ECONOMIC ACTIVITY AND ENERGY
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
What are the 4 economic sectors
Primary, secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
What’s the primary sector and give some examples
-the growth or extraction of raw materials e.g. farming, fishing, mining
what’s the secondary sector and examples
raw materials are processed and turned into a finished product. e.g. manufactory, chemistry
what’s the tertiary sectors and give examples
involves providing services to others/consumers or selling products/goods. e.g. banks, teachers, healthcare, transport
what’s the quaternary sector and give examples
knowledge- based, involves provision of specialist, research and development. e.g. scientists, technology, astronauts
what are an economic sectors a indicator of for a country
indicator of a country’s economic development
what does GDP stand for
gross domestic product
what does the Clark fisher model show
shows changes in the UK economy over time
what three phases are there in time
pre-industrial, industrial (industrial revolution) and post-industrial
what’s the sectors like in the preindustrial period
primary sector dominates with steady increases in secondary and tertiary
what’s the sectors like in the industrial period
Secondary sector increases and becomes dominant with primary sector decreasing and tertiary sector increasing
what are the sectors like in the post industrial phase
tertiary and quaternary sectors increase whilst secondary and primary decrease. Tertiary sector dominates.
why was the primary sector so high in the pre-industrial phases
food supplies where dependent of domestic production and due to lack of mechanisation this made farming the main activity
why did primary sector fall in the industrial phase
as more jobs became available in manufacturing due to mechanisation causing people to move to urban areas where they would get paid more
why was the primary sector so low in post industrial
secondary and tertiary where the main jobs that provided more money than primary jobs
why was secondary sector low in pre-industrial phase
on its way to increase but primary was the main sector due to not enough manufacturing jobs
why did secondary sector begin to increase in the industrial phase
increase mechanisation lead to more jobs forr secondary
Why did secondary sector decline in post industrial phase
Margret thatcher privatised state industries and sold them, leading to deindustrialisation and due to improved technology it meant there was an increase in tertiary and quaternary sectors.
why was tertiary so high in the post industrial phase
as national corporation are increasing in size and power it causes tertiary to increase
what did the post industrial mean for the UK
when manufacturing industry declined and was replaced by growth in service sectors and development in quaternary due to new technology
when did the post industrial phase begin
in 1970s
what was the UK the first country to experience
Industrial revolution
what where the 4 main things during post industrial phase in UK
development of ICT, growth of service industries, finances and research and an increase in quaternary sector
what did development of ICT mean
faster computers, improved internet access, new IT businesses manufacturing hardware and designing software
what did the growth of service industries mean
service/tertiary sector makes up 80% of UK economy, there’s a range in jobs, UK is the second largest exporter of services globally
what does increase in finances and research mean
more financial jobs e.g. accountancy, banking etc. Science and research takes place through government research councils such as university’s
what does deindustrialisation mean
is the decline in the manufacturing industry and the subsequent growth in tertiary and quaternary.
why did deindustrialisation happen
because of machines and technology that replaces peoples jobs and other countries can produce cheaper goofs as labour is less expensive.
what’s some positive impacts of deindustrialisation
improvements in the environments and decreased levels of pollution
developed expertise on secondary and tertiary economic activities
negative impacts of deindustrialisation
led to high numbers of job losses particularly in the north of UK
lead to areas of deprivation especially in inner cities e.g. Liverpool
increased numbers of transnational corporations (TNCs) have moved factories and offices to emerging and developing countries
what is globalisation
the growth and spread of ideas around the world becoming more involved with each other
How have the UK’s government policies changed overtime
1945-1979= created state-run industries e.g. British rail, Government money was spent on propping up declining industries and giving money into country
1979-2010=state run industry’s were sold to private shareholders, privatisation- companies closed down and sold.
