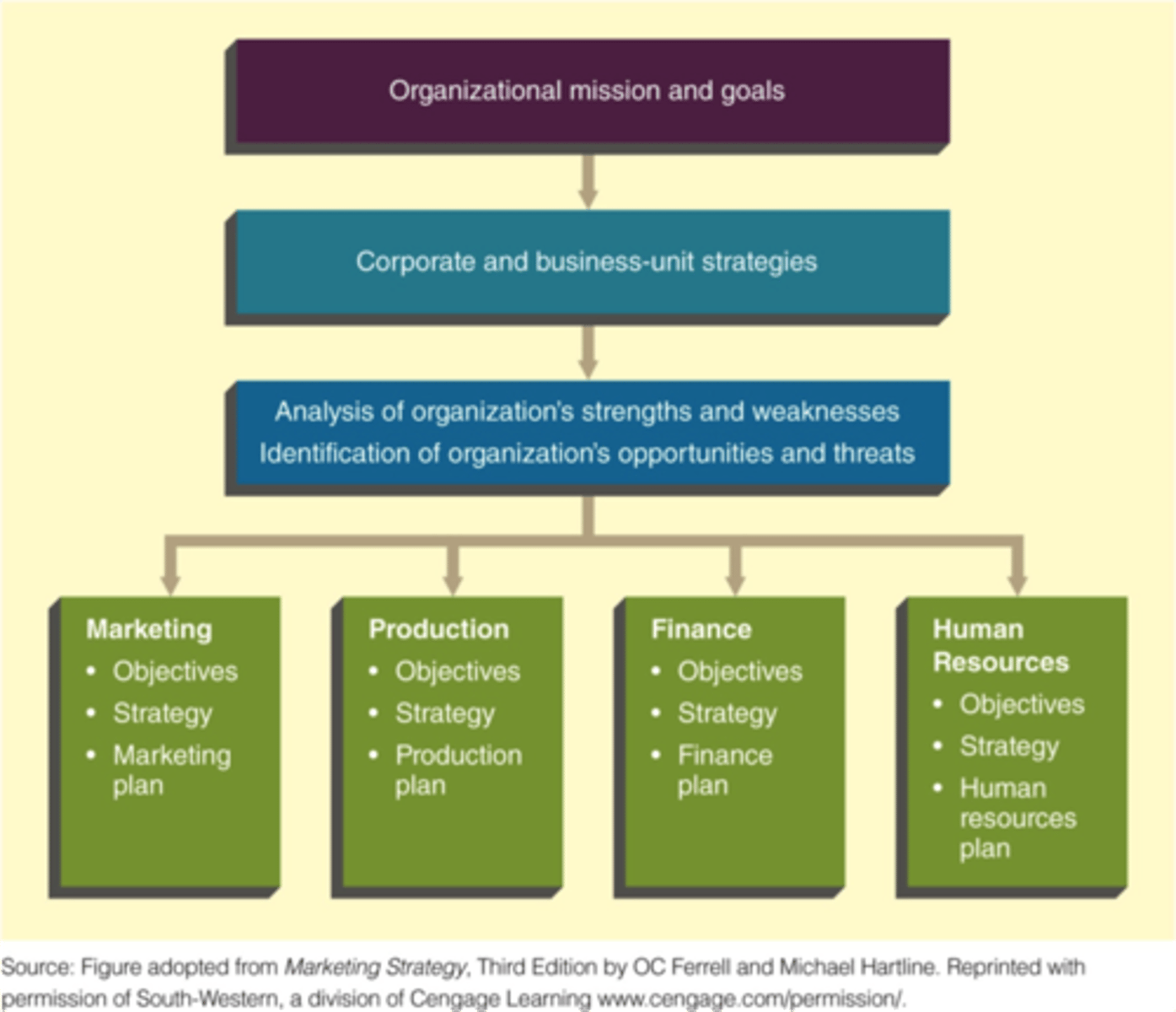
Levels of Strategic Planning
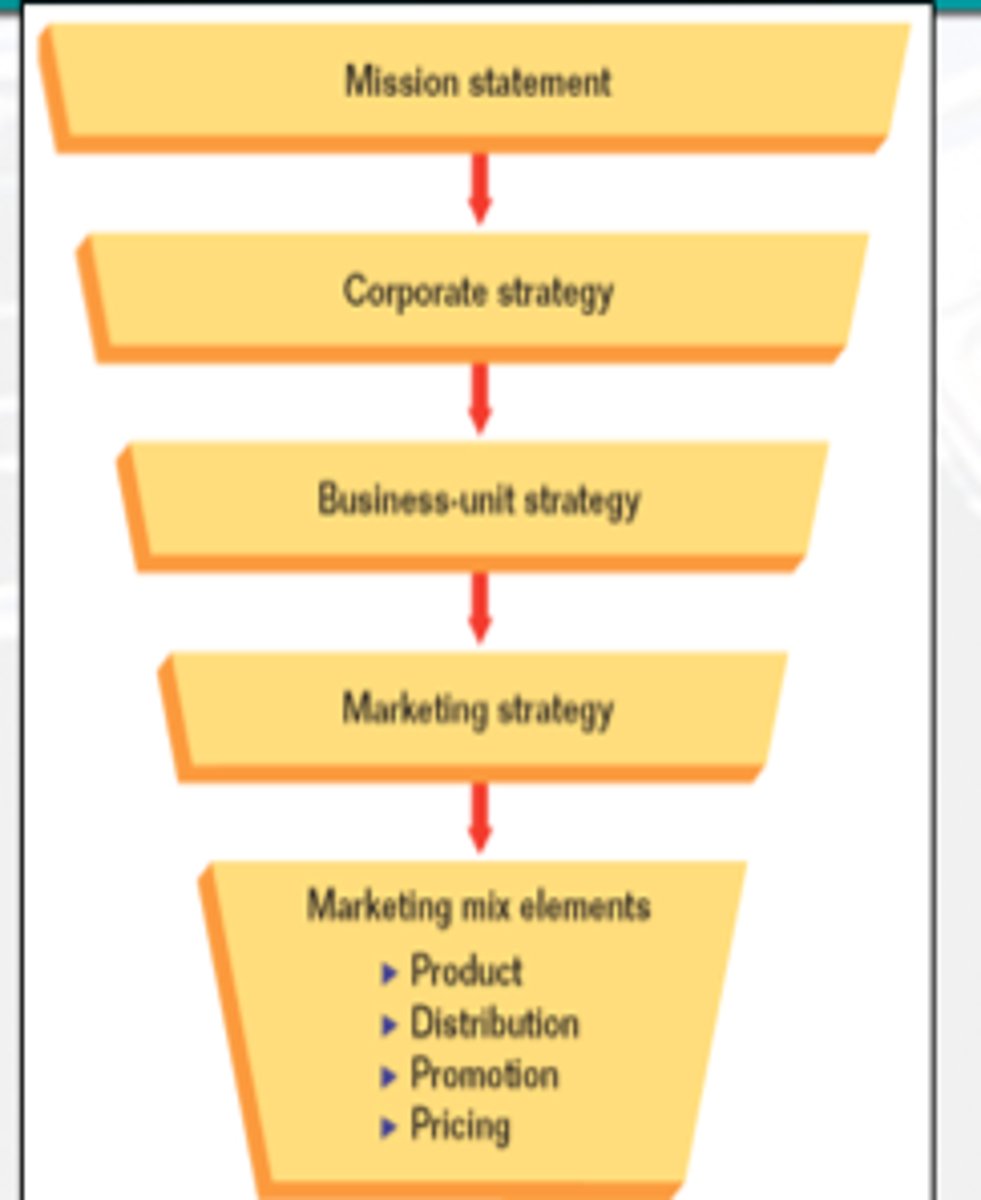
Corporate strategy:
Determines the means for utilizing resources in the functional areas of marketing, production, finance, research and development, and human resources to reach the organization's goals
Corporate strategy planners are concerned with broad issues such as:
Corporate culture, Competition, Differentiation, Diversification, Interrelationships among business units, Environmental and social issues
-Match the resources of the organization with the opportunities and threats in the environment
Strategic business unit (SBU)
-Should be consistent with corporate strategy
-Is a division, product line, or other profit center within the parent company
-Each of these units sells a distinct set of products to an identifiable group of customers, and each competes with a well-defined set of competitors
-The revenues, costs, investments, and strategic plans of each SBU can be separated from those of the parent company and evaluated
Business-Unit Strategies
Strategic planners should recognize the strategic performance capacities of each SBU and allocate scarce resources among those divisions
-A MARKET is a group of individuals and/or organizations that have needs for products in a product class and have the ability, willingness, and authority to purchase those products
-The percentage of a market that actually buys a specific product from a particular company is referred to as that product's (or business unit's) MARKET SHARE
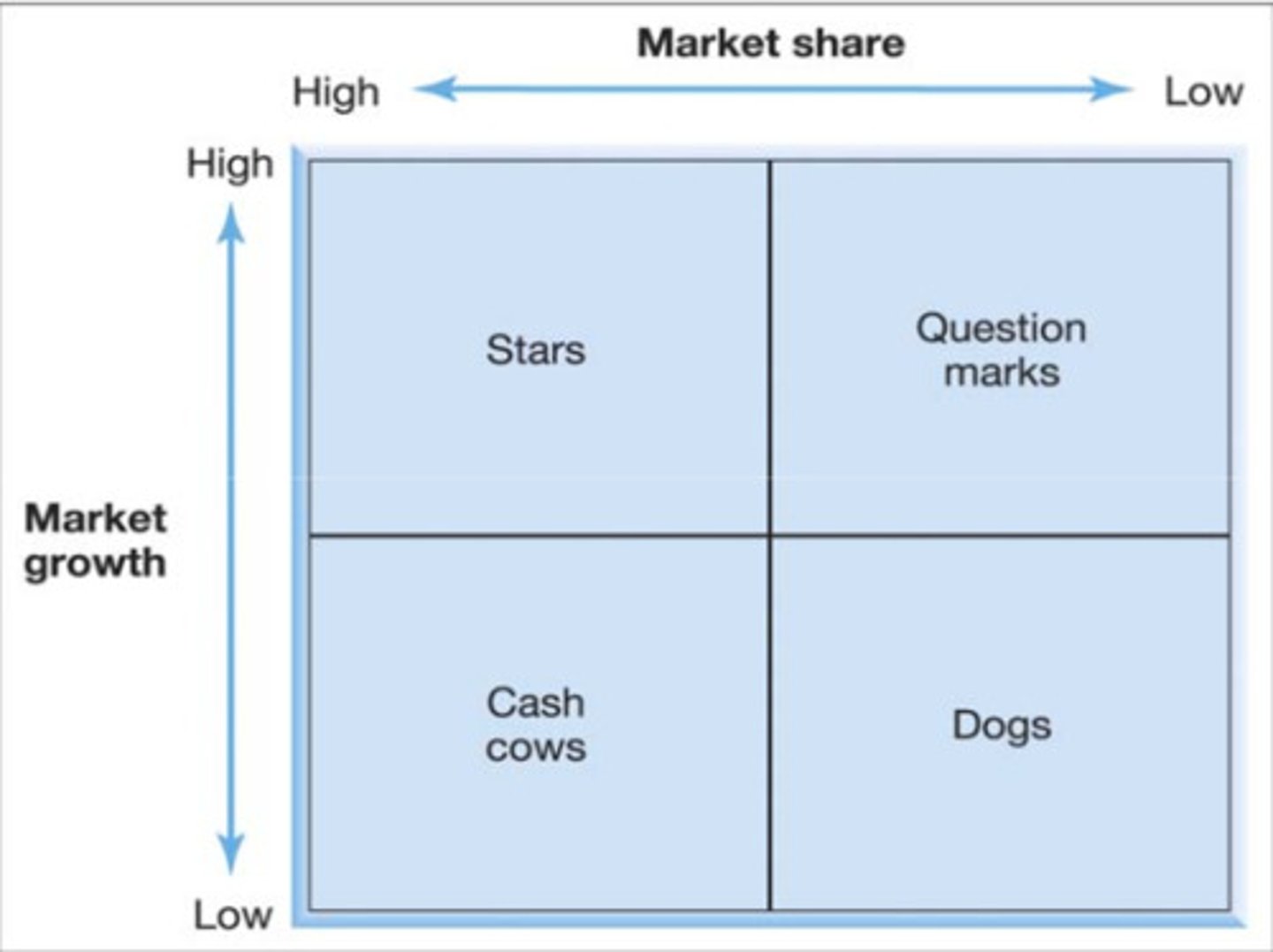
The market growth/market share matrix
Is a helpful business tool, based on the philosophy that a product's market growth rate and its market share are important considerations in determining its market strategy
