Chapter 3: The Cell
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Cell
is the fundamental unit of life
many cells interact to form tissues, organs, and organ systems
differences in cell shape make different functions possible
genes control a cell’s actions and responses
Composite cell
includes many different cell structures at once
most cells contain most of these structures
used to describe the functions and organelles of cells
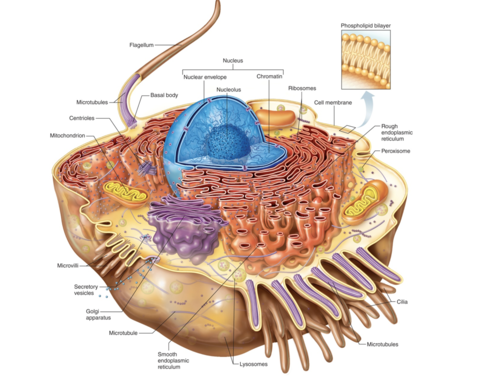
What are the three main parts of a cell ?
Nucleus, Cytoplasm, & Cell membrane
Nucleus
Contains DNA (genetic material) and directs cell’s activities
Cytoplasm
organelles and fluids that make up the majority of the cell; between nucleus and cell membrane
Cell membrane
boundary that encloses the cell
What is within the cytoplasm that is specialized and performs functions for the cell ?
Organelles
Cytosol
organelles that are suspended in a fluid
Cell membrane ( plasma membrane )
is a very thin boundary that contains the cell’s contents
The cell membrane is Selectively Permeable
regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell
helps cells adhere to other cells
What is the cell membrane composed of ?
Mainly of lipids and proteins, and some carbohydrates
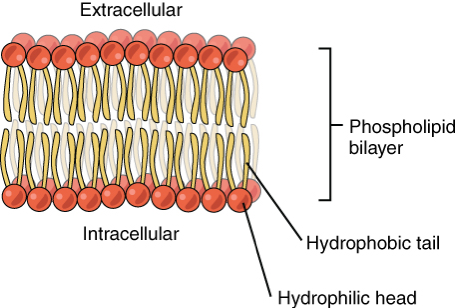
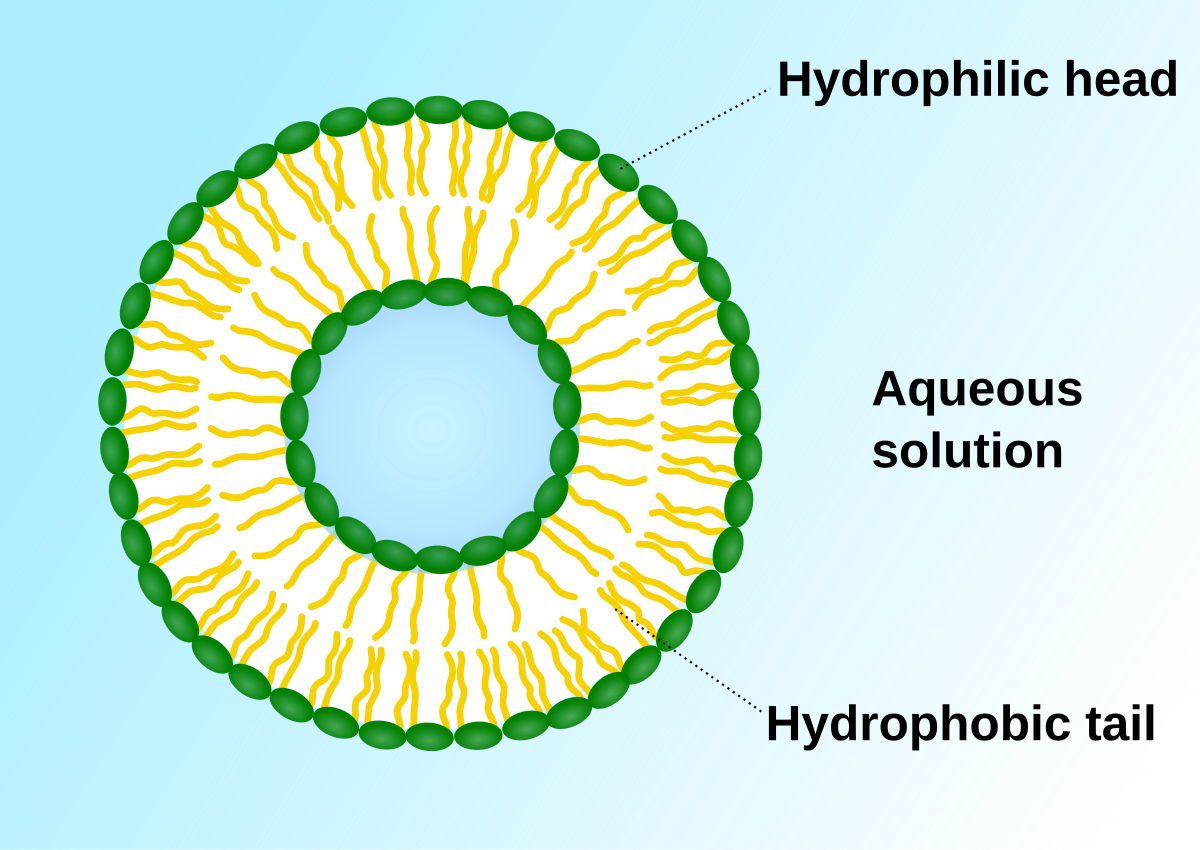
Double layer (bilayer) of phospholipids
the basic framework of the cell membrane consists of a double layer (bilayer) of phospholipids, with fatty acids tails turn inward and the water-soluble heads facing the surfaces
the phospholipids can move, forming a stable fluid film
Many types of _____ are found in the cell membrane.