2010=rebalance the economy, stabilising manufacturing, easier to access loans
what are factors that effect employment
availability of raw materials
globalisation
technology
demographic changes
government policies
why do changes in employment sector changes in countries
as countries develop the number of people employed in each sector changes which can be shown in the Clark fisher model and Pie charts
what type of countries is Kenya, Germany and China
China=emerging country
Kenya=developing country
Germany=developed country
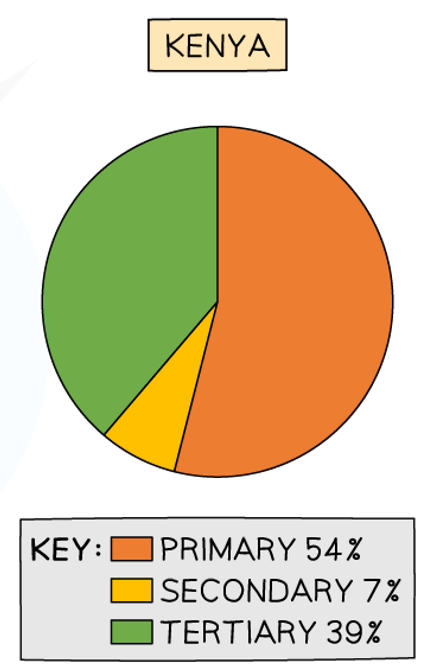
why does Kenya’s employment look like this
significant percentage of people in rural populations are farmers and are dependent on raw material exports to developed and emerging countries
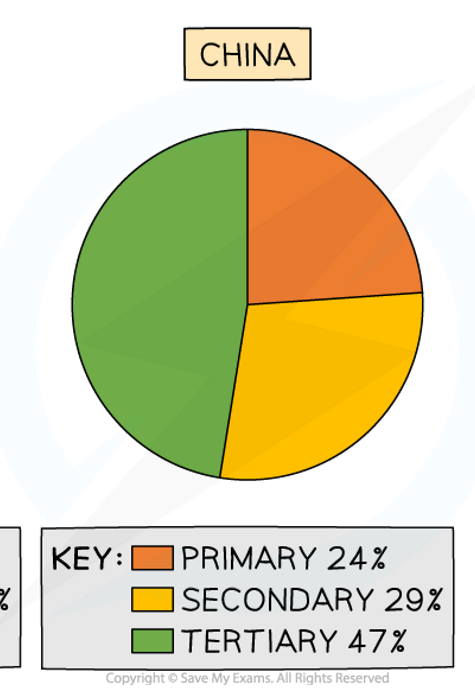
why does China’s employment look like this
more materials may be available in these countries -secondary section
factories are located in emerging counties due to lower costs
government aim to attract companies to locate here
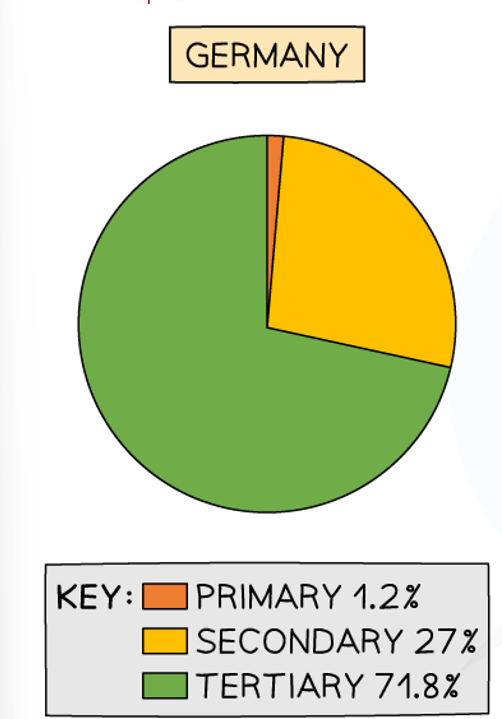
why is Germany’s employment like this
deindustrialisation means fewer jobs in secondary sector
mechanisation means fewer jobs in primary and secondary
tertiary has higher pay and education levels are higher so more people want tertiary jobs
how does availability of raw material effect employment
may have run out/ be unavailable
crop production + livestock may be reduced due to drought, flooding and disease
improvement in technology may reduce amount of raw materials needed
How does Globalisation effect employment
lower costs tend to be in developing + emerging countries
TNC have factories in many country’s
industries such as textiles + steel manufacturing are increasingly located in emerging countries
