Mass Education and Its Role in Society, SOC-2260: Education and Social Problems Overview, Mass Education and Conflict Theory Overview, SOC-2260: Education and Social Problems Overview, Chapter 11 1
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
What is mass education?
A system of publicly accessible, state-funded schooling designed to provide basic literacy, numeracy, and general knowledge to the entire population, often made compulsory and standardized.
What are the two main functions of the mass education system today?
1. Uniform socialization 2. Sorting into different classes
What historical factors contributed to the rise of mass education?
1. The printing press 2. Protestant Reformation 3. Democracy 4. Industrialization
What significant event in the 19th century influenced public education in Canada?
In 1846, Egerton Ryerson drafted the Common School Act, which set the stage for the development of public education in Canada.
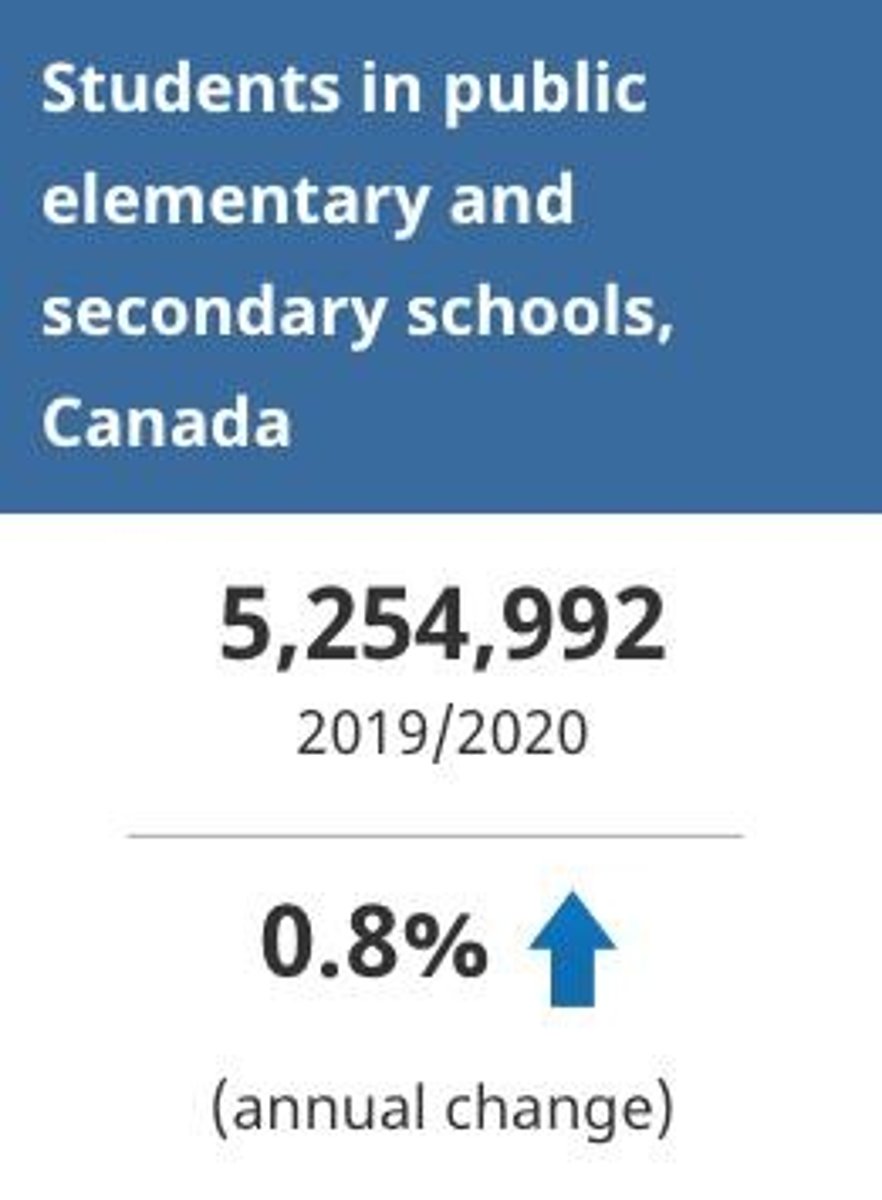
What was the enrollment figure for elementary and secondary school programs in Canada for the 2019/2020 school year?
