Topic 2 - Hybridisation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is hybridisation?
A way of creating localised atomic orbitals that reproduce the observed shapes of molecules.
In carbon atoms, sp3, sp2 and sp hybridisation occurs.
What is sp3 hybridisation?
A type of hybridisation where one s-orbital and three p-orbitals combine to form four equivalent sp3 hybrid orbitals, arranged tetrahedrally around the central atom.
This occurs when an atom bonds to 4 other atoms.
As the orbitals mix, their energies change. The new orbitals have a shape between 2s and 2p, with one orbital lobe dominating the structure.
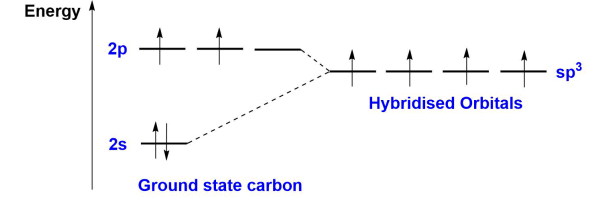
What does the molecular orbital diagram of sp3 hybridised methane look like?
There are 4 sp3 hybridised orbitals, and the overall structure exhibits ¼ S character, and ¾ P character.
What is sp2 hybridisation?
A type of hybridisation where one s-orbital and two p-orbitals combine to form three equivalent sp2 hybrid orbitals, arranged in a trigonal planar shape (120°) around the central atom, with the unhybridised p-orbital perpendicular.
This occurs when an atom bonds to 3 other atoms.
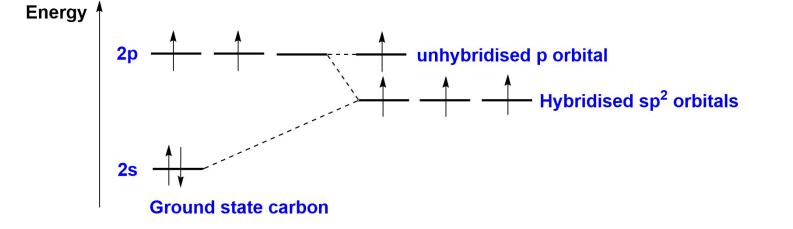
What is the role of the unhybridised p-orbital in sp2 hybridisation?
It is able to form a π bond through edge-on overlap with a neighbouring pz orbital.
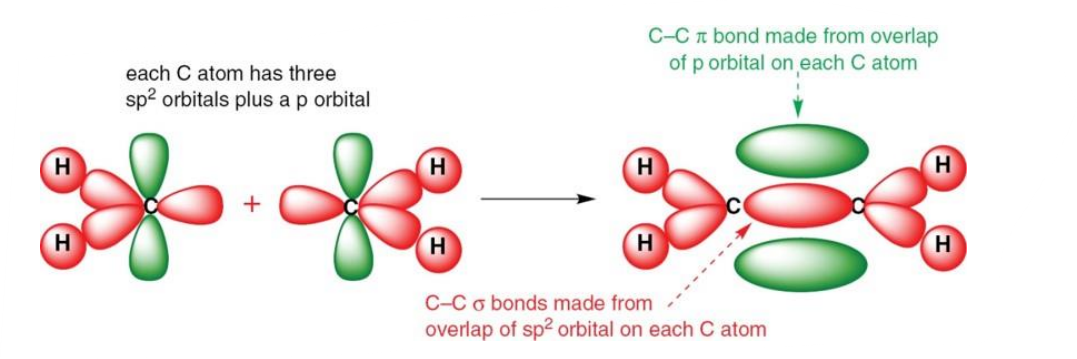
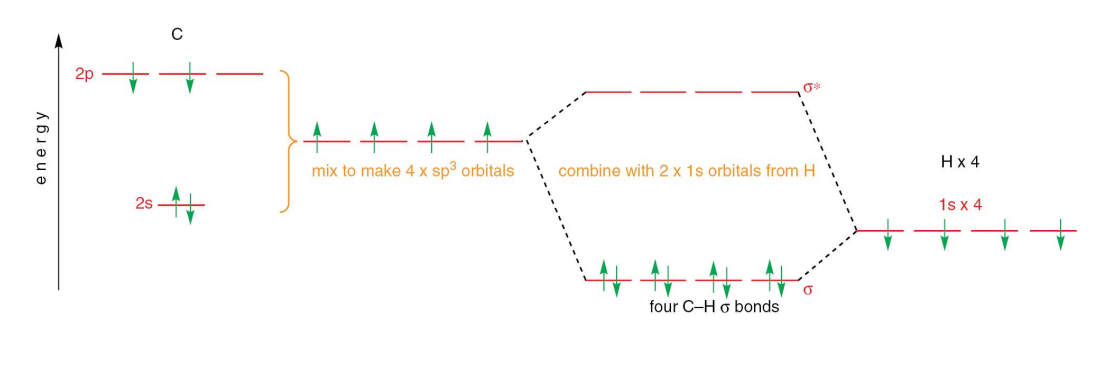
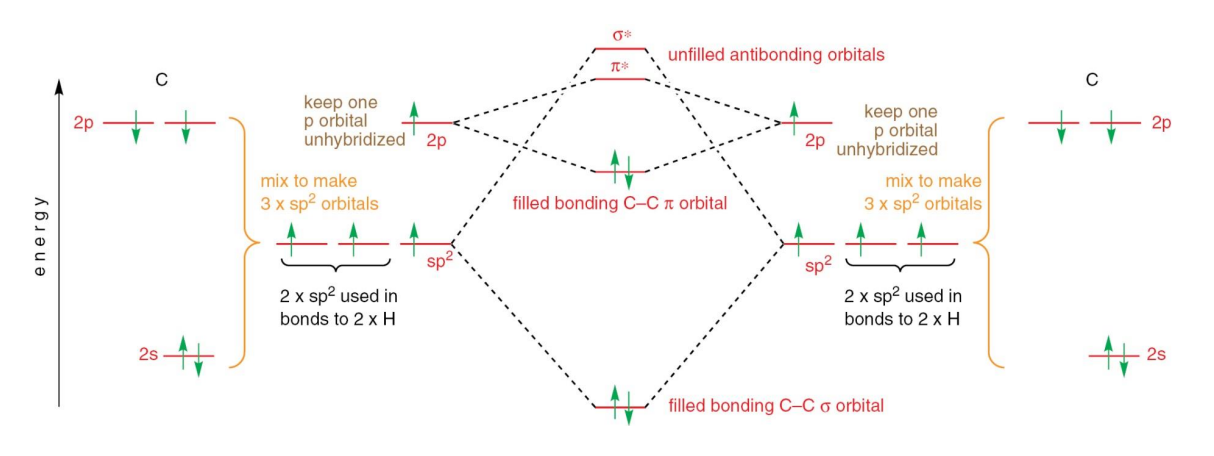
What does the molecular orbital diagram of sp2 hybridised ethene look like?
