sexual reproduction- human physiology
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
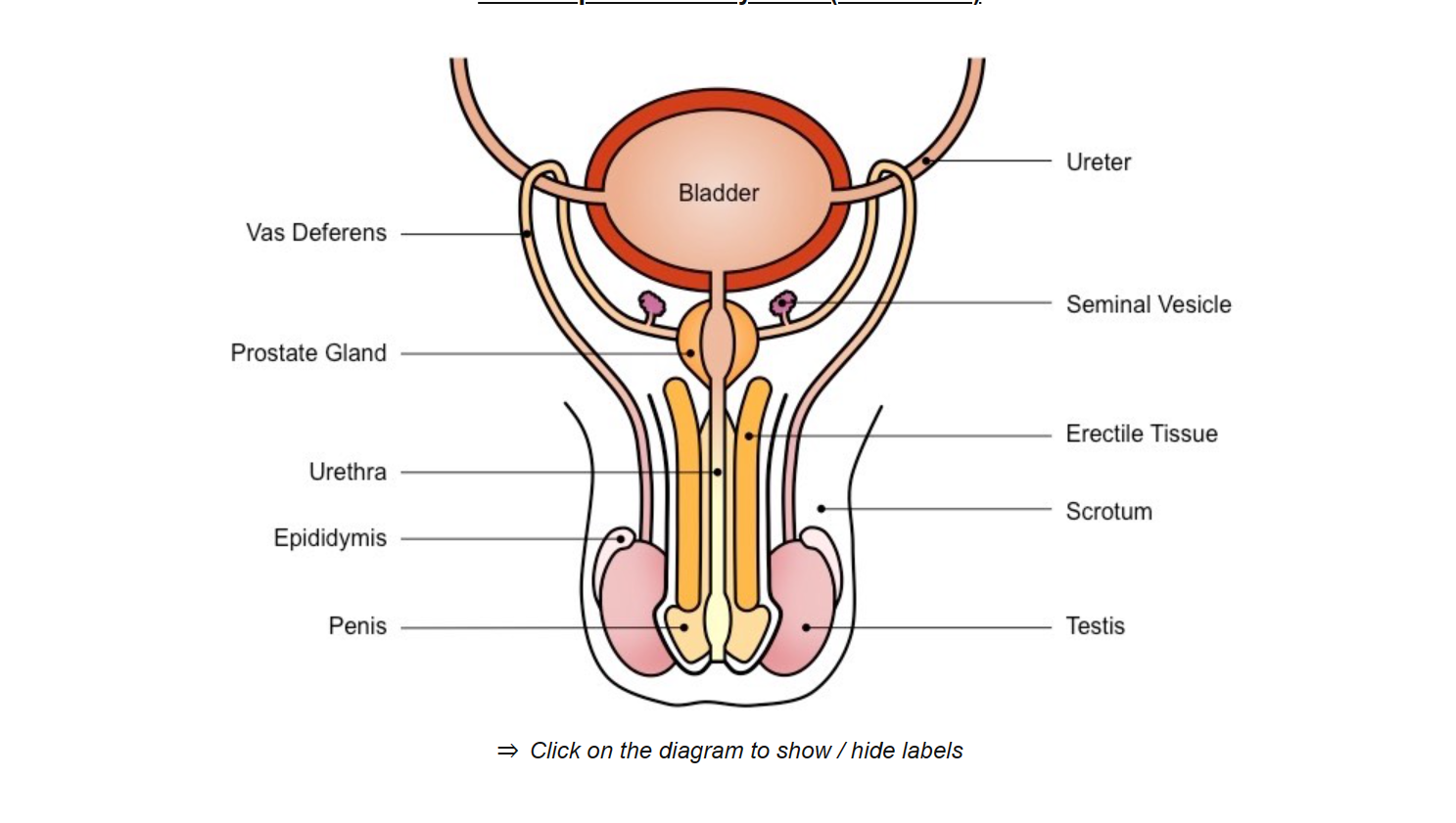
prostate gland
produces alkaline fluid to neutralize vaginal acids
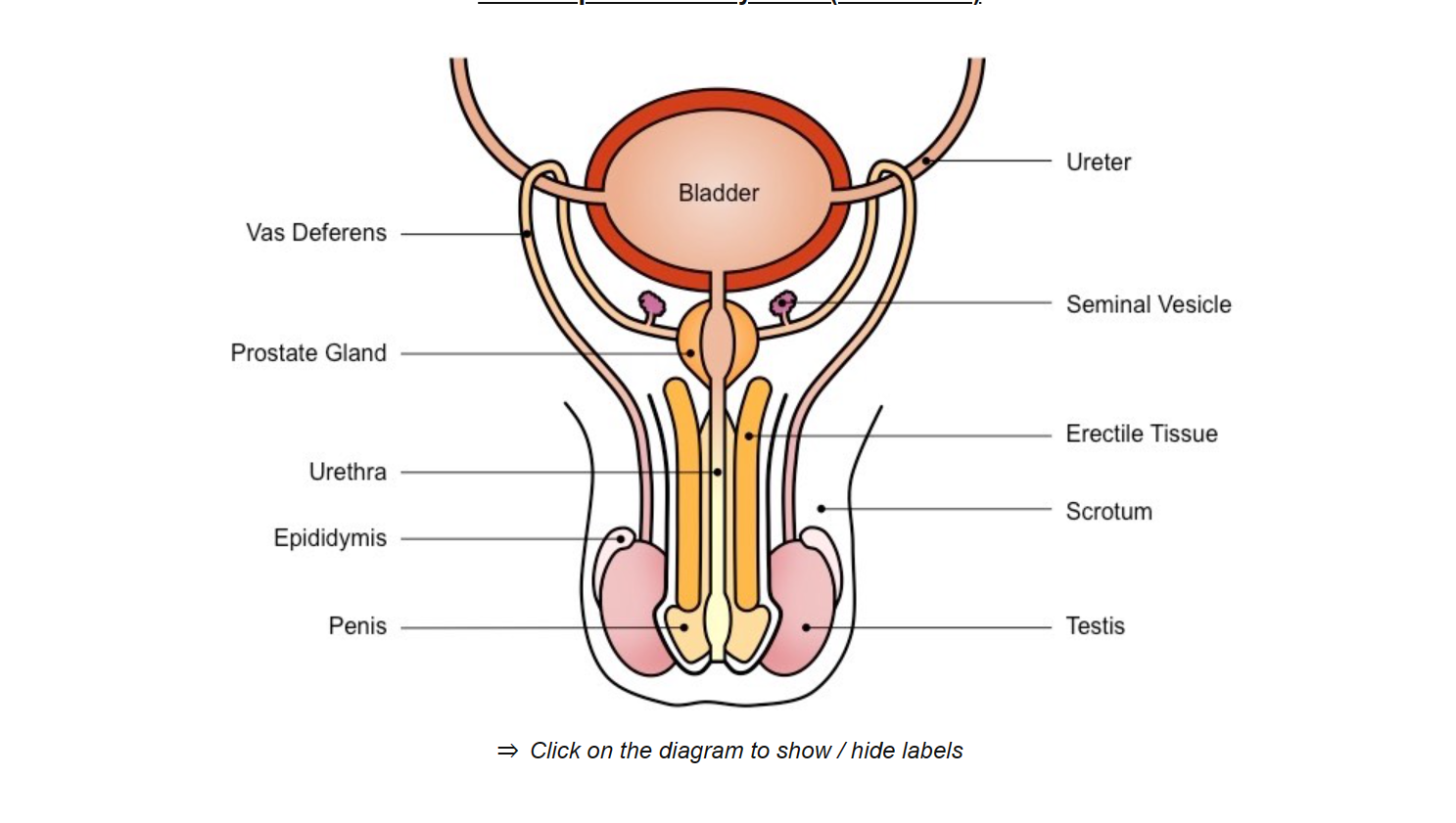
testis
produce testosterone and sperm
uterus
fertilized egg becomes an embryo
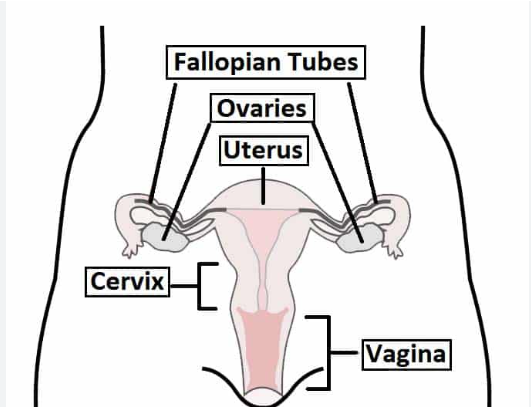
fallopian tube
transports the oocyte to the uterus
fimbria
