Other Forces of Evolution
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
The forces of evolution
Natural Selection
Mutations
Gene flow
Genetic Flow
First Slide
Mutation
-heritable change in genetic information
-mutations in gametes are passed to offspring
-changes in DNA → RNA → Proteins → inherited more new alleles
-+variation
-depending on when the mutation separates and what the last common ancestor there was, there will be more similarities
-without mutations, you may go extinct
Gene Flow
Change in allele frequencies that occurs when individuals move into or out of a population
-more genetic diversity and alleles when interbreeding happens
-with time interbreeding creates a mixed party and selective pressures against the new traits creates natural selection
Reproductive Isolation
stopped or no contact between the two populations, reproduce alone
Genetic drift
random change in allele frequencies between generations due to chance
-bottle neck effect
-founder effect
-nothing to do with selective advantage
Bottlenecking effect
-population reducing event that has nothing to do with survival of the fittest
-hurricane or natural disaster
Founder effect
-population founding
-one bug founds whole island in its image
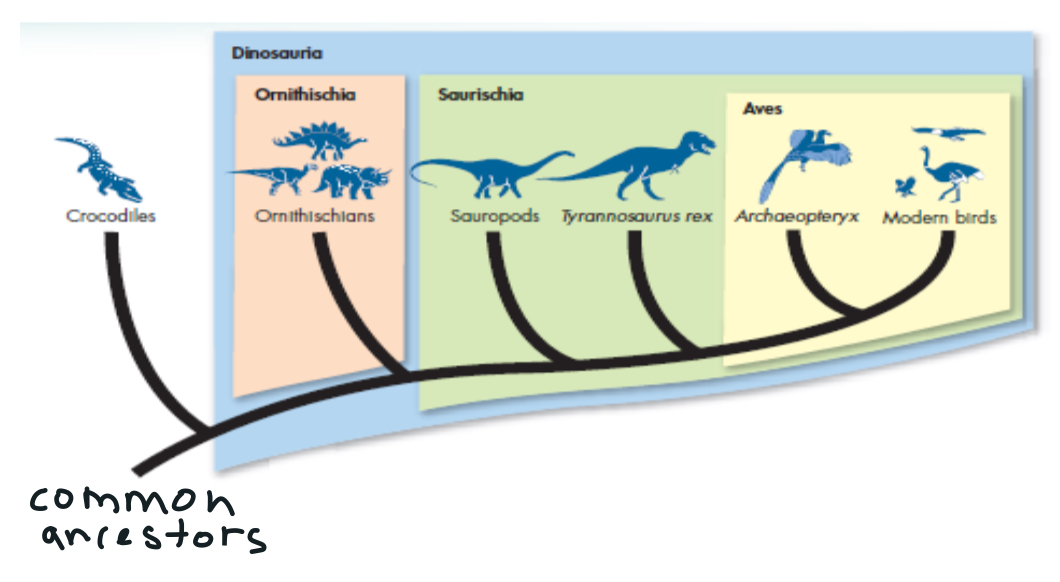
Macroevolutionary Patterns
grand transformations in anatomy, phylogeny, ecology, and behavior taking place in clades
-surviving species such as crocodile
-speciation
-extinction
Speciation
formation of a new species
Extinction
the dying out of an entire species
Background extinction
ongoing extinction caused overtime
Mass extinction
dramatic, probably caused by combination: volcanic eruptions, moving continents, and changing sea levels
End of cretaceous
end of dinosaurs and then start of mammals
Biogeography