-All the companies SBUs and products should be integrated into a single, overall matrix and evaluated to determine strategies for individual products and overall portfolio strategies
Growth Share Matrix
-Stars are products with a dominant share of the market and good prospects for growth
-Cash cows have a dominant share of the market but low prospects for growth
-Dogs have a subordinate share of the market and low prospects for growth
-Question marks have a small share of a growing market and generally require a large amount of cash to build market share
-Long-term health of an organization depends on having some products that generate cash and others that use cash to support growth
Assessing Organizational Resources and Opportunities
The strategic planning process begins with an analysis of the marketing environment, including a thorough analysis of the industry in which the company is operating or intends to sell its products
-Any strategic planning effort must assess the organization's available financial and human resources and capabilities as well as how the level of these factors is likely to change in the future
Market Opportunities and Strategic Windows
-Market opportunity is a combination of circumstances and timing that permits an organization to take action to reach a particular target market
-Strategic windows are temporary periods of optimal fit between the key requirements of a market and the particular capabilities of a company competing in that market
Competitive Advantage
The place where opportunities, core competencies, and strategic windows meet
-The result of a company matching a core competency to opportunities it has discovered in the marketplace
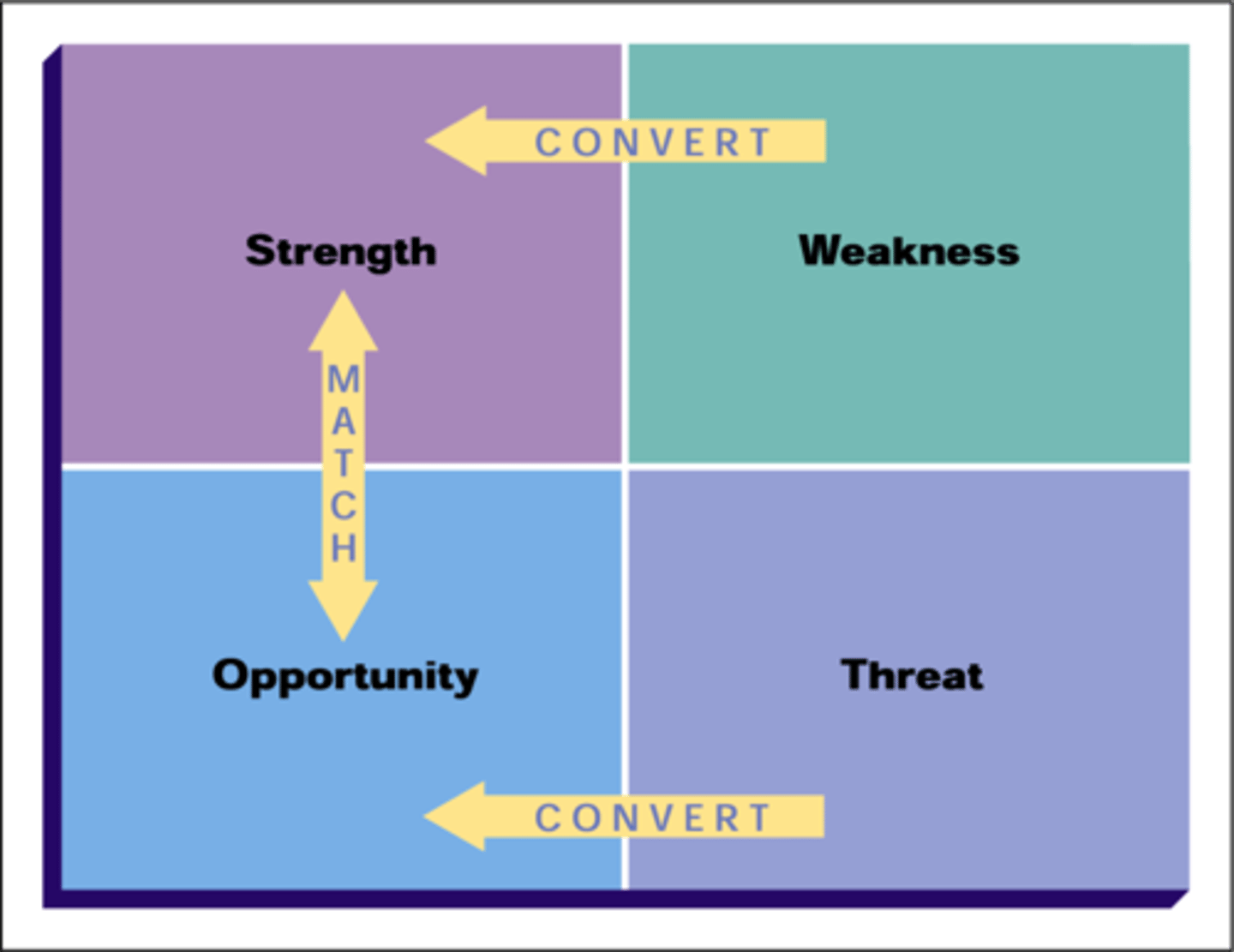
SWOT Analysis