sweep an oocyte from the ovaries to fallopian tubes
ovaries
secretes estrogen and progesterone
oocyte matures prior to release
seminal vesicle
secretes fluid containing fructose - nourishment of sperm cells
secretes mucus - to protect sperm cells
urethra
conducts sperm from prostate gland out of the body via penis
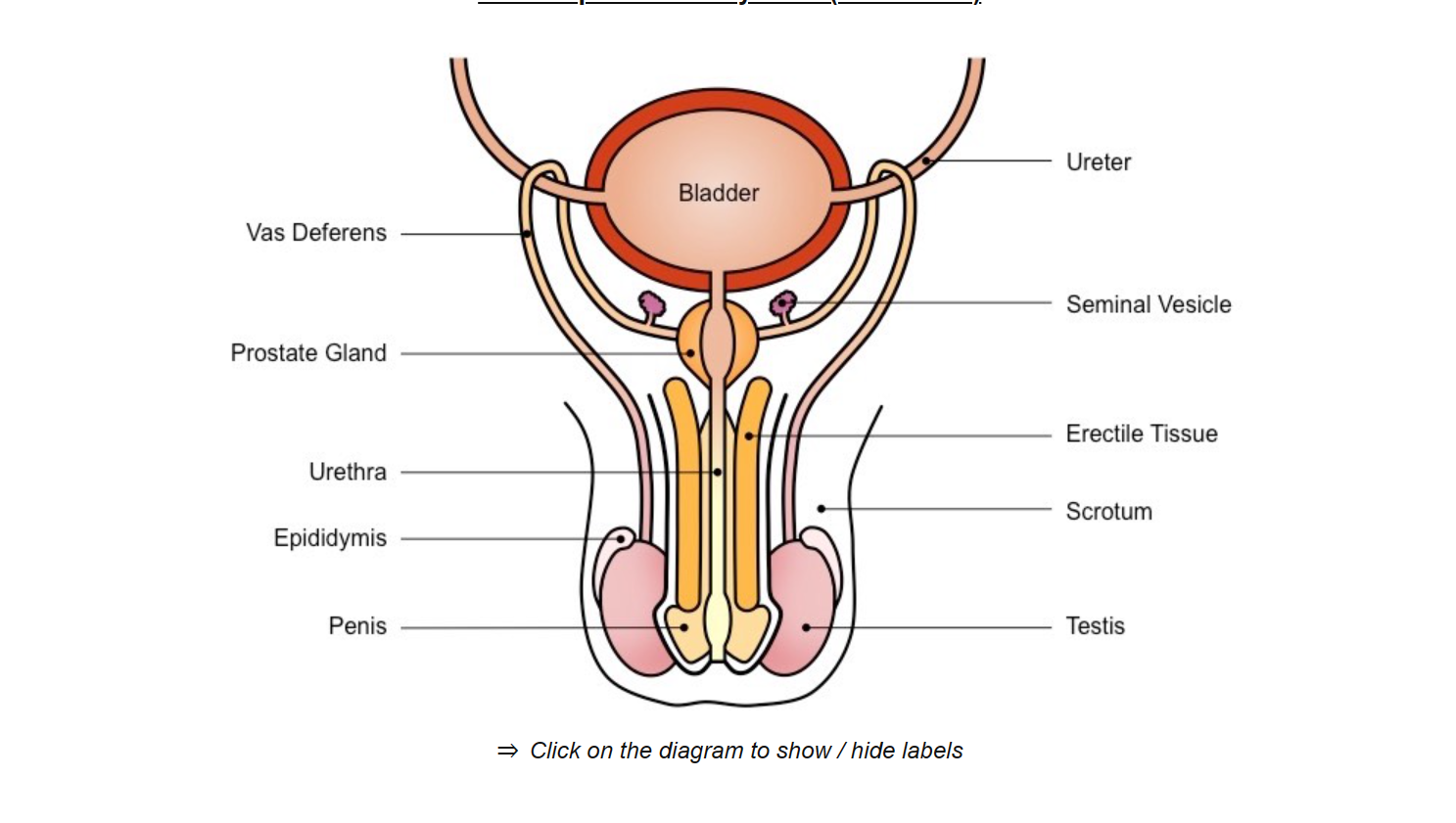
vas deferens
tube
conducts sperm from the testis to the prostate gland during ejaculation.