internet allows improved communication around the world
How does Technology effect employment
fewer jobs in primary and secondary due to mechanisation
internet means companies can manage factories in different countries
how does demographic changes effect employment
increase in population means greater demand for product + services
people may have more disposable income to spend
increase in pop means more workers available
how does government policies effect employment
targets particular economic activities to locate in their countries using tax incentives, infrastructure improvements and grants/cheap rent
international treaties impact what countries can trade
what are the physical factors that effect location
raw materials
land
energy
climate
what are the human factors that effect location
capital
transport
market
labour
government
what factors effect primary sectors and why
land- amount of land available, costs, soil type and resources
market- some crops need to be very close to market e.g. strawberries
labour- fewer workers needed due to mechanisation (developed countries)
government policies - whether subsidies are available
transport- access to roads for transport of crops, animals and materials
climate- precipitation, sunshine and temperatures effect type of crop +livestock grown
What factors effect location of secondary sectors
Raw materials - How close the activity needs to be to raw materials and the types of raw materials will depend on the industry
Land - Large areas of land are often required for factories, so the cost and amount of the land are important
Market - Access to the market is important to be able to sell the goods made
Government policies - Tax incentives, grants, and loans may be available if the economic activity is located in a particular area
Energy - A power source is needed; this used to be coal or water, Energy is now provided by electricity, which can be accessed in many areas
Transport - Access to roads is essential to bring in raw materials and send out the product
what factors effect the location of tertiary sectors
Land - The amount of land depends on the type of economic activity; large retail parks need lots of land
Market - Needs to be close to the customers or service users
Energy - A power source is needed—electricity, which can be accessed in many areas
Labour - Workers needed both skilled and unskilled
Transport - It needs to be accessible for customers, workers and in the case of retail, to bring in the products
what factors effect location of quaternary sectors
Land -Science parks need large areas of land, usually near a university on the rural-urban fringe
Energy - A power source is needed—electricity, which can be accessed in many areas
Labour - Skilled labour is needed, often university graduates
Transport - Needs to be accessible to the workers
what is informal employment
any employment which is unregulated and unofficial also called the ‘grey economy’ , 60% of employment in the world is informal
what are the causes of informal employment
people want to avoid taxes
high levels of rural to urban migration leading to more people than jobs available
lack of qualifications/ doesn’t require certain skills or education
flexible hours to fit around family
costs less to set up
low wages in jobs means people need additional jobs to make enough money
what are the impacts of informal employment
no health care benefit, no sick pay or holiday, no guaranteed pay and exposed health and safety risks
paratransit cause congestion and pollution
