Logistic Growth
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
open populations grow when
b + i > d + e (inputs > outputs)
_______ assumes that density dependent factors limit exponential rates of growth (r is not constant)
logistic equation
________ factors include any factors whose effects become stronger as crowding within a population increases
density dependent
population size is limited at the _______ of the envr
carrying capacity
carrying capacity ____ a stable equilibrium around which pop size will stabilize
is
true or false: carrying capacity changes with varying environmental conditions and is rarely constant
true
all natural populations exhibit pop regulation. The relative importance of DD and DI regulations will depend on the _______ of the species and the _____ and _____ of environmental variation
life history strategy, frequency, intensity
what factors reduce inputs relative to outputs
biotic interactions among organisms (competition, predation)
abiotic fluctuations in environmental conditions (temp)
density dependent
intensity of reduction is related to the density of individuals
density independent
intensity of reduction is unrelated to the density of individuals
biased - reduced fitness
unbiased - random mortality
what factors limit population growth (b, d, r) as population size increases (at higher N)
intraspecific competition increases (limited food/habitat)
predator density increases (higher risk of predator)
parasite density (higher risk of parasitism)
disease (higher rate of disease transmission)
density dependence may
reduce growth, survival and reproduction of inds in a pop, thereby affecting pop growth through b and d (r ) with increased crowding
logistic model of population growth-primary underlying assumption
factors limiting population growth exert stronger effects on b and d as a population grows (population growth is density dependent)
due to density dependence, we should expect ____ to vary with ___
r (=b-d), N
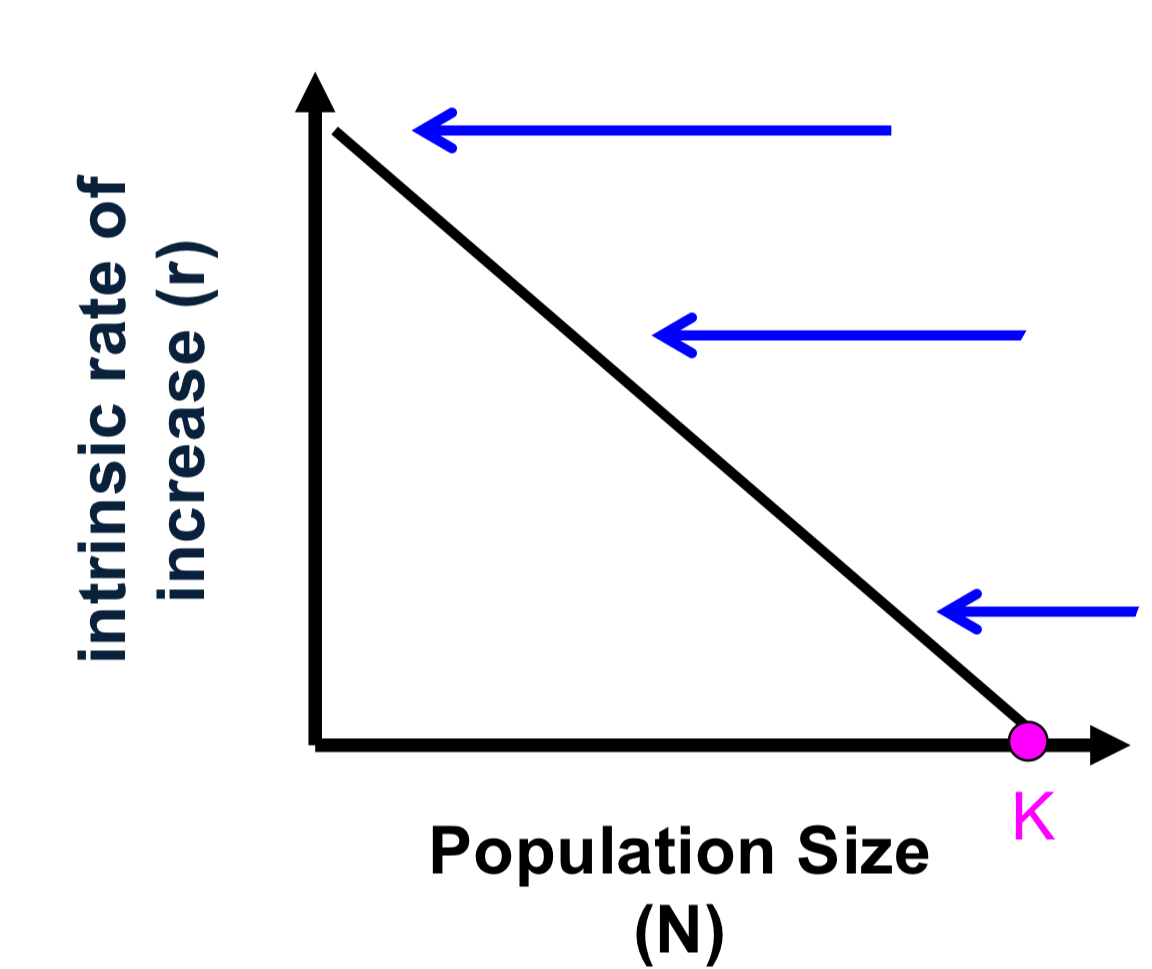
explain the top arrow to the bottom
r is highest at low N (no/low competition: b is high, d is low)
r decreases as N increases (competition increases: b decrease, d increase)
r is lowest at high N (competition increases: b ~ d)
when N=K, r=0 (b=d)
carrying capacity
(K), population size that the envr can carry or support
exponential equation
dN/dt=rN
logistic equation
dN/dt = rN (1- N/K)
the logistic model doesn’t represent the ______ dynamics of natural pops, it represents the ______ dynamics of natural pops
quantitative, qualitative
population sizes below K _____ towards K
increase
