Cellular Energy Acquisition and Metabolism Overview, Energy Generation in Mitochondria: Oxidative Phosphorylation, Intracellular Compartments and Protein Transport Overview
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
Metabolism
Biochemical reactions extracting energy from food.
Activation Energies
Energy required to initiate chemical reactions.
Cellular Respiration
Catabolic process breaking down organic material.
Electron Transport Chain
Series of protein complexes generating ATP.
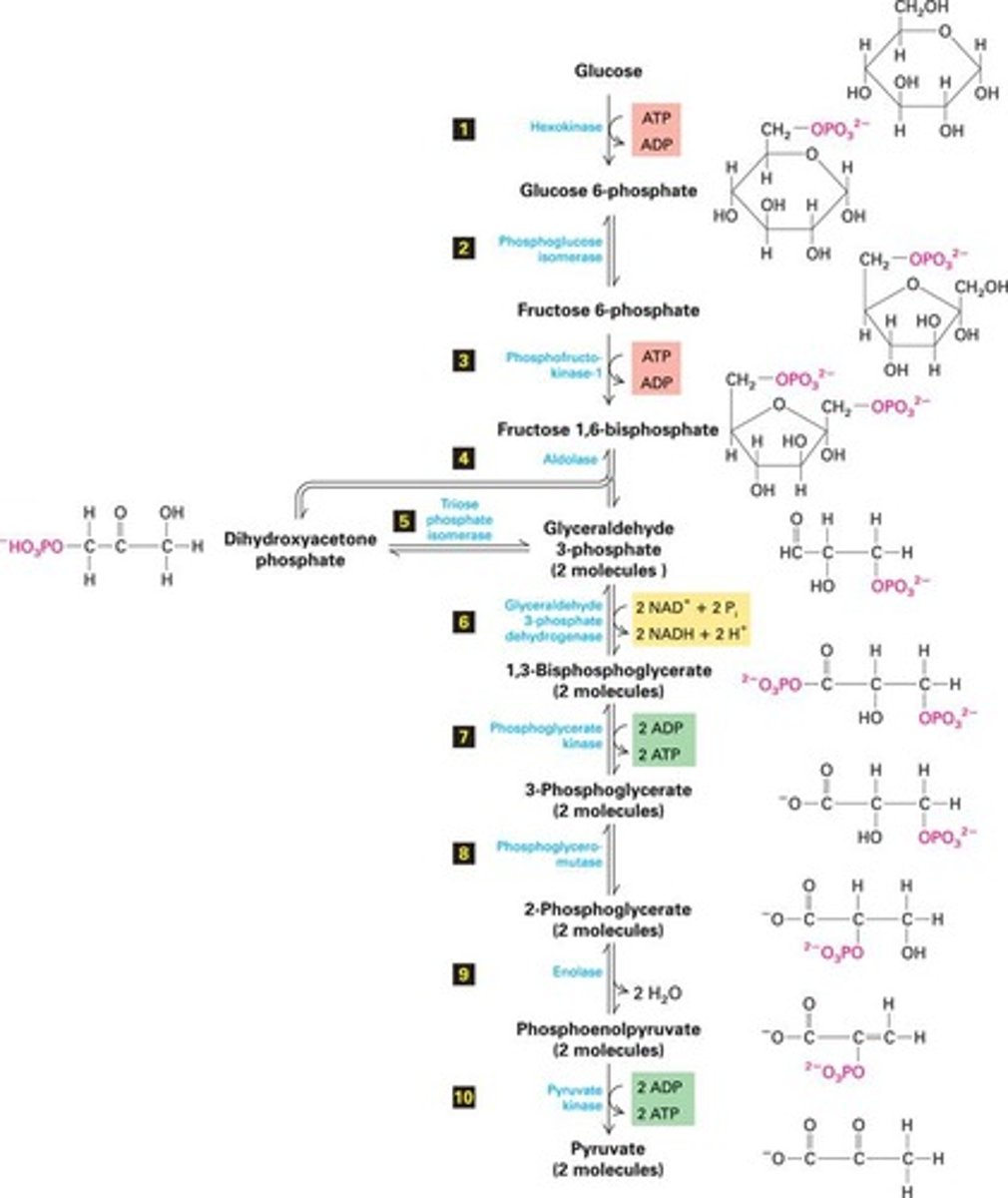
Glycolysis
First stage of sugar breakdown into pyruvate.
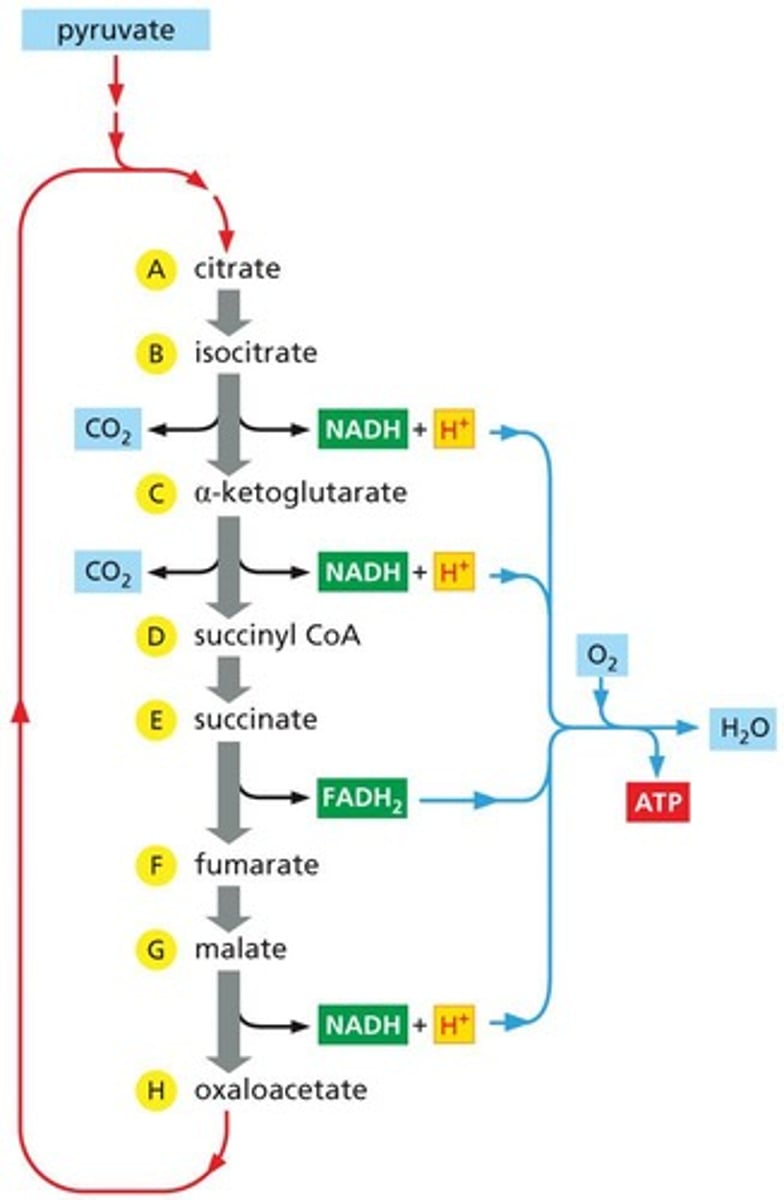
Citric Acid Cycle
Cycle producing GTP, NADH, and FADH2.