Over 5.7 million students were enrolled.
How did the Industrial Revolution affect education in Canada?
It created a need for more job training, linking education to higher productivity.
What was Egerton Ryerson's view on the importance of education?
He believed education is as necessary as light, should be as common as water, and is essential for good government and constitutional liberty.
What was Egerton Ryerson's stance on the education of North American Indians?
He argued that they could not be civilized without religious instruction and should be schooled in separate, denominational, boarding institutions.
What legal doctrine relates to parental rights in education?
In loco parentis, which allows schools to act in the best interests of children in the absence of their parents.
What age range is mandated for compulsory school attendance in Alberta according to the School Act?
Children are required to attend school from ages 6 to 16.
What was the state of literacy and education in the early 1800s?
Only a small minority of people learned to read and write.
By 1950, what percentage of the world's countries had systems of compulsory mass education?
About 10%.
What is the relationship between education and wealth?
Education is both a source and product of wealth.
How did mass education replace traditional institutions in Canada?
It emerged as a key agent of socialization, replacing family and religious institutions as central to instruction and learning.
What is the significance of compulsory attendance laws?
They enforce mandatory school attendance and are supported by truancy officers.
What is the role of mass education in promoting social cohesion?
It standardizes education to create informed citizenship and economic development.
What was a key characteristic of mass education systems in wealthy countries?
They often provide compulsory and standardized education to promote social cohesion.
What did Ryerson argue about partial knowledge?
He stated that partial knowledge is better than total ignorance, as any degree of knowledge lessens danger.
What major societal change did the rise of mass education reflect?
The shift from family and religious institutions to state-funded education as a primary means of socialization.
What is a common characteristic of mass education systems worldwide?
They are designed to be publicly accessible and state-funded.
What was the impact of the Protestant Reformation on education?
It contributed to the rise of mass education by promoting literacy and individual interpretation of religious texts.

What percentage of students in Canada attended public schools in 2019/2020?
91.8% of students attended public schools.
What are the three types of schooling mentioned in the notes?
Public schools, private/independent schools, and home-schooling.
What is the purpose of uniform socialization in education?
To increase social cohesion and solidarity by instilling authority, discipline, and morality in children.
What does the term 'imagined communities' refer to in the context of education?
It refers to the concept of creating a shared identity and belonging among individuals through education.
What is one example of homogenization in education?
Curriculum and standardized testing.
What is Alberta's Bill 27 about?
It aims to provide greater parental control and oversight over education on topics related to sexuality and gender.
What does the Parental Notification and Opt-In provision of Bill 27 require?
School authorities must notify parents and allow them to opt their children into studies on gender identity, sexual orientation, or human sexuality.
What is required for a student under 16 to use a new preferred name or pronouns at school according to Bill 27?
Parental consent is required.
What must schools do if a student aged 16 or 17 requests a new pronoun or name?
Schools must inform parents of the request.
What does Bill 27 mandate regarding third-party materials?
The ministry of education must approve any third-party materials used in instruction on sexuality and gender topics.
What is the role of education according to Structural Functionalism?
Education serves key functions such as transmission of knowledge, socialization, assimilation, and role allocation.
What is role allocation in education?
It is the process by which education assigns individuals to different roles in society based on their abilities, talents, and qualifications.
What does a dysfunctional education system fail to do?
It fails to effectively perform its goals such as knowledge transmission and role allocation.
What does the term 'career' originate from?
The French word 'carrière,' meaning 'race course'.
What is the ideal starting position for everyone in the 'race' of education?
