Cardiovascular Response to Exercise
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Cardiac Output
Volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute.
Preload
Volume of blood in ventricles before contraction.
Stroke Volume
Amount of blood ejected by the heart per beat.
Afterload
Resistance the heart must overcome to eject blood.
Vagus Nerve
Part of the autonomic nervous system, reduces heart rate.
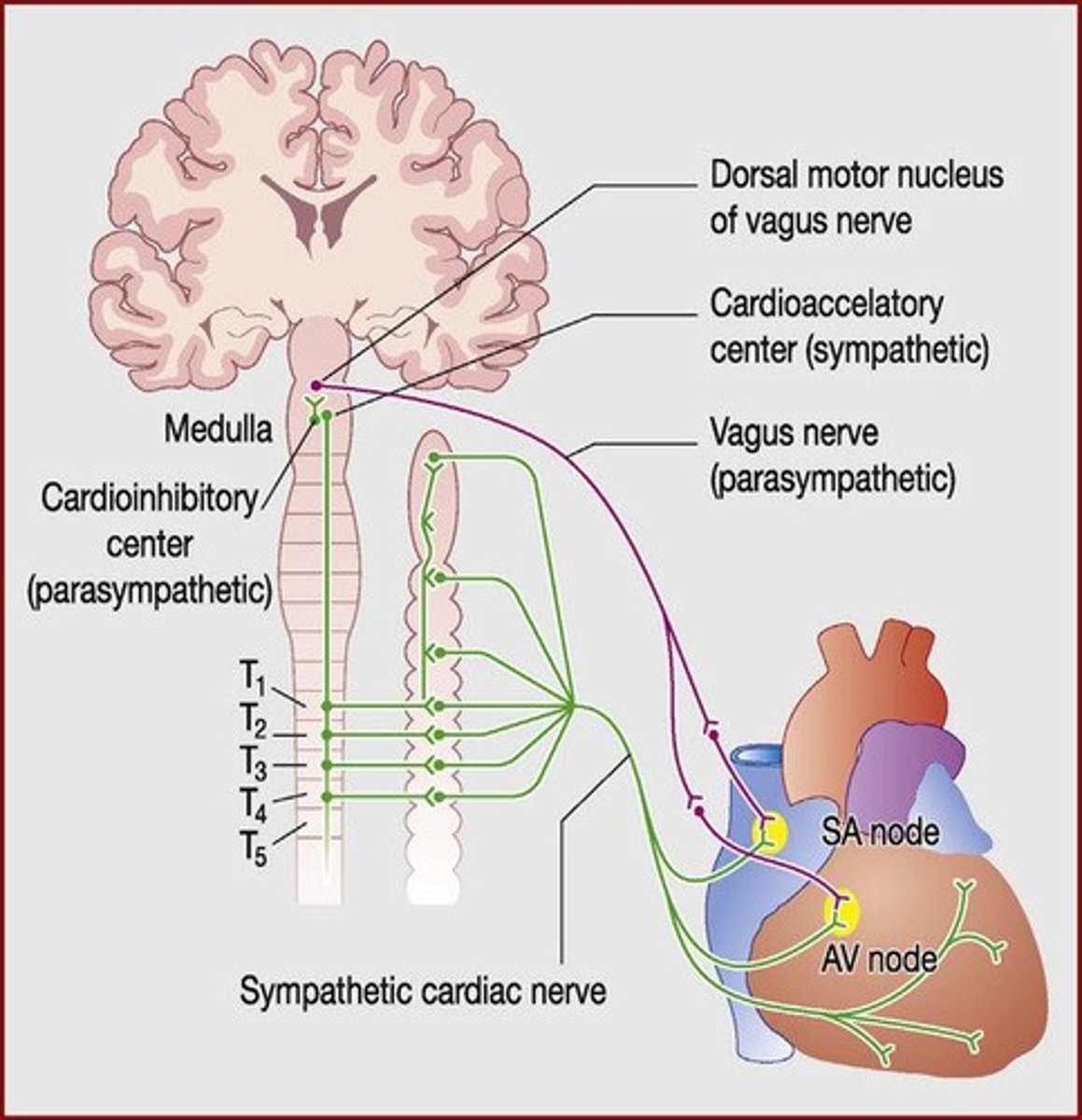
Sympathetic Nervous System
Increases heart rate and contractility during exercise.