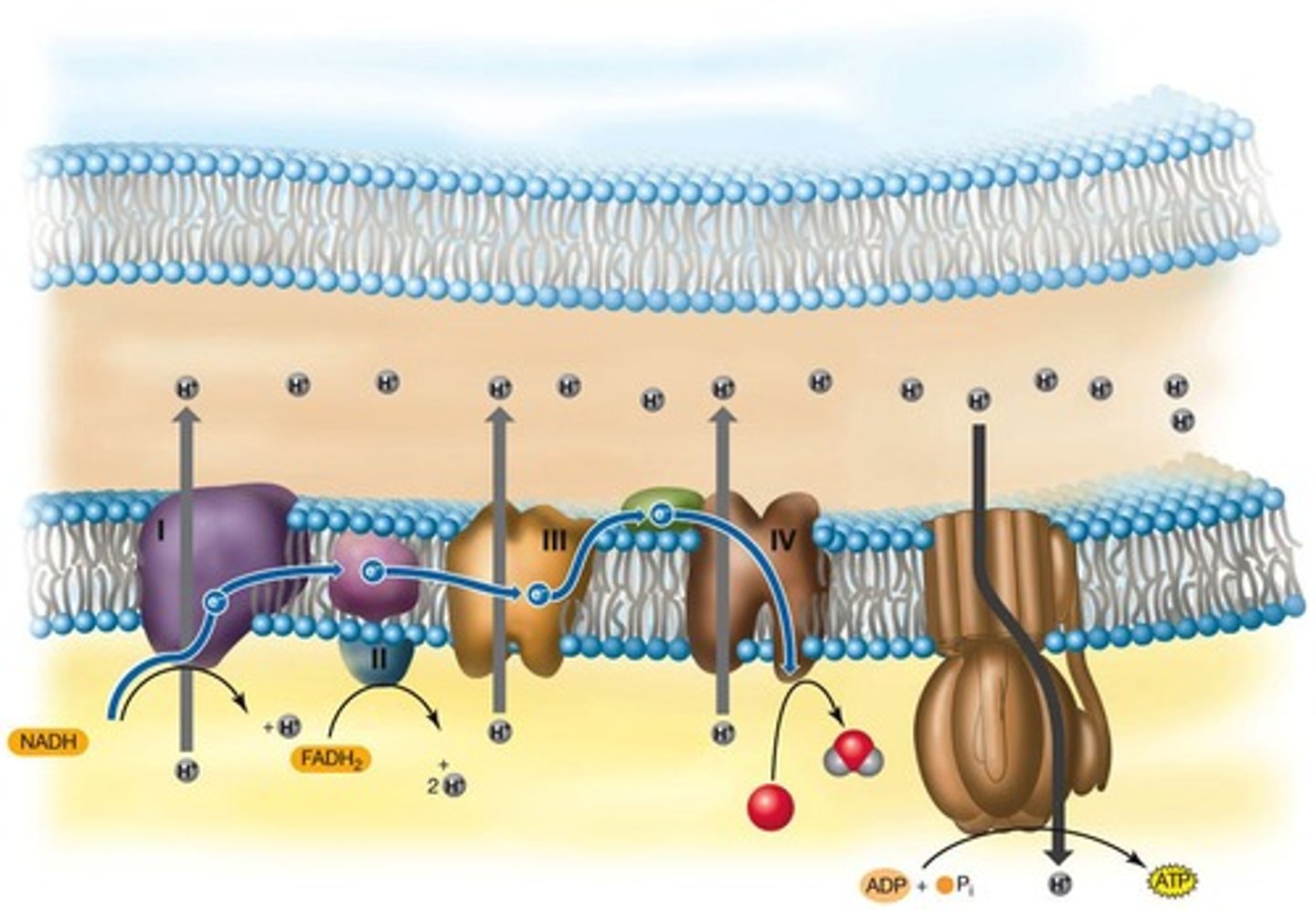
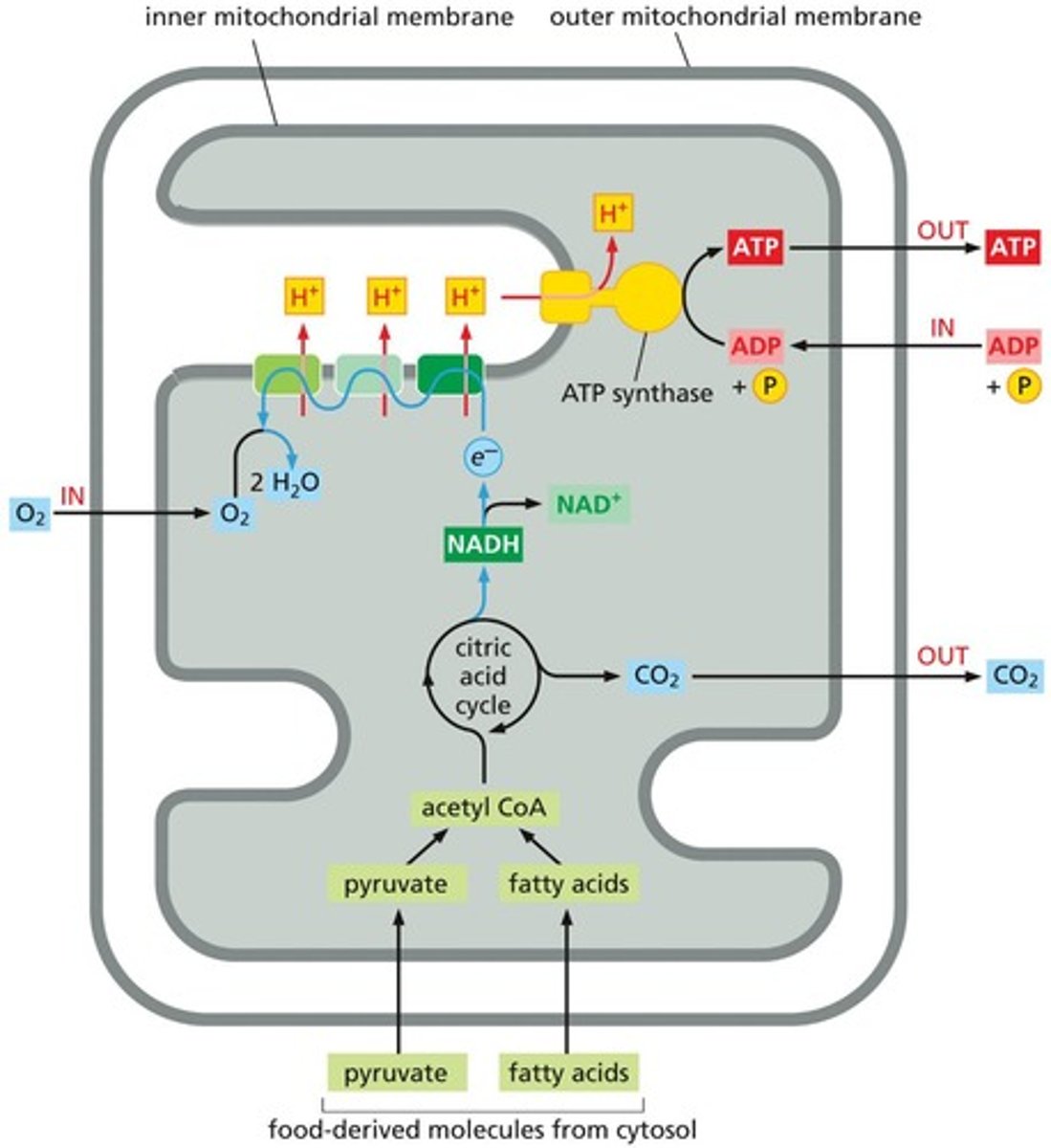
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ATP generation via electron transport and chemiosmosis.
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Direct ATP production from metabolic reactions.
Acetyl-CoA
Key molecule linking glycolysis to citric acid cycle.
Glycogen
Stored form of glucose in animal cells.
Gluconeogenesis
Synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
Energy Charge
Measurement of ATP, ADP, and AMP levels.
Feedback Regulation
Mechanism allowing cells to switch metabolic pathways.
Glycogen Synthase
Enzyme promoting glycogen synthesis from glucose.
