Key Concepts of the Italian Renaissance
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Renaissance
Period of cultural rebirth in Europe.
Firenze/Florence
City where the Renaissance began.
Humanism
Focus on human potential and achievements.

Brunelleschi's Dome of Duomo
Largest masonry dome, formerly largest dome in world. Built with 2 domes.
Brunelleschi
Architect known for the dome of Florence.
Pietra Serena
Neutral gray sandstone used in architecture.
Medici Family
Patrons of art and architecture in Florence.
Fresco
Technique of mural painting on wet plaster.
Linear Perspective
Technique for creating depth in art.
Baptistry of Florence
Biggest baptistry on Earth, located in Florence and constructed in year 1000. 3 squares, windows, etc. represented Holy Trinity.

Ghiverti
Artist known for the Baptistry doors.
Donatello
Famous sculptor of the Renaissance.
Michelangelo
Renowned sculptor and painter of the era. Painted the Sistine Chapel and sculpted Statue of David.
Gutenberg
Inventor of the printing press.
95 Theses
Martin Luther's critique of the Church.

Orsanmichele
Grainery with statues representing guilds.
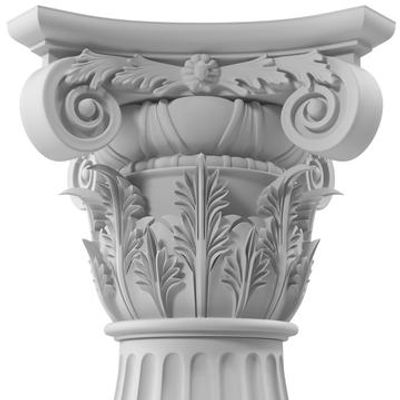

Composite Columns
Architectural style combining Greek elements.
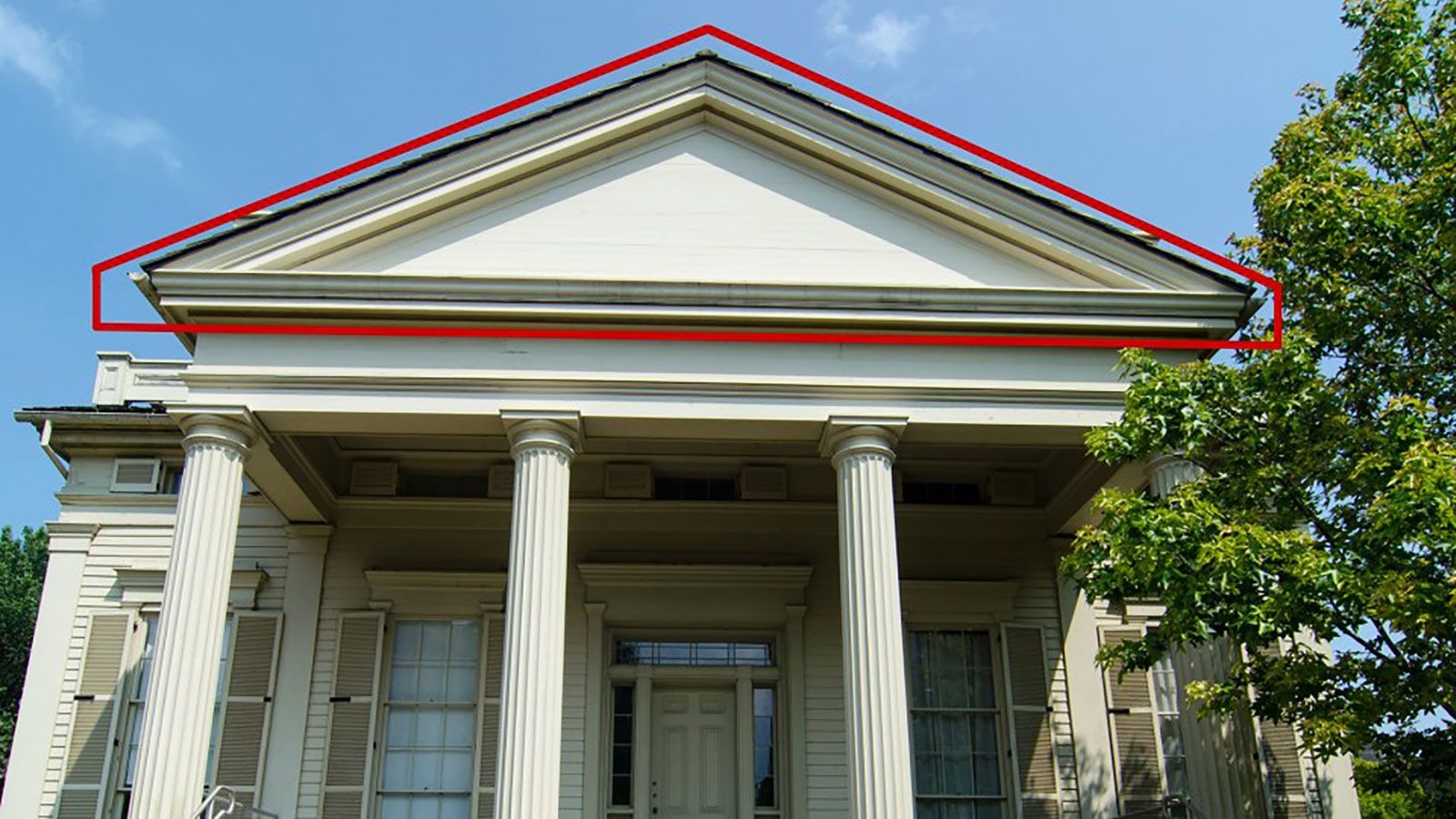