the study of where organisms live now and where they and their ancestors lived in the past.
• Patterns in the distribution of living and fossil species tell us how modern organisms evolved from their ancestors
The two patterns
-closely related but different
-distantly related but similar
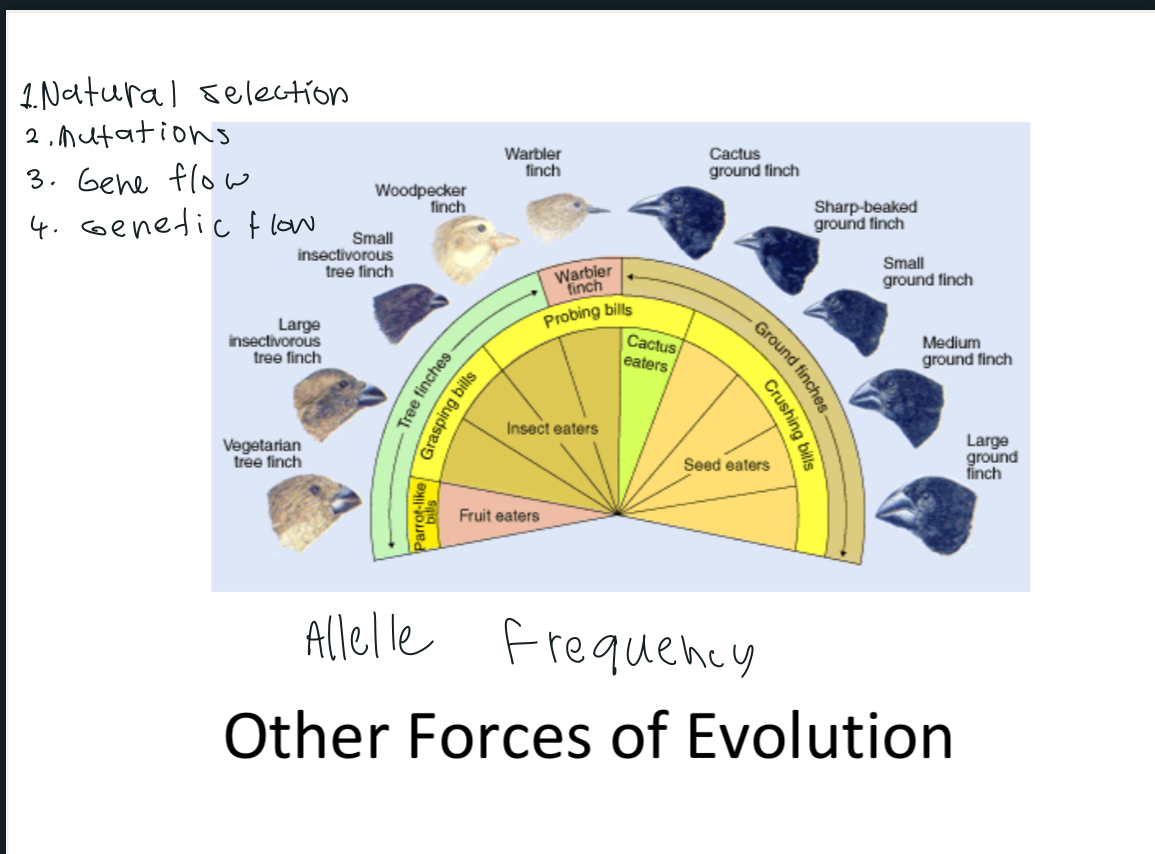
Closely related but different
-radial adaptation
-common closely related ancestor
-example is the finches
Distantly related but similar
-convergent evolution
-rhea,ostrich,emu
-similar environment can sometimes be a cause of this
African euphorbia , Mexican/ US cactus, arid climate
Earth age
4.5 billion years old
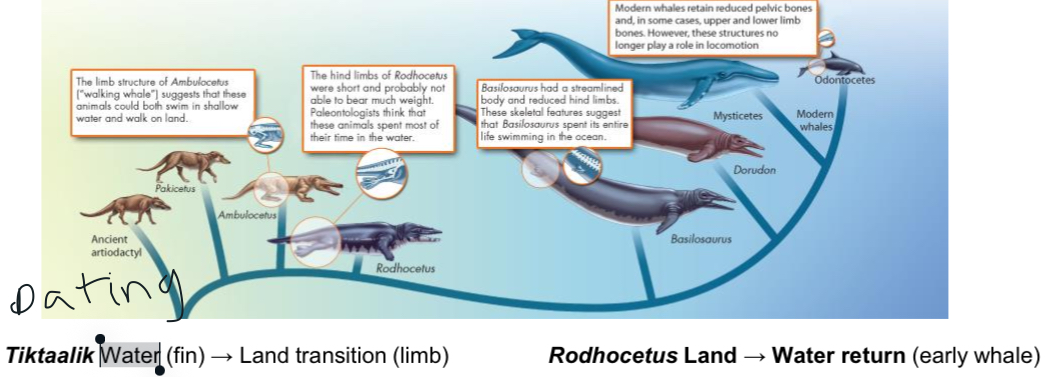
Fossils form a _____ that ___________
Fossils form a series that trace evolution from ancestors to modern species.
Artodactyl to odontocetes
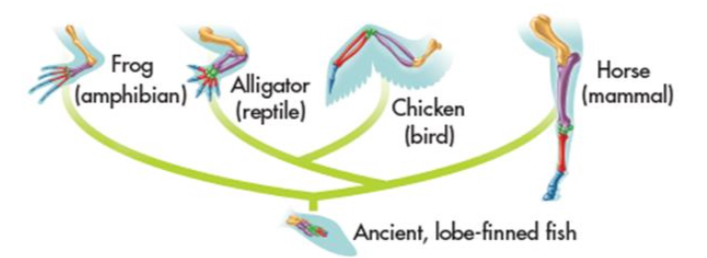
Homologous structures
structures that are shared by related species and that have been inherited from a common ancestor
-clue to common descent is common structure not function
Analogous structures
body parts that share common function but not structure or origin
-wing of bee (exoskeleton and chitin) vs bird (feather and bone)
Vestigial structures
inherited from ancestors but have lost much or all of their original function due to different selection pressures acting on the descendant.
Embryology
conserved developmental genes (HOX) → common ancestors
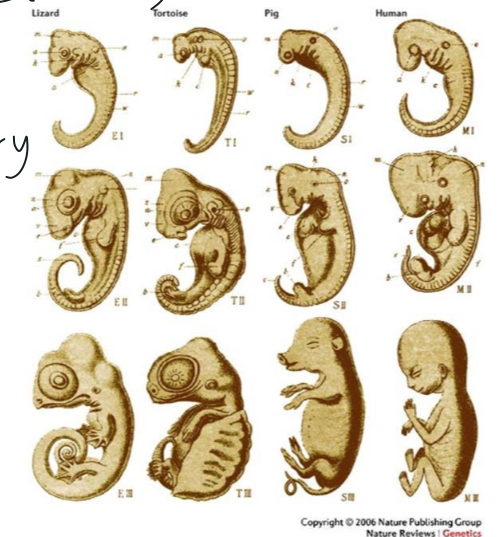
All living cells use
information coded in DNA and RNA to carry information from one generation to the next and to direct protein synthesis.
– bacteria, yeasts, plants, fungi, and animals
Homologous protein (molecule)
– cytochrome c (functions in cellular respiration)
• similar versions found in almost all living cells, from
cells in baker’s yeast to cells in humans