Terminology, Planes, Abdominal Regions, and Body Cavities (Lab 1)
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
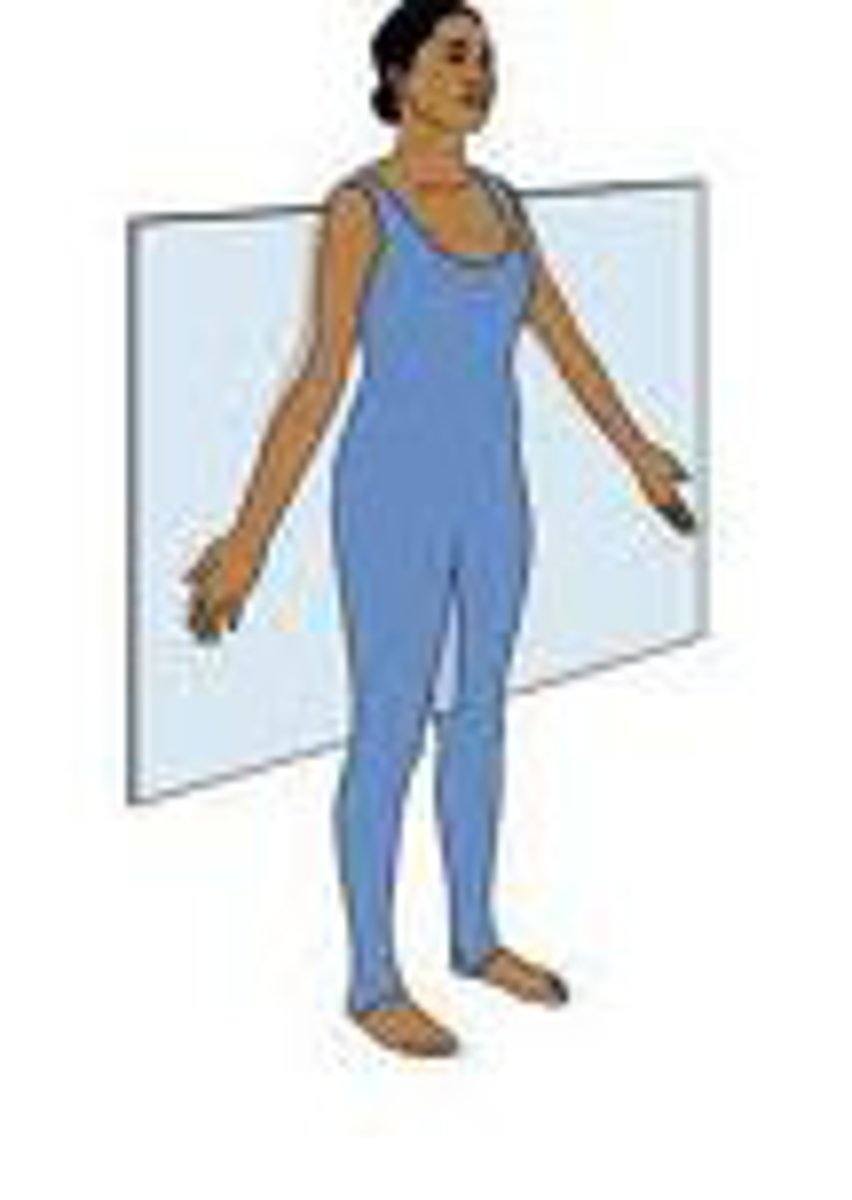
Anatomical position
Standardized position from which to describe directional terms: standing upright, facing the observer, head level, eyes facing forward, arms at the sides, palms turned forward, feet flat on the floor.
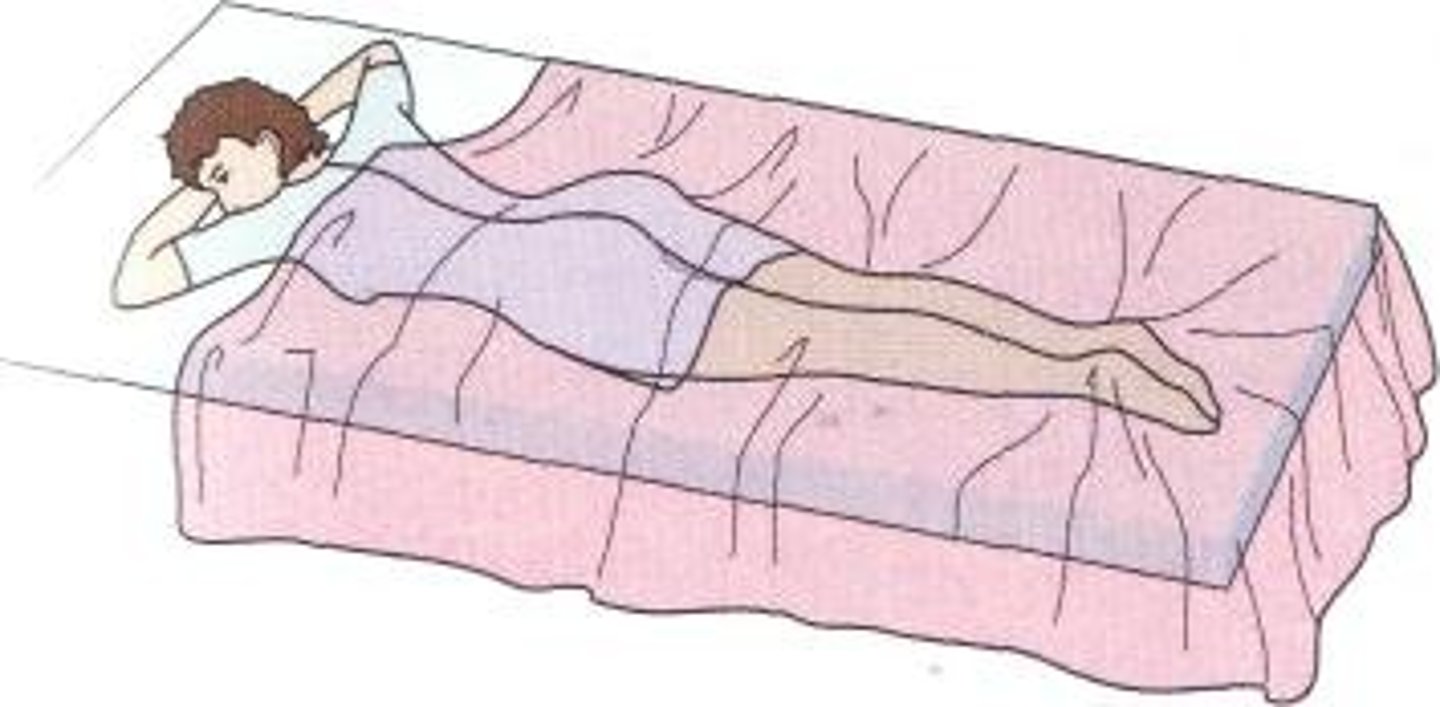
Prone position
Lying face down.
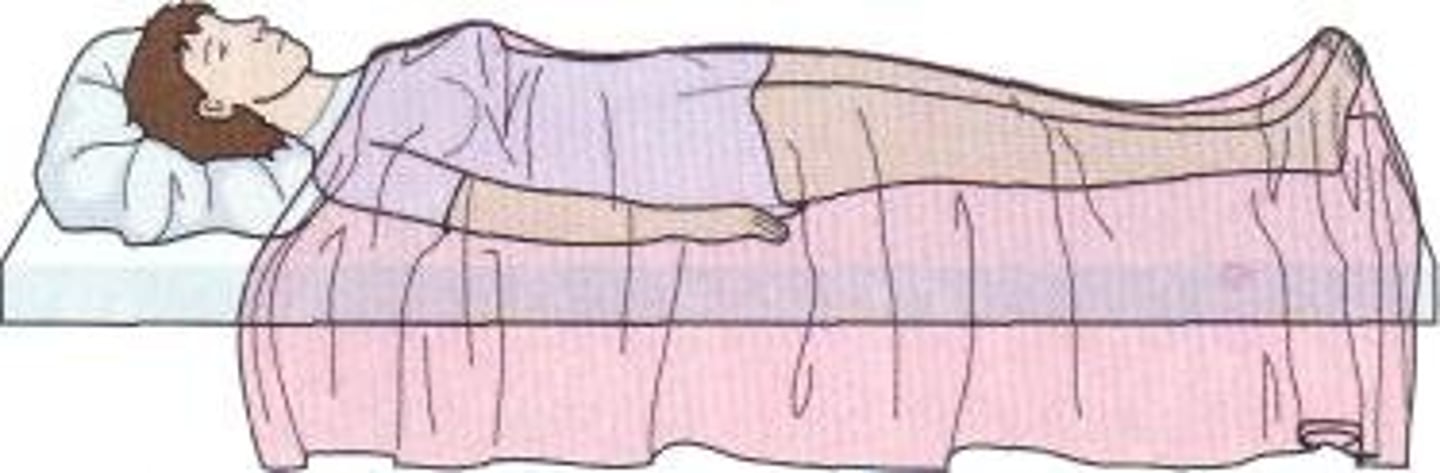
Supine position
Lying face up.
Superior (Cranial)
Above, at a higher level, towards the head.
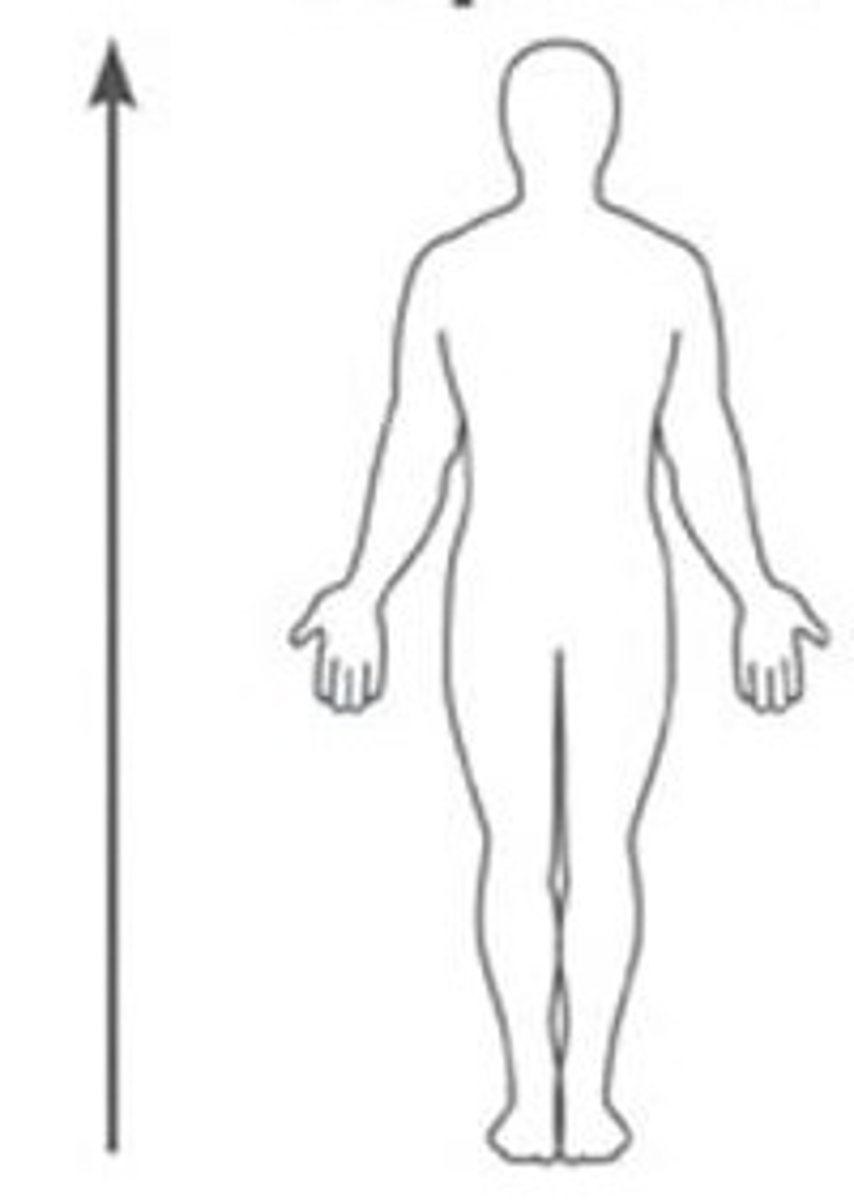
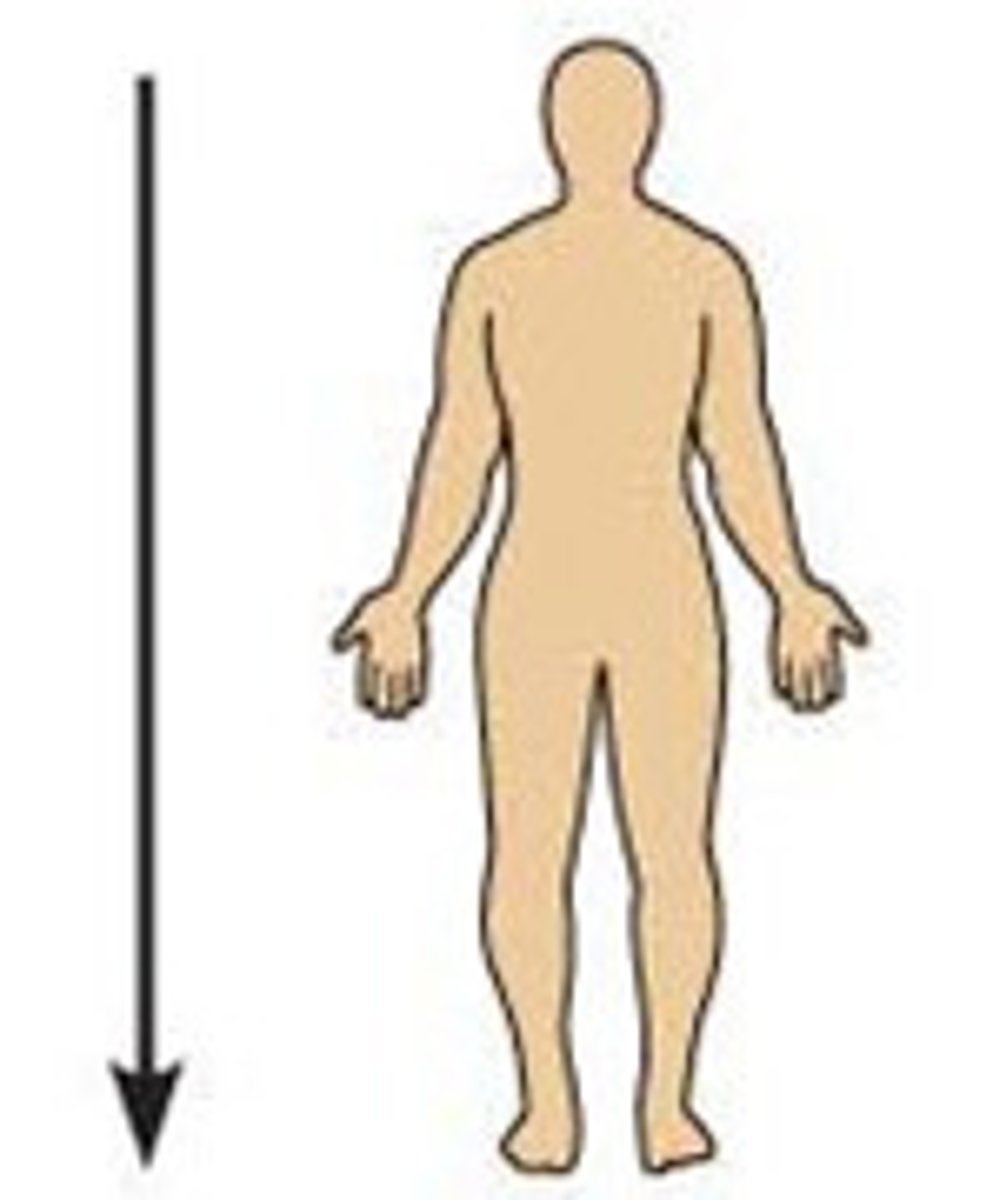
Inferior (Caudal)
Below, at a lower level, away from the head.
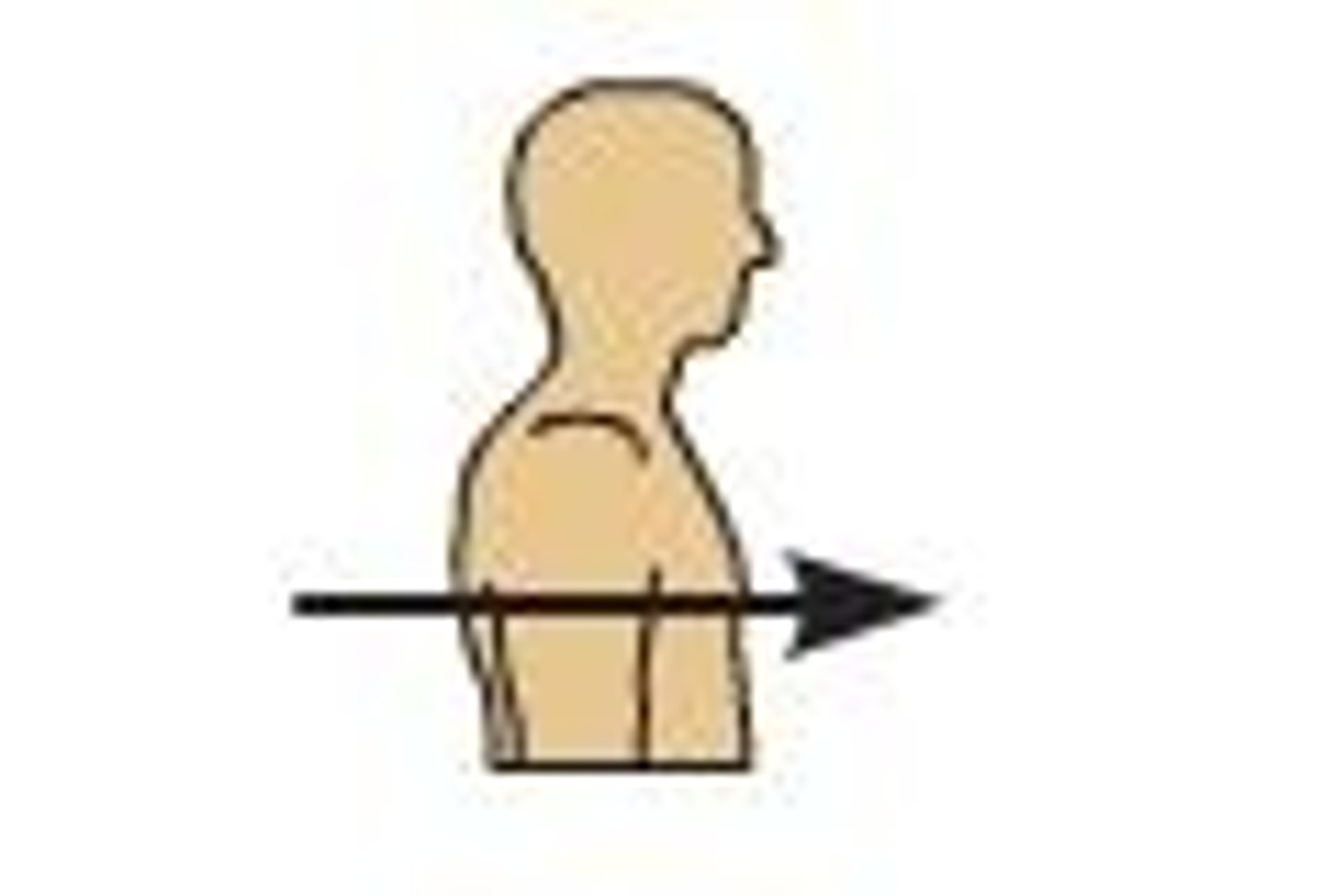
Anterior (Ventral)
At the front of the body.
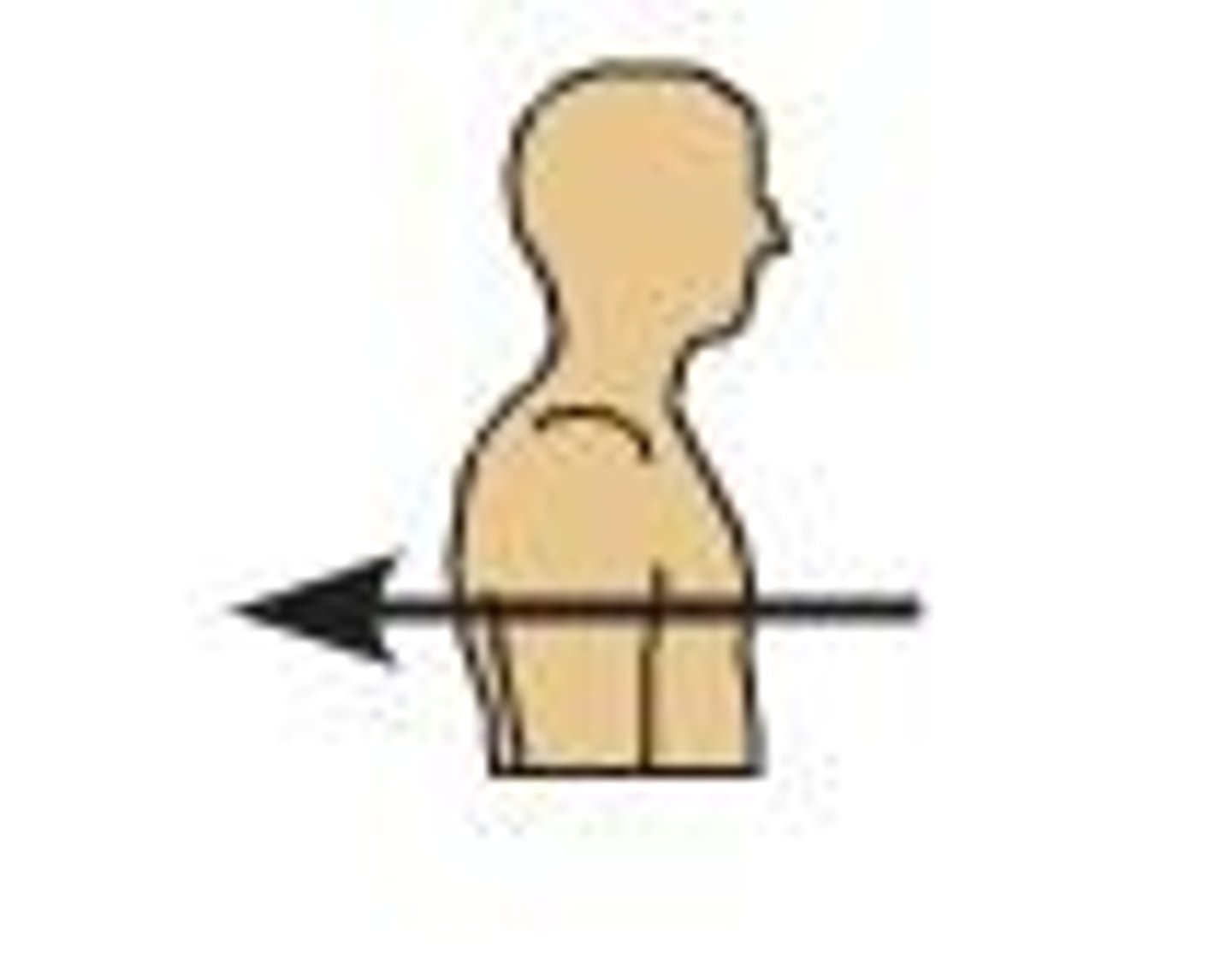
Posterior (Dorsal)
At the back of the body.
Medial
Nearer to the midline of the body.
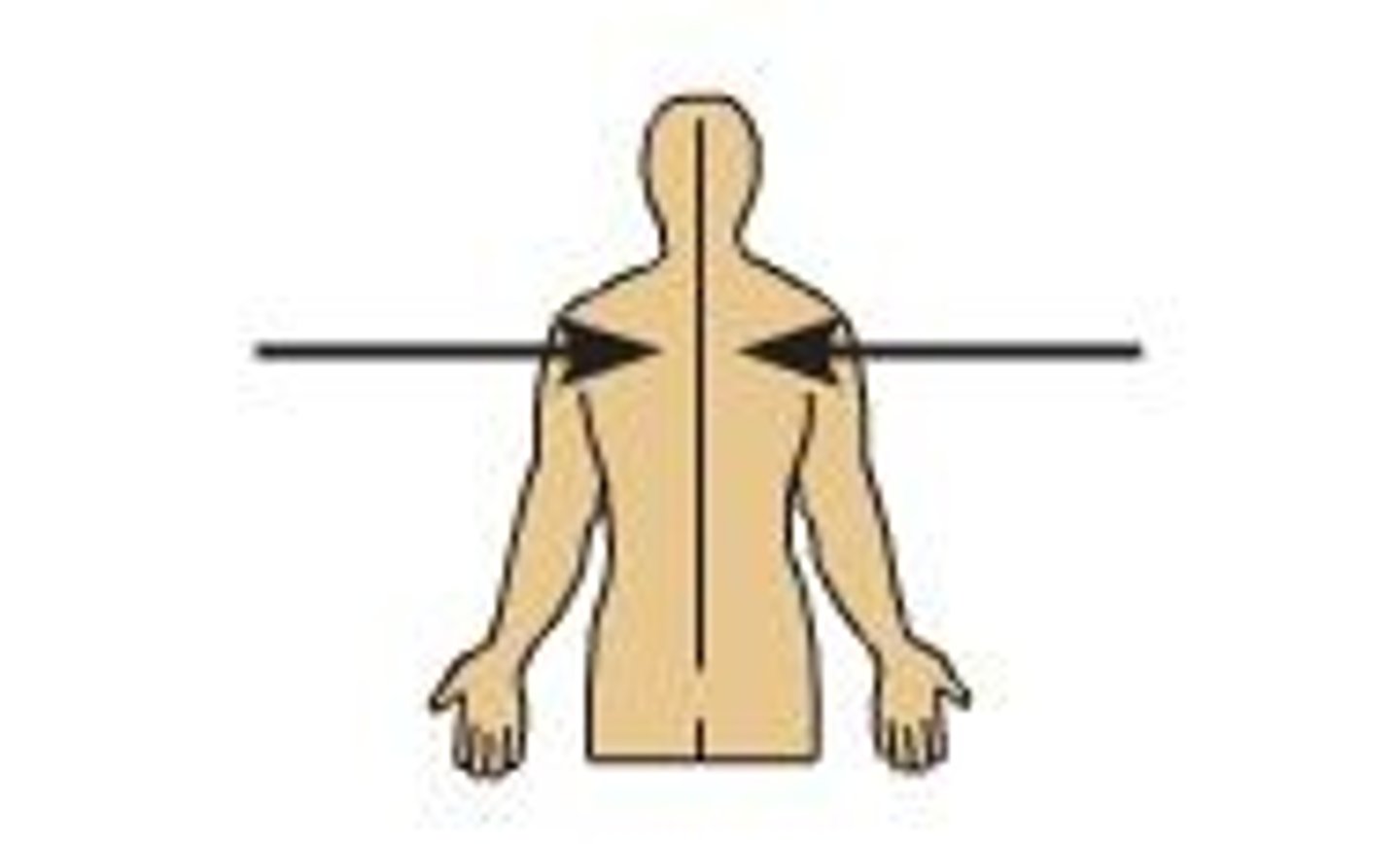
Lateral
Farther from the midline of the body.
Intermediate
Between a medial and lateral structure.
Proximal
Nearer to the attachment of the limb to the trunk.
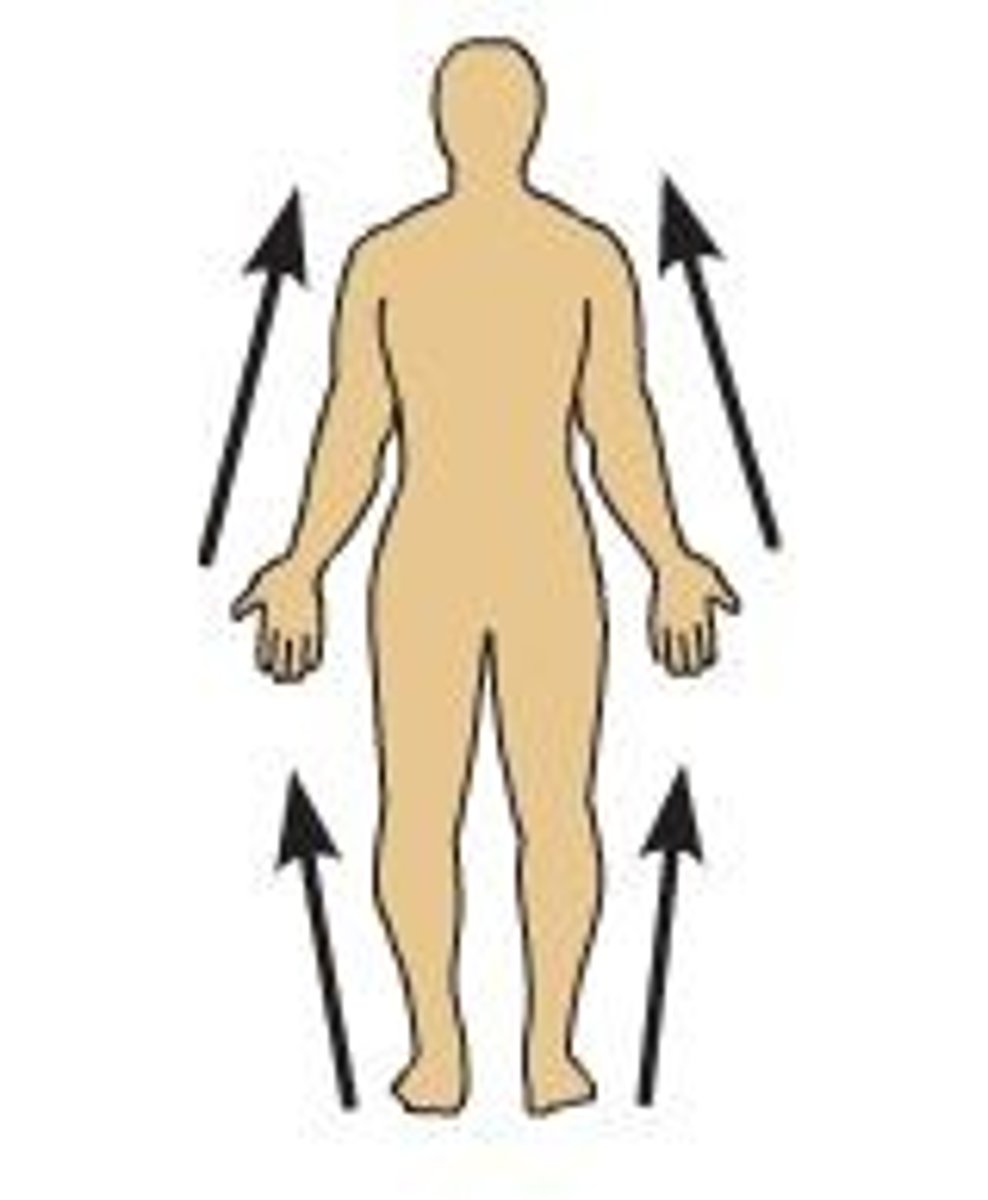
Distal
Farther from the attachment of the limb to the trunk.