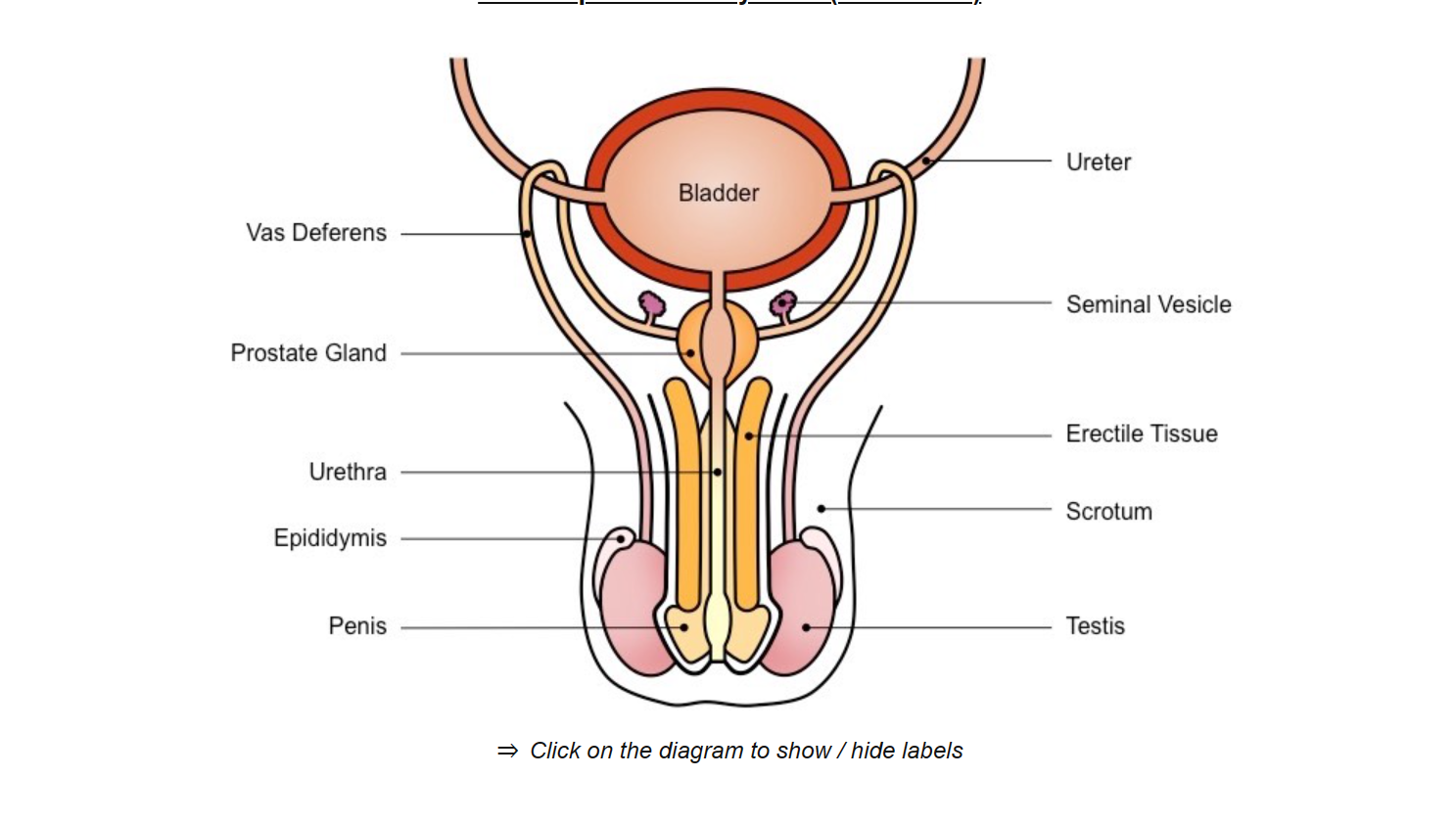
epididymis
sperm develops the ability to be motile
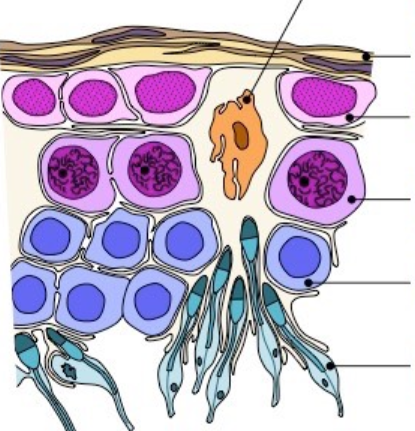
endometrium
the mucous membrane lining of the uterus
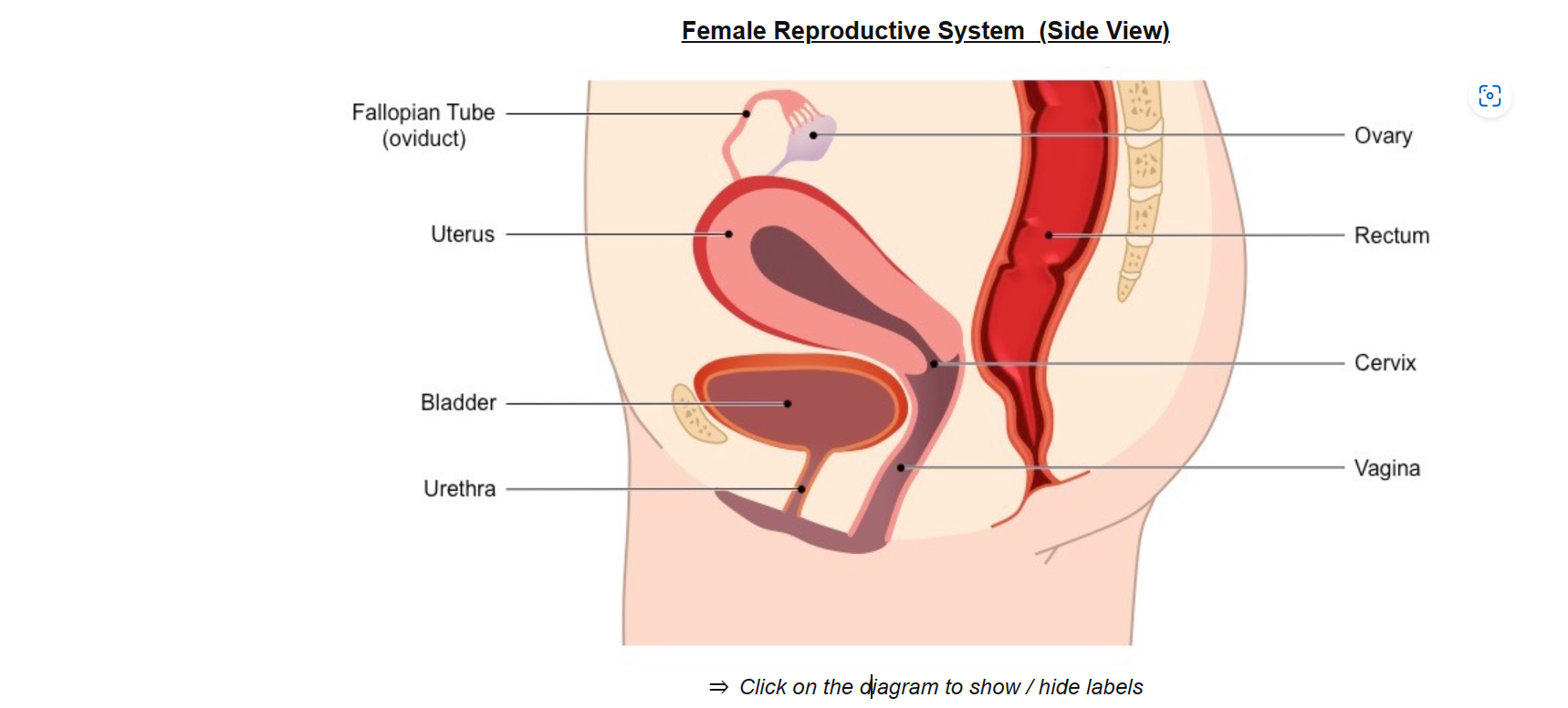
vagina
passage leading to the uterus, by which the penis can enter
pituitary hormones (1), are released from the (2) and act on the (3) to develop (4)
FSH and LH
anterior pituitary gland
ovaries
follicles
ovarian hormones (1), act on the (2) to prepare for pregnancy.
estrogen and progesterone
uterus
estrogen…
thickens endometrium
inhibits FSH and LH for most of the cycle
stimulates FSH and LH pre ovulation
progesterone…
thickens endometrium
inhibits FSH and LH
FSH
stimulates follicular growth in ovaries
LH
causes a surge in ovulation
results in the formation of the corpus luteum
estrogen and progesterone inhibit the secretion of….
FSH and LH
give an example of negative feedback in the menstrual cycle
anterior pituitary gland secretes FSH
the dominant follicle produces estrogen
estrogen inhibits further production of FSH, prevent other follicles from growing
explain what causes progesterone and estrogen levels to drop during menstruation.
the degeneration of the corpus luteum
give an example of positive feedback in the menstrual cycle
estrogen stimulates the secretion of LH
if fertilization occurs…
developing embryo implanted in the endometrium
will release hormones to sustain corpus luteum
corpus luteum secretes…
high levels of progesterone
describe how sperm cells are produced in the testis
spermatogonia undergo meiosis
epididymis is where spermatogonia mature/become motile
develop a flagellum
fructose in semen is secreted by…
seminal vesicle
interstitial cells produce….