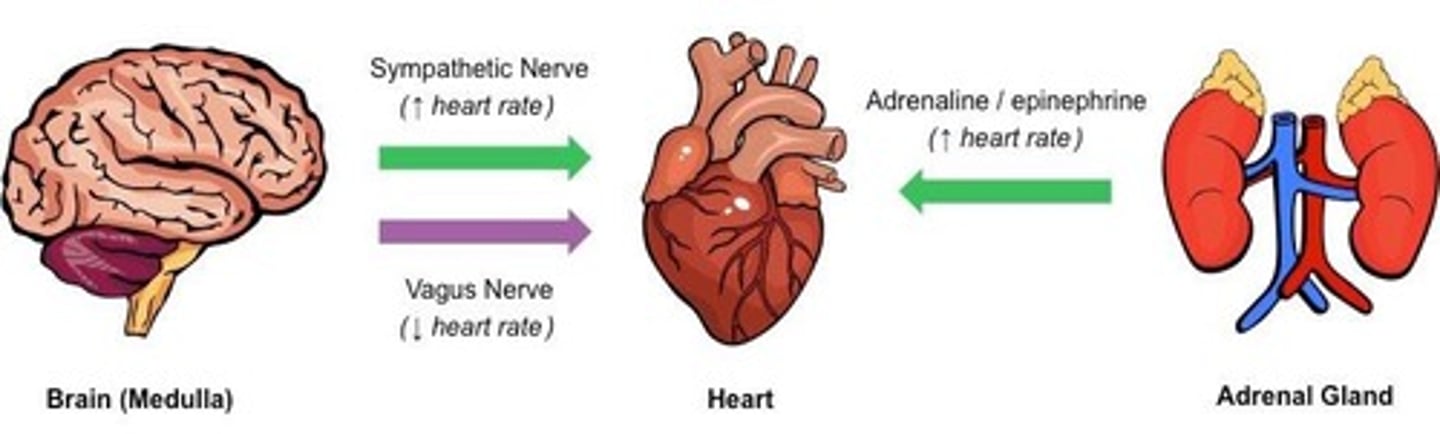
Epinephrine
Hormone that enhances cardiac output and blood flow.
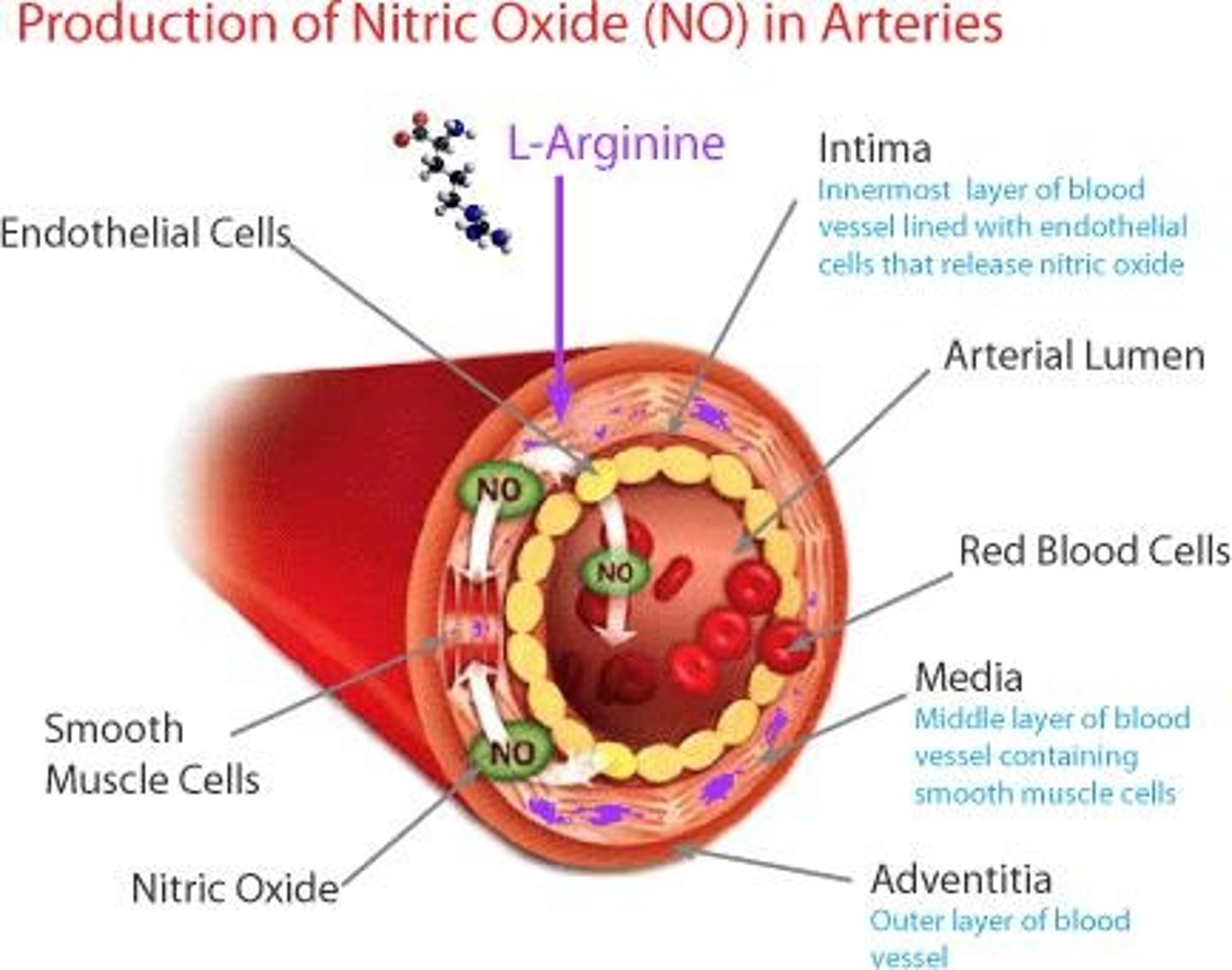
Nitric Oxide (NO)
Vasodilator released to increase blood flow.
