CB570 - Module 8 Liver and Pancreas Pathology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Liver Overview
Located in the upper right abdominal quadrant, organized into lobules with chords of hepatocytes.
All drains into the Terminal Hepatic Venule, then blood returns via the vena cava to the heart.
Should be soft on palpation, hardness can indicate damage or cirrhosis.
Alkaline phosphatase
Key enzyme that is release when hepatocytes are damaged, can be measured in clinical settings.
Portal Tract
Blood vessels in the liver, liver damage can cause portal hypertension.
Jaundice (Icterus)
Buildup of bilirubin that causes yellowing of the skin and eyes when the liver is damaged or excess blood is being processed.
Often seen in neonates as the liver is still developing.
Cholestasis
Retention of bile salts in the liver, can cause salts to dump into the blood stream. Major symptoms are systemic itching (pruritis) and malabsorption.
Bile “lakes” form in the liver.
Types of Hyperbilirubemia (2)
Conjugated - post-hepatic, liver is still functioning to conjugate bilirubin but transport is impaired
Unconjugated - pre-hepatic, liver is unable to process bilirubin at all
Intrahepatic Biliary Obstruction
Can be caused by certain drugs, pregnancy, liver damage and cause blockages in the liver. Typically cause conjugated hyperbilirubemia.
Extrahepatic bile duct obstruction
Can be caused by tumors, autoimmune diseases, and strictures. Prevents bile from draining into the gut.
Hepatic Failure
Characterized by jaundice and encephalopathy. Can be chronic or acute.
Symptoms can include renal failure, bleeding in the skin, estrogen- related phenotypes in males.
Liver Cirrhosis
Scarring of the liver from repeated damage and healing.
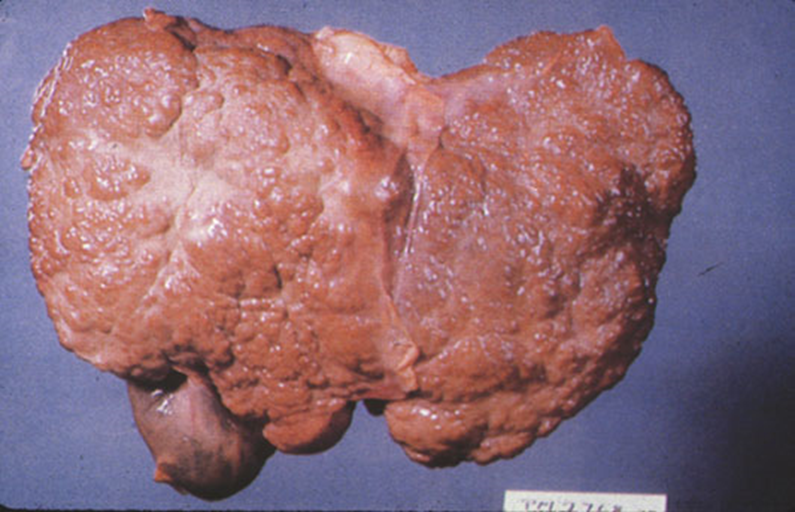
Causes of Liver Cirrhosis (5)
Viruses (Hep A, B, and C)
Hemochromatosis
Autoimmune diseases
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
Alcohol
Which two Hepatitis viruses are capable of chronic disease?
Hepatitis B (10% chronic) and Hepatitis C (80% chronic with recurring symptoms)
Hepatitis A is typically self-limited, most common Hepatitis infection.