Ideally, everyone would start from the same position, relying on personal achievement to advance.
What are the stages of education leading to a career?
Preschool, Kindergarten, Elementary School, Junior High, High School, and Post-secondary.
What is the difference between ascribed status and achieved status?
Ascribed status is assigned at birth, while achieved status is based on personal accomplishments, such as educational attainment.
What is the common belief about educational attainment?
Most believe that educational attainment should be and is an achieved status.
What is the relationship between education and occupational success in Canada?
In Canada, individuals with the most education have the best chance of achieving the highest occupations and incomes, and of avoiding unemployment.
Define social mobility.
Social mobility is the movement, usually of individuals, but sometimes of groups, between different positions within the system of social stratification in any society.
What is intragenerational occupational mobility?
Intrgenerational occupational mobility refers to changes in someone's occupational status throughout their lifetime.
What does human capital theory propose?
Human capital theory proposes a linear relationship between education and job attainment, suggesting that more education leads to better jobs.
According to human capital theory, why do marginalized groups earn less money?
Marginalized groups earn less money than dominant groups because they possess less human capital in the form of education, skill, and experience.
How do Conflict Theorists view the education system?
Conflict Theorists focus on inequalities within the education system, arguing that it perpetuates inequality rather than being a meritocracy.
What is the 'banking model of education'?
The banking model of education is a metaphor where students are seen as empty containers to be filled with information, lacking critical thinking and two-way communication.
Who is associated with the concept of Critical Pedagogy?
Brazilian philosopher and educator Paulo Freire is associated with Critical Pedagogy.
What does Freire criticize about traditional education methods?
Freire criticizes the 'banking model of education' for treating students as passive subjects who merely receive and memorize information.
How does social class affect educational ambitions?
Social class affects educational ambitions and pursuits, with those lower on the economic ladder viewing higher education as more of a privilege than a right.
What is the tendency regarding social class inheritance?
Researchers have found that people are likely to inherit the social class of their parents, with this tendency being higher in some countries than others.
What is a significant concern regarding the Canadian educational system?
There is a concern that the educational system reproduces societal inequalities and helps privileged groups maintain their advantages.
What is the relationship between ideology, parental choice, and educational segregation?
The relationship suggests that parental choice can lead to educational segregation, influenced by underlying ideologies.
What is the significance of the phrase 'the race is rigged' in the context of education?
It implies that systemic inequalities exist within the education system that disadvantage certain groups from the outset.
What is the role of families in educational inequality?
Families can provide a head start in the race towards better careers and higher incomes, impacting children's educational opportunities.
What is the critique of the education system from a Conflict Theory perspective?
Conflict Theory critiques the education system for not being a true meritocracy and instead perpetuating existing inequalities.
What are charter schools, and how are they perceived in the context of education?
Charter schools are often viewed as part of a neoliberal experiment, raising questions about their impact on educational equity and segregation.
What is the significance of Henry Giroux's perspective on education?
Henry Giroux emphasizes that education is a struggle over the future and questions the neutrality of educational practices.
What do researchers suggest about the financial means of children from less affluent families regarding education?
Children from less affluent families often lack the financial means to complete a post-secondary education.
What is the impact of ascribed status in education?
Ascribed status continues to influence educational outcomes, contributing to systemic inequalities.
What is the importance of critical thinking in education according to Critical Pedagogy?
Critical thinking is essential for challenging existing power structures and fostering emancipation among oppressed groups.
What did Freire mean by the 'scope of action' allowed to students in traditional education?
Freire meant that in traditional education, students' actions are limited to receiving and memorizing information, rather than engaging critically.
What is the goal of Critical Pedagogy according to Paulo Freire?
The goal is the emancipation of the oppressed through critical thinking, questioning, and consciousness raising.
What does Critical Pedagogy assert about education?
Education is never neutral, but is a necessarily contested and political act.
What does Freire propose as an alternative to the banking model of education?