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing of blood vessels, reducing blood flow.
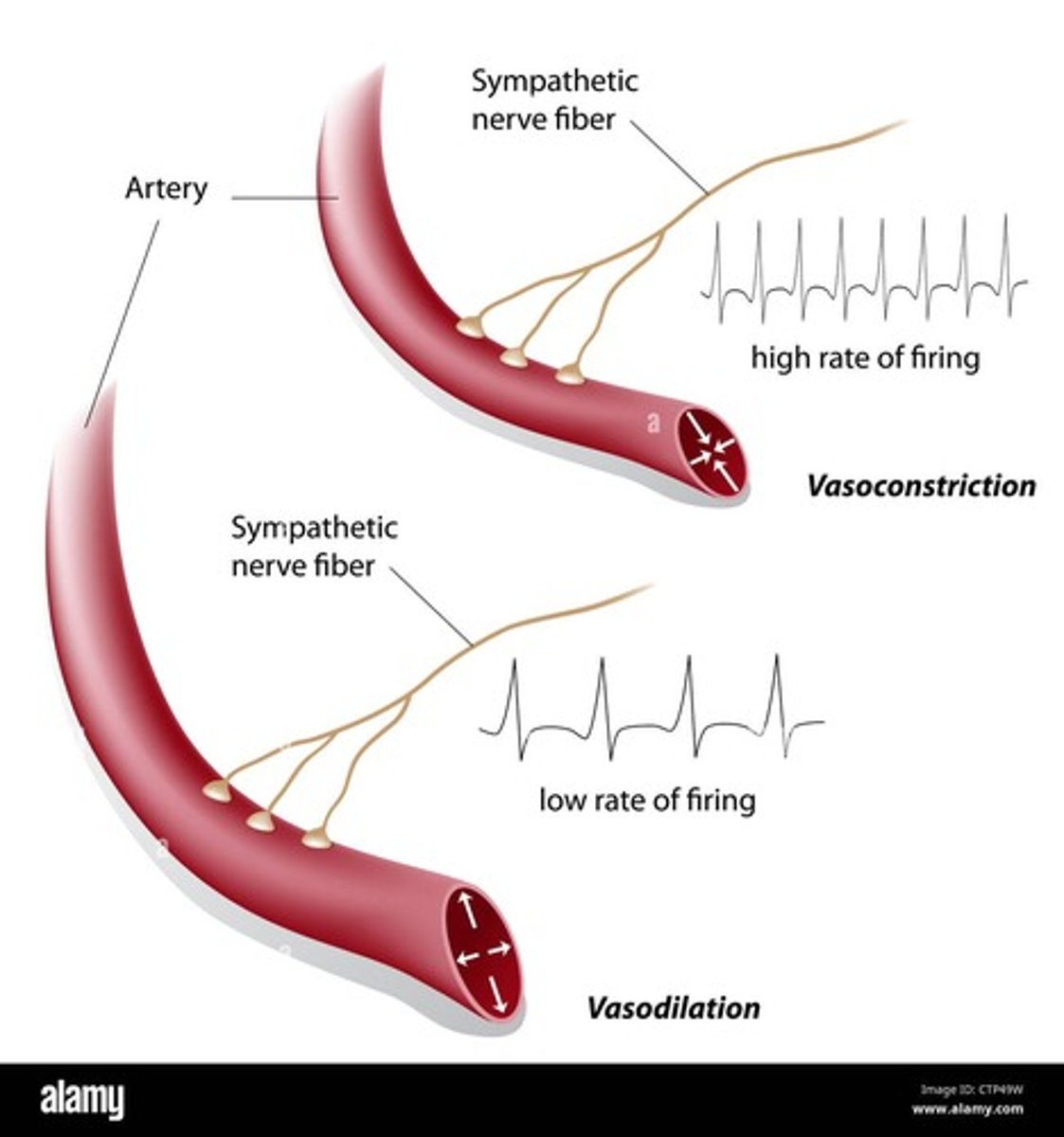
Vasodilation
Widening of blood vessels, increasing blood flow.
Mean Arterial Pressure
Average blood pressure in a person's arteries.
Total Peripheral Resistance (TPR)
Overall resistance to blood flow in the circulatory system.
Mechanical Tension Receptors
Sensors that detect stretch in muscle during exercise.