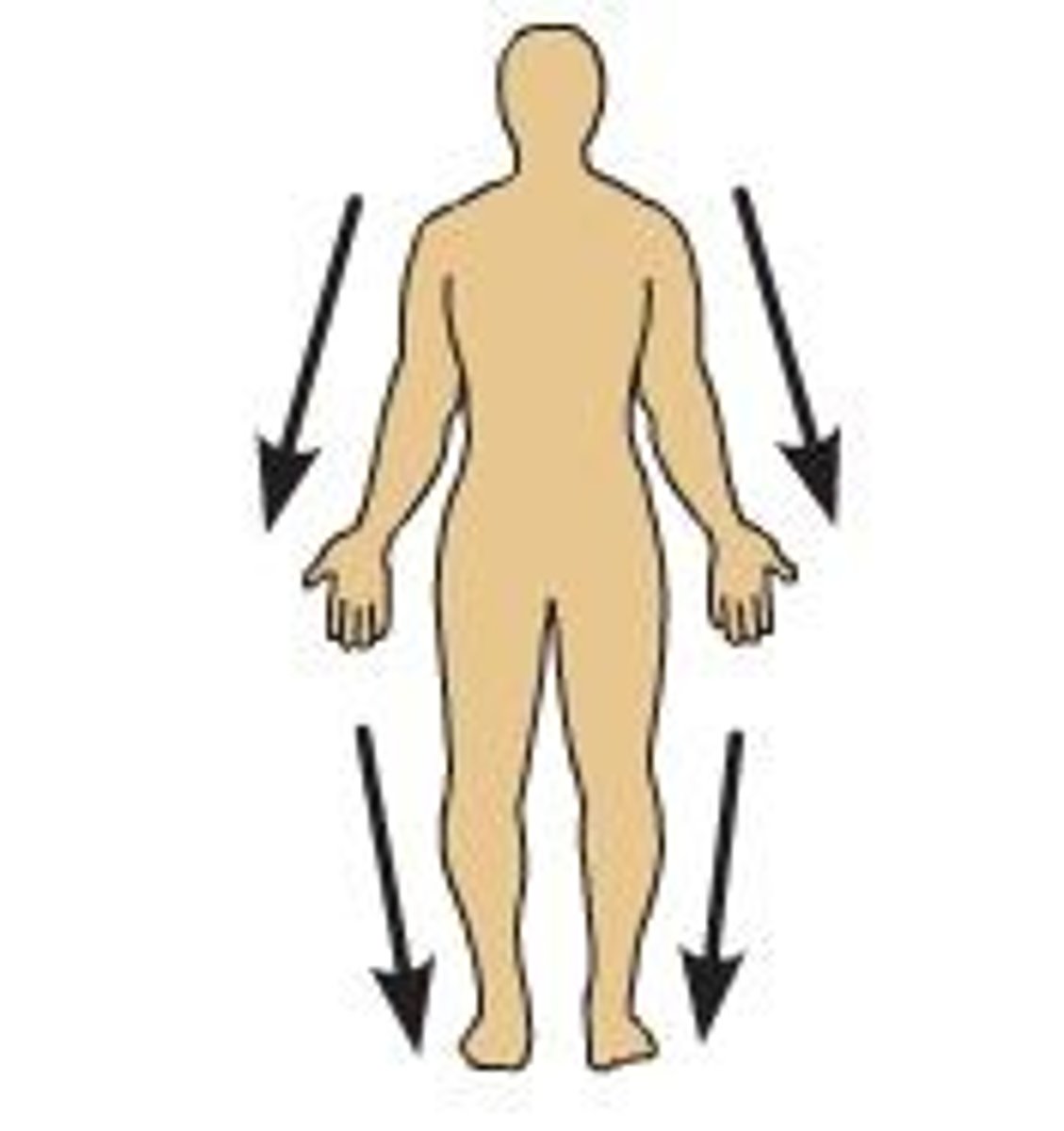
Superficial
Closer to the surface of the body.
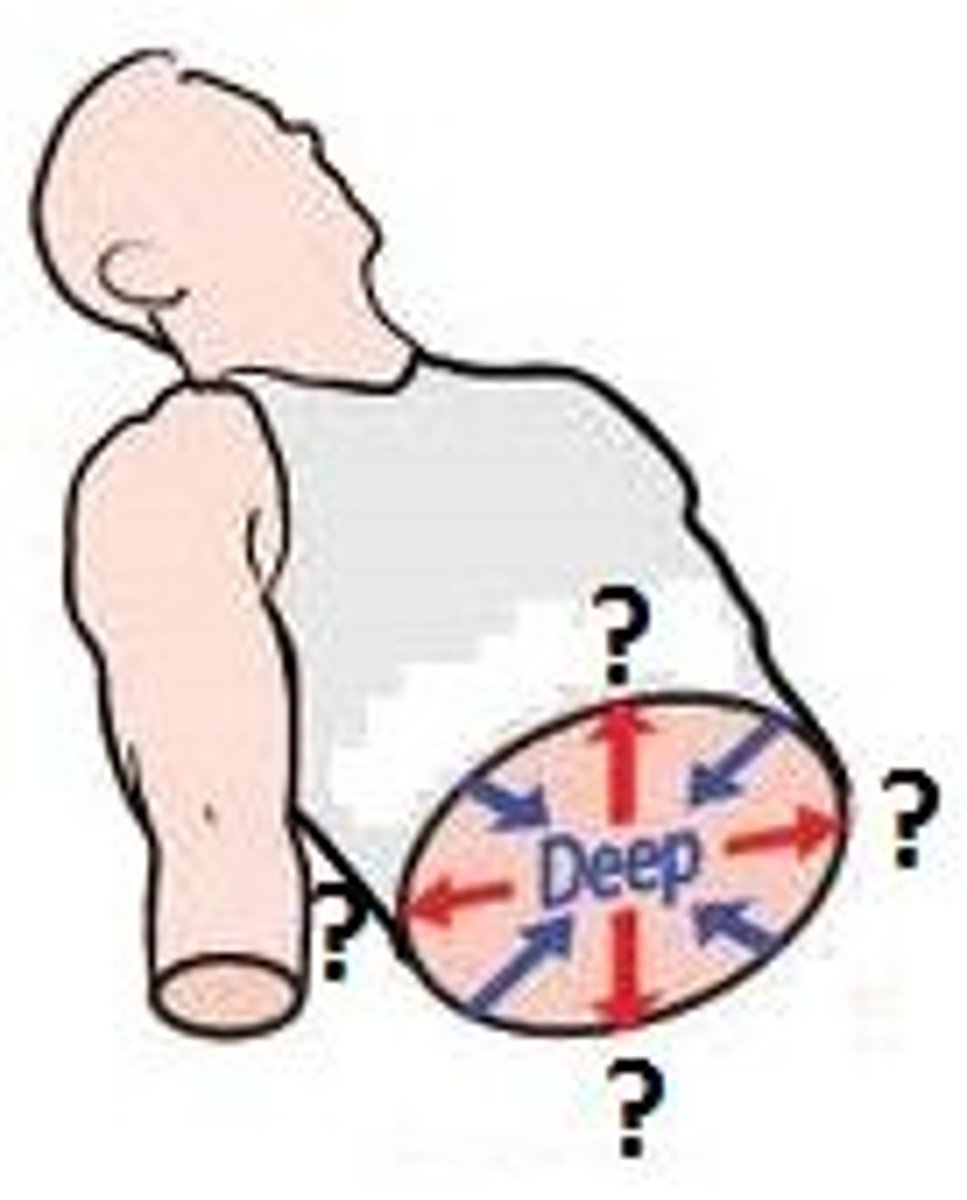
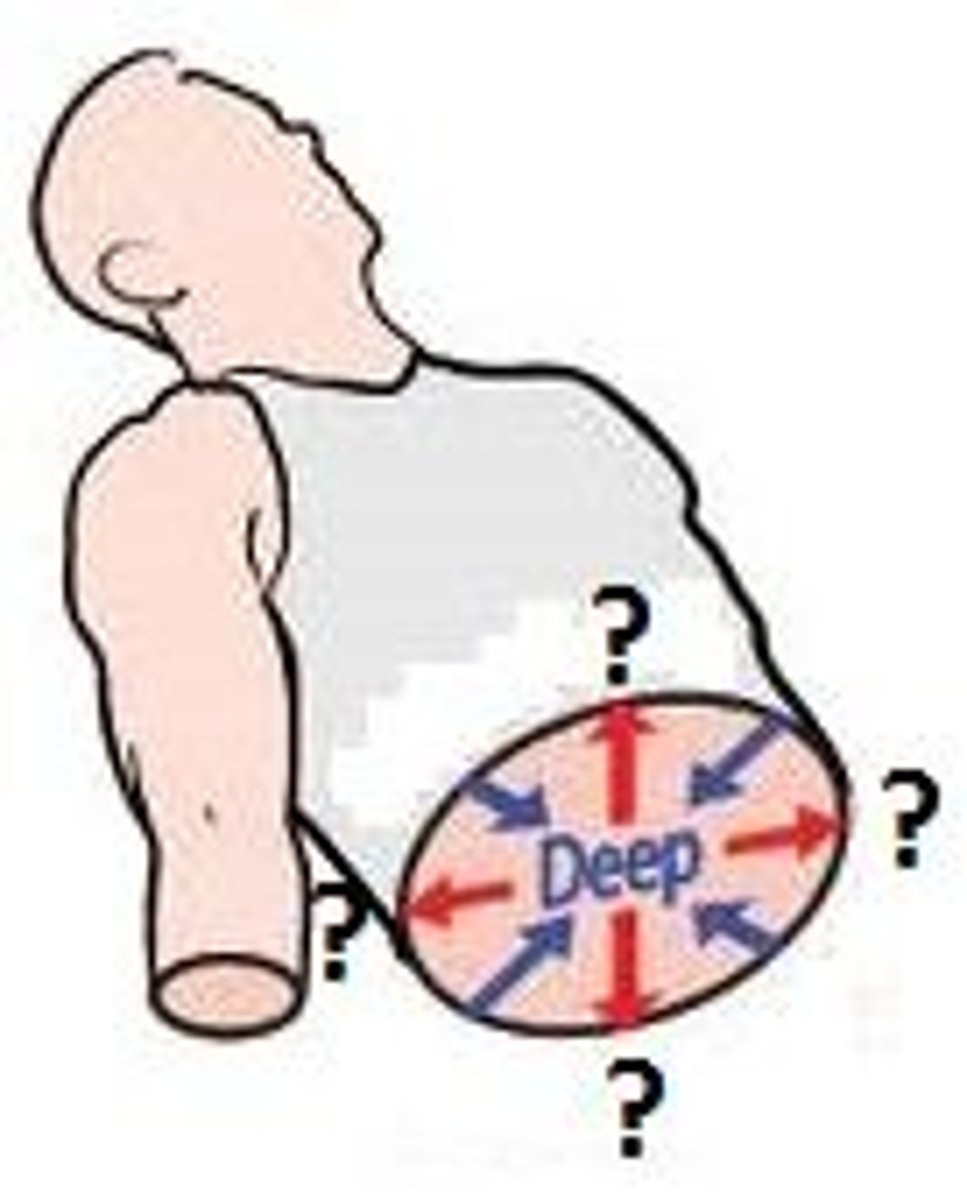
Deep
Farther from the surface of the body.
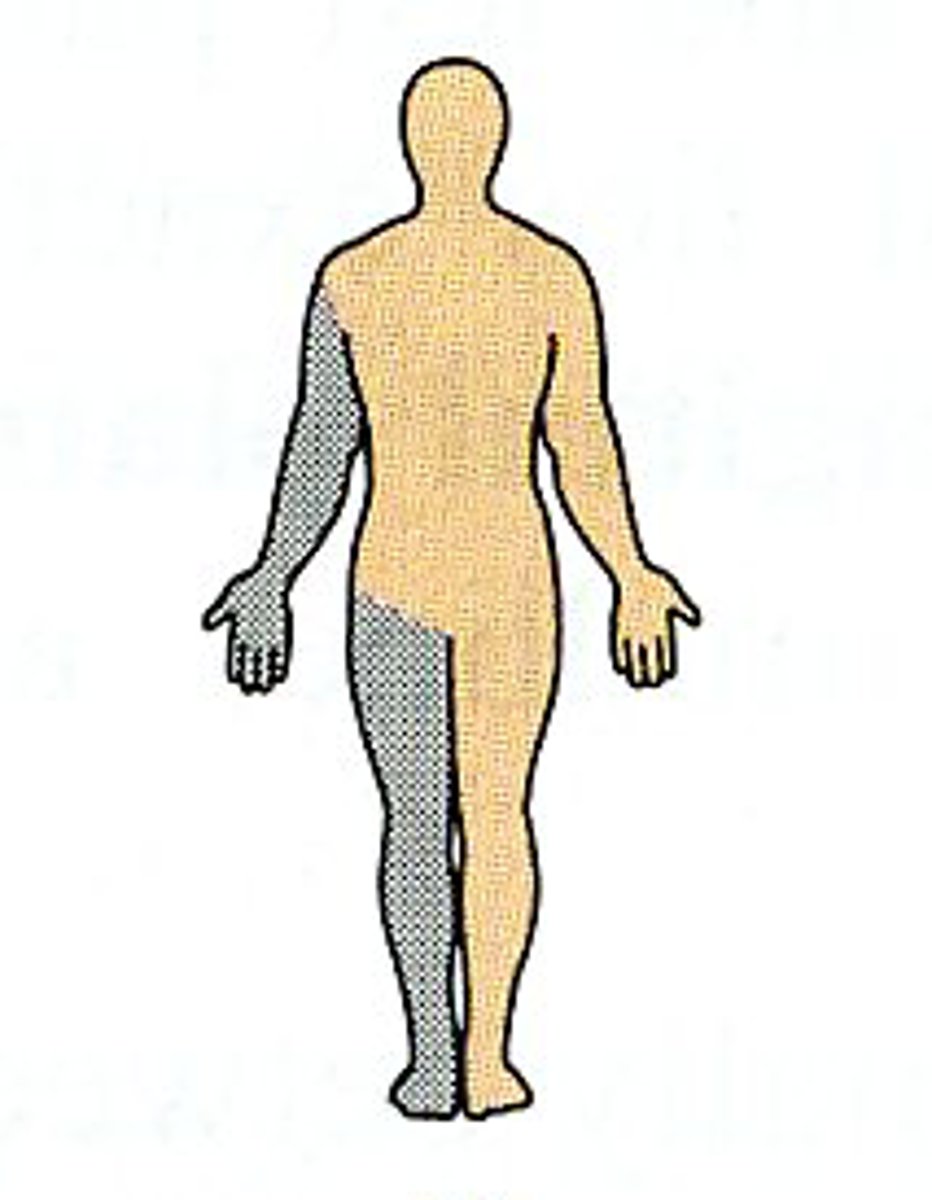
Ipsilateral
Same side of the body.
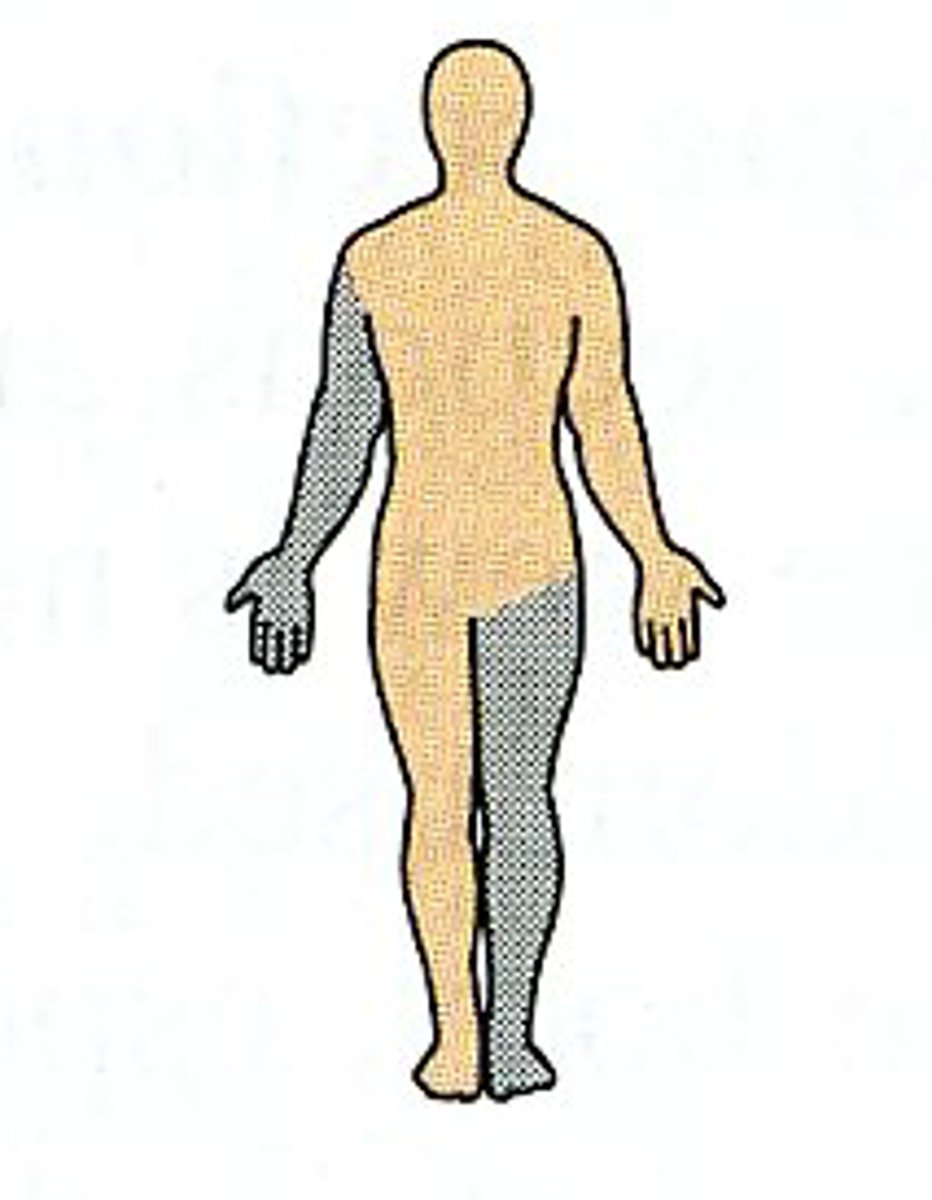
Contralateral
Opposite side of the body.
Parietal
Pertaining to a wall.
Visceral
Pertaining to an organ.
Cephalic
Head.
Cranial
Skull.
Frontal
Forehead.
Facial
Face.
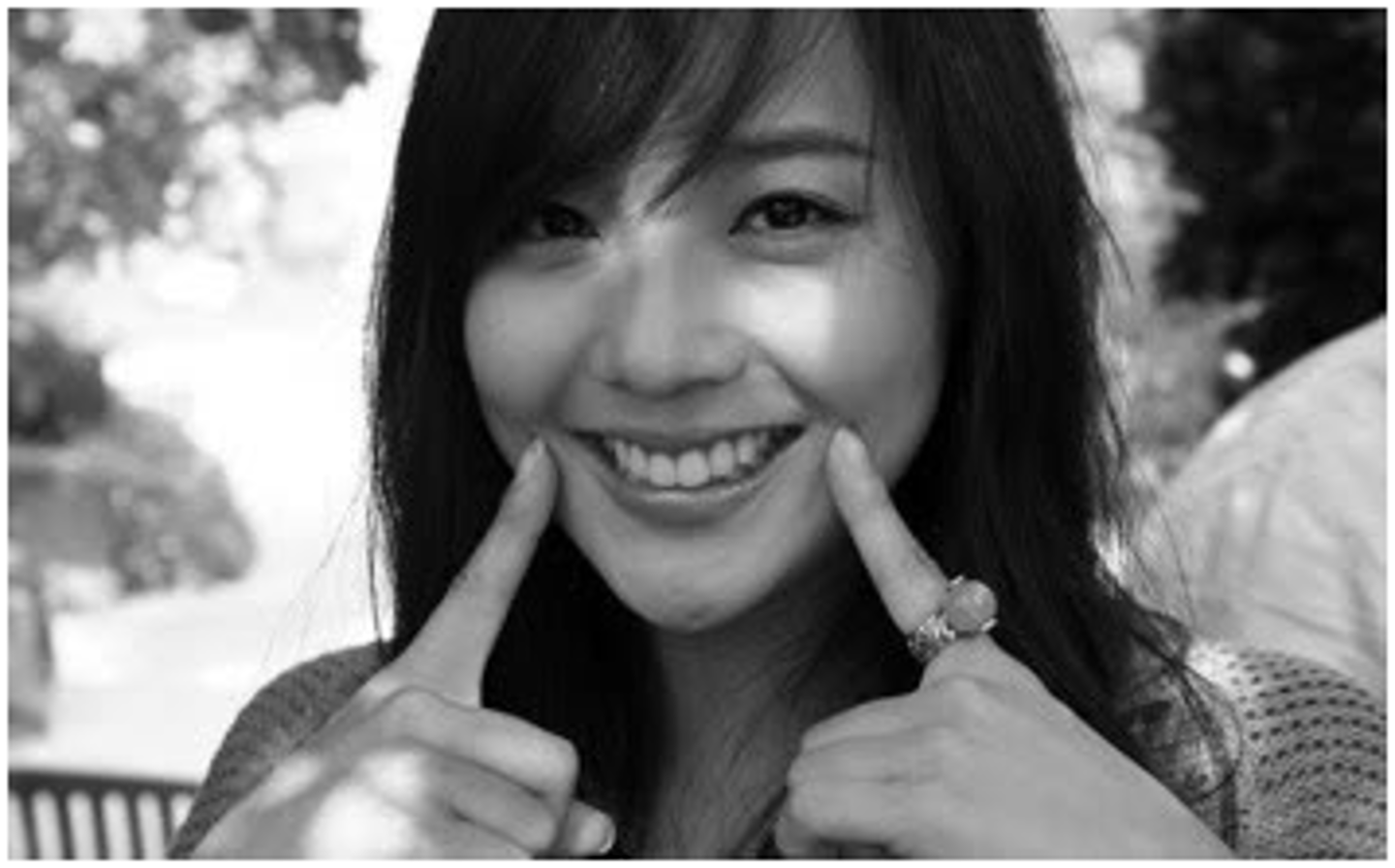

Acromial
High point of the shoulder.
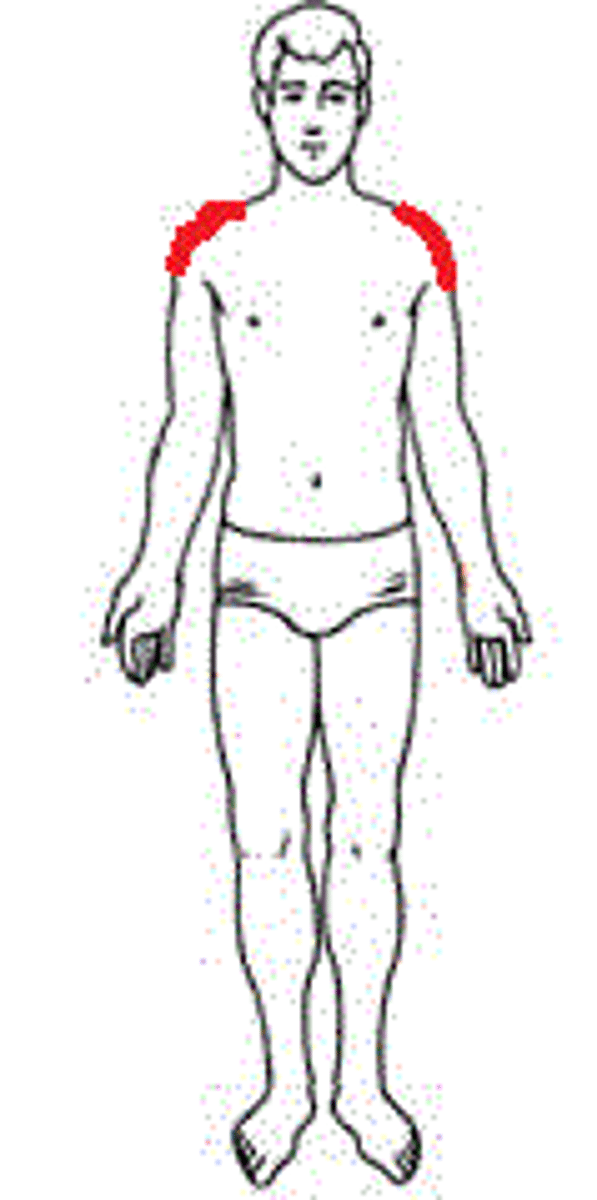
Axillary
Armpit.
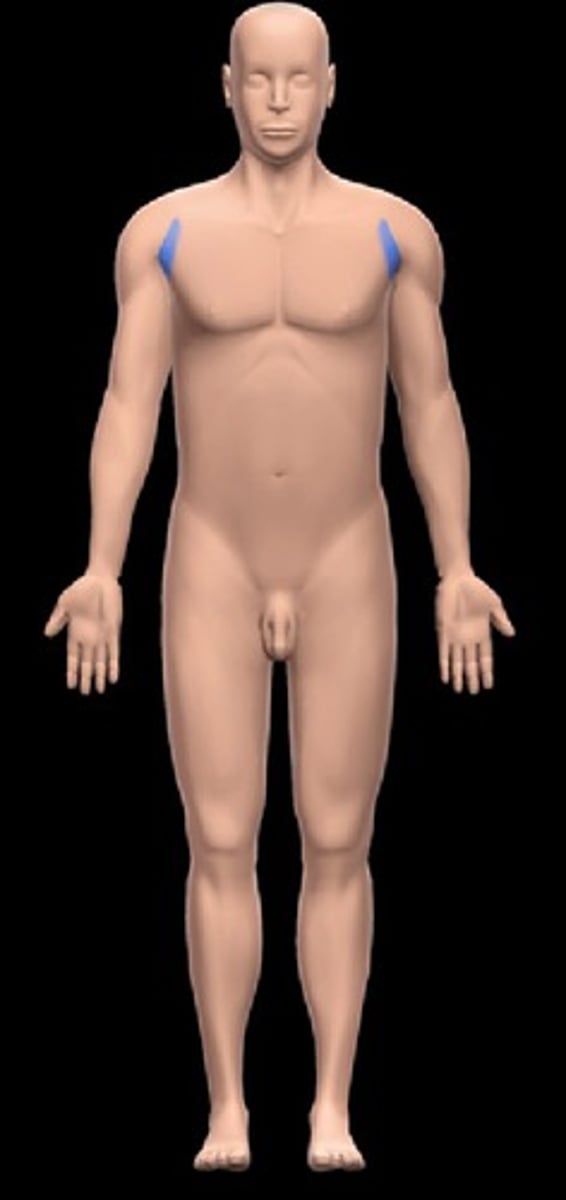
Brachial
Arm.
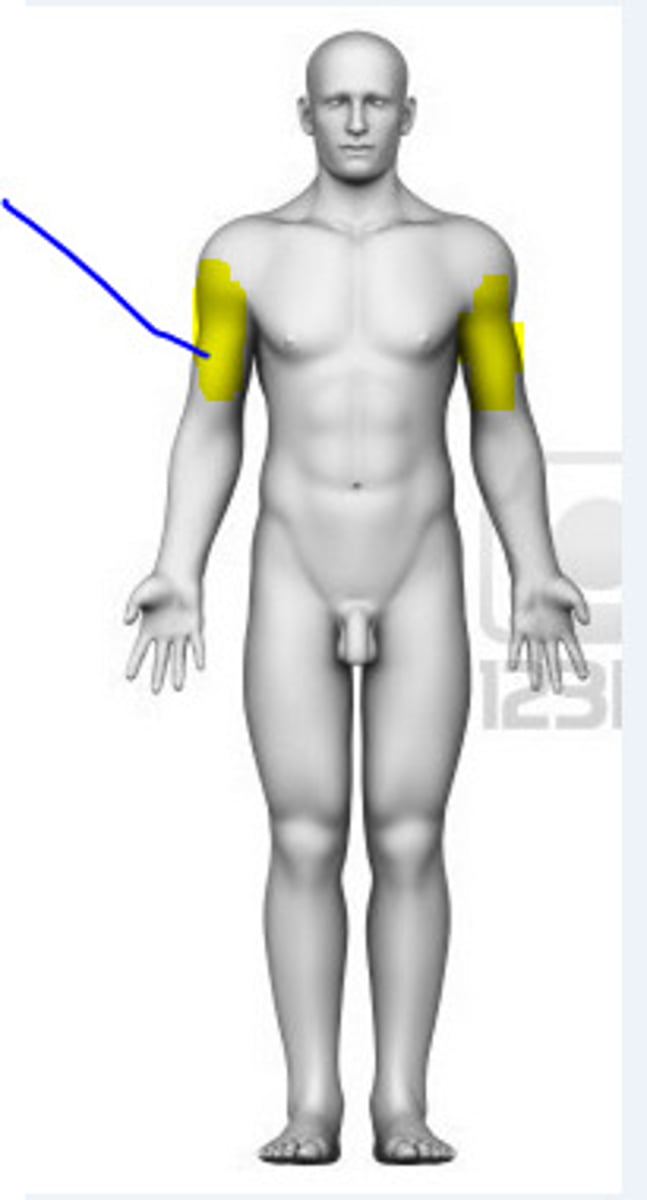
Antebrachial
Forearm.