children may be exposed too health risks, drugs, violence and crime and don’t have opportunity to go to school
workers often exploited by employers
government collect less in tax
what case study are we doing for informal employment
Dhaka, Bangladesh
what are the main types of informal employment in Dhaka
rickshaw drivers
day labourers in construction
waste related workers
workers in small workshops
casual workers in restaurants and hotels
give some background information about Dhaka
is a megacity with population of 22.5 million people
75% population engage in informal employment
690,000 children in Dhaka are involved in informal employment
most informal workers live in informal settlements
What are the characteristics of Dhaka’s informal sector
no training
low pay
long working hours
underemployment
no benefits e.g. healthcare, sick pay
poor/unhealthy working conditions
health and safety risks
exploitation of employers
no legal protection
what does all economic activity involve the use of what two things
resources and energy
the rate at which resources and energy are use up depends on what two factors
population size
rate of development
what is overpopulation
when there are too many people or too few resources to ensure a high standard of living
what is underpopulation
when the population is too small to develop the resources effectively
what is population pressure
occurs when the population is greater than the carrying capacity
what is innovation
new inventions that increase resource availability
population growth can exceed what…
can exceed the rate that resource availability grows
which two people came up with theories of the relationship between population and resources
Thomas Malthus and Ester Boserup
what are both theories concerned with
concerned with the relationship between population and resources