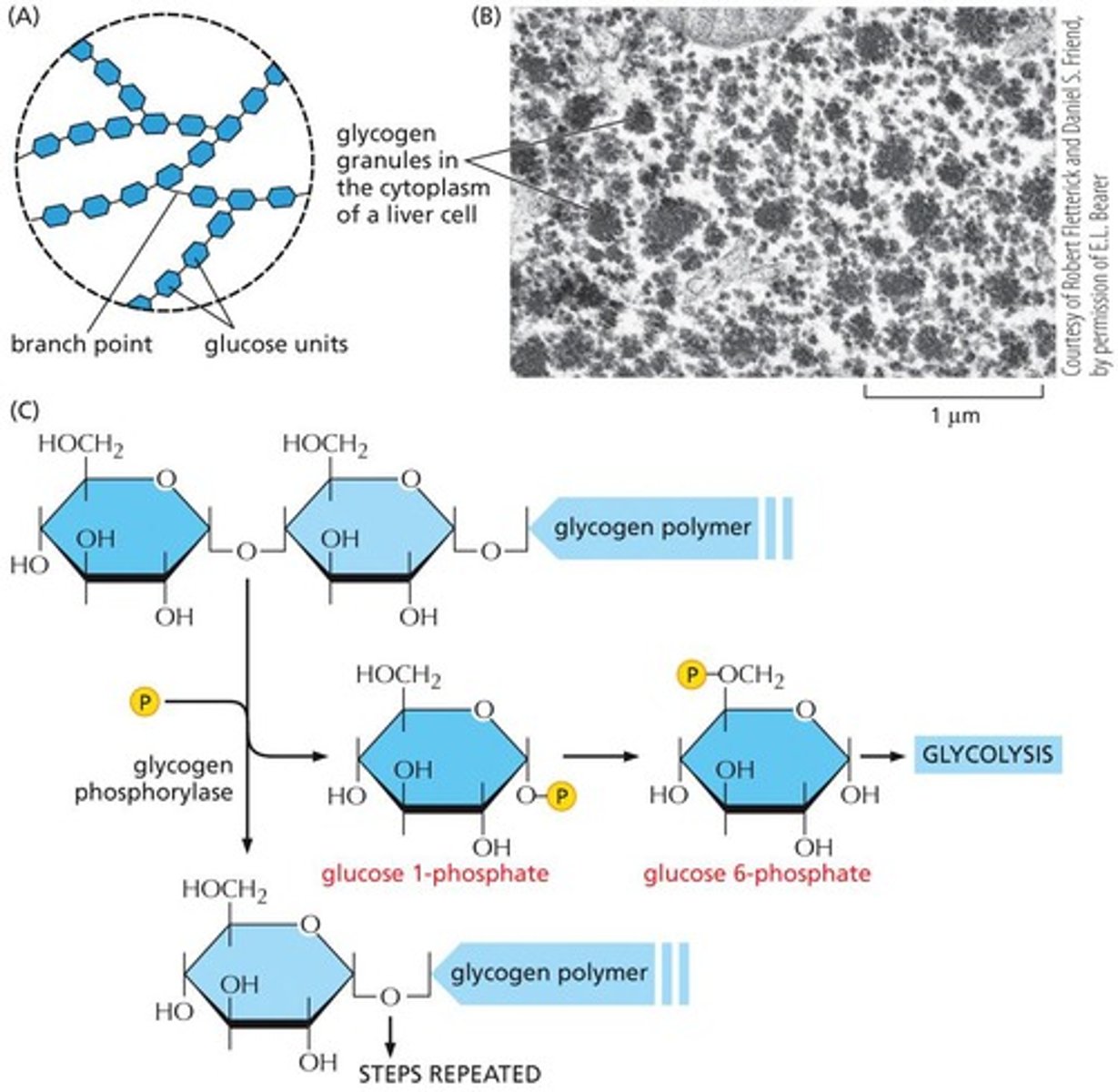
Glycogen Phosphorylase
Enzyme breaking down glycogen to glucose.
ATP Turnover
Rate at which ATP is consumed and regenerated.
Pyruvate
End product of glycolysis, precursor to acetyl-CoA.
NADH
Electron carrier generated in glycolysis and citric acid cycle.
FADH2
Electron carrier produced in the citric acid cycle.
Building Blocks
Components derived from macromolecule digestion for synthesis.
High-Energy Electrons
Electrons released during cellular respiration for ATP production.
Energy Yield
Amount of energy produced from metabolic processes.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Uses food energy to produce ATP in mitochondria.
Photosynthesis
Converts sunlight energy into chemical energy in chloroplasts.
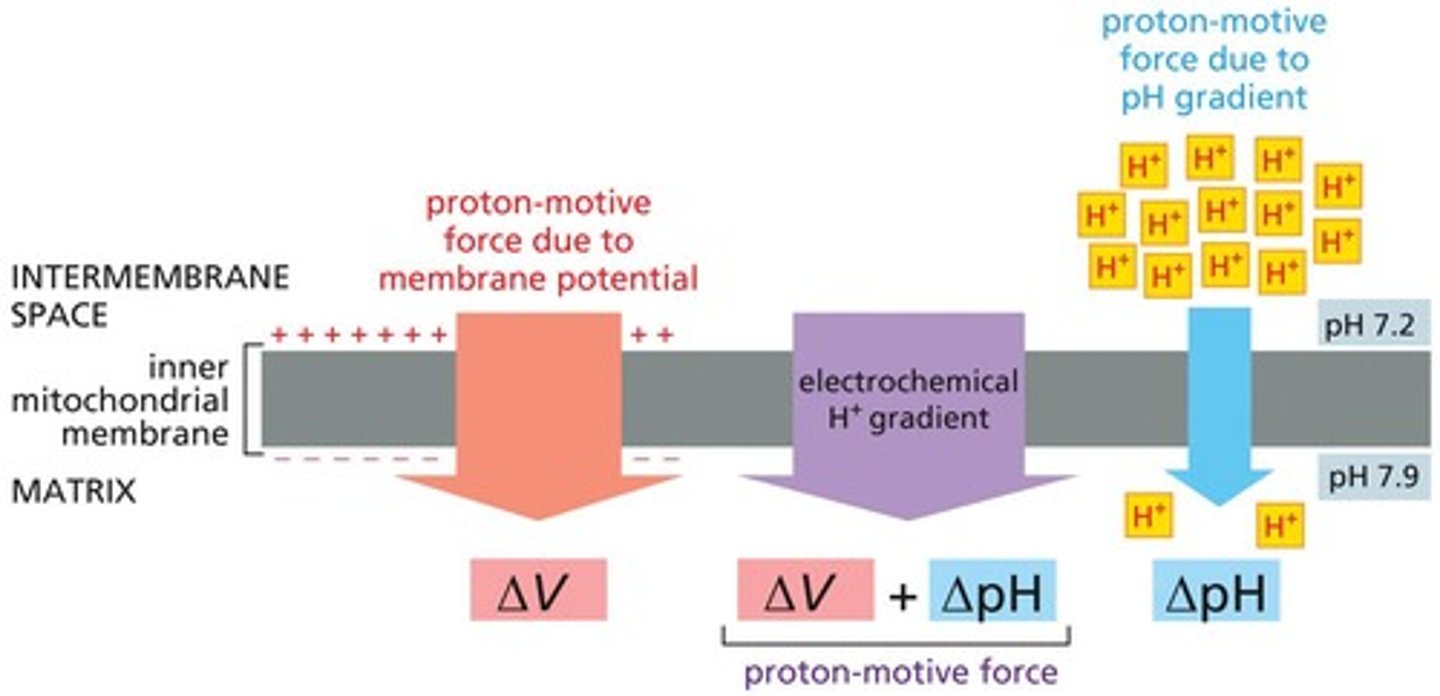
Proton Gradient
Difference in proton concentration across a membrane.