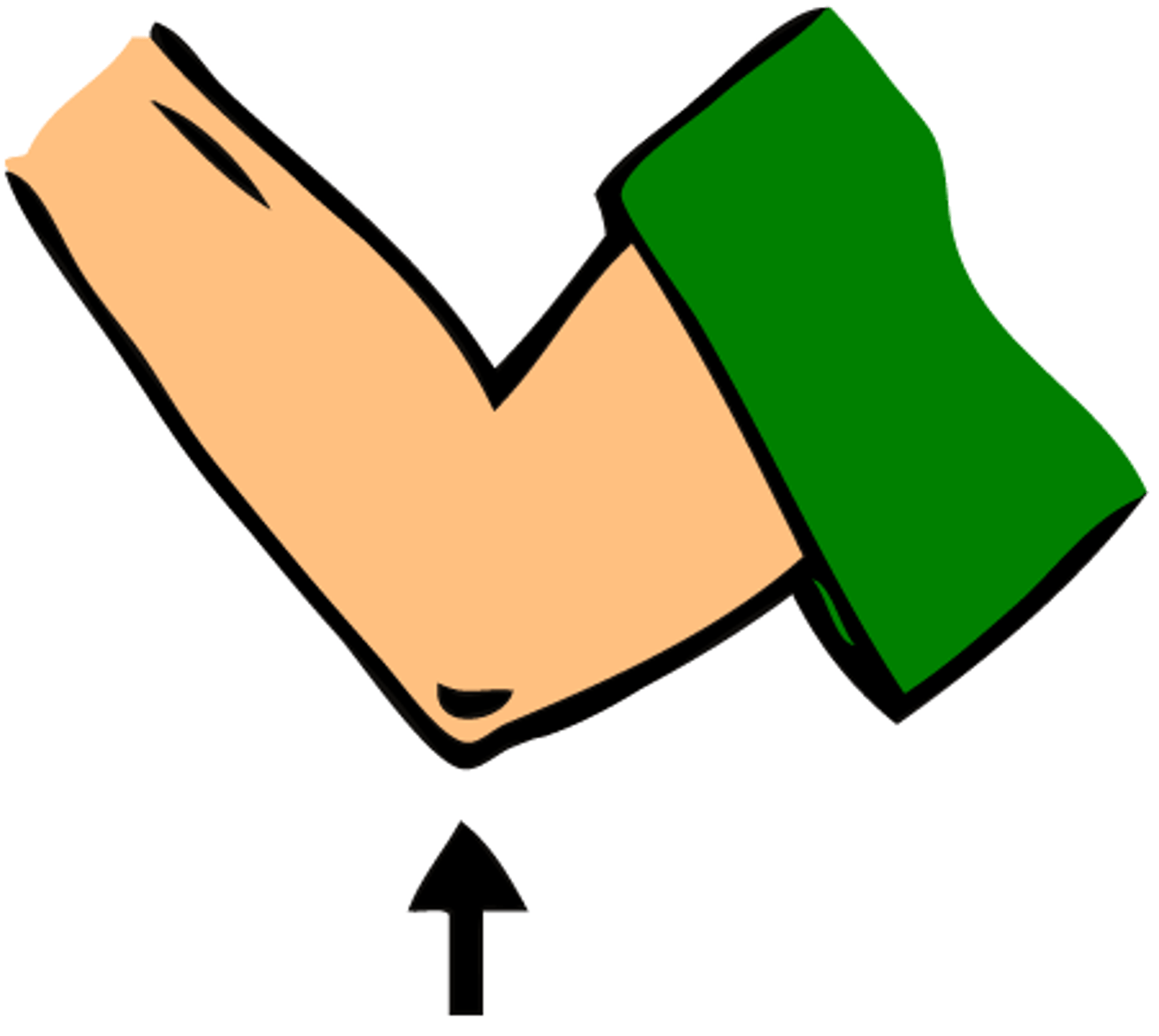
Antecubital
Front of elbow.
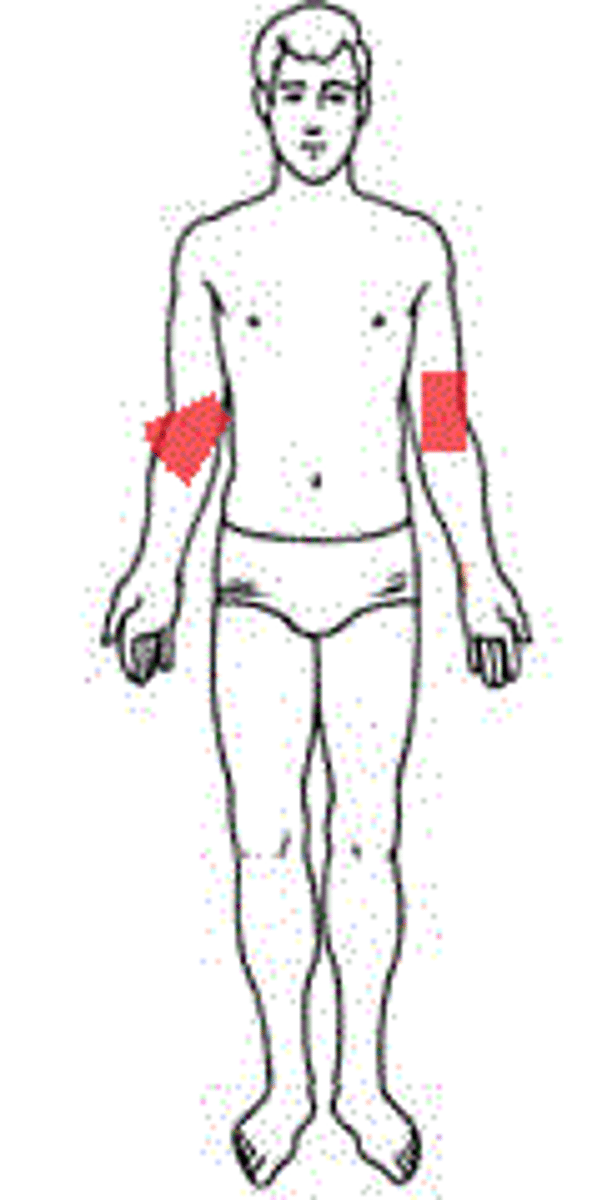
Olecranon
Back of elbow.
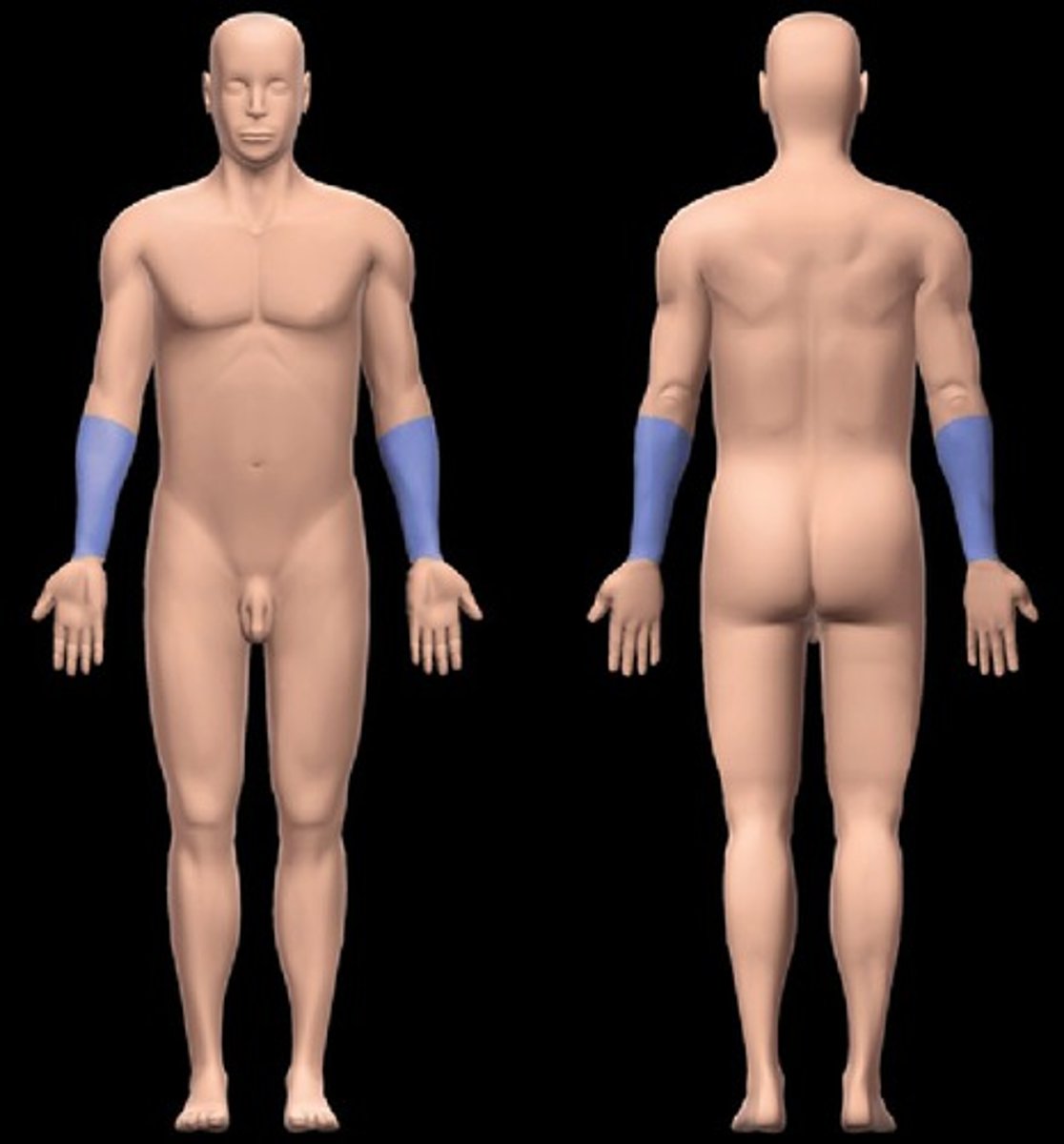
Manual/Manus
Hand.
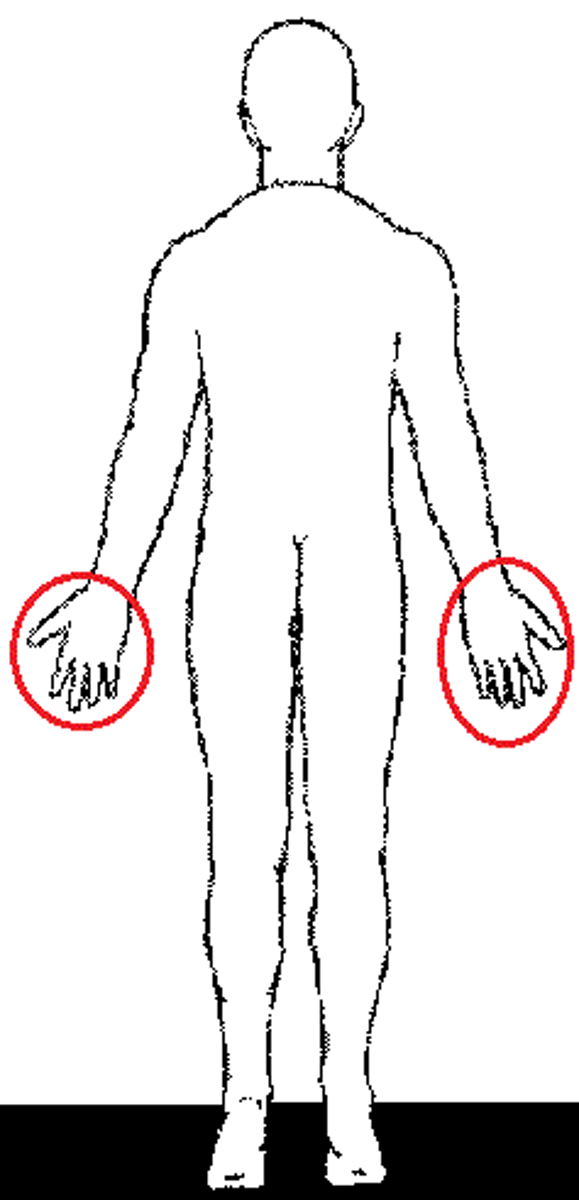
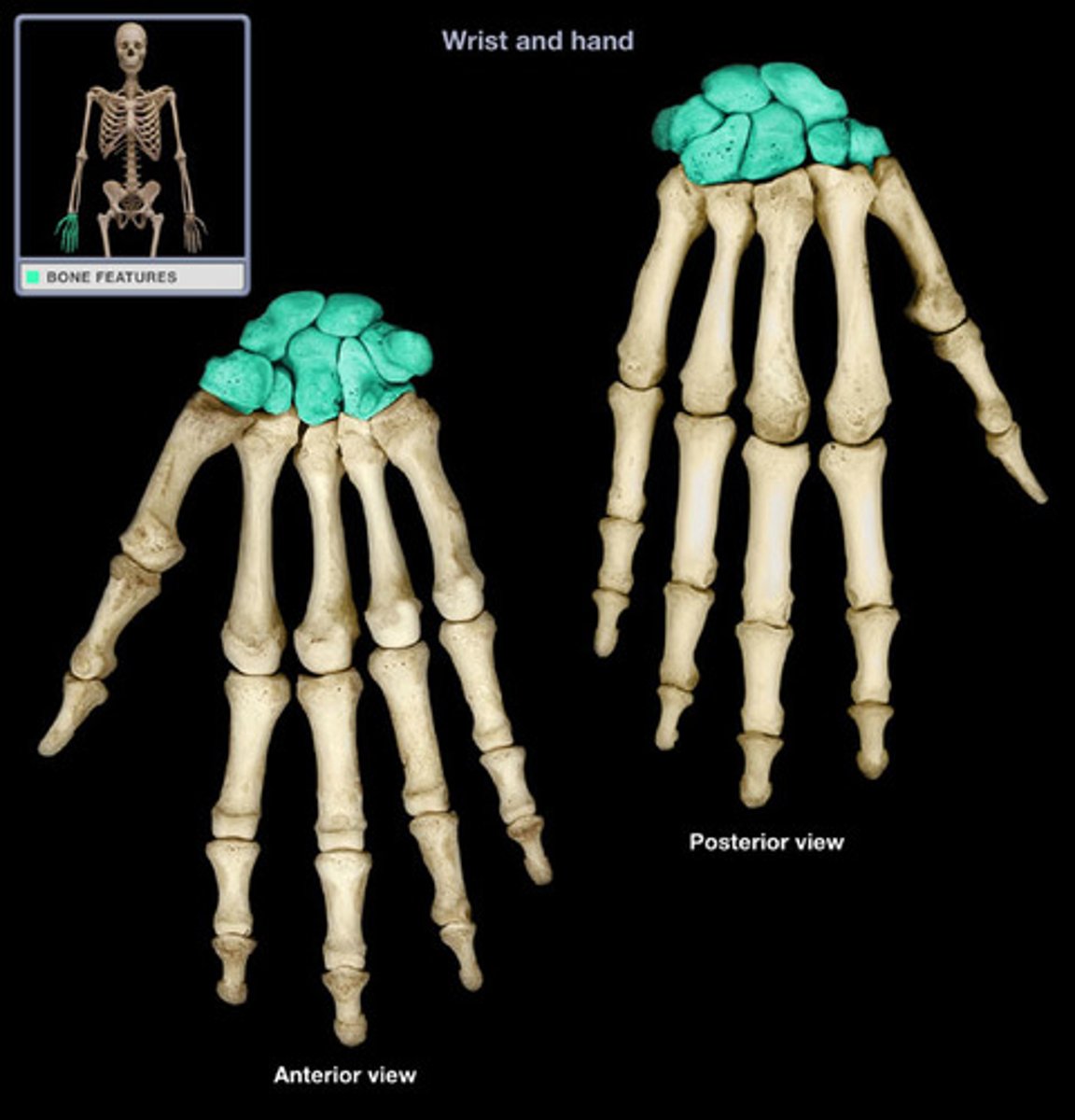
Carpal
Wrist.
Palmar
Palm.
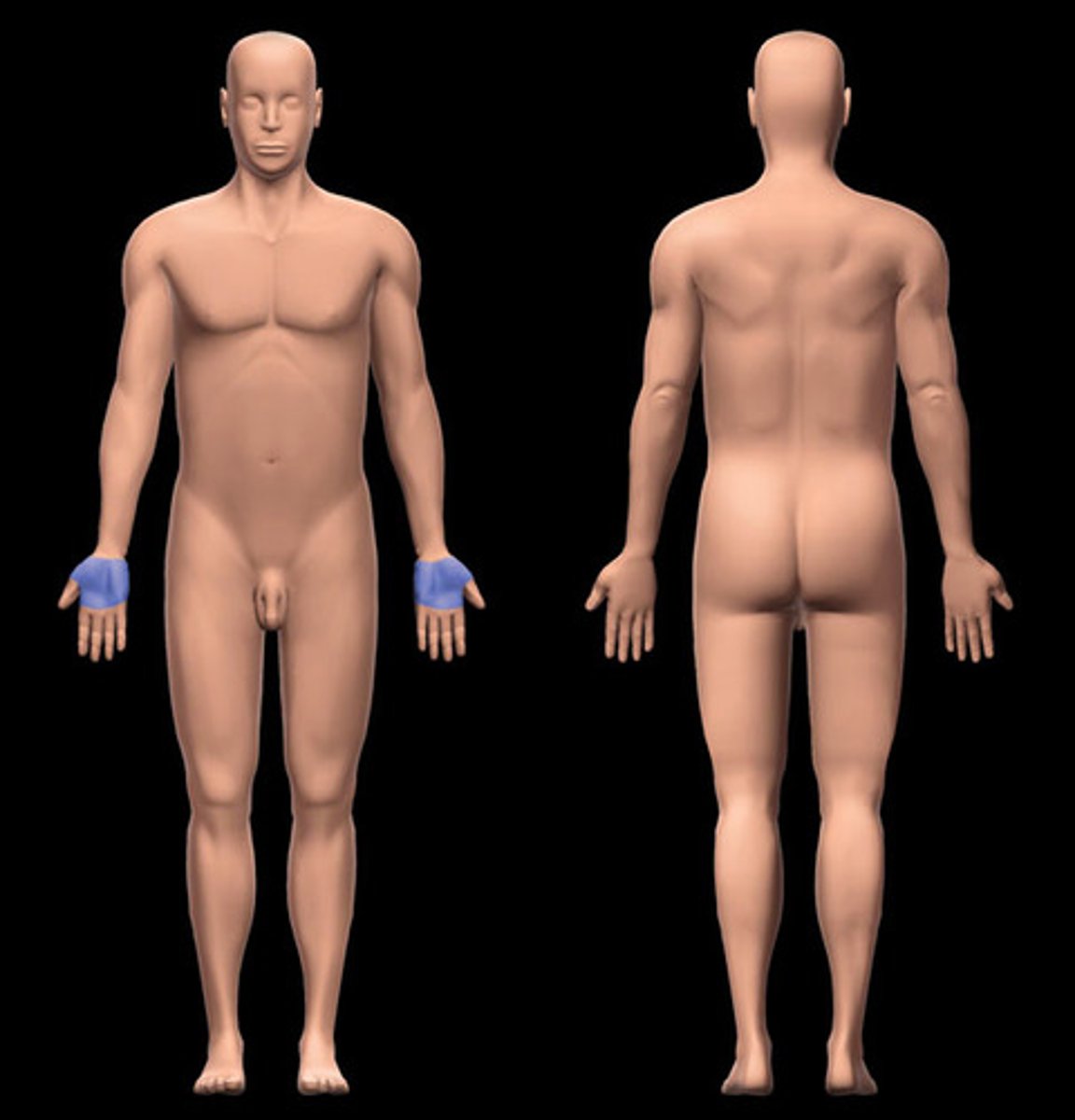
Pollex
Thumb.
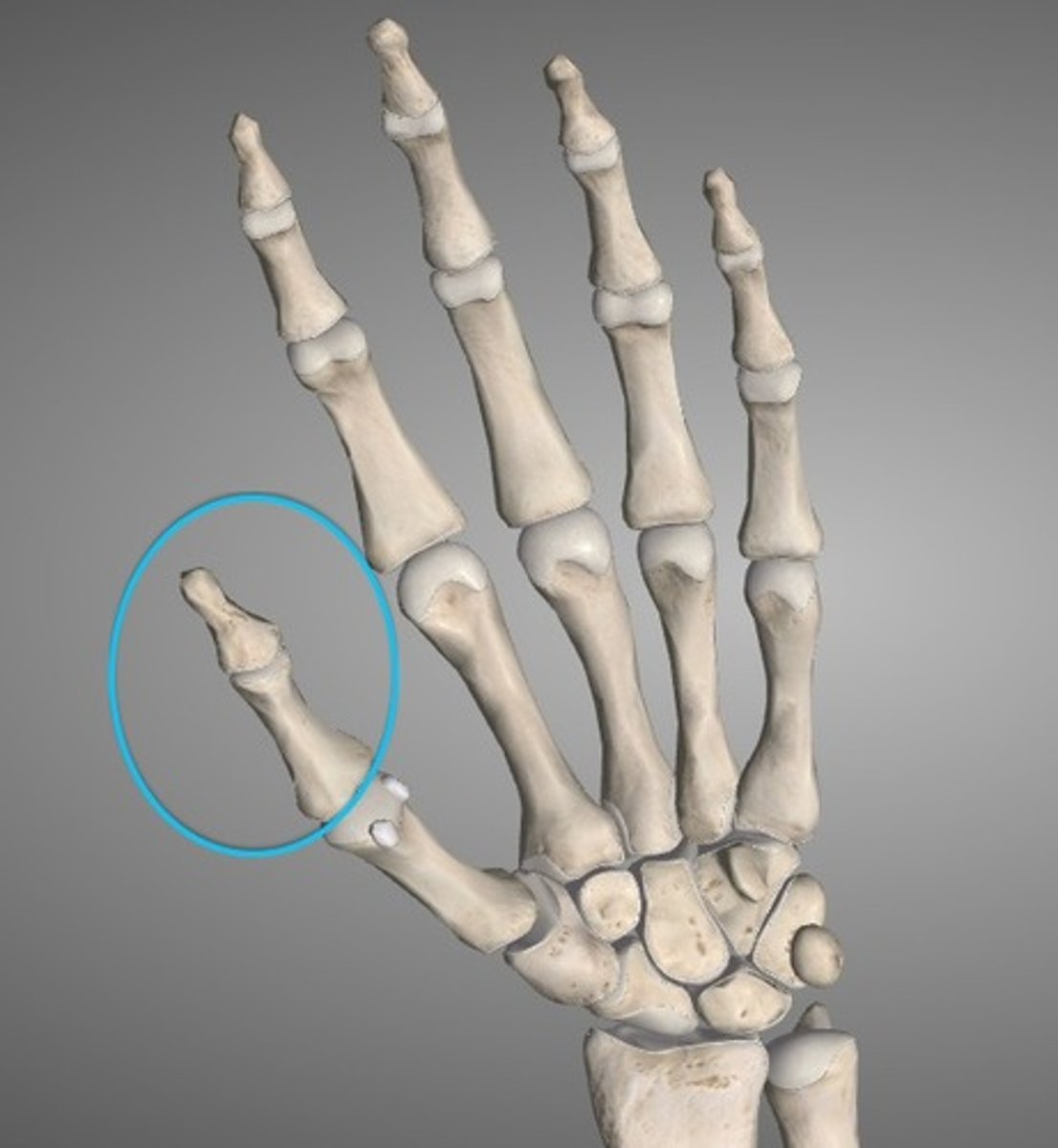
Digital/Phalangeal (upper)
Fingers.
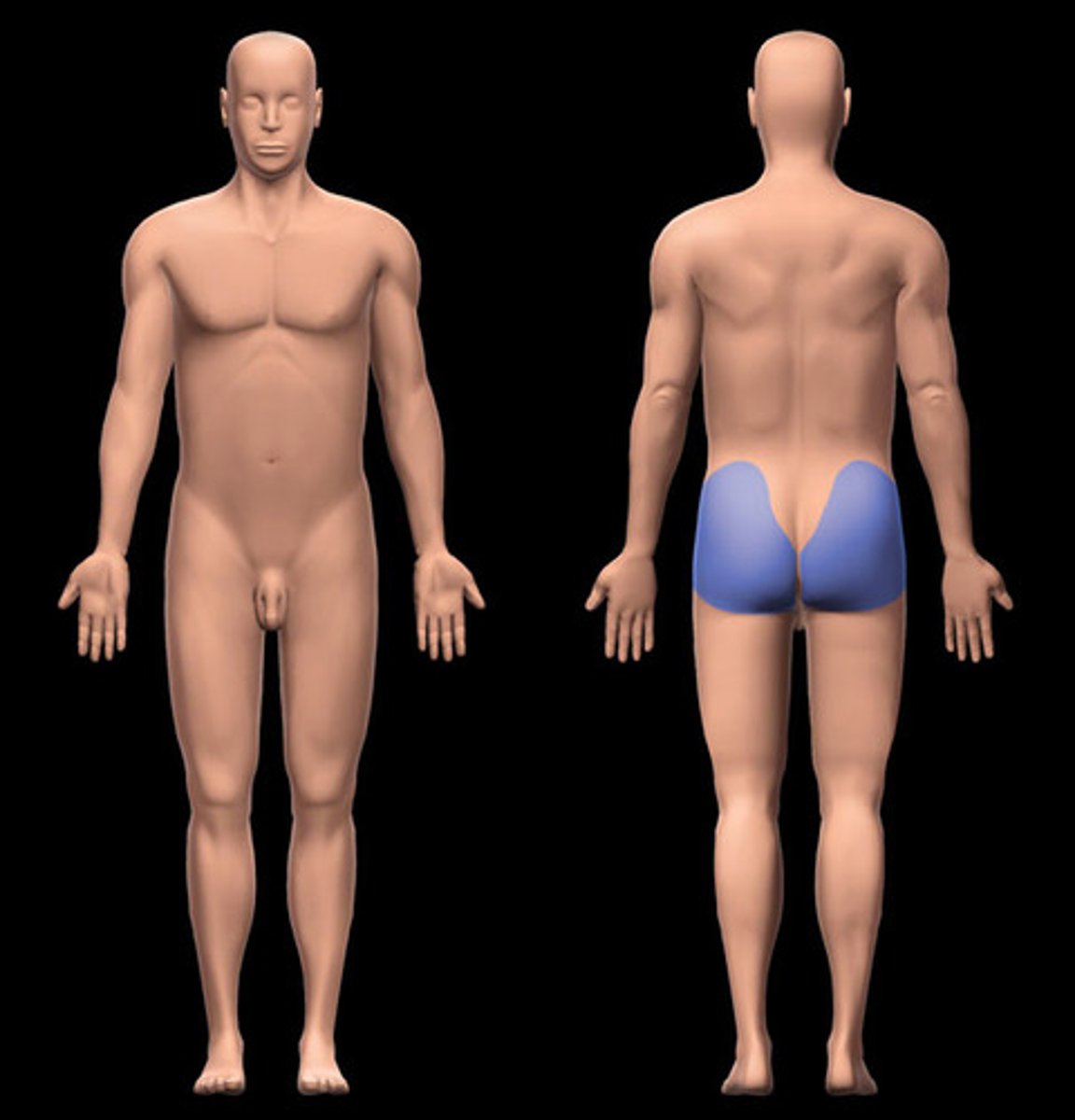
Gluteal
Buttock.
Inguinal
Groin.