There is a 2s, 2px and 2pY orbital, producing 3 sp2 orbitals.
It exhibits 1/3 S character, and 2/3 P character.
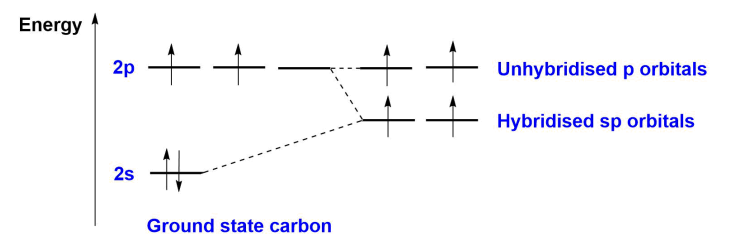
What is sp hybridisation?
A type of hybridisation where one s-orbital and one p-orbital combine to form two equivalent sp hybrid orbitals, oriented linearly at 180° around the central atom.
It exhibits ½ S character and ½ P character.
What is the role of the unhybridised p-orbitals in sp hybridisation?
The two sp orbitals are involved in forming σ bonds, which leaves the unhybridised Pz and PY orbitals for π bonding.
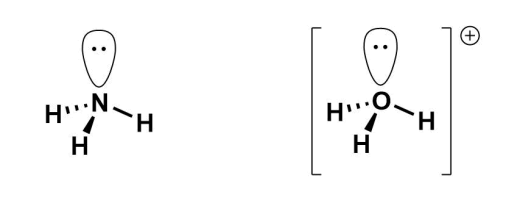
What is sp3 hybridisation in heteroatoms?
Heteroatoms have lone pairs which usually fill hybrid orbitals.
They have tetrahedral geometry, but can be altered by the number of lone pairs.
What is sp2 and sp hybridisation in heteroatoms?
A heteroatom with sp2 hybridisation has 3 sp2 orbitals and one p-orbital. The parent shape is trigonal planar, e.g. propanone (acetone).
A heteroatom with sp hybridsation has 2 sp orbitals and 2 p-orbitals. The parent shape is linear, e.g. cyanide ion.
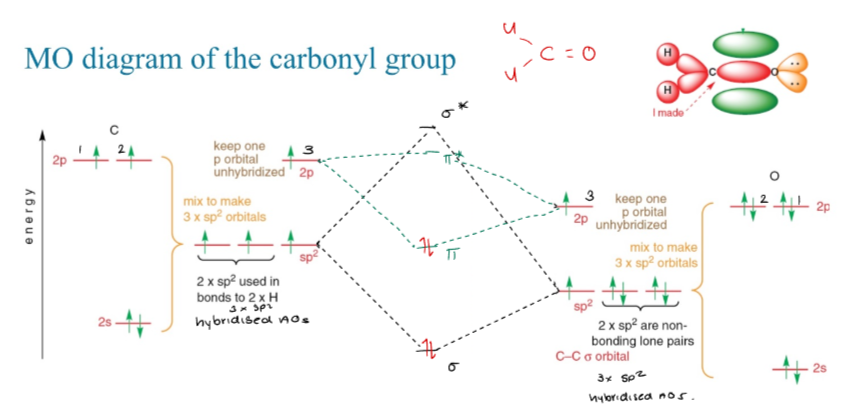
What is the molecular orbital diagram of a carbonyl?
The molecular orbital diagram of a carbonyl shows the interaction of the carbon's sp2 hybrid orbitals with the oxygen's sp2 hybrid orbital, forming a σ bond, along with π bonds formed by the overlapping p-orbitals. This results in a planar structure with distinct bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals.
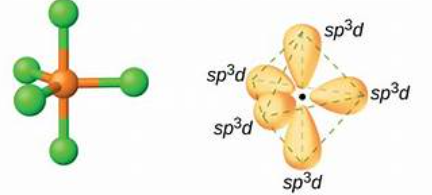
What is sp3d hybridsation?
Sp3d hybridisation involves the mixing of one s, three p, and one d orbital, resulting in five hybrid orbitals. The geometry is trigonal bipyramidal, with a notable example being ClF3.