Hepatitis B or C Worst Case Scenario Progression (4)
Acute Hep B or C
Chronic Hep B or C
Liver Cirrhosis
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
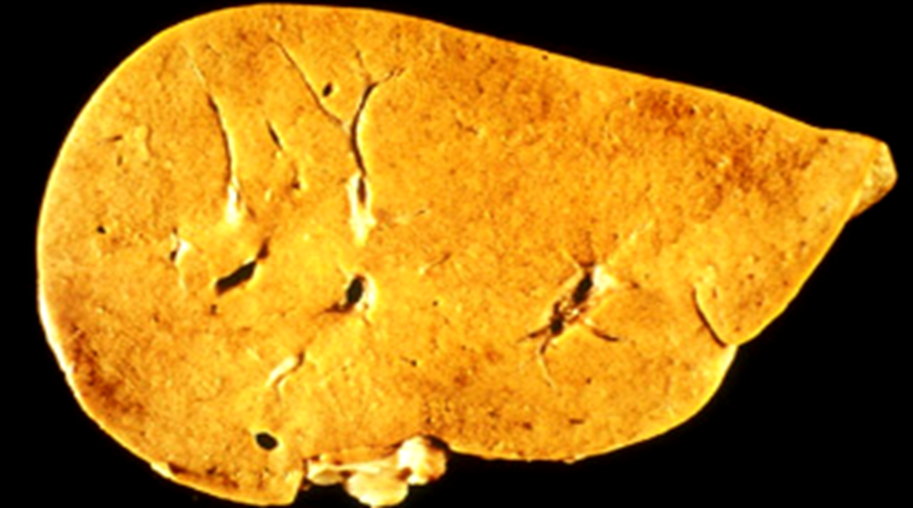
Fatty Liver Disease
Excessive alcohol consumption causes fatty buildup in the liver, this is reversible.

Complications of Liver Cirrhosis (5)
Portal hypertension
Encephalopathy (from high ammonia levels)
Esophageal Varices
Ascites
Splenomegaly and hypersplenism
Hemochromatosis
Excessive iron uptake, causes s buildup of iron in various organs.
Treated by phlebotomy.
Diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma are potential complications.
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Primary liver cancer, can be caused by cirrhosis or iron overload.
Metastatic liver cancer
Most common liver tumor, as the high blood flow through he liver makes this a likely place for metastasis.
Hepatic adenoma
Linked with high estrogen levels. Benign but could lead to dangerous bleeds.
Hemangioma
Most common benign tumor of the liver, blood vessel tumor.
Kaposi sarcoma
Linked with HHV-8 infection, typically seen in immunodeficient individuals.
Malignant tumor with multiple cutaneous and visceral lesions.
Gallstone Types (2)
Pigmented - made of precipitated bilirubin
Non-pigmented - made of precipitated cholesterol
Pigmented Gallstones
Can be related to sickle cell anemia or bilirubin anemia, causes pigmented gallstones.
Non-pigmented Gallstones
Cholesterol stones, can be related to hypercholesteremia and high estrogen levels. Most common type of gallstone.
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Probably autoimmune, affects larger bile ducts which coalesce to form the hepatic duct
Primary biliary cirrhosis
Autoimmune disease, anti-mitochondrial antibodies are a marker
Exocrine and Endocrine Functions of the Pancreas
Exocrine - secrete enzymes that end up in the common bile duct for digestion
Endocrine - make hormones like insulin, glucagon.
Acute Pancreatitis
Amylase and ligase are released, which can cause widespread damage.
Caused by acinar cell injury and duct obstruction.
Risk Factors of Acute Pancreatitis (6)
Ethanol
Gallstones
Viruses (mumps, HIV, cytomegalovirus)
Shock
Blunt trauma
Therapeutic drugs (immunosuppressives)
Signs of Pancreatitis
Hemorrhage in the pancreas
Fat necrosis/saponification of the pancreas
Chronic Pancreatitis
Associated with calcification and intestinal malabsorption.
Complications involve pseudocysts, pain from fibrosis, stone in the duct, diabetes
Pancreatic Carcinoma
Extremely deadly cancer due to its tendency to metastasize quickly to the liver and spleen.
Pancreatic Islet Cell Neoplasia
Insulinoma, tumors produce insulin and cause hypoglycemia. Clonal proliferation of beta cells.
Glucagonoma
Pancreatic tumor that secretes glucagon.
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Unrelenting peptic ulcer disease due to gastrin from a pancreatic tumor.