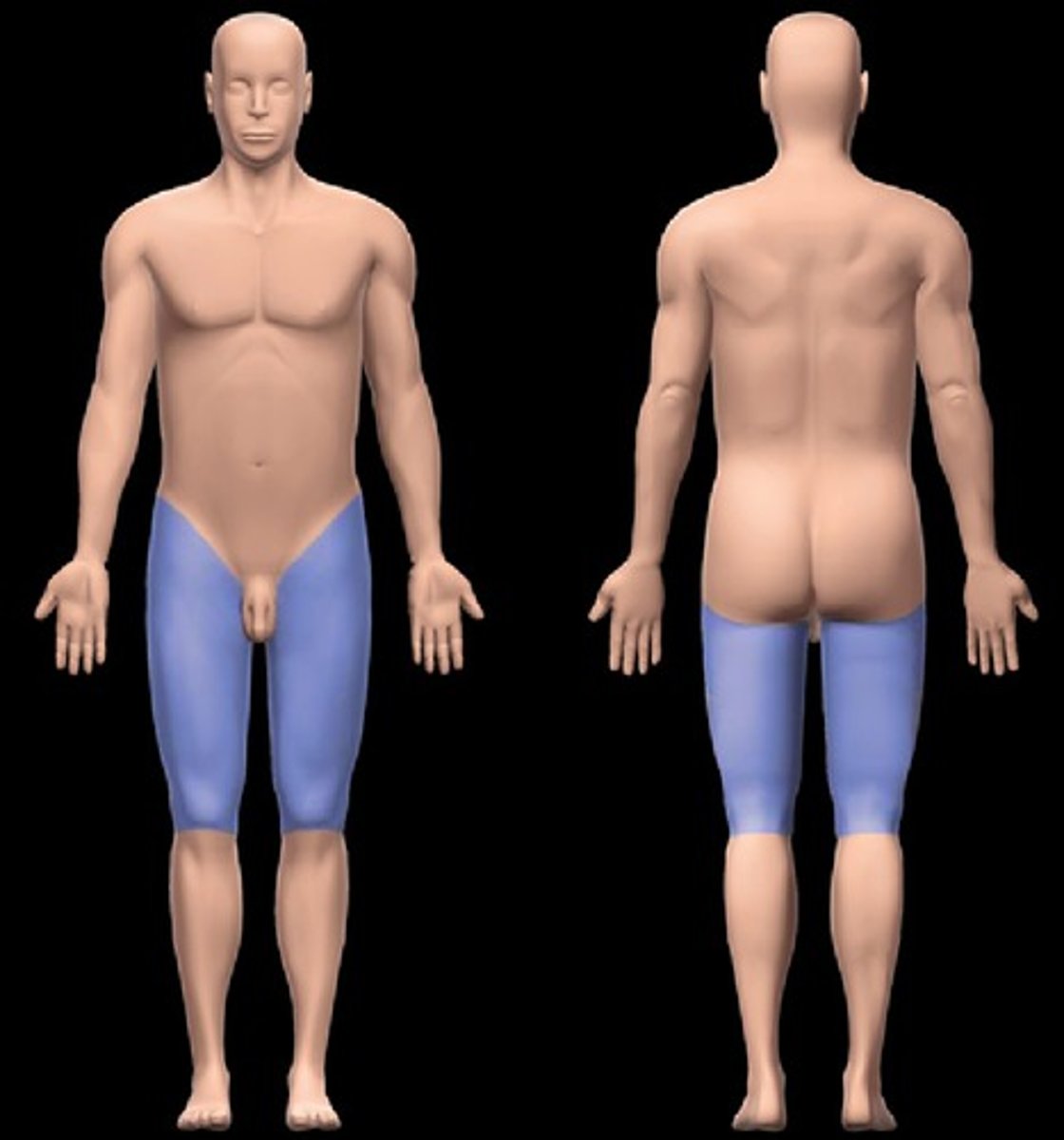
Femoral
Thigh.
Patellar
Front of knee.
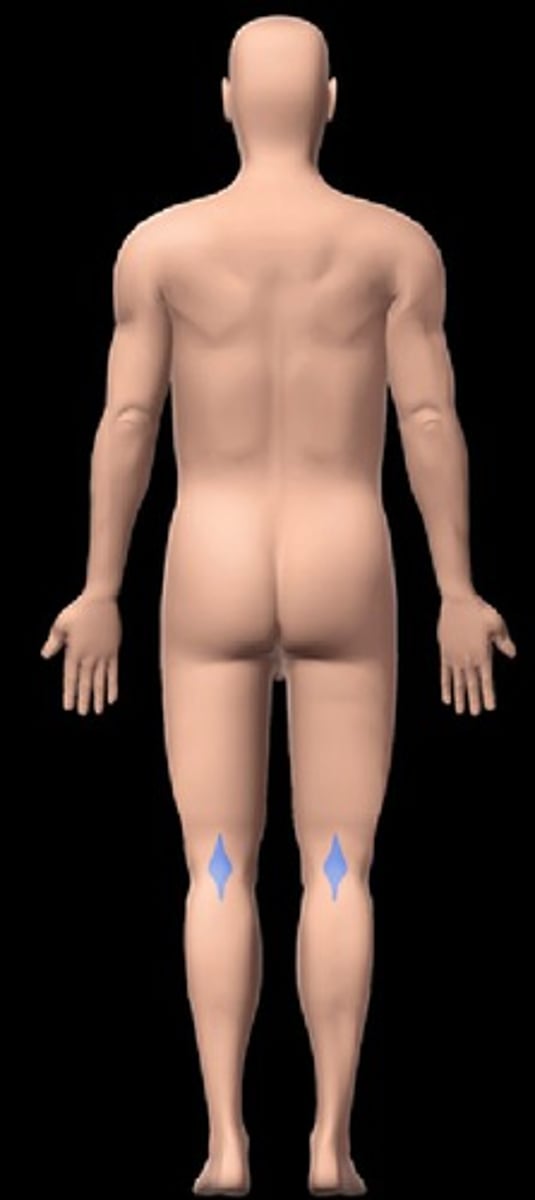
Popliteal
Back of knee.
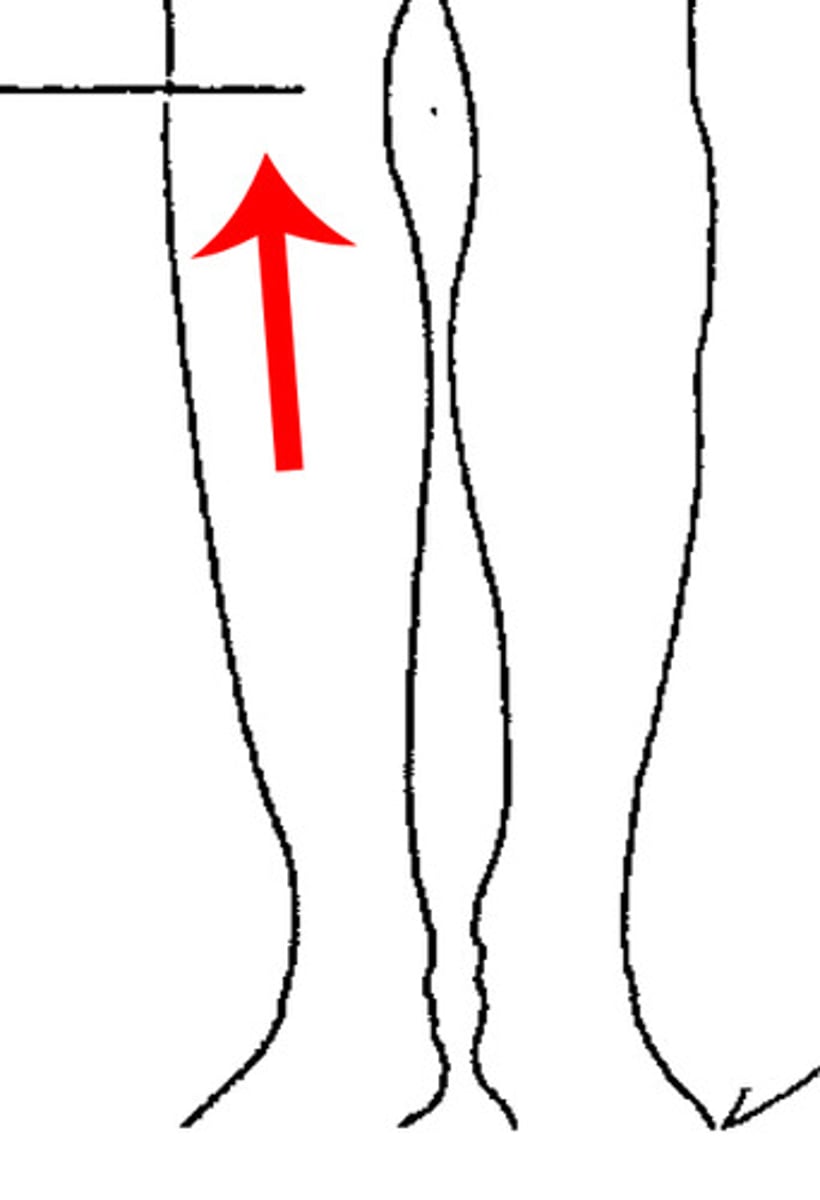
Crural
Front of leg (Shin).
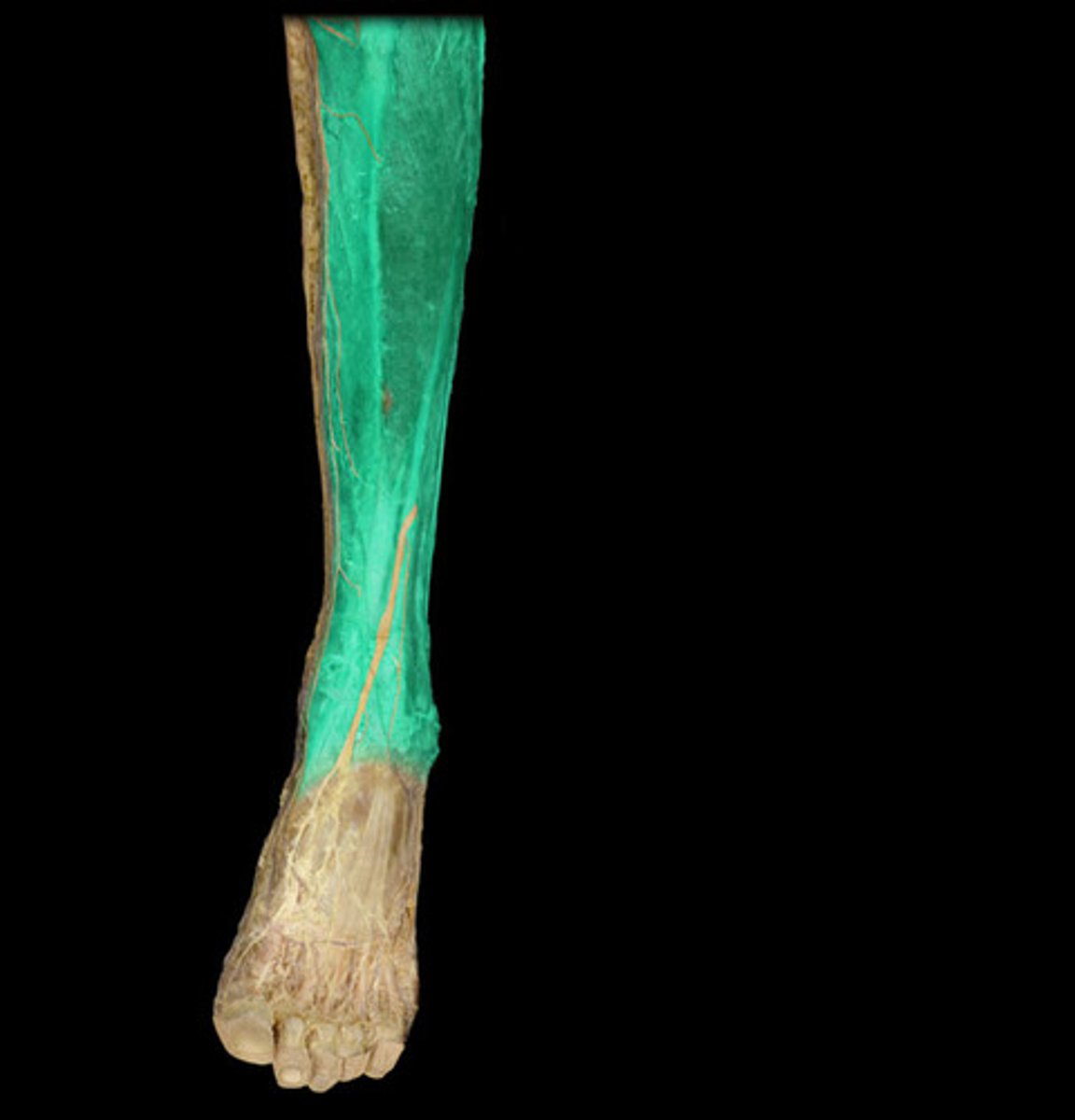
Sural
Back of leg (Calf).
Tarsal
Ankle.
Pedal
Foot.

Calcaneal
Heel.
Plantar
Sole of foot.
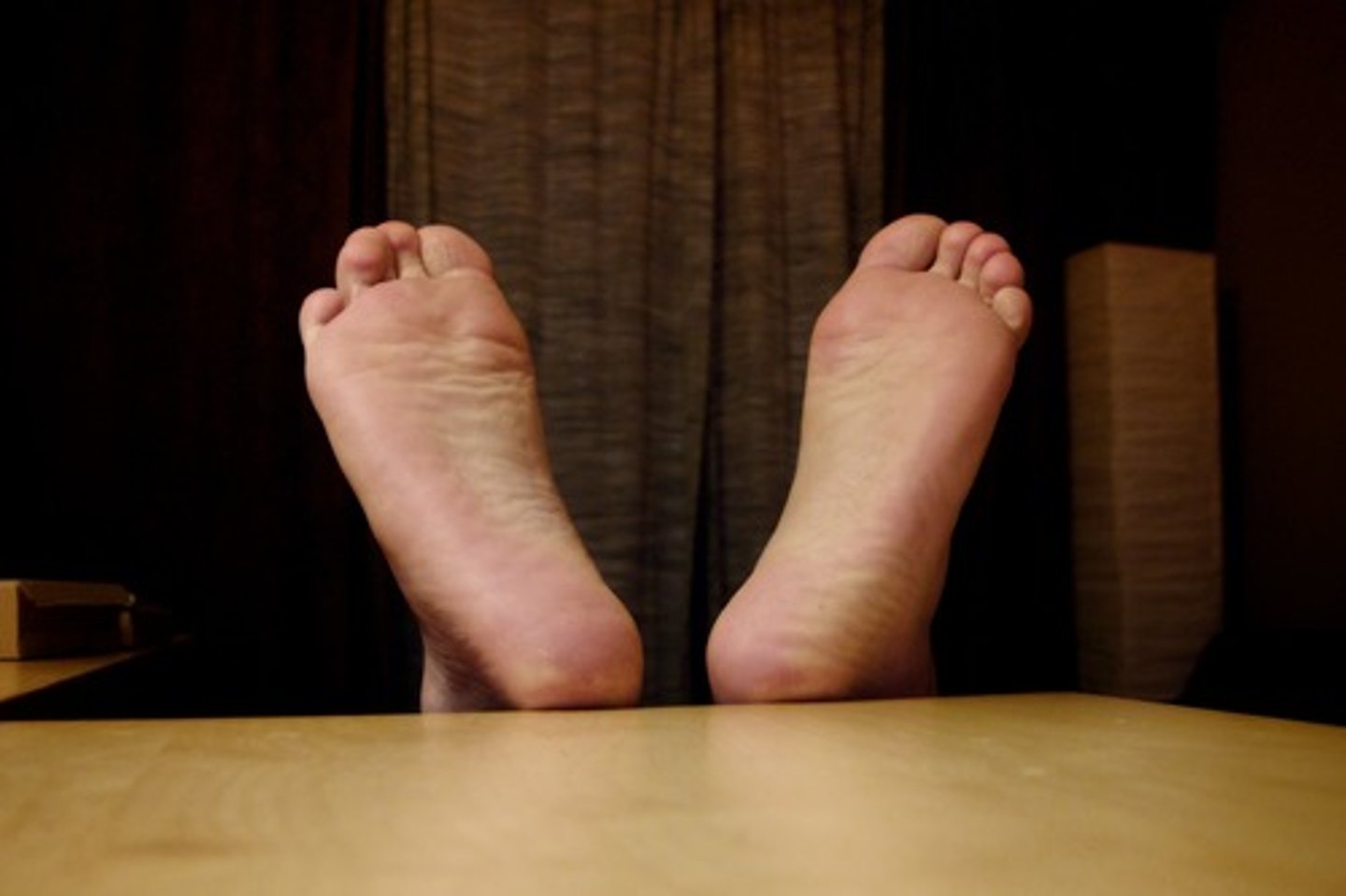

Hallux
Great toe.
Digital/Phalangeal (lower)
Toes.
Cervical
Neck.
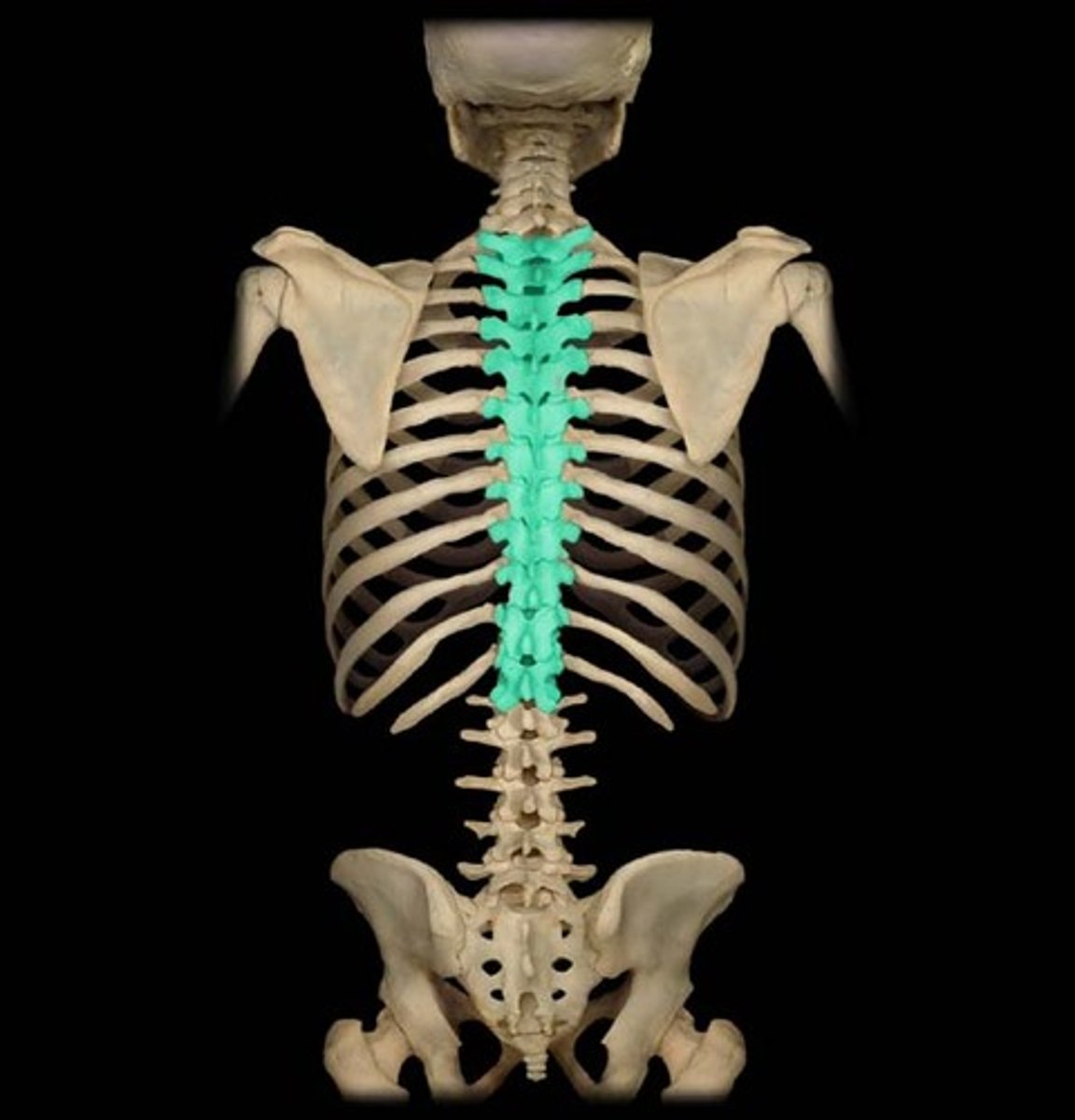
Thoracic
Middle back.
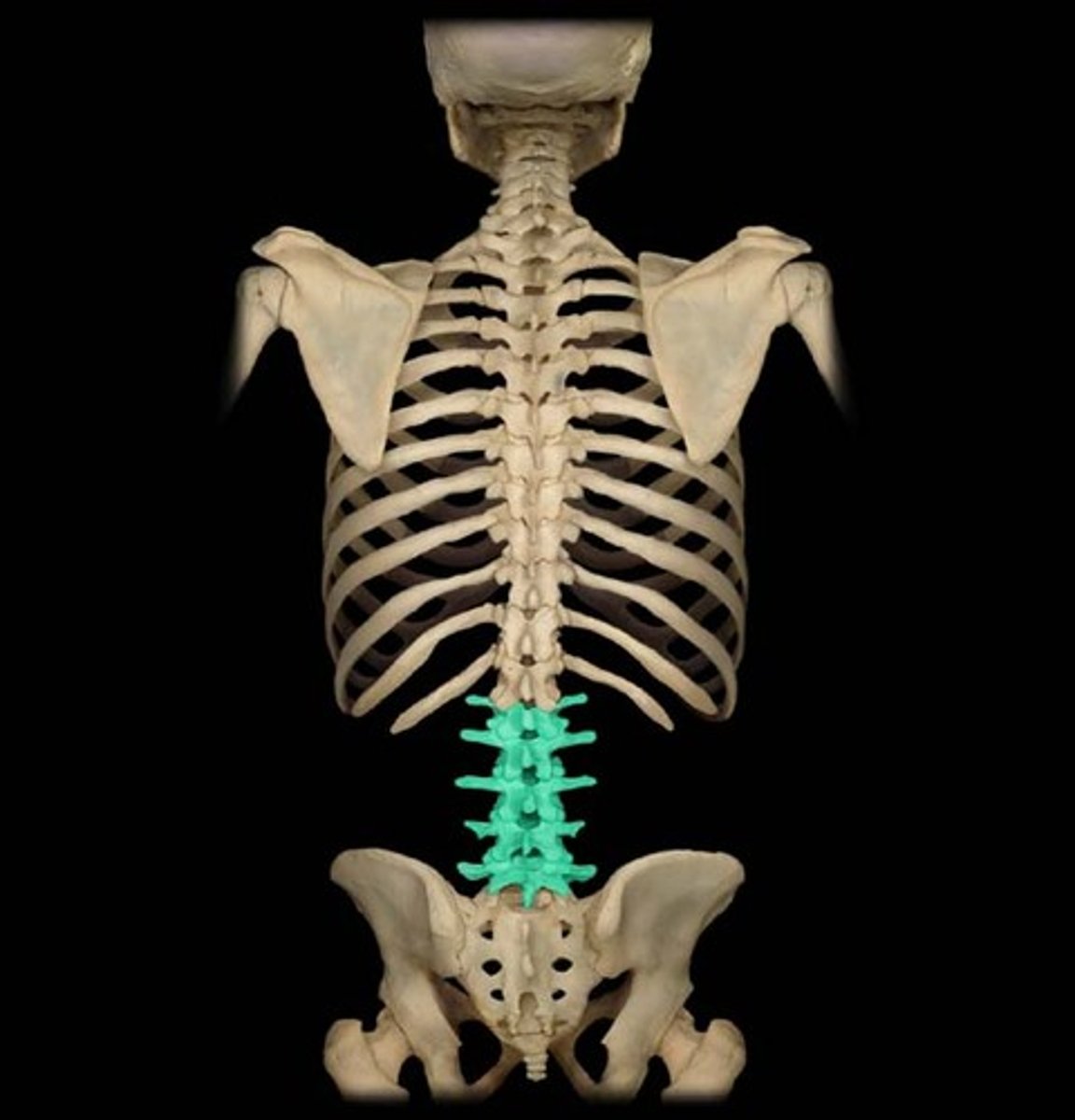
Lumbar
Low back.
Thorax
Chest.
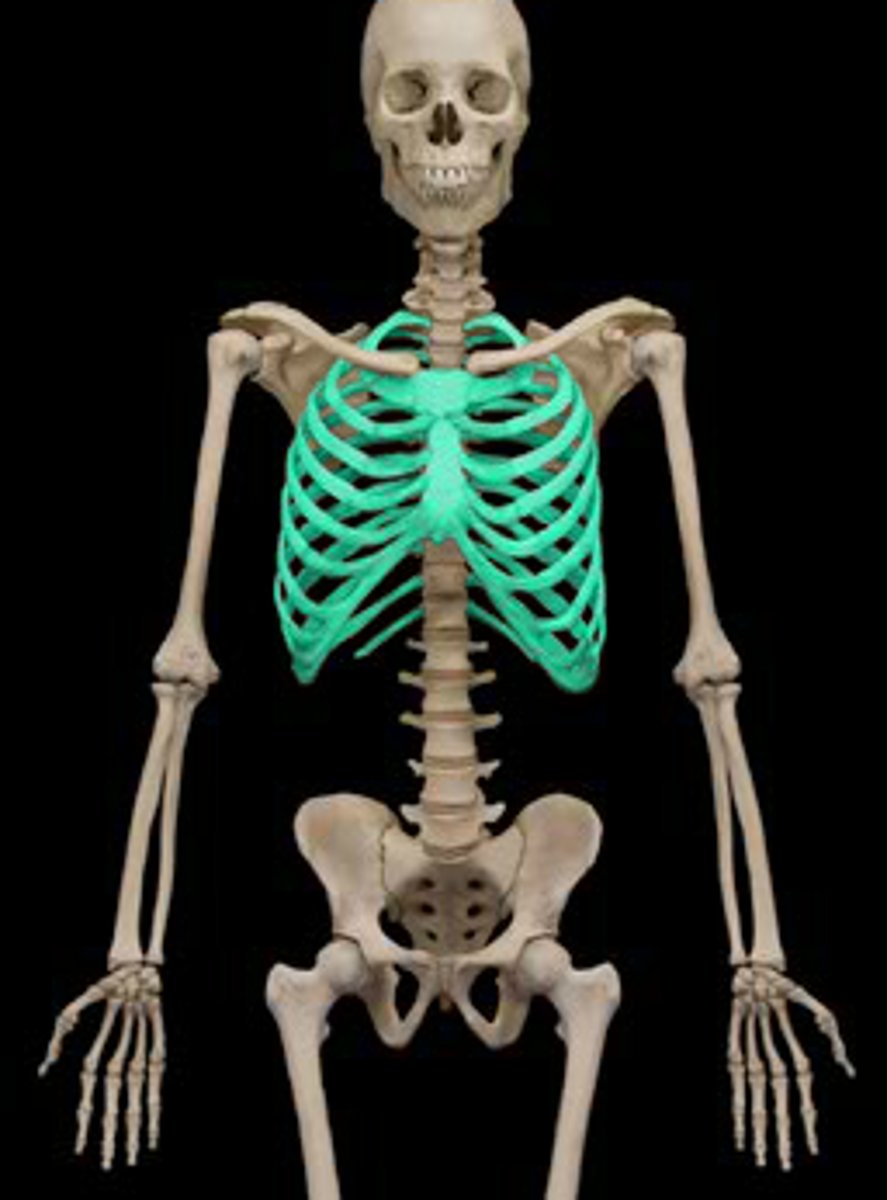
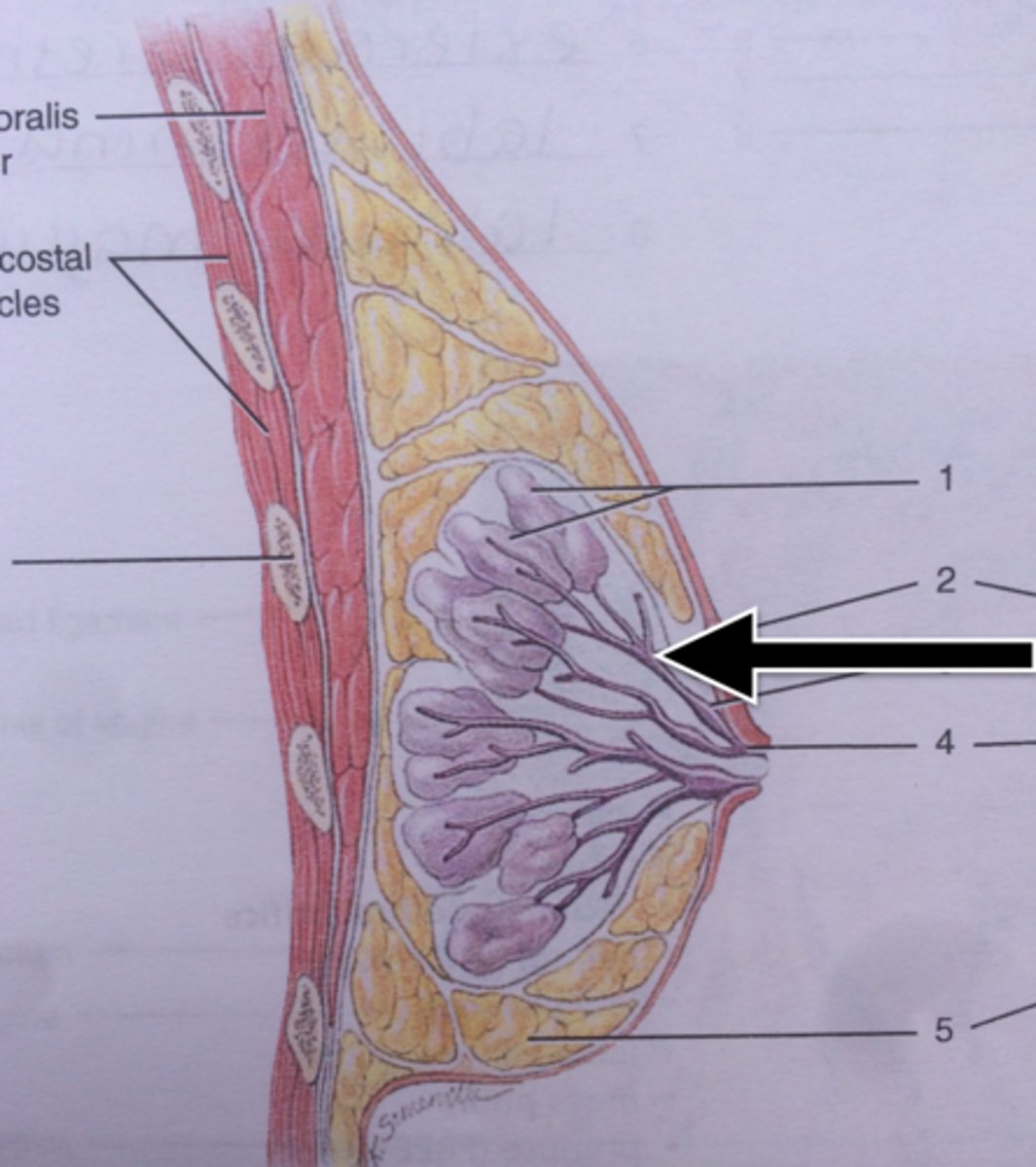
Mammary
Breast.