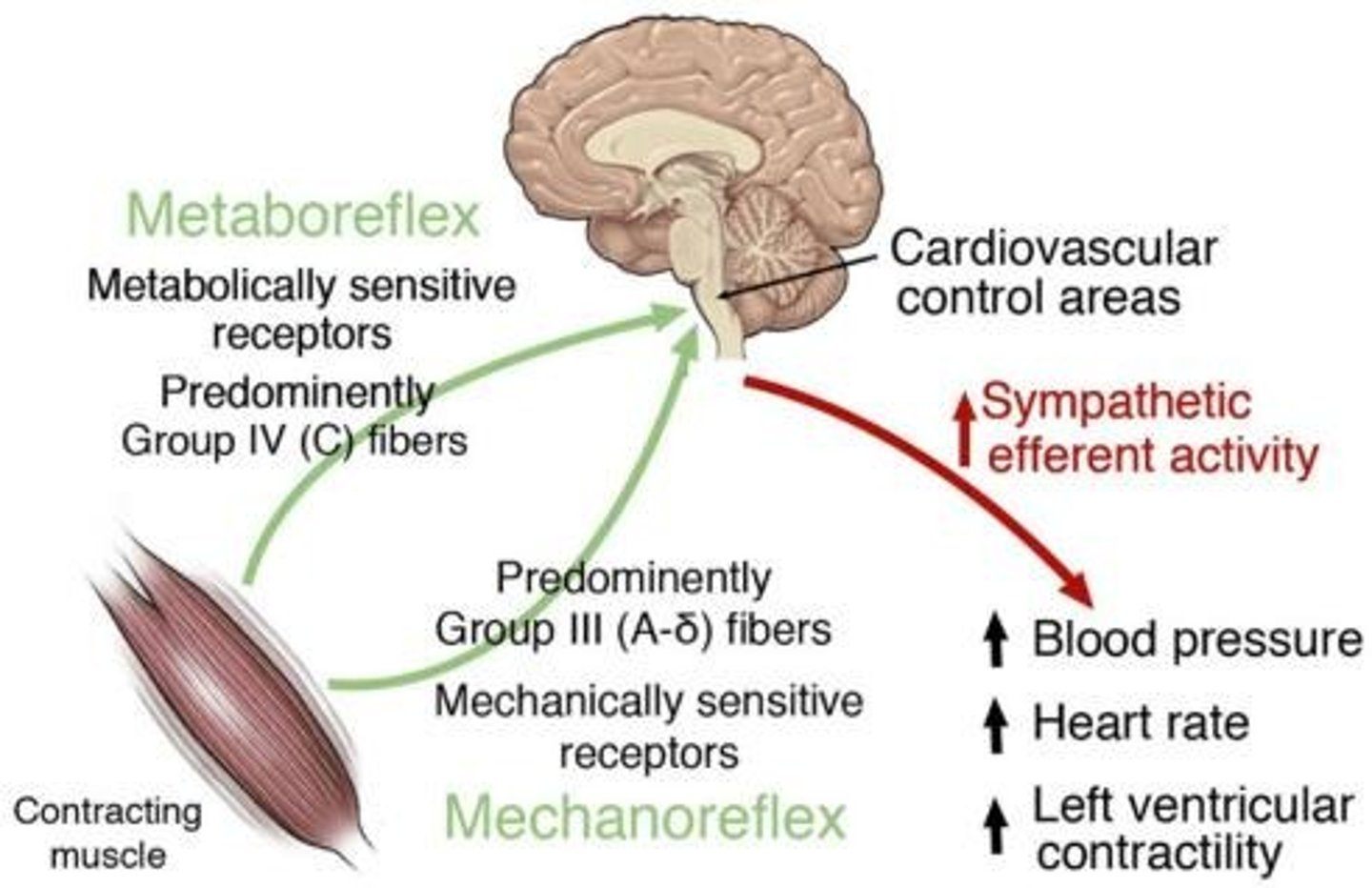
Metaboreceptors
Receptors sensitive to metabolic changes in muscles.
End-Diastolic Volume
Volume of blood in ventricles at the end of diastole.
End-Systolic Volume
Volume of blood remaining in ventricles after contraction.
Skeletal Muscle Pump
Mechanism aiding venous return during muscle contraction.