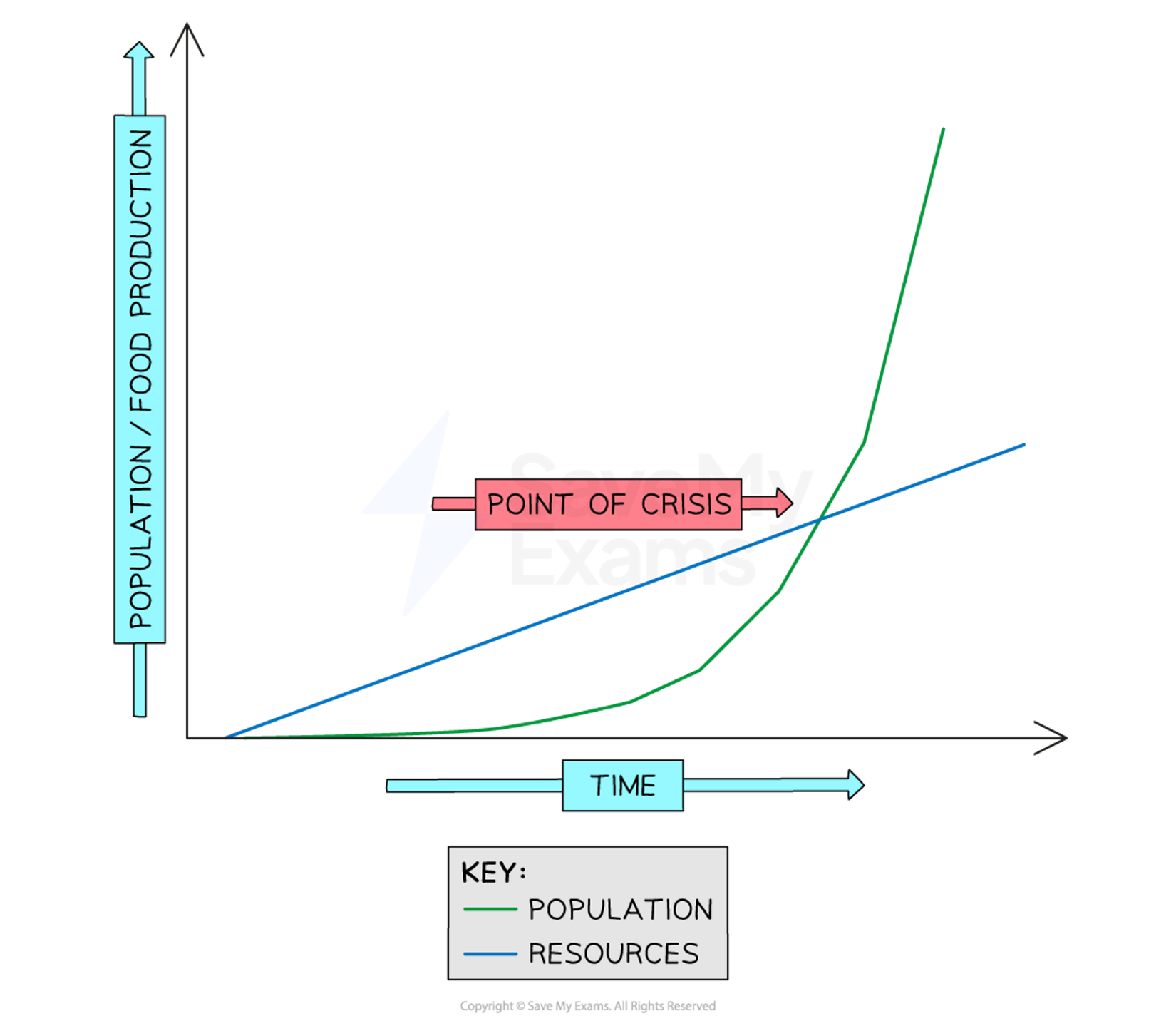
what is Thomas Malthus theory and who is he
-he is a British economist who developed a pessimistic (negative) view on population growth and resources (1766-1834)
-his main ideas where that population growth is increasing faster than the food supply and we cant sustain population so it will stops as a result of a Malthusian catastrophe - famine, disease, war/ death
-he states population growth at a geometric rate (2,4,8,16) and resource availability grows arithmetically (1,2,3,4)
-preventative checks- factors to decrease birth rate
-positive checks-what increases death rates
what is the modern perspective on Malthus views and what’s it called
Neo Malthusians argue that: we have now used most of the available agricultural land, amount of fertile land is in decline, food prices are increasing, population continues to increase suggesting that population control is essential to avoid Malthusian catastrophe
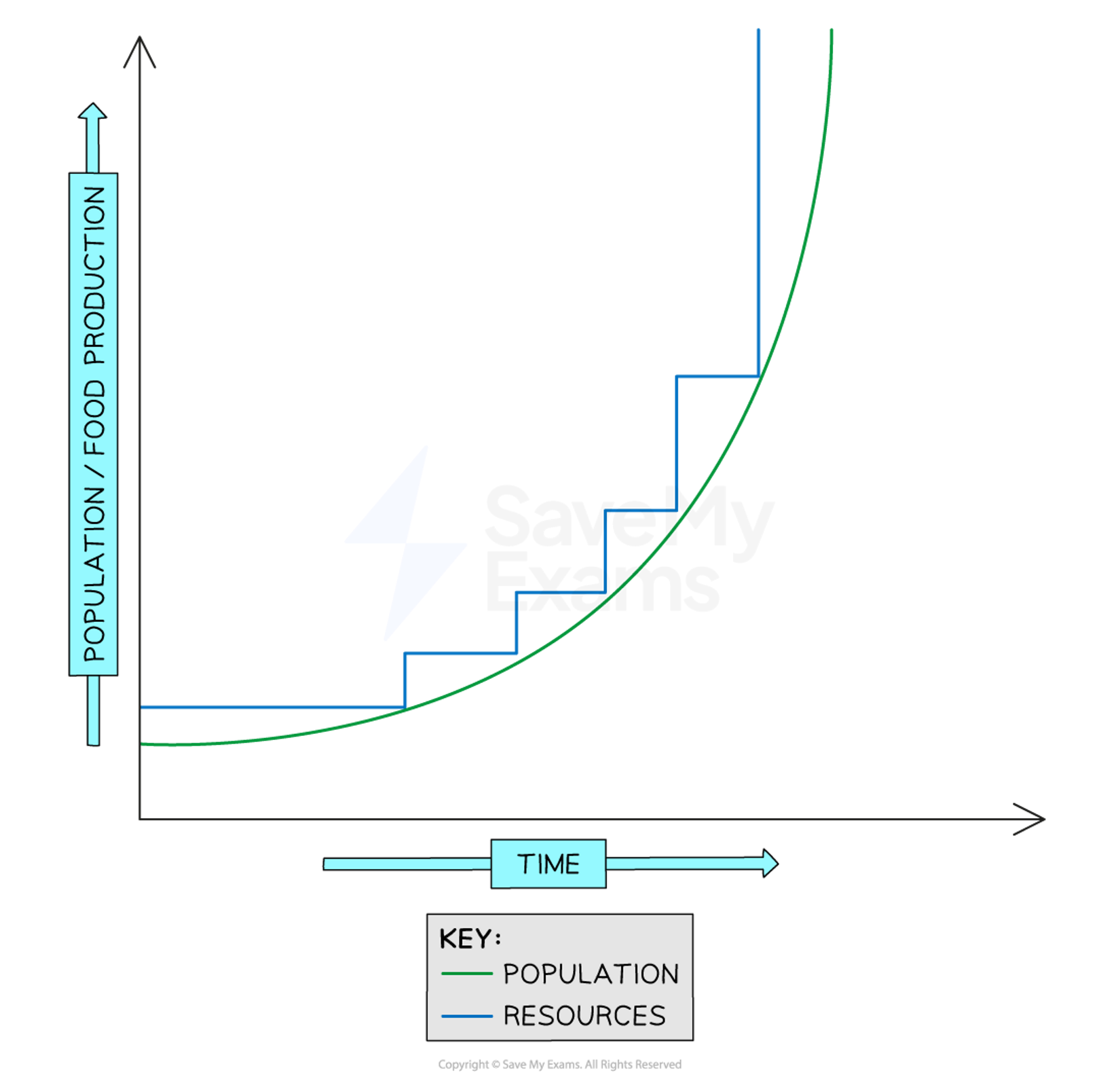
who is Ester Boserup and what was her theory
She was a Danish economist who believed in human innovation and adaptability- her view was optimistic
-born in 1910-1999
her key ideas where: population growth stimulates agricultural innovation and developments/inventions in technology to increase food supply. Renewable resources will replace non renewable resources. “necessity is the mother of invention”→ people are key resources and use brain power
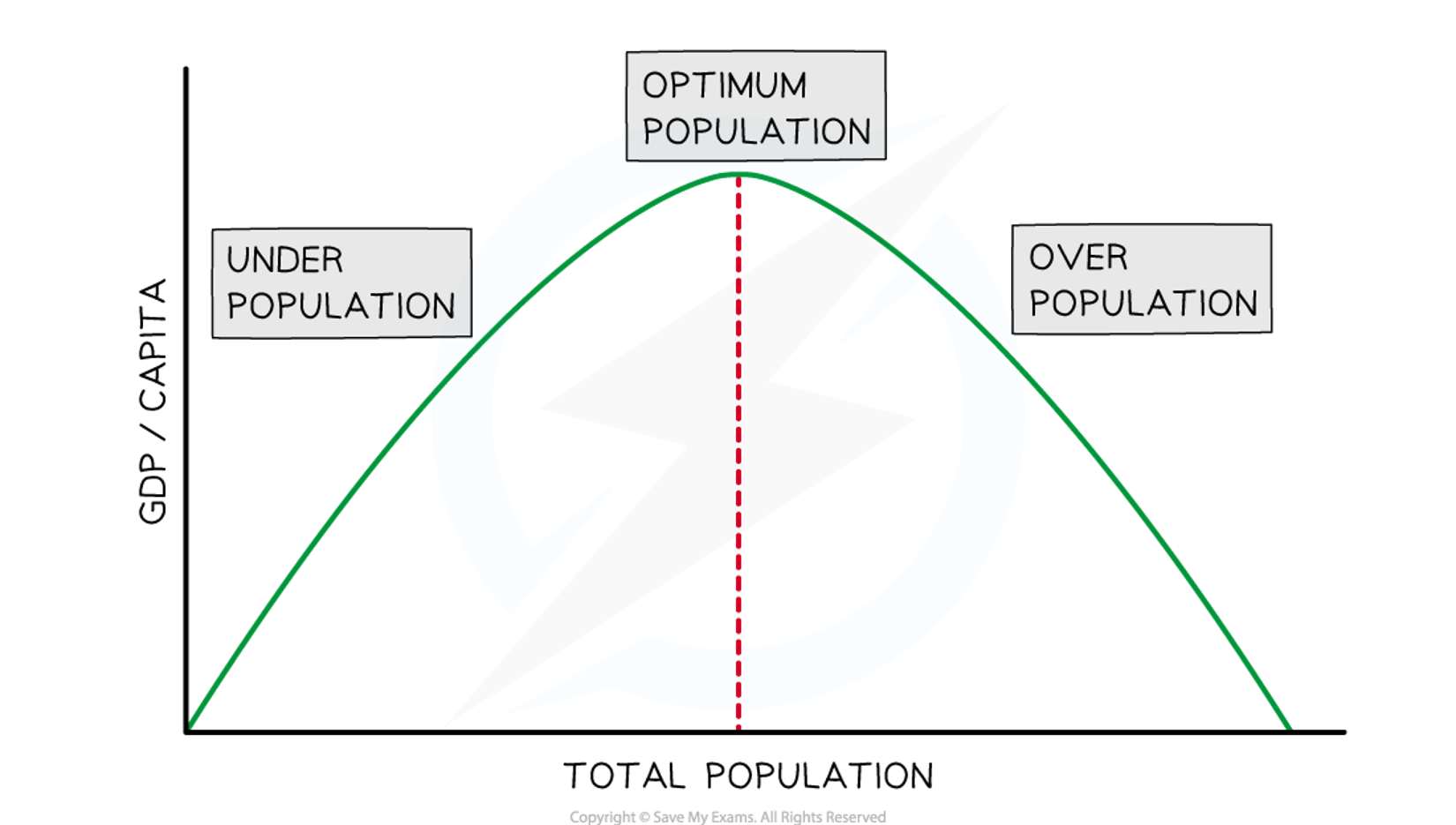
What does this graph show
optimum theory of population
what are the causes of increased energy demand
Population growth and development are the two main causes of the increase in energy demand:
The higher demand for food leads to more intensive farming which requires more energy for machines, light and heat