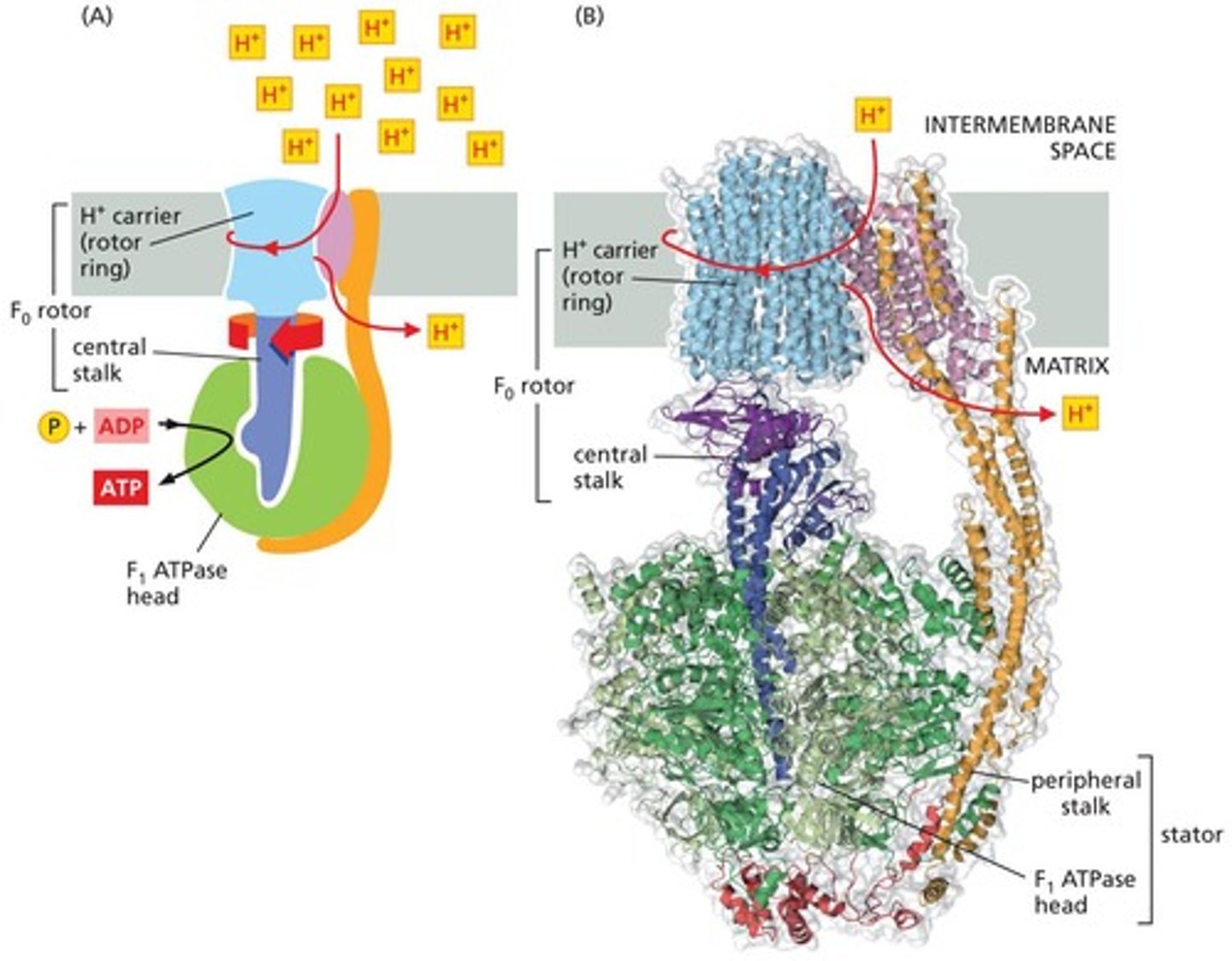
ATP Synthase
Enzyme that synthesizes ATP using proton gradient energy.
Chemiosmotic Coupling
Links ATP formation with proton gradient generation.
Citric Acid Cycle
Oxidizes acetyl-CoA to produce high-energy electrons.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Series of complexes that transfer electrons and pump protons.
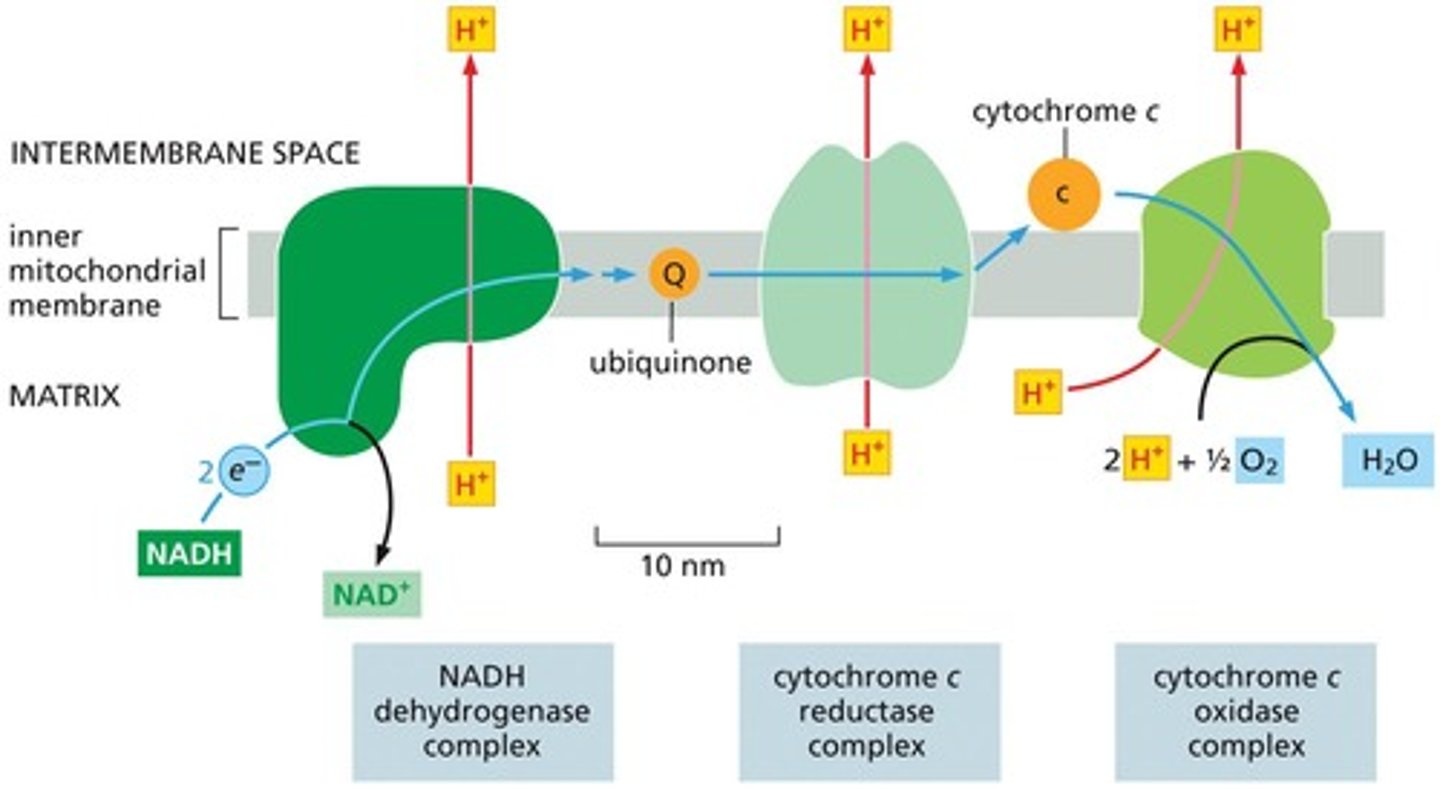
NADH
Electron carrier that donates electrons to the ETC.
FADH2
Another electron carrier with lower ATP production efficiency.
Proton Pumping
Process of moving protons to create a gradient.
Electrochemical Gradient
Combination of electrical and chemical gradients across a membrane.
Proton-Motive Force
Energy stored in the electrochemical gradient.
NADH Dehydrogenase Complex
First complex in ETC that accepts electrons from NADH.
Cytochrome C Reductase Complex
Second complex in ETC involved in electron transfer.
Cytochrome C Oxidase Complex
Final complex in ETC that reduces oxygen.
ATP Hydrolysis
Process of breaking down ATP to release energy.