population size above K ____ towards K
decrease
density dependent factors …
tend to bring populations under control and maintain their size close to K
caused by biotic factors (competition, predators, parasites, disease)
density independent factors…
tend to reduce populations far below K and initiate periods of population recovery
caused by abiotic factors (temp, water)
density independent ex: thrips
explain thrips during the spring, summer and winter
density independence
spring: ideal for flowering - high resource abundance and mild climate so increased b, decrease d - large N increase
summer: hot and dry - high d due to extreme heat and low water - large N decrease
winter: cool and rainy - low b due to cooler temps - stable N
*thrips - population size mirrors what
seasonal changes in weather
the relative importance of D-D and D-I factors will depend on:
intensity and frequency of environmental (abiotic) fluctuations (life history characteristics of the population/species)
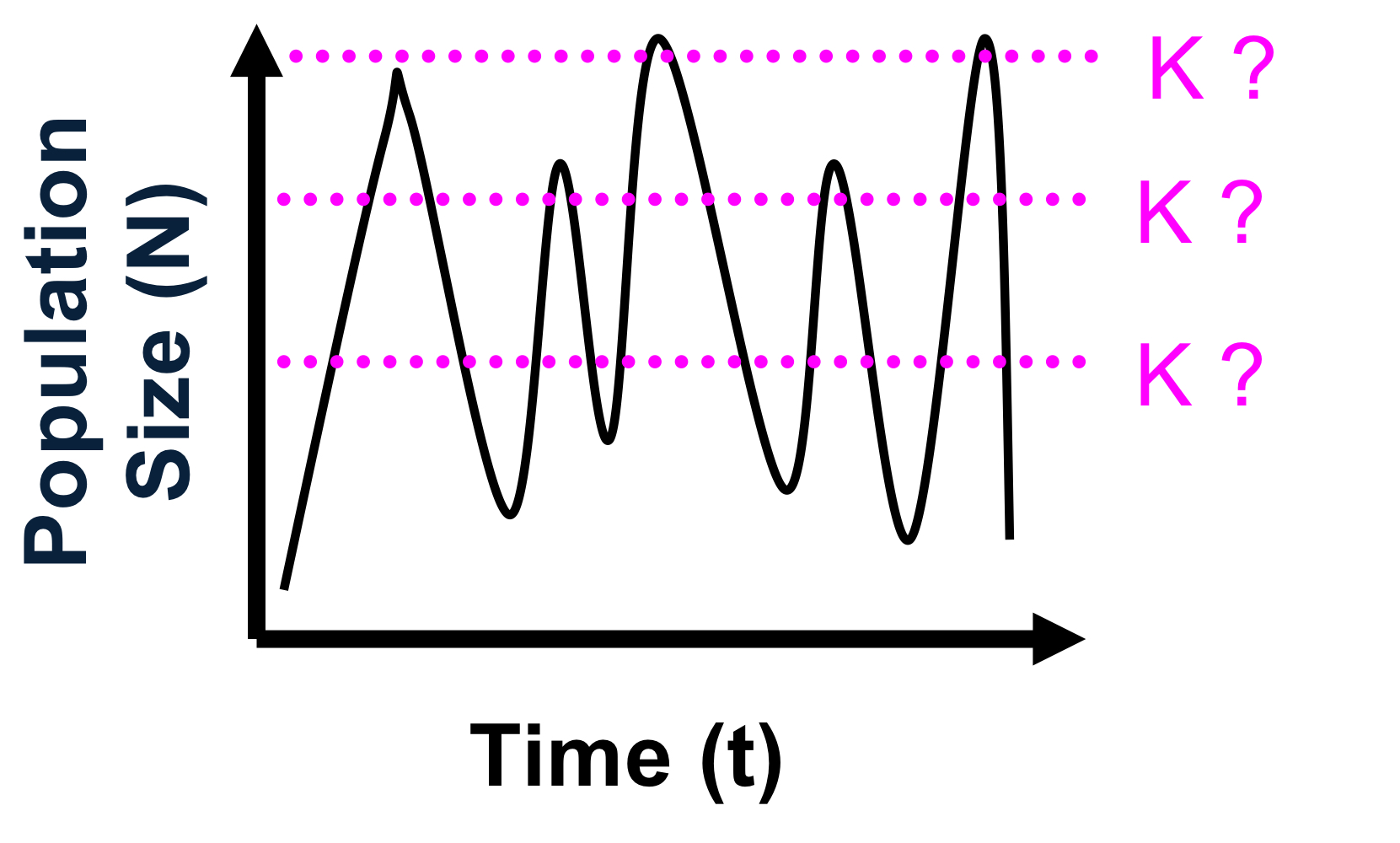
explain the graph
frequent and extreme environmental fluctuations
r selected
mechanism of regulation: density independent
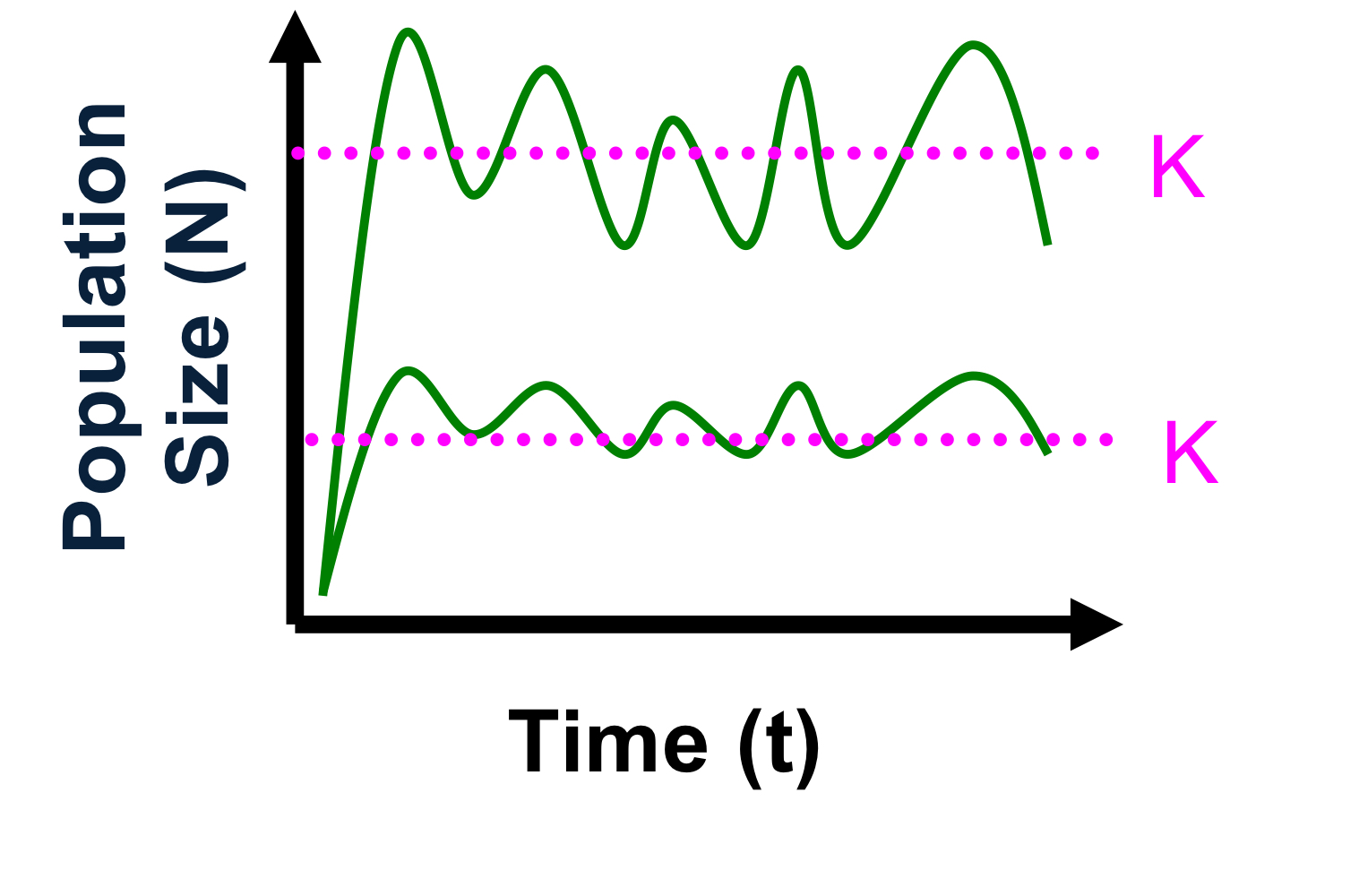
explain the graph
infrequent and mild environmental fluctuations
k selected
mechanisms of regulation: density dependent