Triangular Pediment
Architectural feature adopted from Roman design.

Brunelleschi's Piazza
Square designed by architect Brunelleschi.
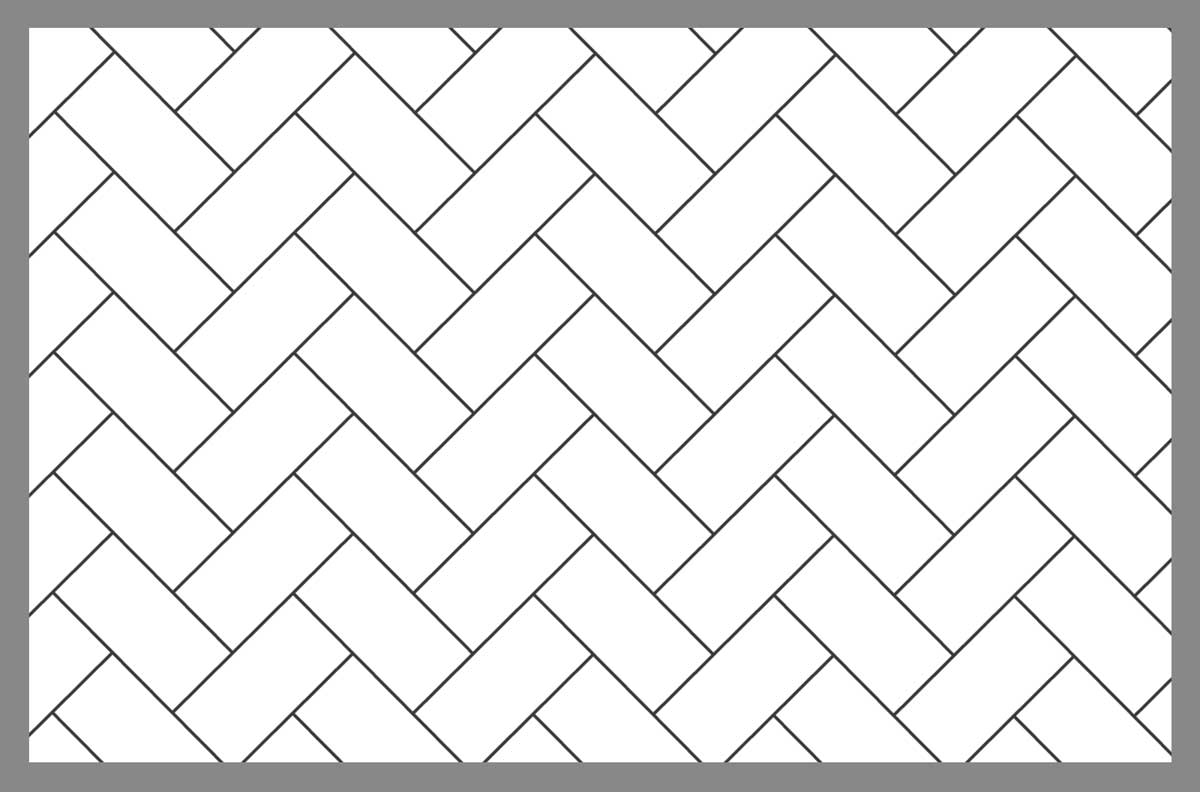
Herringbone Pattern
Brick pattern used in dome construction.
Cardinal Prince Leopold
Notable figure during the Renaissance period.
Cement Pozzolana
Material used in Roman construction, adopted to Italian architecture.
Medici Equestrian Statue
Statue symbolizing Medici power and influence.
Sibyls and Prophets
Figures painted in the Sistine Chapel.
Giorante
Part of fresco painting technique.
Lorenzo Magnifico
Patron of the arts, known as 'the Magnificent.'
Architectural Power
Used by families to display wealth.
Renaioli Pescaia
river connecting Florence and Pisa