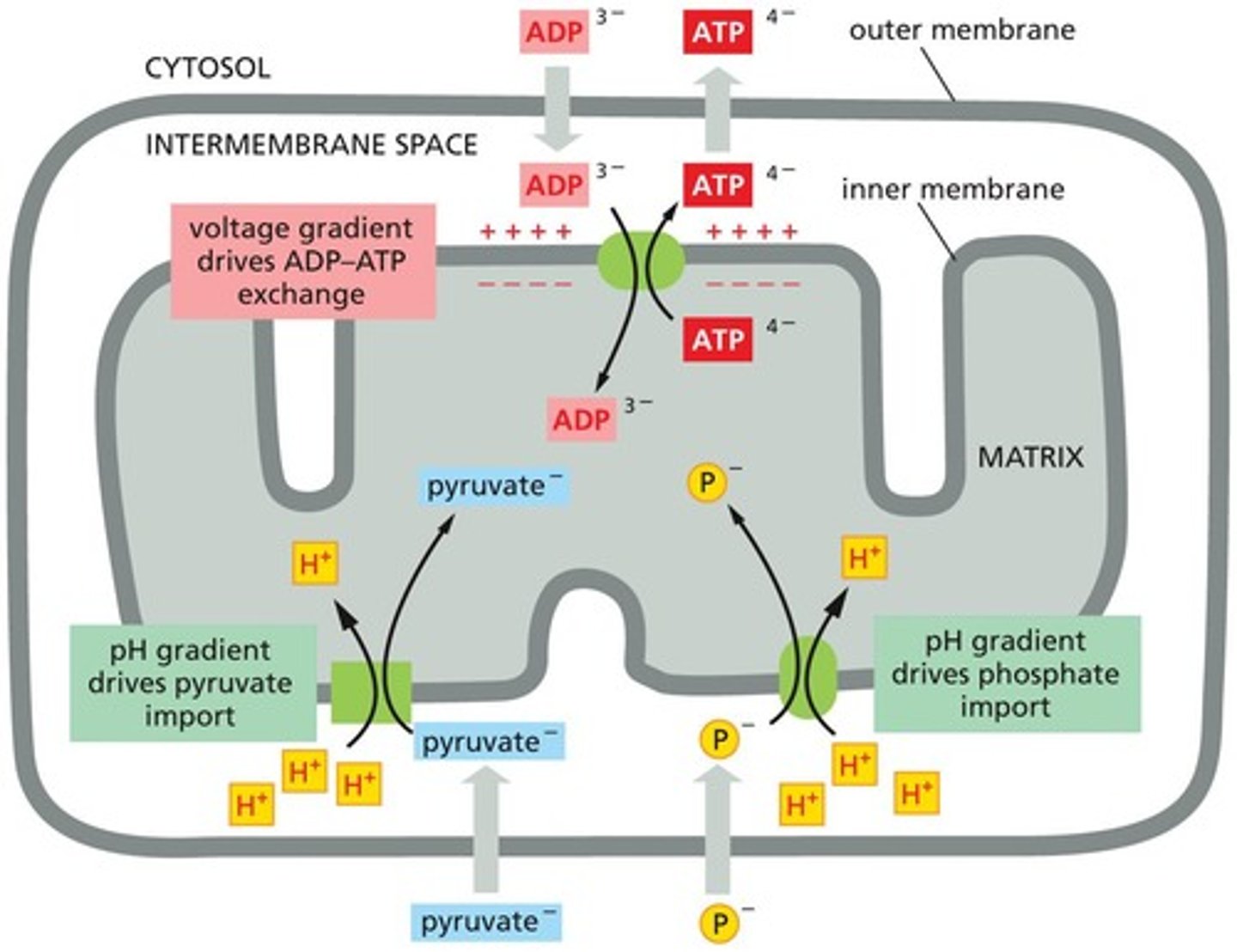
Antiporter
Transport protein that moves substances in opposite directions.
ADP to ATP Conversion
Rapid process maintaining high ATP/ADP ratio in cells.
Cellular Respiration Efficiency
38-50% energy capture from glucose during respiration.
Redox Potential
Measure of an electron's affinity for reduction.
Ubiquinone
Electron shuttle that carries electrons and protons.
Cytochrome C
Electron carrier with a porphyrin ring and iron.
Oxygen-Binding Site
Site in cytochrome c oxidase that binds molecular oxygen.
Water Formation Reaction
4e- + 4H+ + O2 → 2H2O in ETC.
Mitochondrial Dynamics
Mitochondria change structure and location based on energy needs.
Proton Gradient Utilization
Gradient drives transport of pyruvate and phosphate.
Prokaryotic Cells
Single compartment cytoplasm without membrane-enclosed organelles.
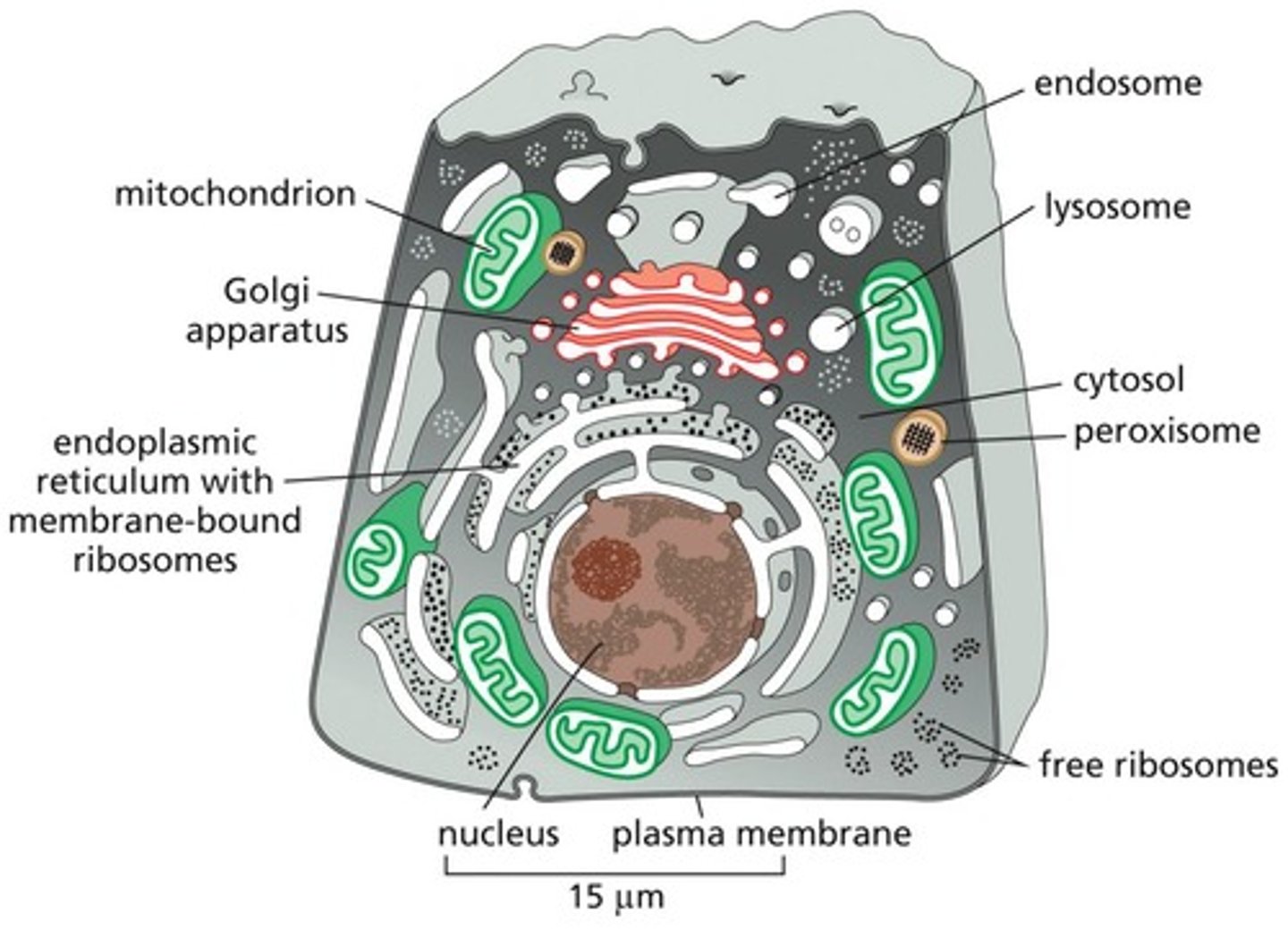
Eukaryotic Cells
Multiple internal compartments with membrane-enclosed organelles.