Abdominal
Abdomen (Stomach).
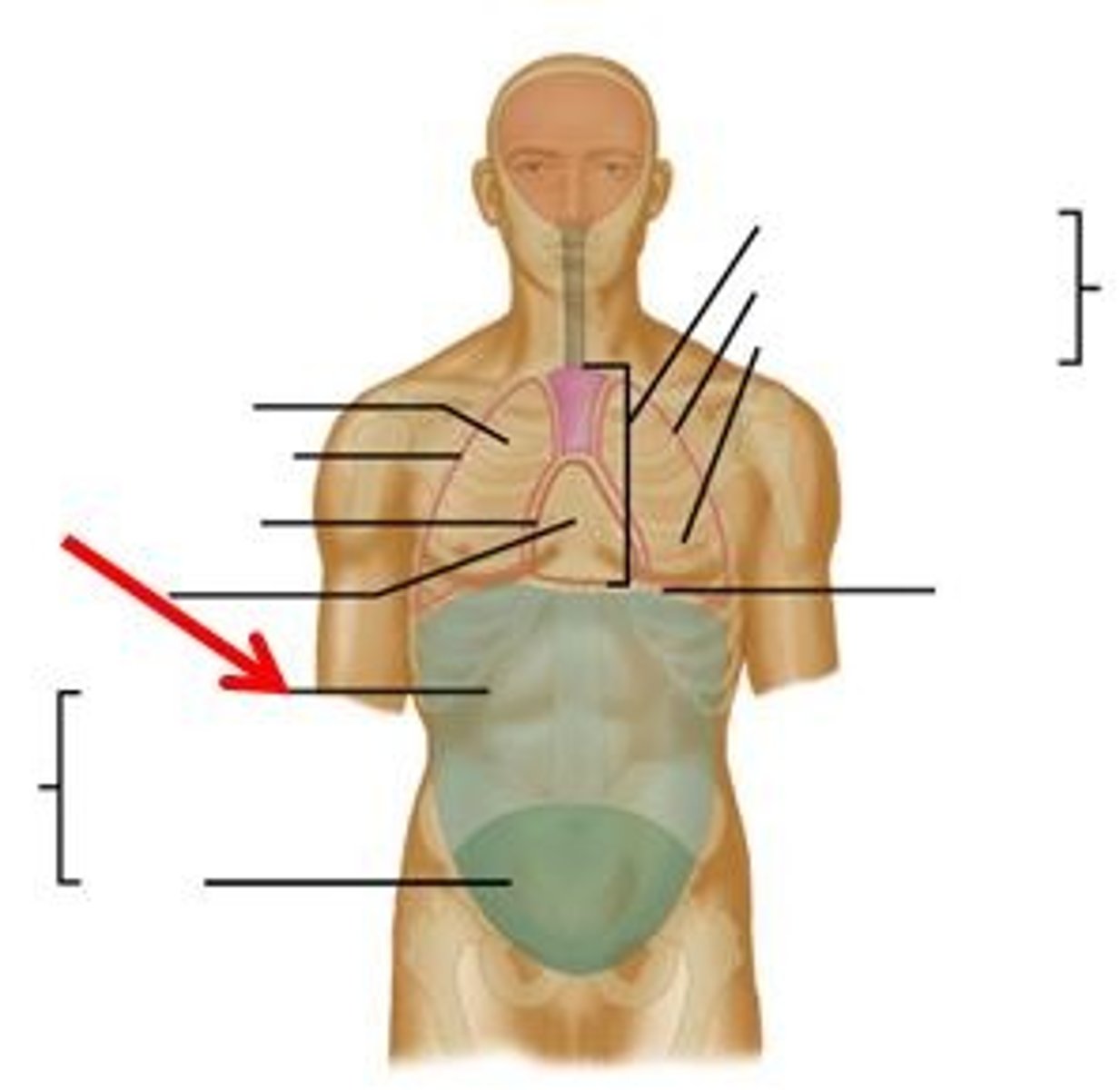
Umbilical
Navel (Belly button).
Pelvic
Pelvis.
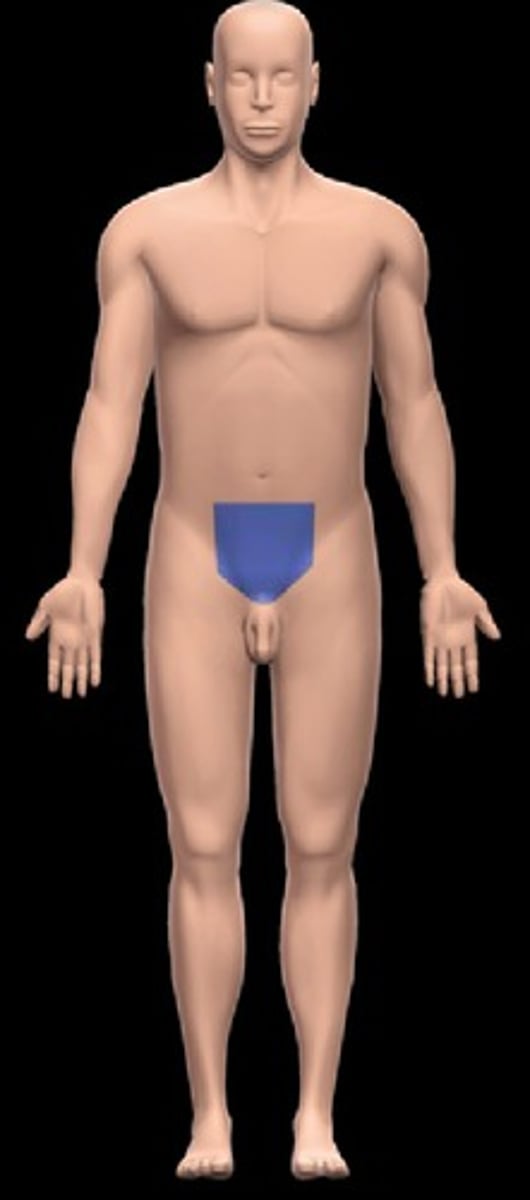
Pubic
Front of pelvis.
Plane
An imaginary flat surface that passes through the body.
Section
One of the 2 surfaces (pieces) resulting when cut by a plane.
Sagittal Plane
Divides the body or an organ into left and right sides.
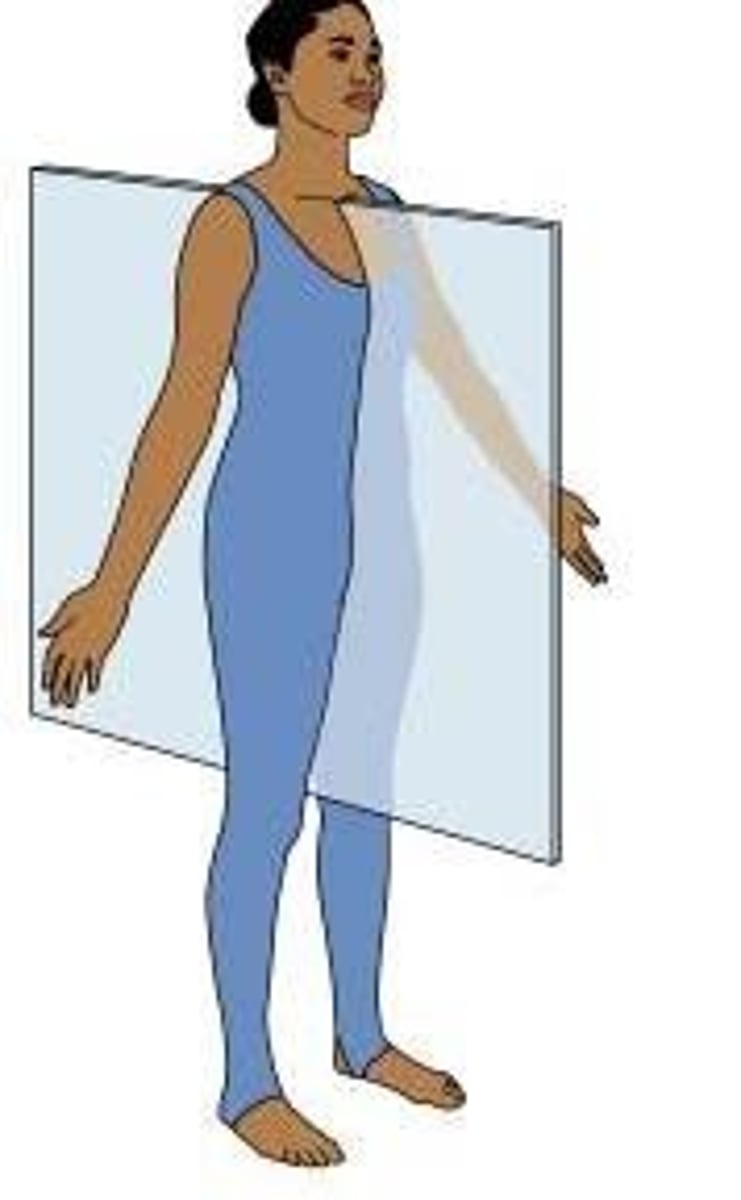
Midsagittal
Sagittal plane producing equal halves.
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
Divides the body or an organ into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions.

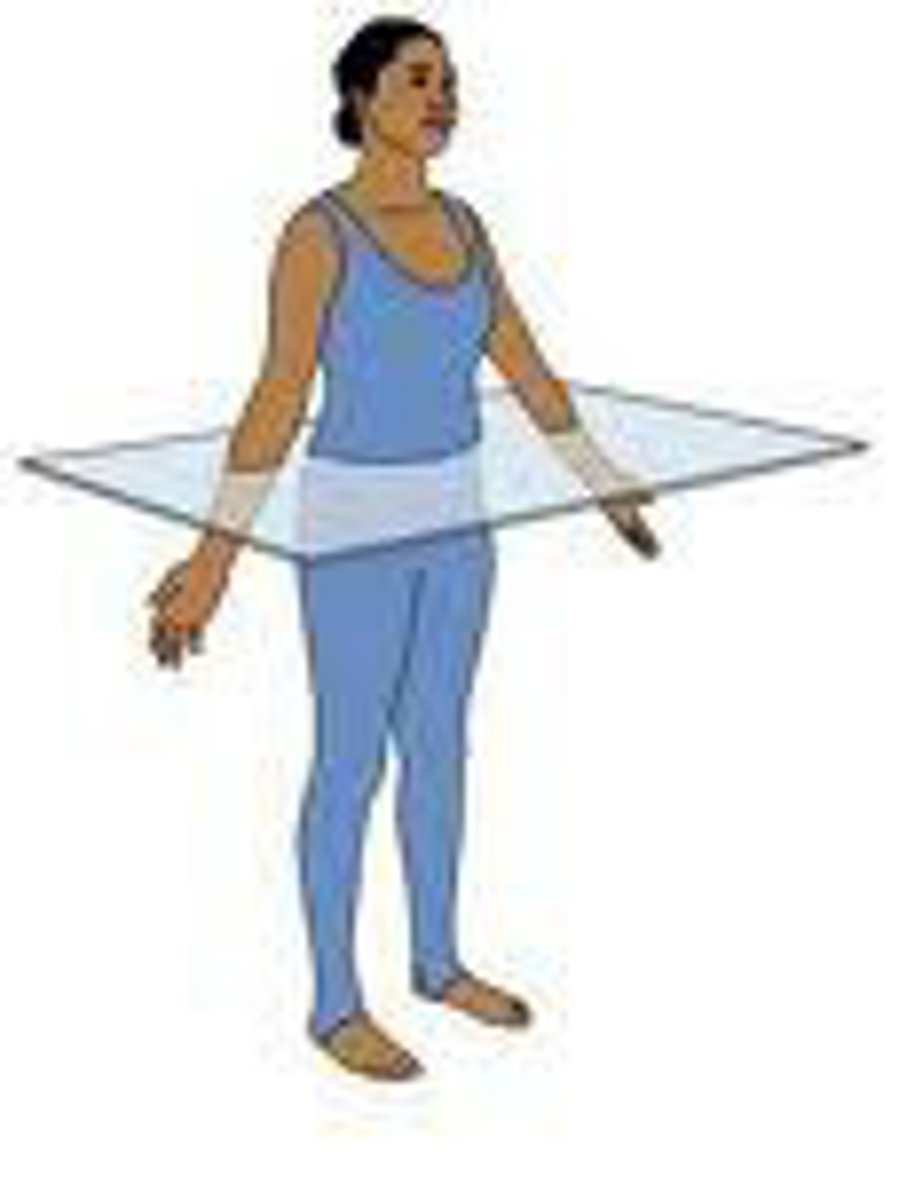
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane
Divides the body or an organ into upper (superior) or lower (inferior) portions.
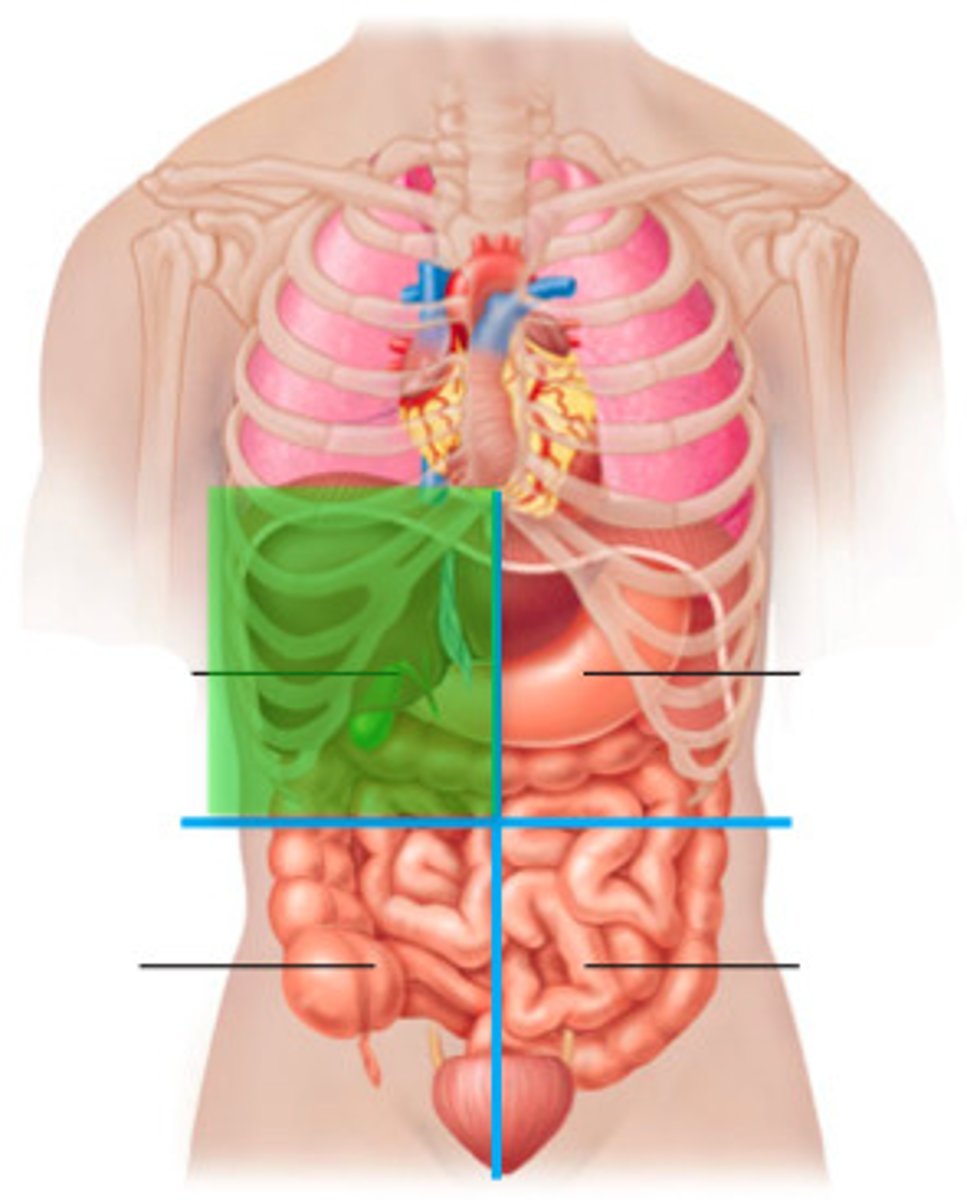
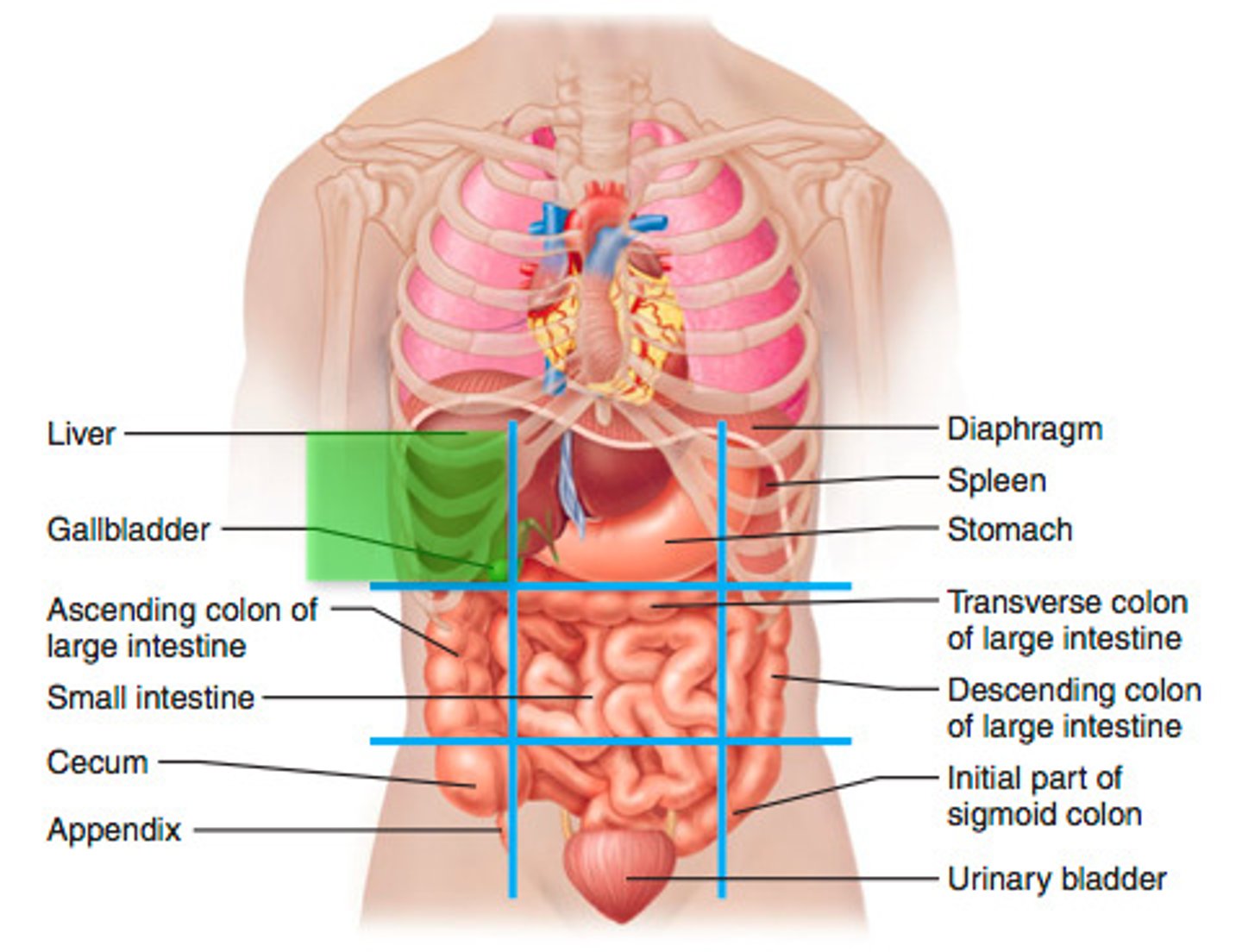
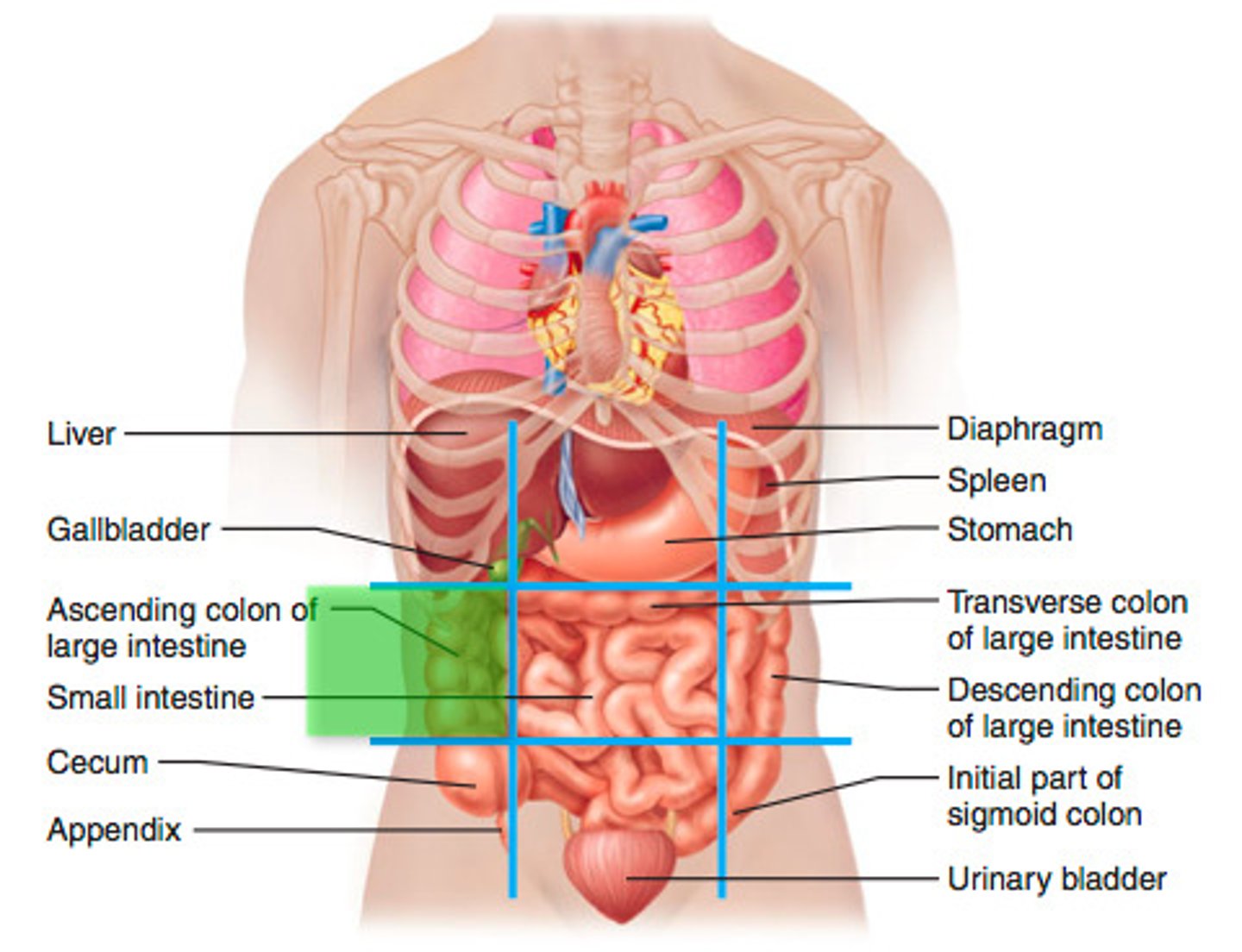
Left upper quadrant (LUQ)
One of the four abdominopelvic quadrants.
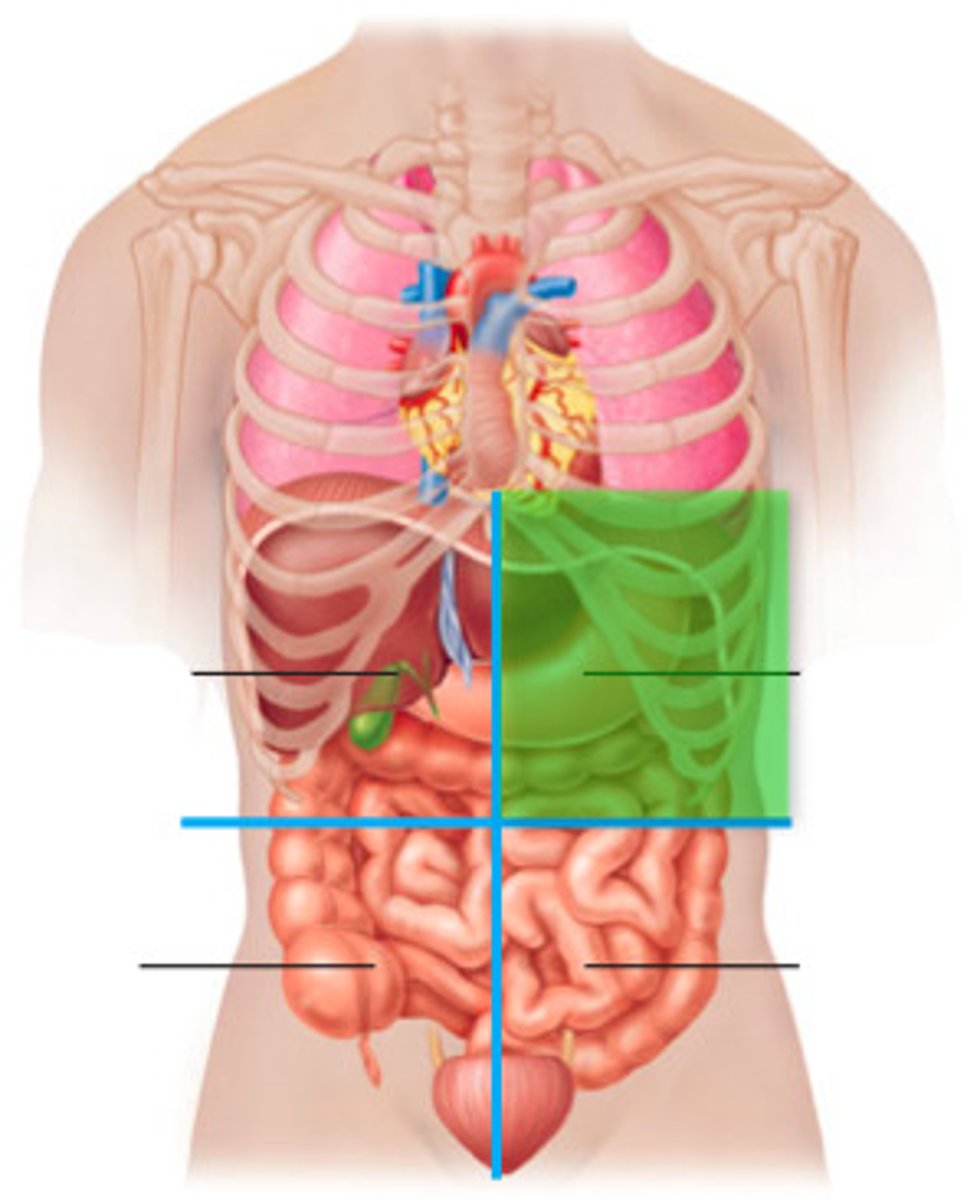
Right upper quadrant (RUQ)
One of the four abdominopelvic quadrants.