proteins
Some proteins function as _____ on the cell surface
receptors
Other proteins transport ions or molecules across cell membrane, such as _______
ion channels
Other proteins are used for ______________; this helps identify cells as “self”, protecting them from attack by the immune system
cell identification
some proteins will protrude into the cell will anchor supportive rods and tubules, forming a cytoskeleton
What makes most of the cell volume ?
cytoplasm
The Cytoplasm consist of ?
a clear liquid (cytosol)
a supportive cytoskeleton
networks of membranes and organelles
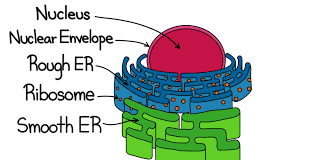
Ribosomes
tiny structures composed of RNA and protein
produce proteins for the cell
not membranous
found in cytoplasm or bound to rough endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
made up of membranes, flattened sacs, and vesicles
provides a tubular transport system inside the cell
functions as a transport network throughout the cell
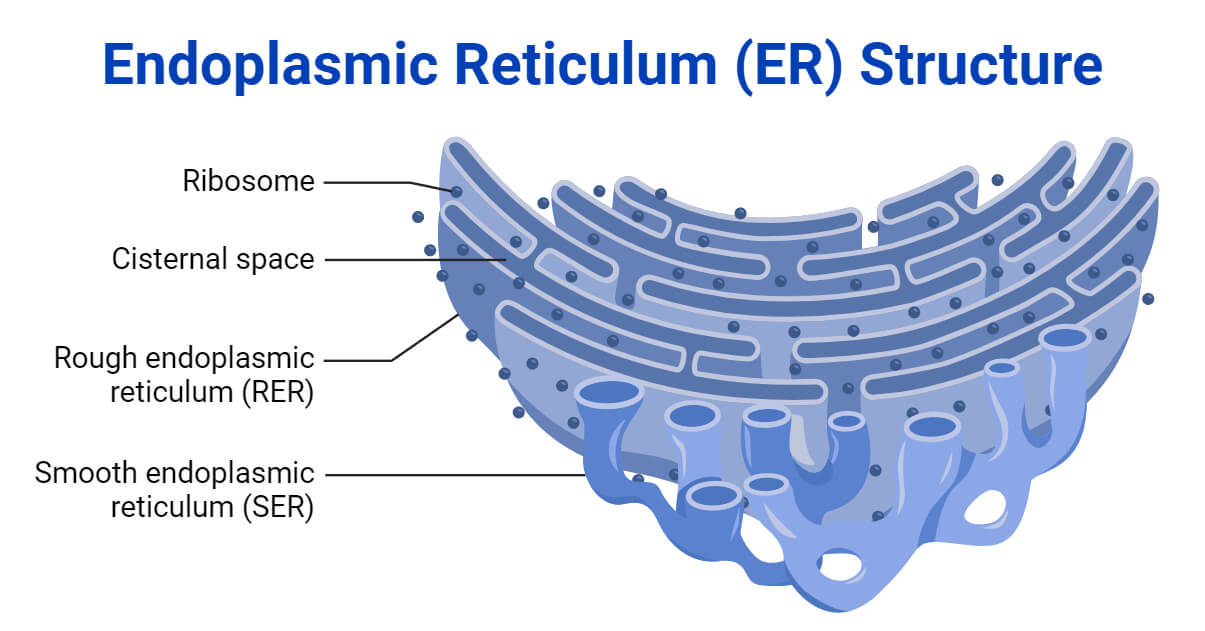
Rough ER
contains ribosomes and functions in protein synthesis and processing
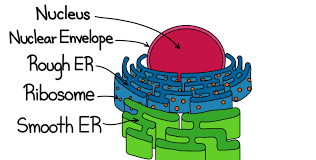
Smooth ER
does not contain ribosomes and functions in lipid synthesis, absorption of fats, and metabolism of drugs
Vesicles
membranous sacs
store or transport substances within or between cells
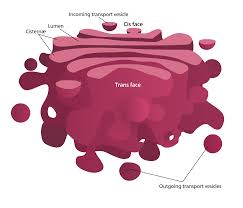
Golgi apparatus
composed of flattened, membranous sacs
refines, packages, and transports proteins formed in the rough ER
vesicles formed in the ER travel to the Golgi apparatus, which may modify their contents by adding sugar molecules to the proteins, to stabilize their structure or to enable folding