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Influences cell size and biochemical efficiency.

Nucleus
Contains genomic DNA and synthesizes ribosomes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesis of proteins and lipids; detoxification.
Rough ER
Studded with ribosomes; synthesizes proteins for membranes.
Smooth ER
Synthesizes lipids and detoxifies harmful substances.
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies and distributes proteins and lipids from ER.
Lysosomes
Breaks down macromolecules and worn-out organelles.
Peroxisomes
Contains enzymes for lipid breakdown and detoxification.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell; site of ATP synthesis.
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis in plant cells; contains thylakoids.
Endosomes
Involved in sorting and transporting endocytosed materials.
Cell Volume
Determined by the amount of cytoplasm and organelles.
Ion Gradients
Used for energy demands and biochemical processes.
Differentiation
Specialization of cells in multicellular organisms.
Membrane-enclosed Organelles
Structures that compartmentalize cellular functions.
Biochemical Processes
Chemical reactions essential for cell function.
Compartment Sorting
Transport of materials to/from organelles.
Endomembrane System
Includes ER, Golgi, lysosomes, and vesicles.
Vesicular Exchange
Communication between organelles and plasma membrane.
Cytosolic Ribosomes
Most proteins synthesized by ribosomes in cytosol.
Sorting Signal
Amino acid sequence directing protein destination.
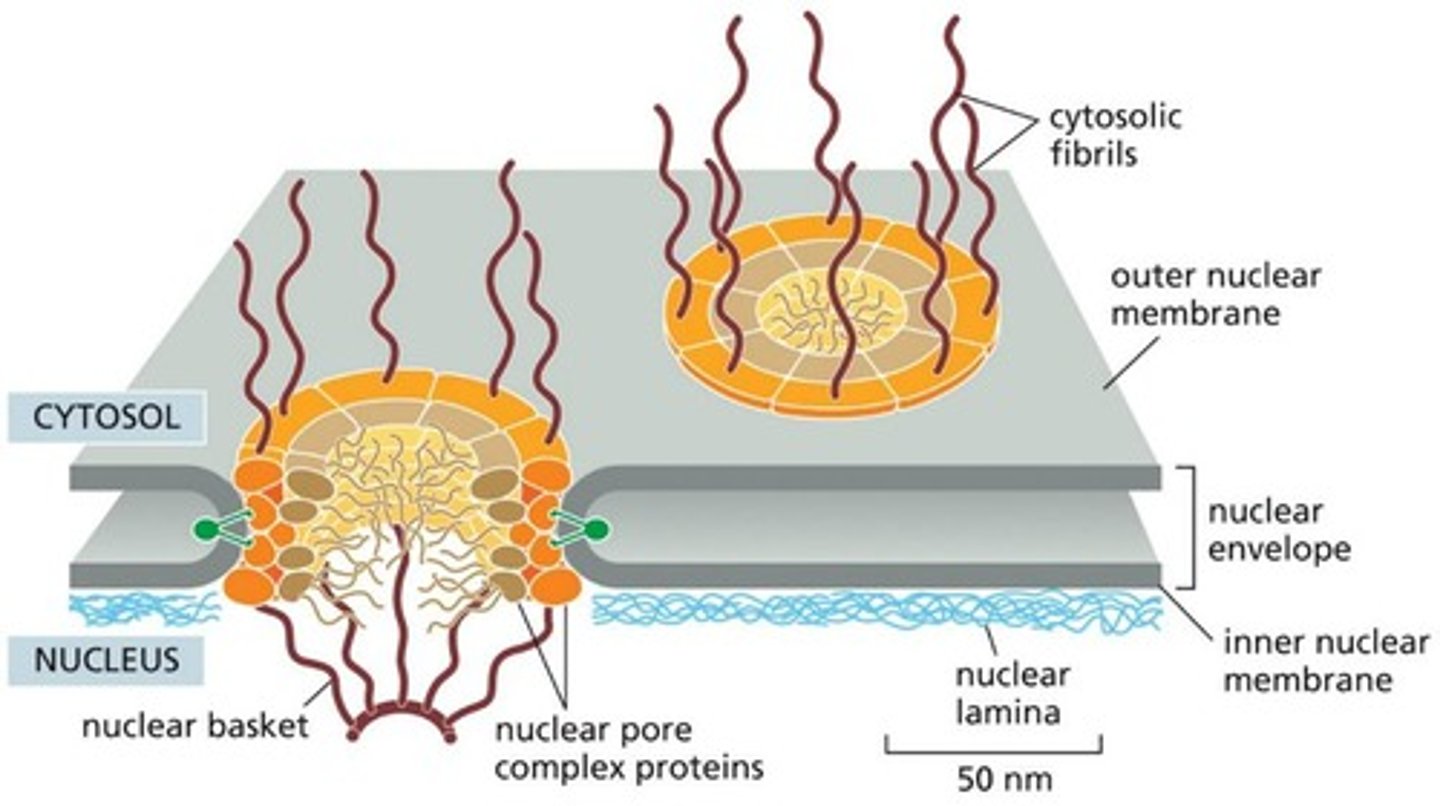
Nuclear Pores
Gateways for molecules entering/exiting nucleus.
Protein Translocators
Membrane proteins facilitating protein transport.
Transport Vesicles
Carry proteins between endomembrane system organelles.
Signal Sequence
15-60 amino acids directing protein sorting.
Nuclear Envelope
Double membrane surrounding the nucleus.
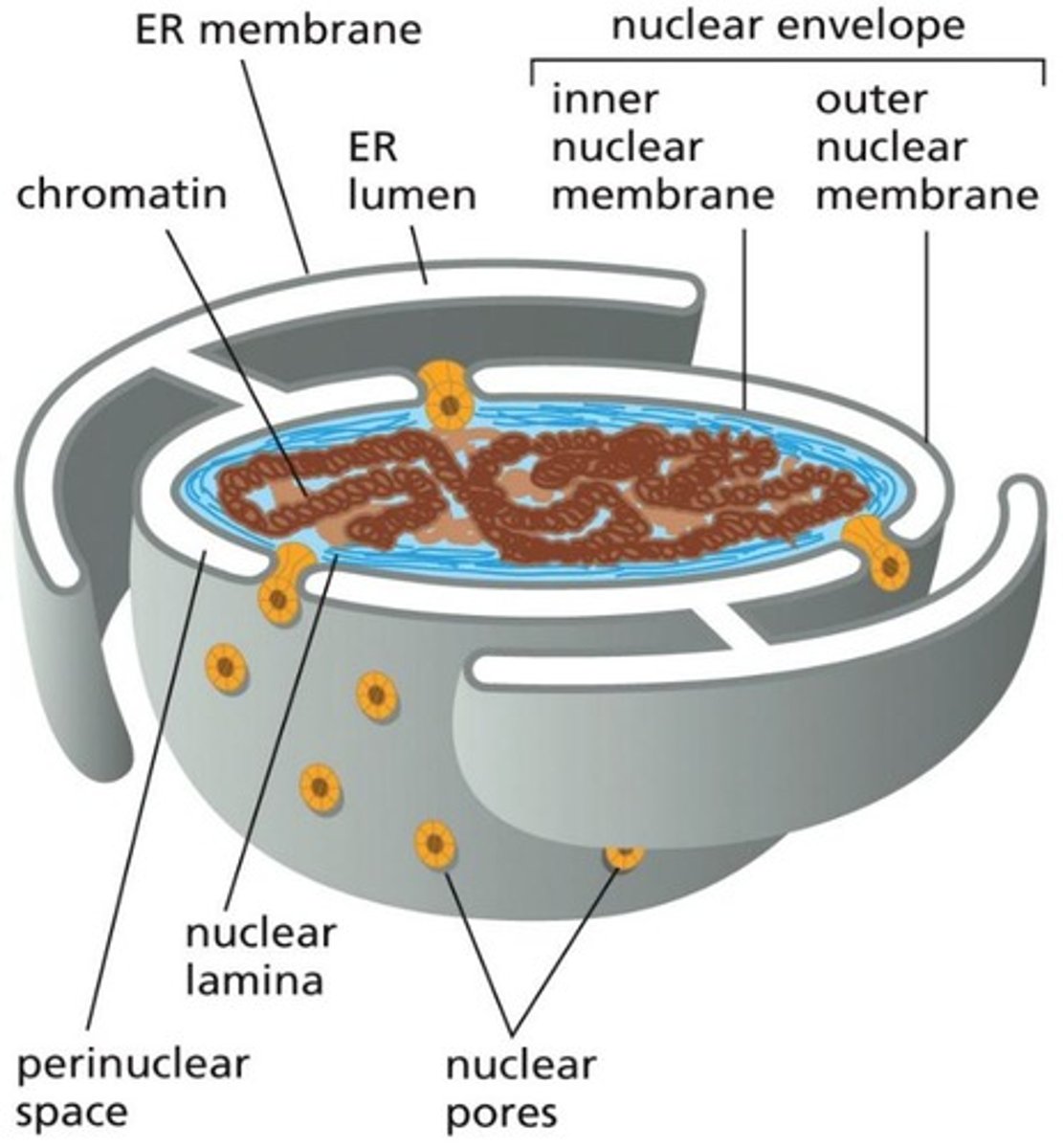
Inner Nuclear Membrane
Anchors nuclear lamina and binds chromosomes.