The 'problem-posing approach' which encourages critical thinking and dialogue.
What is the percentage of students in Canada that were home-schooled in 2019/2020?
0.7%.

When were charter schools introduced in Alberta?
In 1994.
What is the enrollment percentage of students in charter schools in Alberta as of 2022-23?
1.4%.
What educational philosophy does the Alberta Classical Academy emphasize?
A traditional liberal arts education rooted in classical literature, history, logic, and virtue ethics.
What was the economic impact of postsecondary institutions in Canada during the 'Golden Era'?
Postsecondary institutions grew from about 0.5% of GDP to 2.5% of GDP between 1950 and 1970.
What marked the beginning of cuts and neglect in postsecondary education in Canada?
The neoliberal shift of the 1970s.
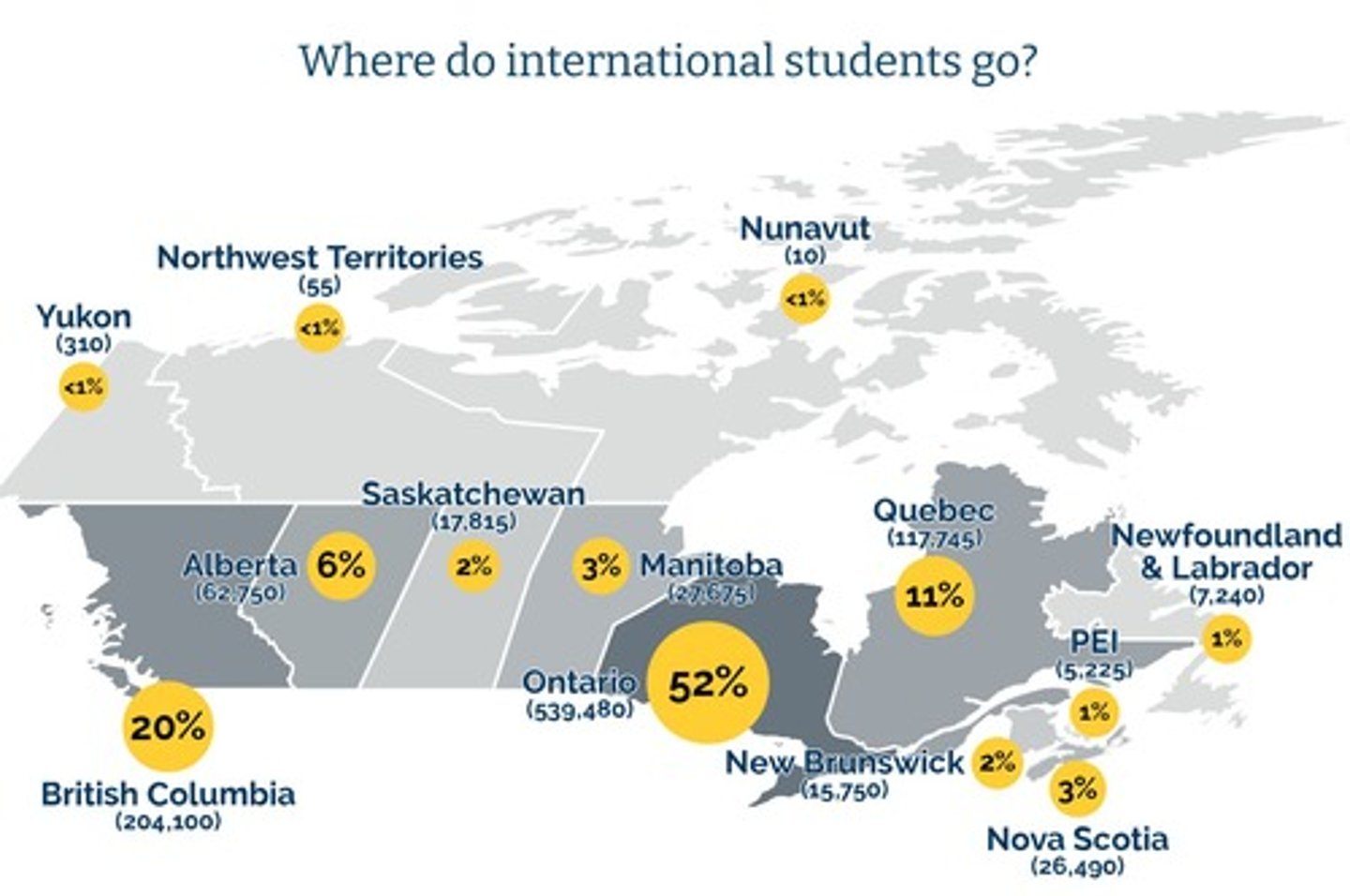
How many international students were in Canada at the end of 2022?