Increasing industry requires energy for heating, lighting and machinery
There is more transport all of which requires energy in the form of petrol, diesel or electricity
Urbanisation increases with development increasing domestic appliances, heating, lighting
Increased wealth means people buy more appliances and technology which require energy
what countries tend to have higher energy consumption
in developed counties such as Canada, Norway
what countries tend to have lower energy consumption
developing countries such as all if Africa, Chad
what is the main energy source and how much does it supply to the worlds primary energy
fossil fuels which supply 844% of worlds primary energy
how much renewable energy makes up the energy mix
11%
what is energy poverty
when people do not have access to modern energy supplies
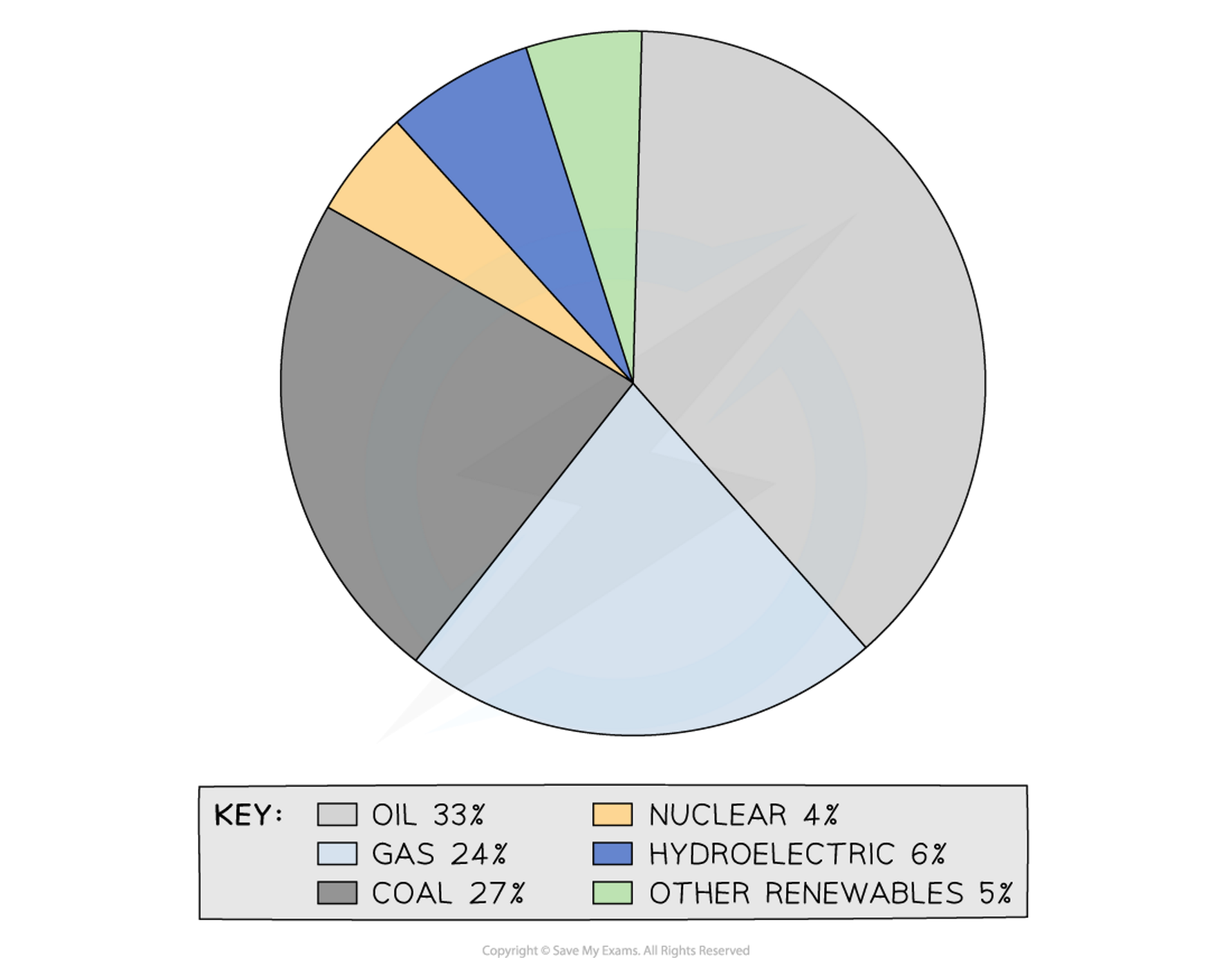
what does this pie chart show
shows the global energy sources/ consumption
what are some environmental concerns with the amount of energy consumed
non renewable sources link to pollution and global warming
impact of fossil fuels
why are energy sources not evenly distributed across the world
because some areas produce little energy due to lack of natural resources or do not have enough money to exploit the resources
what country’s are the main producers of fossil fuels for primary energy
USA, Canada, Norway, Russia, Middle East, Australia
what is an energy gap
energy gap is when a country cannot meet the demand for energy using its own resources
what do countries do when they have an energy gap
they have to import energy to meet their demand
what does having an energy gap mean for the country
means the country is not energy secure
what does a country need to be energy secure