testosterone
role of testosterone in spermatogenesis
the maturation of sperm cells
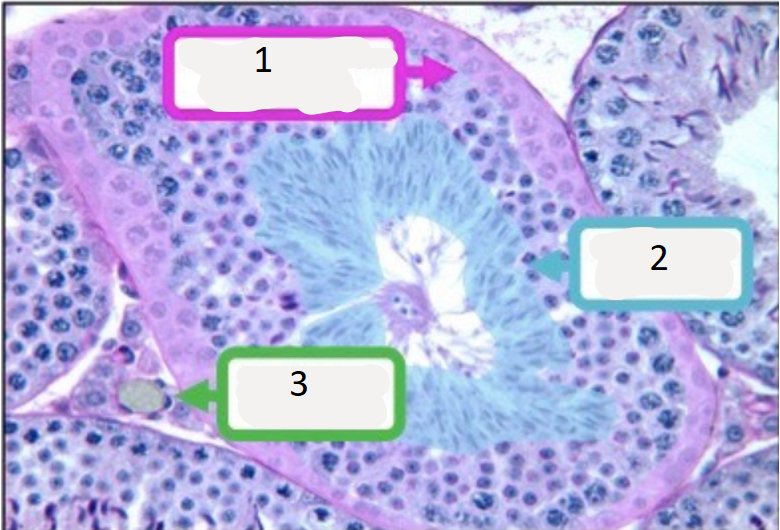
name number 1
germline epithelium
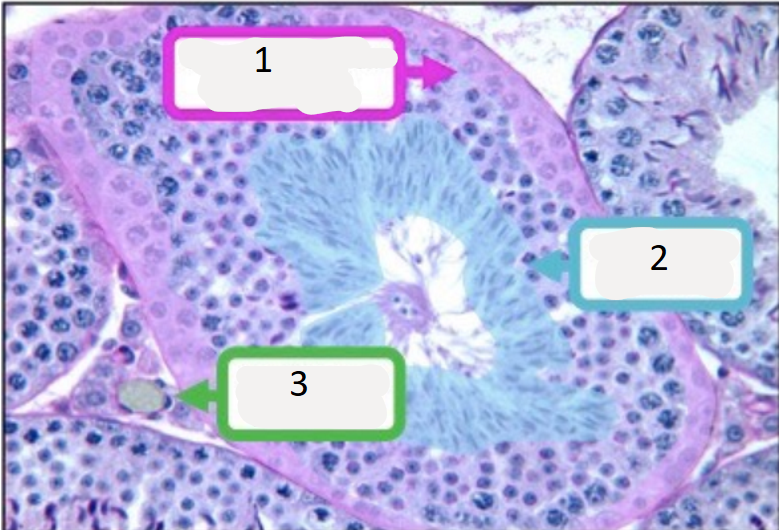
name number 2
spermatozoa
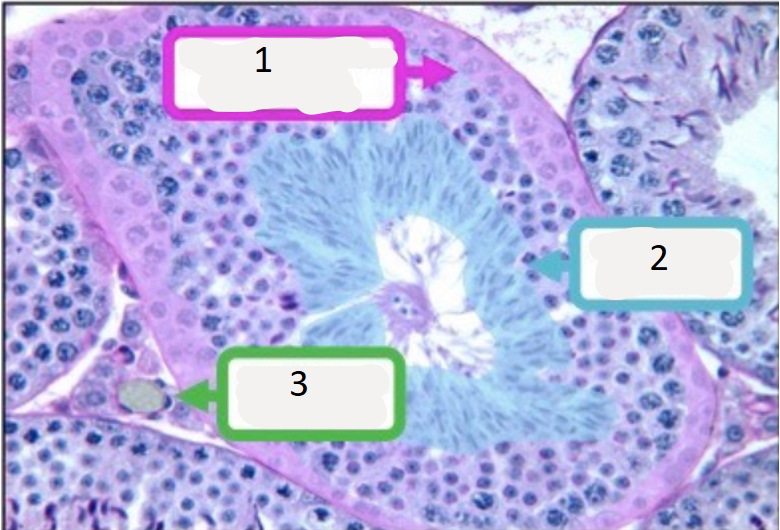
name number 3
interstitial cell
when does the stage of mitosis in oogenesis start
in foetal development; thousands of oogonia get produced before entering growth.
