MICROPARA (15): Nonspecific Host Defense Mechanisms in Microbiology
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Ability to ward off disease
Capacity of an organism to defend itself against a disease/withstand the
effects of a harmful environmental agent.
Resistance
non specific defense mechanisms
first line of defense and second line of defense
first line of defense
- skin
- mucous membranes
- secretion of skin and mucous membranes
second line of defense
- phagocytic white blood cells
- antimicrobial proteins
- the inflammatory response
specific defense mechanisms (immune system)
third line of defense
- lymphocytes
- antibodies
Defenses that protect against all
pathogens.
Non specific Defense Mechanisms
Protection against specific
pathogens.
Specific Defense Mechanisms
Vulnerability or lack of resistance. The state of being predisposed to, sensitive to, or of lacking the ability to resist a pathogen, familial disease, or a drug.
Susceptibility
Non-specific natural barriers which restrict entry of pathogen.
First Line of Defense
skin and mucous membranes
Innate non-specific immune defense provide rapid local response to pathogen after it has entered host.
Second Line of Defense
Ex: Fever, phagocytes (macrophages
and neutrophils), inflammation, and
interferon.
Antigen specific immune responses, specifically target and attack invaders that get past first two lines of defense.
Third Line of Defense
Ex: Antibodies and Lymphocytes.
Proteins produced by the immune system to identify and neutralize pathogens.
Antibodies
A type of white blood cell that is part of the immune system.
Lymphocytes
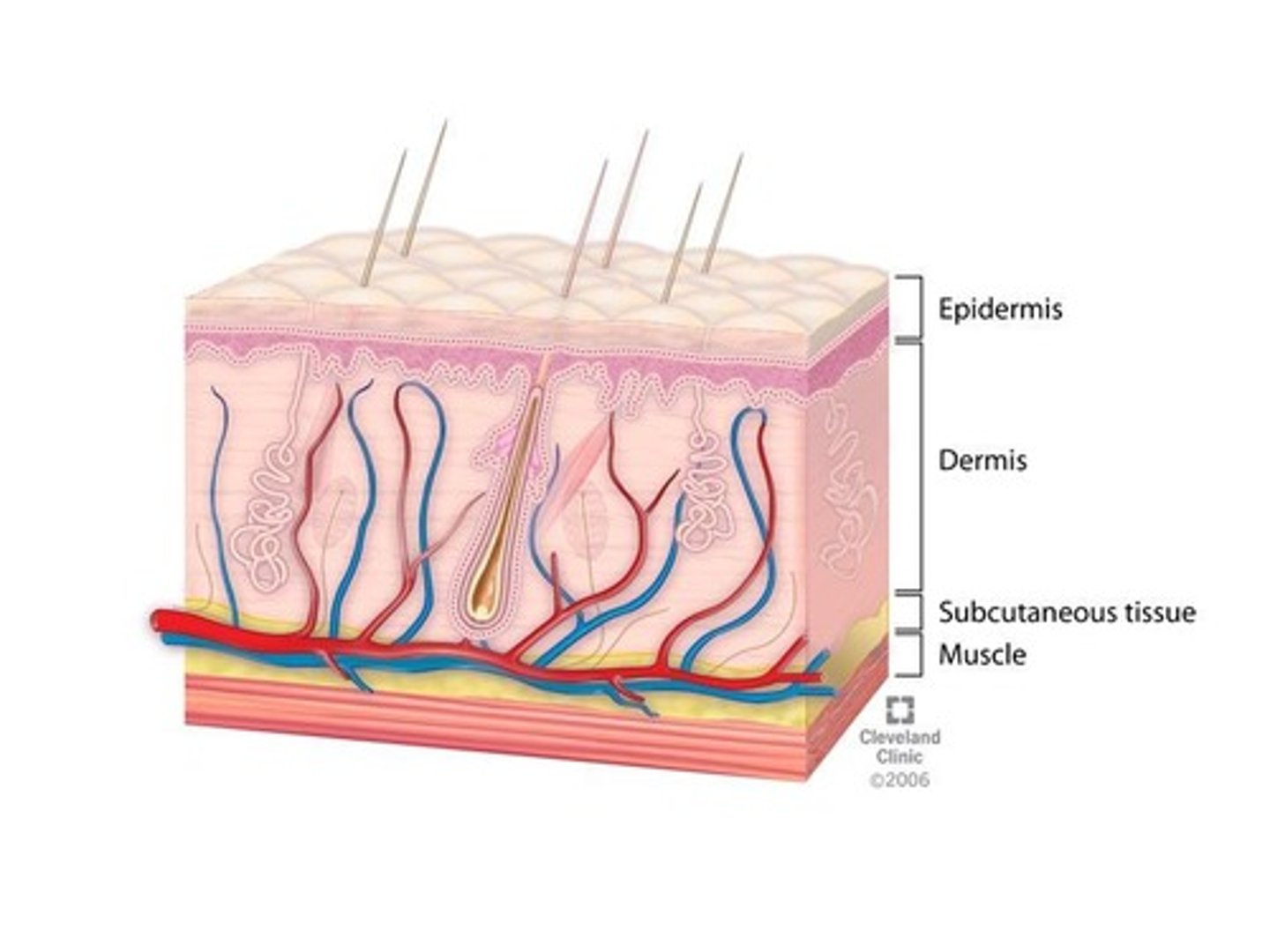
Thin outer layer of epithelial tissue that contains Langerhans cells, dead cells, and keratin (waterproof).