uninterrupted/reliable supply of energy
accessible energy
affordable energy
why does the UK have a widening energy gap
renewable energy is not as efficient and so cant replace in full energy from fossil fuels
cheaper to import fossil fuels than to exploit the resources in the UK
what factors can affect energy security
war/conflict
energy sources running out
natural hazards
cost
political disputes
environmental concerns
give examples of non renewable resources
gas, oil, coal, nuclear
what are non-renewable resources
are unsustainable as at some point they will run out or the economic and environmental costs will become too high
give the advantages and disadvantages of Gas (non renewable)
Advantages |
|
Disadvantages |
|
give the advantages and disadvantages of oil
Advantages |
|
Disadvantages |
|
advantages and disadvantages for coal
Advantages |
|
Disadvantages |
|
advantages and disadvantages for nuclear
Advantages |
|
Disadvantages |
|
what are renewable energy resources
resources that are sustainable and will never run out
examples of renewable resources
Hydroelectric
Wave/tidal
Wind
Solar
Geothermal
Biomass/waste
advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric energy
Advantages |
|
Disadvantages |
|
advantages and disadvantages for wave/tidal energy
Advantages |
|
Disadvantages |
|
advantages and disadvantages of wind energy
Advantages |
|
Disadvantages |
|
advantages and disadvantages of solar energy
Advantages |
|
Disadvantages |
|
advantages and disadvantages of geothermal energy
Advantages |
|
Disadvantages |
|
advantages and disadvantages of biomass/waste
Advantages |
|
Disadvantages |
|
why is sustainable energy management essential
to ensure future generations are to have the energy resources they need
to limit climate change