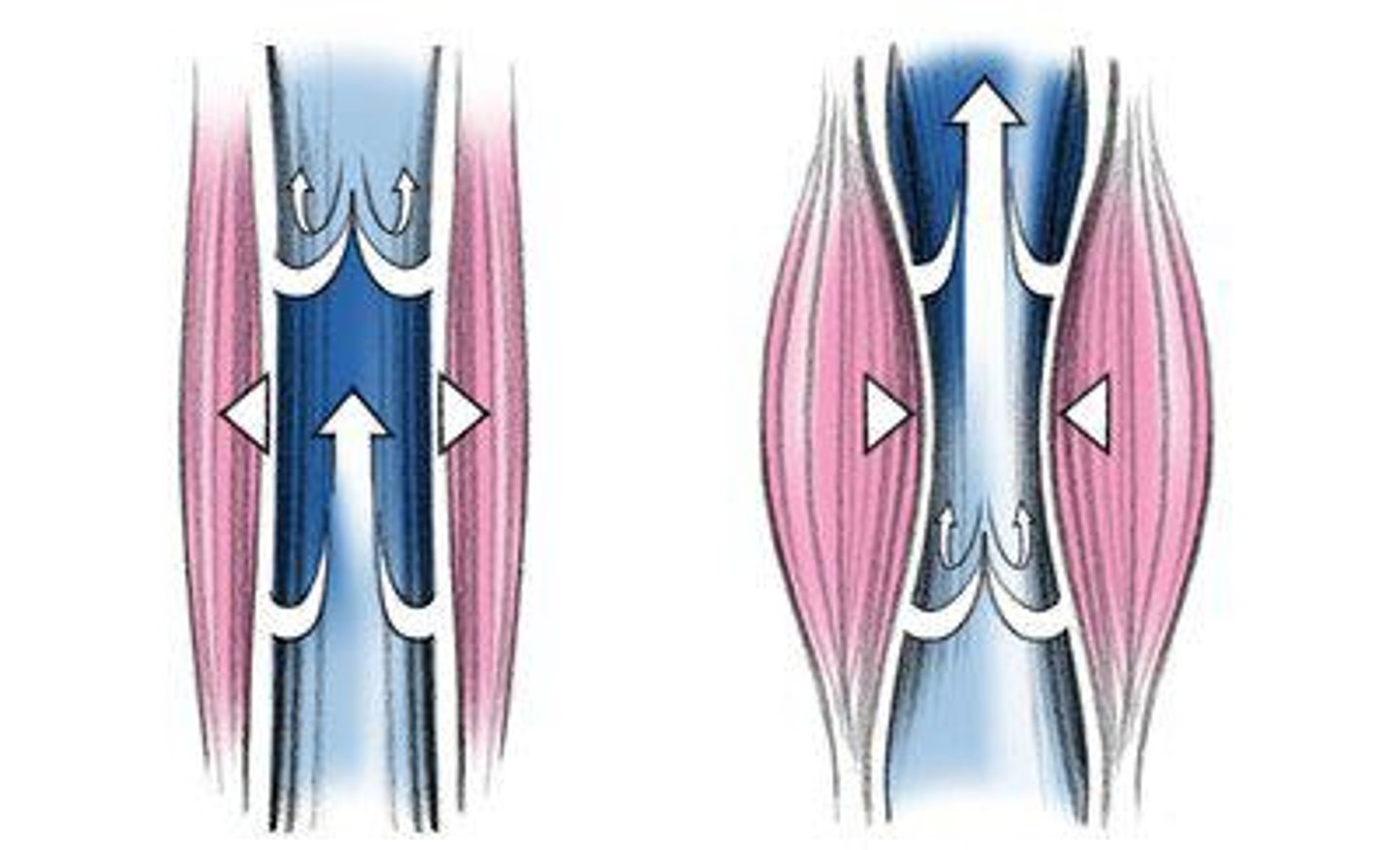
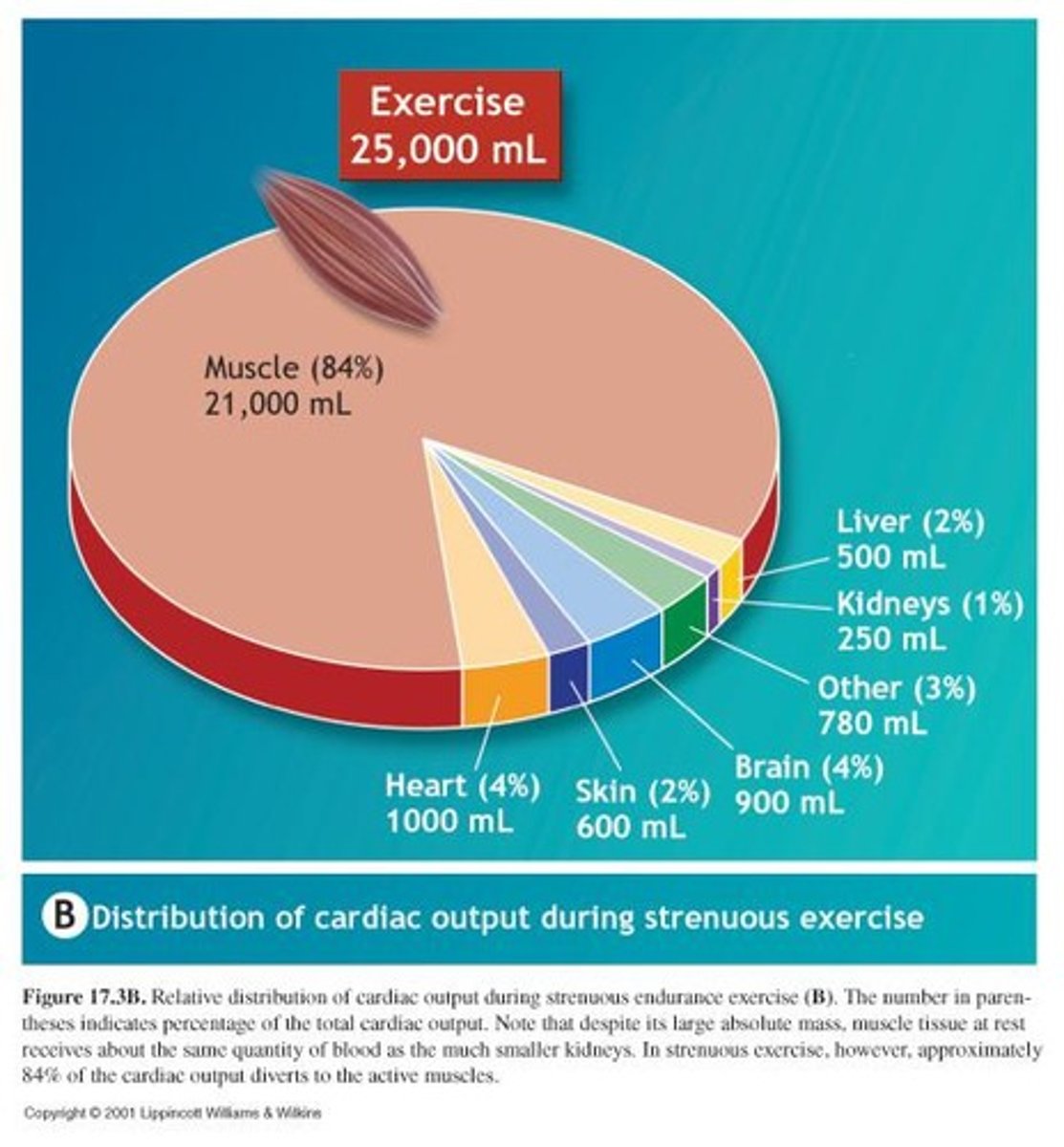
Blood Flow Distribution
Redistribution of blood to active muscles during exercise.