-Strengths and weaknesses
-Opportunities and threats
a tool marketers use to assess an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
The Four-Cell SWOT Matrix
First-mover advantage
Is the ability of an innovative company to achieve long-term competitive advantages by being the first to offer a certain product in the marketplace
-Build a firm's reputation as a market leader
-Market is free of competition
-Establish brand loyalty for the firm due to its customer's costs to switch later on
-Firm can protect its trade secrets or technology through patents
Target Market Selection
Identification and analysis of a target market provides a foundation on which a company can develop a marketing mix
A sustainable competitive advantage
is one that the competition cannot copy in the foreseeable future
Analyzing Actual Performance
-Sales analysis uses sales figures to evaluate a firm's current performance and is the most common method of evaluation because sales data partially reflect the target market's reactions to a marketing mix and often are readily available
-Marketing cost analysis breaks down and classifies costs to determine which are associated with specific marketing efforts
Environmental Forces
Environmental Scanning
The process of collecting information about forces in the marketing environment
Environmental Analysis
-The process of assessing and interpreting the information gathered through environmental scanning
-How you deal with the information collected during scanning
Responding to Environmental Forces
Marketers take two approaches to environmental forces:
1. Passive - Accepting them as uncontrollable
2. Proactive - Attempting to influence and shape them
Brand Competitors
Firms that market products with similar features and benefits to the same customers at similar prices