Outer Nuclear Membrane
Continuous with endoplasmic reticulum membrane.
Nuclear Pore Complex
30 proteins forming selective gating structure.
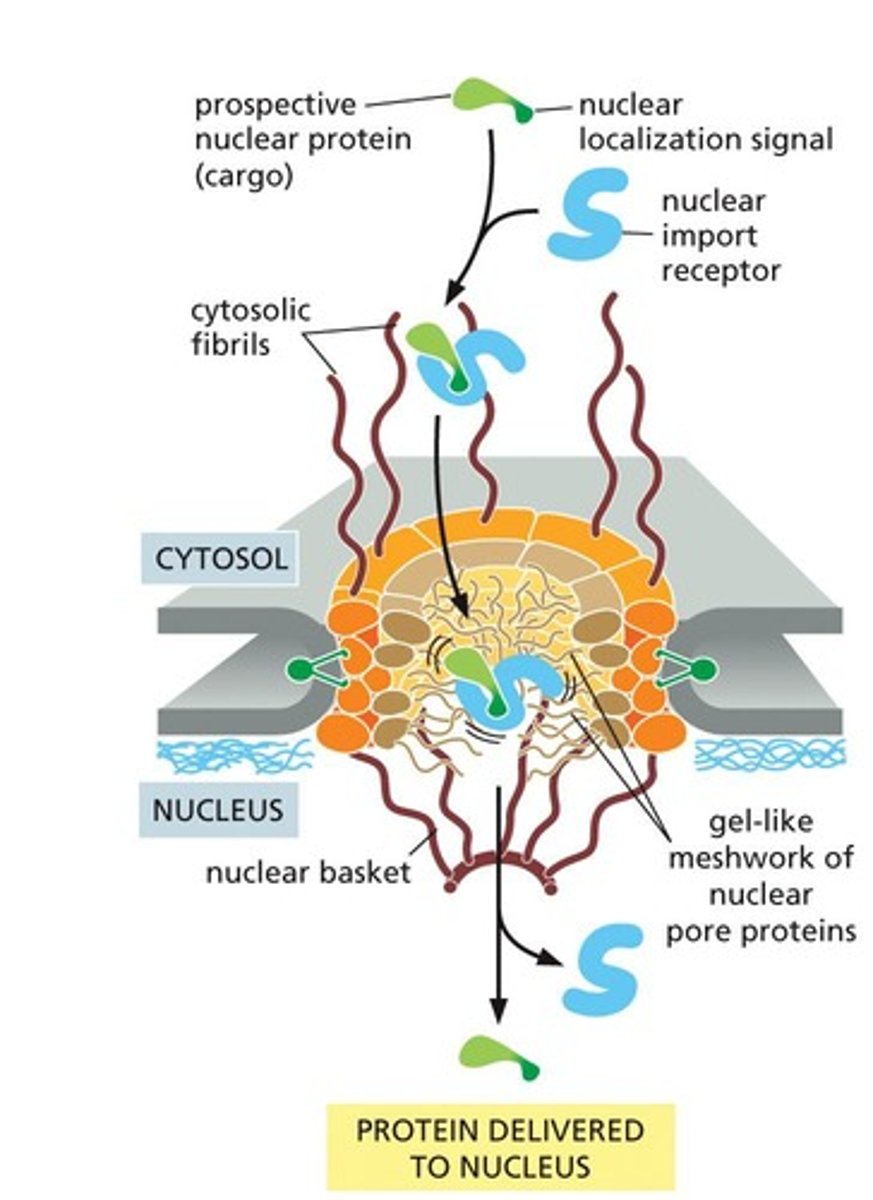
Energy-Dependent Passage
Requires energy for nuclear pore transport.
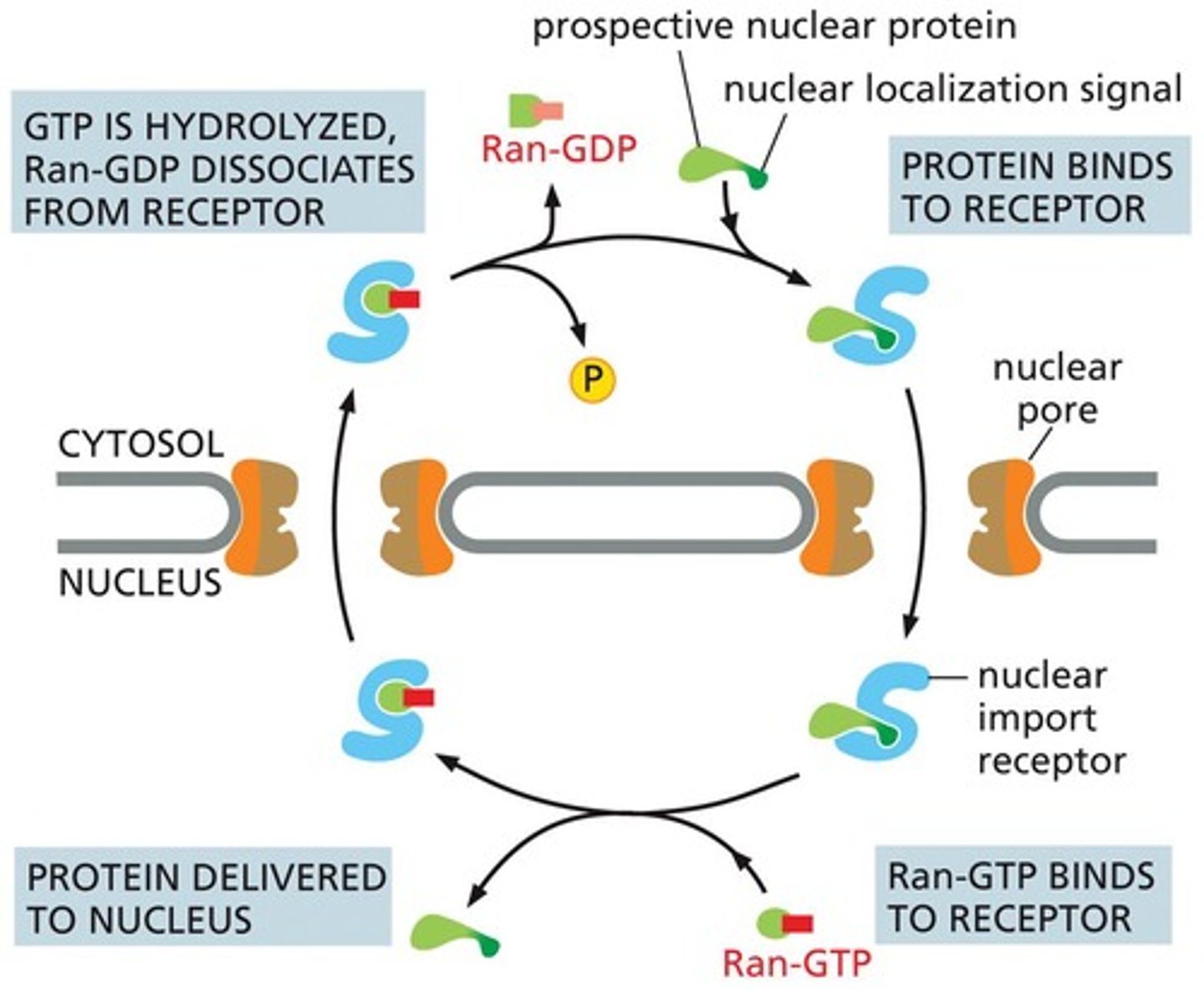
Nuclear Localization Signal
Sequence binding import receptor for nuclear entry.