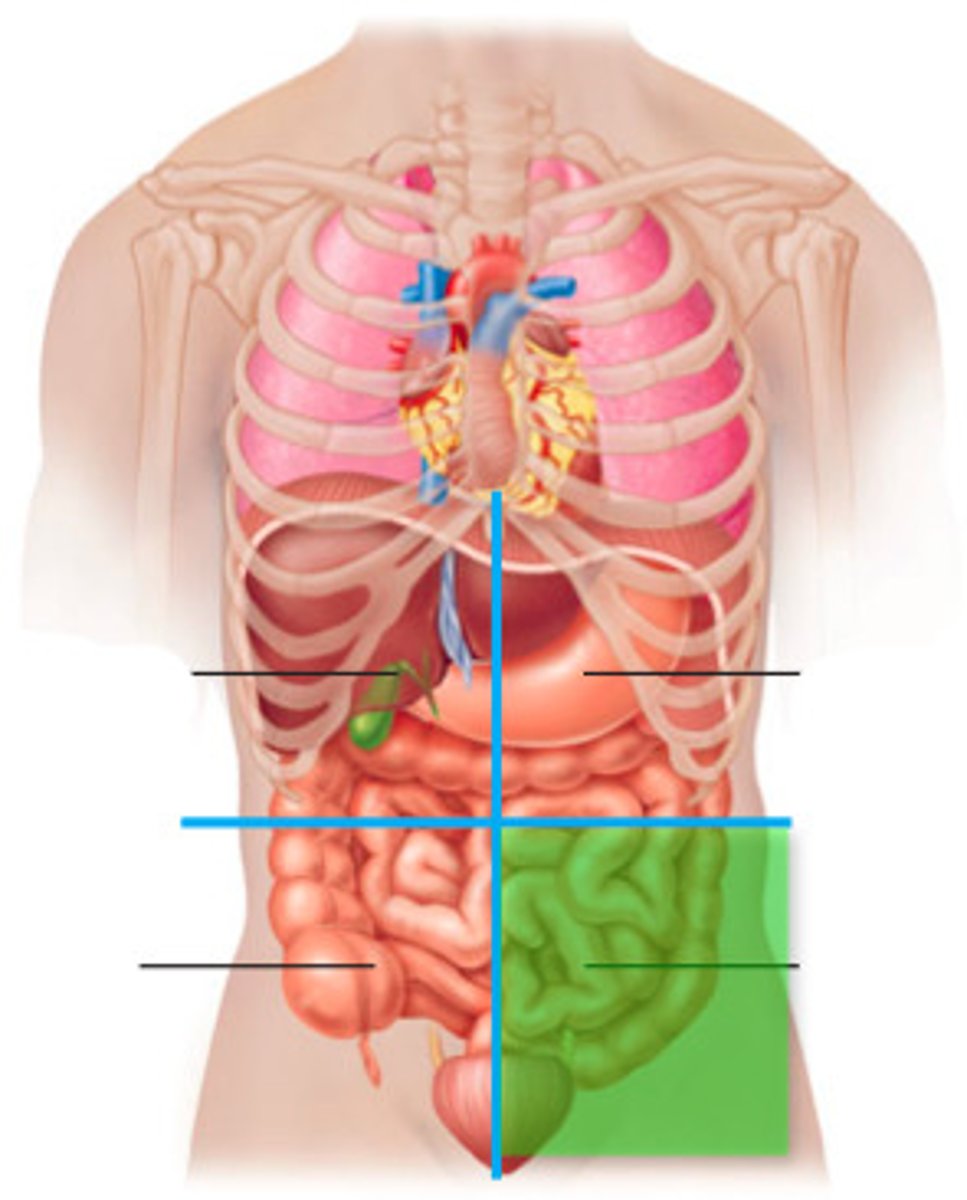
Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
One of the four abdominopelvic quadrants.
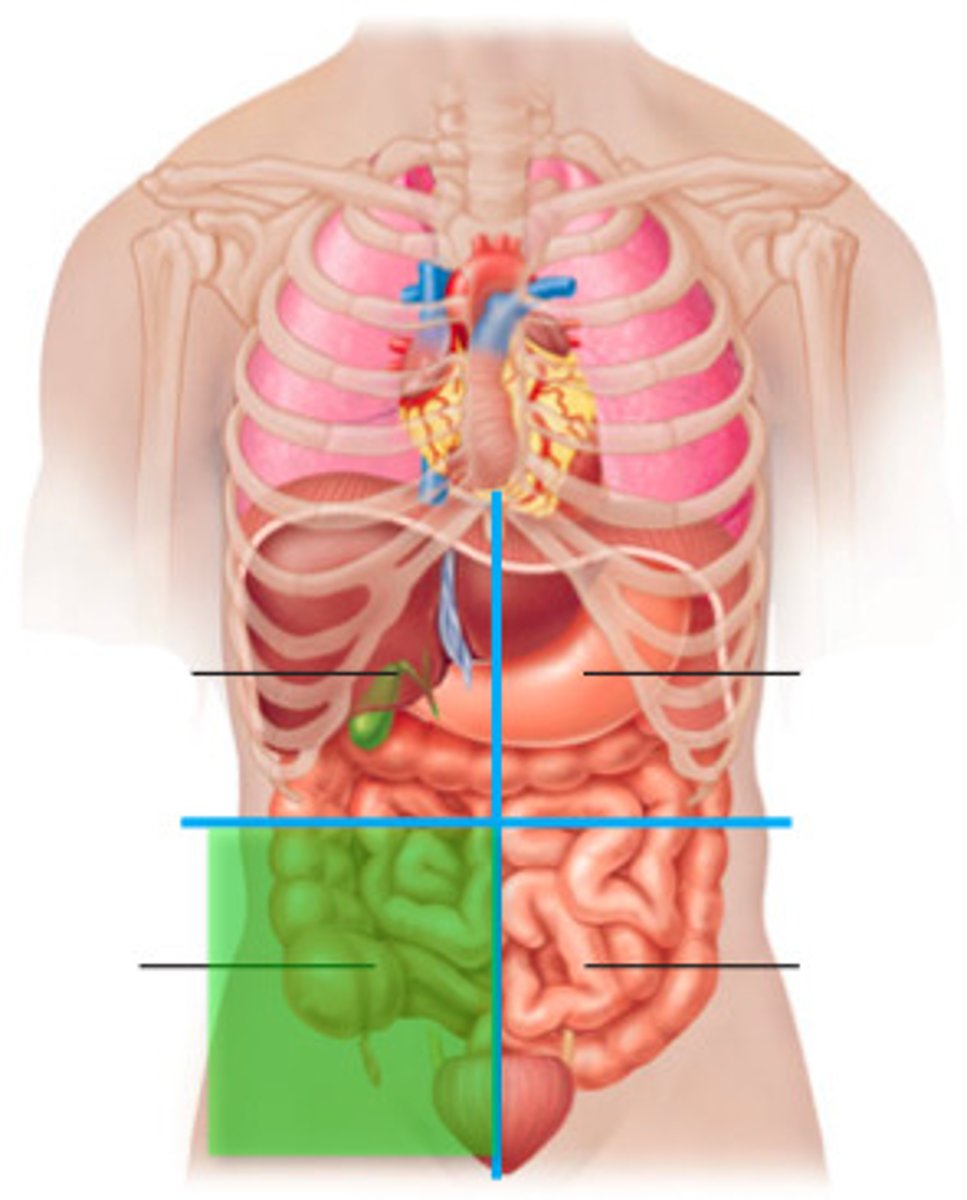
Left lower quadrant (LLQ)
One of the four abdominopelvic quadrants.
Left hypochondriac
One of the nine abdominopelvic regions.

Epigastric
One of the nine abdominopelvic regions.
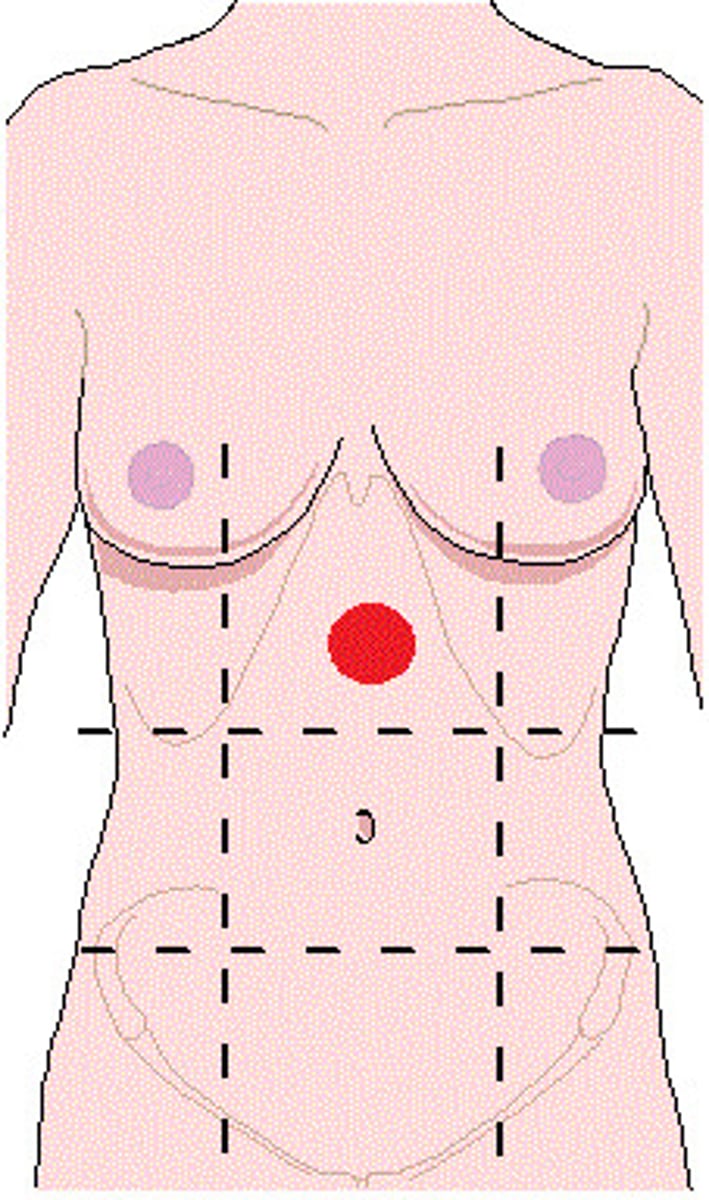
Right hypochondriac
One of the nine abdominopelvic regions.
Left lumbar
One of the nine abdominopelvic regions.
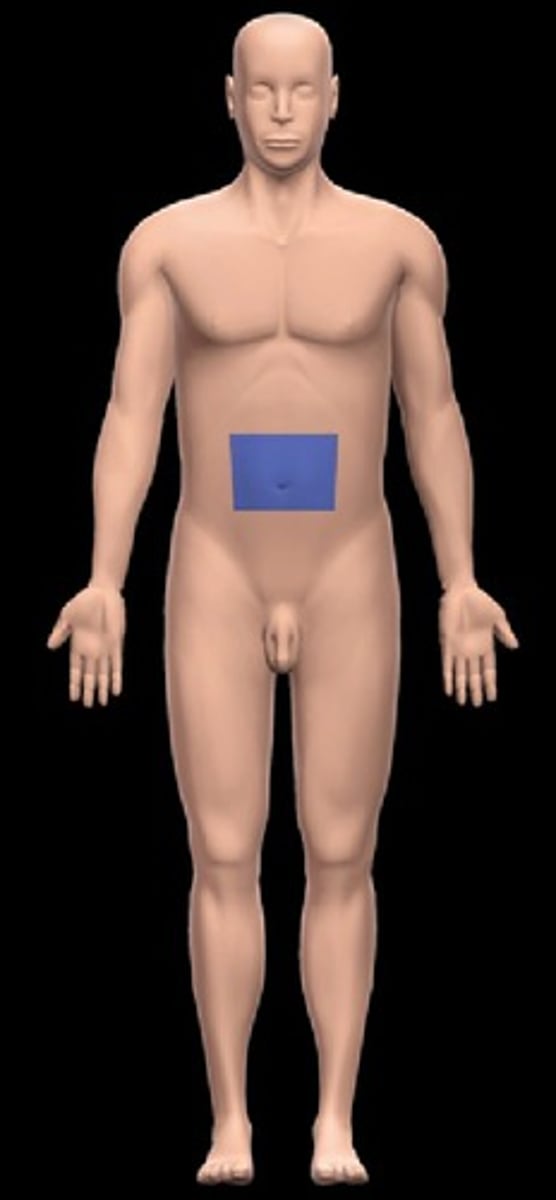
Umbilical
One of the nine abdominopelvic regions.
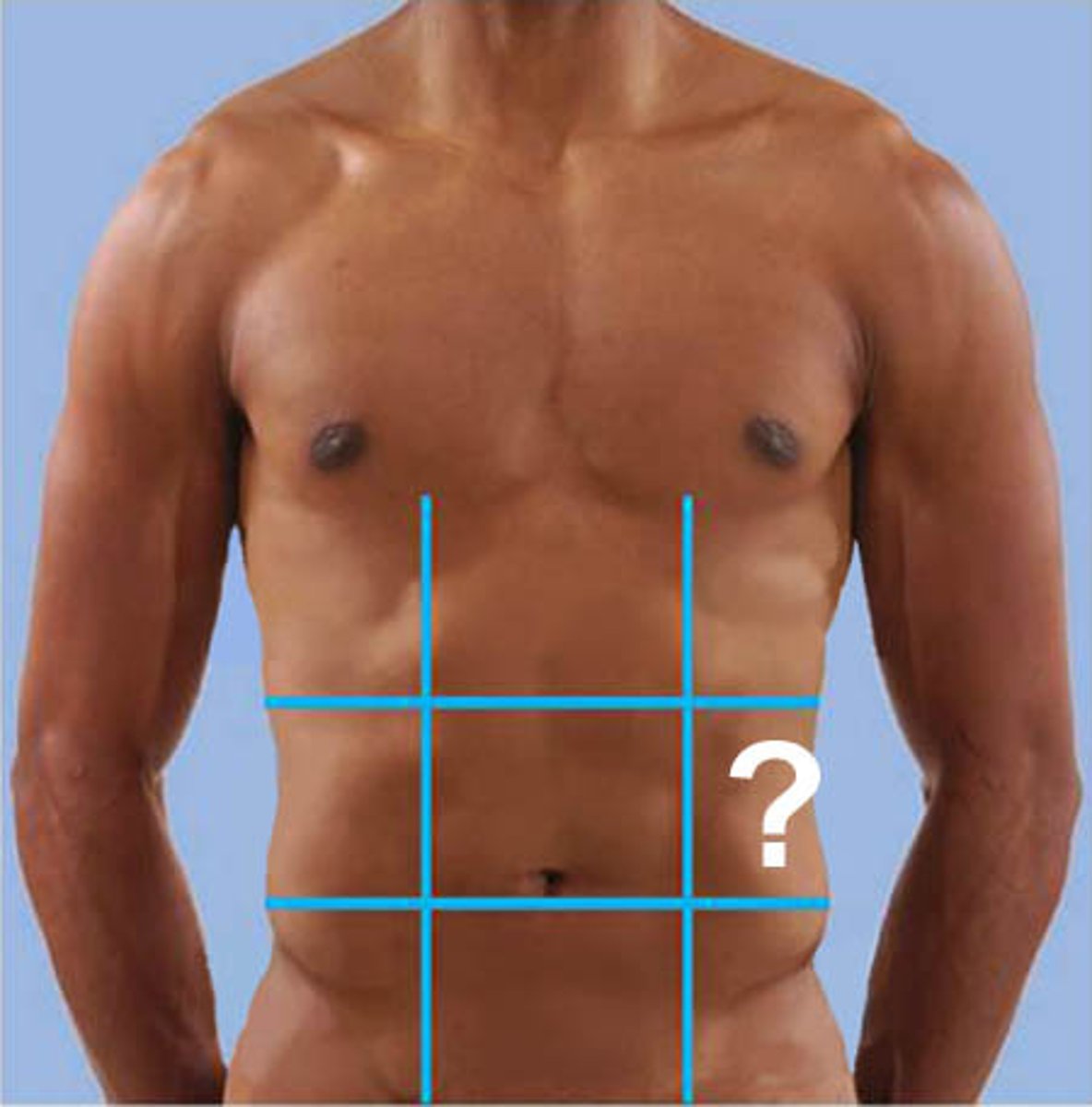
Right lumbar
One of the nine abdominopelvic regions.
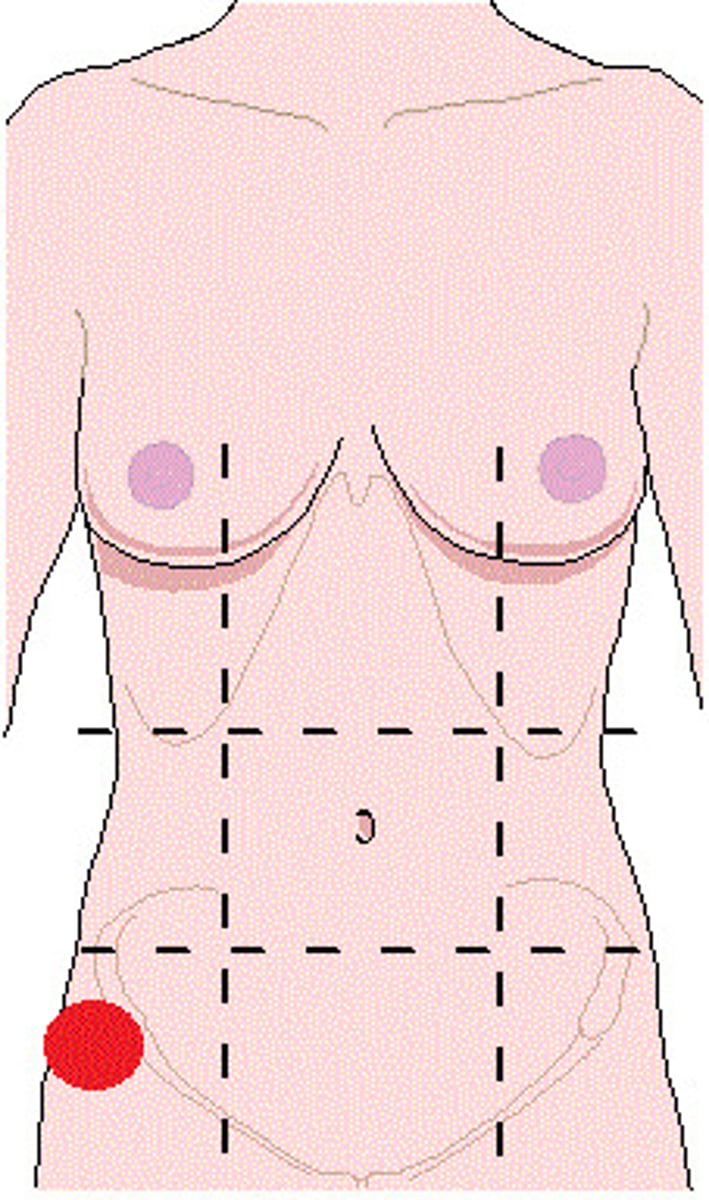
Left inguinal
One of the nine abdominopelvic regions.
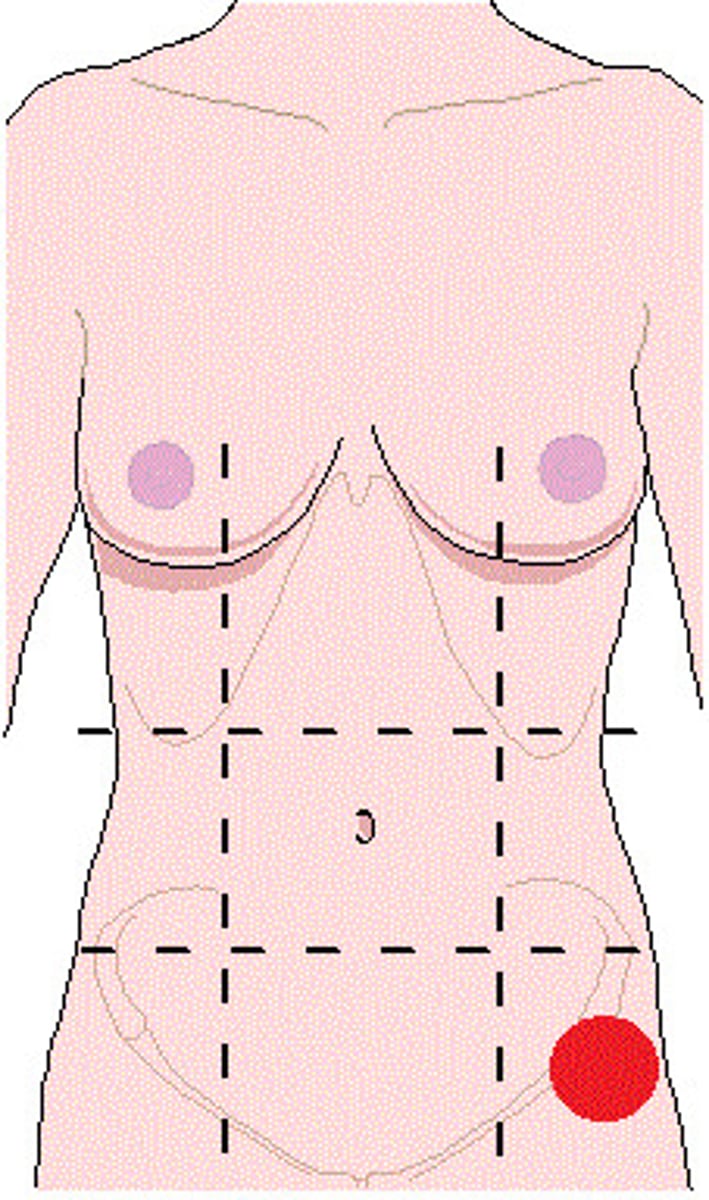
Hypogastric (pubic)
One of the nine abdominopelvic regions.
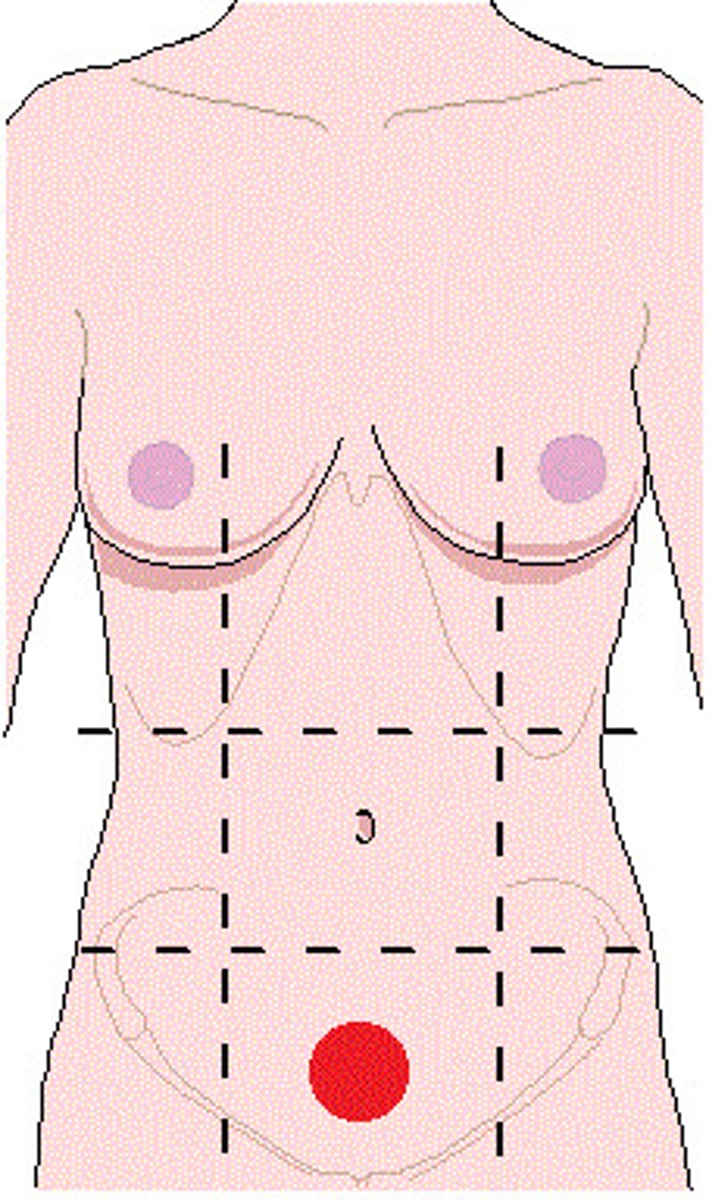
Right inguinal
One of the nine abdominopelvic regions.
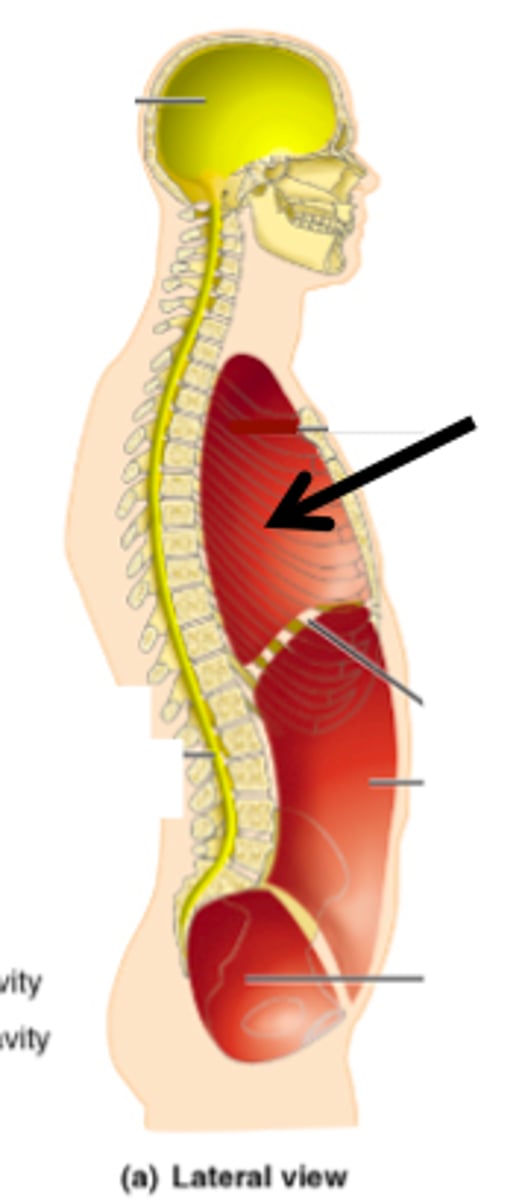
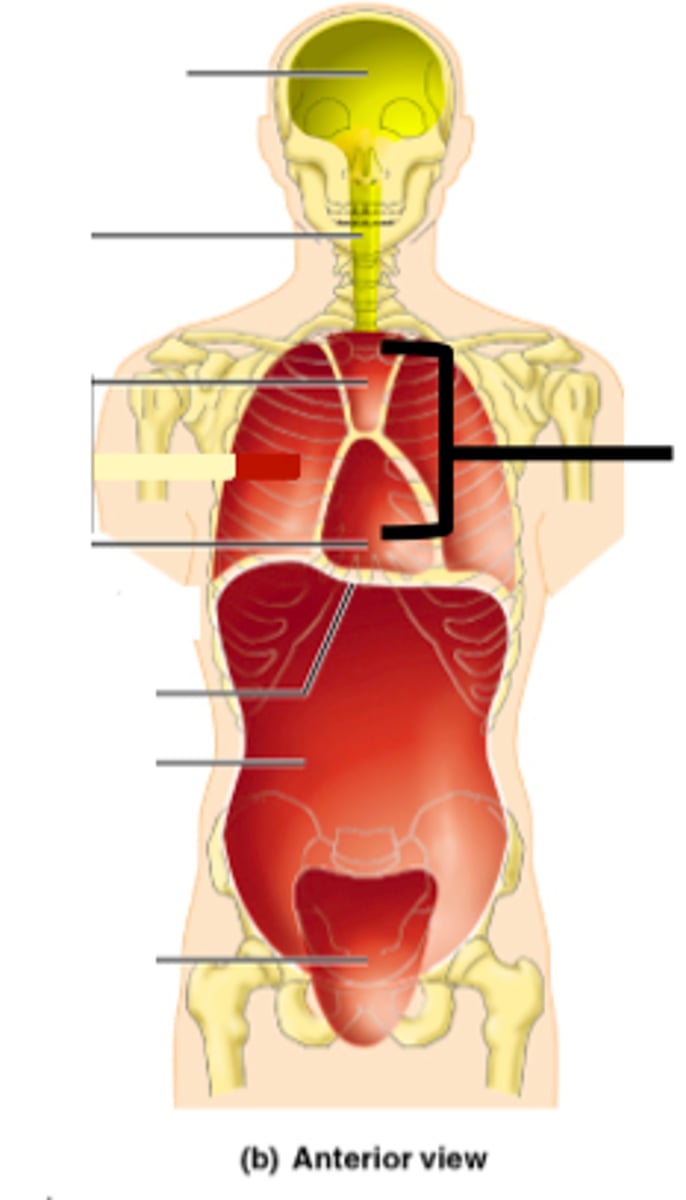
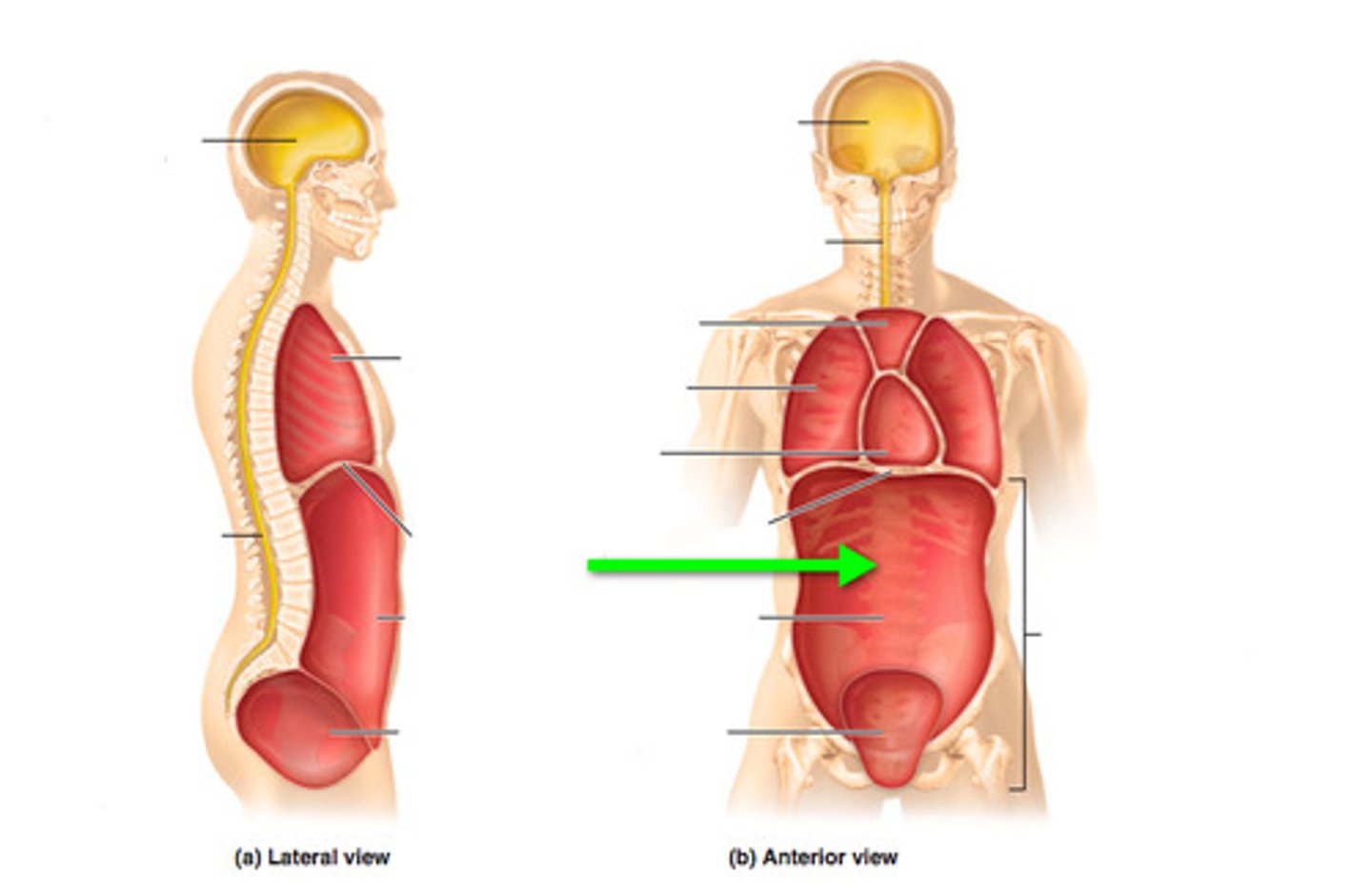
Posterior (dorsal) body cavity
Contains the cranial cavity and vertebral cavity.