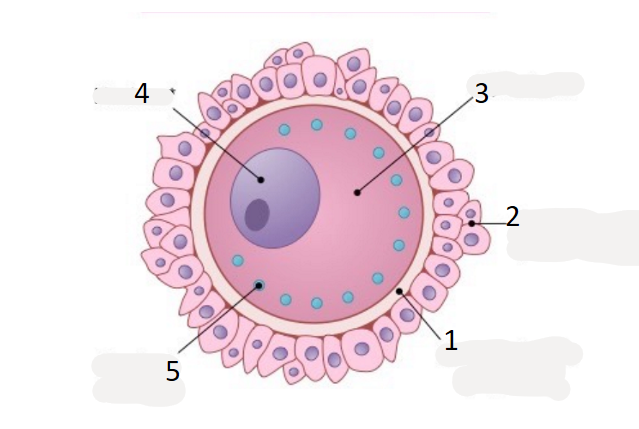
name 1
zona pellucida
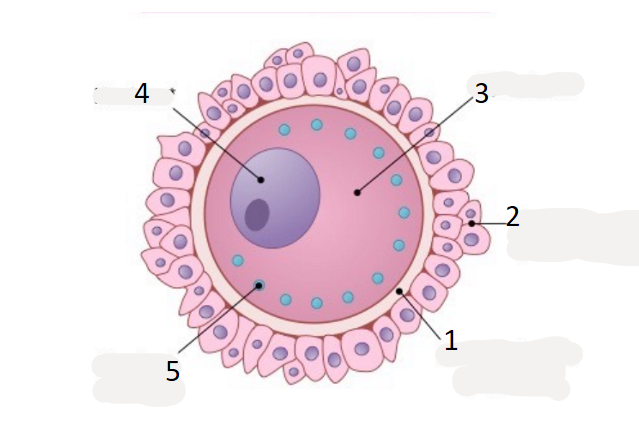
name 2
corona radiata
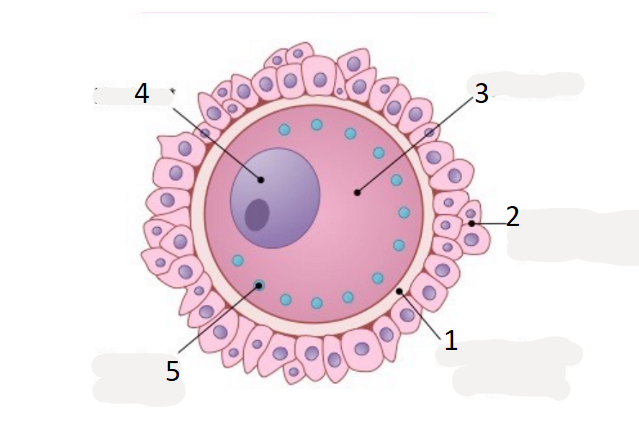
name 3
cytoplasm
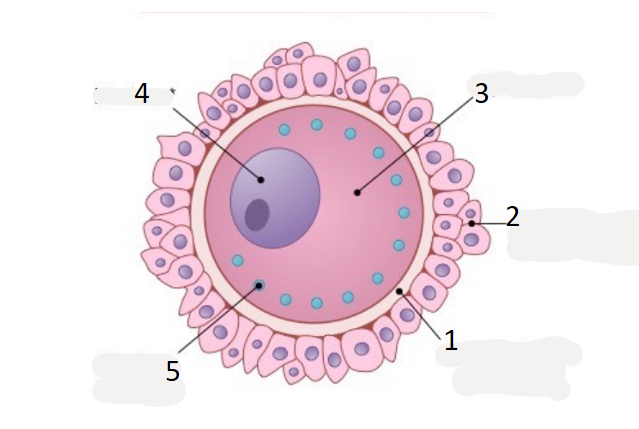
name 5
cortical granule
placenta: secretes: (1) and (2)
(1) stops (a) and develops (b)
(2) develops (a) and (b)
1) progesterone
a) contractions, b) endometrium
2) estrogen
a) mammary glands, b) myometrium
where does a blastocyst implant itself?
endometrium
what is the role of hCG during pregnancy
prevents the degeneration of the corpus luteum, until placenta develops.
After fertilisation, the zygote undergoes (1) to form a (2)
mitotic divisions
morula
trophoblast
part of the blastocyst that develops into the placenta.
where does the development of a blastocyst occur
fallopian tube
what happens after a blastocyst gets implanted into the endometrium
it secretes hCG
describe the process of fertilization
enzymes make acrosome unstable
uterine chemicals dissolve sperms cholesterol coat
acrosome releases enzymes to soften jelly coat