Product Competitors
Firms that compete in the same product class but market products with different features, benefits, and prices
Generic Competitors
Firms that provide very different products that solve the same problem or satisfy the same basic customer need
Total Budget Competitors
Firms that compete for the limited financial resources of the same customers
Monopolistic Competition
A competitive structure in which a firm has many potential competitors and tries to develop a marketing strategy to differentiate its product
Pure Competition
A market structure characterized by an extremely large number of sellers, none strong enough to significantly influence price or supply
-Does not exist in the real world, although some industries come close
The Business Cycle
A pattern of economic fluctuations that has four stages:
1. Prosperity - Low unemployment and relatively high total income, which together ensure high buying power
2. Recession - Unemployment rises and total buying power declines, stifling both consumer and business spending
3. Depression - Unemployment is extremely high, wages are very low, total disposable income is at a minimum, and consumers lack confidence in the economy
4. Recovery - The economy moves from depression or recession to prosperity
Willingness to Spend
An inclination to buy because of expected satisfaction from a product, influenced by the ability to buy and numerous psychological and social forces
Factors that affect consumers' general willingness to spend:
-Expectations about future employment
-Income levels
-Prices
-Family size
-General economic conditions
Cause-related marketing
The practice of linking products to a particular social cause on an ongoing or short-term basis
Strategic philanthropy