807,260.
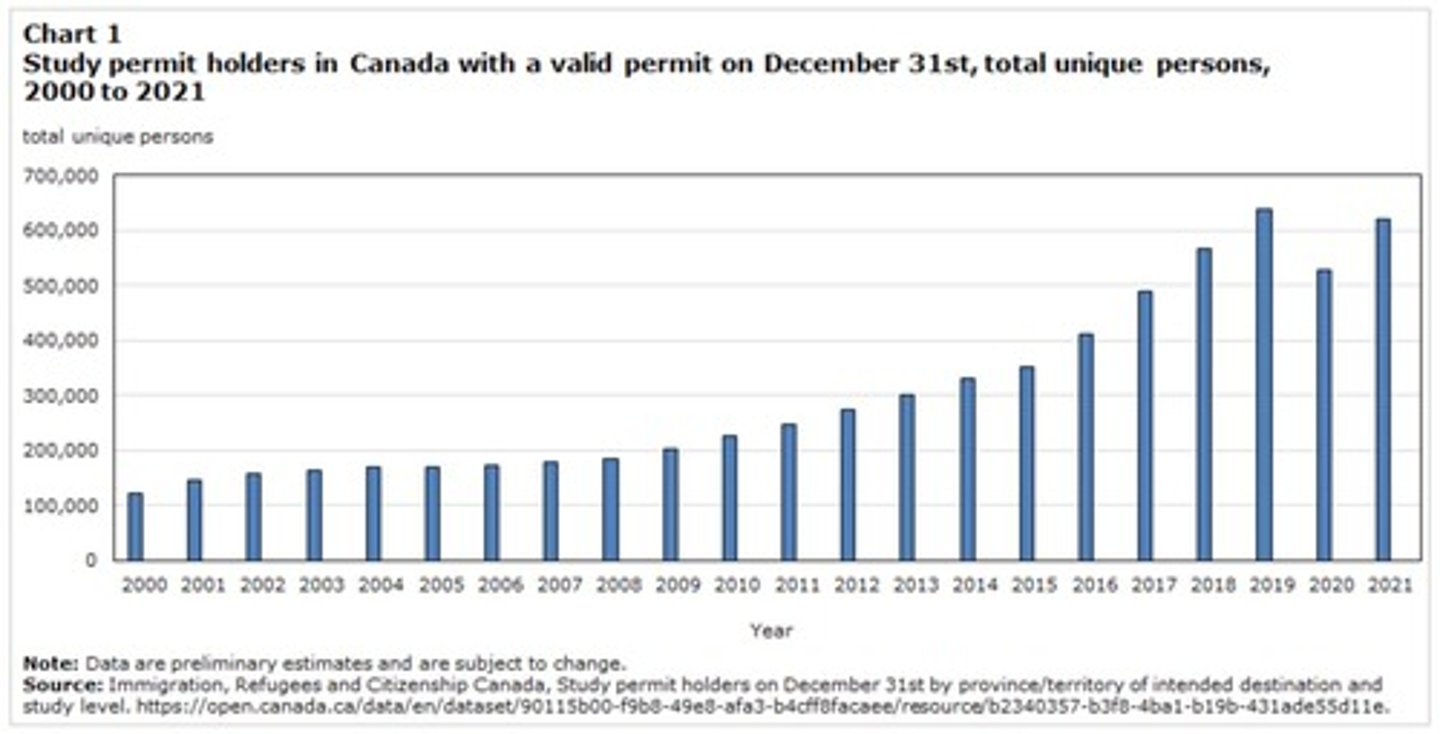
What was the international student population in Canada by 2023?