Ran-GTP
Molecule facilitating protein release in nucleus.
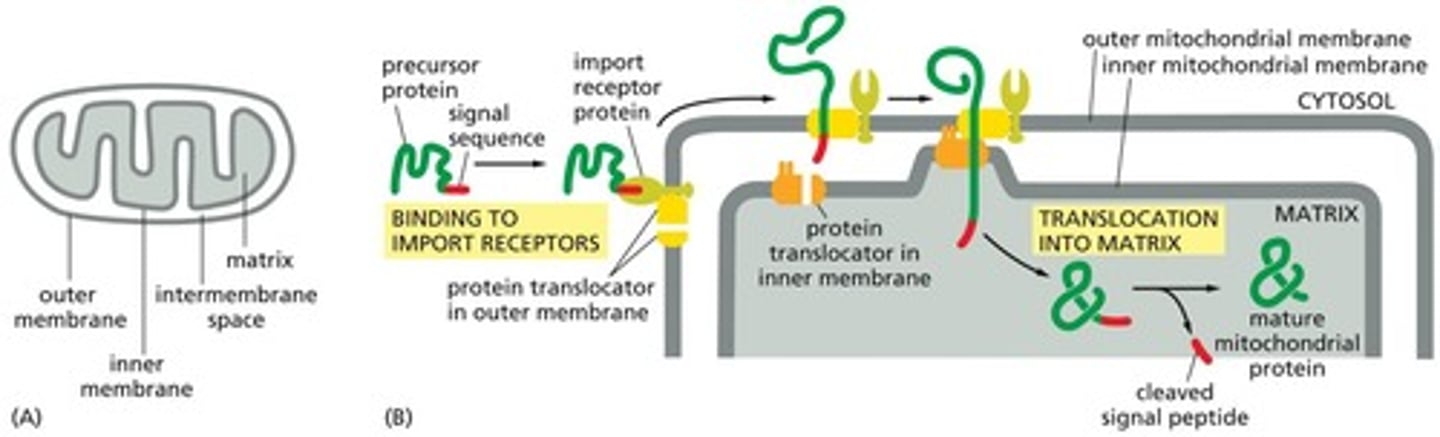
Mitochondrial Precursor Protein
Protein needing import receptor for mitochondrial entry.
Chaperone Proteins
Assist in refolding proteins after import.
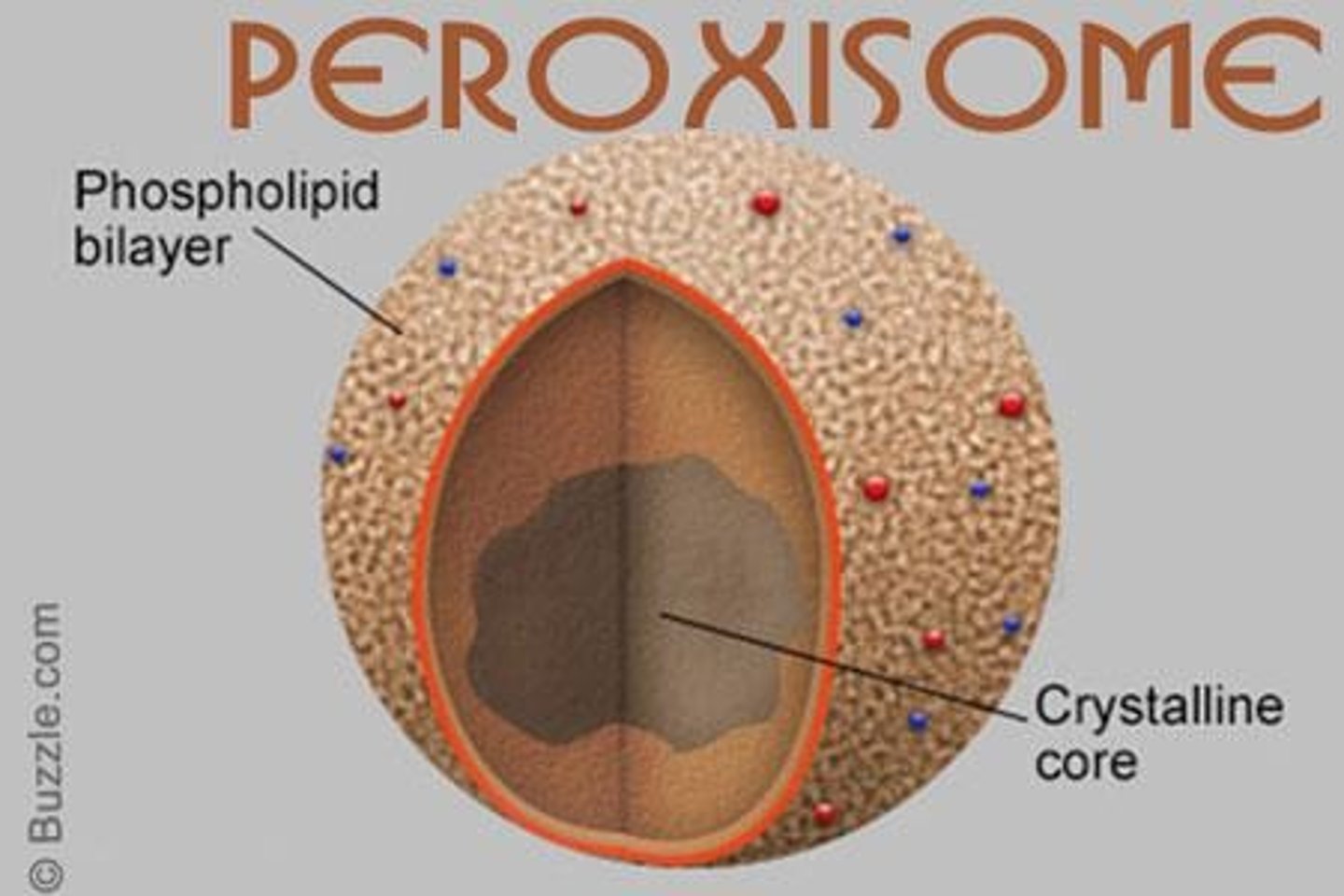
Peroxisomes
Organelles digesting toxins and synthesizing phospholipids.
Signal Peptidase
Enzyme cleaving signal sequence in mitochondria.
Lipid-Carrying Proteins
Transport phospholipids to mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Cytosolic Proteins
Proteins that lack signal sequences for sorting.
Myelin Sheath
Insulating layer around nerve fibers, enhancing signal transmission.
Cytosol
Fluid component of the cytoplasm where proteins are synthesized.
Translocator Protein
Protein that facilitates cargo entry into peroxisomes.
Peroxisome
Organelle involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Extensive membrane system for protein and lipid synthesis.
Soluble Proteins
Proteins fully translocated into ER lumen for processing.
Integral-Membrane Proteins
Proteins partially embedded in ER membrane, involved in signaling.
Exocytosis
Process of vesicles fusing with plasma membrane to release contents.
Common Pool of Ribosomes
Ribosomes function freely or membrane-bound.

Translation
Process of synthesizing polypeptides from mRNA.
Soluble Proteins
Proteins synthesized in the ER and released into lumen.
Signal-Recognition Particle (SRP)
Binds ER signal sequence and ribosome, slowing translation.