The synergistic use of organizational core competencies and resources to address key stakeholders' interests and achieve both organizational and social benefits
Marketing research can involve two forms of data:
1. Qualitative data yields descriptive non-numerical information
2. Quantitative data yields empirical information that can be communicated through numbers
-Marketers conduct either exploratory research or conclusive research
The Five Steps of the Marketing Research Process
Step 1: Locating and Defining Problems of Research Issues
Step 2: Designing the Research Project
Step 3: Collecting Data
Step 4: Interpreting research findings
Step 5: Reporting research findings
Methods of Collecting Primary Data
-Population- All the elements, units, or individuals of interest to researchers for a specific study
-Sample- A limited number of units chosen to represent the characteristics of a total population
-Sampling- The process of selecting representative units from a total population
Probability Sampling
A type of sampling in which every element in the population being studied has a known chance of being selected for study
-Random Sampling - All units in a population have an equal chance of appearing in the sample, and the various events that occur have an equal or known chance of taking place
-Stratified Sampling - The population is divided into groups with a common attribute and a random sample is chosen within each group
Non-probability Sampling
A sampling technique in which there is no way to calculate the likelihood that a specific element of the population being studied will be chosen
-Quota Sampling - A non-probability sampling technique in which researchers divide the population into groups and then arbitrarily choose participants from each group