Andrea Pisano North Doors
Ghiberti’s out of proportion doors
Ribs
Dome part- ladders to alleviate stress
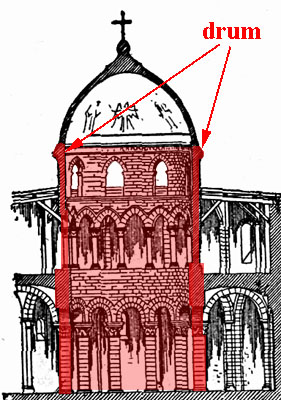
Drum
Dome part- octangular wall around dome
Inside Dome
dome on dome
San Lorenzo Florence
Church adopting Triangular Pediments and Triumphant Arches


Uffizi
office building
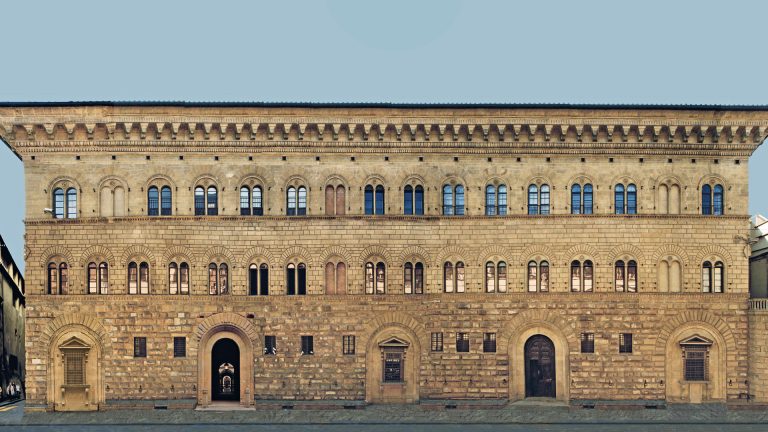

Michelozzo Palazzo Medici
Built in 1444, 3 story building with line refinement. Bands between floors, so it becomes progressively smoother.
Medici’s Statue of Hades
Hades statue to flex knowledge

Sistine Chapel
Funded by Pope Sistine, forced Michelangelo to paint it, including famous “God and Adam”
Fresco
“fresh” in Italian, referred to plaster on a brick/stone wall painted over so it lasts forever.
Statue of David
Statue of Biblical David, constructed as celebration for driving Medici family out. Built perfectly, as it weighed over 6 tons.
Michelangelo’s Technique
OBSERVE marble early in the morning to see flaws with angled sunlight
TASTE powdered marble to detect minerals
FEEL for different temperatures in the block
Surface rustication
range of masonry techniques used in classical architecture giving visible surfaces a finish texture that contrasts with smooth, squared-block masonry called ashlar.
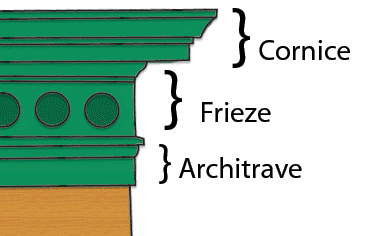
Cornice line
Greek horizontal molding on buildings