Over one million.

What percentage of international students worldwide studied in Canada in 2019?
About 5%.
What is one challenge faced by post-secondary students in Canada?
Challenges can include cultural adjustment, financial constraints, or academic pressures.
What does the term 'immigration factory' refer to in the context of international students?
It refers to the perception that studying in Canada is a pathway to immigration.
What was found in the 2021 report from Ontario's auditor general regarding international students?
The increase in international students was influenced by their perception of post-secondary education as a pathway for immigration.
What is the work hour limitation for international students in Canada as of September 2024?
International students are not allowed to work more than 24 hours per week.
What is a potential solution for challenges faced by international students in Canada?
Possible solutions could include increased support services, mentorship programs, or financial aid.
What significant change occurred in the perception of international students' pathways to residency?
Only about a small percentage of those on student visas obtain permanent residency within a decade.
Four factors leading to the rise of mass education
The printing press, Protestant Reformation, Democracy, Industrialization.
Egerton Ryerson
Egerton Ryerson helped draft the Common School Act of 1846, which laid the foundation for public education in Canada.
Egerton Ryerson's perspective on education for North American Indians
He believed North American Indians could only be civilized through religious instruction, agricultural training, and schooling in English-only, denominational, boarding institutions.
Percentage of Canadian students attending public schools in 2019/2020
91.8%.
Main goal of uniform socialization in education
To promote social cohesion and solidarity by instilling authority, discipline, and morality in children.
Alberta's Bill 27
Bill 27 aims to provide greater parental control and oversight over education related to sexuality and gender topics, including requiring parental consent for pronoun use and opt-in for instruction.
Structural functionalism in education
The view that education serves key functions in society, such as transmission of knowledge, socialization, and role allocation.
Origin of the word 'career'
The word 'career' originates from the French word 'carrière,' meaning 'race course.'
Sorting into classes in education
Sorting refers to the way education assigns individuals to different roles in society based on their abilities, talents, and qualifications.
Human Capital Theory
The theory that there is a direct relationship between education and job attainment: more education leads to better job prospects.
Conflict Theory and education
It argues that education perpetuates inequalities in society rather than being a 'great equalizer.'
Social class and educational attainment
People from higher social classes are more likely to achieve higher levels of education and subsequently higher-paying jobs, while those from lower classes face more barriers to higher education.
Critical pedagogy
A teaching approach that encourages critical thinking and challenges traditional power dynamics in education, aiming for the emancipation of oppressed groups.
Passive receivers of knowledge
A concept where students are passive receivers of knowledge, with no critical thinking or active communication.
Henry Giroux's view on education
He argues that all education is a struggle over what kind of future we want for young people.
Charter schools
Charter schools are public schools that are run by private organizations or groups, often with more flexibility in curriculum and management, but they are publicly funded.
Parental choice and educational segregation
Parental choice in education may lead to educational segregation, as wealthier families are more likely to choose better-funded private or charter schools, leaving disadvantaged families in underfunded public schools.
Golden Era in post-secondary education in Canada
The period from 1950-1970 when postsecondary institutions grew significantly, contributing to a larger portion of GDP.
Neoliberal shift in post-secondary education
The beginning of cuts and neglect, influencing the current state of post-secondary education.
Challenges due to funding cuts in colleges and universities
They have had to innovate, but this innovation may come at the cost of long-term sustainability and the quality of education.
International students in Canada by the end of 2022
807,260 international students.