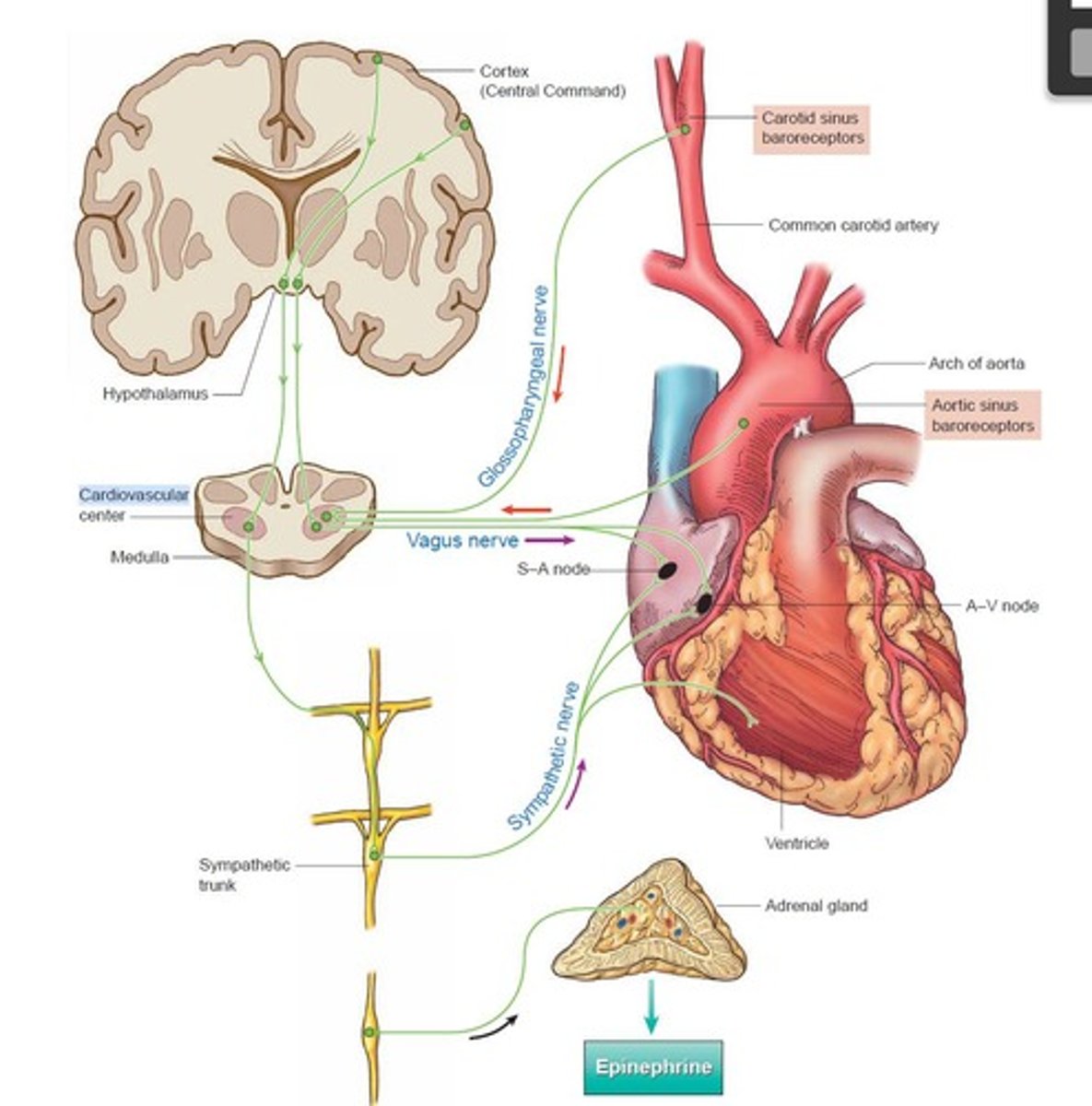
Cardiovascular Control Centre
Brain region regulating heart and blood vessel activity.
Anticipatory Response
Physiological adjustments made before exercise begins.
Incremental Exercise
Gradually increasing exercise intensity or workload.
Local Factors
Substances like metabolites that influence blood vessel behavior.
Exercise Onset
Initial phase of physical activity triggering cardiovascular changes.
Cardiovascular Regulation
Mechanisms controlling heart and blood vessel function.