Epidermis
Thick inner layer of connective tissue where infections are rare in intact skin.
Dermis
"skin loving" fungi
dermatophytes
Line gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and respiratory tracts.
Mucous Membranes
secretes mucus which maintains moist surfaces.
epithelial layer
virus that cause HPV
papillomavirus
a microaerophilic, gram-negative, spirochaete bacterium with subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel, and yaws.
treponema pallidum
Continual washing and blinking prevents microbes from settling on the surface.
Lacrimal Apparatus
Washes microbes from teeth and mouth mucous membranes.
Saliva
Thick secretion that traps many microbes.
Mucus
Coated with mucus to filter dust, pollen, and microbes.
Nose Hair
Cilia on mucous membranes of lower respiratory tract move upwards towards throat at 1-3 cm/hour.
Ciliary Escalator
Expel foreign objects.
Coughing and Sneezing
Covers larynx during swallowing, protecting the respiratory system from infections.
Epiglottis
mechanical defense
1. Skin
2. Mucous membrane
3. Lacrimal Apparatus
4. Saliva
5. Mucus
6. Nose hair
7. Ciliary Escalator
8. Coughing and Sneezing
9. Epiglottis
Chemical Defense
1. Sebum
2. pH
3. Perspiration
4. Lysozyme
Oily substance produced by sebaceous glands that forms a protective layer over skin.
Sebum
sebum contains these that help inhibit growth of certain pathogenic bacteria and fungi
unsaturated fatty acids
Low, skin pH usually between 3 and 5, caused by lactic acid and fatty acids.
pH
Produced by sweat glands and contains lysozyme and acids.
Perspiration
Enzyme that breaks down gram-positive cell walls, found in nasal secretions, saliva, and tears.
Lysozyme
Derived from the Greek words 'Eat and cell'.
Phagocytosis
> macrophages
> occasionally eosinophils
> neutrophils
Phagocytic cells that originated from monocytes that leave blood and enter infected tissue.
Macrophages
White blood cells that predominate early in infection.
Neutrophils
Occasionally involved in phagocytosis.
Eosinophils
stages of phagocytosis
1. Chemotaxis
2. Adherence
3. Ingestion
4. Digestion
Phagocytes are chemically attracted to the site of infection.
Chemotaxis
Phagocytes' plasma membrane attaches to the surface of pathogen or foreign material.
Adherence
Coating process with opsonins that facilitates attachment.
Opsonization
Includes antibodies and complement proteins.
Opsonin
Plasma membrane of phagocytes extends projections (pseudopods) which engulf the microbe.
Ingestion
The sac in which a microbe is enclosed during phagocytosis.
Phagosome
Inside the cell, phagosome fuses with lysosome to form a phagolysosome.
Digestion
The structure formed when a phagosome fuses with a lysosome.
Phagolysosome
Kill most bacteria within 30 minutes.
Lysosomal enzymes
after digestion, these undigestible material are discharged
residual body
Triggered by tissue damage due to infection, heat, wound, etc.
Inflammation
Function of Inflammation
1.Destroy and remove pathogens.
2. If destruction is not possible, to limit
effects by confining the pathogen and its
products.
3. Repair and replace tissue damaged by
pathogen and its products.
Characterized by major symptoms such as redness, pain, heat, swelling, and loss of function.
Acute Inflammation
major symptoms of inflammation
local manifestation:
systematic manifestaton:
local manifestation:
1. redness
2. pain
3. heat
4. swelling
5. loss of function
systematic manifestation:
1. fever
2. chills
3. myalgia
4. malaise
A type of inflammation that produces a serum-like exudate.
Serous Inflammation
Inflammation of mucous membranes in an airway or cavity of the body.
Catarrhal Inflammation
a type of inflammation that occurs when fibrinogen escapes from an injury and is converted to fibrin.
Fibrinous Inflammation
a type of inflammation that is characterized by a large number of erythrocytes in the exudate.
Hemorrhagic Inflammation
When pus is produced as a result of inflammation.
Suppurative Inflammation
A serious condition that occurs when pus builds up in a body cavity.
Emyema
A chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation in the large intestine and rectum.
Ulcerative Colitis
Can occur in a variety of internal organs, including the gallbladder, bile duct, pancreas, lungs, kidneys, and eyeballs.
Gangrenous Inflammation
A severe inflammation of the large intestine's inner lining caused by an overgrowth of Clostridioides difficile.
Pseudomembranous Colitis