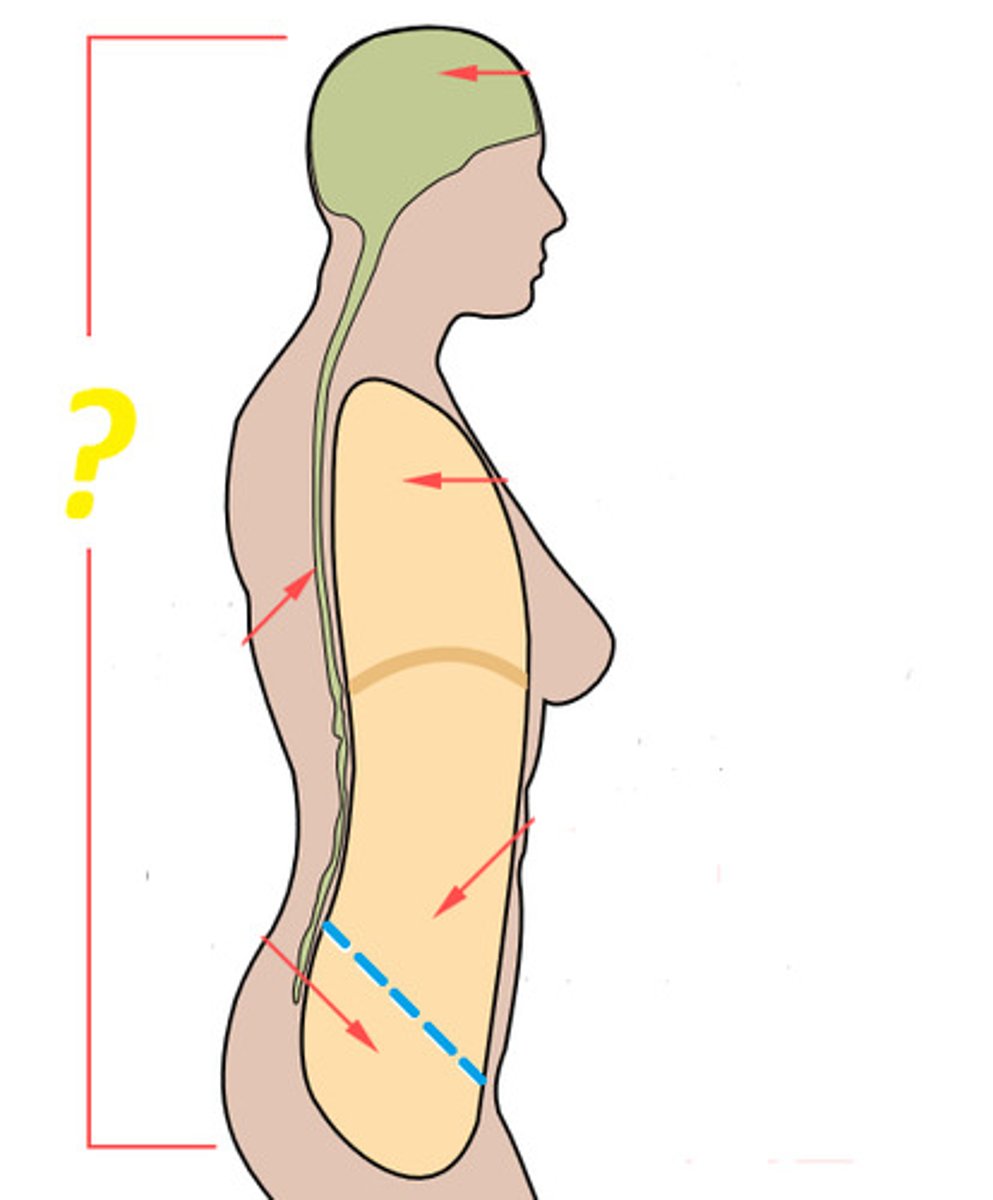
Cranial cavity
Formed by bones of the skull, contains the brain.
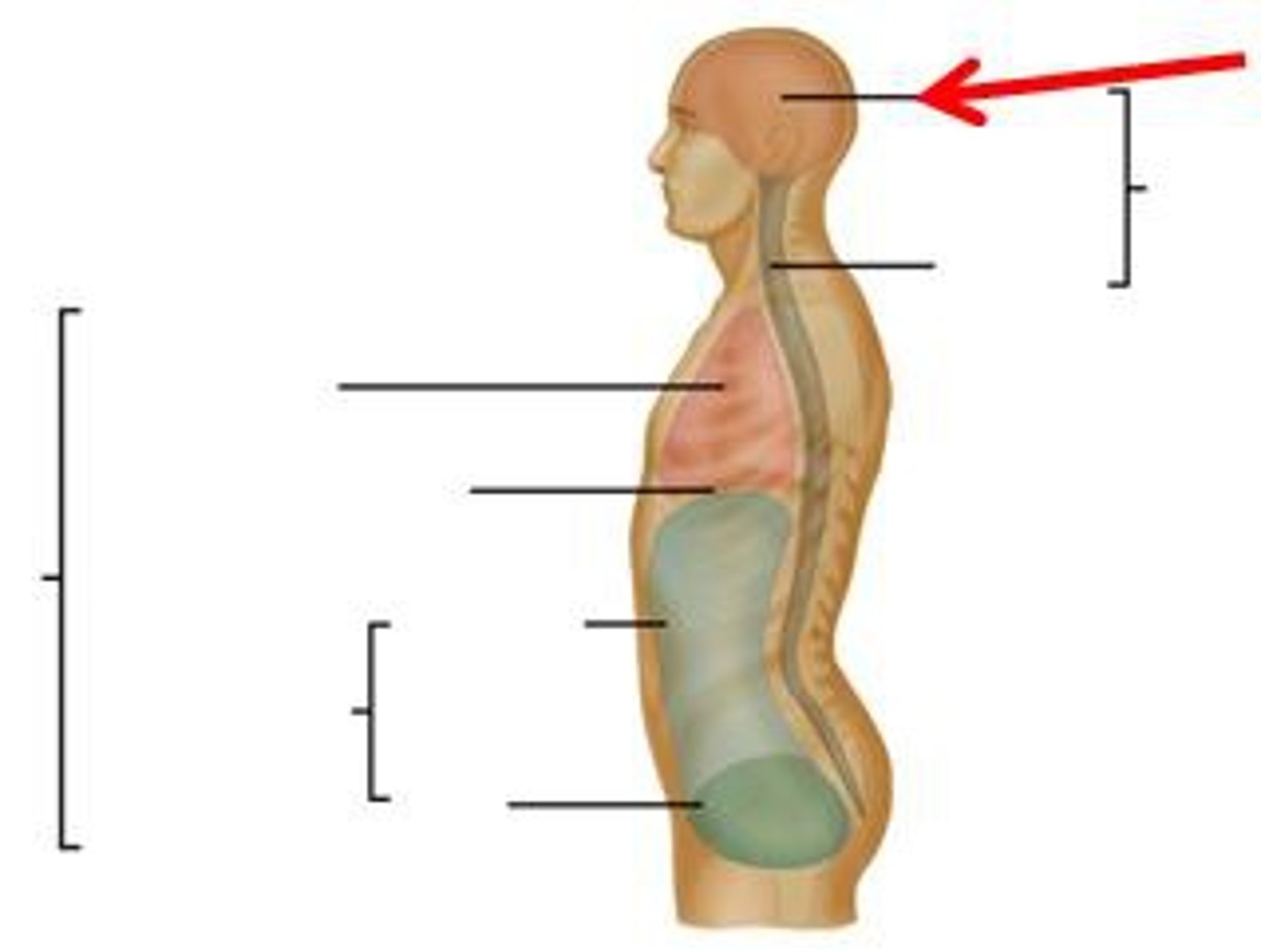
Vertebral cavity
Formed by the vertebrae, contains the spinal cord.
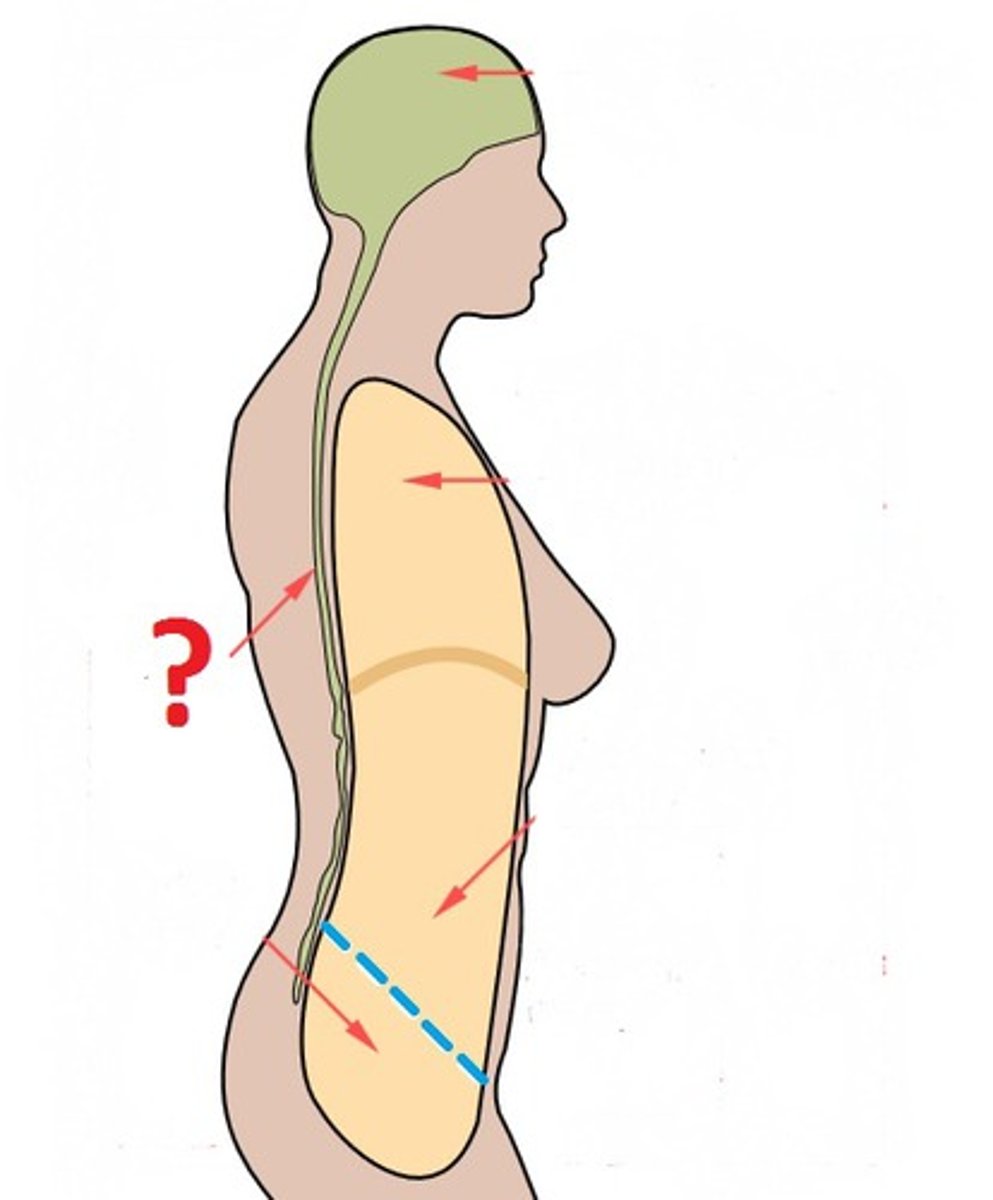
Anterior (ventral) body cavity
Divided by the diaphragm into thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity.
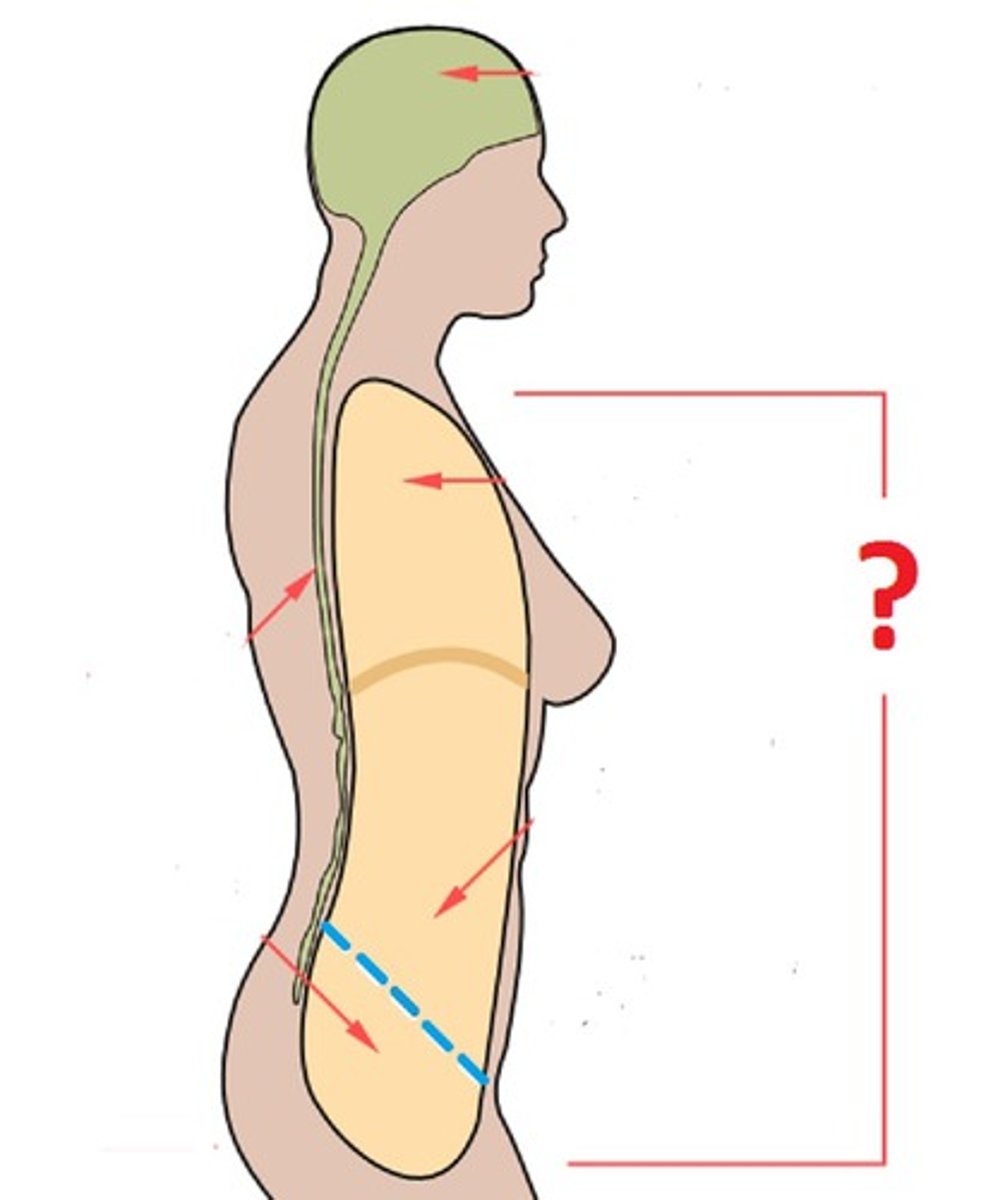
Serous Membranes
Thin, slippery membrane that lines the body cavities (not open to the outside) and cover organs.
Parietal layer
Lines cavity wall.
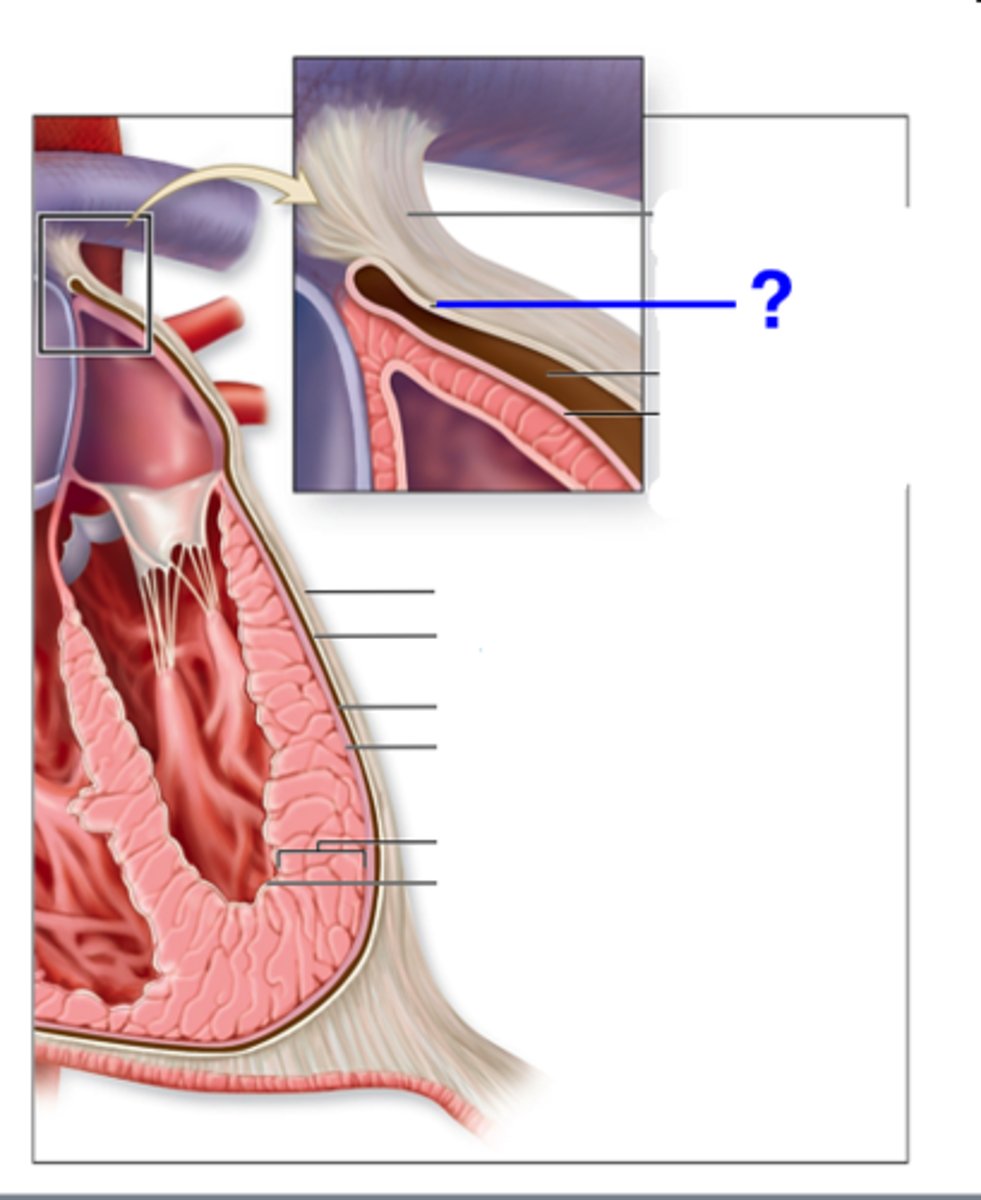
Parietal layer
lines cavity wall
Visceral layer
covers the organs
Serous fluid
reduces friction
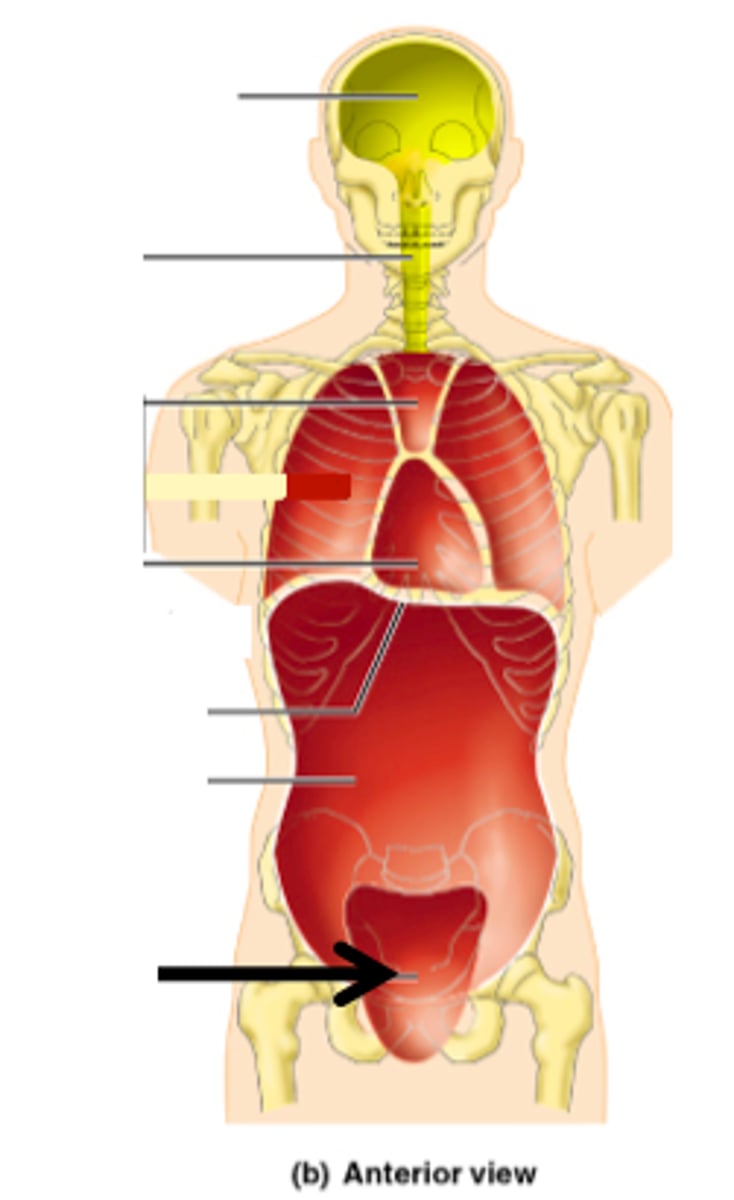
Thoracic cavity
surrounded by the chest wall and diaphragm
Mediastinum
midline structure which divides the thoracic cavity into 2 pleural cavities
Right and left pleural cavities
contain right and left lungs
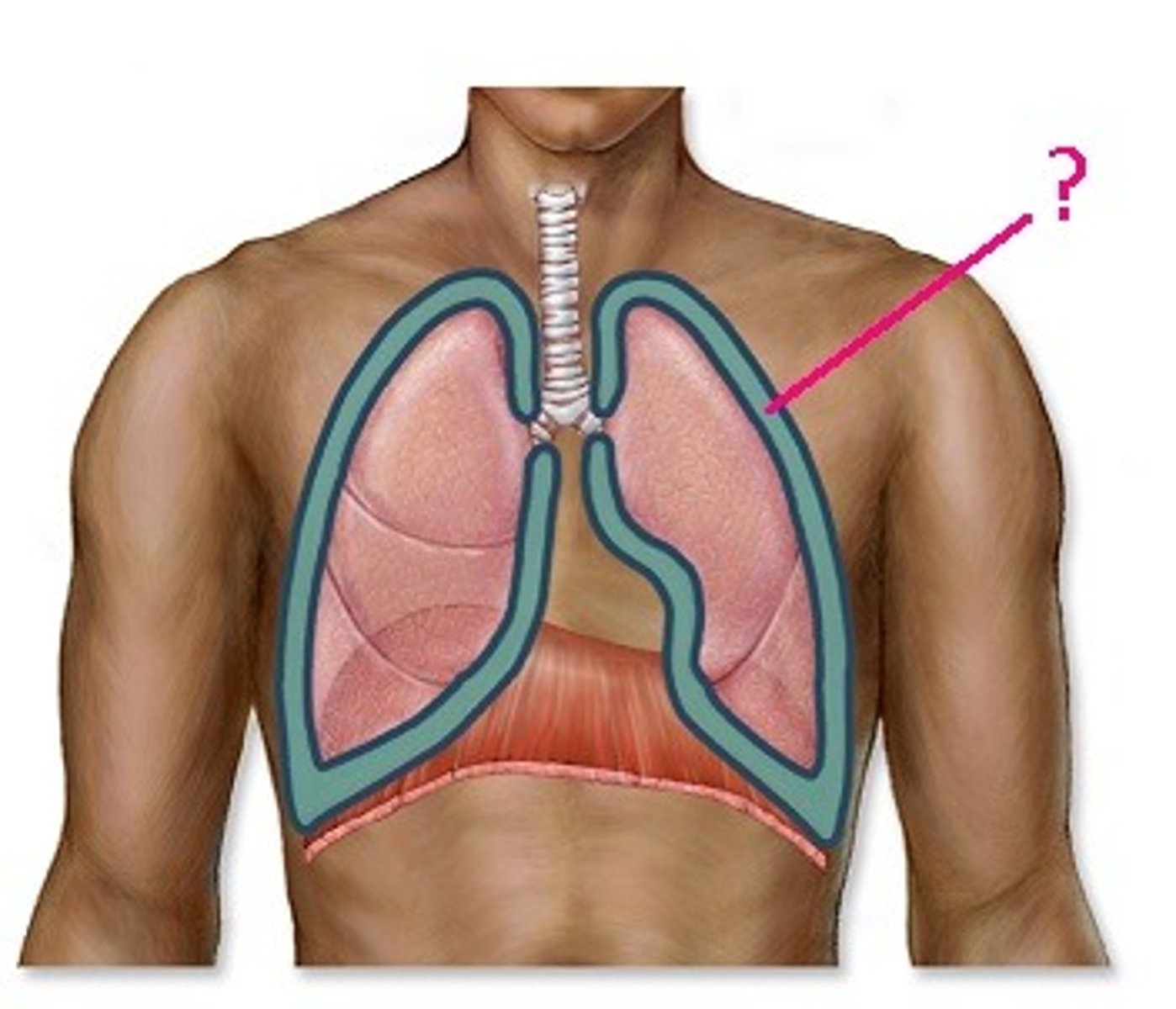
Pleura
each pleural cavity is lined by a serous membrane known as
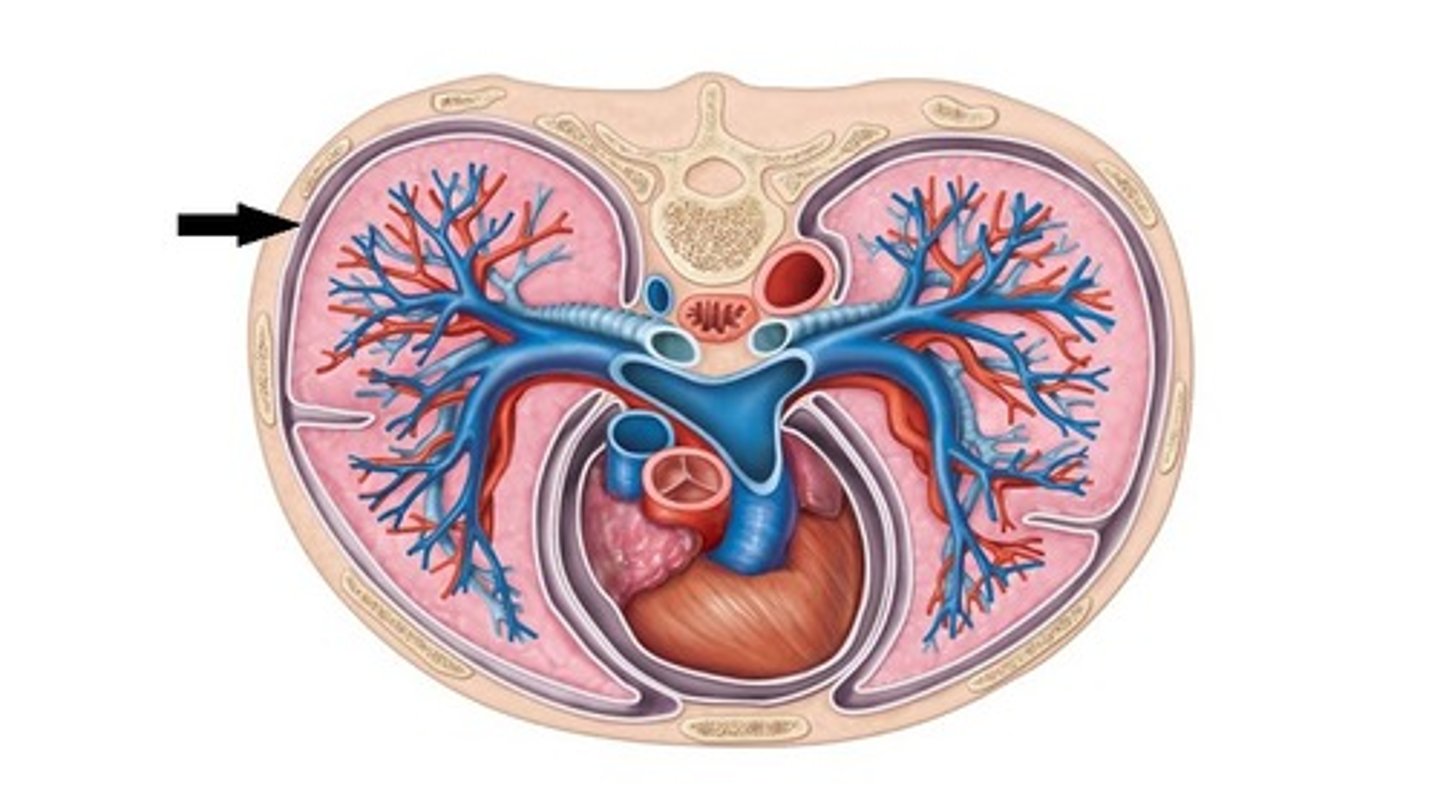
Visceral pleura
covers the lungs
Parietal pleura
