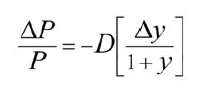CFP - Investment
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
correlation coefficient
-1 to 1+
1+ = perfect correlation
0 = no correlation
-1 = perfect negative correlation
margin call
purchase price x (1-initial margin/1-maint. Margin)
strong form
all information
semi strong form
all public information is reflected in current prices. insider information will help
weak form
only past information is reflected in current prices. fundamental and insider information can help
standard deviation
- 68 - 34
- 95 - 13.5
- 99 - 2
in the money, at the money, out of the money
in = exercise < common stock price
at = exercise = common stock price
out = exercise > common stock price
intrinsic value
stock price - current price
Beta
captures systematic risk
Pim = Correlation coefficient
Covariance
How investment move in relation to each other
Pij x Oi x Oj
Pij = Correlation Coefficient
Oi = std dev investment 1
Oj = std dev investment 2
Required rate of return
(D1 / P) + G
D1 = dividend payment
P = market price
G = Dividend Growth Rate
Dividend Growth Model
answer = intrinsic value
compare answer to current market price
V = D1 / (r-g)
D1 = Dividend payment
r = required rate
g = Dividend Growth Rate if multiple, calculate for final year then use formula
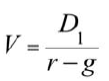
Sharpe Ratio
Measures return per unit of total risk. compare two funds to see what one give best return for risk
= Rp-Rf / Op
Rp = portfolio return
Rf = Risk Free
Op = Std dev
Treynor Ratio
Measures return per unit of systematic risk.
Compare fund to market
Current Yield
Annual Interest / Current Market Price
Yield to Call
interest rates fall, will be called
FV = 1 x call %
PV = -1000
PMT = /2
N = x2
yield to maturity
2x /2
FV = 1
Holding period return
return from time you owned it
(end value - beg value +/- cash flow) / beg investment
Security Market Line
shows a security's EXPECTED return as a function of its systematic risk. defined by CAPM
above - undervalued
lower - overvalued
Expected Return
(%1 x %2) + (%1 x %2)
%1 = probability %
%2 = return %
long hedge
transaction where the asset is not currently held but futures are purchased to lock in current prices.
short hedge
transaction involving the sale of futures while holding the asset
Capital asset Pricing Model
rf + (rm-rf)b
rf = risk free
rm = market return
b = beta
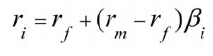
duration
y= yield
c = coupon rate
t = periods till maturity
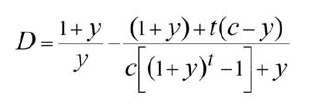
capitalization approach
earnings / cap rate
alpha
positive means manager outperformed market on risk adjusted basis
indicates how much the realized return differs from the required return
arbitrage pricing theory (APT)
a stock's price depends upon variables other than the market return and the volatility of returns of the stock.
time weighted return
best for evaluating a portfolio managers performance
indifference curve
higher the curve more satisfied the investor
depict investors preference for risk and return
Averse = concave
serial bonds
Series of maturity dates = multiple maturity dates
Typically municipalities
% change in bond price
-duration x change in yield/ (1 + current yield)
capital asset pricing model
expected rate of return
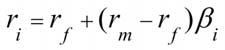
change in bond price (formula)
Delta = Change