a new vesicle pinches off the Golgi apparatus and may then move to the cel membrane to secrete its contents to the outside (exocytosis)
Vesicular Movement
vesicles formed in the ER travel to the Golgi apparatus, which may modify their contents buy adding sugar molecules to the proteins, to stabilize their structure or to enable folding
a new vesicle pinches off the Golgi apparatus and may then move to the cell membrane to secrete its contents to the outside (exocytosis)
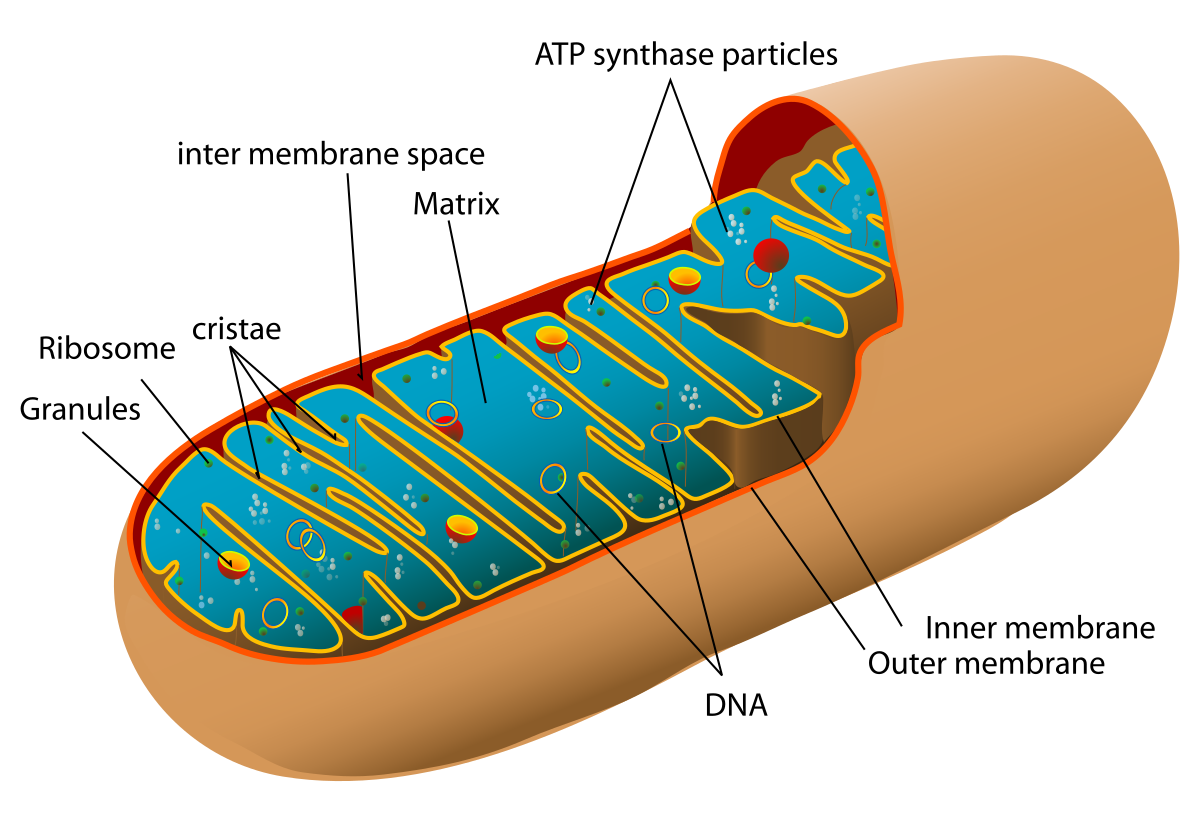
Mitochondria (ATP)
elongated fluid-filled sacs
house many chemical reactions that extract energy from nutrients
contain enzymes needed for cellular respiration
the inner membrane of the mitochondrion is folded into cristae, which hold the enzymes needed in energy transformations to make ATP
store the energy in chemical bonds of ATP
very active cells contain thousands of mitochondria
mitochondria have their own DNA and reproduce by dividing
Lysosomes
membranous sacs
contain enzymes that break down nutrients, ingested, materials, debris, worn out cell parts, cholesterol (in some cells), toxins, and drugs
Peroxisomes
also membranous sacs
contain a different set of enzymes than lysosomes
their enzymes function in the breakdown of fatty acids and hydrogen peroxide, and detoxification of alcohol
In the cytoplasm, there are several structures, which are not organelles, but rather part of the ________.
cytoskeleton
_________ and _________ are thin, threadlike structures that serve as the cytoskeleton of the cell.
Microfilaments and microtubules