lines the pleural cavity (walls)
Upper portion of Mediastinum
contains blood vessels, trachea, esophagus, and thymus
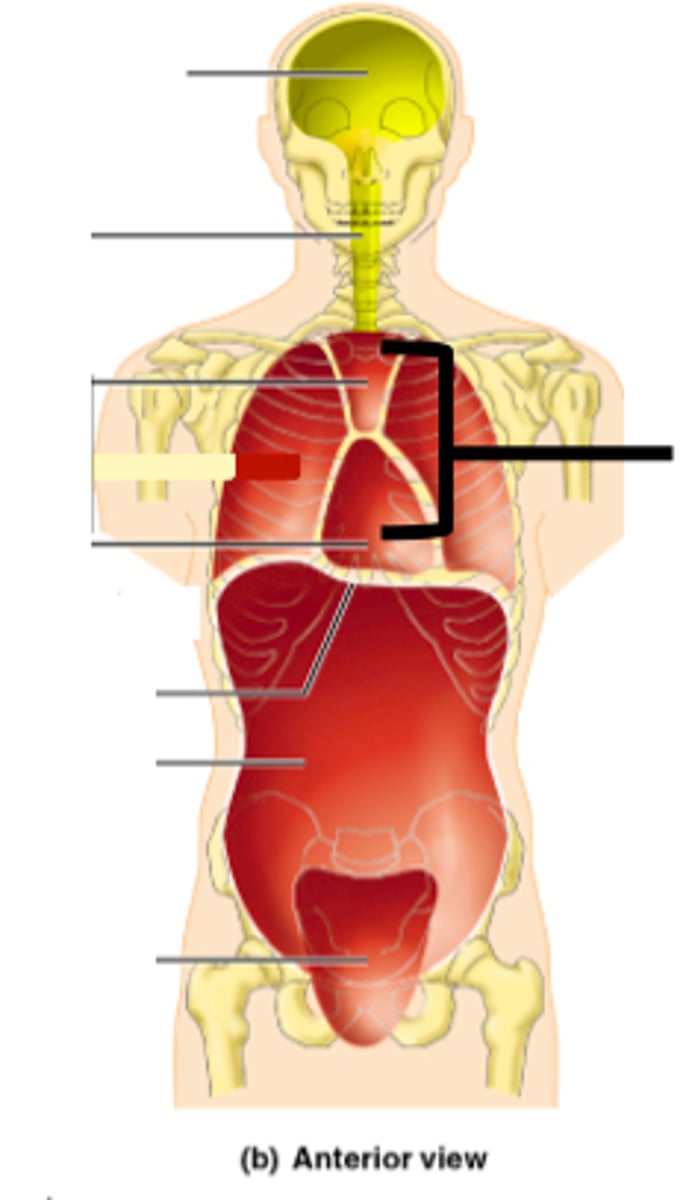
Lower portion of Mediastinum
contains pericardial cavity
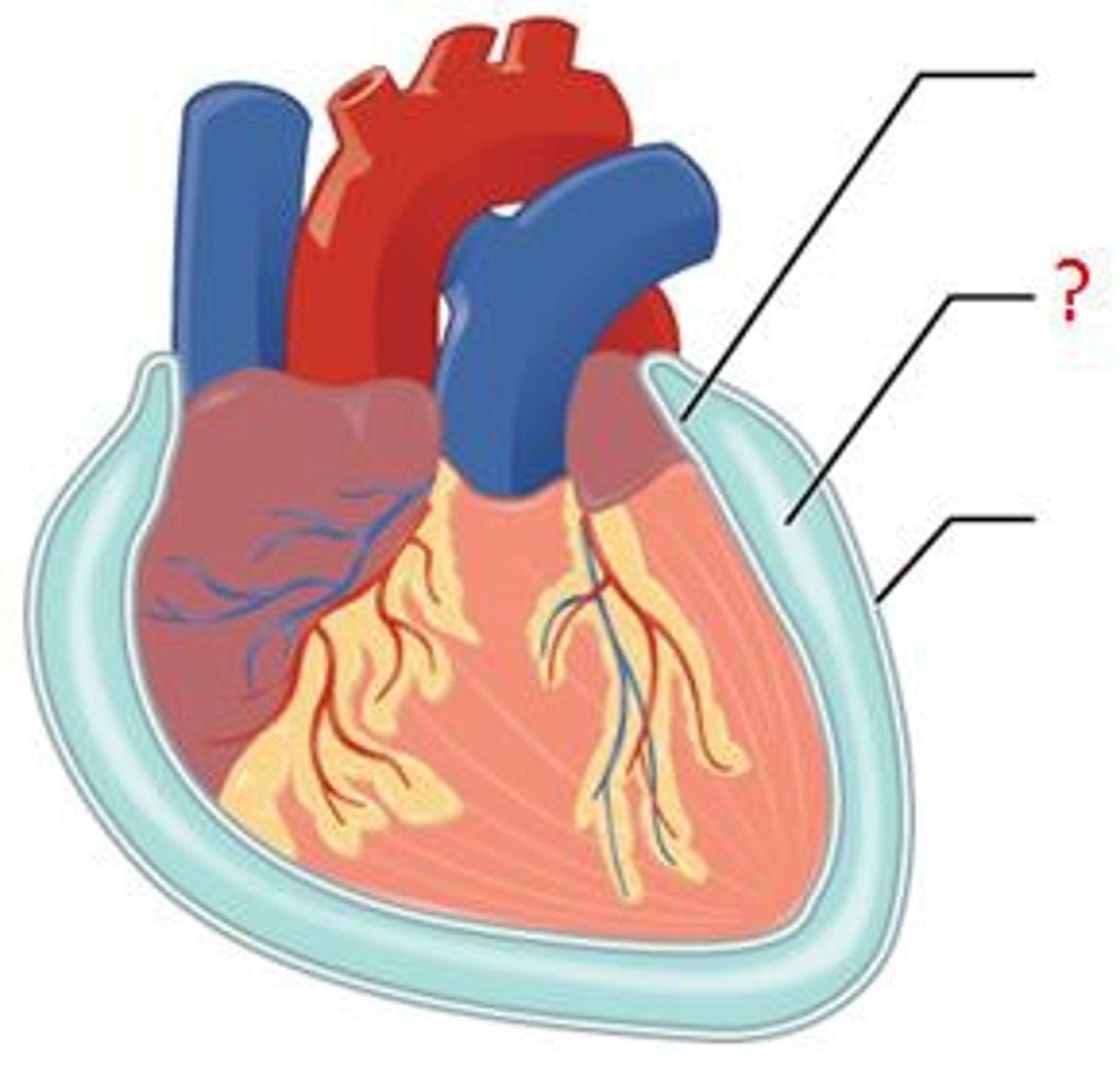
Pericardial cavity
the heart is located within the pericardial cavity
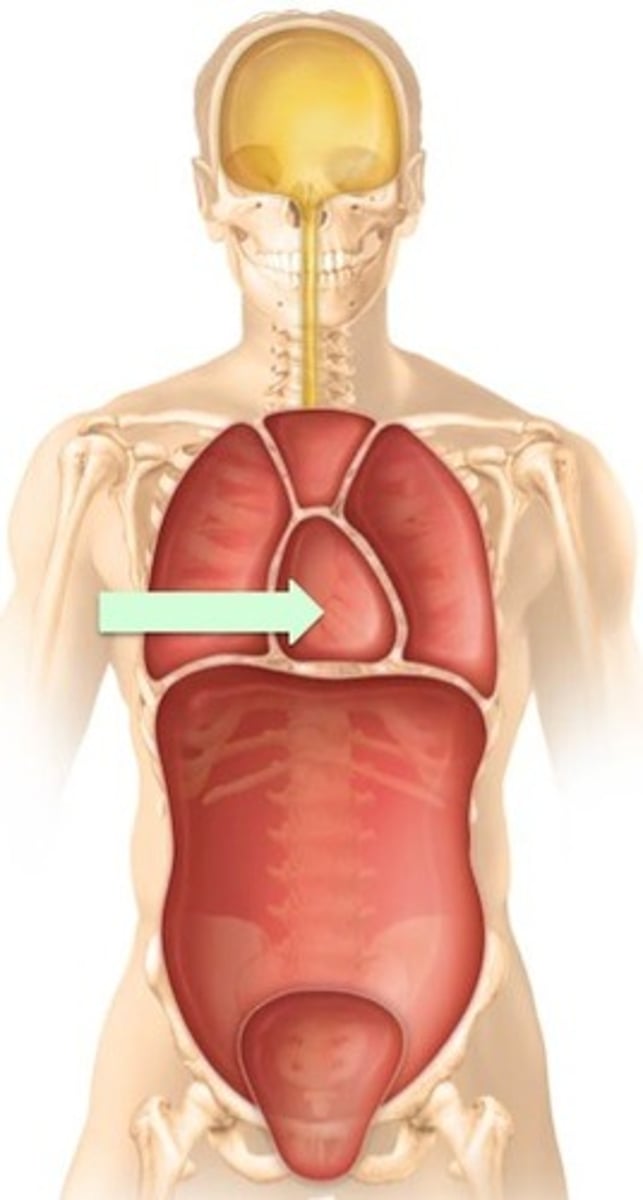
Pericardium
the pericardial cavity is lined by a serous membrane known as the pericardium
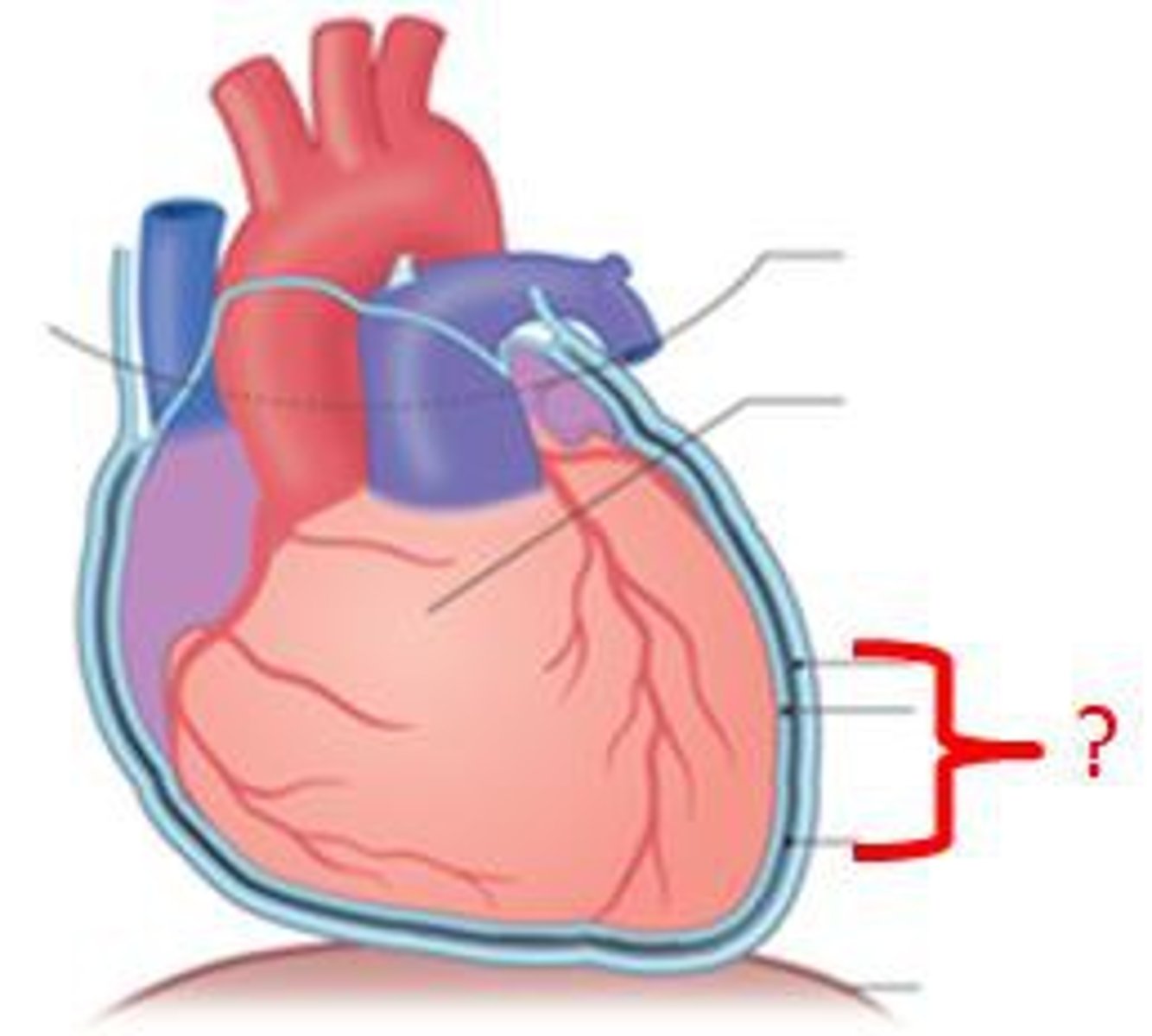
Visceral pericardium
covers the heart
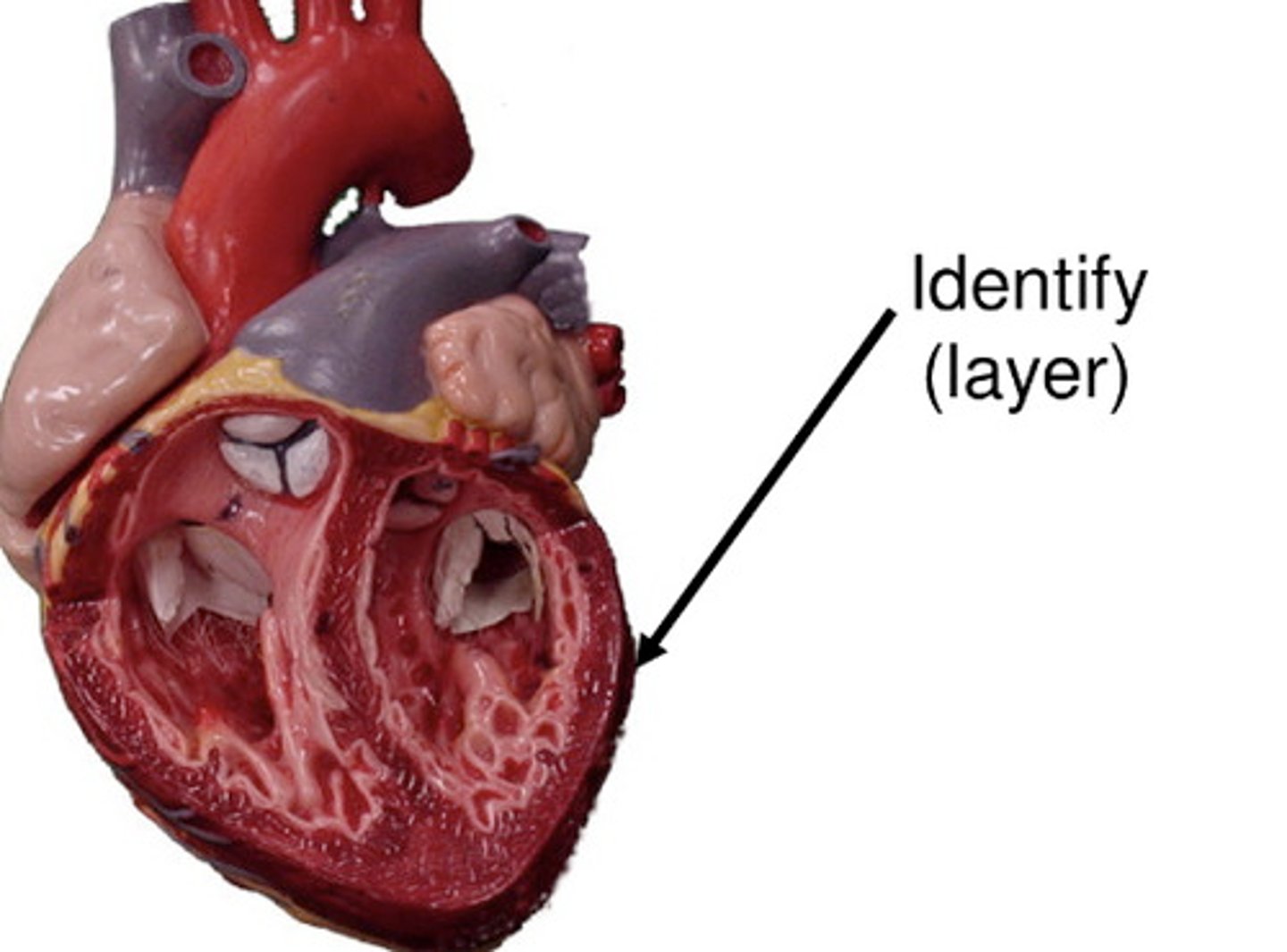
Parietal pericardium
lines the pericardial cavity (walls)
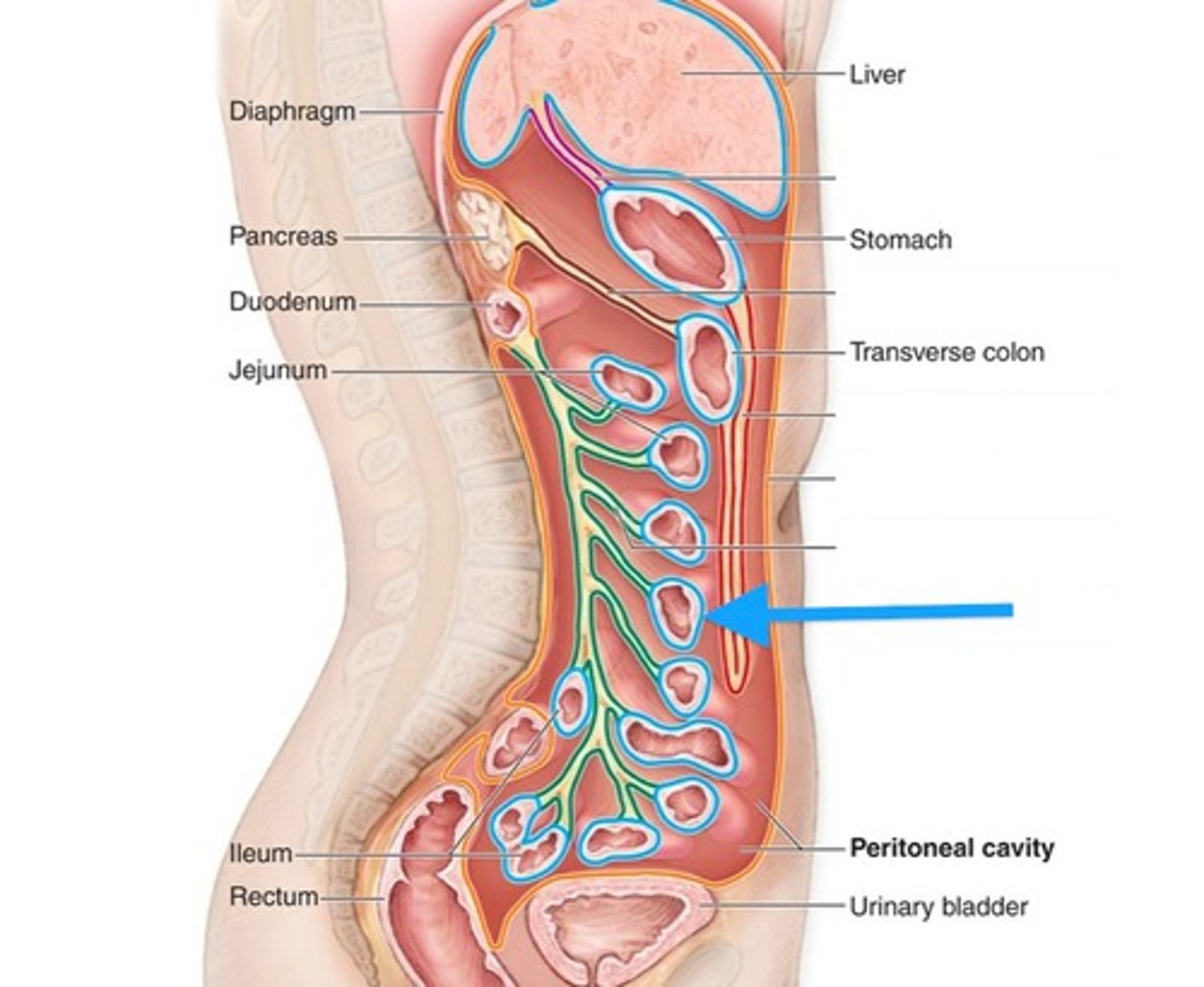
Abdominopelvic cavity
the abdominal cavity and upper part of pelvic cavity is also known as the peritoneal cavity
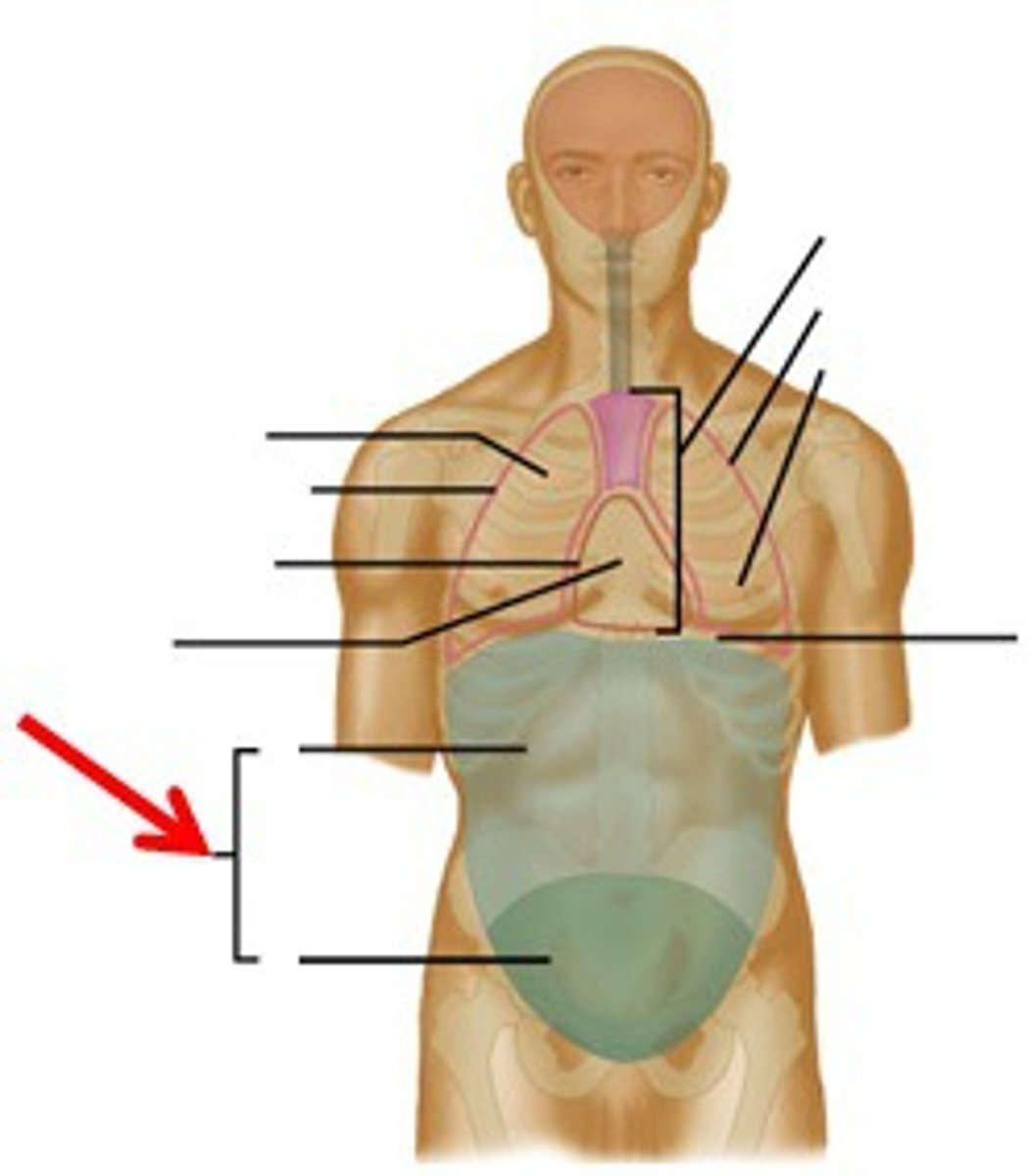
Abdominal cavity
contains many digestive glands and organs
Pelvic cavity
contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and lower digestive tract
Peritoneum
the abdominopelvic cavity is lined by a serous membrane known as the
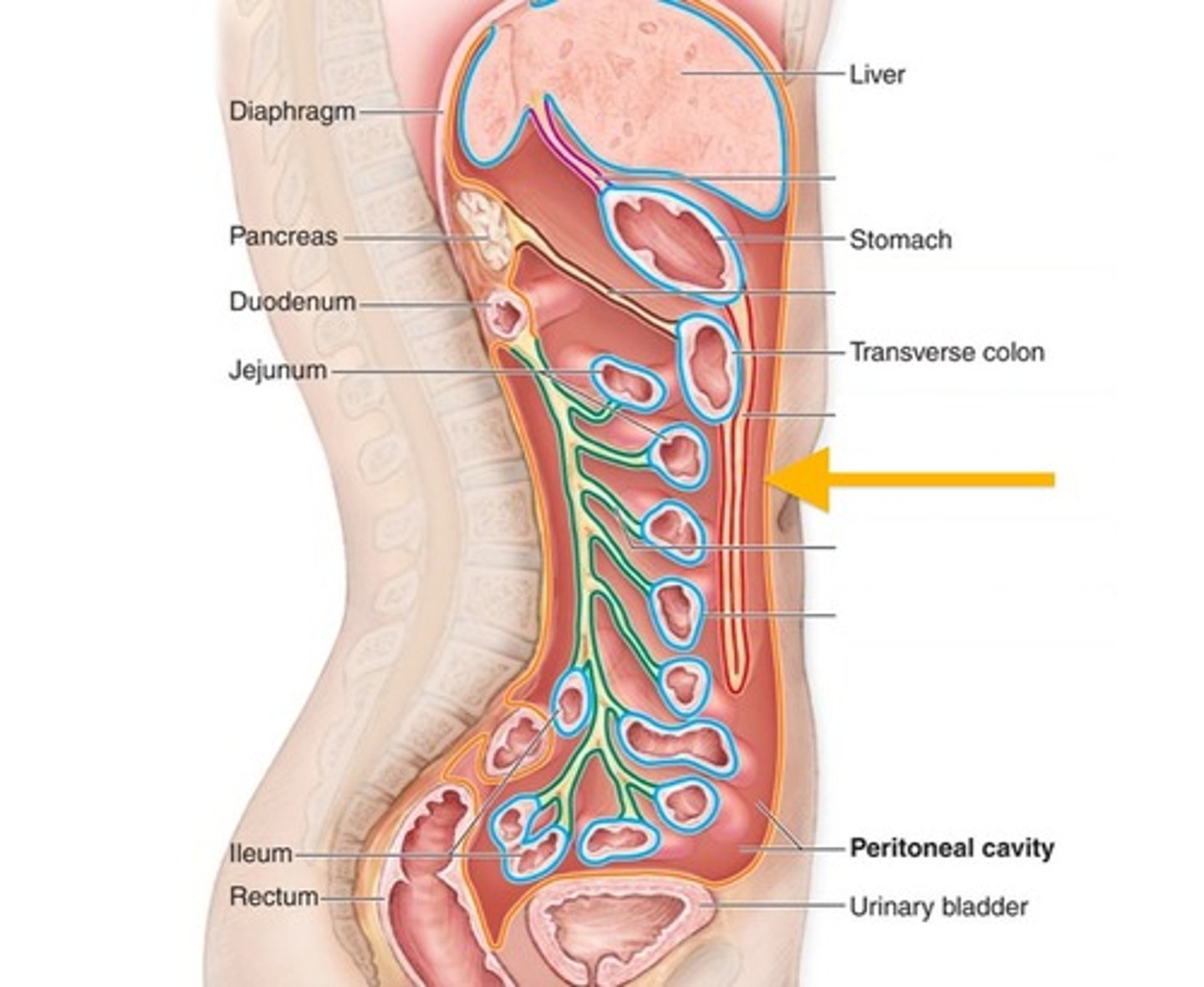
Visceral peritoneum
covers the abdominopelvic organs